Using Unilateral Strength, Power and Reactive Strength Tests to Detect the Magnitude and Direction of Asymmetry: A Test-Retest Design
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Procedures
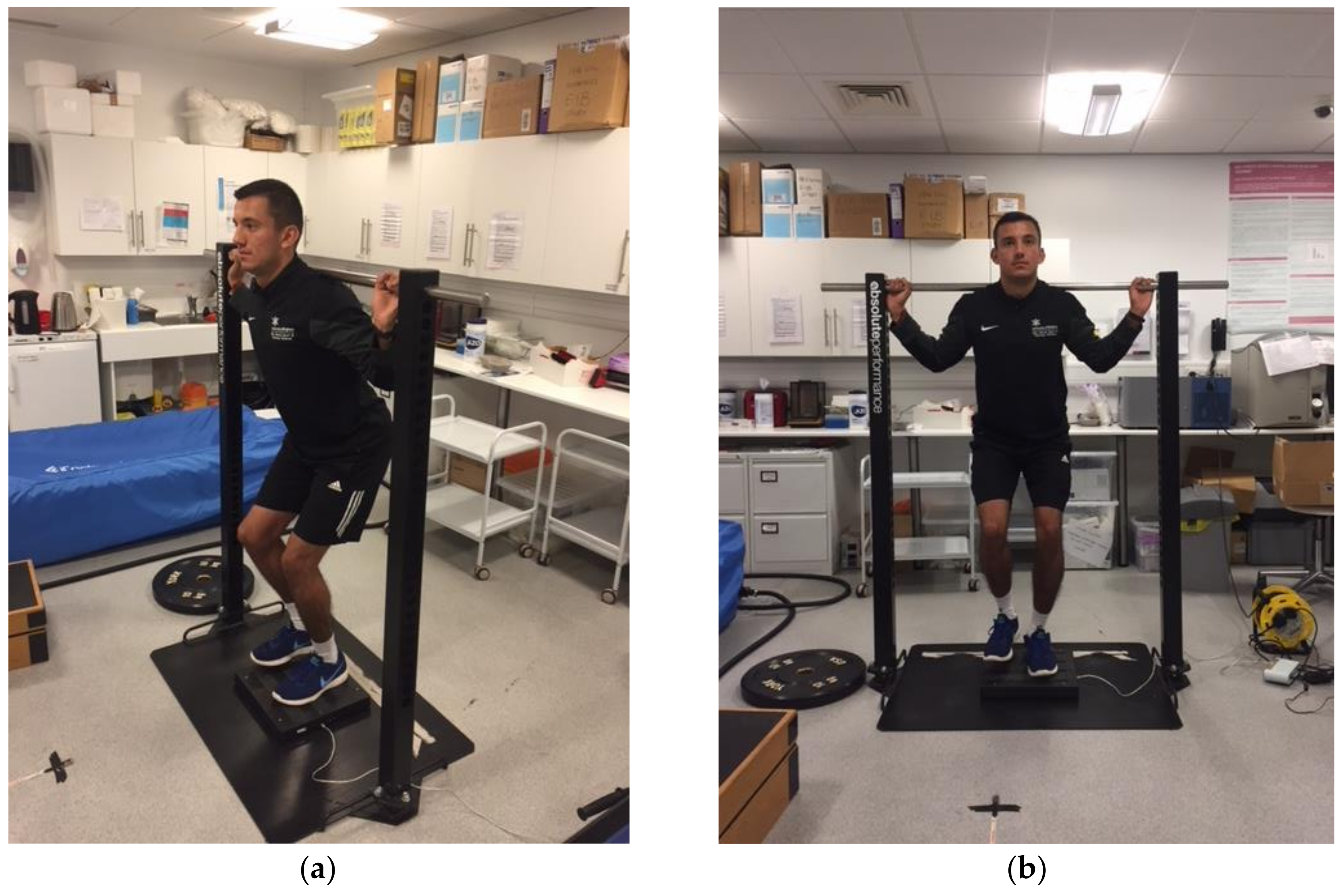
2.3.1. Unilateral Isometric Squat
2.3.2. Unilateral Countermovement Jump
2.3.3. Unilateral Drop Jump
2.4. Statistical Analysis
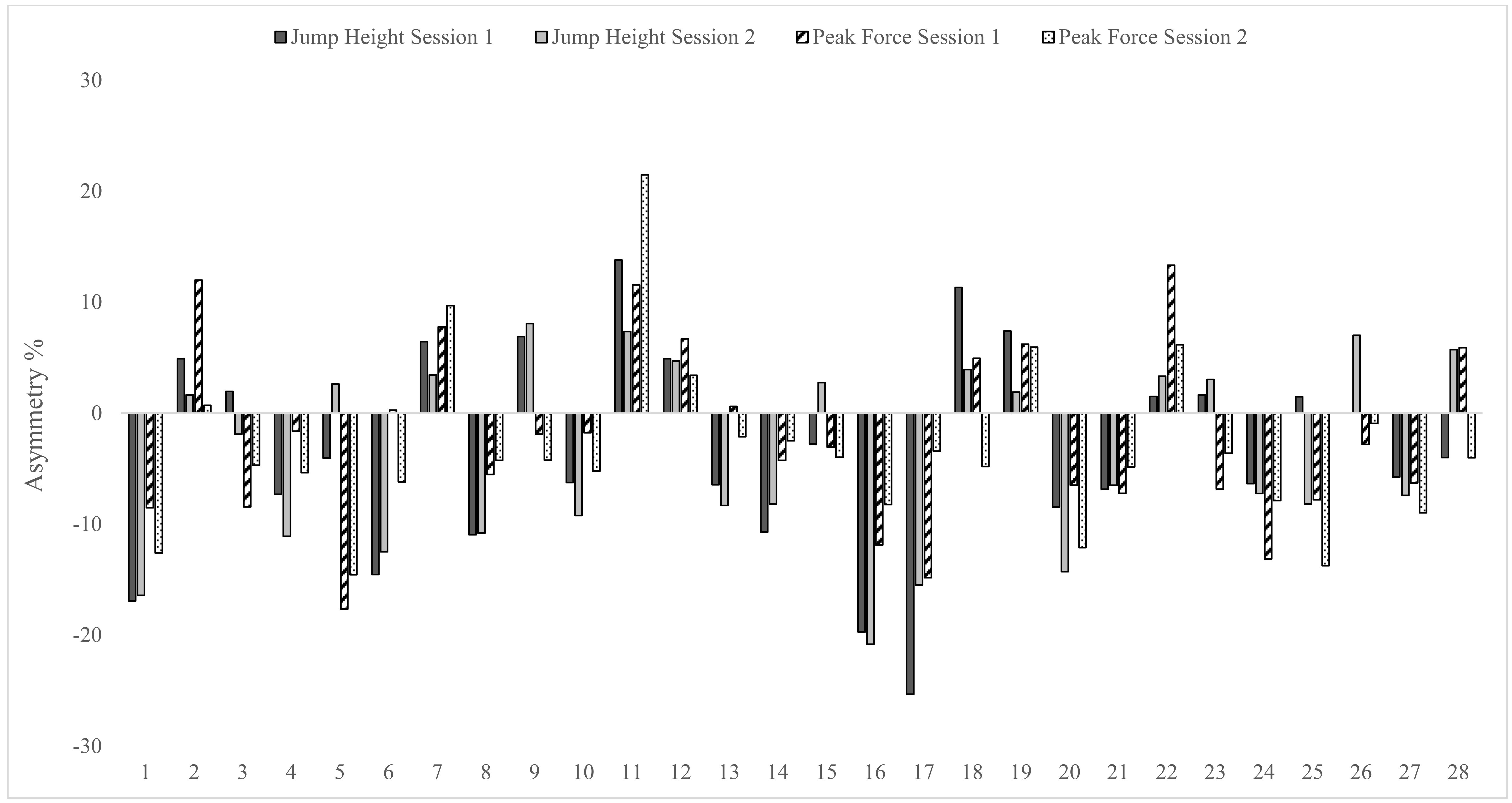
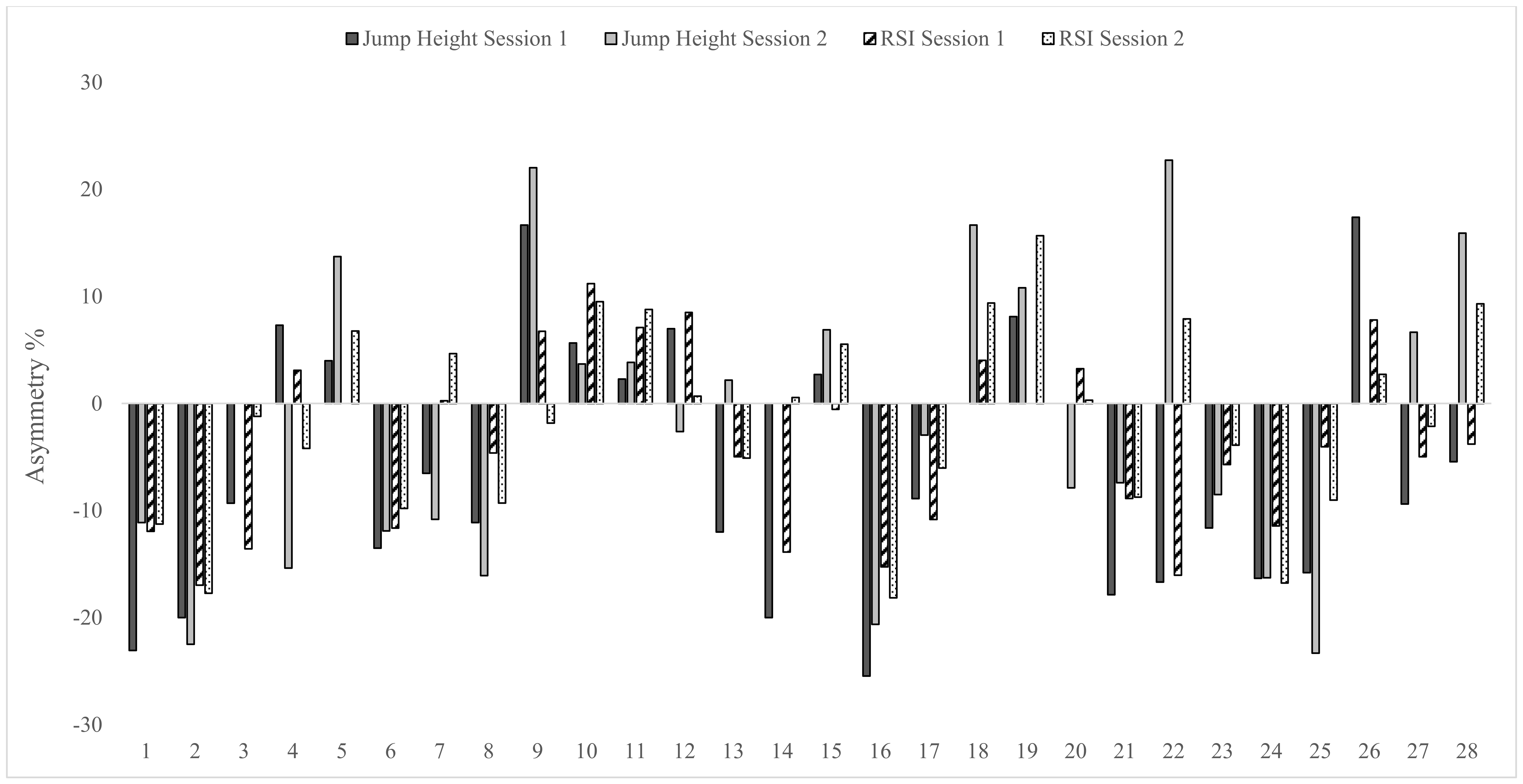
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bishop, C.; Read, P.; Chavda, S.; Turner, A. Asymmetries of the lower limb: The calculation conundrum in strength training and conditioning. Strength Cond. J. 2016, 38, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, D.; Plummer, H.; Oliver, G. Predicting asymmetrical lower extremity strength deficits in college-aged men and women using common horizontal and vertical power field tests: A possible screening mechanism. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 1632–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, D.; Sanfilippo, J.; Binkley, N.; Heiderscheit, B. Lean mass asymmetry influences force and power asymmetry during jumping in collegiate athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceroni, D.; Martin, X.; Delhumeau, C.; Farpour-Lambert, N. Bilateral and gender differences during single-legged vertical jump performance in healthy teenagers. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, R.; Gerber, A.; Nimphius, S.; Shim, J.; Doan, B.; Robertson, M.; Pearson, D.; Craig, B.; Hakkinen, K.; Kraemer, W. Determination of functional strength imbalance of the lower extremities. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2006, 20, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Heise, G. Influence of weight distribution asymmetry on the biomechanics of a barbell squat. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos’Santos, T.; Thomas, C.; Jones, P.; Comfort, P. Assessing muscle-strength asymmetry via a unilateral-stance isometric midthigh pull. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, N.; Nimphius, S.; Cochrane, J.; Newton, R. Reliability and validity of unilateral and bilateral isometric strength measures using a customised, portable apparatus. J. Aust. Strength Cond. 2012, 20, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Costa Silva, J.; Detanico, D.; Dal Pupo, J.; Freitas, C. Bilateral asymmetry of knee and ankle isokinetic torque in soccer players u20 category. Revista Brasileira de Cineantropometria & Desempenho Humano 2015, 17, 195–204. [Google Scholar]
- Ruas, C.; Brown, L.; Pinto, R. Lower-extremity side-to-side strength asymmetry of professional soccer players according to playing position. Kinesiology 2015, 2, 188–192. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, C.; Lake, J.; Loturco, I.; Papadopoulos, K.; Turner, A.; Read, P. Interlimb asymmetries: The need for an individual approach to data analysis. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018. Published ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meylan, C.; McMaster, T.; Cronin, J.; Mohammed, N.; Rogers, C.; de Klerk, M. Single-leg lateral, horizontal, and vertical jump assessment: Reliability, interrelationships, and ability to predict sprint and change of direction performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloney, S.; Fletcher, I.; Richards, J. A comparison of methods to determine bilateral asymmetries in vertical leg stiffness. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloney, S.; Richards, J.; Nixon, D.; Harvey, L.; Fletcher, I. Do stiffness and asymmetries predict change of direction performance? J. Sports Sci. 2017, 35, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, J.; Mundy, P.; Comfort, P.; McMahon, J.; Suchomel, T.; Carden, P. Concurrent validity of a portable force plate using vertical jump force-time characteristics. J. Appl. Biomech. 2018, 34, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormack, S.; Newton, R.; McGuigan, M.; Doyle, T. Reliability of measures obtained during single and repeated countermovement jumps. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2008, 3, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gathercole, R.; Sporer, B.; Stellingwerff, T.; Sleivert, G. Alternative countermovement-jump analysis to quantify acute neuromuscular fatigue. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2015, 10, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, C.; Turner, A.; Jarvis, P.; Chavda, S.; Read, P. Considerations for selecting field-based strength and power fitness tests to measure asymmetries. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 2635–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read, P.; Oliver, J.; De Ste Croix, M.; Myer, G.; Lloyd, R. Consistency of field-based measures of neuromuscular control using force-plate diagnostics in elite male youth soccer players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 3304–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.; Brazier, J.; Bishop, C.; Chavda, S.; Cree, J.; Read, P. Data analysis for strength and conditioning coaches: Using excel to analyse reliability, differences, and relationships. Strength Cond. J. 2015, 37, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockie, R.; Callaghan, S.; Berry, S.; Cooke, E.; Jordan, C.; Luczo, T.; Jeffriess, M. Relationship between unilateral jumping ability and asymmetry on multidirectional speed in team-sport athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 3557–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, C.; Read, P.; McCubbine, J.; Turner, A. Vertical and horizontal asymmetries are related to slower sprinting and jump performance in elite youth female soccer players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018. Published ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos’Santos, T.; Thomas, C.; Jones, P.; Comfort, P. Asymmetries in single and triple hop are not detrimental to change of direction speed. J. Trainol. 2017, 6, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Impellizzeri, F.; Rampinini, E.; Maffiuletti, N.; Marcora, S. A vertical jump force test for assessing bilateral strength asymmetry in athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 2044–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloney, S. The relationship between asymmetry and athletic performance: A critical review. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018. Published ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, J.; Mundy, P.; Comfort, P.; Suchomel, T. Do the peak and mean force methods of assessing vertical jump force asymmetry agree? Sports Biomech. 2018. Published ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffiuletti, N.; Aagaard, P.; Blazevich, A.; Folland, J.; Tillin, N.; Duchateau, J. Rate of force development: Physiological and methodological considerations. Eur. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 116, 1091–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, N.; Watkins, J.; Kilduff, L.; Bevan, H.; Bennett, M. Development of a criterion method to determine peak mechanical power output in a countermovement jump. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 1552–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavda, S.; Bromley, T.; Jarvis, P.; Williams, S.; Bishop, C.; Turner, A.; Lake, J.; Mundy, P. Force-time characteristics of the countermovement jump: Analyzing the curve in Excel. Strength Cond. J. 2018. (Published ahead of print). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, J. Quantifying test-retest reliability using the intraclass correlation coefficient and SEM. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2005, 19, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koo, T.; Li, M. A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, G.; Neville, A. Statistical methods for assessing measurement error (reliability) in variables relevant to sports medicine. Sports Med. 1998, 26, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, W.; Marshall, S.; Batterham, J.; Hanin, J. Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viera, A.; Garrett, J. Understanding the interobserver agreement: The kappa statistic. Fam. Med. 2005, 37, 36–363. [Google Scholar]
- Haff, G.; Stone, M.; O’Bryant, H.; Harman, E.; Dinan, C.; Johnson, R.; Han, K.-H. Force-time dependent characteristics of dynamic and isometric muscle actions. J. Strength Cond. Res. 1997, 11, 269–272. [Google Scholar]

