Effects of Physical Training on Physical and Psychological Parameters in Individuals with Patella Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Study Coding
2.4. Assessment of Methodological Study Quality
2.5. Statistical Analyses
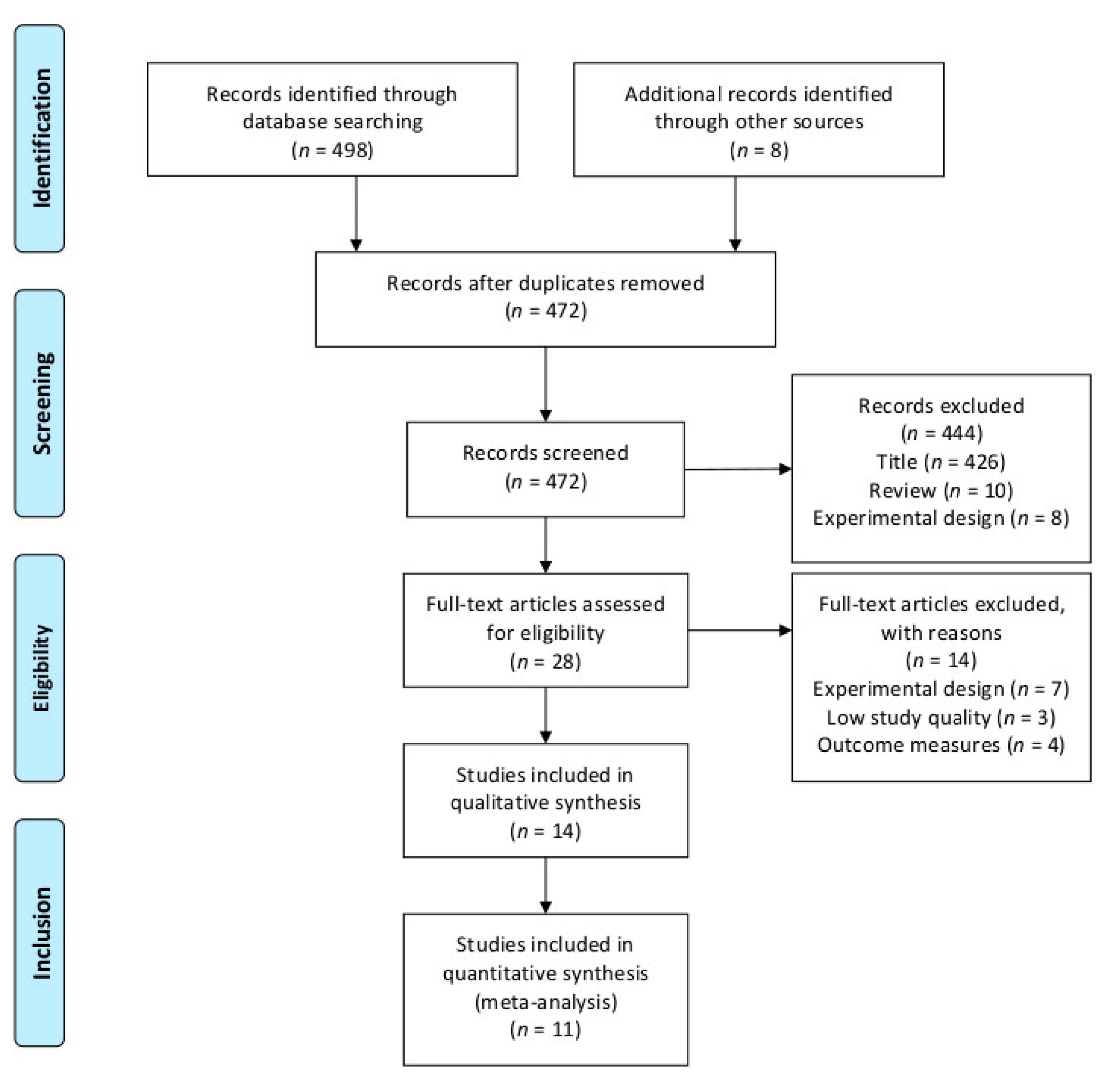
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Included Studies
3.2. Methodological Study Quality
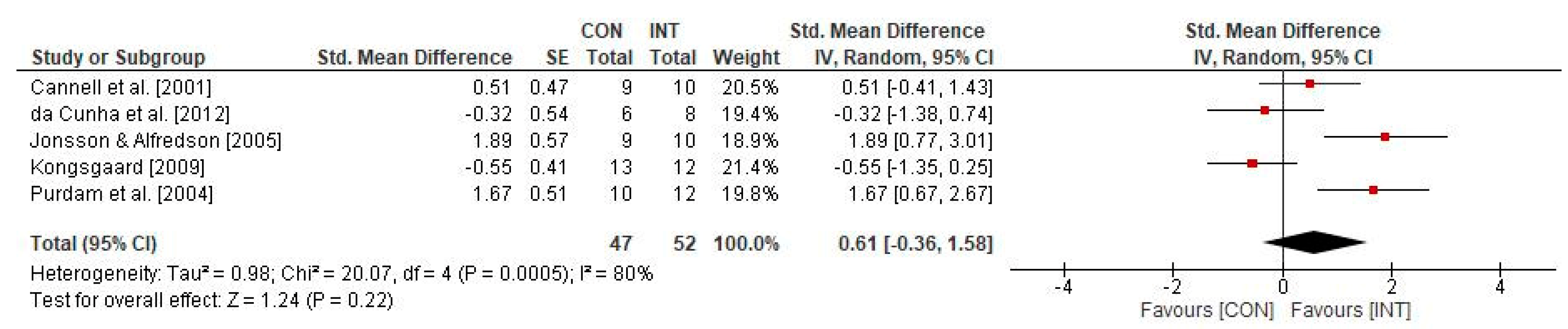
3.3. Effects of Physical Training on Physical Parameters in Individuals with Patella Tendinopathy
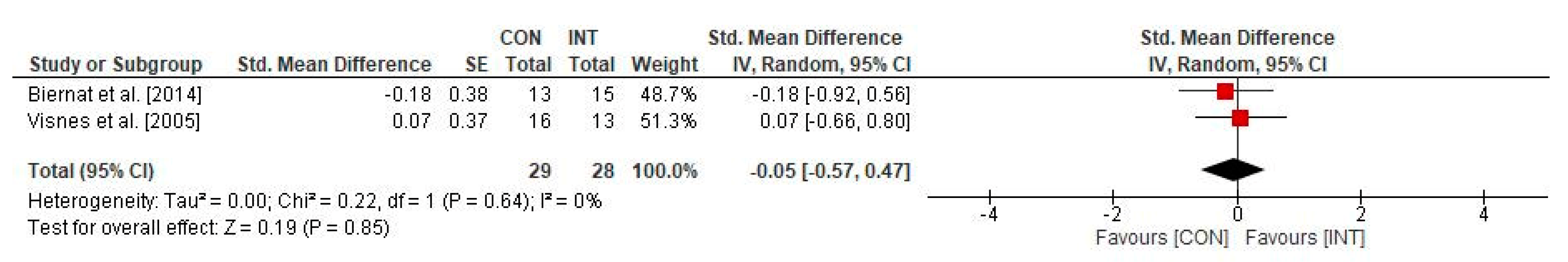
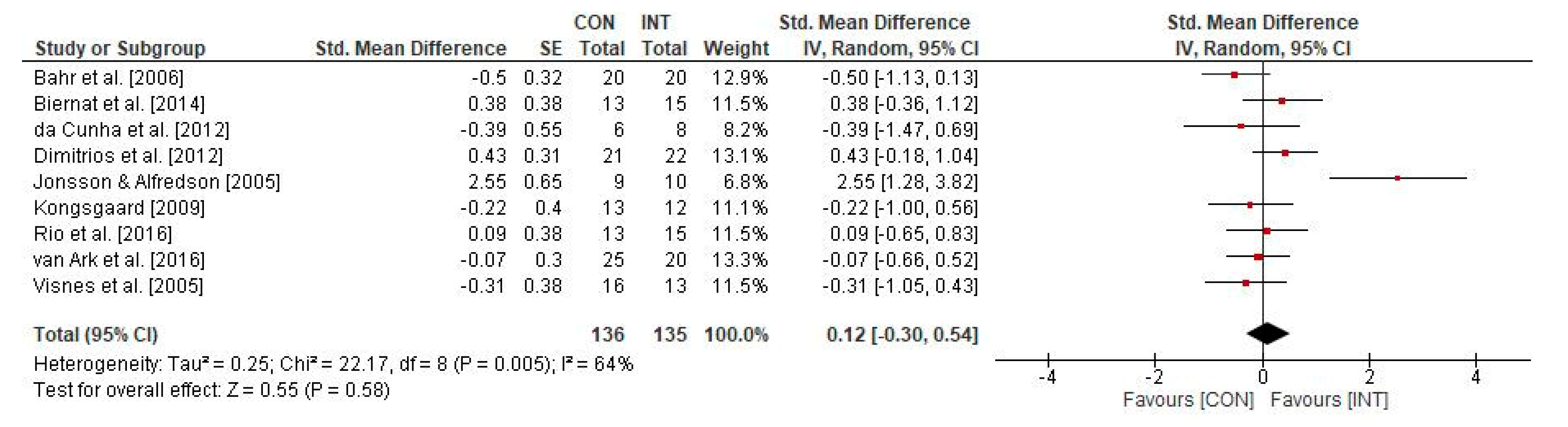
3.4. Effects of Physical Training on Psychological Parameters in Individuals with Patella Tendinopathy
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Physical Training on Physical Parameters in Individuals with Patella Tendinopathy
4.2. Effects of Physical Training on Psychological Parameters in Individuals with Patella Tendinopathy
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dalton, S.E. Overuse injuries in adolescent athletes. Sports Med. 1992, 13, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaux, J.-F.; Forthomme, B.; Le Goff, C.; Crielaard, J.-M.; Croisier, J.-L. Current opinions on tendinopathy. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2011, 10, 238–253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cook, J.L.; Khan, K.M.; Kiss, Z.S.; Griffiths, L. Patellar tendinopathy in junior basketball players: A controlled clinical and ultrasonographic study of 268 patellar tendons in players aged 14–18 years. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2000, 10, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisslen, K.; Alfredson, H.; Peers, K.H.E. Neovascularisation and pain in jumper’s knee: A prospective clinical and sonographic study in elite junior volleyball players: Commentary. Br. J. Sports Med. 2005, 39, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, Ø.B.; Engebretsen, L.; Bahr, R. Prevalence of jumper’s knee among elite athletes from different sports: A cross-sectional study. Am. J. Sports Med. 2005, 33, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.L.; Purdam, C.R. The challenge of managing tendinopathy in competing athletes. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 48, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwerver, J.; Bredeweg, S.W.; Akker-Scheek, I.V.D. Prevalence of jumper’s knee among nonelite athletes from different sports. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 1984–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, D.; Figueroa, F.; Calvo, R. Patellar tendinopathy. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2016, 24, e184–e192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, C.; Fu, S.-C.; Chua, E.; Hu, X.; Rolf, C.; Mattila, V.M.; Qin, L.; Yung, P.S.-H.; Chan, K.-M. Critical review on the socio-economic impact of tendinopathy. Asia-Pac. J. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rehabil. Technol. 