The Effect of Lower Body Anaerobic Pre-loading on Upper Body Ergometer Time Trial Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. General Procedure
2.3. Body Composition
2.4. Incremental Double Pull Exercise on Upper Body Skiing Ergometer
2.5. Skiing Ergometer Performance
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neiva, H.; Marques, M.C.; Barbosa, T.M.; Izquierdo, M.; Marinho, D. Warm-Up and Performance in Competitive Swimming. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burnley, M.; Davison, G.; Baker, J.R. Effects of Priming Exercise on VO2 Kinetics and the Power-Duration Relationship. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkerson, D.P.; Koppo, K.; Barstow, T.J.; Jones, A.M. Effect of prior multiple-sprint exercise on pulmonary O2 uptake kinetics following the onset of perimaximal exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 97, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Kröll, J.; Lindinger, S.; Pfusterschied, J.; Stöggl, T. High intensity exercise warm-up, inhibition of glycolysis and its practical consequences. In Proceedings of the 6th International Congress on Science and Skiing, St. Christoph am Arlberg, Austria, 14–19 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Purge, P.; Hofmann, P.; Merisaar, R.; Mueller, A.; Tschakert, G.; Mäestu, J.; Jürimäe, J. The Effect of Upper Body Anaerobic Pre-loading on 2000-m Ergometer-Rowing Performance in College Level Male Rowers. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2017, 16, 264–271. [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer, P.; Müller, A.; Tschakert, G.; Sattler, M.C.; Hofmann, P. Performance Enhancing Effect of Metabolic Pre-conditioning on Upper-Body Strength-Endurance Exercise. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parolin, M.L.; Chesley, A.; Matsos, M.P.; Spriet, L.L.; Jones, N.L.; Heigenhauser, G.J.F. Regulation of skeletal muscle glycogen phosphorylase and PDH during maximal intermittent exercise. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 1999, 277, E890–E900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, G.A. Cell-cell and intracellular lactate shuttles. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 5591–5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, G.A. The Science and Translation of Lactate Shuttle Theory. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 757–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bishop, D.; Bonetti, D.; Dawson, B. The effect of three different warm-up intensities on kayak ergometer performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, N.; Nishida, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Tanigawa, S.; Nishiyasu, T. Effects of work-matched moderate- and high-intensity warm-up on power output during 2-min supramaximal cycling. Biol. Sport 2018, 35, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnley, M.; Doust, J.H.; Jones, A.M. Effects of Prior Warm-up Regime on Severe-Intensity Cycling Performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, C.J.; Pyne, D.; Thompson, K.G.; Rattray, B. Warm-Up Strategies for Sport and Exercise: Mechanisms and Applications. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 1523–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangsbo, J.; Michalsik, L.; Petersen, A. Accumulated O2Deficit during Intense Exercise and Muscle Characteristics of Elite Athletes. Int. J. Sports Med. 1993, 14, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitanos, G.C.; Williams, C.; Boobis, L.H.; Brooks, S. Human muscle metabolism during intermittent maximal exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1993, 75, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burnley, M.; Doust, J.H.; Carter, H.; Jones, A.M. Effects of prior exercise and recovery duration on oxygen uptake kinetics during heavy exercise in humans. Exp. Physiol. 2001, 86, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iaia, F.M.; Perez-Gomez, J.; Nordsborg, N.; Bangsbo, J. Effect of previous exhaustive exercise on metabolism and fatigue development during intense exercise in humans. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Robergs, R.; Pascoe, D.D.; Costill, D.L.; Fink, W.J.; Chwalbinska-Moneta, J.; A Davis, J.; Hickner, R. Effects of warm-up on muscle glycogenolysis during intense exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1991, 23, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.; Nimmo, M. Effects of active, passive or no warm-up on metabolism and performance during high-intensity exercise. J. Sports Sci. 2001, 19, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaesser, G.A.; Ward, S.A.; Baum, V.C.; Whipp, B.J. Effects of infused epinephrine on slow phase of O2 uptake kinetics during heavy exercise in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1994, 77, 2413–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohnert, B.; A Ward, S.; Whipp, B.J. Effects of prior arm exercise on pulmonary gas exchange kinetics during high-intensity leg exercise in humans. Exp. Physiol. 1998, 83, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanis, G.; Nevill, M.; Lakomy, H. Effects of previous dynamic arm exercise on power output during repeated maximal sprint cycling. J. Sports Sci. 1994, 12, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brien, D.M.; McKenzie, D.C. The effect of induced alkalosis and acidosis on plasma lactate and work output in elite oarsmen. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1989, 58, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, B.J.; Robinson, S.; Wiegman, D.L.; Aulick, L.H. Effect of warm-up on metabolic responses to strenuous exercise. Med. Sci. Sports 1975, 7, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, F.; Verdi, M.; Junior, B.R.S.; Caponi, S. 50th Anniversary of the Declaration of Helsinki: The Double Standard Was Introduced. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 600–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Chafi, H.; Guo, B.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Murray, K.B.; Zheng, J.; Jia, G.; Information, P.E.K.F.C. Quantitative Comparison of 2 Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Systems in Assessing Body Composition and Bone Mineral Measurements. J. Clin. Densitom. 