The Prevalence and Severity of External Auditory Exostosis in Young to Quadragenarian-Aged Warm-Water Surfers: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Testing Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Lifetime Prevalence of Exostosis
4.2. Exostosis in Other Aquatic Activities
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirkland, T. Australia Riding the Wave of the Surf Park Boom. Available online: https://www.abc.net.au/news/2018-04-04/surfing-parks-in-demand-across-australia/9618728 (accessed on 6 October 2019).
- Doering, A. From He’e Nalu to Olympic Sport: A Century of Surfing Evolution. In Sport Tourism Development, 3rd ed.; Higham, J., Hinch, T., Eds.; Channel View Publications: Bristol, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.H.; Eiseman, B.; Straehley, C.J.; Orloff, B.G. Surfing Injuries at Waikiki. JAMA 1977, 237, 668–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Base, L.H.; Alves, M.A.F.; Martins, E.O.; Costa, R.F. Injuries among Professional Surfers. Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte 2007, 13, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banzella, N.V.; Garrett, J.; Gomes, A.; Novack, L.; Osiecki, R.; Korelo, R. Influence of Practice Time on Surfing Injuries. Fisioterapia em Movimento 2017, 30, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Dimmick, S.; Gillett, M.; Sheehan, P.; Sutton, C.; Anderson, S.E. Acute Injuries and Chronic Pathology of the Head and Face Sustained While Surf Board Riding. Trauma 2014, 16, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, J.; Hing, W.; Walsh, J.; Abbott, A.; Sheppard, J.M.; Climstein, M. Acute Injuries in Recreational and Competitive Surfers: Incidence, Severity, Location, Type, and Mechanism. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015, 43, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hay, C.; Barton, S.M.S.; Sulkin, T. Recreational Surfing Injuries in Cornwall, United Kingdom. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2009, 20, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lowdon, B.J.; Pateman, N.A.; Pitman, A.J. Surfboard-Riding Injuries. Med. J. Aust. 1983, 2, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minghelli, B.; Nunes, C.; Oliveira, R. Injuries in Recreational and Competitive Surfers: A Nationwide Study in Portugal. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2018, 58, 1831–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathanson, A.; Haynes, P.; Galanis, D. Surfing Injuries. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2002, 20, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.M.; Bennett, D.; Carter, M.; Garewal, D.; Finch, C.F. Acute Injury and Chronic Disability Resulting from Surfboard Riding. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2004, 7, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulkestad, G.; Drogset, J. Surfing Injuries in Norwegian Arctic Waters. Open Sports Sci. J. 2016, 9, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon, D.F.; Lawson, M.L.; Derkay, C.S.; Hoffmann, K.; McCook, J. Surfer’s Ear: External Auditory Exostoses Are More Prevalent in Cold Water Surfers. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2002, 126, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umeda, Y.; Nakajima, M.; Yoshioka, H. Surfer’s Ear in Japan. Laryngoscope 1989, 99 (Pt 1), 639–641. [Google Scholar]
- Attlmayr, B.; Smith, I.M. Prevalence of ‘Surfer’s Ear’ in Cornish Surfers. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2015, 129, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleyiannis, F.W.; Cockcroft, B.D.; Pinczower, E.F. Exostoses of the External Auditory Canal in Oregon Surfers. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 1996, 17, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, D.F.N. The Relationship of Osteomata of the External Auditory Meatus to Swimming: Hunterian Lecture Delivered at the Royal College of Surgeons of England on 19th April 1962. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 1962, 31, 187–201. [Google Scholar]
- Simas, V.; Furness, J.; Hing, W.; Pope, R.; Walsh, J.; Climstein, M. Ear Discomfort in a Competitive Surfer. Aust. Fam. Physician 2016, 45, 644–646. [Google Scholar]
- Hurst, W.B. A Review of 64 Operations for Removal of Exostoses of the External Ear Canal. Aust. J. Otolaryngol. 2018, 4, 187–190. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, E.W.; McManus, T.C. Surgery for External Auditory Canal Exostoses and Osteomata. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1994, 108, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gilse, P. Des Observations Ulterieures Sur La Genese Exostoses Du Conduitexterne Par L’iritatio D’eau Froid. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1938, 26, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, E.; Osmon, P. New Bone Growth Due to Cold Water in the Ears. Arch. Otolaryngol. 1942, 36, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, G.E. The Relationship between Auditory Exostoses and Cold Water: A Latitudinal Analysis. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1986, 71, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, W.; Bailey, M.; Hurst, B. Prevalence of External Auditory Canal Exostoses in Australian Surfboard Riders. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2004, 118, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furness, J.W.; Hing, W.; Abbott, A.; Walsh, J.; CLimstein, M. Retrospective Analysis of Acute Injuries in Recreational and Competitive Surfers: Injury Location, Type and Mechanism. Int. J. Aquat. Res. Educ. 2014, 8, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Global Sea Temperature. World Sea Temperatures. Available online: https://www.seatemperature.org/ (accessed on 1 October 2019).
