Abstract
Interstitial light elements play an important role in magnetic materials by improving the magnetic properties through changes of the unit cell volume or through orbital hybridization between the magnetic and interstitial atoms. In this review focusing on the effects of interstitial atoms in Mn-based compounds, which are not well researched, the studies of interstitial atoms in three kinds of magnetic materials (rare-earth Fe-, Mn-, and rare-earth-based compounds) are surveyed. The prominent features of Mn-based compounds are interstitial-atom-induced changes or additional formation of magnetism—either a change from antiferromagnetism (paramagnetism) to ferromagnetism or an additional formation of ferromagnetism. It is noted that in some cases, ferromagnetic coupling can be abruptly caused by a small number of interstitial atoms, which has been overlooked in previous research on rare-earth Fe-based compounds. We also present candidates of Mn compounds, which enable changes of the magnetic state. The Mn-based compounds are particularly important for the easy fabrication of highly functional magnetic devices, as they allow on-demand control of magnetism without causing a large lattice mismatch, among other advantages.
1. Introduction
Some crystal structures possess interstitial crystallographic sites, which light elements such as hydrogen, boron, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms can occupy. There is a rather long history of metallurgical, physical, and chemical research studies on interstitial atoms [1,2]. In past years, domain control of ferromagnets has been studied [1]. Since the 1980s, interstitial atoms have attracted intense attention related to the improvement of magnetic properties of rare-earth Fe and Co-based permanent magnets [2,3,4,5,6].
Interstitial atoms have two major roles—influencing the stability of the crystal structure and in the modification or change in magnetic properties. In the former case, small amounts of interstitial light elements are required to stabilize the desired crystal structure; compounds without interstitial atoms would not exist in thermal equilibrium. In the latter case, interstitial atoms affect the crystal structure parameters, such as the interatomic distances between magnetic atoms or the orbital hybridization between magnetic and interstitial atoms, consequently meaning the magnetic ordering temperature, the magnetic moment, the magnetic structure, and other factors can be altered.
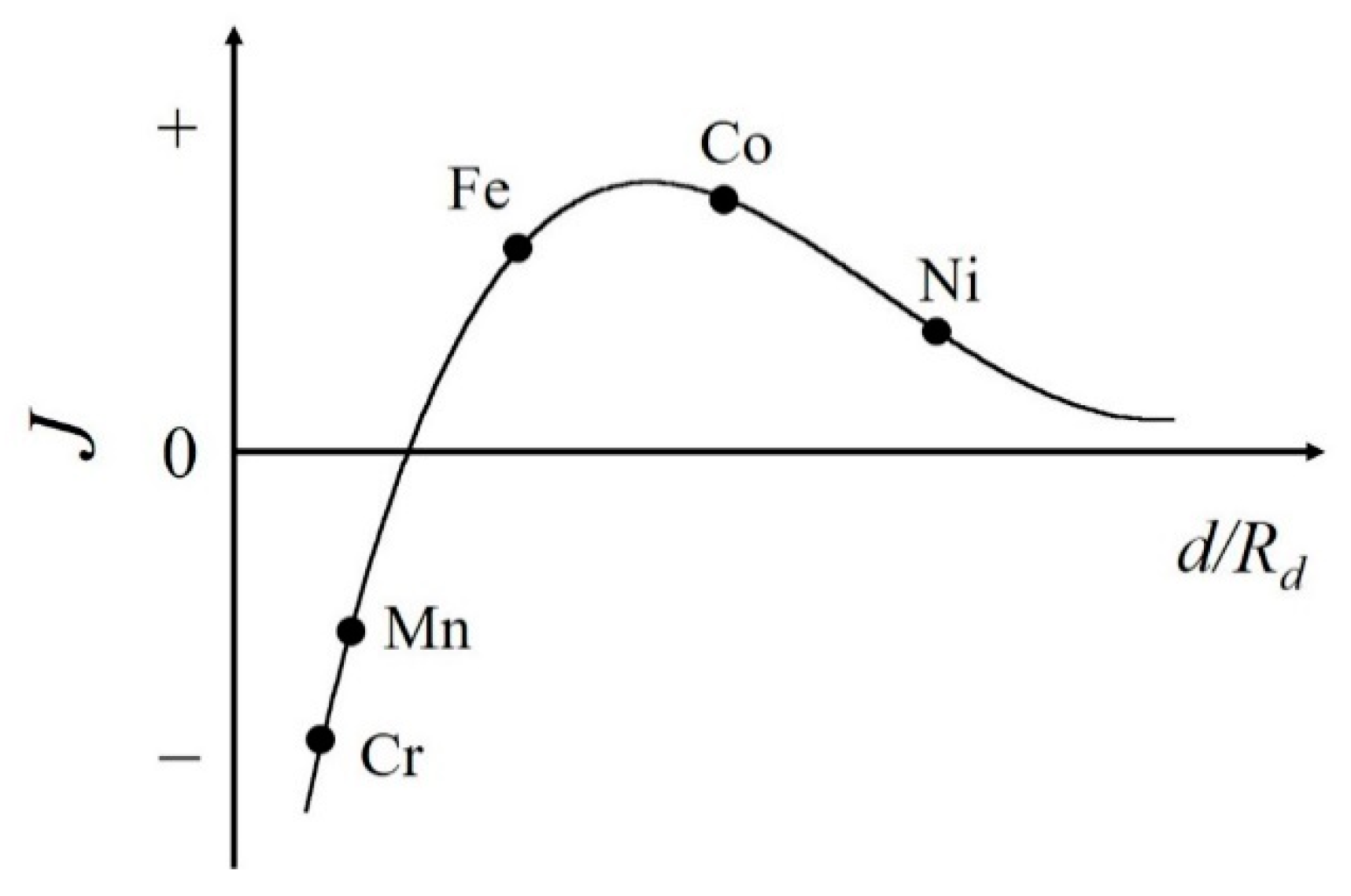
The most well-studied platforms for interstitial atoms are rare-earth Fe-based permanent magnets. The improvements of the magnetic properties have mainly been achieved through the addition of light elements such as boron, carbon, and nitrogen atoms. The Bethe–Slater curve is one of the criteria needed to understand whether metal 3d transition elements of Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, and Ni possess ferromagnetic (FM) or antiferromagnetic (AFM) states (see Figure 1) [7,8,9,10]. This curve exhibits the exchange coupling as a function of the interatomic distance. Fe falls in the FM region near to the border between FM and AFM states. Therefore, in Fe-based compounds, a shorter Fe–Fe distance (shrinkage of the unit cell volume) favors an AFM state, while a longer Fe–Fe distance (an expansion of the unit cell volume) favors the FM state [11,12,13]. With increasing Fe–Fe distance, smaller overlapping of 3d wave functions makes the 3d band narrower, which leads to the FM state, and in most cases the Curie temperature TC is enhanced.
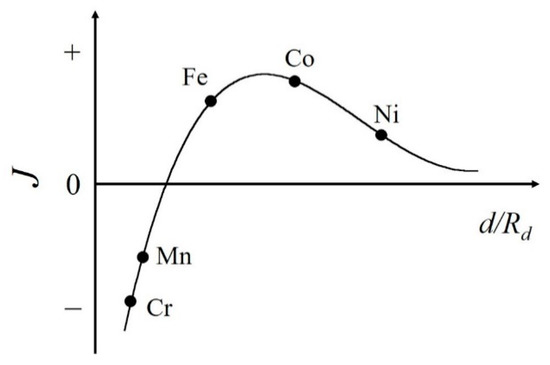
Figure 1.
Schematic view of the Bethe–Slater curve. Here, J, d, and Rd represent the magnetic exchange coupling between atoms, the interatomic distance, and the radius of the 3d shell, respectively.
On the other hand, the effects of interstitial atoms in Mn-based compounds are not well researched. As shown in Figure 1, the Mn atom itself shows the AFM ground state, however the expanded Mn–Mn distance in Mn-based compounds leads to the FM state. Mn compounds are indispensable for both FM and AFM materials. For example, MnBi and MnAl have attracted much attention as permanent magnets [14,15,16,17,18]. MnSi has been extensively studied as a magnetic material with a skyrmion state, which is a noncollinear magnetic structure. The skyrmion domains can be driven by the low current density threshold [19]. Recently, Mn3Sn has been intensively studied as a topological antiferromagnet [20] and is a candidate next-generation spintronics material. If the effects of interstitial atoms are well understood, they can be highly useful in the development of spintronics devices or highly functional magnetic devices, which can be developed via easy on-demand control of the magnetic state.
In this review, we present information on the effects of interstitial atoms in rare-earth Fe-, Mn-, and rare-earth-based compounds, especially focusing on Mn-based compounds. We introduce the frequently studied Mn-based compounds, showing the changes of magnetic states caused by the interstitial atoms, as well as our recent results. Interestingly, a change in the magnetic ground state or an additional formation of the FM state caused by interstitial atoms is possible. Specifically, our results highlight an abrupt emergence of FM exchange coupling above room temperature caused by the addition of a small amount of light elements, which has not been clearly reported for rare-earth Fe-based compounds. Additionally, candidate crystal structures for Mn compounds are presented, in which a magnetic state can be changed using interstitial atoms. Finally, perspectives concerning the development of magnetic devices based on Mn-based compounds and the strategy for further improvement of magnetic properties are outlined.
2. Rare-Earth Fe-Based Compounds
2.1. Th2Zn17-Type
R2Fe17Nx (R = light rare-earth) represents the permanent magnets with the hexagonal Th2Zn17-type structure (space group: Rm, No. 166). There is an interstitial Wyckoff position 9e for nitrogen atoms. The roles of nitrogen atoms are the enhancement of TC and the saturated magnetization Ms and the change in magnetic anisotropy. For example, TC = 389 K and Ms = 1.00 T at a room temperature of Sm2Fe17 are increased to 749 K and 1.54 T, respectively, in Sm2Fe17N3 (see Table 1). Moreover, the in-plane anisotropy in Sm2Fe17 is changed to uniaxial anisotropy by the nitriding, which is advantageous for application as permanent magnets.

Table 1.
The magnetic and structural properties of rare-earth Fe-based compounds with and without interstitial atoms, where a and c are the lattice parameters, and V is the unit cell volume. RT means the room temperature. Data are from the references listed in the table.
The addition of nitrogen atoms expands the lattice parameters a and c, resulting in the increased Fe–Fe interatomic distance and the enhancement of TC. Actually, in Sm2Fe17N3, TC is almost doubled, which is much larger than that in the case of ThMn12-type compounds (see also Section 2.2 and Table 1). The difference is well correlated with the rate of unit-cell-volume change ∆V/V by the interstitial atoms, which is defined by
where Vw/o and Vw are the unit cell volumes without and with interstitial atoms, respectively. We note here that the compound without interstitial atoms is hereafter often called the parent compound. For example, ∆V/V = 6.6% in Sm2Fe17N3 is larger than that in ThMn12-type SmFe11TiN (2.7%). The larger ∆V/V for Sm2Fe17N3 is ascribed to the fact that Fe magnetic moments in the Th2Zn17-type structure are less itinerant.
2.2. ThMn12-Type
The well studied system is RFe11Ti (R: rare-earth) series (I4/mmm, No. 139). This structure allows the interstitial nitrogen atoms to occupy the 2b site. In SmFe11TiN or NdFe11TiN, the nitrogen addition enhances TC by about 30%, which is smaller than that of the Th2Zn17-type system (see Table 1). As mentioned above this is due to the smaller ∆V/V under the addition of nitrogen (2.7% for SmFe11TiN and 3.9% for NdFe11TiN). The magnetic anisotropy of RFe11Ti is determined primarily due to the single-ion contribution of R ion, thus NdFe11Ti and SmFe11Ti show the planar and c axis anisotropies, respectively. In each compound, the sign of magnetic anisotropy constant K1 is reversed by the nitrogen addition and a good candidate of the permanent magnet is consequently NdFe11TiN.
The first-principle studies have revealed that NdFe12N, which possesses an Fe concentration higher than that of NdFe11TiN and is more favorable for a permanent magnet, has excellent magnetic properties [35,36,37], however, it is thermodynamically unstable in bulk form. The thin film fabrication allows the growth of NdFe12Nx, which shows a superior Ms = 1.7 T compared to Nd–Fe–B magnets [38]. The coercivity of NdFe12Nx is rather low, however, a born doped Sm(Fe0.8Co0.2)12 is recently reported to be a highly coercive material with 1.2 T [39]. The microstructure of the compound exhibits columnar-shaped Sm(Fe0.8Co0.2)12 grains, surrounded by a born-rich amorphous phase. The domain wall pinning at the grain boundary is responsible for the high coercivity [39].
Mao et al. reported a BH energy product of ThMn12-type compound [40]. They have investigated the magnetic properties of powdered PrFe12-xVx and the nitride compound. Pr(Fe, V)12N1.6 exhibits the maximum BH energy product of 135 kJ/m3.
2.3. BaCd11-Type
The tetragonal BaCd11-type structure represented by RFe9Si2Cx (Table 1) is a candidate for a next-generation rare-earth Fe-based permanent magnet. It is interesting that the addition of carbon atoms is required to stabilize the BaCd11-type structure. In RFe9Si2Cx, the carbon atom occupies the interstitial 8c site of the tetragonal space group of I41/amd (No. 141). TC progressively increases with the increase of x, for example, TC = 367 K of SmFe9Si2C0.5 is enhanced to 492 K in SmFe9Si2C1.5, accompanying the volume expansion [30]. The magnetic anisotropy depends on the R atom; in-plane anisotropy is observed in R = Ce or Nd, whilst on the other hand, R = Sm possesses the c axis anisotropy.
2.4. Remark on Hybridization Effect
Through the extensive studies of rare-earth Fe-based permanent magnets, it is revealed that stronger orbital hybridization in the covalent bond between Fe and an interstitial atom tends to reduce the magnetic moment. The strength of the covalent bond is well reflected by ∆V/V under the addition of light elements; ∆V/V is not so large when the hybridization is stronger. ∆V/V is generally larger for the nitrogen addition compared to the carbon one (see, for example, Sm2Fe17N3 and Sm2Fe17C3 in Table 1).
3. Mn-Based Compounds
In this section, we gathered as many Mn-based room temperature ferromagnets as possible.