2016, 4, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, A.; Koolhaas, W.; Zwerver, J.; Diercks, R.L.; Nieuwenhuis, K.; Van Der Worp, H.; Brouwer, S.; Akker-Scheek, I.V.D. The impact of patellar tendinopathy on sports and work performance in active athletes. Res. Sports Med. 2017, 25, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, E.; Kidgell, D.; Purdam, C.; Gaida, J.; Moseley, G.L.; Pearce, A.J.; Cook, J. Isometric exercise induces analgesia and reduces inhibition in patellar tendinopathy. Br. J. Sports Med. 2015, 49, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, M.A.; Cook, J.; Purdam, C.R.; Kiss, Z.S.; Alfredson, H. Eccentric decline squat protocol offers superior results at 12 months compared with traditional eccentric protocol for patellar tendinopathy in volleyball players. Br. J. Sports Med. 2005, 39, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtaugh, B.; Ihm, J.M. Eccentric training for the treatment of tendinopathies. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2013, 12, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kongsgaard, M.; Kovanen, V.; Aagaard, P.; Doessing, S.; Hansen, P.; Laursen, A.H.; Kaldau, N.C.; Kjaer, M.; Magnusson, S.P. Corticosteroid injections, eccentric decline squat training and heavy slow resistance training in patellar tendinopathy. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2009, 19, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziv, G.; Lidor, R. Vertical jump in female and male volleyball players: A review of observational and experimental studies. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nippert, A.H.; Smith, A.M. Psychologic stress related to injury and impact on sport performance. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 19, 399–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, H.-J.K.; Chagas, M.H.; Szmuchrowski, L.A.; Araujo, S.R.; Campos, C.E.; Giannetti, M.R. Usefulness of the jump-and-reach test in assessment of vertical jump performance. Percept. Motor Skills 2010, 110, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, G.; Dizdar, D.; Jukic, I.; Cardinale, M. Reliability and factorial validity of squat and countermovement jump tests. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2004, 18, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohrer, H.; Nauck, T. Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the VISA-P Questionnaire for German-speaking patients with patellar tendinopathy. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2011, 41, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijur, P.E.; Silver, W.; Gallagher, E.J. Reliability of the visual analog scale for measurement of acute pain. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2001, 8, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, M.D.; Burrows, L.; Parent, E. Intrarater and interrater reliability of the single-leg squat test. Athl. Ther. Today 2010, 15, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visnes, H.; Hokstrud, A.; Cook, J.; Bahr, R. No effect of eccentric training on jumperʼs knee in volleyball players during the competitive season. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2005, 15, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, S.; Lyng, K.; Graven-Nielsen, T.; Riel, H.; Olesen, J.L.; Larsen, L.H.; Rathleff, M.S. Isometric exercise and pain in patellar tendinopathy: A randomized crossover trial. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2020, 23, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahr, R.; Fossan, B.; Løken, S.; Engebretsen, L. Surgical treatment compared with eccentric training for patellar tendinopathy (jumperʼs knee). J. Bone Jt. Surgery-Am. Vol. 2006, 88, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Cunha, R.A.; Dias, A.N.; Santos, M.B.; Lopes, A.D. Comparative study of two protocols of eccentric exercise on knee pain and function in athletes with patellar tendinopathy: Randomized controlled study. Rev. Bras. Med. Esporte 2012, 18, 167–170. [Google Scholar]
- Rio, E.K.; Van Ark, M.; Docking, S.; Moseley, G.L.; Kidgell, D.; Gaida, J.E.; Akker-Scheek, I.V.D.; Zwerver, J.; Cook, J. Isometric contractions are more analgesic than isotonic contractions for patellar tendon pain. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2017, 27, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, C.G.; Sherrington, C.; Herbert, R.D.; Moseley, A.M.; Elkins, M. Reliability of the PEDro scale for rating quality of randomized controlled trials. Phys. Ther. 2003, 83, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ark, M.; Cook, J.L.; Docking, S.I.; Zwerver, J.; Gaida, J.; Akker-Scheek, I.V.D.; Rio, E. Do isometric and isotonic exercise programs reduce pain in athletes with patellar tendinopathy in-season? A randomised clinical trial. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernat, R.; Trzaskoma, Z.; Trzaskoma, Ł; Czaprowski, D. Rehabilitation protocol for patellar tendinopathy applied among 16- to 19-year old volleyball players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, P. Superior results with eccentric compared to concentric quadriceps training in patients with jumper’s knee: A prospective randomised study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2005, 39, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purdam, C.R.; Johnsson, P.; Alfredson, H.; Lorentzon, R.; Cook, J.L.; Khan, K.M. A pilot study of the eccentric decline squat in the management of painful chronic patellar tendinopathy. Br. J. Sports Med. 2004, 38, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannell, L.J.; Taunton, J.E.; Clement, D.B.; Smith, C.; Khan, K.M. A randomised clinical trial of the efficacy of drop squats or leg extension/leg curl exercises to treat clinically diagnosed jumper’s knee in athletes: Pilot study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2001, 35, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hozo, S.P.; Djulbegovic, B.; Hozo, I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2005, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasinopoulos, D.; Pantelis, M.; Kalliopi, S. Comparing the effects of eccentric training with eccentric training and static stretching exercises in the treatment of patellar tendinopathy. A controlled clinical trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2011, 26, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Green, S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Deeks, J.