Magnetic and Magnetocaloric Effect of Laves Phase Compounds Er(Fe0.8−xMn0.2−yCox+y)2 with x, y = 0.0 or 0.1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Structure Analysis
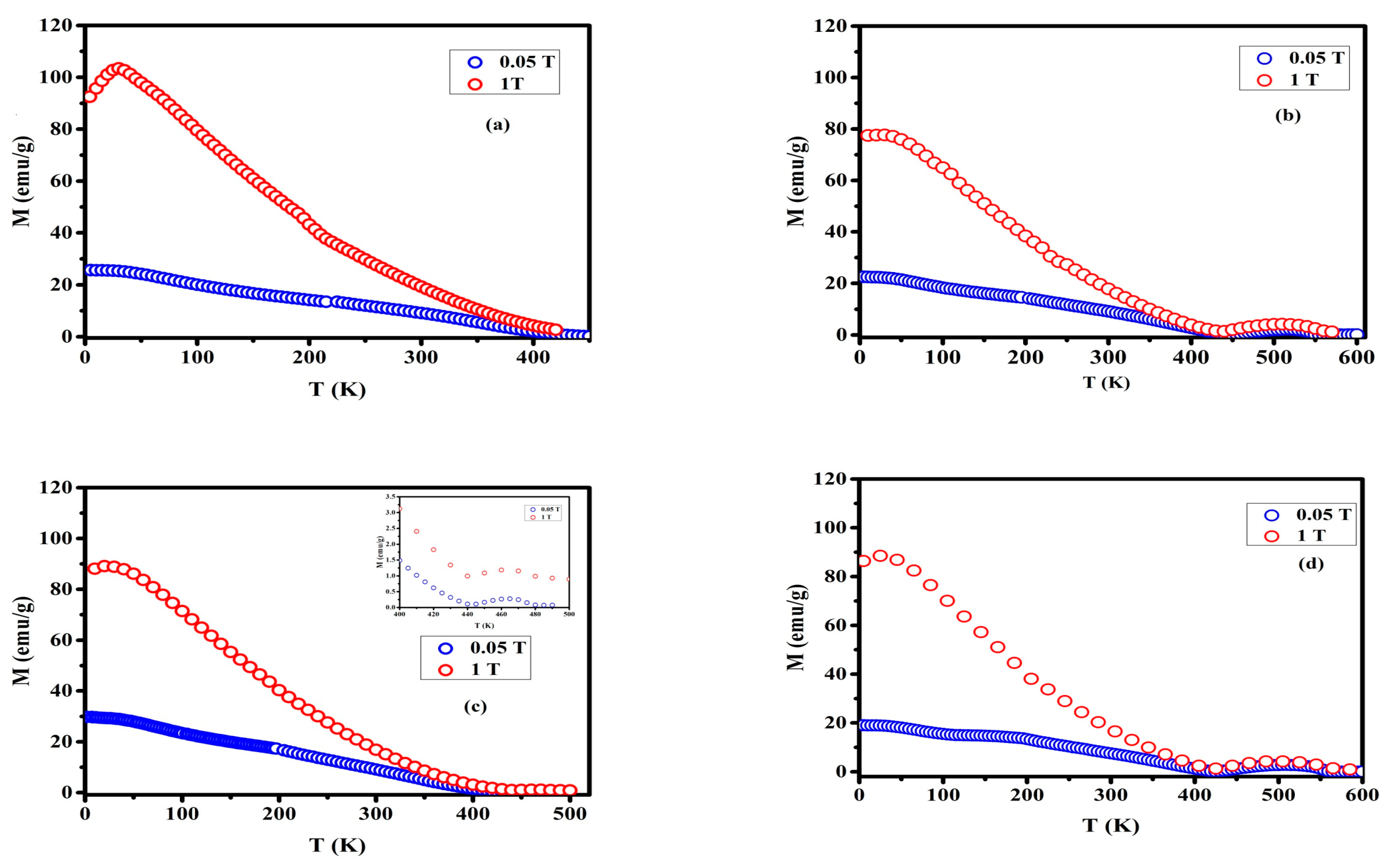
3.2. Magnetic Properties
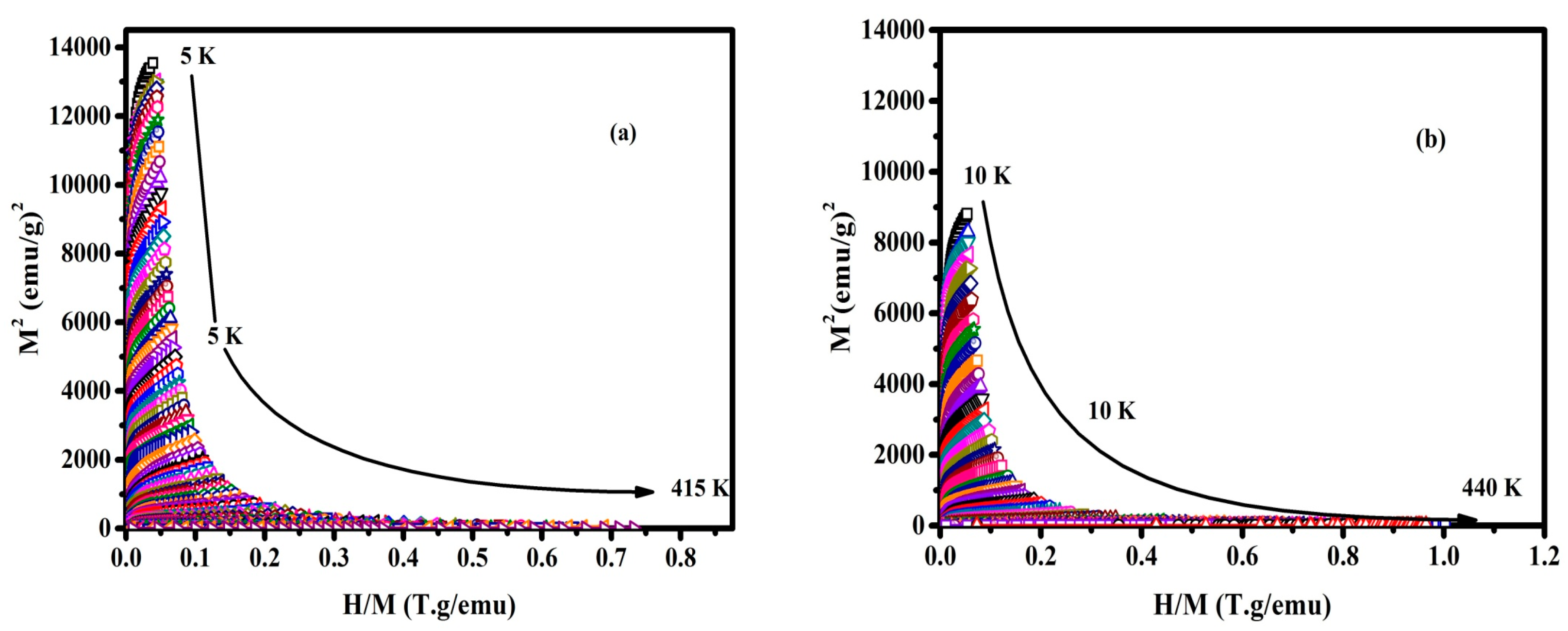
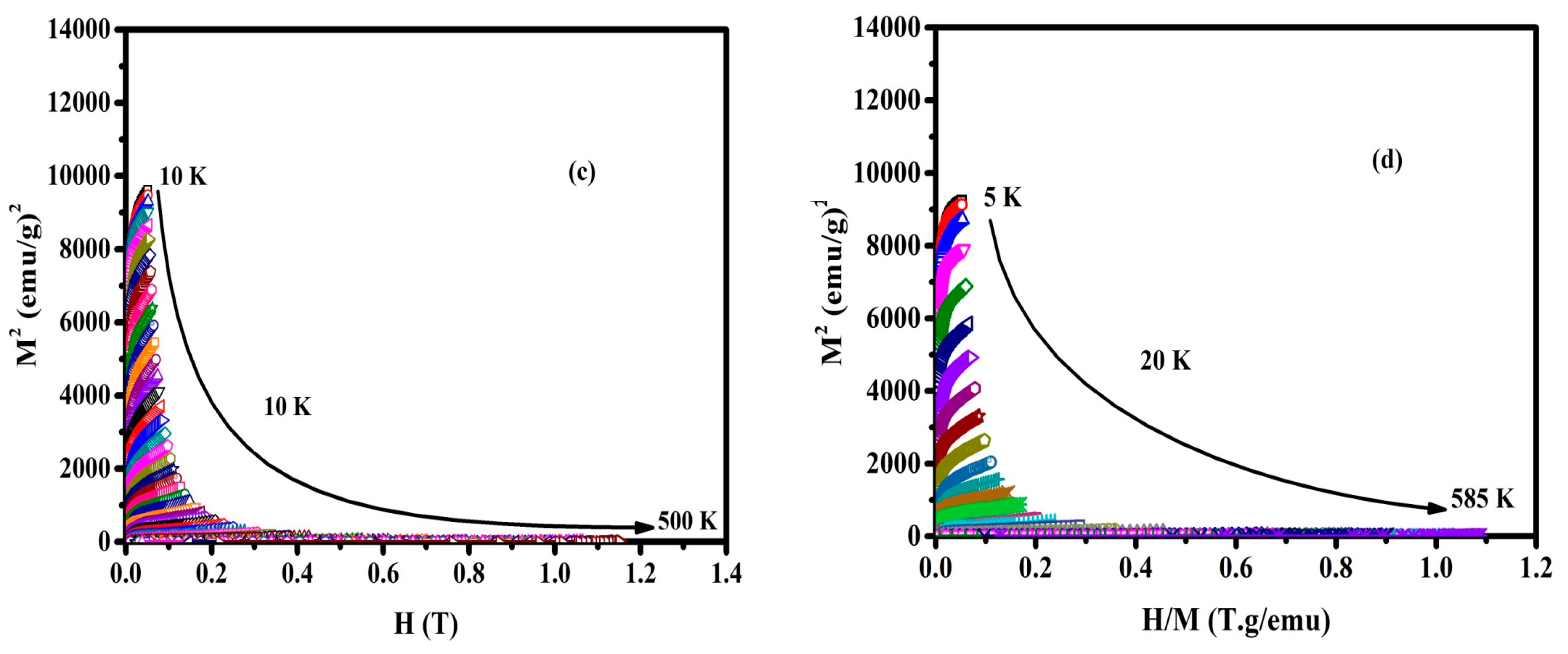
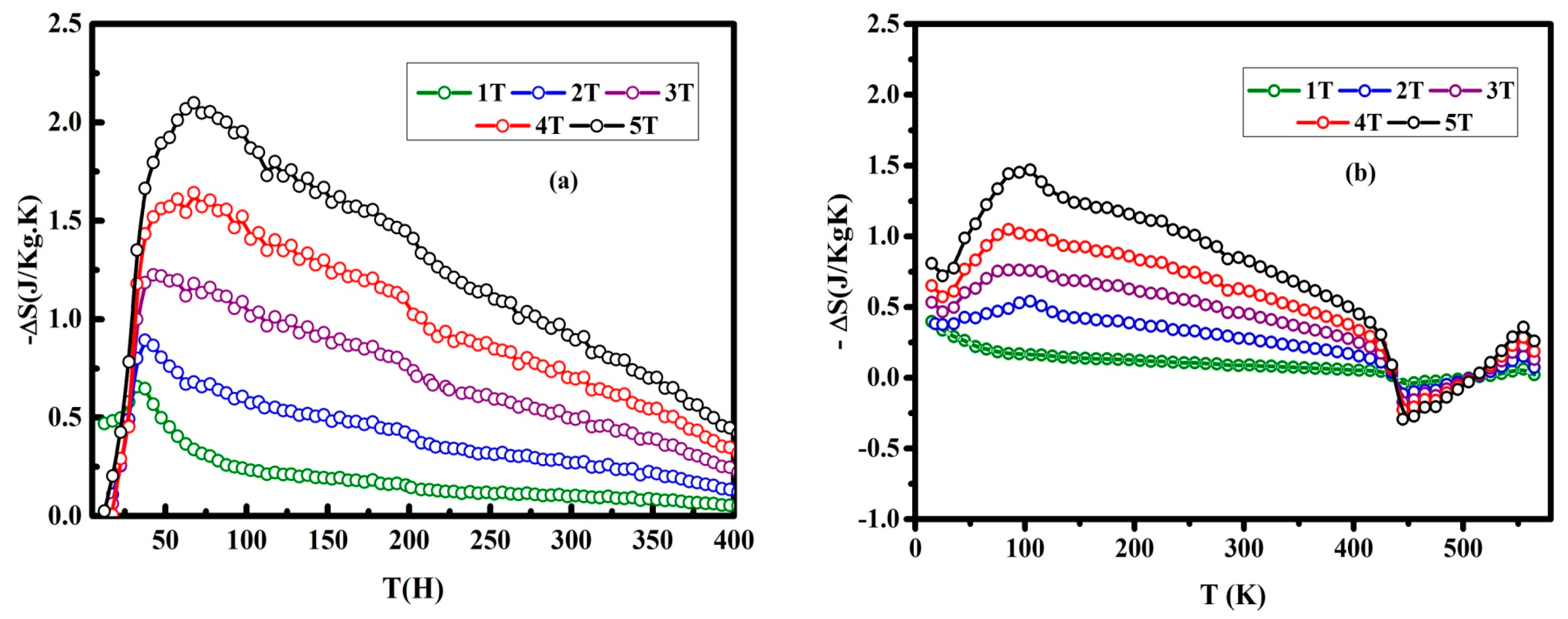
3.3. Magnetocaloric Properties
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pecharsky, V.K.; Gschneidner, J.K.A. Giant Magnetocaloric Effect in Gd5(Si2Ge2). Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 4494–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujieda, S.; Hasegawa, Y.; Fujita, A.; Fukamichi, K. Direct measurement of magnetocaloric effects in itinerant-electron metamagnets La(FexSi1−x)13 compounds and their hydrides. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 272, 2365–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegus, O.; Brück, E.; Buschow, K.H.J.; De Boer, F.R. Transition-metal-based magnetic refrigerants for room-temperature applications. Nature 2002, 415, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Ranke, P.J.; De Campos, A.; Caron, L.; Coelho, A.A.; Gama, S.; De Oliveira, N.A. Calculation of the giant magnetocaloric effect in the MnFeP0.45As0.55 compound. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 70, 094410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tishin, A.M. Magnetocaloric effect: Current situation and future trends. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 316, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brück, E.; Tegus, O.; Thanh, D.; Buschow, K. Magnetocaloric refrigeration near room temperature (invited). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 310, 2793–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, H.; Tanabe, Y. Giant magnetocaloric effect of MnAs1−xSbx. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 3302–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.D.; Wang, D.H.; Zhang, C.; Xuan, H.C.; Gu, B.X.; Du, Y.W. Low-field inverse magnetocaloric effect in Ni50−xMn39+xSn11 Heusler alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 042507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trung, N.T.; Zhang, L.; Caron, L.; Buschow, K.H.J.; Brück, E. Giant magnetocaloric effects by tailoring the phase transitions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 172504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trung, N.T.; Biharie, V.; Zhang, L.; Caron, L.; Buschow, K.H.J.; Brück, E. From single- to double-first-order magnetic phase transition in magnetocaloric Mn1−xCrxCoGe compounds. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 162507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, E.; Wang, W.; Feng, L.; Zhu, W.; Li, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, G.; Jiang, C.; Xu, H.; et al. Stable magnetostructural coupling with tunable magnetoresponsive effects in hexagonal ferromagnets. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Gottschall, T.; Skokov, K.P.; Moore, J.D.; Gutfleisch, O. Giant magnetocaloric effect driven by structural transitions. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecharsky, A.O.; Gschneidner, J.K.; Pecharsky, V.K. The giant magnetocaloric effect of optimally prepared Gd5Si2Ge2. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 78, 4722–4728. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, F.-X.; Qian, X.L.; Sun, J.R.; Wang, G.J.; Zhang, X.X.; Cheng, Z.H.; Shen, B.G. Magnetic entropy change and its temperature variation in compounds La(Fe1−xCox)11.2Si1.8. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 3620–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, H.; Tomekawa, S.; Shiga, M. Magnetocaloric effect of ErCo2. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 196, 689–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, S.; Myalikgulyev, G.; Tishin, A.; Annaorazov, M.; Asatryan, K.; Tyurin, A. The magnetocaloric effect in Fe49Rh51 compound. Phys. Lett. A 1990, 148, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohei, T.; Wada, H.; Kanomata, T. Large magnetocaloric effect of Mn3−xCoxGaC. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 272, E585–E586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, V.; Shapiro, A.J.; Shull, R.D. Reduction of hysteresis losses in the magnetic refrigerant Gd5Ge2Si2 by the addition of iron. Nature 2004, 429, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.G.; Geng, D.; Zhang, Z.D. Reversible room-temperature magnetocaloric effect in Mn5PB2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 202504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.J.; Van Stapele, R.P. Magnetic Properties of the intermetallic compounds RFe2. Le J. de Phys. Colloq. 