Unilateral Exercise and Bilateral Vascular Health in Female Tennis Players and Active Controls
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
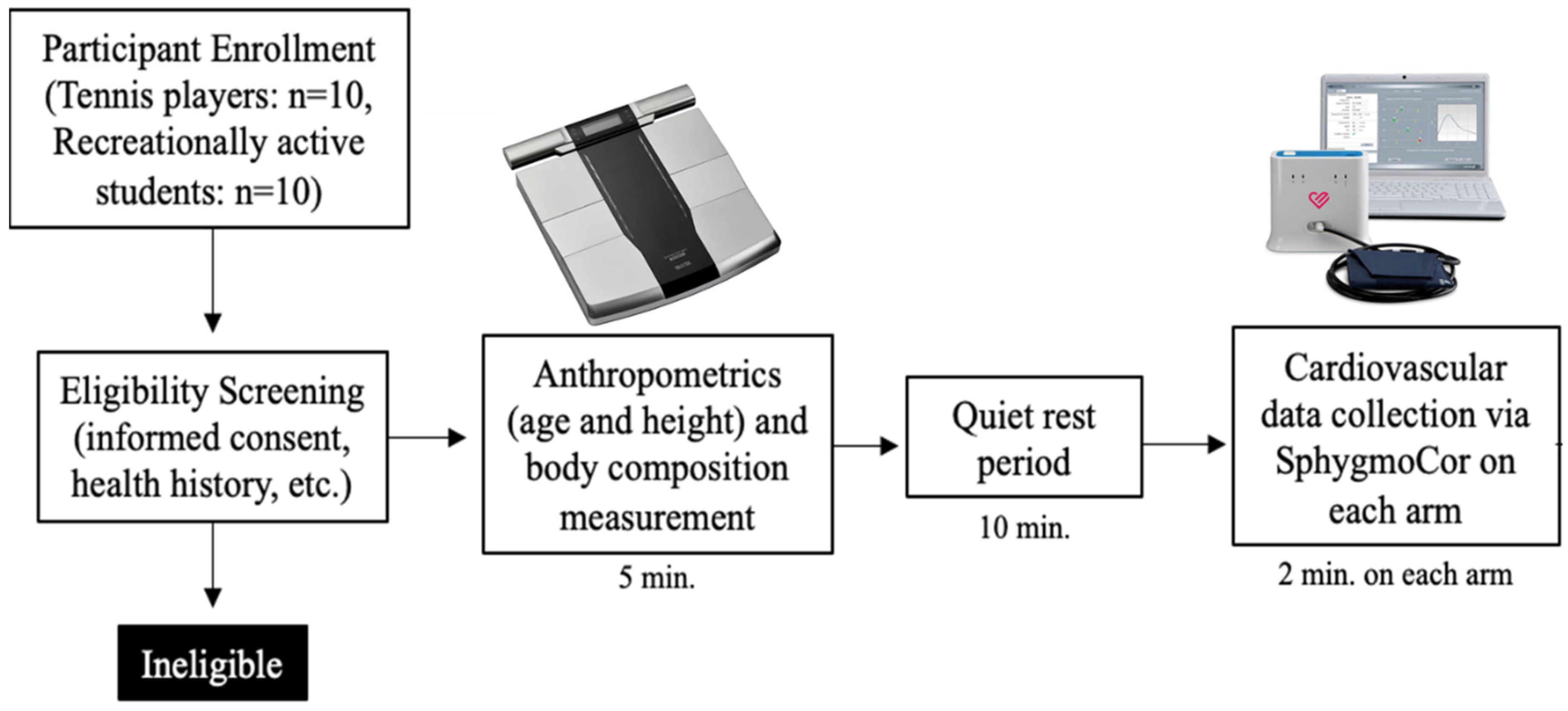
2.1. Subjects and General Procedures
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subject Characteristics of TP and RA Controls
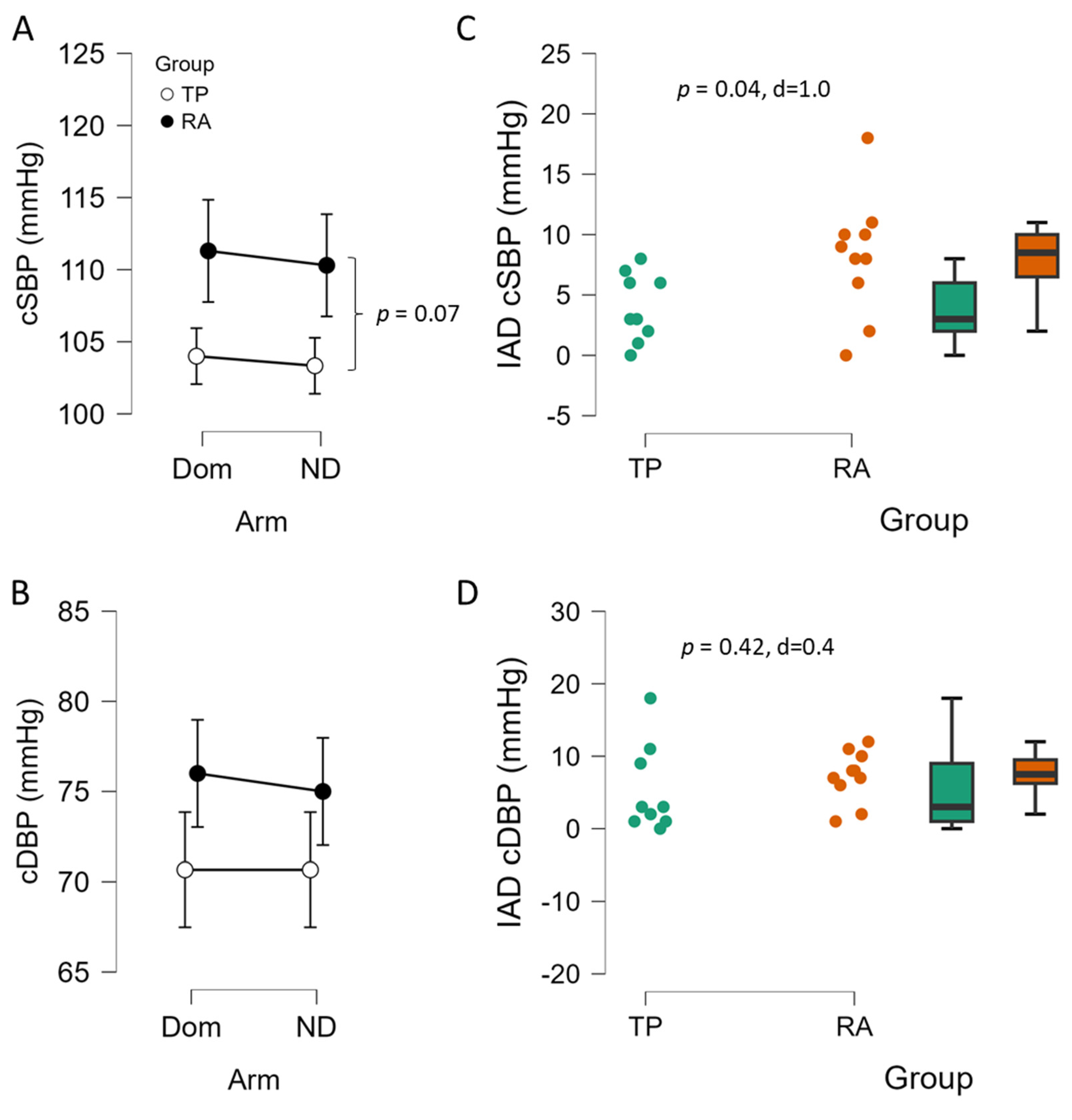
3.2. Blood Pressure and Interarm Differences Between TP and RA Controls
3.3. The Role of Arm in Pulse Wave Analysis Estimates of Arterial Stiffness of TP and RA Controls
4. Discussion
4.1. Interarm Differences in Blood Pressure
4.2. Bilateral Differences and Training Level
4.3. Experimental Considerations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cardiovascular Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 23 August 2024).