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Higgins, J.P.T., Green, S., Eds.; The Cochrane Collaboration: Chichester, UK, 2008; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Visnes, H.; Bahr, R. The evolution of eccentric training as treatment for patellar tendinopathy (jumper’s knee): A critical review of exercise programmes. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everhart, J.S.; Cole, D.; Sojka, J.H.; Higgins, J.D.; Magnussen, R.A.; Schmitt, L.C.; Flanigan, D.C. Treatment options for patellar tendinopathy: A systematic review. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2017, 33, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.Y.; Wong, S.H. Effects of isometric, eccentric, or heavy slow resistance exercises on pain and function in individuals with patellar tendinopathy: A systematic review. Physiother. Res. Int. 2018, 23, e1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| References | No. of Subjects (Tendons); Sex; Age (Mean ± SD, or Range); Training Status; Sport | Diagnosis | Groups (Subjects/Tendons); Treatment Type | Treatment Modality: No. of Training Weeks/Sessions; No. of Sets/Reps/Duration Per Exercise; Training Intensity | Test Modality, Outcome Measures | PEDro |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| van Ark et al. [29] | 29 (45); 2 F, 27 M; 23.0 ± 4.7 yrs; sub-elite; volleyball, basketball | Palpation | INT (n = 13/20); strength training (isometric quadriceps training, leg extension machine) CON (n = 16/25); strength training (concentric quadriceps training, leg extension machine) | 4 wk/12 sessions; 5 sets of 45 s hold at 60° flexion at 80% MVIC 4 wk/12 sessions; 4 sets of 8 reps (4 s eccentric, 3 s concentric) at 80% 8 RM | Physical: NT Psychological: VISA-P (score), SLDS (Numeric Rating Scale 0–0) at pre-/post-intervention | 5 |
| Rio et al. [27] | 20 (28); 2 F, 18 M; ≥16 yrs; elite and sub-elite; volleyball, basketball | Imaging, SLDS test | INT (n = 10/15); strength training (isometric quadriceps training, leg extension machine) CON (n = 10/13); strength training (concentric quadriceps training, leg extension machine) | 4 wk/12 sessions; 5 sets of 45 s hold at 60° flexion at 80% MVIC 4 wk/12 sessions; 4 sets of 8 reps (4 s eccentric, 3 s concentric) at 80% 8 RM | Physical: NT Psychological: VISA-P (score) at pre-/post-intervention | 6 |
| Biernat et al. [30] | 28 (NR); M; 17.0 ± 0.1 yrs; recreational; volleyball | Imaging | INT (n = 15/NR); volleyball training + strength exercises (eccentric) CON (n = 13/NR); volleyball training only | 4 wk/daily; 3 sets of 15 reps on decline board followed by 20 wk/daily; 3 sets of 15 reps on unstable decline board 24 wk/12 sessions; 5 sets of 45 s hold at 60° flexion at 80% MVIC | Physical: Isokinetic leg strength; CMJ (cm, W) Psychological: VISA-P (score) at pre-/mid-/post-intervention | 5 |