| Test/Metric | Test Session 1 | Test Session 2 | Between Session | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICC (95% CI) | CV (95% CI) | SEM | ICC (95% CI) | CV (95% CI) | SEM | ICC (95% CI) | CV (95% CI) | ||
| Iso Squat | PF-L (N) | 0.94 (0.88–0.97) | 5.4 (3.7–7.2) | 107.5 | 0.96 (0.92–0.98) | 4.9 (4.0–5.7) | 78.8 | 0.93 (0.86–0.97) | 6.4 (4.1–8.6) |
| PF-R (N) | 0.93 (0.87–0.96) | 5.7 (4.2–7.2) | 105.1 | 0.94 (0.89–0.97) | 5.5 (4.1–6.9) | 106.2 | 0.86 (0.72–0.93) | 7.7 (5.6–9.8) | |
| Imp-L (N·s) | 0.89 (0.80–0.94) | 13.7 (10.0–17.4) | 23.6 | 0.89 (0.81–0.95) | 10.1 (8.0–12.3) | 21.2 | 0.90 (0.80–0.95) | 8.9 (6.2–11.5) | |
| Imp-R (N·s) | 0.92 (0.85–0.96) | 12.1 (9.5–14.8) | 22.0 | 0.90 (0.83–0.95) | 10.6 (8.1–13.1) | 20.2 | 0.85 (0.70–0.93) | 12.9 (9.4–16.4) | |
| SLCMJ | JH-L (m) | 0.89 (0.81–0.95) | 4.8 (3.8–5.9) | 0.01 | 0.87 (0.77–0.93) | 4.2 (3.2–5.3) | 0.01 | 0.82 (0.65–0.91) | 3.7 (1.9–5.5) |
| JH-R (m) | 0.81 (0.68–0.90) | 5.4 (4.1–6.7) | 0.01 | 0.85 (0.74–0.92) | 5.0 (4.0–6.0) | 0.01 | 0.78 (0.59–0.89) | 4.2 (2.5–5.8) | |
| PF-L (N) | 0.89 (0.80–0.94) | 5.8 (4.5–7.1) | 67.7 | 0.93 (0.88–0.97) | 4.9 (4.1–5.6) | 42.9 | 0.85 (0.71–0.93) | 6.2 (4.3–8.1) | |
| PF-R (N) | 0.93 (0.87–0.96) | 5.3 (4.2–6.4) | 48.0 | 0.90 (0.82–0.95) | 5.0 (3.9–6.2) | 50.2 | 0.83 (0.67–0.92) | 6.3 (4.4–8.2) | |
| SLDJ | JH-L (m) | 0.90 (0.82–0.95) | 7.5 (5.4–9.7) | 0.01 | 0.94 (0.89–0.97) | 7.1 (4.3–9.9) | 0.01 | 0.74 (0.49–0.87) | 10.1 (6.3–13.9) |
| JH-R (m) | 0.90 (0.82–0.95) | 8.1 (5.9–10.2) | 0.01 | 0.93 (0.87–0.96) | 6.8 (5.3–8.4) | 0.01 | 0.75 (0.53–0.87) | 11.2 (8.0–14.5) | |
| RSI-L | 0.87 (0.77–0.93) | 4.9 (3.7–6.0) | 0.06 | 0.93 (0.88–0.97) | 4.0 (2.6–5.3) | 0.05 | 0.70 (0.37–0.86) | 6.7 (4.5–8.9) | |
| RSI-R | 0.91 (0.84–0.95) | 4.7 (3.3–6.2) | 0.06 | 0.88 (0.79–0.94) | 5.9 (4.3–7.4) | 0.07 | 0.84 (0.68–0.92) | 5.1 (3.4–6.8) | |
| Test/Metric | Test Session 1 | Test Session 2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best Score | Asymmetry (%) | Average Score | Asymmetry (%) | Best Score | Asymmetry (%) | Average Score | Asymmetry (%) | ||
