Thermoregulatory, Cardiovascular and Perceptual Responses of Spectators of a Simulated Football Match in Hot and Humid Environmental Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Study Protocol
2.4. Outcome Parameters
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
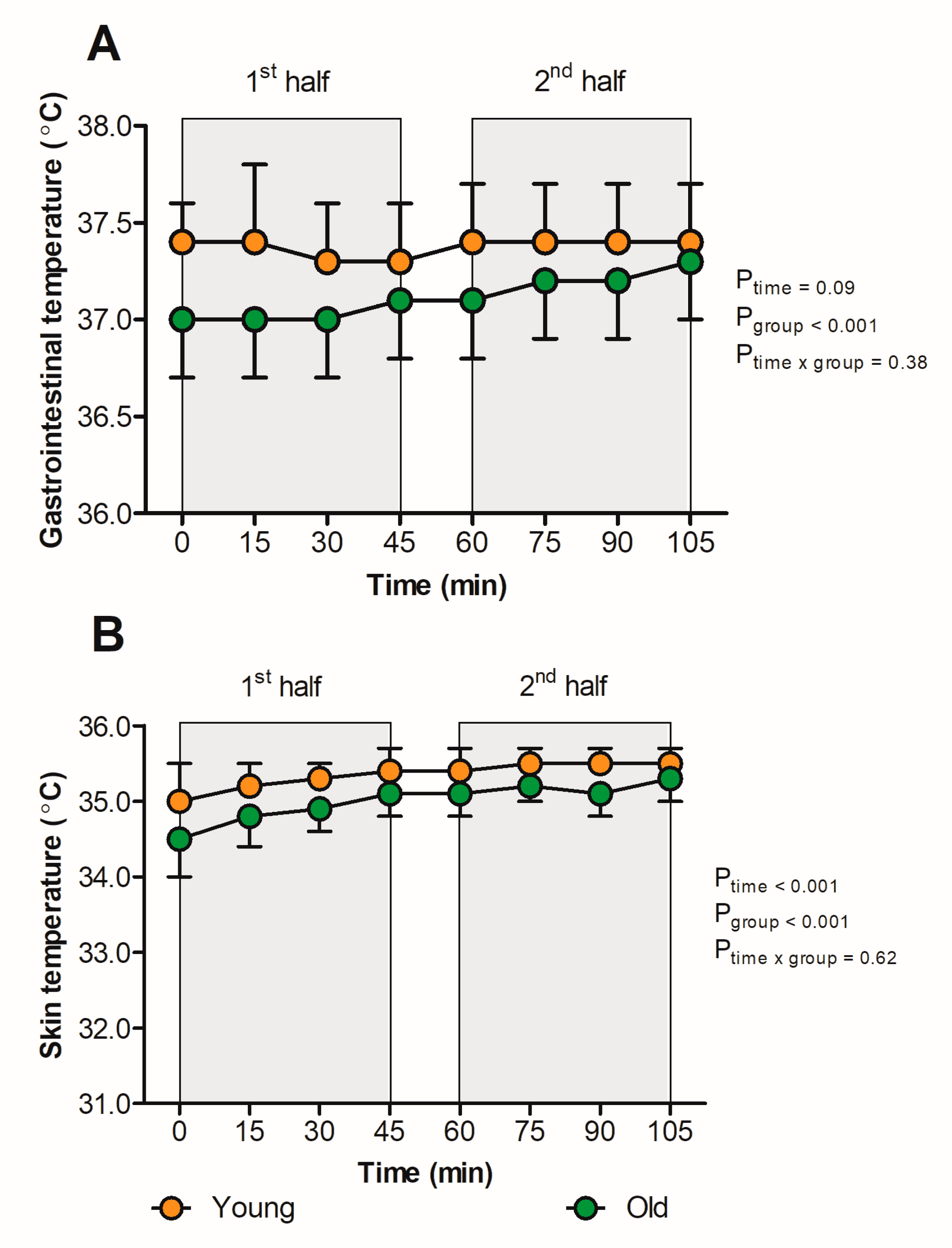
3.1. Thermal Responses
3.2. Cardiovascular Responses
3.3. Perceptual Outcomes
3.4. Fluid Balance
4. Discussion
4.1. Thermal Strain
4.2. Cardiovascular Strain
4.3. Perceptual Strain
4.4. Fluid Balance Responses
4.5. Young versus Older Adults
4.6. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bongers, C.; de Korte, J.Q.; Eijsvogels, T. Infographic. Keep it cool and beat the heat: Cooling strategies for exercise in hot and humid conditions. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 55, 643–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, Y.; Yanovich, R. Heatstroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2449–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nybo, L.; Rasmussen, P.; Sawka, M.N. Performance in the heat-physiological factors of importance for hyperthermia-induced fatigue. Compr. Physiol. 2014, 4, 657–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eijsvogels, T.M.H.; de Korte, J.Q.; Bongers, C.C.W.G. Beat the heat: How to become a gold medalist at the Tokyo Olympics. Temperature 2021, 8, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia, A.; Hoyos, J.; Pérez, M.; Santalla, A.; Chicharro, J.L. Inverse relationship between VO2max and economy/efficiency in world-class cyclists. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 2079–2084. [Google Scholar]
- Periard, J.D.; Eijsvogels, T.M.H.; Daanen, H.A.M. Exercise under heat stress: Thermoregulation, hydration, performance implications, and mitigation strategies. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 1873–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racinais, S.; Alonso, J.M.; Coutts, A.J.; Flouris, A.D.; Girard, O.; Gonzalez-Alonso, J.; Hausswirth, C.; Jay, O.; Lee, J.K.; Mitchell, N.; et al. Consensus recommendations on training and competing in the heat. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25 (Suppl. 1), 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bongers, C.C.; Hopman, M.T.; Eijsvogels, T.M. Cooling interventions for athletes: An overview of effectiveness, physiological mechanisms, and practical considerations. Temperature 2017, 4, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Freitas, C.R.; Scott, D.; McBoyle, G. A second generation climate index for tourism (CIT): Specification and verification. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2008, 52, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periard, J.D.; Racinais, S.; Sawka, M.N. Adaptations and mechanisms of human heat acclimation: Applications for competitive athletes and sports. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2015, 25 (Suppl. 1), 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, W.L.; Craighead, D.H.; Alexander, L.M. Heat waves, aging, and human cardiovascular health. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2014, 46, 1891–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; FitzGerald, G.; Guo, Y.; Jalaludin, B.; Tong, S. Impact of heatwave on mortality under different heatwave definitions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2016, 89–90, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, C.; Honold, J.; Lauf, S.; Lakes, T. Urban heat stress: Novel survey suggests health and fitness as future avenue for research and adaptation strategies. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 044021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanos, J.K.; Kosaka, E.; Iida, A.; Yokohari, M.; Middel, A.; Scott-Fleming, J.; Brown, R.D. Planning for spectator thermal comfort and health in the face of extreme heat: The Tokyo 2020 Olympic marathons. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandall, C.G.; Wilson, T.E.; Marving, J.; Vogelsang, T.W.; Kjaer, A.; Hesse, B.; Secher, N.H. Effects of passive heating on central blood volume and ventricular dimensions in humans. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crandall, C.G.; Wilson, T.E. Human cardiovascular responses to passive heat stress. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 5, 17–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vargas, N.T.; Slyer, J.; Chapman, C.L.; Johnson, B.D.; Temple, J.L.; Mietlicki-Baase, E.G.; Schlader, Z.J. The motivation to behaviorally thermoregulate during passive heat exposure in humans is dependent on the magnitude of increases in skin temperature. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 194, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowell, L.B.; Brengelmann, G.L.; Murray, J.A. Cardiovascular responses to sustained high skin temperature in resting man. J. Appl. Physiol. 1969, 27, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, S.S.; McLellan, T.M.; Tenaglia, S. The thermophysiology of uncompensable heat stress—Physiological manipulations and individual characteristics. Sports Med. 2000, 29, 329–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanos, J.K.; Thomas, W.M.; Grundstein, A.J.; Hosokawa, Y.; Liu, Y.; Casa, D.J. A multi-scalar climatological analysis in preparation for extreme heat at the Tokyo 2020 Olympic and Paralympic Games. Temperature 2020, 7, 191–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lieberman, H.R.; Bathalon, G.P.; Falco, C.M.; Kramer, F.M.; Morgan, C.A., 3rd; Niro, P. Severe decrements in cognition function and mood induced by sleep loss, heat, dehydration, and undernutrition during simulated combat. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 57, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malcolm, R.A.; Cooper, S.; Folland, J.P.; Tyler, C.J.; Sunderland, C. Passive Heat Exposure Alters Perception and Executive Function. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevention and management of heat-related illness among spectators and staff during the Olympic games—Atlanta, July 6–23, 1996. JAMA 1996, 276, 593–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbar, O.; Morris, N.; Epstein, Y.; Gass, G. Comparison of thermoregulatory responses to exercise in dry heat among prepubertal boys, young adults and older males. Exp. Physiol. 2004, 89, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, C.G.; Kenney, W.L. Effects of age and acclimation on responses to passive heat exposure. J. Appl. Physiol. 1993, 75, 2162–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellon, R.F.; Lind, A.R.; Weiner, J.S. The physiological reactions of men of two age groups to a hot environment. J. Physiol. 1956, 133, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, A.; Candas, V. Ageing and thermal responses during passive heat exposure: Sweating and sensory aspects. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 100, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers, C.; Daanen, H.A.M.; Bogerd, C.P.; Hopman, M.T.E.; Eijsvogels, T.M.H. Validity, Reliability, and Inertia of Four Different Temperature Capsule Systems. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, D.M.; Carter, J.M.; Richmond, V.L.; Blacker, S.D.; Rayson, M.P. The effect of cool water ingestion on gastrointestinal pill temperature. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 9886:2004; Ergonomics—Evaluation of Thermal Strain by Physiological Measurements. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- Gagge, A.P.; Stolwijk, J.A.J.; Hardy, J.D. Comfort and Thermal Sensations and Associated Physiological Responses at Various Ambient Temperatures. Environ. Res. 1967, 1, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huskisson, E.C. Measurement of pain. Lancet 1974, 2, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawka, M.N.; Burke, L.M.; Eichner, E.R.; Maughan, R.J.; Montain, S.J.; Stachenfeld, N.S. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Exercise and fluid replacement. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casa, D.J.; Armstrong, L.E.; Hillman, S.K.; Montain, S.J.; Reiff, R.V.; Rich, B.S.; Roberts, W.O.; Stone, J.A. National athletic trainers’ association position statement: Fluid replacement for athletes. J. Athl. Train. 2000, 35, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cramer, M.N.; Jay, O. Biophysical aspects of human thermoregulation during heat stress. Auton. Neurosci. 2016, 196, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravanelli, N.; Bongers, C.C.W.G.; Jay, O. The Biophysics of Human Heat Exchange. In Heat Stress in Sport and Exercise, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- Rowell, L.B. Human cardiovascular adjustments to exercise and thermal stress. Physiol. Rev. 1974, 54, 75–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagge, A.P. A new physiological variable associated with sensible and insensible perspiration. Am. J. Physiol.-Leg. Content 1937, 120, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M. Die Regulation der Körpertemperatur bei Muskelarbeit. Skand. Arch. Physiol. 1938, 79, 193–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbert-Lampen, U.; Leistner, D.; Greven, S.; Pohl, T.; Sper, S.; Volker, C.; Guthlin, D.; Plasse, A.; Knez, A.; Kuchenhoff, H.; et al. Cardiovascular events during World Cup soccer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Yoda, T.; Crawshaw, L.I.; Yasuhara, S.; Saito, Y.; Kasuga, M.; Nagashima, K.; Kanosue, K. Regional differences in temperature sensation and thermal comfort in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 105, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gagge, A.P.; Stolwijk, J.A.J.; Saltin, B. Comfort and Thermal Sensations and Associated Physiological Responses during Exercise at Various Ambient Temperatures. Environ. Res. 1969, 2, 209–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winslow, C.E.A.; Herrington, L.P.; Gagge, A.P. Relations between atmospheric conditions, physiological reactions and sensations of pleasantness. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1937, 26, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukazawa, T.; Havenith, G. Differences in comfort perception in relation to local and whole body skin wettedness. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerrett, N.; Redortier, B.; Voelcker, T.; Havenith, G. A comparison of galvanic skin conductance and skin wettedness as indicators of thermal discomfort during moderate and high metabolic rates. J. Termal Biol. 2013, 38, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blatteis, C.M. Age-dependent changes in temperature regulation—A mini review. Gerontology 2012, 58, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravel, H.; Chaseling, G.K.; Barry, H.; Debray, A.; Gagnon, D. Cardiovascular control during heat stress in older adults: Time for an update. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2021, 320, H411–H416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.; Bi, P.; Nitschke, M.; Pisaniello, D.; Newbury, J.; Kitson, A. Older persons and heat-susceptibility: The role of health promotion in a changing climate. Health Promot. J. Aust. 2011, 22, S17–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Omori, K.; Kuwahara, T.; Ogura, Y.; Ueda, H. Sex- and menstrual cycle-related differences in sweating and cutaneous blood flow in response to passive heat exposure. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 94, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarche, D.T.; Notley, S.R.; Louie, J.C.; Poirier, M.P.; Kenny, G.P. Fitness-related differences in the rate of whole-body evaporative heat loss in exercising men are heat-load dependent. Exp. Physiol. 2018, 103, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Total Group (n = 48) | Young Group (n = 27) | Old Group (n = 21) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 43 ± 19 | 29 ± 11 | 62 ± 7 | <0.001 |
| Sex (n(%) male) | 30 (63%) | 14 (52%) | 16 (76%) | 0.08 |
| Weight (kg) | 77.8 ± 12.4 | 75.2 ± 11.8 | 81.3 ± 12.7 | 0.09 |
| Height (cm) | 181 ± 9 | 181 ± 10 | 180 ± 8 | 0.66 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.8 ± 2.8 | 22.8 ± 2.4 | 25.0 ± 2.9 | 0.006 |
| Total Group (n = 48) | Young Group (n = 27) | Old Group (n = 21) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline Tcore (°C) | 37.3 ± 0.4 | 37.5 ± 0.3 | 37.0 ± 0.3 | <0.001 |
| Peak Tcore (°C) | 37.5 ± 0.3 | 37.6 ± 0.3 | 37.3 ± 0.3 | 0.005 |
| Baseline Tskin (°C) | 32.8 ± 0.8 | 32.9 ± 0.8 | 32.7 ± 0.8 | 0.66 |
| Peak Tskin (°C) | 35.4 ± 0.3 | 35.6 ± 0.2 | 35.3 ± 0.2 | 0.001 |
| Baseline HR (bpm) | 76 ± 15 | 82 ± 14 | 68 ± 13 | 0.007 |
| Peak HR (bpm) | 81 ± 14 | 86 ± 12 | 75 ± 14 | 0.022 |
| Baseline MAP (mmHg) | 96 ± 8 | 92 ± 5 | 101 ± 9 | 0.003 |
| Peak MAP (mmHg) | 100 ± 8 | 97 ± 6 | 104 ± 9 | 0.015 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Korte, J.Q.; Eijsvogels, T.M.H.; Hopman, M.T.E.; Bongers, C.C.W.G. Thermoregulatory, Cardiovascular and Perceptual Responses of Spectators of a Simulated Football Match in Hot and Humid Environmental Conditions. Sports 2023, 11, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11040078
de Korte JQ, Eijsvogels TMH, Hopman MTE, Bongers CCWG. Thermoregulatory, Cardiovascular and Perceptual Responses of Spectators of a Simulated Football Match in Hot and Humid Environmental Conditions. Sports. 2023; 11(4):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11040078
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Korte, Johannus Q., Thijs M. H. Eijsvogels, Maria T. E. Hopman, and Coen C. W. G. Bongers. 2023. "Thermoregulatory, Cardiovascular and Perceptual Responses of Spectators of a Simulated Football Match in Hot and Humid Environmental Conditions" Sports 11, no. 4: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11040078
APA Stylede Korte, J. Q., Eijsvogels, T. M. H., Hopman, M. T. E., & Bongers, C. C. W. G. (2023). Thermoregulatory, Cardiovascular and Perceptual Responses of Spectators of a Simulated Football Match in Hot and Humid Environmental Conditions. Sports, 11(4), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11040078