| Dimitrios et al. [35] | 43 (NR); 12 F, 31 M; 27 ± 5 yrs; recreational; NR | Palpation, SLDS test | INT (n = 22/NR); strength (eccentric) and stretching (static) exercises CON (n = 21/NR); strength (eccentric) exercises | 4 wk/20 sessions; 3 sets of 15 reps on decline board, weight increased when pain-free, static quadriceps/hamstrings stretching before and after the eccentric training, 4 exercises of 30 s 4 wk/20 sessions, 3 sets of 15 reps on decline board, weight increased when pain-free | Physical: NT Psychological: VISA-P (score) at pre-/post-intervention | 5 |
| da Cunha et al. [26] | 17 (14); 3 F, 14 M; 25 ± 8 yrs; recreational; volleyball, soccer, athletics, basketball, handball, capoeira, jiu jitsu, triathlon, skating | Imaging | INT (n = 10/8); strength (eccentric) training, maximum pain CON (n = 7/6); strength (eccentric) training, pain-free | 12 wk/36 sessions; 3 sets of 15 reps, weight increased when reps possible, pain mandatory 12 wk/36 sessions; 3 sets of 15 reps, weight increased when pain-free | Physical: NT Psychological: VISA-P (score), VAS (0–10) at pre-/mid-/post-intervention | 7 |
| Kongsgaard et al. [14] | 25 (25); 25 M; 32 ± 8 yrs; recreational; running, soccer, basketball, floorball, handball | Palpation, imaging | INT (n = 12/12); strength (eccentric) training CON I (n = 13/13); strength (dynamic) trainingCON II (n = 12/12); peritendinous corticosteroid injections | 12 wk/168 sessions; 3 sets of 15 reps on 25° decline board, pain-acceptable, weight increased when pain diminished 12 wk/36 sessions; 4 sets of 6–15 reps, pain-acceptable ultrasound-guided injections of 1 mL of 40 mg/mL methylprednisolon | Physical: MVIC Psychological: VISA-P (score), VAS (0–100) at pre-/post-intervention and 6 months post-intervention | 6 |
| Bahr et al. [25] | 35 (40); 5 F, 30 M; 30 ± 8 yrs; recreational; running, soccer, handball, martial arts | Palpation, imaging | INT (n = NR/20); eccentric decline squat, sports from wk 8+ CON (n = NR/20); surgical treatment, sports from wk 8+ | 12 wk; 9.3 ± 4.1 sessions per wk; 3 sets of 15 reps on 25° decline board to 90° knee flexion, moderate pain mandatory (VAS = 4/5), weight increased when VAS < 3 12 wk post-operative training; sessions increased weekly; 10.1 ± 4.3 sessions per wk; wk 1: isometric quadriceps exercises, wk 2: adding walking, wk 3: adding cycling and high squats, wk 4: adding step-ups to a low (5–6 cm) step, wk 5: step-downs from a low (5–6 cm) step, wk 6: adding eccentric squat training similar to INT group but without any pain | Physical: Leg press strength (kg); CMJ (cm) at pre-intervention only Psychological: VISA-P (score) at pre-/post-intervention and 6 and 12 months post-intervention | 7 |
| Jonsson and Alfredson [31] | 15 (19); 2 F, 13 M; 25 ± 9 yrs; recreational; running, soccer, basketball, floorball, handball | Palpation, imaging | INT (n = 8/10); strength (eccentric) training CON (n = 7/9); strength (concentric) training | 12 wk/168 sessions; 3 sets of 15 reps on 25° decline board, pain mandatory, weight increased when reps not painful 12 wk/168 sessions; 3 sets of 15 reps concentric knee extension from 70° knee flexion on 25° decline board, pain mandatory | Physical: NT Psychological: VISA-P (score), VAS (0–100) at pre-/post-intervention | 4 |