| Iso Squat | PF-L (N) | 1597.0 ± 438.9 | 8.4 ± 6.8 | 1519.7 ± 414.8 | 8.6 ± 5.9 | 1631.3 ± 394.2 | 8.9 ± 6.9 | 1561.8 ± 392.3 | 9.0 ± 6.5 |
| PF-R (N) | 1595.1 ± 397.3 | 1519.1 ± 382.4 | 1643.2 ± 433.4 | 1570.8 ± 424.6 | |||||
| Imp-L (N·s) | 199.5 ± 71.2 | 15.5 ± 11.4 | 177.7 ± 69.3 | 14.5 ± 11.3 | 190.8 ± 64.0 | 9.6 ± 7.8* | 174.5 ± 59.4 | 10.9 ± 6.7 | |
| Imp-R (N·s) | 192.9 ± 77.9 | 174.4 ± 75.0 | 191.9 ± 64.0 | 176.1 ± 61.6 | |||||
| SLCMJ | JH-L (m) | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 7.2 ± 6.1 | 0.20 ± 0.03 | 7.8 ± 5.9 | 0.22 ± 0.03 | 7.1 ± 5.0 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 7.6 ± 4.9 |
| JH-R (m) | 0.20 ± 0.03 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 0.20 ± 0.03 | |||||
| PF-L (N) | 863.4 ± 204.0 | 7.5 ± 5.1 | 811.5 ± 177.6 | 7.1 ± 4.5 | 847.0 ± 162.3 | 6.6 ± 4.8 | 807.7 ± 156.5 | 6.6 ± 4.7 | |
| PF-R (N) | 830.8 ± 181.5 | 793.4 ± 174.0 | 818.6 ± 158.7 | 779.6 ± 141.8 | |||||
| SLDJ | JH-L (m) | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 10.1 ± 8.7 | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 11.1 ± 6.9 | 0.14 ± 0.04 | 10.7 ± 8.6 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | 10.8 ± 7.5 |
| JH-R (m) | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | |||||
| RSI-L | 1.31 ± 0.17 | 8.1 ± 4.8 | 1.25 ± 0.18 | 7.5 ± 5.1 | 1.23 ± 0.20 | 7.3 ± 4.7 | 1.19 ± 0.20 | 7.4 ± 5.2 | |
| RSI-R | 1.26 ± 0.20 | 1.21 ± 0.20 | 1.23 ± 0.20 | 1.17 ± 0.20 | |||||
| Test/Metric | Best Score | Asymmetry % (from Best Score) | Average Score | Asymmetry % (from Average Score) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iso Squat | PF-L (N) | 0.08 (0.80 to −0.63) | 0.08 (0.79 to −0.64) | 0.10 (0.82 to −0.61) | 0.07 (0.79 to −0.64) |
| PF-R (N) | 0.12 (0.83 to −0.60) | 0.13 (0.84 to −0.59) | |||
| Imp-L (N·s) | −0.13 (0.59 to −0.85) | −0.60 (0.14 to −1.33) | −0.05 (0.67 to −0.77) | −0.38 (0.34 to −1.10) | |
| Imp-R (N·s) | −0.01 (0.70 to −0.73) | 0.03 (0.74 to −0.69) | |||
| SLCMJ | JH-L (m) | 0.33 (1.05 to −0.39) | −0.03 (0.69 to −0.74) | 0.33 (1.05 to −0.39) | −0.03 (0.68 to −0.75) |