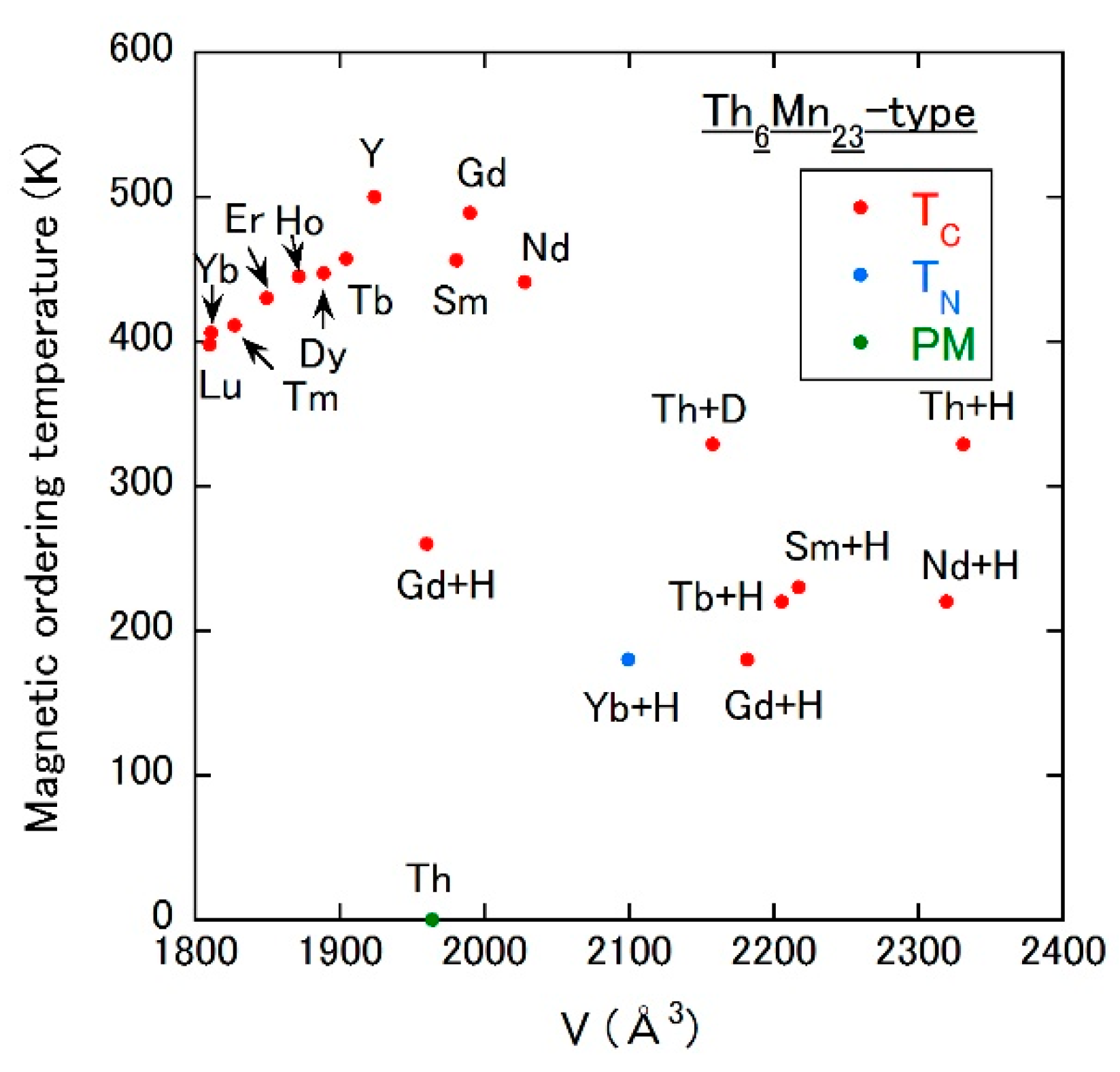
3.1. Hydrogen-Absorbed (R or Th)6Mn23
R6Mn23 (R = rare earth) series and Th6Mn23 crystallize into the cubic Th6Mn23-type structure with the space group Fmm (No. 225). R atoms occupy the 24e site, and Mn atoms the 4b, the 24d and the two 32f sites. All R6Mn23 compounds show FM orderings at a TC higher than 300 K, which are induced by Mn magnetic moments. On the other hand, Th6Mn23 remains a paramagnet down to low temperatures. The hydrogen absorption generally expands the unit cell volume (see Figure 2 and Table 4), whereas the occupation site of the hydrogen atom is not clear. Although the TC of non-hydrogenated R6Mn23 rises with increasing volume, most of the hydrogen-absorbed compound shows the suppressed TC compared to each parent compound. For example [41], TC = 461 K of Gd6Mn23 is reduced to TC = 2.66 K in Gd6Mn23Hx. The saturated moment is also highly reduced (49 µB/f.u. to 14.2 µB/f.u.) [41]. The opposite behavior is confirmed for Th6Mn23, in spite of the similar volume change by the hydrogenation. The hydrogenated Th6Mn23 shows an emergence of ferromagnetism with TC = 335 K, although the saturated moment of Mn is not so high (16.5 µB/f.u.) [41]. Considering that R and Th ions are in the trivalent and the tetravalent state, respectively, the exchange coupling between Mn magnetic moments would significantly depend on the valence electron count per atom (VEC). We note that Th6Mn23 is the typical Mn-based compound showing the change in magnetic state by interstitial atoms. The saturated moment induced in the FM state of the hydrogenated compound is rather low, indicating a strong orbital hybridization between Mn and hydrogen atoms and/or a complex magnetic structure.
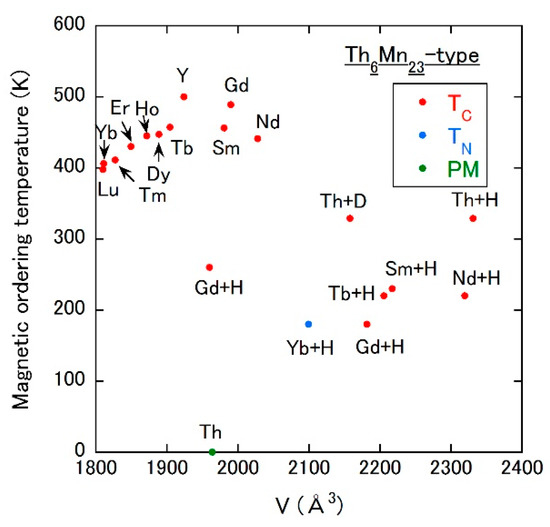
Figure 2.
Magnetic ordering temperature vs. unit cell volume plot of Th6Mn23-type Mn compounds. TN is the Néel temperature. PM means the paramagnetic state. For example, Th + H (Th + D) means the hydrogen (deuterium)-absorbed Th6Mn23.
3.2. Hydrogen-Absorbed YMn2
The crystal structure of YMn2 is the cubic MgCu2-type structure with the space group of Fdm (No. 227). Y and Mn atoms occupy the 8a and the 16d site, respectively. YMn2 can absorb hydrogen atoms as in R6Mn23. Although YMn2 is paramagnetic down to low temperatures, YMn2Hx shows a lattice expansion under hydrogenation, which induces a ferromagnetism with TC = 284 K and a saturation moment of 0.52 µB/f.u. [41]. There are many RMn2 compounds with the same structure, however, we do not make the magnetic ordering temperature vs. unit cell volume plot, because the accurate nature of the magnetic order is still unknown for each compound [42]. YMn2 can also be regarded as the compound, realizing the change from paramagnetism to ferromagnetism by interstitial atoms.
3.3. Carbon-Added Mn5Si3
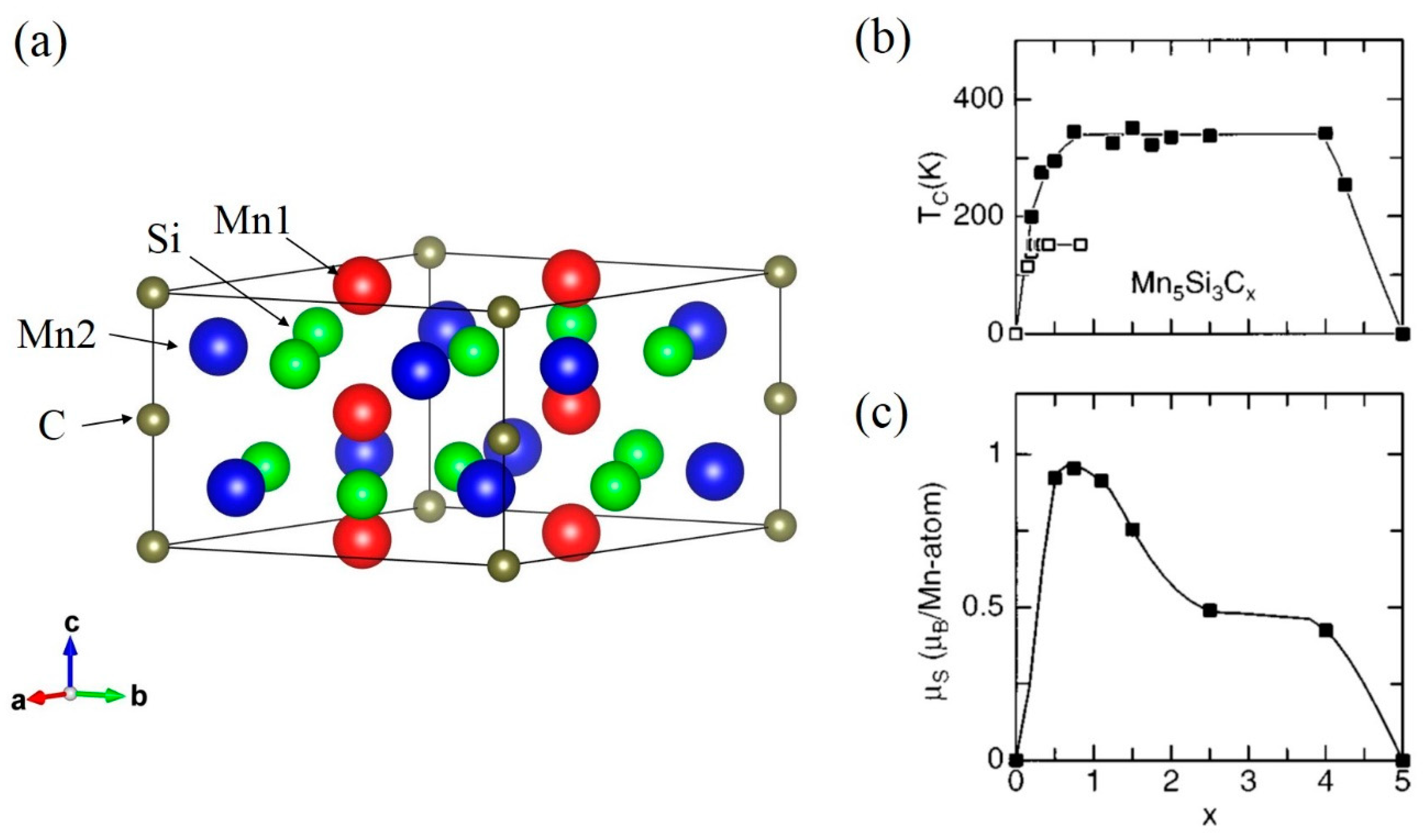
This system shows a change from the AFM to FM state by the carbon addition. The hexagonal Mn5Si3-type structure is known as a superior platform for studying interstitial chemistry [43]. The space group is P63/mcm (No. 193), in which the Wyckoff positions are the 4d for Mn1, the 6g for Mn2 and the 6g for Si (see also Figure 3a). Carbon atoms occupy the 2b site. While the parent compound Mn5Si3 shows an AFM ordering at the Néel temperature TN = 98 K, a thin film Mn5Si3Cx becomes a room-temperature ferromagnet with TC = 350 K as shown in Figure 3b (see the filled squares) [44,45]. In [44], the appearance of the FM state is ascribed to the enhanced Mn–Mn interaction mediated by added carbon. Associated with the unit cell volume expansion by the carbon addition, the saturation Mn moment rapidly increases to 1 µB/Mn at x = 0.75 (see Figure 3c). However, the x dependence of TC is peculiar: a TC plateau of 350 K in a rather wide x range, where the saturation Mn moment is steadily reduced as x is increased above 0.75. We speculate that the hybridization between Mn2 and C atoms is strong, due to the short Mn2–C distance (see Figure 3a). As x is increased, the magnetic moment of Mn2 would be decreased, but that of Mn1 under well localized state due to the weak influence of the carbon addition would be enhanced. The rather strong Mn1–Mn1 magnetic interaction would be responsible for the plateau of TC, while the decreasing Mn2 moment with increasing x would contribute to the reduction in the saturation moment.
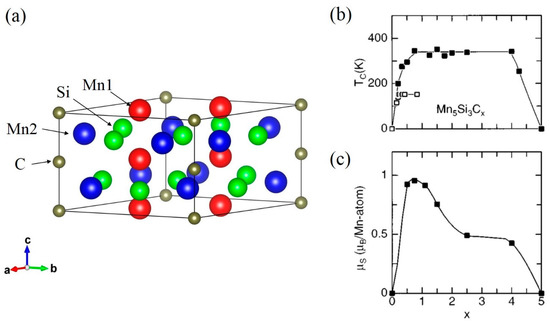
Figure 3.
(a) Crystal structure of Mn5Si3Cx, where the solid line represents the unit cell. x dependence of (b) TC and (c) the saturation magnetic moment for Mn5Si3Cx. In (b), the filled and the open squares indicate the thin film and bulk samples, respectively. Reproduced with permission from [44].
3.4. (R or Actinide)Mn2Si2 and Its Germanides
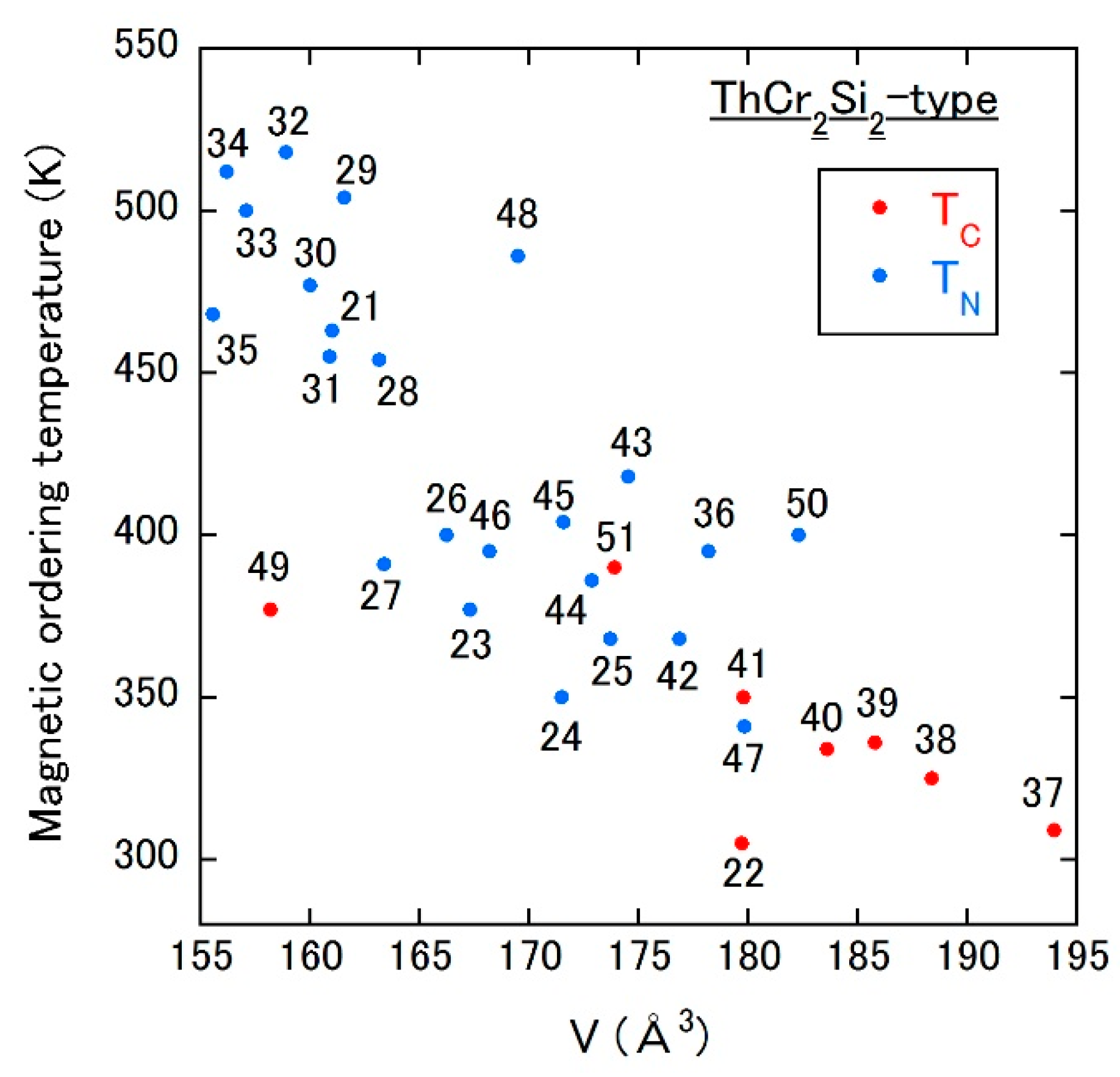
Despite the absence of a report on the addition of light elements in these compounds, the magnetic ordering temperature vs. unit cell volume plot shows the thought-provoking results as shown in Figure 4. These compounds possess the tetragonal ThCr2Si2-type structure (I4/mmm, No. 139), where Mn atoms at the 4d sites form the layered structure perpendicular to the c axis. R (Actinide) and Si (Ge) atoms occupy the 2a and the 4e sites, respectively. In the case of RMn2Si2, only the R = La compound exhibits an FM state and the other compounds AFM one (see 21–35 in Figure 4). When Si is replaced by Ge, FM (AFM) states are observed for R = La to Sm (R = the other elements) as shown in 36–47 of Figure 4. Figure 4 provides a good correlation between the magnetic ordering temperature and the unit cell volume throughout the two series: systematically descending ordering temperature with expanding volume. Furthermore, magnetic structure changes from AFM to FM at approximately 179 Å3, which is consistent with the picture of the Bethe–Slater curve. The inverse trend is confirmed in (U or Th)Mn2Si2 and its germanide (see 48 and 49 (50 and 51) in Figure 4), that is, the crossover from the FM to AFM state occurs by increasing the volume in each system. This can be ascribed to the difference of valence between rare-earth (trivalent) and actinide (maybe tetravalent) elements as in the case of Th6Mn23-type compounds.