- Hutt, J.A.; Black, K.P.; Mead, S.T. Classification of Surf Breaks in Relation to Surfing Skill. Spec. Issue J. Coast. Res. Surfing 2001, 29, 66–81. [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin, J.M.; Stewart, I.A. The Prevalence of Exostoses in the External Auditory Meatus of Surfers. Clinic. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1998, 23, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simas, V.; Remnant, D.; Furness, J.; Bacon, C.J.; Moran, R.W.; Hing, W.A.; Climstein, M. Lifetime Prevalence of Exostoses in New Zealand Surfers. J. Prim. Health Care 2019, 11, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Ikeda, M. Does Cold Water Truly Promote Diver’s Ear? Undersea Hyperb. Med. 1998, 25, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Karegeannes, J.C. Incidence of Bony Outgrowths of the External Ear Canal in U.S. Navy Divers. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 1995, 22, 301–306. [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone, D.M.; Smith, K.A.; Lange, B. Scuba Diving and Otology: A Systematic Review with Recommendations on Diagnosis, Treatment and Post-Operative Care. Diving Hyperb. Med. 2017, 47, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, M.; Barbara, M.; Filipo, R. External Ear Canal Exostosis and Aquatic Sports. ORL J. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. Its Relat. Spec. 1984, 46, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.C.; Liu, C.Y.; Shiao, A.S.; Wang, T. Ear Problems in Swimmers. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2005, 68, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roydhouse, N. Swimmer’s Ears. Can. J. Appl. Sport Sci. 1980, 5, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adams, W.S. The Aetiology of Swimmers’ Exostoses of the External Auditory Canals and of Associated Changes in Hearing. Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1949, 42, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.D.; Schuman, T.A.; Scott, T.A.; Mann, S.E.; Davidson, M.A.; Labadie, R.F. Exostoses of the External Auditory Canal in White-Water Kayakers. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, A.; Tong, R.; Neil, R.; Owens, D.; Tomkinson, A. External Auditory Canal Exostoses in White Water Kayakers. Br. J. Sports Med. 2010, 44, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeev, I.; Notkina, N.; Smith, I.M. Exostoses of the External Auditory Canal: A Long-Term Follow-up Study of Surgical Treatment. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 2004, 29, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, B.F.; Cervantes, W.K.; Doyle, J.; Karamzadeh, A.M.; Boys, P.; Brauel, G.; Mushtaq, E. Prevalence of External Auditory Canal Exostoses in Surfers. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1999, 125, 969–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alexander, V.; Lau, A.; Beaumont, E.; Hope, A. The Effects of Surfing Behaviour on the Development of External Auditory Canal Exostosis. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2015, 272, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, H.; Tono, T.; Kawano, H. Incidence of External Auditory Canal Exostoses in Competitive Surfers in Japan. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 145, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Group (n = 23) | Males (n = 19) | Females (n = 4) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 35.4 (8.3) | 35.9 (7.5) | 33.0 (12.7) | 0.06 |