- Promoting Cardiovascular Health in the Developing World: A Critical Challenge to Achieve Global Health. In Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Preventing the Global Epidemic of Cardiovascular Disease: Meeting the Challenges in Developing Countries; Fuster, V., Kelly, B.B., Eds.; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2010. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK45693/ (accessed on 27 March 2025). [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Alonso, A.; Beaton, A.Z.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Boehme, A.K.; Buxton, A.E.; Carson, A.P.; Commodore-Mensah, Y.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2022 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 145, E153–E639. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pugsley, M.K.; Tabrizchi, R. The vascular system: An overview of structure and function. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2000, 44, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, S.; Fujimoto, N.; Hastings, J.L.; Carrick-Ranson, G.; Bhella, P.S.; Hearon, C.M.; Levine, B.D. The effect of lifelong exercise frequency on arterial stiffness. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 2783–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernberg, U.; Fernström, M.; Hurtig-Wennlöf, A. Higher Total Physical Activity is Associated with Lower Arterial Stiffness in Swedish, Young Adults: The Cross-Sectional Lifestyle, Biomarkers, and Atherosclerosis Study. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2021, 17, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecelja, M.; Chowienczyk, P. Role of arterial stiffness in cardiovascular disease. JRSM Cardiovasc. Dis. 2012, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.N.; DeVan, A.E.; Schleifer, J.L.; Anton, M.M.; Cortez-Cooper, M.Y.; Tanaka, H. Arterial compliance of rowers: Implications for combined aerobic and strength training on arterial elasticity. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 290, H1596–H1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, N.J.; Dawson, E.A.; Birk, G.K.; Cable, N.T.; George, K.; Whyte, G.; Thijssen, D.H.J.; Green, D.J. Exercise and arterial adaptation in humans: Uncoupling localized and systemic effects. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 110, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.J.; Fowler, D.T.; O’Driscoll, J.G.; Blanksby, B.A.; Taylor, R.R. Endothelium-derived nitric oxide activity in forearm vessels of tennis players. J. Appl. Physiol. 1996, 81, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinoway, L.I.; Much, T.I.; Minotti, J.R.; Zelis, R. Enhanced maximal metabolic vasodilatation in the dominant forearms of tennis players. J. Appl. Physiol. 1986, 61, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.E.; Warren, F.C.; Boddy, K.; McDonagh, S.T.J.; Moore, S.F.; Goddard, J.; Reed, N.; Turner, M.; Alzamora, M.T.; Ramos Blanes, R.; et al. Associations Between Systolic Interarm Differences in Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes and Mortality: Individual Participant Data Meta-Analysis, Development and Validation of a Prognostic Algorithm: The INTERPRESS-IPD Collaboration. Hypertension 2021, 77, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Makhamreh, H.K.; Sadalla, A.A.; Alhawari, H.; Bedros, A.W.; Kahlous, M.M.; Amer, M.A.; Al-Mubarak, B.A.; Hussein, M.; Toubasi, A.A.; Chichan, H.T. Inter-Arm Blood Pressure Difference an Indicator of Coronary Artery Disease. High. Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2023, 30, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.B.; Oh, M.K.; Kim, H.G.; Ki, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.M. Inter-arm Differences in Simultaneous Blood Pressure Measurements in Ambulatory Patients without Cardiovascular Diseases. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2013, 34, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.E.; Taylor, R.S.; Shore, A.C.; Campbell, J.L. The difference in blood pressure readings between arms and survival: Primary care cohort study. BMJ 2012, 344, E1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, I.; Gona, P.