2016, 19, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, D.H.; Hetrick, R.P.; Kendall, K.L.; E Smith-Ryan, A.; E Jackson, M.; Stout, J.R. Characterization of the work–time relationship during cross-country ski ergometry. Physiol. Meas. 2013, 35, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegge, A.M.; Bucher, E.; Ettema, G.; Faude, O.; Holmberg, H.-C.; Sandbakk, Ø. Gender differences in power production, energetic capacity and efficiency of elite cross-country skiers during whole-body, upper-body, and arm poling. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2015, 116, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, P.; Jürimäe, T.; Jürimäe, J.; Purge, P.; Mäestu, J.; Wonisch, M.; Pokan, R.; Von Duvillard, S.P. HRTP, Prolonged Ergometer Exercise, and Single Sculling. Int. J. Sports Med. 2007, 28, 964–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, G. Borg’s Perceived Exertion and Pain Scales; Ergonomics; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-88011-623-7. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge: London, UK, 1988; ISBN 978-0-203-77158-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Marshall, S.W.; Batterham, A.M.; Hanin, J. Progressive Statistics for Studies in Sports Medicine and Exercise Science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Losnegard, T.; Mikkelsen, K.; Rønnestad, B.R.; Hallén, J.; Rud, B.; Raastad, T. The effect of heavy strength training on muscle mass and physical performance in elite cross country skiers. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 21, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastin, P.B. Energy System Interaction and Relative Contribution During Maximal Exercise. Sports Med. 2001, 31, 725–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secher, N.H. Physiological and Biomechanical Aspects of Rowing. Sports Med. 1993, 15, 24–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Brown, A.M.; Frontera, W.R. Principles of Exercise Physiology: Responses to Acute Exercise and Long-term Adaptations to Training. PMR 2012, 4, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, E.; Holmberg, H.-C.; Ørtenblad, N.; Björklund, G. Metabolic Responses and Pacing Strategies during Successive Sprint Skiing Time Trials. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 2544–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, D. Warm Up II. Sports Med. 2003, 33, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hébert-Losier, K.; Zinner, C.; Platt, S.; Stöggl, T.; Holmberg, H.-C. Factors that Influence the Performance of Elite Sprint Cross-Country Skiers. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 319–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Participants (n = 13) | Min | Max | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 15.4 | 24.9 | 18.3 ± 2.9 |
| Height (cm) | 171.0 | 190.0 | 180.8 ± 4.6 |
| Body Mass (kg) | 55.2 | 82.7 | 70.8 ± 7.3 |
| Fat (%) | 12.9 | 26.3 | 15.5 ± 3.5 |
| VO2max (L/min−1) | 2.85 | 5.19 | 4.06 ± 0.58 |
| VO2max (mL min−1 kg−1) | 49.82 | 66.42 | 57.32 ± 5.30 |
| VEmax (L min−1) | 109.90 | 184.60 | 146.6 ± 24.3 |
| HR at VT1 (beats min−1) | 136 | 178 | 154.2 ± 11.4 |
| P at VT1 (W) | 82 | 163 | 127.0 ± 25.5 |