1971, 32, C1-672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.J. Magnetic Properties of some Cubic Rare-Earth-Iron Compounds of the Type RFe2 and RxY1−xFe2. J. Appl. Phys. 1970, 41, 4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mican, S.; Benea, D.; Mankovsky, S.; Polesya, S.; Gînscă, O.; Tetean, R. Magnetic behaviour of Er1−xZrxFe2 intermetallic compounds. J. Physics Condens. Matter 2013, 25, 466003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, A.; Singh, N.K.; Mudryk, Y.; Nayak, A.K.; Suresh, K.G.; Nigam, A.K.; Pecharsky, V.K. Magnetostructural transition in Ce(Fe0.975Ga0.025)2 compound. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 09E133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anikin, M.S.; Tarasov, E.N.; Kudrevatykh, N.V.; Zinin, A.V. Untypical Temperature Dependence of the Magnetocaloric Effect in the Dy(Co1−xFex)2 (x = 0.10; 0.15) Compounds. Solid State Phenom. 2015, 233, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anikin, M.S.; Tarasov, E.; Kudrevatykh, N.; Osadchenko, V.; Zinin, A. About the Role of Fe-Ions in the Formation of Magnetocaloric Effect in Ho(Co1−xFex)2 Compounds. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2015, 127, 635–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, M.; Yusuf, S.; Mukadam, M.D.; Shashikala, K. Magnetocaloric effect and critical behavior near the paramagnetic to ferrimagnetic phase transition temperature in TbCo2−xFex. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 174402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, J.-D.; Shen, B.-G.; Sun, J.-R. Magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effect in TbCo2−xFex compounds. Chin. Phys. 2007, 16, 3843. [Google Scholar]