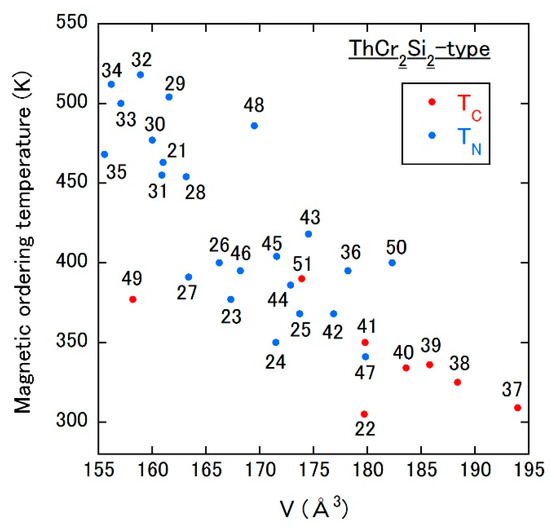
Figure 4.
Magnetic ordering temperature vs. unit cell volume plot of ThCr2Si2-type Mn compounds. The numbers in the figure correspond to those in Table 4 (21–47 for R-containing compounds, and 48–51 for U- or Th-containing compounds).
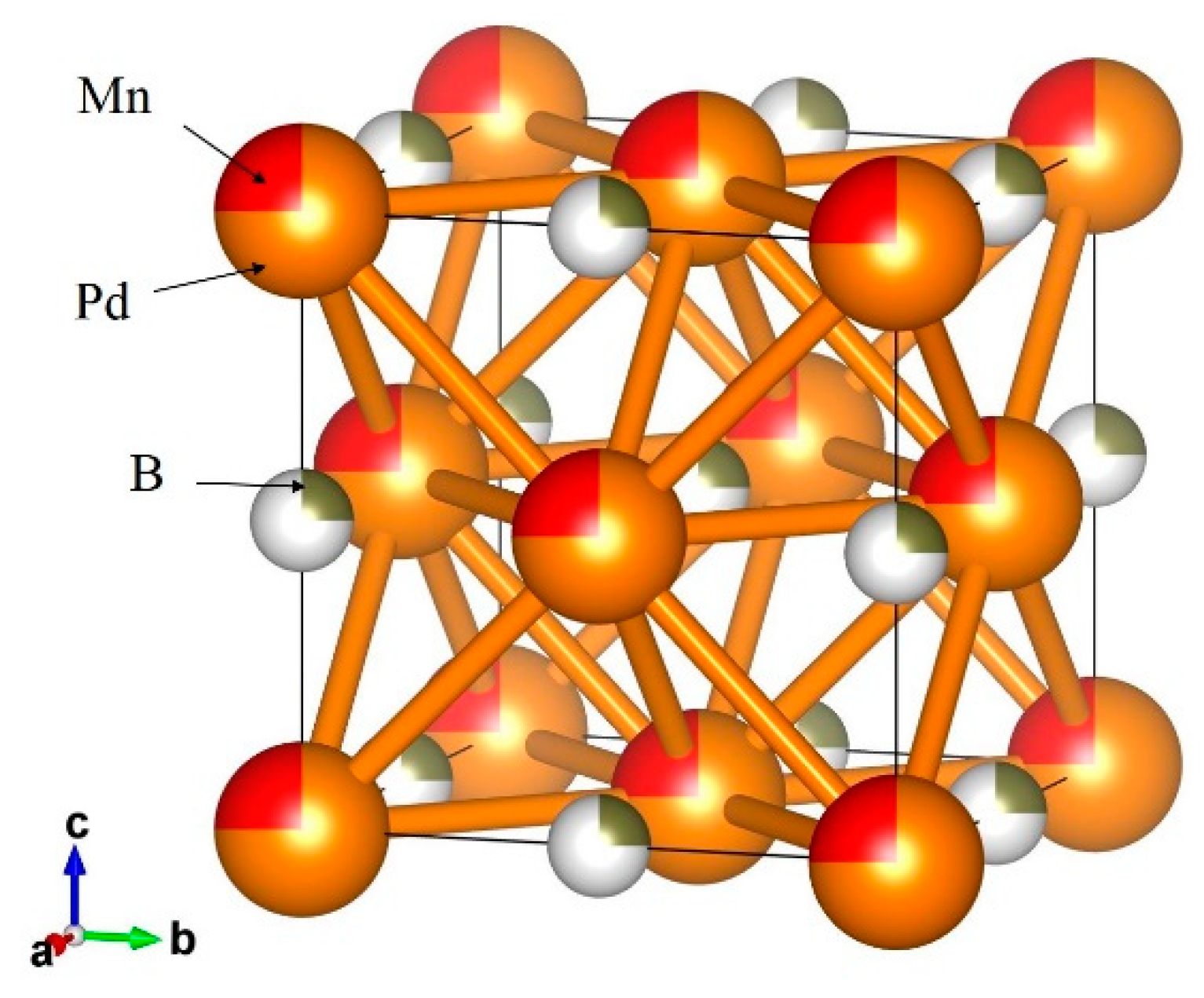
3.5. Boron-Added Pd0.75Mn0.25 Alloy
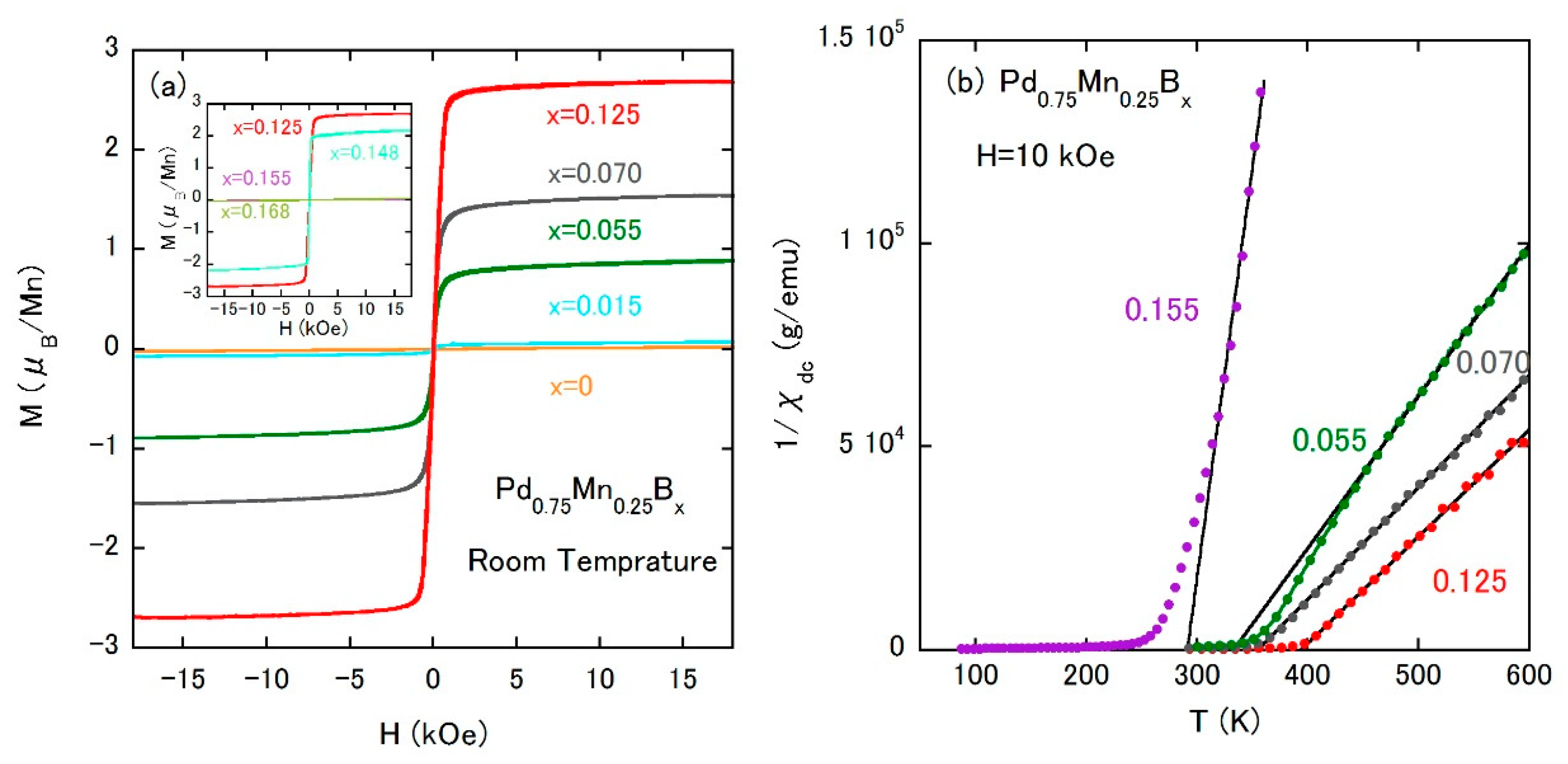
The disordered face-centered-cubic (fcc) Pd1−xMnx alloys are the well studied spin-glass system [46]. The crystal structure is described by the space group of Fmm (No. 225), possessing only the 4a site (see Figure 5), that is randomly occupied by Pd and Mn atoms. At x = 0.25, the spin-glass transition temperature TSG is 45 K [47]. The Pd0.75Mn0.25 alloy can incorporate boron atoms [48,49] with the solubility limit of approximately x ~ 0.16 in Pd0.75Mn0.25Bx. According to the structure report [50] of PdHx with the same structure, interstitial atoms prefer the octahedral sites (the 4b site, see Figure 5). The volume expansion occurs with the increase of x as shown in Table 2. Figure 6a shows the isothermal magnetization curves of Pd0.75Mn0.25Bx at room temperature, which demonstrate the emergence of room temperature ferromagnetism by the slight addition of boron atoms. To elucidate the impact of the boron addition on the effective magnetic moment of Mn atoms, temperature dependences of inverse dc magnetization 1/χdc are measured as shown in Figure 6b. All measured samples follow the Curie–Weiss law above TC (see the solid lines in Figure 6b, and the extracted effective magnetic moment µeff and the Weiss temperature θ are summarized in Table 2). µeff of the parent compound is 4.85 µB/Mn, which is once reduced by the boron addition, that is a signature of hybridization between the Mn and boron atoms. However, the value grows with increasing TC up to 390 K, which is the maximum value in this system. Furthermore, µeff is comparable to the saturation moment in Figure 6a. These facts suggest that the hybridization would be rather weak due to the wide space of the octahedral cavity and/or the rather low occupancy derived from being born at the octahedral site (e.g., 12.5% at x = 0.125). In the latter case, a Mn atom near the boron atom possesses a reduced magnetic moment and that with no neighboring boron atom would show an enhanced moment. Above x = 0.148, both TC and µeff are reduced, which designates the dominating orbital hybridization between Mn and boron atoms, which is also consistent with the small change in the unit cell volume.
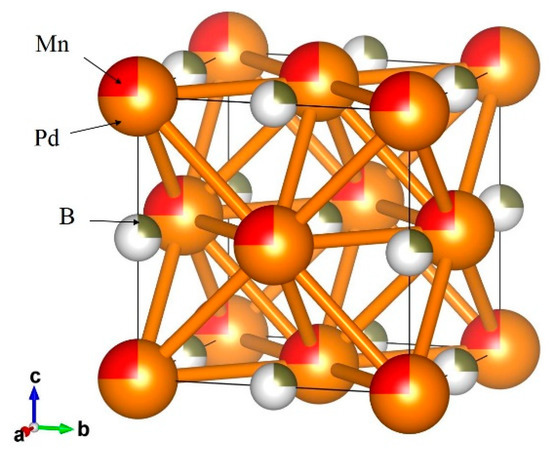
Figure 5.
Crystal structure of Pd0.75Mn0.25Bx. The solid line represents the unit cell.

Table 2.
Lattice parameter, unit cell volume, µeff, θ and TC of Pd0.75Mn0.25Bx.
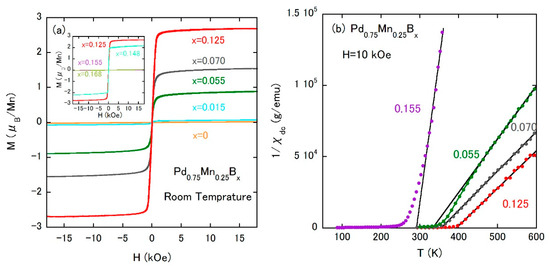
Figure 6.
(a) Isothermal magnetization curves of Pd0.75Mn0.25Bx at room temperature. Reproduced with permission from [49]; (b) temperature dependences of the inverse χdc of Pd0.75Mn0.25Bx. The external field is 10 kOe.