| HR at VT2 (beats min−1) | 165 | 195 | 181.3 ± 8.5 |
| P at VT2 (W) | 129 | 222 | 186.2 ± 28.2 |
| Pmax (W) | 180 | 345 | 270.1 ± 42.1 |
| HRmax (beats min−1) | 185 | 206 | 198.6 ± 6.9 |
| Participants (n = 13) | Time200 m (s) | Time400 m (s) | Time600 m (s) | Time800 m (s) | Time1000 m (s) | Time (s) | RPEbefore | RPEafter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TTlow | 44.8 ± 4.2 | 44.9 ± 4.4 | 45.6 ± 4.0 | 45.7 ± 3.1 | 44.1 ± 2.6 | 225.1 ± 17.6 | 0.6 ± 0.8 | 8.9 ± 0.9 |
| TThigh | 44.3 ± 3.7 | 44.4 ± 3.5 | 45.8 ± 3.4 | 46.6 ± 3.2 | 45.2 ± 3.5 | 226.1 ± 15.7 | 1.4 ± 1.2 | 9.5 ± 0.7 |
| Dif | 0.5 ± 1.6 | 0.6 ± 1.6 | −0.2 ± 1.4 | −0.8 ± 1.5 | −1.1 ± 1.9 | −0.9 ± 4.6 | −0.8 ± 1.2 | −0.7 ± 1.1 |
| p | 0.28 | 0.21 | 0.05 * | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.47 | 0.04 * | 0.05 * |
| Effect size | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.29 | 0.42 | 0.06 | 1.0 | 0.67 |
| N = 13 | Before Warm-Up | After Warm-Up | Before TT | After TT | After TT 3 min | After TT 6 min | After TT 9 min | After TT 12 min | After TT 15 min | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
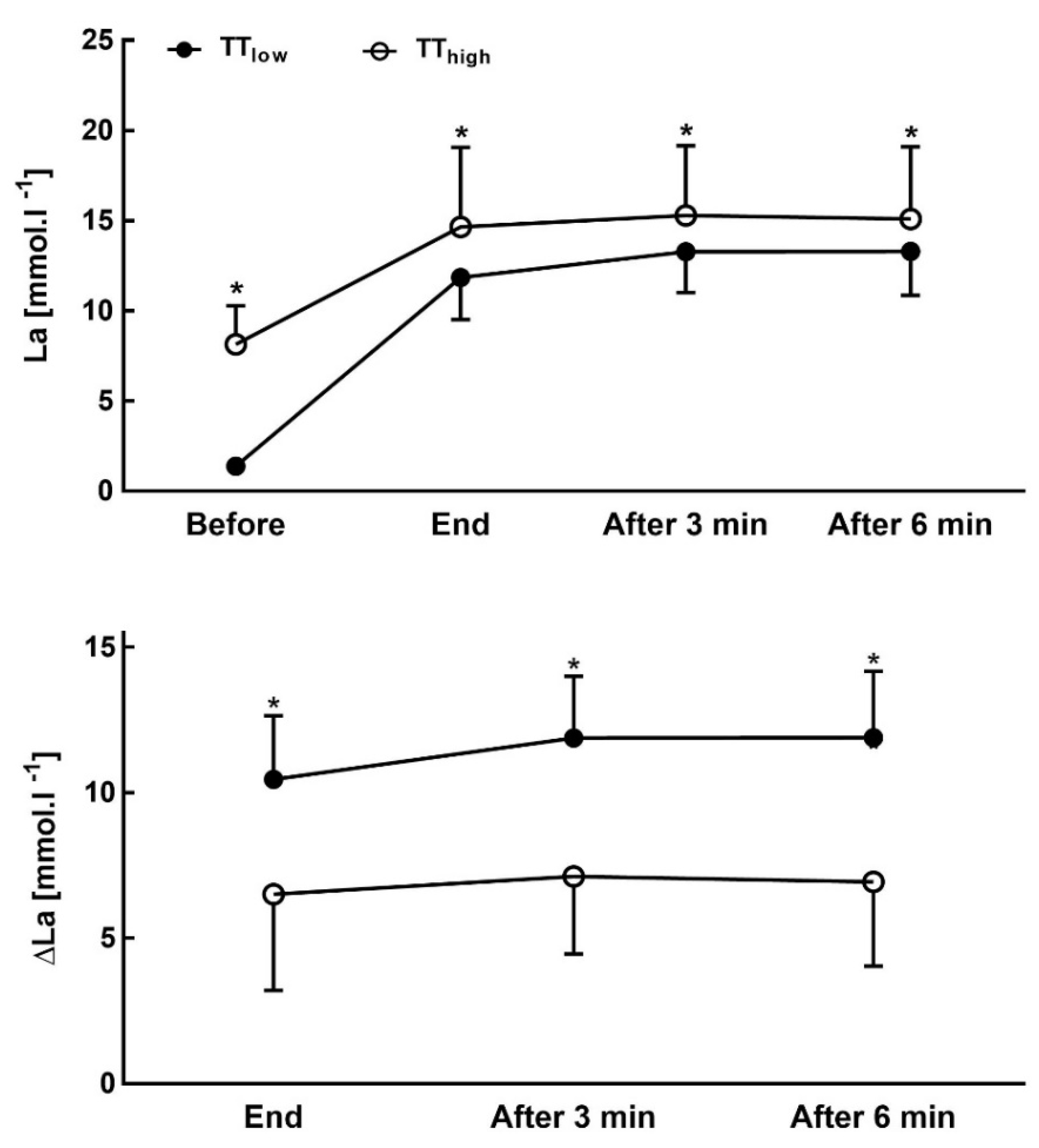
| Lactate | TTlow | 1.9 ± 0.7 | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 11.8 ± 2.4 | 13.3 ± 2.4 | 13.3 ± 2.4 | 12.7 ± 2.7 | 12.1 ± 2.6 | 10.9 ± 2.9 |
| TThigh | 1.8 ± 0.6 | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 8.2 ± 2.2 * | 14.7 ± 4.6 * | 15.3 ± 4.0 * | 15.1 ± 4.2 * | 14.7 ± 4.1 * | 13.7 ± 4.1 * | 12.6 ± 4.3 * | |
| Difference | 5.6% | 0% | 82.9% | 19.7% | 13.1% | 11.9% | 13.6% | 11.7% | 13.5% | |
| Effect Size | 0.2 | 0.0 | 4.3 * | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| Glucose | TTlow | 5.3 ± 0.9 | 4.5 ± 0.5 | 4.9 ± 0.5 | 5.0 ± 0.4 | 6.2 ± 0.7 | 6.0 ± 0.8 | 5.7 ± 0.6 | 5.6 ± 0.6 | 5.5 ± 0.6 |
| TThigh | 5.3 ± 1.0 | 4.5 ± 0.4 | 4.5 ± 0.8 | 4.9 ± 1.0 | 6.2 ± 1.0 | 5.9 ± 1.1 | 5.8 ± 0.8 | 5.6 ± 0.7 | 5.4 ± 0.9 | |
| Difference | 0.0% | 0.0% | 8.2% | 2.0% | 0.0% | 1.7% | 1.7% | 0.0% | 1.8% | |
| Effect Size | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Purge, P.; Valiulin, D.; Kivil, A.; Müller, A.; Tschakert, G.; Jürimäe, J.; Hofmann, P. The Effect of Lower Body Anaerobic Pre-loading on Upper Body Ergometer Time Trial Performance. Sports 2021, 9, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9060079
Purge P, Valiulin D, Kivil A, Müller A, Tschakert G, Jürimäe J, Hofmann P. The Effect of Lower Body Anaerobic Pre-loading on Upper Body Ergometer Time Trial Performance. Sports. 2021; 9(6):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9060079
Chicago/Turabian StylePurge, Priit, Dmitri Valiulin, Allar Kivil, Alexander Müller, Gerhard Tschakert, Jaak Jürimäe, and Peter Hofmann. 2021. "The Effect of Lower Body Anaerobic Pre-loading on Upper Body Ergometer Time Trial Performance" Sports 9, no. 6: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9060079
APA StylePurge, P., Valiulin, D., Kivil, A., Müller, A., Tschakert, G., Jürimäe, J., & Hofmann, P. (2021). The Effect of Lower Body Anaerobic Pre-loading on Upper Body Ergometer Time Trial Performance. Sports, 9(6), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9060079