- Chaaba, I.; Othmani, S.; Haj-Khlifa, S.; Fruchart, D.; Cheikhrouhou-Koubaa, W.; Cheikhrouhou, A.; De Rango, P. Magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of Er(Co1−xFex)2 intermetallic compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 439, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaaba, I.; Othmani, S.; Haj-Khlifa, S.; De Rango, P.; Fruchart, D. Effect of Hydrogen on the Structure, Magnetic and Magnetocaloric Properties of Laves Phase Type-Compounds RE(Fe0.25Co0.75)2Hy with RE = Ho and Er, y = 0.0, 3.0, 3.5. Solid State Phenom. 2019, 289, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyushin, A.; Wallace, W. Magnetic and structural studies of rare earth-iron-manganese laves phase ternaries I. J. Solid State Chem. 1976, 17, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyushin, A.; Wallace, W. Magnetic and structural studies of rare earth-iron-manganese laves phase ternaries II. J. Solid State Chem. 1976, 17, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merches, M.; Narasimhan, K.S.V.L.; Wallace, W.E.; Ilyushin, A. Magnetic Properties of R(Fe1−xMnx)2 Compounds (R = Gd, Tb, By, Ho or Er). AIP Conf. Proc. 1976, 34, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Carvajal, J. Fullprof. 2k, Version 4.6 c. Physica B 2002, 55, 192. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=mJgatLIAAAAJ&hl=en (accessed on 4 September 2017).