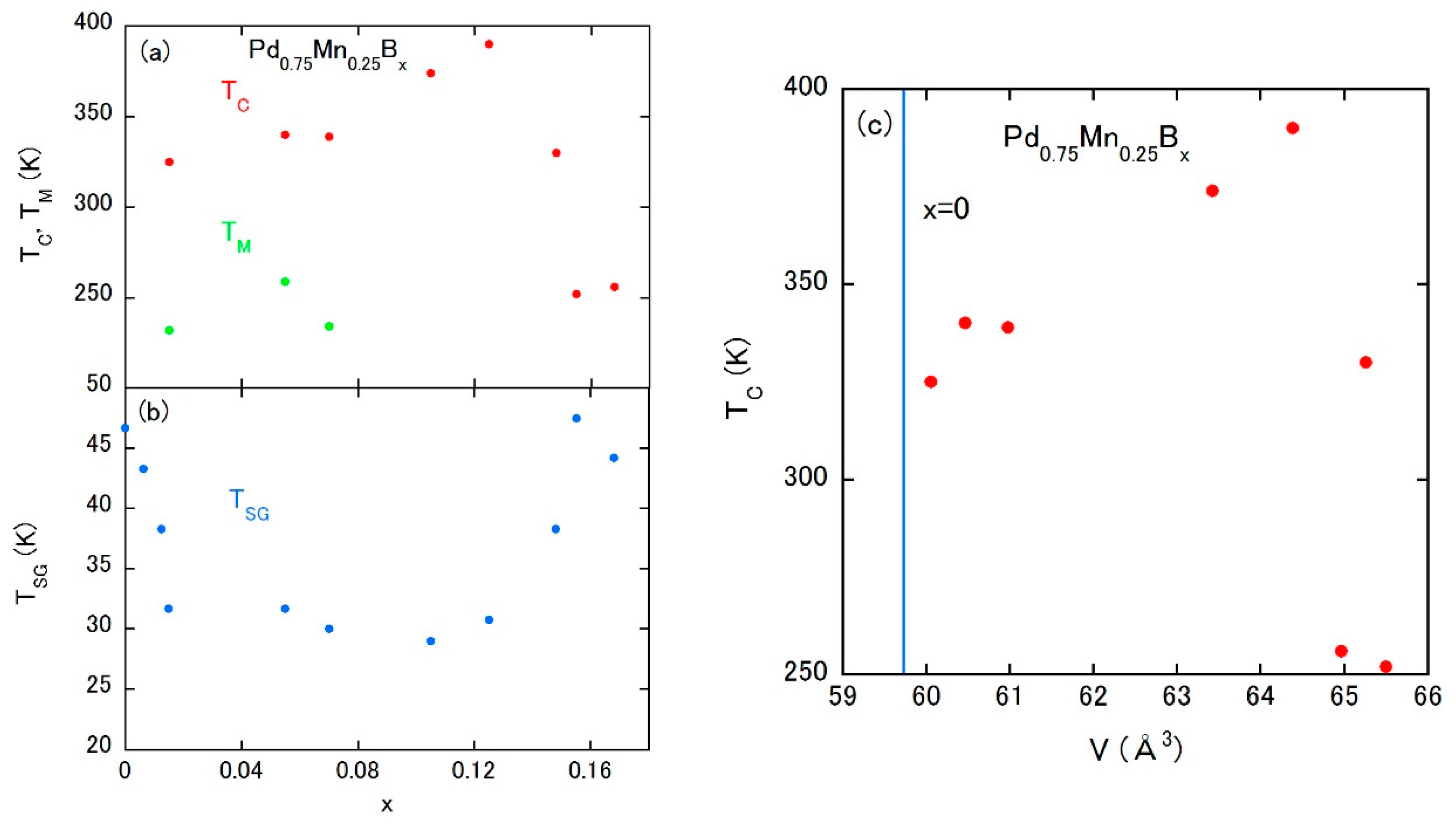
The magnetic phase diagram is constructed as shown in Figure 7a,b. At lower x, a coexistence of the fcc phase and the ordered derivative phase (AuCu3) of fcc occurs [48,49]. The latter phase is responsible for another magnetic ordering at TM [49]. The spin-glass state survives under the emergence of FM state, and both ordering temperatures seem to compete with each other. Therefore, this system is considered to be the typical Mn-based compound presenting the additional formation of the FM state, coexisting with the spin-glass state of Mn atoms at low temperatures. Figure 7c displays the relationship between the TC and the unit cell volume. The vertical blue line is drawn at the volume of the parent compound showing only the spin-glass state. A linear correlation between the TC and the unit cell volume in the region of V = 60–64 Å3 indicates a TC higher than 300 K even at the blue line, which means a possible abrupt birth of FM exchange coupling.
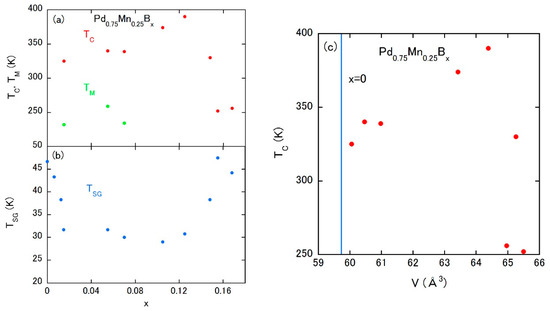
Figure 7.
(a,b) Magnetic phase diagram of Pd0.75Mn0.25Bx; (c) TC vs. V plot of Pd0.75Mn0.25Bx.
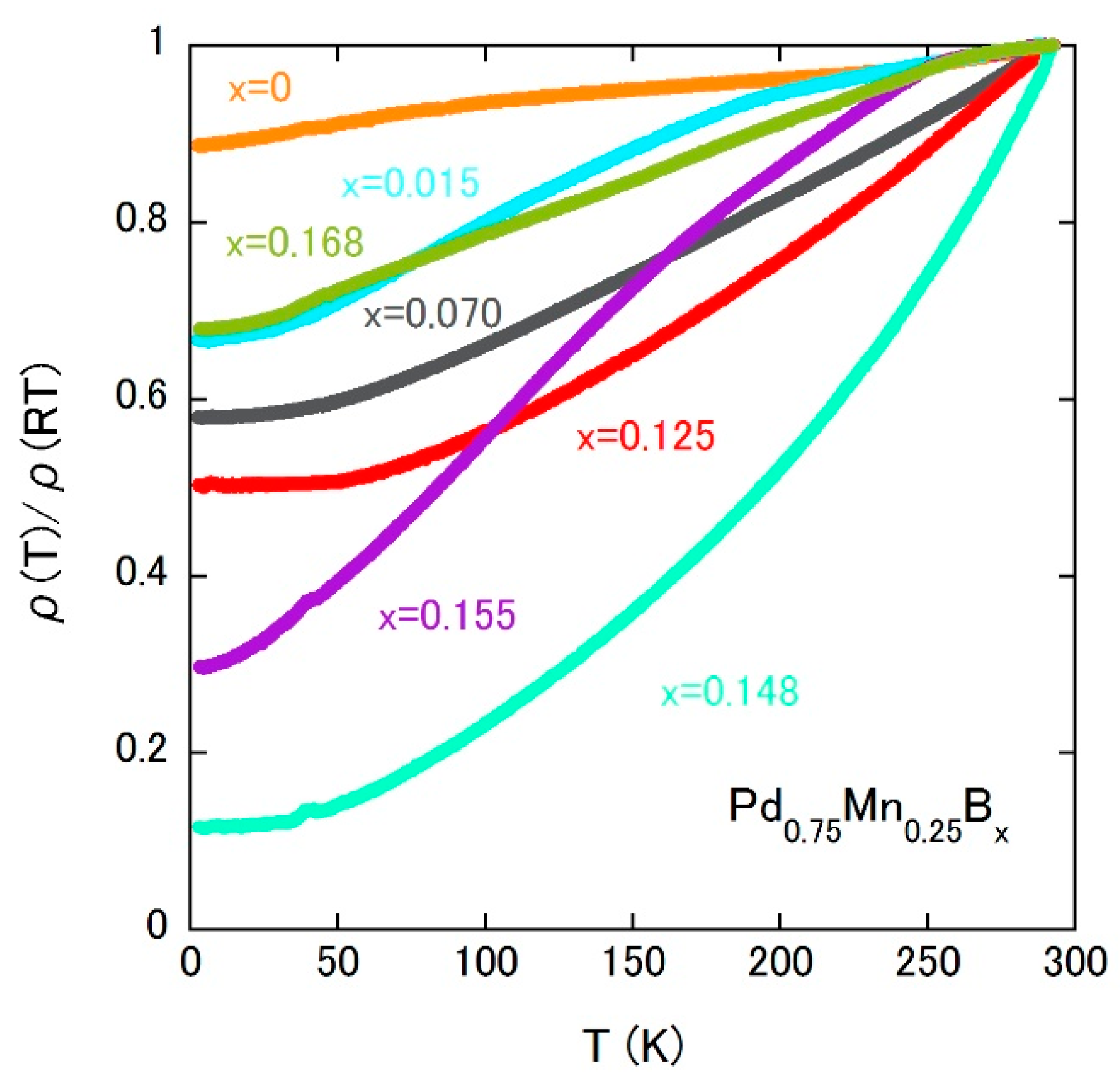
We remarked on the transport properties of Pd0.75Mn0.25Bx. Figure 8 shows the temperature dependences of electrical resistivity, which highlight the rather large temperature dependence below TC even in the disordered alloy. Considering that the spin-glass parent compound shows a weak temperature dependence, the FM interaction might produce some coherence effect on the electrical conductivity.
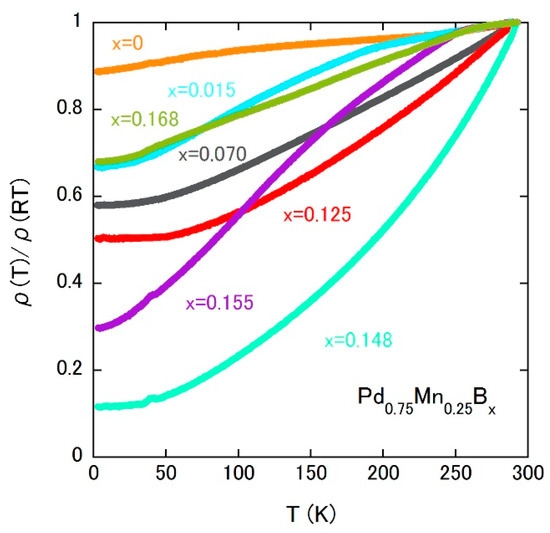
Figure 8.
Temperature dependences of the electrical resistivity of Pd0.75Mn0.25Bx.
3.6. Boron-Added Sm2Mn8Al9
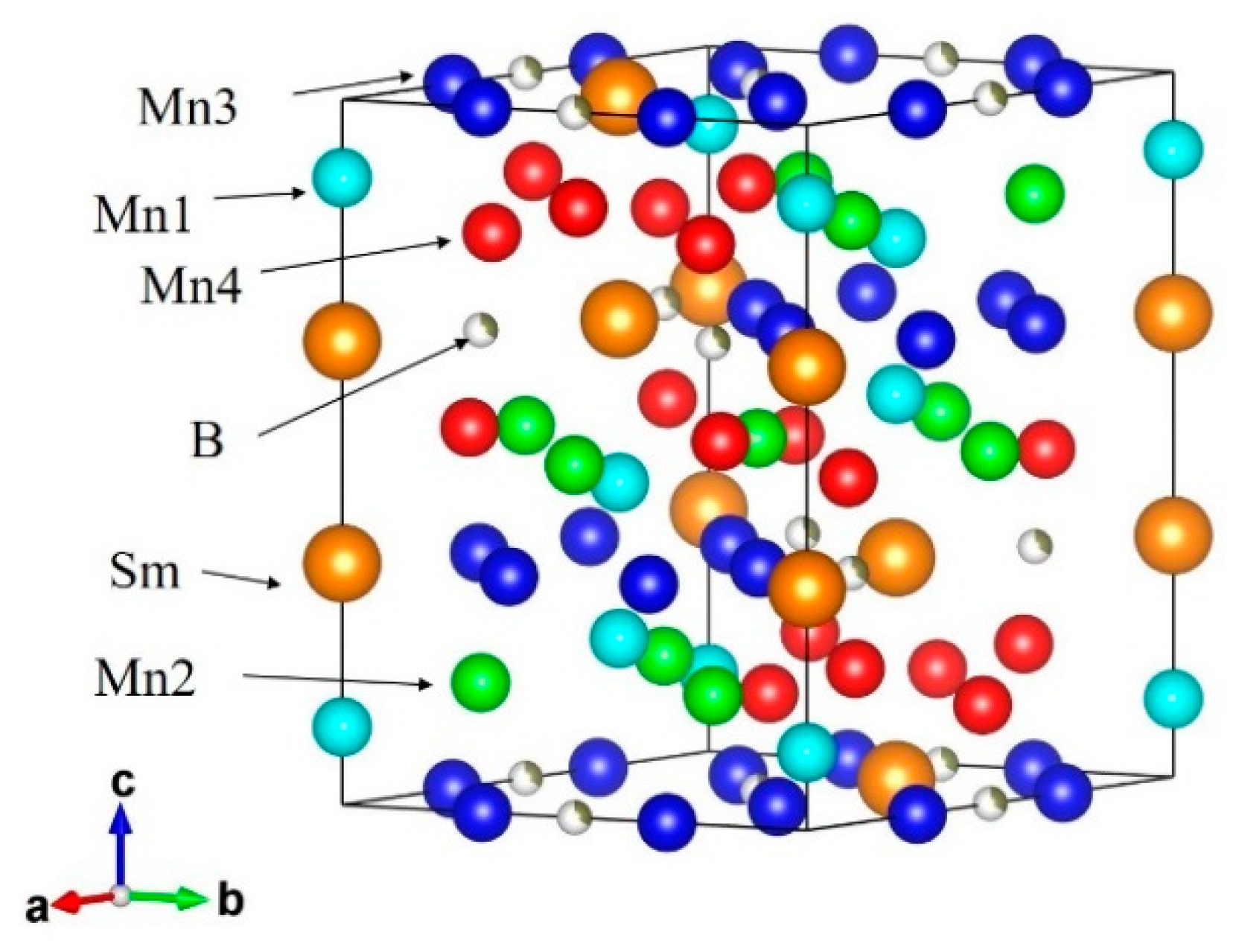
Sm2Mn8Al9 is isostructural to R2Fe17Nx, as mentioned in Section 2.1, and allows the interstitial B atoms at the 9e site (see Figure 9) [51]. In the present case, Mn and Al atoms randomly occupy the Zn sites of hexagonal Th2Zn17-type structure (space group: Rm, No. 166). There is only one Wyckoff position 6c for Sm atoms, but Mn and Al atoms have four Wyckoff positions 6c, 9d, 18f and 18h, which are tentatively represented by Mn1, Mn2, Mn3 and Mn4, respectively, in Figure 9. The boron concentration dependences of lattice parameters and unit cell volume for Sm2Mn8Al9Bx, determined with the help of the Rietveld refinement program [52], are listed in Table 3. The solubility limit would be x ~ 1. ∆V/V at x ≥ 0.1 is much smaller than that of Pd0.75Mn0.25Bx, which suggests the stronger orbital hybridization between Mn and boron atoms in Sm2Mn8Al9Bx (see also Section 2.4). We note here that the nearest neighbor atoms of boron are Mn3 and Mn4, which amount to 71% of all Mn atoms (see also Figure 9). This may lead to a large increase in hybridization under a small variation of volume by the interstitial atoms.
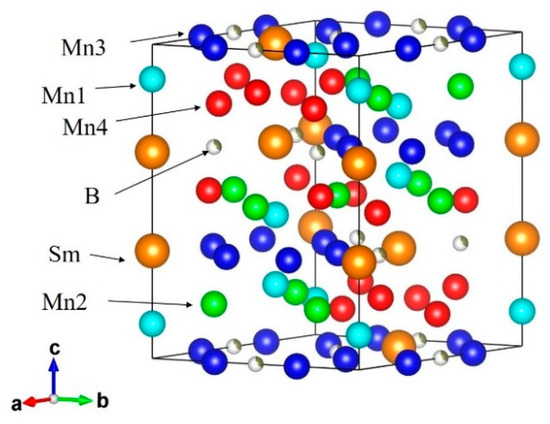
Figure 9.