| Visnes et al. [23] | 29 (29); 10 F, 19 M; 27 ± 4 yrs; elite; volleyball | Palpation | INT (n = 13/13); strength (eccentric) training CON (n = 16/16); volleyball training only | 12 wk/168 sessions; 3 sets of 15 reps on 25° decline board to 90° knee flexion, 2 s eccentric phase, weight increased when VAS < 5 volleyball training as usual without information on training load | Physical: CMJ (cm), SJ (cm) Psychological: VISA-P (score) at pre-/post-intervention and 6 and 24 wk post-intervention | 7 |
| Purdam et al. [32] | 17 (22); 4 F, 13 M; 25 yrs; recreational; floorball, soccer, volleyball, running, ice hockey, high jump, skiing | Palpation, imaging | INT (n = 8/12); strength (eccentric) training, decline squat CON (n = 9/10); strength (eccentric) training, flat-surface squat | 12 wk/168 sessions; 3 sets of 15 reps on 25° decline board to 90° knee flexion, some pain mandatory, weight increased when reps not painful 12 wk/168 sessions; 3 sets of 15 reps on flat surface to 90° knee flexion, some pain mandatory, weight increased when reps not painful | Physical: NT Psychological: VAS (0–100) at pre-/post-intervention | 5 |
| Cannell et al. [33] | 19 (NR); 6 F, 13 M; 26 ± 7 yrs; recreational; basketball, soccer, running, volleyball, tennis, squash, rowing, American football, gymnastics | Palpation | INT (n = 10/NR); progressive strength (eccentric) training, drop squats CON (n = 9/NR); progressive strength (concentric) training, leg extension/curl | 12 wk/60 sessions; 3 sets of 20 reps, pain mandatory, weight increased when reps not painful; activity (running) added when reps not painful 12 wk/60 sessions; 3 sets of 10 reps with 5 kg each leg extension/leg curl exercise, weight increased when reps not painful; activity (running) added when reps not painful | Physical: Isokinetic leg strength Psychological: VAS (0–10) at pre-/mid-/post-intervention | 7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niering, M.; Muehlbauer, T. Effects of Physical Training on Physical and Psychological Parameters in Individuals with Patella Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports 2021, 9, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9010012
Niering M, Muehlbauer T. Effects of Physical Training on Physical and Psychological Parameters in Individuals with Patella Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports. 2021; 9(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiering, Marc, and Thomas Muehlbauer. 2021. "Effects of Physical Training on Physical and Psychological Parameters in Individuals with Patella Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Sports 9, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9010012
APA StyleNiering, M., & Muehlbauer, T. (2021). Effects of Physical Training on Physical and Psychological Parameters in Individuals with Patella Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports, 9(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9010012