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Jaff, M.R.; Murabito, J.M. The Systolic Blood Pressure Difference Between Arms and Cardiovascular Disease in the Framingham Heart Study. Am. J. Med. 2014, 127, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanhewicz, A.E.; Wong, B.J. Counterpoint: Investigators should not control for menstrual cycle phase when performing studies of vascular control that include women. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 129, 1117–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasold, K.L.; Parks, A.C.; Phelan, D.M.L.; Pontifex, M.B.; Pivarnik, J.M. Reliability and Validity of Commercially Available Low-Cost Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis. Int. J. Sport. Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2019, 29, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBlauw, J.A.; Churchill, A.I.; Yunda, B.C.; Kotarsky, C.J.; Caldwell, A.; Ives, S.J. The effects of short-term caloric restriction on cardiometabolic health in overweight/obese men and women: A single-arm trial. Physiol. Rep. 2023, 11, e15856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, T.; Nakagomi, A.; Okada, S.; Ohno, Y.; Kobayashi, Y. Invasive validation of a novel brachial cuff-based oscillometric device (Sphygmo Cor XCEL) for measuring central blood pressure. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagomi, A.; Shoji, T.; Okada, S.; Ohno, Y.; Kobayashi, Y. Validity of the augmentation index and pulse pressure amplification as determined by the SphygmoCor XCEL device: A comparison with invasive measurements. Hypertens. Res. 2018, 41, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntner, P.; Shimbo, D.; Carey, R.M.; Charleston, J.B.; Gaillard, T.; Misra, S.; Myers, M.G.; Ogedegbe, G.; Schwartz, J.E.; Townsend, R.R.; et al. Measurement of blood pressure in humans: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2019, 73, E35–E66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denham, J.; Brown, N.J.; Tomaszewski, M.; Williams, B.; O’Brien, B.J.; Charchar, F.J. Aortic augmentation index in endurance athletes: A role for cardiorespiratory fitness. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 116, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachopoulos, C.; Aznaouridis, K.; O’Rourke, M.F.; Safar, M.E.; Baou, K.; Stefanadis, C. Prediction of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality with central haemodynamics: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 1865–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppe, M.W.; Hotfiel, T.; Stückradt, A.; Grim, C.; Ueberschär, O.; Freiwald, J.; Baumgart, C. Effects of passive, active, and mixed playing strategies on external and internal loads in female tennis players. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | TP (n = 10) | RA (n = 10) | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 19.4 ± 1.5 | 21.2 ± 1.1 | p = 0.750 |
| Height (cm) | 163.9 ± 5.1 | 166.1 ± 5.3 | p = 0.520 |
| Weight (kg) | 62.4 ± 11.5 | 62.1 ± 14.4 | p = 0.987 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.9 ± 2.0 | 21.3 ± 4.3 | p = 0.860 |
| Body fat (%) | 22.6 ± 6.9 | 23.4 ± 8.0 | p = 0.434 |
| Heart rate (beats/min) | 70 ± 10.5 | 74 ±12.4 | p = 0.422 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thongphok, C.E.; Gyampo, A.O.; Fioraso, E.; Ramolins, A.O.; Hills, E.G.; Coates, C.E.; Ives, S.J. Unilateral Exercise and Bilateral Vascular Health in Female Tennis Players and Active Controls. Sports 2025, 13, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13040107
Thongphok CE, Gyampo AO, Fioraso E, Ramolins AO, Hills EG, Coates CE, Ives SJ. Unilateral Exercise and Bilateral Vascular Health in Female Tennis Players and Active Controls. Sports. 2025; 13(4):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13040107
Chicago/Turabian StyleThongphok, Chanhtel E., Abena O. Gyampo, Elisa Fioraso, Anneli O. Ramolins, Elianna G. Hills, Claire E. Coates, and Stephen J. Ives. 2025. "Unilateral Exercise and Bilateral Vascular Health in Female Tennis Players and Active Controls" Sports 13, no. 4: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13040107
APA StyleThongphok, C. E., Gyampo, A. O., Fioraso, E., Ramolins, A. O., Hills, E. G., Coates, C. E., & Ives, S. J. (2025). Unilateral Exercise and Bilateral Vascular Health in Female Tennis Players and Active Controls. Sports, 13(4), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports13040107