Crystal structure of Sm2Mn8Al9Bx; the solid line represents the unit cell.

Table 3.
Lattice parameter, unit cell volume, µeff, θ and TC due to Mn moments of Sm2Mn8Al9Bx. Assuming that a negligible contribution of the Sm magnetic moment is usually smaller than the Mn moment value, µeff is calculated.
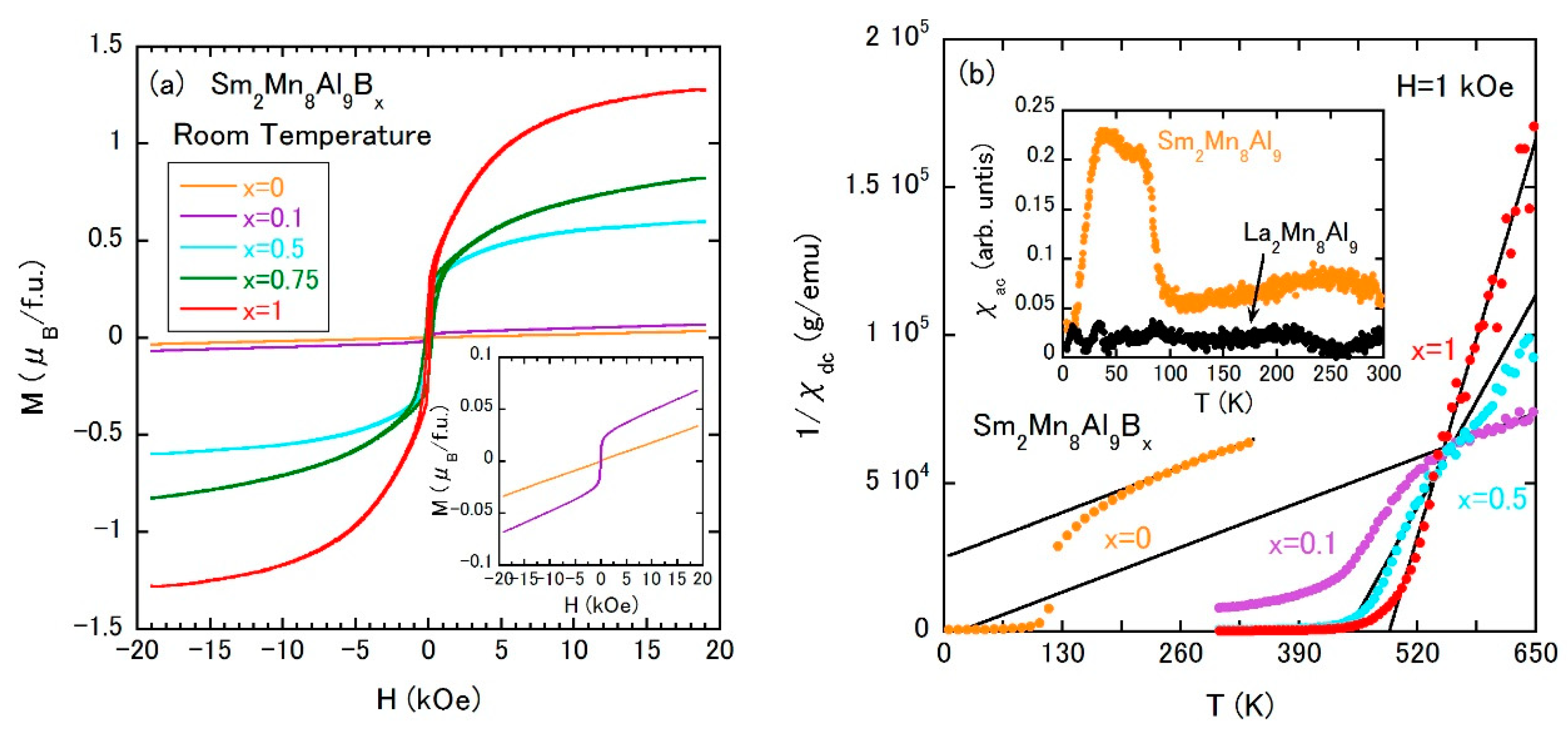
The isothermal magnetization curves are measured at room temperature as shown in Figure 10a, which have revealed the abrupt emergence of ferromagnetism at even a small amount of boron atoms. The temperature dependences of 1/χdc demonstrate that boron-added samples follow the Curie–Weiss law above TC (see the solid lines in Figure 10b). Sm2Mn8Al9 shows a FM behavior below approximately 100 K. Taking into account that the La-counterpart does not show a magnetic ordering at that temperature (see the ac magnetization χac results in the inset of Figure 10b), the low-temperature magnetic transition in the parent compound is due to Sm ions. The µeff and Weiss temperature of each sample are summarized in Table 3. As x is increased, µeff is rapidly reduced, which is indicative of strong orbital hybridization, which is also supported by the weak x dependence of the unit cell volume. It is to be pointed out that the paramagnetic Mn moment abruptly forms the FM state at room temperature even when the density of boron atoms is substantially low. Under a strong orbital hybridization between Mn and boron atoms, the lattice expansion might not be essential for the formation of FM coupling at room temperature.
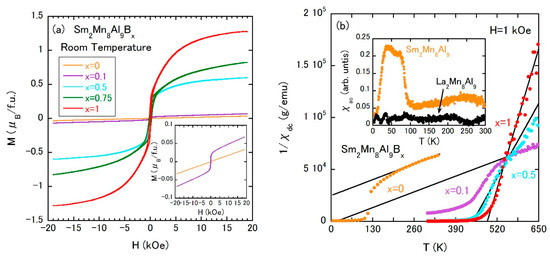
Figure 10.
(a) Isothermal magnetization curves of Sm2Mn8Al9Bx at room temperature; (b) temperature dependences of the inverse χdc of Sm2Mn8Al9Bx. The external field is 1 kOe, the inset is the temperature dependences of χac of Sm2Mn8Al9 and La2Mn8Al9.
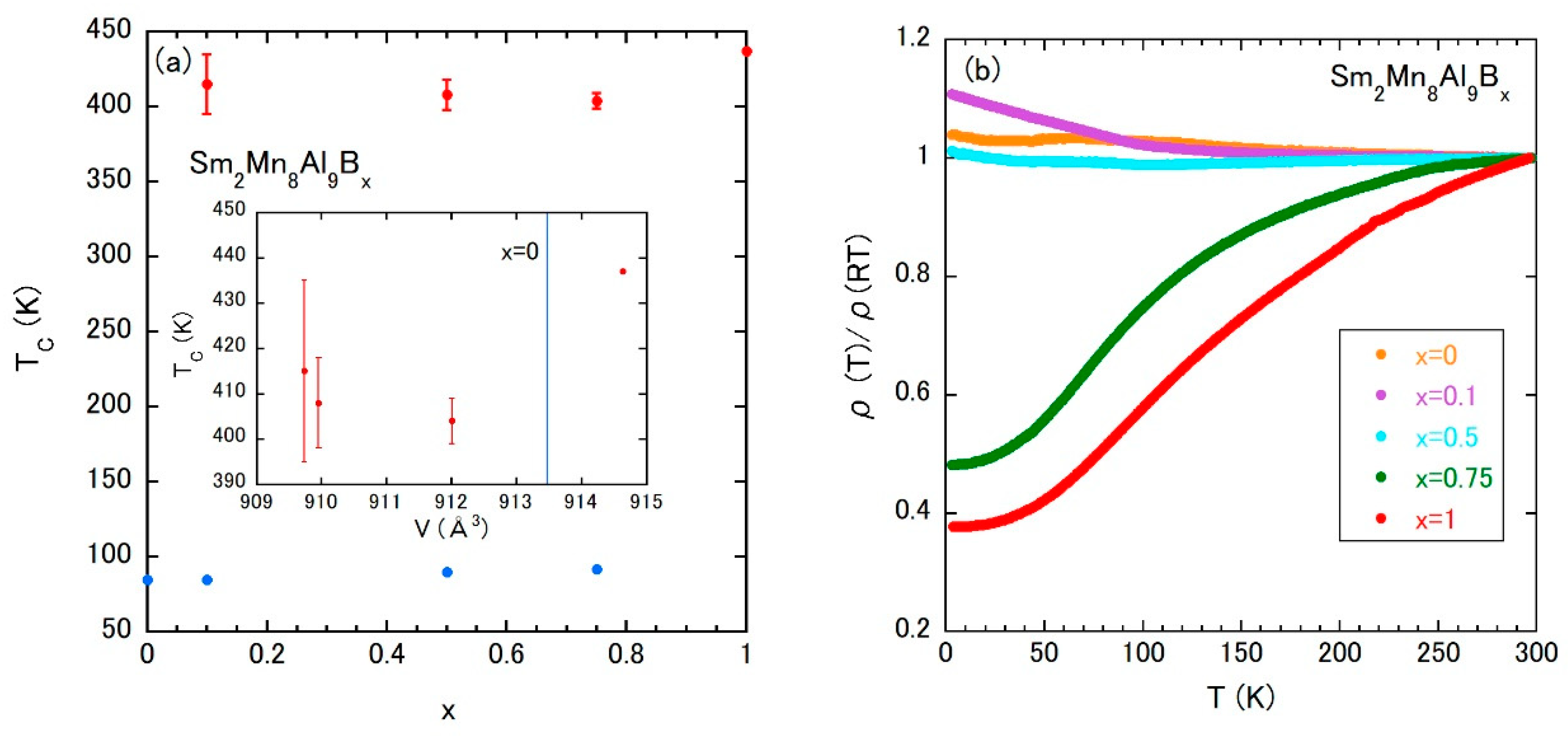
The magnetic properties of Sm2Mn8Al9Bx are summarized as a magnetic phase diagram in Figure 11a. The χac (T) measurements indicate the survival of magnetic ordering due to Sm ions at approximately 85 K, which is independent of the room temperature FM state and seems to disappear at x = 1. The high-temperature TC due to Mn atoms shows a shallow minimum at x = 0.75. The inset of Figure 11a is the high-temperature TC vs. V plot, in which V at x = 0 is denoted by the vertical blue line as in Figure 7c. The observation of room temperature ferromagnetism at both sides of the vertical line strongly suggests that the birth of room temperature FM coupling between Mn atoms is not related to the volume change. The effect of volume change, as studied well in rare-earth Fe-based magnets, is triggered by the appearance of the FM state due to Mn atoms.
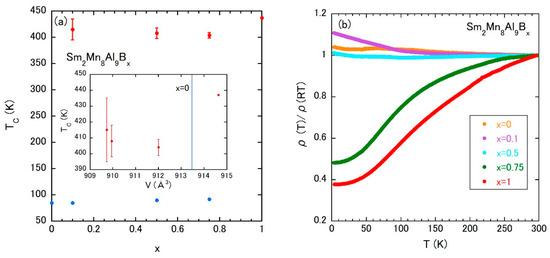
Figure 11.
(a) Magnetic phase diagram of Sm2Mn8Al9Bx; the inset is TC vs. V plot of Sm2Mn8Al9Bx; and (b) temperature dependences of electrical resistivity of Sm2Mn8Al9Bx.
The temperature dependence of ρ exhibits a drastic change as shown in Figure 11b. The carriers would show a localized nature up to x = 0.5, however, metallic behavior is observed above x = 0.75. The localized behavior is also reported in isostructural Mn compounds [53] such as Gd2MnxAl17−x and Tb2MnxAl17−x. The shift to the itinerant Mn moment with increasing x and/or some coherence effect of the FM Mn-moment observed in Pd0.75Mn0.25Bx would be responsible for the metallic temperature dependence.
3.7. Brief Summary of Mn-Based Compounds
As in the rare-earth Fe-based compounds, the interstitial atoms give rise to the enhancement of FM interaction in the weak hybridization regime leading to the appearance of room temperature ferromagnetism. However, the Mn compounds surveyed above manifest the change or additional formation of magnetism by the interstitial atoms, while many rare-earth Fe-based parent compounds are already ferromagnets. The change from paramagnetic to FM state is observed in hydrogen-absorbed Th6Mn23, hydrogen-absorbed YMn2 or Sm2Mn8Al9Bx. The result of Mn5Si3Cx thin film may be a rare example of change from the AFM to FM state by the interstitial atoms. In Pd0.75Mn0.25Bx, the room temperature ferromagnetism is induced by a slight addition of boron, while the low-temperature magnetic ground state of the parent compound is unchanged. This can be regarded as an example of the additional formation of magnetism by interstitial atoms. It should be noted that, in some cases, the change or additional formation of a magnetic state seems to abruptly occur, which is valuable for future research. We note here that the magnetic structures have been divided into FM and AFM, although some compounds may show a more complicated state such as canted AFM, and spiral AFM. In the future, discussion taking into account a more microscopic mechanism of the magnetic ordering would be necessary.
We add the comment on Mn-based Heusler compounds, which show a rich variety of physical properties such as the topological Hall effect, shape-memory and so on [54,55,56]. While many Mn-based Heusler compounds show ferromagnetism, a Heusler compound, allowing interstitial atoms, has not been reported to our knowledge.
3.8. Candidate Showing a Change in Magnetism by Interstitial Atoms
Mn compounds may be a superior platform to examine the change in the magnetic state or the additional formation of new magnetic coupling by interstitial atoms. We noted that, in some cases, the change to FM state or the additional formation of the FM state would occur irrespectively of interstitial atom-induced volume change. Notwithstanding, hereafter, we continue to discuss, based on the unit cell volume, because the results of Mn5Si3Cx, Pd0.75Mn0.25Bx and Sm2Mn8Al9Bx are not well analyzed systematically by comparing several compounds with the same crystal structure. In other words, the magnetic ordering temperature vs. unit cell volume plot as shown in Figure 2 could not be constructed due to the absence of well investigated other Mn compounds in these crystal structures. Therefore, at the present stage, we believe that it is still valuable to survey the magnetic structures of compounds using the unit cell volumes. In this subsection, especially bearing a change in magnetism by interstitial atoms in mind, we seek a qualifying Mn compound using the magnetic ordering temperature vs. a unit cell volume plot. We selected the crystal structures allowing the site occupation of interstitial atoms: Ni3Sn, ThMn12, Fe2P, Ni2In, LiAlSi, TiNiSi, AuCu and Cu2Sb-type structures.