| Surfing experience (years) | 20.4 (9.9) | 21.4 (8.23) | 13.8 (10.9) | 0.17 |
| Winter surfing sessions (number) | 14.0 (8.3) | 12.9 (8.3) | 19.0 (6.8) | 0.19 |
| Winter surfing sessions (hours/session) | 1.7 (0.6) | 1.8 (0.7) | 1.6 (0.3) | 0.11 |
| Surfing stance: | ||||
| • Regular (left leg forward, %) | 87.0 | 84.2 | 25.0 | – |
| • Goofy (right leg forward, %) | 13.0 | 15.8 | 75.0 | – |
| Board type: | – | |||
| • Short board (%) | 95.7 | 100.0 | 75.0 | |
| • Long board (%) | 4.3 | 0.0 | 25.0 |
| Parameter | Group (n = 23) | Males (n = 19) | Females (n = 4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exostosis identified (%) | 69.6 | 68.4 | 75.0 |
| Exostosis by Age Quartile (%) | |||
| • ≤ 31 years | 66.70 | 75.0 | 50.0 |
| • 32 to ≤ 37 years | 83.3 | 83.3 | 0.0 |
| • 38 to ≤ 41 years | 80.0 | 80.0 | 0.0 |
| • ≥ 42 years | 83.3 | 83.3 | 100.0 |
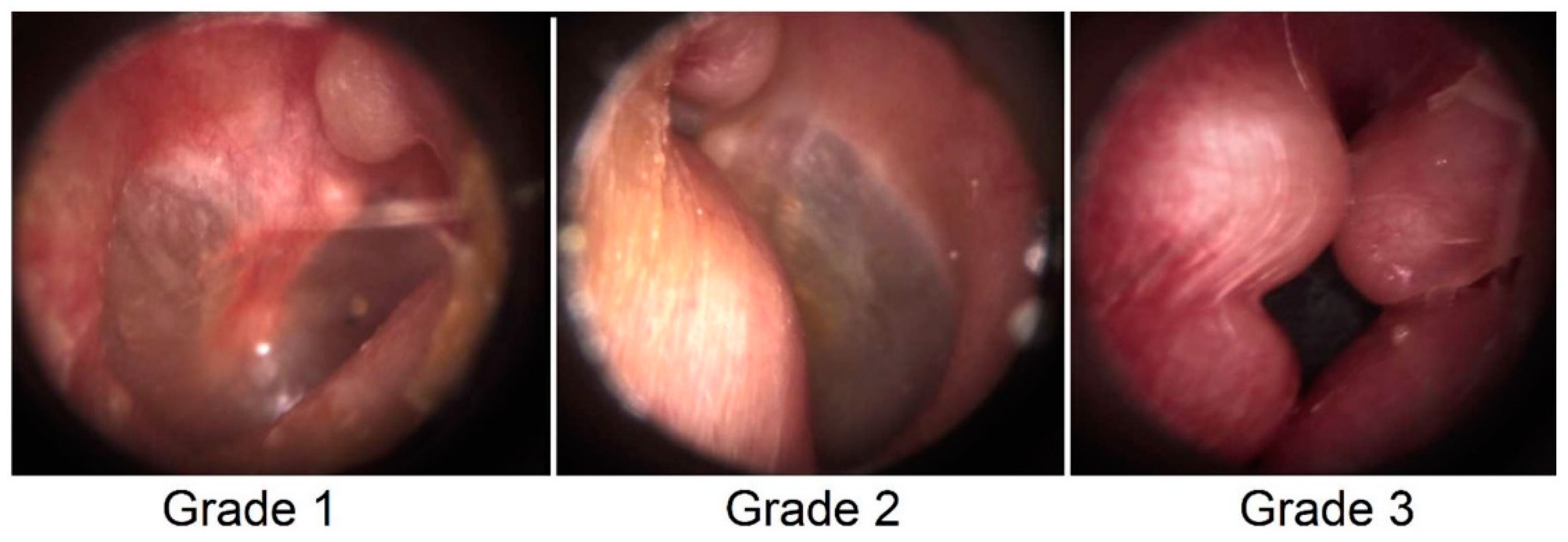
| Exostosis Severity (1 to 3) | |||
| • no visable exostosis (%) | 41.3 | 42.1 | 16.7 |
| • Grade 1 (%) | 30.4 | 26.3 | 66.7 |
| • Grade 2 (%) | 10.9 | 10.5 | 16.7 |
| • Grade 3 (%) | 17.4 | 21.1 | 0.0 |
| Exostosis Bilateral | |||
| • Yes (%) | 80.0 | 76.9 | 100.0 |
| Exostosis location and severity | |||
| • Right ear | 52.2 | 52.6 | 50.0 |
| Grade 1 (%) | 41.7 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| Grade 2 (%) | 25.0 | 30.0 | 0.0 |
| Grade 3 (%) | 33.3 | 40.0 | 0.0 |
| • Left ear | 65.2 | 63.2 | 75.0 |
| Grade 1 (%) | 60.0 | 58.3 | 66.7 |
| Grade 2 (%) | 13.3 | 8.3 | 33.3 |
| Grade 3 (%) | 26.7 | 33.3 | 0.0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simas, V.; Hing, W.; Furness, J.; Walsh, J.; Climstein, M. The Prevalence and Severity of External Auditory Exostosis in Young to Quadragenarian-Aged Warm-Water Surfers: A Preliminary Study. Sports 2020, 8, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports8020017
Simas V, Hing W, Furness J, Walsh J, Climstein M. The Prevalence and Severity of External Auditory Exostosis in Young to Quadragenarian-Aged Warm-Water Surfers: A Preliminary Study. Sports. 2020; 8(2):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports8020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimas, Vini, Wayne Hing, James Furness, Joe Walsh, and Mike Climstein. 2020. "The Prevalence and Severity of External Auditory Exostosis in Young to Quadragenarian-Aged Warm-Water Surfers: A Preliminary Study" Sports 8, no. 2: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports8020017
APA StyleSimas, V., Hing, W., Furness, J., Walsh, J., & Climstein, M. (2020). The Prevalence and Severity of External Auditory Exostosis in Young to Quadragenarian-Aged Warm-Water Surfers: A Preliminary Study. Sports, 8(2), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports8020017








