Liquation Cracking Tendency of Novel Al-Mg-Zn Alloys with a Zn/Mg Ratio below 1.0 during Fusion Welding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
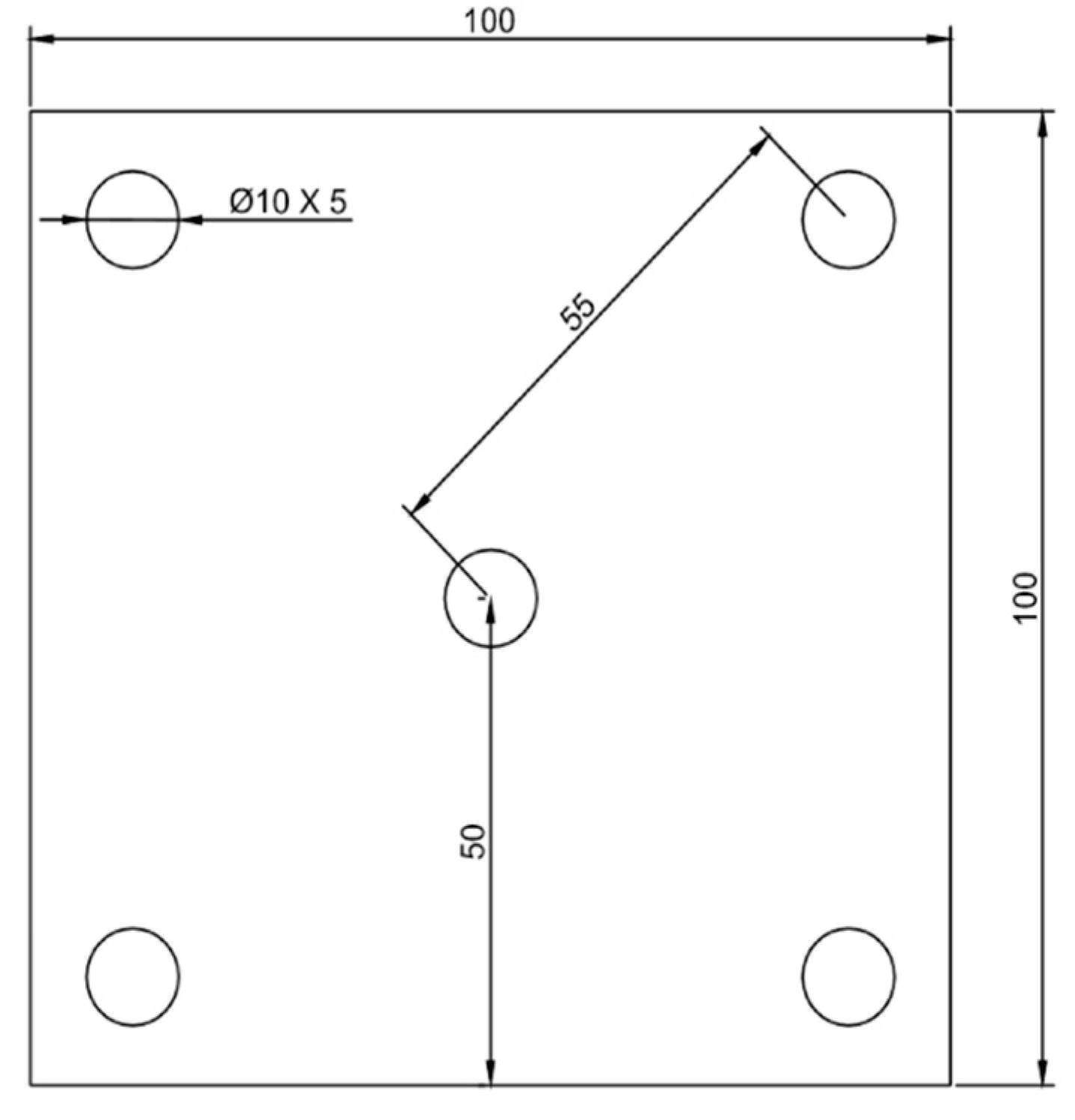
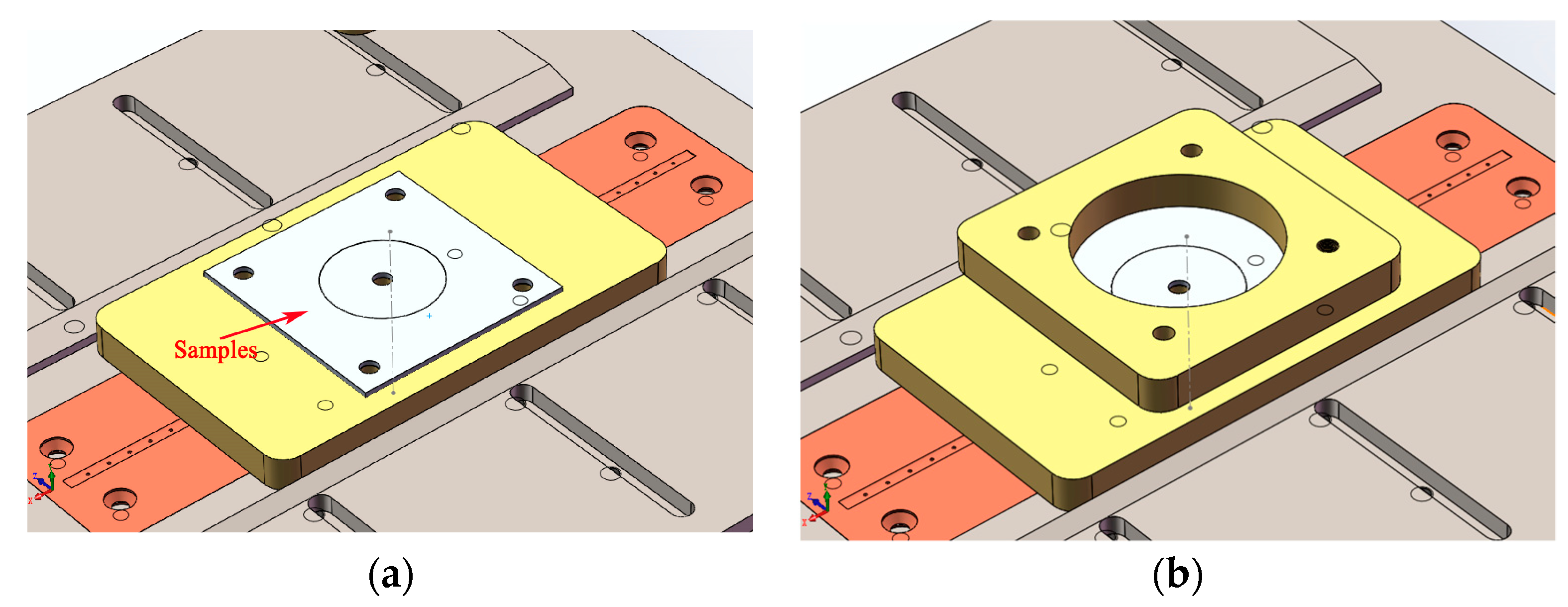
2.2. Circular-Patch Welding Test
2.3. Microstructure Observation and Simulation