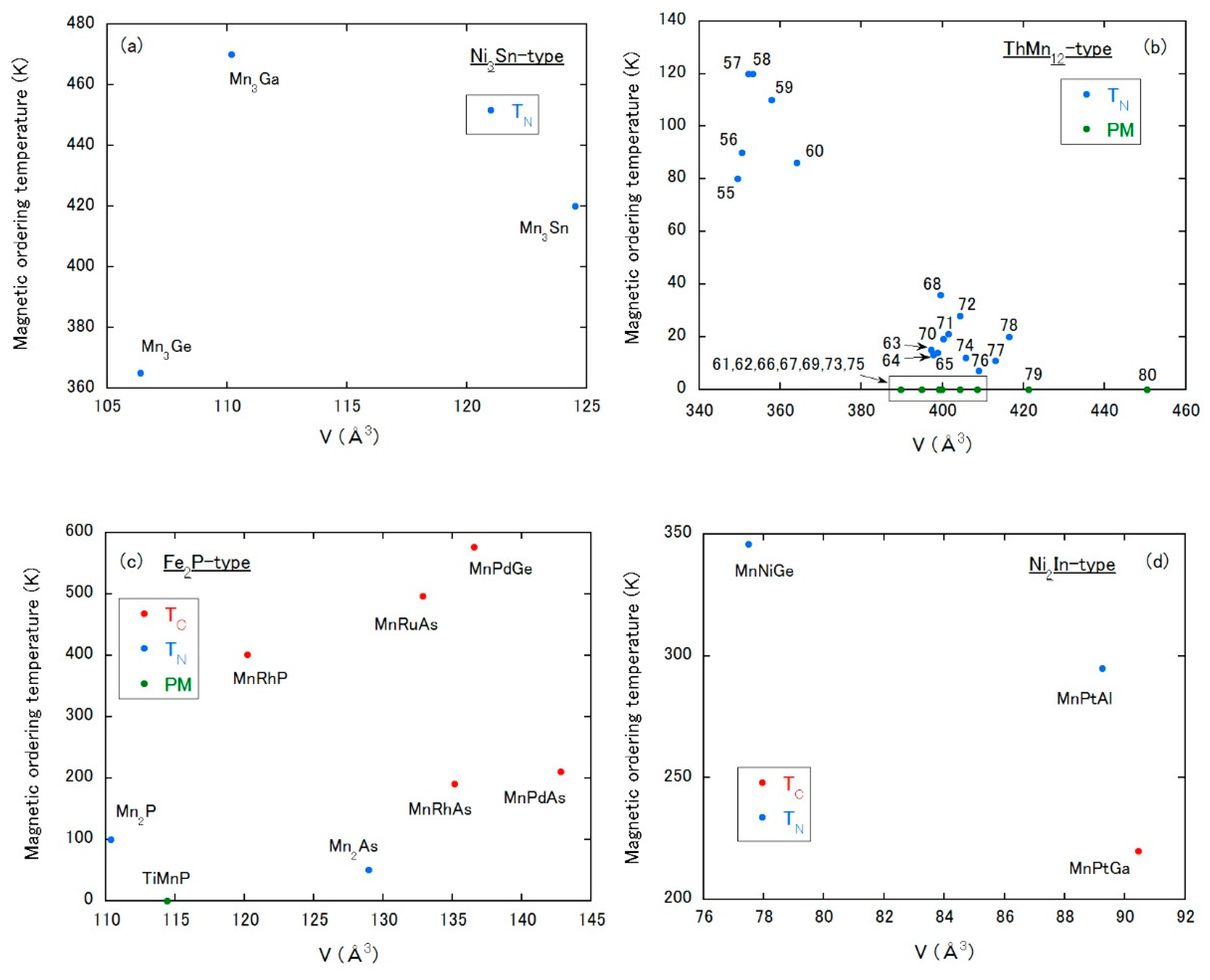
3.8.1. Ni3Sn-Type Structure
This hexagonal structure (P63/mmc, No. 194) is recently attractive as a topological AFM substance [20] represented by Mn3Sn. All Ni3Sn-type compounds displayed in Figure 12a possess only one crystallographic 6h site for the Mn atom. As seen in Figure 12a, only the AFM state has been observed and a change to FM state would be difficult.
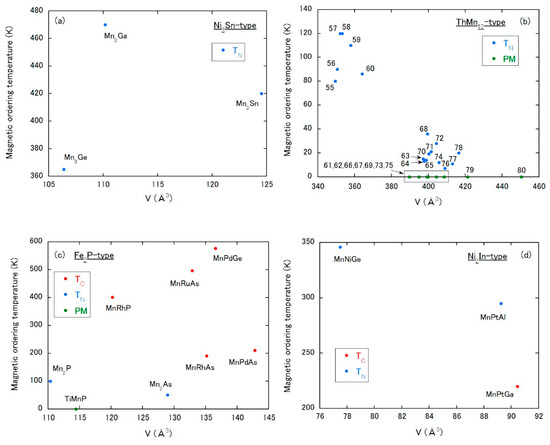
Figure 12.
Magnetic ordering temperature vs. unit cell volume plot of Mn-based compounds with (a) Ni3Sn-type, (b) ThMn12-type, (c) Fe2P-type and (d) Ni2In-type, respectively. PM means a paramagnetic state down to low temperatures. The numbers in (b) correspond to those in Table 4.
3.8.2. ThMn12-Type Structure
The tetragonal ThMn12-type structure (I4/mmm, No. 139) is well studied in rare-earth Fe-based compounds (see Section 2.2). In the Mn compounds with this structure, Mn atoms occupy the 8f, 8i, 8j sites. As shown in Figure 12b, the magnetic properties are dominated by the AFM state. We note that, except for compounds No. 55–60, the AFM orderings of compounds containing rare-earth elements are triggered by the magnetic moments of rare-earth, and Mn atoms do not carry moments. Basically, with increasing volume, TN tends to be suppressed. In this class of compounds, a change from AFM to a paramagnetic state of Mn atoms by interstitial atoms may be anticipated.
3.8.3. Fe2P-Type Structure
The compounds with the hexagonal Fe2P-type structure (P2m, No. 189) displayed in Figure 12c possess the 3g site for the Mn atom, except Mn2P and Mn2As, in which there exists the 3g and 3f sites for Mn atoms. Figure 12c indicates a possible crossover from paramagnetic to FM state across the volume of approximately 115–120 Å3 for compounds with only the 3g Mn site.
3.8.4. Ni2In-Type Structure
The Ni2In-type structure is hexagonal with the space group of P63/mmc (No. 194). Each compound has only one Mn site of the 2a. In this structure, TN at a smaller volume tends to be suppressed as the volume is expanded and seems to transform to TC with further increasing volume (Figure 12d). The compounds with the ThMn12-, the Fe2P- or the Ni2In-type structure may be good candidates for examining a change in magnetic state by interstitial atoms as a function of the unit cell volume.
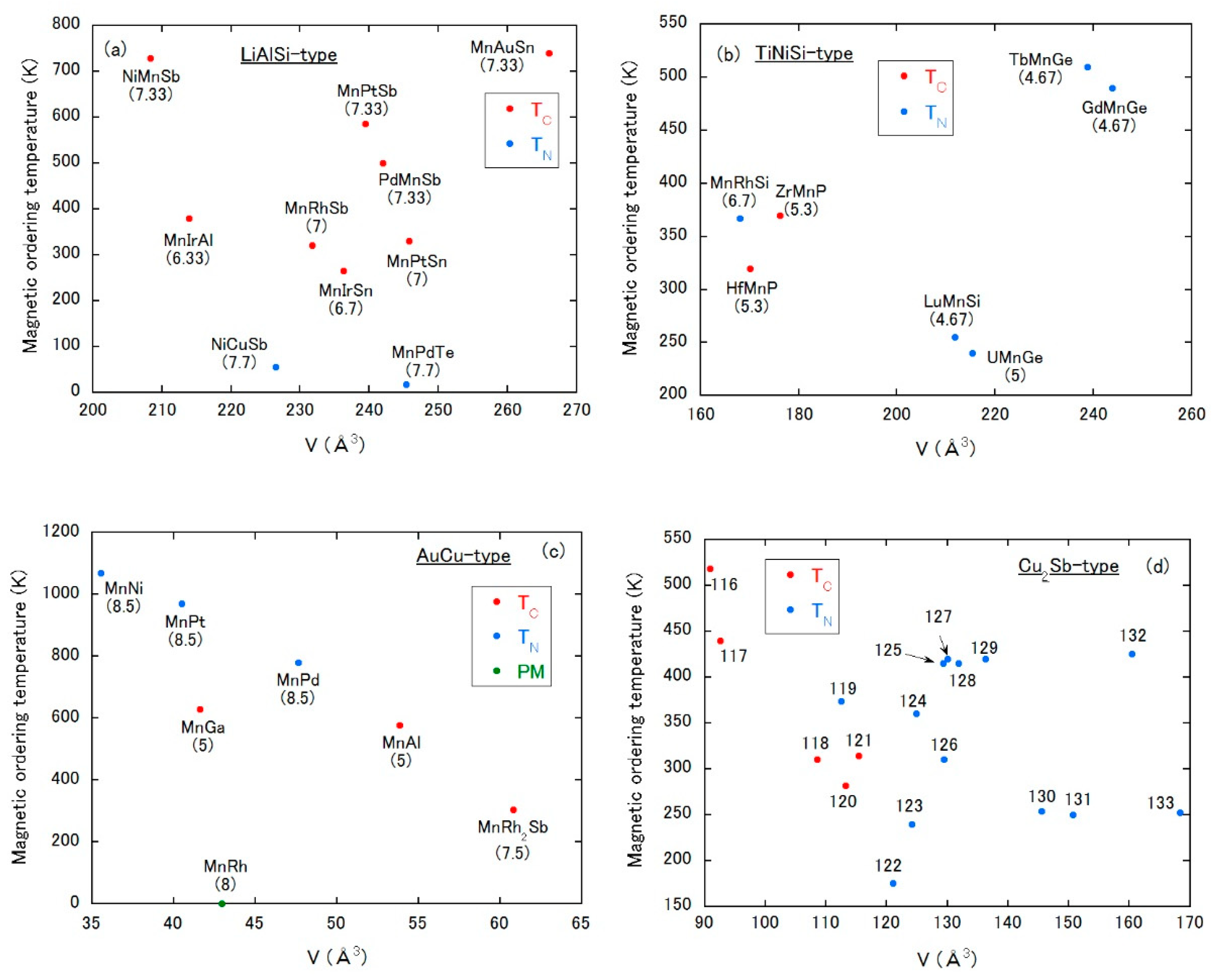
3.8.5. LiAlSi-Type Structure
This structure is cubic with the space group of F3m (No. 216). Each compound in Figure 13a possesses one Mn site with the 4a, 4b or 4c, depending on the literature. The magnetic ordering types of the cubic compounds would be classified by the VEC, which is different from the results of Figure 12a–d. The VEC values are denoted under the chemical formulae in Figure 13a. Except for the compounds with VEC = 7.7 showing the AFM state, all compounds undergo FM as one. In FM compounds, TC tends to increase as the VEC is increased. If interstitial atoms change VEC from 7.33 to 7.7, a change between FM and AFM states might be possible, which may be a new phenomenon induced by interstitial atoms.
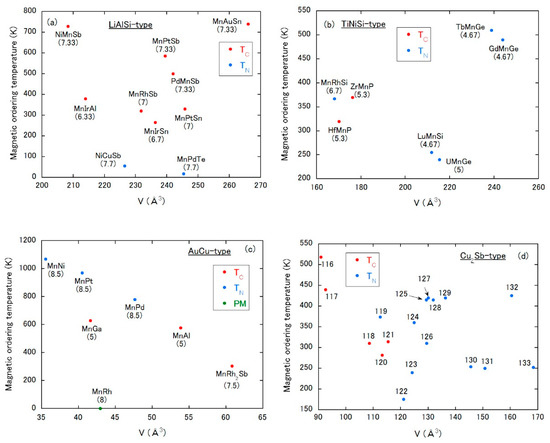
Figure 13.
Magnetic ordering temperature vs. unit cell volume plot of Mn-based compounds with (a) LiAlSi-type, (b) TiNiSi-type, (c) AuCu-type and (d) Cu2Sb-type, respectively. PM means a paramagnetic state down to low temperatures. In (a–c), valence electron count per atom (VEC) is denoted under each chemical formula. The numbers in (d) correspond to those in Table 4.
3.8.6. TiNiSi-Type Structure
This is the famous orthorhombic structure with the space group Pnma (No. 62). Mn atoms occupy the 4c site. As shown in Figure 13b, the border between AFM and FM states may be situated at V = 180–200 Å3. Moreover, only the compounds accompanied by VEC = 5.3 show the FM ground state. The interstitial alloying with the change in VEC might be effective for a magnetic state change.
3.8.7. AuCu-Type Structure
The AuCu-type structure is tetragonal with the space group of P4/mmm (No. 123). Except for MnRh2Sb, Mn atoms occupy two crystallographic sites called the 1a and 1c sites. In MnRh2Sb, Mn sites are reduced to the 1a one. As in the LiAlSi-type structure, the magnetic ordering type would be correlated with VEC; the AFM or paramagnetic state is observed for a VEC larger than 8, and the FM state for VEC = 5 or 7.5. Under a fixed VEC value, TN systematically decreases with increasing volume, while the volume dependence of TC is very weak for ferromagnets.
3.8.8. Cu2Sb-Type Structure
This is the tetragonal structure (P4/nmm, No. 129), in which Mn atoms occupy the 2a site. Contrary to the prediction of the Bethe–Slater curve, a volume expansion favors an AFM state. The magnitude of the magnetic ordering temperature is likely suppressed by expanding the volume.
4. Rare-Earth-Based Compounds
4.1. R5Si3Bx
The Mn5Si3-type R5Si3 allows for interstitial boron atoms, which leads to volume reduction with an increasing boron concentration [118]. For the parent compound with x = 0, the AFM orderings are observed in R = Gd and Tb at TN = 75 and 69 K, respectively. On the other hand, R = Dy and Ho show the FM orderings at TC = 120 and 11 K, respectively. By adding boron atoms, the TN of R = Gd and Tb are slightly reduced to 67 K in both cases, and the changes of TC in R = Dy and Ho are also subtle; TC remains at 120 K in R = Dy and is slightly enhanced to 15 K in R = Ho. In each compound, µeff does not so largely depend on the boron addition, which means a weak hybridization between rare earth and boron atoms.
4.2. NdScSiCx
This compound crystallizes into the tetragonal La2Sb-type structure (I4/mmm, No. 139) [119]. The interstitial carbon atoms expand the a axis and contract the c axis. The latter fact, in particular, enhances the chemical bonding between Nd and C and decreases TC = 171 K in the parent NdScSi to 50 K at x = 0.5. Taking into account that the 4f orbital of a rare-earth atom is usually well localized, the drastic change in magnetic ordering temperature is unexpected as in R5Si3Bx. Thus, the large modification of TC in this compound is very interesting.
5. Perspectives
5.1. Application of Mn-Based Magnetic Materials
The change in magnetism between FM and AFM states or the additional formation of new magnetic coupling at rather high temperatures by interstitial atoms is substantially valuable in a magnetic device integrated with both FM and AFM materials due to the easy on-demand control of magnetism in the fabrication process. At the present stage, Mn-based compounds fulfill the requirement of change or the additional formation of magnetism, while in Fe-based compounds, only improvements of FM properties are extensively investigated and the change (or the additional formation) of the magnetic state is not well explored. Focusing on the research area of the permanent magnet, a rare-earth Mn-based permanent magnet is still missing, although the MnBi-type magnets are well known. Based on the Bethe–Slater curve, Mn atoms favor the FM state with expanding Mn–Mn distance. Therefore, the density of Mn could not be so increased as in rare-earth Fe-based permanent magnets, resulting in a smaller saturation magnetization. However, there exists a large gap of BH energy product between the NdFeB magnets and ferrite magnets, and a rare-earth Mn-based permanent magnet may be a good candidate filling the gap [120].