| JH-R (m) | 0.33 (1.05 to −0.39) | 0.33 (1.05 to −0.39) | |||
| PF-L (N) | −0.09 (0.63 to −0.81) | −0.18 (0.53 to −0.90) | −0.02 (0.69 to −0.74) | −0.11 (0.61 to −0.82) | |
| PF-R (N) | −0.07 (0.64 to −0.79) | −0.09 (0.63 to −0.80) | |||
| SLDJ | JH-L (m) | −0.28 (0.44 to −1.00) | 0.07 (0.79 to −0.64) | −0.28 (0.44 to −1.00) | −0.04 (0.67 to −0.76) |
| JH-R (m) | −0.28 (0.44 to −1.00) | 0.00 (0.72 to −0.72) | |||
| RSI-L | −0.43 (0.29 to −1.15) | −0.18 (0.54 to −0.90) | −0.32 (0.40 to −1.04) | −0.03 (0.69 to −0.74) | |
| RSI-R | −0.15 (0.57 to −0.87) | −0.20 (0.52 to −0.92) | |||
| Test/Metric | Kappa Coefficient | Descriptor | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isometric Squat | Peak Force | 0.64 | Substantial |
| Impulse at 0.3s | 0.29 | Fair | |
| SLCMJ | Jump Height | 0.64 | Substantial |
| Peak Force | 0.66 | Substantial | |
| SLDJ | Jump Height | 0.36 | Fair |
| Reactive Strength Index | 0.56 | Moderate | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bishop, C.; Read, P.; Chavda, S.; Jarvis, P.; Turner, A. Using Unilateral Strength, Power and Reactive Strength Tests to Detect the Magnitude and Direction of Asymmetry: A Test-Retest Design. Sports 2019, 7, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7030058
Bishop C, Read P, Chavda S, Jarvis P, Turner A. Using Unilateral Strength, Power and Reactive Strength Tests to Detect the Magnitude and Direction of Asymmetry: A Test-Retest Design. Sports. 2019; 7(3):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7030058
Chicago/Turabian StyleBishop, Chris, Paul Read, Shyam Chavda, Paul Jarvis, and Anthony Turner. 2019. "Using Unilateral Strength, Power and Reactive Strength Tests to Detect the Magnitude and Direction of Asymmetry: A Test-Retest Design" Sports 7, no. 3: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7030058
APA StyleBishop, C., Read, P., Chavda, S., Jarvis, P., & Turner, A. (2019). Using Unilateral Strength, Power and Reactive Strength Tests to Detect the Magnitude and Direction of Asymmetry: A Test-Retest Design. Sports, 7(3), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports7030058