- Clementi, E.; Raimond, D.I.; Reinhardt, W.P. Atomic Screening Constants from SCF Functions II. J. Chem. Phys. 1967, 47, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Saxce, T.; Berthier, Y.; Fruchart, D. Magnetic and structural properties of the ternary hydride phases of ErFe2. J. Less Common Met. 1985, 107, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dariel, M.P.; Atzmony, U. Bulk magnetic anisotropy constants of the rare-earth iron Laves compounds. Int. J. Magn. 1973, 4, 213. Available online: www.iaea.org›inis›collection›NCLCollectionStore›_PublicPDF (accessed on 16 June 2020).
- Bargouth, M.O.; Will, G. Neutron diffraction study of ErFe2. Le J. Phys. Colloq. 1971, 32, C1-675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Tremolet de Lacheisserie, E.; Gignoux, D.; Schenker, M. Magnetism; Grenoble Sciences: Grenoble, France, 2005; ISBN 0 387 22967 1. E-book ISBN 0 387 23062 9. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden, G.J.; Bunbury, D.S.P.; Guimaraes, A.P. Mössbauer Studies of Iron-Rare Earth Intermetallics. J. Appl. Phys. 1968, 39, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, W.E. Mössbauer Effect Measurements of Hyperfine Interactions in Laves Phases Containing Fe Combined with Ti, Zr, Y, and the Lanthanide Metals. J. Chem. Phys. 1964, 41, 3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burzo, E. On the magnetic properties of Y(FexCo1−x)2 compounds. Solid State Commun. 1978, 25, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidukova, I.Y.; Dubenko, I.S.; Levitin, R.Z.; Markosyan, A.S.; Pirogov, A.N. Nature of the magnetism of the subsystem in RMn2 compounds. Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 1988, 94, 236242. [Google Scholar]
- Schaafsma, A.; Besnus, M.; Vincze, I.; Van Der Woude, F. Effect of Mn on the magnetic moments of Fe in intermetallic compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1980, 1149–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Takeshita, T.; Wallace, W. Hydrogen induced magnetic ordering in Th6Mn23. Solid State Commun. 1977, 23, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commandré, M.; Fruchart, D.; Rouault, A.; Sauvage, D.; Shoemaker, C.; Shoemaker, D. Etude par diffraction neutronique des composés Mn23Y6Dx. J. Phys. Lett. 1979, 40, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.J.; Sherwood, R.C. Magnetic properties and hydrogen absorption in rare-earth intermetallics of the type RMn2 and R6Mn23. J. Appl. Phys. 1977, 48, 4643–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, I.V.; Coey, J.M.D.; Givord, D.; Harris, I.R.; Hanitsch, R. Concerted European Action on Magnets (CEAM); Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 72–73. [Google Scholar]
- Belorizky, E.; Fremy, M.A.; Gavigan, J.P.; Givord, D.; Li, H.S. Evidence in rare-earth (R)–transition metal (M) intermetallics for a systematic dependence of R-M exchange interactions on the nature of the R atom. J. Appl. Phys. 1987, 61, 3971–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.J.; de Boer, F.R. Physics of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-306-48408-7. [Google Scholar]
- Fruchart, D.; Berthier, Y.; De Saxce, T.; Vulliet, P. Etudes structurales et magnetiques des formes cubiques et rhomboedriques LnFe2Hx, Ln = Er, Tb. J. Solid State Chem. 1987, 67, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontonnier, L.; Fruchart, D.; Soubeyroux, J.; Triantafillidis, G.; Berthier, Y. Structural and magnetic behaviour of LuFe2Hx. J. Less Common Met. 1991, 172, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talik, E.; Kulpa, M.; Mydlarz, T.; Kusz, J.; Böhm, H. Magnetic properties of ErMn2 single crystals. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 348, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, B. On a generalised approach to first and second order magnetic transitions. Phys. Lett. 1964, 12, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, B.; Meng, X.; Chen, Z. Review on research of room temperature magnetic refrigeration. Int. J. Refrig. 2003, 26, 622–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschneidner, K.A.; Pecharsky, V.K. Magnetocaloric Materials. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2000, 30, 387–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikitin, S.A.; Talalaeva, E.V.; Chernikova, L.A.; Andreenko, A.S. Magnetocaloric effects in rare-earth magnetic materials. Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 1973, 65, 2058. [Google Scholar]
- Rhyne, J.J.; Sankar, S.G.; Wallace, W.E. Sublattice magnetization of ErFe2—H. In Rare Earths in Modern Science and Technology; McCarthy, G.J., Rhyne, J.J., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978; ISBN 978-1-4613-3054-7. [Google Scholar]
- Cyrot, M.; Gignoux, D.; Givord, F.; Lavagna, M. Magnetism of the rare earth, 3d–Theoretical review. J. Phys. Colloq. 1979, 40, C5-171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyrot, M.; Lavagna, M. Density of states and magnetic properties of the rare-earth compounds RFe2, RCo2 and RNi2. J. Phys. 1979, 40, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khmelevskyi, S.; Mohn, P. The order of the magnetic phase transitions in RCo2 (R = rare earth) intermetallic compounds. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2000, 12, 9453–9464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balli, M.; Fruchart, D.; Gignoux, D. Magnetic behaviour and experimental study of the magnetocaloric effect in the pseudobinary Laves phase Er1−xDyxCo2. J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 509, 3907–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, W.E.; Malik, S.K.; Takeshita, T.; Sankar, S.G.; Gualtieri, D.M. Magnetic properties of hydrides of the rare earths and rare earth intermetallics. J. Appl. Phys. 1978, 49, 1486–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardman, K. Site magnetization of cubic and hexagonal HoMn2. J. Appl. Phys. 1982, 53, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiga, M. Magnetic ordering and frustration in itinerant systems: RMn2. J. Magn. Mag. Mat. 1994, 4, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Tepëшина, И.; Cwik, J.; Tereshina, E.; Politova, G.A.; Burkhanov, G.; Chzhan, V.; Ilyushin, A.; Miller, M.; Zaleski, A.; Nenkov, K.; et al. Multifunctional Phenomena in Rare-Earth Intermetallic Compounds With a Laves Phase Structure: Giant Magnetostriction and Magnetocaloric Effect. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashikala, K.; Raj, P.; Sathyamoorthy, A.; Rao, T.V.C.; Siruguri, V.; Paranjpe, S.K. ErFe2–H2 system. II. Non-collinear magnetic ordering. Philos. Mag. B 1999, 79, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul-Boncour, V.; Isnard, O.; Shtender, V.; Skourski, Y.; Guillot, M. Origin of the metamagnetic transitions in Y1−xErxFe2(H,D)4.2 compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 512, 167018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, N.H.; Brommers, P.E. Aspects of Rare Earth-Transition metal Intermetallics. In Advanced Magnetism and Magnetic Materials—Volume 1; Duc, N.H., Ed.; Vietnam National University Press: Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 2014; ISBN 978-604-62-4371-7. [Google Scholar]