5.2. Towards Further on-Demand Control of Magnetism
Further improvement of magnetic properties in the on-demand control would be achieved by another strategy such as a composition effect and carrier doping. If a metallurgical phase diagram of a target compound possesses a homogeneity range, the magnetic ordering temperature often varies with the atomic composition. For example, the TC of Tb2Co2Ga ranges rather widely from 75 to 145 K by changing the starting composition [121]. Such a composition effect is reported in other compounds [122,123,124] such as Nd3Pd20Ge6, Tb3Co3Ga and Mn1+xGa. In many cases, the crystal structure parameters slightly change, which heavily affects the magnetic exchange interactions.
The magnetic anisotropy energy is one of the important factors in characterizing a ferromagnet. It is known that it can be tuned by doping, mainly due to the variation of the density of states near the Fermi level. The doping effect is reported in, for example, Ni2MnGa, SmCo5-xFe, MnBi, Nd2Fe17X (X = C or N), Ce2AuP3 and so on [125,126,127,128,129]. Taking into account the crystal symmetry, which is related to the magnetic anisotropy energy, a lower crystal symmetry with more tunable crystal parameters might be favorable.
5.3. Comments on Control of Magnetism by External Field
Another interesting control of magnetism is the manipulation of spin by external fields such as the electric field and the optical light. For example, the employment of an electric double-layer transistor has achieved a control of magnetism by weak voltage [130]. Recently, an optical change in magnetism through the Kondo effect has been reported [131]. The interstitial atoms may precisely control the magnetism so that only a small magnitude of external field is required for the device working, and the power consumption can be highly reduced.
5.4. Comments on Critical Behavior
From the fundamental viewpoint, research into critical behavior is interesting. Actually, in strongly correlated electron systems, there have been plenty of studies for seeking a quantum critical point under the suppression of magnetism [132,133,134,135,136]. We speculate that a formation of FM exchange coupling above room temperature would be a discontinuous phenomenon as mentioned in the results of Mn-based compounds. While it is not well investigated for rare-earth Fe-based compounds, we note that RFe11TiCx and RFe11TiCx show a finite change in TC at an infinitely zero value of volume expansion depending on R species [137].
6. Summary
This review surveyed the studies of interstitial atoms in rare-earth Fe-, Mn-, rare-earth-based magnetic materials, especially focusing on the Mn-based compounds since the effect of interstitial atoms is not well investigated. The light elements would occupy the interstitial sites in the respective crystal structure, and change the unit cell volume, although the degree of change depends on the strength of orbital hybridization between the magnetic and interstitial atoms. The light elements are occasionally essential for the stabilization of the desired crystal structure. In the abundant studies of rare-earth Fe-based permanent magnets, the role of interstitial atoms seems to be restricted to the enhancements of TC and saturated magnetization, and the change in easy magnetization direction. In several Mn-based compounds, magnetic ordering temperature and the magnetization also tends to be increased with the increasing density of interstitial atoms after the appearance of FM states. However, it is peculiar for the Mn-based compounds that the change or additional formation of magnetism by interstitial atoms is possible: the change from the AFM (paramagnetic) to FM state or the additional formation of the FM state coexisting with the ground state of Mn atoms in the parent compound. Furthermore, the FM exchange coupling would abruptly emerge under a slight addition of interstitial elements, and this is an important research topic for a deep understanding of interstitial atom engineering. The candidates of Mn-based compounds, possibly showing the change in magnetism by interstitial atoms, are briefly discussed. We note that not only the unit cell volume but also the VEC should be taken into account to design the change in magnetism. The change between AFM and FM states by just controlling the number of interstitial atoms is a very promising elemental technology for making highly functional magnetic devices integrated with both FM and AFM materials without a large lattice mismatch.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.K., N.S. and M.T.; methodology, J.K., N.S. and M.T.; formal analysis, J.K., K.S., T.H. and F.H.; writing—original draft preparation, J.K.; writing—review and editing, J.K., N.S. and M.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
J.K. is grateful for the support provided by Comprehensive Research Organization of Fukuoka Institute of Technology.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Goldschmidt, H.J. Interstitial Alloys; Butterworths: London, UK, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Grandjean, F.; Long, G.J.; Buschow, K.H.J. Interstitial Intermetallic Alloys; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Han, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Du, H. Researh and Development of Interstitial Compounds. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 2103806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieves, P.; Arapan, S.; Maudes-Raedo, J.; Marticorena-Sánchez, R.; Del Brío, N.L.; Kovacs, A.; Echevarria-Bonet, C.; Salazar, D.; Weischenberg, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Database of novel magnetic materials for high-performance permanent magnet development. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2019, 168, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D. Perspective and Prospects for Rare Earth Permanent Magnets. Engineering 2020, 6, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Gabay, A.M.; Schönhöbel, A.M.; Martín-Cid, A.; Barandiaran, J.M.; Niarchos, D. ThMn12-Type Alloys for Permanent Magnets. Engineering 2020, 6, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, J.C. Cohesion in Monovalent Metals. Phys. Rev. 1930, 35, 509–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, J.C. Atomic Shielding Constants. Phys. Rev. 1930, 36, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, A.; Bethe, H. Handbuch der Physik; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1933; Volume 24, p. 595. [Google Scholar]
- Cardias, R.; Szilva, A.; Bergman, A.; Marco, I.D.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Lichtenstein, A.I.; Nordström, L.; Klautau, A.B.; Eriksson, O.; Kvashnin, Y.O. The Bethe-Slater curve revisited; new insights from electronic structure theory. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givord, D.; Lemaire, R. Magnetic Transition and Anomalous Thermal Expansion in R2Fe17 Compounds. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1970, MAG-10, 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Palstra, T.T.M.; Nieuwenhuys, G.J.; Mydosh, J.A.; Buschow, K.H.J. Mictomagnetic, ferromagnetic, and antiferromagnetic transitions in La(FexAl1−x)13 intermetallic compounds. Phys. Rev. B 1985, 31, 4622–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, J.; Yakabe, G.; Nakayama, A.; Nishizaki, T.; Tsubota, M. Competition between ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic states in Al8.5-xFe23Ge12.5+x (0 ≤ x ≤ 3). J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 284, 121188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Gondō, Y. Temperature Dependence of the Magneto-Optic Effect and Resonance Phenomena in Oriented MnBi Films. J. Appl. Phys. 1964, 35, 1024–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Hong, Y.K.; Bae, S.; Lee, J.J.; Jalli, J.; Abo, G.S.; Neveu, N.; Kim, S.G.; Choi, C.J.; Lee, J.G. Saturation magnetization and crystalline anisotropy calculations for MnAl permanent magnet. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 09A731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, A.M.; Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Cui, J. New anisotropic MnBi permanent magnets by field-annealing of compacted melt-spun alloys modified with Mg and Sb. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 495, 165860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Xu, C.; Wang, T.; Song, Y.; Yang, H.; Lu, W. Enhanced magnetization and energy product in isotropic nanocrystalline Mn55Al45 alloys with boron doping. Intermetallics 2018, 101, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, C. Stabilization of τ-phase in carbon-doped MnAl magnetic alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 755, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonietz, F.; Mühlbauer, S.; Pfleiderer, C.; Neubauer, A.; Münzer, W.; Bauer, A.; Adams, T.; Georgii, R.; Böni, P.; Duine, R.A.; et al. Spin Transfer Torques in MnSi at Ultralow Current Densities. Science 2010, 330, 1648–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuji, S.; Kiyohara, N.; Higo, T. Large anomalous Hall effect in a non-collinear antiferromagnet at room temperature. Nature 2015, 527, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Coey, J.M.D.; Otani, Y.; Hurley, D.P.F. Magnetic properties of a new series of rare-earth iron nitrides: R2Fe17Ny (y approximately 2.6). J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1990, 2, 6465–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, T.; Fujimoto, T. Kerr microscopy observation of nitrogenated Sm2Fe17 intermetallic compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1992, 103, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D. Novel Permanent Magnetic Materials. Phys. Scr. 1991, T39, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.-N.; Sun, K.; Fen, Y.-B.; Zhang, J.-X.; Hu, B.-P.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Rao, X.-L.; Liu, G.-C. Structural and intrinsic magnetic properties of Sm2Fe17Ny (y = 2 − 8). J. Alloy. Compd. 1993, 194, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D.; Hurley, D.P.F. New interstitial rare-earth iron intermetallics produced by gas phase reaction. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1992, 104–107, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, C.N.; Takeshita, T. Interstitial carbonation of the Sm2Fe17 phase by reaction with hydrocarbons. J. Alloy. Compd. 1992, 190, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D.; Otani, Y. Magnetic properties of R2Fe17N3-δ. J. Magn. Soc. Jpn. 1991, 15, 677–684. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.-S.; Coey, J.M.D. Magnetic Properties of Ternary Rare-Earth Transition-Metal Compounds. In Handbook of Magnetic Materials VI; Buschow, K.H.J., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Coey, J.M.D.; Sun, H.; Hurley, D.P.F. Intrinsic magnetic properties of new rare-earth iron intermetallic series. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1991, 101, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harashima, Y.; Terakura, K.; Kino, H.; Ishibashi, S.; Miyake, T. First-Principles Study of Structural and Magnetic Properties of R(Fe, Ti)12 and R(Fe, Ti)12N (R = Nd, Sm, Y). JPS Conf. Proc. 2015, 5, 011021. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.-S.; Cao, L.; Shen, B.-G. Structures and magnetic properties of the nitrides (Nd1-xDyx)TiFe11Ny. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1993, 124, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, Y.; Miyake, T.; Hono, K. Potential and issues of permanent magnet candidate compound Nd(FeM)12N with ThMn12-type structure. Mater. Jpn. 2016, 55, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-C.; Zhang, X.-D.; Kong, L.-S.; Pan, Q. Magnetocrystalline anisotropies of RTiFe11Nx compounds. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1991, 58, 2042–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y. A study on the effect of hydrogen in the compounds with BaCd11-type structure. Solid State Commun. 2001, 119, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, T.; Terakura, K.; Harashima, Y.; Kino, H.; Ishibashi, S. First-Principles Study of Magnetocrystalline Anisotropy and Magnetization in NdFe12, NdFe11Ti, and NdFe11TiN. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2014, 83, 043702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harashima, Y.; Terakura, K.; Kino, H.; Ishibashi, S.; Miyake, T. First-principles study on stability and magnetism of NdFe11M and NdFe11MN for M = Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 203904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukazawa, T.; Akai, H.; Harashima, Y.; Miyake, T. First-principles study of intersite magnetic couplings in NdFe12 and NdFe12X (X = B, C, N, O, F). J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 053901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Ohsuna, T.; Yano, M.; Kato, A.; Kaneko, Y. Permanent magnetic properties of NdFe12Nx sputtered films epitaxially grown on V buffer layer. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 053903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehri-Amina, H.; Tamazawa, Y.; Kambayashi, M.; Saito, G.; Takahashi, Y.K.; Ogawa, D.; Ohkubo, T.; Hirosawa, S.; Doi, M.; Shima, T.; et al. Achievement of high coercivity in Sm(Fe0.8Co0.2)12 anisotropic magnetic thin film by boron doping. Acta Mater. 2020, 194, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Zhang, X.; Ji, C.; Chang, H.; Cheng, B.; Yang, Y.; Du, H.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; et al. Structural and magnetic properties of PrFe12−xVx and their nitrides. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.J.; Sherwood, R.C. Magnetic properties and hydrogen absorption in rare-earth intermetallics of the type RMn2 and R6Mn23. J. Appl. Phys. 1977, 48, 4643–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiga, M. Magnetism and spin fluctuations of laves phase manganese compounds. Phys. B + C 1988, 149, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, J.D.; Garcia, E.; Guloy, A.M.; Hurng, W.-M.; Kwon, Y.-U.; Leon-Escamilla, E.A. Widespread Interstitial Chemistry of Mn5Si3-Type and Related Phases. Hidden Impurities and Opportunities. Chem. Mater. 1998, 10, 2824–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdzik, M.; Sürgers, C.; Kelemen, M.; Löhneysen, H.v. Ferromagnetism in carbon-doped Mn5Si3 films. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 6013–6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sürgers, C.; Gajdzik, M.; Fischer, G.; Löhneysen, H.V.; Welter, E.; Attenkofer, K. Preparation and structural characterization of ferromagnetic Mn5Si3Cx films. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 174423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.K.; Ohshima, K.; Wey, M.Y.; Miida, R.; Kimoto, T. Structure and magnetism of fcc Pd-Mn alloys. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 49, 15715–15722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, M.H.; Sellmyer, D.J. Spin-glass-like freezing in disordered MnPd3 and CrPd3 alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 1984, 55, 1735–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sakamoto, Y.; Takao, K.; Nagaoka, Y.; Kida, H.; Flanagan, T.B. Investigations of ordered structures in boron-containing Pd3Mn alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 1993, 197, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, J.; Sakaguchi, K. New room-temperature ferromagnet: B-added Pd0.75Mn0.25 alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 468, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worsham, J.E., Jr.; Wilkinson, M.K.; Shull, C.G. Neutron-diffraction observations on the palladium-hydrogen and palladium-deuterium systems. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1957, 3, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, J.; Hara, T.; Sakaguchi, K.; Shirakawa, N.; Tsubota, M. Emergence of room-temperature ferromagnetism in boron-added Mn compounds. In Proceedings of the Joint European Magnetic Symposia 2019, Uppsala, Sweden, 26–30 August 2019; p. 158. [Google Scholar]
