Neuromuscular Adjustments Following Sprint Training with Ischemic Preconditioning in Endurance Athletes: Preliminary Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Training Intervention
2.4. Ischemic Preconditioning
2.5. Testing Procedures and Data Collection
2.5.1. Baseline
2.5.2. Familiarization
2.5.3. 30-s Wingate Test
2.5.4. Electromyography Recording and Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
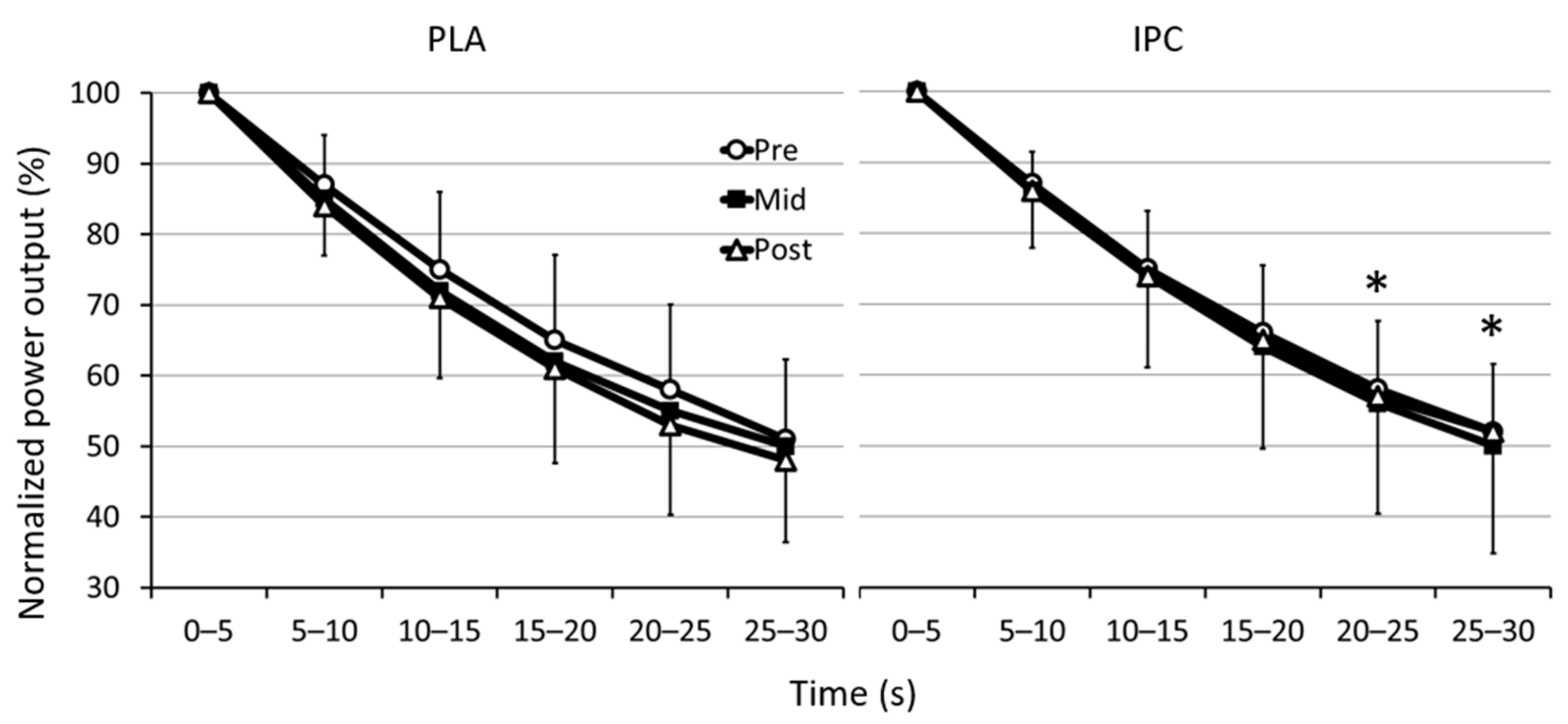
3.1. Mechanical Data
3.2. Electromyographic Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salvador, A.F.; De Aguiar, R.A.; Lisbôa, F.D.; Pereira, K.L.; Cruz, R.S.d.O.; Caputo, F. Ischemic Preconditioning and Exercise Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2016, 11, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsay, A.; Petersen, C.; Blackwell, G.; Ferguson, H.; Parker, G.; Steyn, N.; Gieseg, S.P. The Effect of 1 Week of Repeated Ischaemic Leg Preconditioning on Simulated Keirin Cycling Performance: A Randomised Trial. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2017, 3, e000229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, T.N.; Sabino-Carvalho, J.L.C.; Lopes, T.R.; Ribeiro, I.C.; Succi, J.E.; Da Silva, A.C.; Silva, B.M. Ischemic Preconditioning and Repeated Sprint Swimming. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2016, 48, 1967–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enko, K.; Nakamura, K.; Yunoki, K.; Miyoshi, T.; Akagi, S.; Yoshida, M.; Toh, N.; Sangawa, M.; Nishii, N.; Nagase, S.; et al. Intermittent Arm Ischemia Induces Vasodilatation of the Contralateral Upper Limb. J. Physiol. Sci. 2011, 61, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.G.; Birk, G.K.; Cable, N.T.; Atkinson, G.; Green, D.J.; Jones, H.; Thijssen, D.H.J. Remote Ischemic Preconditioning Prevents Reduction in Brachial Artery Flow-Mediated Dilation after Strenuous Exercise. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2012, 303, H533–H538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis-Deschênes, P.; Joanisse, D.R.; Billaut, F. Ischemic Preconditioning Increases Muscle Perfusion, Oxygen Uptake, and Force in Strength-Trained Athletes. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kilding, A.E.; Sequeira, G.M.; Wood, M.R. Effects of Ischemic Preconditioning on Economy, VO2 Kinetics and Cycling Performance in Endurance Athletes. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 118, 2541–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caru, M.; Lalonde, F.; Daigle, C.; Comtois, A.S.; Curnier, D. The Effect of Remote Ischemic Preconditioning at Moderate- and High-Intensity Steady-State Cycling Exercise amongst Amateur Athletes. Med. Dello Sport 2019, 72, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slysz, J.T.; Burr, J.F. Impact of 8 Weeks of Repeated Ischemic Preconditioning on Running Performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 119, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, A.; Petersen, C.; Ferguson, H.; Blackwell, G.; Rickerby, S. Lack of a Dose Response from 7 Days of Ischemic Preconditioning in Moderately Trained Cyclists. Sport. Med. Int. Open 2018, 2, E91–E97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richard, P.; Billaut, F. Combining Chronic Ischemic Preconditioning and Inspiratory Muscle Warm-Up to Enhance On-Ice Time-Trial Performance in Elite Speed Skaters. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marocolo, M.; Billaut, F.; da Mota, G.R. Ischemic Preconditioning and Exercise Performance: An Ergogenic Aid for Whom? Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paradis-Deschênes, P.; Joanisse, D.R.; Mauriège, P.; Billaut, F. Ischemic Preconditioning Enhances Aerobic Adaptations to Sprint-Interval Training in Athletes Without Altering Systemic Hypoxic Signaling and Immune Function. Front. Sport. Act. Living 2020, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, P.B.; Jenkins, D.G. The Scientific Basis for High-Intensity Interval Training. Sport. Med. 2002, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelly, L.E.; Gillen, J.B. Finding the Metabolic Stress ‘Sweet Spot’: Implications for Sprint Interval Training-Induced Muscle Remodelling. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 4573–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Novaes, J.; da Silva Telles, L.G.; Monteiro, E.R.; da Silva Araujo, G.; Vingren, J.L.; Silva Panza, P.; Reis, V.M.; Laterza, M.C.; Vianna, J.M. Ischemic Preconditioning Improves Resistance Training Session Performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basmajian, J.V.; de Luca, C.J. Muscles Alive: Their Functions Revealed by Electromyography, 5th ed.; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Amann, M.; Runnels, S.; Morgan, D.E.; Trinity, J.D.; Fjeldstad, A.S.; Wray, D.W.; Reese, V.R.; Richardson, R.S. On the Contribution of Group III and IV Muscle Afferents to the Circulatory Response to Rhythmic Exercise in Humans. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 3855–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, D.J.; Petrie, S.G.; Zhou, B.-H.; Guanche, C.A.; Baratta, R.V. Myoelectric and Mechanical Changes Elicited by Ischemic Preconditioning in the Feline Hindlimb. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 1997, 7, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, S.D.; Bezodis, N.E.; Glaister, M.; Pattison, J.R. The Effect of Ischemic Preconditioning on Repeated Sprint Cycling Performance. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2015, 47, 1652–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, R.S.d.O.; de Aguiar, R.A.; Turnes, T.; Salvador, A.F.; Caputo, F. Effects of Ischemic Preconditioning on Short-Duration Cycling Performance. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.; Concon, V.; Meloni, M.; De Souza, E.O.; Barroso, R. Effects of Resistance Training Combined with Ischemic Preconditioning on Muscle Size and Strength in Resistance-Trained Individuals. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 2020, 60, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, M.; Stylianides, G.; Djaoui, L.; Dellal, A.; Chamari, K. Session-RPE Method for Training Load Monitoring: Validity, Ecological Usefulness, and Influencing Factors. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, B.M.d.; Moro, V.L.; Rossato, M.; Lucas, R.D.d.; Diefenthaeler, F. Effects of Saddle Height on Performance and Muscular Activity During the Wingate Test. J. Phys. Educ. 2017, 28, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borg, G. Borg’s Perceived Exertion and Pain Scales by Gunnar Borg, 1st ed.; Human Kinetics: Windsor, ON, Canada, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hermens, H.J.; Freriks, B.; Disselhorst-Klug, C.; Rau, G. Development of Recommendations for SEMG Sensors and Sensor Placement Procedures. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2000, 10, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.J.; Billaut, F. Influence of Cerebral and Muscle Oxygenation on Repeated-Sprint Ability. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batterham, A.M.; Hopkins, W.G. Making Meaningful Inferences About Magnitudes. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2006, 1, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Marshall, S.W.; Batterham, A.M.; Hanin, J. Progressive Statistics for Studies in Sports Medicine and Exercise Science. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hawley, J.A.; Myburgh, K.H.; Noakes, T.D.; Dennis, S.C. Training Techniques to Improve Fatigue Resistance and Enhance Endurance Performance. J. Sports Sci. 1997, 15, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paixão, R.; da Mota, G.; Marocolo, M. Acute Effect of Ischemic Preconditioning Is Detrimental to Anaerobic Performance in Cyclists. Int. J. Sports Med. 2014, 35, 912–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, N.; Mahony, B.; Tracey, C.; Fawkner, S.; Murray, A. Effect of Ischemic Preconditioning on Repeated Sprint Ability in Team Sport Athletes. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lalonde, F.; Curnier, D.Y. Can Anaerobic Performance Be Improved by Remote Ischemic Preconditioning? J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marocolo, M.; da Mota, G.; Simim, M.; Appell Coriolano, H.-J. Myths and Facts About the Effects of Ischemic Preconditioning on Performance. Int. J. Sports Med. 2015, 37, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, S.; Della-Morte, D.; Dave, K.R.; Sacco, R.L.; Perez-Pinzon, M.A. Biomarkers for Ischemic Preconditioning: Finding the Responders. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bar-Or, O. The Wingate Anaerobic Test. Sport. Med. 1987, 4, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margaria, R.; Oliva, R.D.; Di Prampero, P.E.; Cerretelli, P. Energy Utilization in Intermittent Exercise of Supramaximal Intensity. J. Appl. Physiol. 1969, 26, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCartney, N.; Heigenhauser, G.J.; Jones, N.L. Power Output and Fatigue of Human Muscle in Maximal Cycling Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1983, 55, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, A.M.; St Clair Gibson, A.; Lambert, M.I.; Nobbs, L.; Noakes, T.D. Effects of Supramaximal Exercise on the Electromyographic Signal. Br. J. Sports Med. 2003, 37, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Halley, S.L.; Marshall, P.; Siegler, J.C. The Effect of Ischaemic Preconditioning on Central and Peripheral Fatiguing Mechanisms in Humans Following Sustained Maximal Isometric Exercise. Exp. Physiol. 2018, 103, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, P.W.; Rasmussen, S.B.; Krogh, M.; Halley, S.; Siegler, J.C. Changes in the Quadriceps Spinal Reflex Pathway after Repeated Sprint Cycling Are Not Influenced by Ischemic Preconditioning. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 120, 1189–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdle, B.; Fugl-Meyer, A.R. Is the Mean Power Frequency Shift of the EMG a Selective Indicator of Fatigue of the Fast Twitch Motor Units? Acta Physiol. Scand. 1992, 145, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupa, E.J.; Roy, S.H.; Kandarian, S.C.; De Luca, C.J. Effects of Muscle Fiber Type and Size on EMG Median Frequency and Conduction Velocity. J. Appl. Physiol. 1995, 79, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuura, R.; Ogata, H.; Yunoki, T.; Arimitsu, T.; Yano, T. Effect of Blood Lactate Concentration and the Level of Oxygen Uptake Immediately before a Cycling Sprint on Neuromuscular Activation during Repeated Cycling Sprints. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2006, 25, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Downey, J.M.; Davis, A.M.; Cohen, M.V. Signaling Pathways in Ischemic Preconditioning. Heart Fail. Rev. 2007, 12, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, M.; Proctor, L.T.; Sebranek, J.J.; Pegelow, D.F.; Dempsey, J.A. Opioid-Mediated Muscle Afferents Inhibit Central Motor Drive and Limit Peripheral Muscle Fatigue Development in Humans. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisafulli, A.; Tangianu, F.; Tocco, F.; Concu, A.; Mameli, O.; Mulliri, G.; Caria, M.A. Ischemic Preconditioning of the Muscle Improves Maximal Exercise Performance but Not Maximal Oxygen Uptake in Humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blain, G.M.; Mangum, T.S.; Sidhu, S.K.; Weavil, J.C.; Hureau, T.J.; Jessop, J.E.; Bledsoe, A.D.; Richardson, R.S.; Amann, M. Group III/IV Muscle Afferents Limit the Intramuscular Metabolic Perturbation during Whole Body Exercise in Humans. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 5303–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cruz, R.S.d.O.; Pereira, K.L.; Lisbôa, F.D.; Caputo, F. Could Small-Diameter Muscle Afferents Be Responsible for the Ergogenic Effect of Limb Ischemic Preconditioning? J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 122, 718–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| IPC | PLA | IPC vs. PLA | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRE | MID | POST | PRE | MID | POST | PRE-MID | MID-POST | PRE-POST | |
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | %D (ES) | |||||||
| PPO (W) | 1077.6 ± 208.0 | 1122.0 ± 251.2 | 1131.4 ± 273.8 | 1008.3 ± 84.9 | 1052.9 ± 139.4 | 1093.6 ± 185.2 | −0.4% (−0.03) | −2.9% (−0.18) | −3.3% (−0.21) |
| PPO/kg (W/kg) | 14.1 ± 2.1 | 14.4 ± 2.1 | 14.9 ± 2.9 | 13.7 ± 1.8 | 14.1 ± 1.8 | 14.9 ± 2.0 | −0.5% (−0.26) | −1.3% (−0.24) | −3.5% (−0.24) |
| MPO (W) | 750.5 ± 115.4 | 751.0 ± 114.1 | 759.1 ± 105.5 | 704.9 ± 101.1 | 708.5 ± 108.4 | 717.6 ± 97.1 | −0.3% (−0.02) | −0.2% (−0.02) | −0.6% (−0.04) |
| MPO/kg (W/kg) | 9.9 ± 1.3 | 9.9 ± 1.2 | 10.0 ± 1.1 | 9.5 ± 0.9 | 9.5 ± 1.2 | 9.7 ± 0.9 | −0.2% (−0.03) | −0.5% (−0.05) | −0.7% (−0.06) |
| Fatigue index (%) | 48.1 ± 9.6 | 50.4 ± 15.0 | 48.4 ± 17.1 | 48.8 ± 11.3 | 49.9 ± 10.7 | 52.3 ± 11.6 | −0.6% (−0.02) | −10.0% (−0.46) | −10.5% (−0.49) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bouffard, S.; Paradis-Deschênes, P.; Billaut, F. Neuromuscular Adjustments Following Sprint Training with Ischemic Preconditioning in Endurance Athletes: Preliminary Data. Sports 2021, 9, 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9090124
Bouffard S, Paradis-Deschênes P, Billaut F. Neuromuscular Adjustments Following Sprint Training with Ischemic Preconditioning in Endurance Athletes: Preliminary Data. Sports. 2021; 9(9):124. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9090124
Chicago/Turabian StyleBouffard, Stéphan, Pénélope Paradis-Deschênes, and François Billaut. 2021. "Neuromuscular Adjustments Following Sprint Training with Ischemic Preconditioning in Endurance Athletes: Preliminary Data" Sports 9, no. 9: 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9090124
APA StyleBouffard, S., Paradis-Deschênes, P., & Billaut, F. (2021). Neuromuscular Adjustments Following Sprint Training with Ischemic Preconditioning in Endurance Athletes: Preliminary Data. Sports, 9(9), 124. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports9090124