- Moriya, T. Developments of the theory of spin fluctuations and spin fluctuation-induced superconductivity. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2006, 82, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Melnikov, N.B.; Reser, B.I.; Grebennikov, V. Spin-fluctuation theory beyond Gaussian approximation. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2010, 43, 195004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bentouaf, A.; Mebsout, R.; Rached, H.; Amari, S.; Reshak, A.H.; Aissa, B. Theoretical investigation of the structural, electronic, magnetic and elastic properties of binary cubic C15-Laves phases TbX2 (X = Co and Fe). J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 689, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, N.; Anh, D.K.; Brommer, P. Metamagnetism, giant magnetoresistance and magnetocaloric effects in RCo2-based compounds in the vicinity of the Curie temperature. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2002, 319, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, E. Entropy and magnetocaloric effect in ferrimagnets RCo2. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 2017, 124, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balli, M.; Fruchart, D.; Gignoux, D. A study of magnetism and magnetocaloric effect in Ho1−xTbxCo2 compounds. J. Magn. Mag. Mat. 2007, 314, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anikin, M.S.; Tarasov, E.N.; Kudrevatykh, N.V.; Volegov, A.S.; Zinin, A.V. Magnetic properties of R(Co0.88Fe0.12)2 quasi-biany compounds. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1389, 012061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Compounds | Cell Parameter (Å) | Cell Volume (Å3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Er(Fe0.8Mn0.2)2 | 1 | 7.313(3) | 391.18(3) |
| Er(Fe0.8Mn0.1Co0.1)2 | 2 | 7.265(5) | 383.54(2) |
| Er(Fe0.7Mn0.2Co0.1)2 | 3 | 7.281(1) | 386.02(1) |
| Er(Fe0.7Mn0.1Co0.2)2 | 4 | 7.246(1) | 380.42(2) |
| Compounds | Molar Mass (g/mol.) | Msat (emu/g) | Msat (µB/f.u.) | <µ3d> (µB/f.u.) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Er(Fe0.8Mn0.2)2 | 1 | 278.586 | 122.38 | 6.10 | 1.45 |
| Er(Fe0.8Mn0.1Co0.1)2 | 2 | 279.385 | 100.04 | 5.00 | 2.00 |
| Er(Fe0.7Mn0.2Co0.1)2 | 3 | 279.204 | 105.23 | 5.26 | 1.87 |
| Er(Fe0.7Mn0.1Co0.2)2 | 4 | 280.003 | 98.41 | 4.93 | 2.04 |
| Compounds | Compensation Temperature (K) | Curie Temperature TC (K) | −ΔSM (J·kg−1·K−1) T<Tcomp/T> Tcomp | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Er(Fe0.8Mn0.2)2 | 1 | no | 355 | 2.11 |
| Er(Fe0.8Mn0.1Co0.1)2 | 2 | 435 | 550 | 1.47/0.37 |
| Er(Fe0.7Mn0.2Co0.1)2 | 3 | 445 | 475 | 1.5/0.07 |
| Er(Fe0.7Mn0.1Co0.2)2 | 4 | 425 | 555 | 1.53/0.29 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Othmani, S.; Chaaba, I.; Haj-Khlifa, S.; de Rango, P.; Fruchart, D. Magnetic and Magnetocaloric Effect of Laves Phase Compounds Er(Fe0.8−xMn0.2−yCox+y)2 with x, y = 0.0 or 0.1. Metals 2020, 10, 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10091247
Othmani S, Chaaba I, Haj-Khlifa S, de Rango P, Fruchart D. Magnetic and Magnetocaloric Effect of Laves Phase Compounds Er(Fe0.8−xMn0.2−yCox+y)2 with x, y = 0.0 or 0.1. Metals. 2020; 10(9):1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10091247
Chicago/Turabian StyleOthmani, Safa, Ichrak Chaaba, Sonia Haj-Khlifa, Patricia de Rango, and Daniel Fruchart. 2020. "Magnetic and Magnetocaloric Effect of Laves Phase Compounds Er(Fe0.8−xMn0.2−yCox+y)2 with x, y = 0.0 or 0.1" Metals 10, no. 9: 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10091247
APA StyleOthmani, S., Chaaba, I., Haj-Khlifa, S., de Rango, P., & Fruchart, D. (2020). Magnetic and Magnetocaloric Effect of Laves Phase Compounds Er(Fe0.8−xMn0.2−yCox+y)2 with x, y = 0.0 or 0.1. Metals, 10(9), 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10091247