- Izumi, F.; Momma, K. Three-dimensional visualization in powder diffraction. Solid State Phenom. 2007, 130, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotur, B.Y.; Palasyuk, A.M.; Bauer, E.; Michor, H.; Hilscher, G. Uncommon conductivity of R–Mn–Al (R = Gd, Tb) ternary compounds. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2001, 13, 9421–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, T.; Felser, C.; Parkin, S.S.P. Simple rules for the understanding of Heusler compounds. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2011, 39, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Singh, C.; Mukharjee, P.K.; Nath, R.; Nayak, A.K. Observation of the topological Hall effect and signature of room-temperature antiskyrmions in Mn-Ni-Ga D2d Heusler magnets. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 99, 134404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.; Zavareh, M.G.; Mejía, C.S.; Hofmann, K.; Albert, B.; Felser, C.; Nicklas, M.; Singh, S. Reversible adiabatic temperature change in the shape memory Heusler alloy Ni2.2Mn0.8Ga: An effect of structural compatibility. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2018, 2, 122401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, P.; Vernière, A.; Mazet, T.; Malaman, B. Magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of R6Mn23 (R = Y, Nd, Sm, Gd-Tm, Lu) compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 2690–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvyashchenko, A.V.; Popova, S.V.; Makhotkin, V.E.; Fradkov, V.A.; Zaritskii, V.N. Investigations of the magnetic properties of the Yb6Mn23 intermetallic compound. J. Less-Common Met. 1984, 96, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.K.; Takeshita, T.; Wallace, W.E. Hydrogen induced magnetic ordering in Th6Mn23. Solid State Commun. 1977, 23, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushow, K.H.J. Magnetic properties of the ternary hydrides of Nd6Mn23 and Sm6Mn23. Solid State Commun. 1981, 40, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardman-Rhyne, K.; Rhyne, J.J.; Prince, E.; Crowder, C.; James, W.J. Magnetic and crystallographic structure of Y6Mn23D23. Phys. Rev. B 1984, 29, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardman-Rhyne, K.; Kevin Smith, H.; Wallace, W.E. Magnetic and crystallographic structure of Th6Mn23Dx. J. Less-Common Met. 1984, 96, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourarian, F.; Boltich, E.B.; Wallace, W.E.; Craig, R.S.; Malik, S.K. Magnetic characteristics of R6Mn23 hydrides (R = Gd, Ho or Er). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1980, 21, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourarian, F.; Boltich, E.B.; Wallace, W.E.; Malik, S.K. Effect of absorbed hydrogen on magnetic ordering in Tb6Mn23 and Dy6Mn23. J. Less-Common Met. 1980, 74, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szytuła, A.; Szott, I. Magnetic properties of ternary RMn2Si2 and RMn2Ge2 compounds. Solid State Commun. 1981, 40, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.; Campbell, S.J.; Edge, A.V.J. EuMn2Ge2 and EuMn2Si2: Magnetic structures and valence transitions. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 69, 174432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szytuka, A.; Siek, S.; Leciejewicz, J.; Zygmunt, A.; Ban, Z. Neutron diffraction study of UT2X2 (T: Mn, Fe, X: Si, Ge) intermetallic systems. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1988, 49, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukamichi, K. Antiferromagnetic Materials; Kyoritsu: Tokyo, Japan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liu, G.D.; Ding, B.; Liu, E.K.; Jafri, H.M.; Hou, Z.P.; Wang, W.H.; Ma, X.Q.; Wu, G.H. Transition from Anomalous Hall Effect to Topological Hall Effect in Hexagonal Non-Collinear Magnet Mn3Ga. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, M.; Artigas, M.; Bacmann, M.; Fruchart, D.; Skolozdra, R.; Soubeyroux, J.L.; Wolfers, P. Comparison of the magnetic properties of ErMn12−xFex series with their related hydrides and carbides. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 196, 703–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankiewicz, J.; Bartolomé, J.; Fruchart, D. Spin Disorder Scattering in Magnetic Metallic Alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 106602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.B.; Yelon, W.B.; James, W.J.; Cai, S.; Eckert, D.; Handstein, A.; Müller, K.H.; Yang, Y.C. Structural and magnetic properties of R(FexMn1−x)12 (R = Ho, Y). Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 064444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piqué, C.; Blanco, J.A.; Burriel, R.; Abad, E.; Artigas, M.; Fernández-Díaz, M.T. Influence of 3d−4f interactions in the magnetic phases of RFexMn12−x (R=Gd, Tb, and Dy) compounds: Coexistence of ferromagnetism and antiferromagnetism at different crystallographic sites. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 224424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchmayr, H. Magnetic properties of rare earth--Manganese compounds. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1966, 2, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Kohara, T. Magnetism of ScMn4Al8. In Proceedings of the Physical Society of Japan Autumn Meeting 2005, Kyotanabe, Japan, 19–22 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Felner, I.; Nowik, I. Magnetism and hyperfine interactions of 57Fe, 151Eu, 155Gd, 161Dy, 166Er and 170Yb in RM4Al8 compounds (R = rare earth or Y, M = Cr, Mn, Fe, Cu). J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1979, 40, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourée-Vigneron, F.; Pinot, M.; Olès, A.; Baran, A.; Suski, W. UCr4Al8 and UMn4Al8: Neutron diffraction study. Solid State Commun. 1990, 75, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, N.P.; Klaasse, J.C.P.; Brück, E.; de Boer, F.R.; Buschow, K.H.J. Magnetic properties of GdT4Al8 and GdT6Al6 compounds (T = Cr, Mn, Cu). J. Alloy. Compd. 2001, 315, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schobinger-Papamantellos, P.; Fischer, P.; de Groot, C.H.; de Boer, F.R.; Buschow, K.H.J. Magnetic properties and neutron diffraction of TbMn4Al8. J. Alloy. Compd. 1996, 232, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baran, A.; Suski, W.; Mydlarz, T. Magnetic properties of the (U, Th) (Cr, Mn)4Al8 compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1987, 63, 196–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruchart, R.; Roger, A.; Senateur, J.P. Crystallographic and Magnetic Properties of Solid Solutions of the Phosphides M2P, M = Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, and Ni. J. Appl. Phys. 1969, 40, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, B.K.; Ericsson, T.; Haggstrom, L.; Verma, H.R.; Andersson, Y.; Rundqvist, S. A Mossbauer study of the (Fe1-xMnx)2P system. J. Phys. C 1987, 20, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Asahi, R.; Kishida, Y.; Masuoka, Y.; Sugiyama, J. Measurement and ab initio calculation of the structural parameters and physical properties of 3d transition intermetallics TiMP (M = Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, or Ni). Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 046505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanomata, T.; Kawashima, T.; Utsugi, H.; Goto, T.; Hasegawa, H.; Kaneko, T. Magnetic properties of the intermetallic compounds MM’X (M = Cr, Mn, M’ = Ru, Rh, Pd, and X = P, As). J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 69, 4639–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeitschko, W.; Johnson, V. High pressure Mn2As with Fe2P-type structure. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B 1972, 28, 1971–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomé, J.; García, J.; Floría, L.M.; Falo, F.; Navarro, R.; Fruchart, D.; Bacmann, M.; de Jongh, L.J. A magnetic Kosterlitz-Thouless transition in quasi 2-d MnRhAs? J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1986, 54–57, 1547–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bażela, W. Magnetic properties of intermetallic compounds RhMnGe, PdMnGe, Pd1.5Mn0.5Si, Pd1.5Mn0.5Ge and RhMnSi. J. Less-Common Met. 1984, 100, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazela, W.; Szytuła, A.; Todorović, J.; Tomkowicz, Z.; Zięba, A. Crystal and magnetic structure of NiMnGe. Phys. Status Solidi A 1976, 38, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brück, E.; van Streepen, T.; Duijn, H.G.M.; Haanappel, E.G.; de Boer, F.R.; Buschow, K.H. J Magnetic and transport properties of MnPtAl1-xGax compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1988, 177–181, 767–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.J.; De Mooij, D.B. Crystal structure and magnetic properties of PtMnGa and PtMnAl. J. Less-Common Met. 1984, 99, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kübler, J. Ab initio estimates of the Curie temperature for magnetic compounds. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2006, 18, 9795–9808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, V.V.; Kawamura, N.; Suzuki, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Mankey, G.J.; Raj, P.; Sathyamoorthy, A.; Joshi, A.G.; Malik, S.K. Evidence for a magnetic moment on Ir in IrMnAl from x-ray magnetic circular dichroism. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 214413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.J.; van Engen, P.G.; Jongebreur, R. Magneto-optical properties of metallic ferromagnetic materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1983, 38, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masumoto, H.; Watanabe, K. New Compounds of the Clb, Cl Types of RhMnSb, IrMnSn and IrMnAl, New L21 (Heusler) Type of Ir2MnAl and Rh2MnAl Alloys, and Magnetic Properties. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1972, 32, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikazumi, S. Physics of Ferromagnetism; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Helmholdt, R.B.; Buschow, K.H.J. A neutron diffraction and magnetization study of PdMnTe. J. Less-Common Met. 1986, 123, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offernes, L.; Ravindran, P.; Kjekshus, A. Prediction of large polar Kerr rotation in the Heusler-related alloys AuMnSb and AuMnSn. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 2862–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckman, O.; Lundgren, L. Compounds of transition elements with nonmetals. In Handbook of Magnetic Materials; Buschow, K.H.J., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1991; Volume 6, pp. 181–287. [Google Scholar]
- Lamichhane, T.N.; Taufour, V.; Masters, M.W.; Parker, D.S.; Kaluarachchi, U.S.; Thimmaiah, S.; Bud’ko, S.L.; Canfield, P.C. Discovery of ferromagnetism with large magnetic anisotropy in ZrMnP and HfMnP. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 092402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventutini, G.; ljjaali, I.; Ressouche, E.; Malaman, B. Neutron diffraction study of the HoMnSi, LuMnSi and Sc0.9Lu0.1MnSi compounds. J. Alloy. Compd. 1997, 256, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.-D.; Pöttgen, R.; Chevalier, B.; Gaudin, E.; Matar, S.F. The ternary germanides UMnGe and U2Mn3Ge. Solid State Sci. 2013, 21, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, G.; Malaman, B.; Ressouche, E. Neutron diffraction study of the TbMnGe compound. J. Alloy. Compd. 1996, 243, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosek, V.; Vernière, A.; Ouladdiaf, B.; Malaman, B. Crystal and magnetic structures of the R(=Y, Dy–Tm)MnGe compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 256, 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umetsu, R.Y.; Fukamichi, K.; Sakuma, A. Electrical and magnetic properties of antiferromagnetic L10-type Mn alloys. Mater. Jpn. 2004, 43, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.Z.; Marinescu, M.; Liu, J.F. Ferromagnetic Tetragonal L10-Type MnGa Isotropic Nanocrystalline Microparticles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 3322–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, A. Electronic Structure and Magnetocrystalline Anisotropy Energy of MnAl. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1994, 63, 1422–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suits, J.C. New magnetic compounds with Heusler and Heusler-related structures. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 14, 4131–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umetsu, R.Y.; Mitsui, Y.; Yuito, I.; Takeuchi, T.; Kawarada, H. Substitution Effects of Cr or Fe on the Curie Temperature for Mn-Based Layered Compounds MnAlGe and MnGaGe With Cu2Sb-Type Structure. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, K.; Shinohara, T.; Watanabe, H. Magnetic Properties of A New Ferromagnetic Compound MnGaGe. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1972, 32, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, H.; Endo, S.; Notsu, Y.; Ono, F.; Kanomata, T.; Kaneko, T. Pressure Effect on Curie Temperature in MnZnSb. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 32, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beleanu, A.; Kiss, J.; Kreiner, G.; Köhler, C.; Müchler, L.; Schnelle, W.; Burkhardt, U.; Chadov, S.; Medvediev, S.; Ebke, D.; et al. Large resistivity change and phase transition in the antiferromagnetic semiconductors LiMnAs and LaOMnAs. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 184429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kido, H.; Hoshikawa, T.; Shimada, M.; Koizumi, M. Preparation and magnetic properties of YMnSi. Phys. Status Solidi A 1985, 88, K39–K43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovtchenkova, I.A.; Nikitin, S.A.; Ivanova, T.I.; Tskhadadze, G.A.; Chistyakov, O.D.; Badurski, D. Magnetocaloric effect and magnetoresistance in GdxLa1−xMnSi compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 300, e493–e496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welter, R.; Venturini, G.; Ressouche, E.; Malaman, B. Magnetic properties of TbMnSi, determined by susceptibility measurements and neutron diffraction study. J. Alloy. Compd. 1994, 210, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welter, R.; Venturini, G.; Ressouche, E.; Malaman, B. Neutron diffraction studies of the CeFeSi-type CaMnSi and CaMnGe compounds. Solid State Commun. 1996, 97, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welter, R.; Venturini, G.; Ressouche, E.; Malaman, B. Crystallographic data and magnetic properties of new CeFeSi-type RMnGe compounds (R = La Sm) studied by magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements. J. Alloy. Compd. 1995, 228, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dascoulidou, A.; Müller, P.; Bronger, W. Ternäre Mangan-Verbindungen AMnX (A ≙ Mg, Ca, Sr oder Ba; X ≙ Si, Ge oder Sn): Neutronenbeugungsuntersuchungen zur Charakterisierung der magnetischen Eigenschaften. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1998, 624, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, J.; Yahia, M.B.; Babizhetskyy, V.; Bauer, J.; Cordier, S.; Guérin, R.; Hiebl, K.; Rocquefelte, X.; Saillard, J.-Y.; Halet, J.-F. Mn5Si3-type host-interstitial boron rare-earth metal silicide compounds RE5Si3: Crystal structures, physical properties and theoretical considerations. J. Solid State Chem. 2006, 179, 2310–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahon, T.; Gaudin, E.; Villesuzanne, A.; Chevalier, B.; Tencé, S. Effect of Carbon Insertion on the Structural and Magnetic Properties of NdScSi. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 15255–15268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coey, J.M.D. New permanent magnets; manganese compounds. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2014, 26, 064211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Terada, H.; Shirakawa, N.; Tsubota, M.; Kitagawa, J. The Impact of the Composition Effect on Ferromagnetic Properties of Tb2Co2Ga. Metals 2019, 9, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, J.; Takeda, N.; Sakai, F.; Ishikawa, M. Effect of composition in (RE)3Pd20Ge6 (RE = La, Ce and Nd). J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1999, 68, 3413–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, J.; Terada, H.; Shirakawa, N.; Tsubota, M.; Nose, A.; Tanaka, S. Composition effect in ferromagnetic properties of Tb3Co3Ga. Results Phys. 2019, 15, 102591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.M.; Yue, M.; Zhang, H.G.; Wang, M.L.; Yu, F.; Huang, Q.Z.; Ryan, D.H.; Altounian, Z. Intrinsic magnetic properties of single-phase Mn1+xGa (0 < x < 1) alloys. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17086. [Google Scholar]
- Enkovaara, J.; Heczko, O.; Ayuela, A.; Nieminen, R.M. Coexistence of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic order in Mn-doped Ni2MnGa. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 67, 212405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, P.; Mazin, I.I.; Papaconstantopoulos, D.A. Effects of doping on the magnetic anisotropy energy in SmCo5-xFex and YCo5-xFex. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 69, 134408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, A.; Manabe, Y.; Kota, Y. First principles calculation of magnetocrystalline anisotropy energy of MnBi and MnBi1-xSnx. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2013, 82, 073704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, T.; Parker, D.S. Magnetic properties and magnetocrystalline anisotropy of Nd2Fe17, Nd2Fe17X3, and related compounds. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyahara, J.; Shirakawa, N.; Setoguchi, Y.; Tsubota, M.; Kuroiwa, K.; Kitagawa, J. Hill plot focusing on Ce compounds with high magnetic ordering temperatures and consequent study of Ce2AuP3. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2018, 31, 3559–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Ueno, K.; Fukumura, T.; Yuan, H.T.; Shimotani, H.; Iwasa, Y.; Gu, L.; Tsukimoto, S.; Ikuhara, Y.; Kawasaki, M. Electrically Induced Ferromagnetism at Room Temperature in Cobalt-Doped Titanium Dioxide. Science 2011, 332, 1065–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, J.; Kitajima, D.; Shimokawa, K.; Takaki, H. Photoinduced Kondo effect in CeZn3P3. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 035122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, G.R. Non-Fermi-liquid behavior in d- and f-electron metals. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2001, 73, 797–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, D.; Ishikawa, M.; Kitagawa, J.; Takeda, N. Suppression of Antiferromagnetism by Kondo Effect and Quantum Critical Behavior in CeCoGe 3-xSix (0 ≤ x ≤ 3). J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1998, 67, 2495–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custers, J.; Gegenwart, P.; Wilhelm, H.; Neumaier, K.; Tokiwa, Y.; Trovarelli, O.; Geibel, C.; Steglich, F.; Pépin, C.; Coleman, P. The break-up of heavy electrons at a quantum critical point. Nature 2003, 424, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhneysen, H.V.; Rosch, A.; Vojta, M.; Wölfle, P. Fermi-liquid instabilities at magnetic quantum phase transitions. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2007, 79, 1015–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-L.; Hallas, A.M.; Grube, K.; Kuntz, S.; Spieß, B.; Bayliff, K.; Besara, T.; Siegrist, T.; Cai, Y.; Beare, J.; et al. Quantum Critical Point in the Itinerant Ferromagnet Ni1−xRhx. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 117203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akayama, M.; Fujii, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Tatami, K. Physical properties of nitrogenated RFe11Ti intermetallic compounds (R = Ce, Pr and Nd) with ThMn12-type structure. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1994, 130, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).