2.4. Determination of the Weld Metal’s Composition
3. Results and Discussion
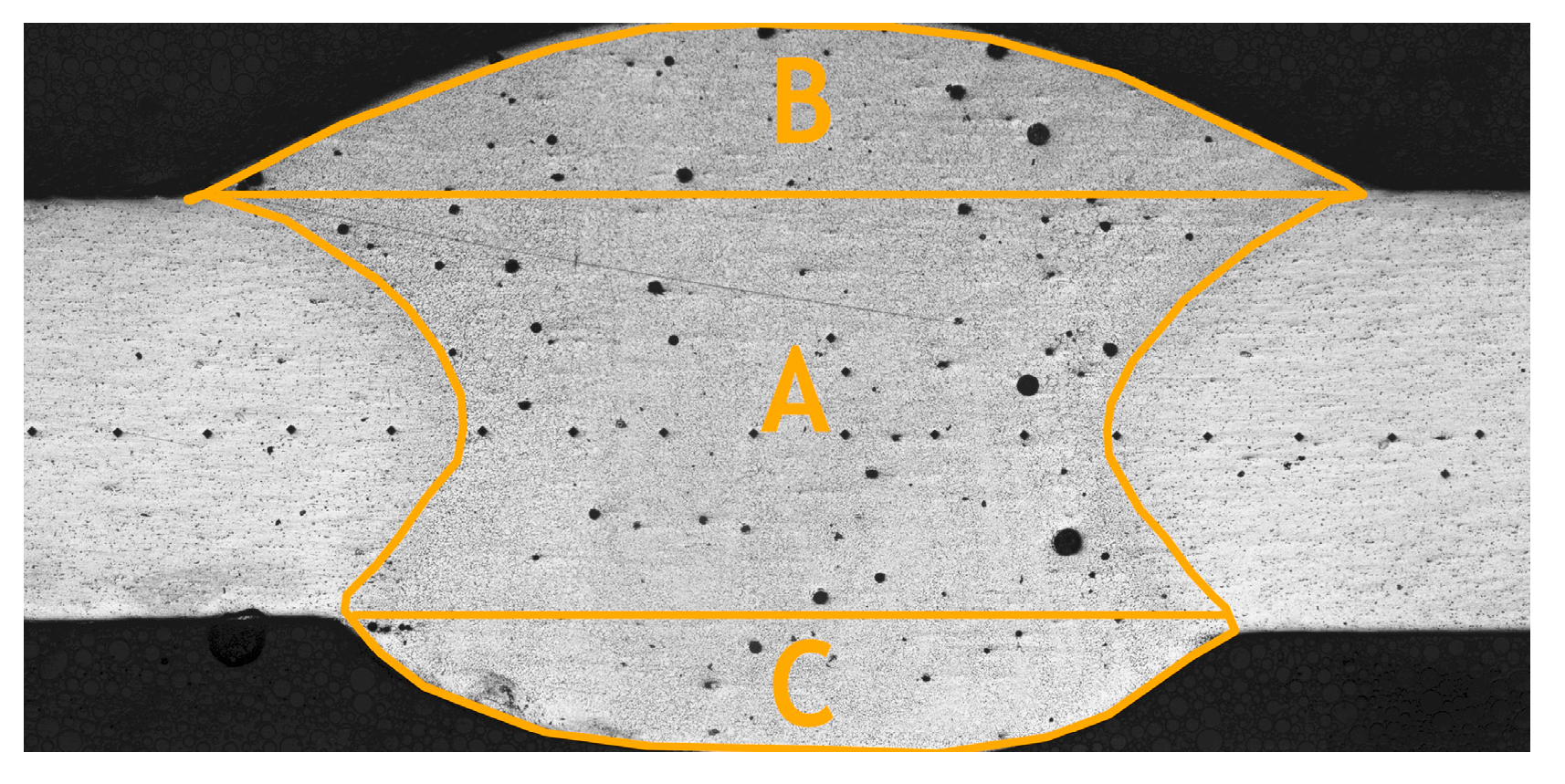
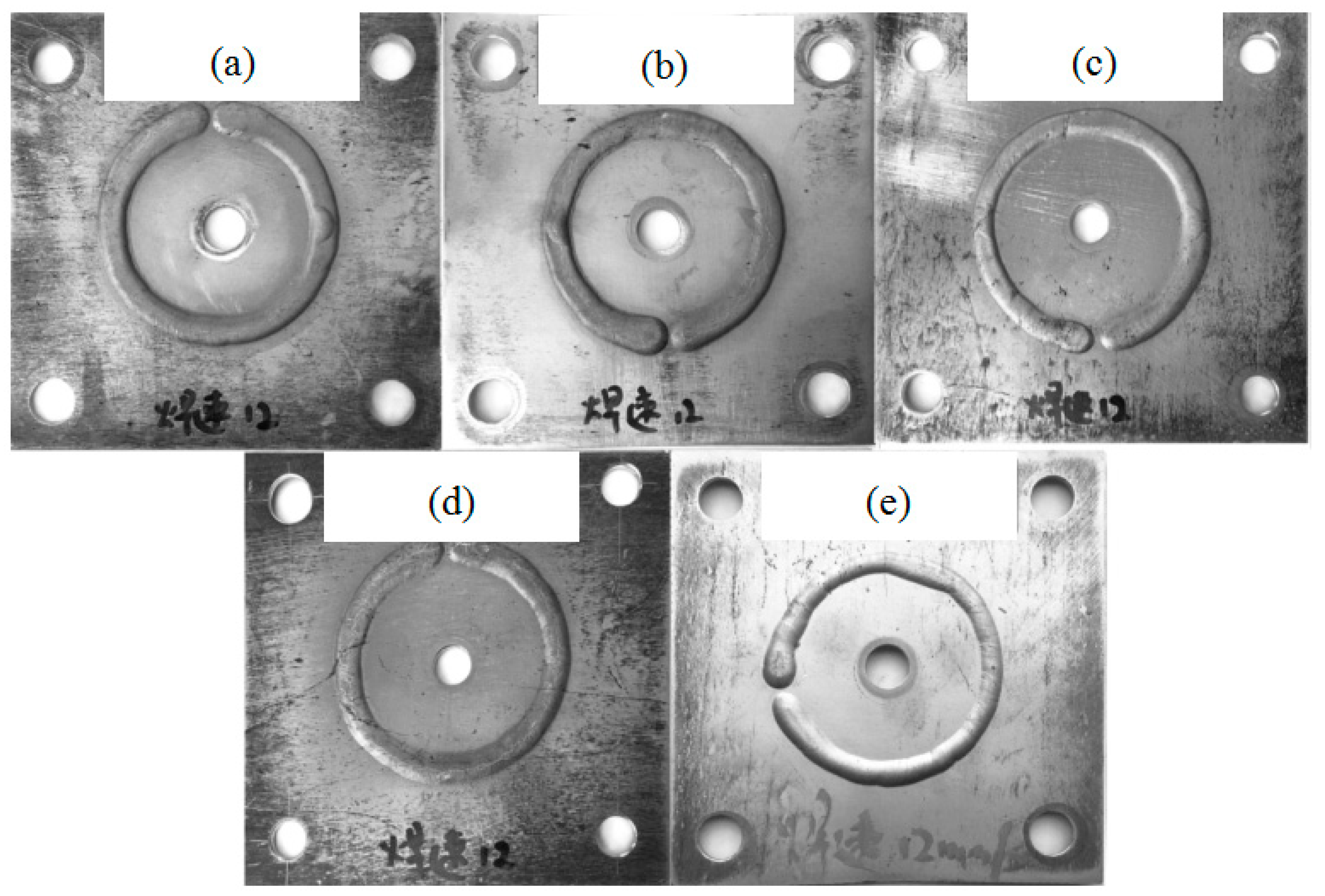
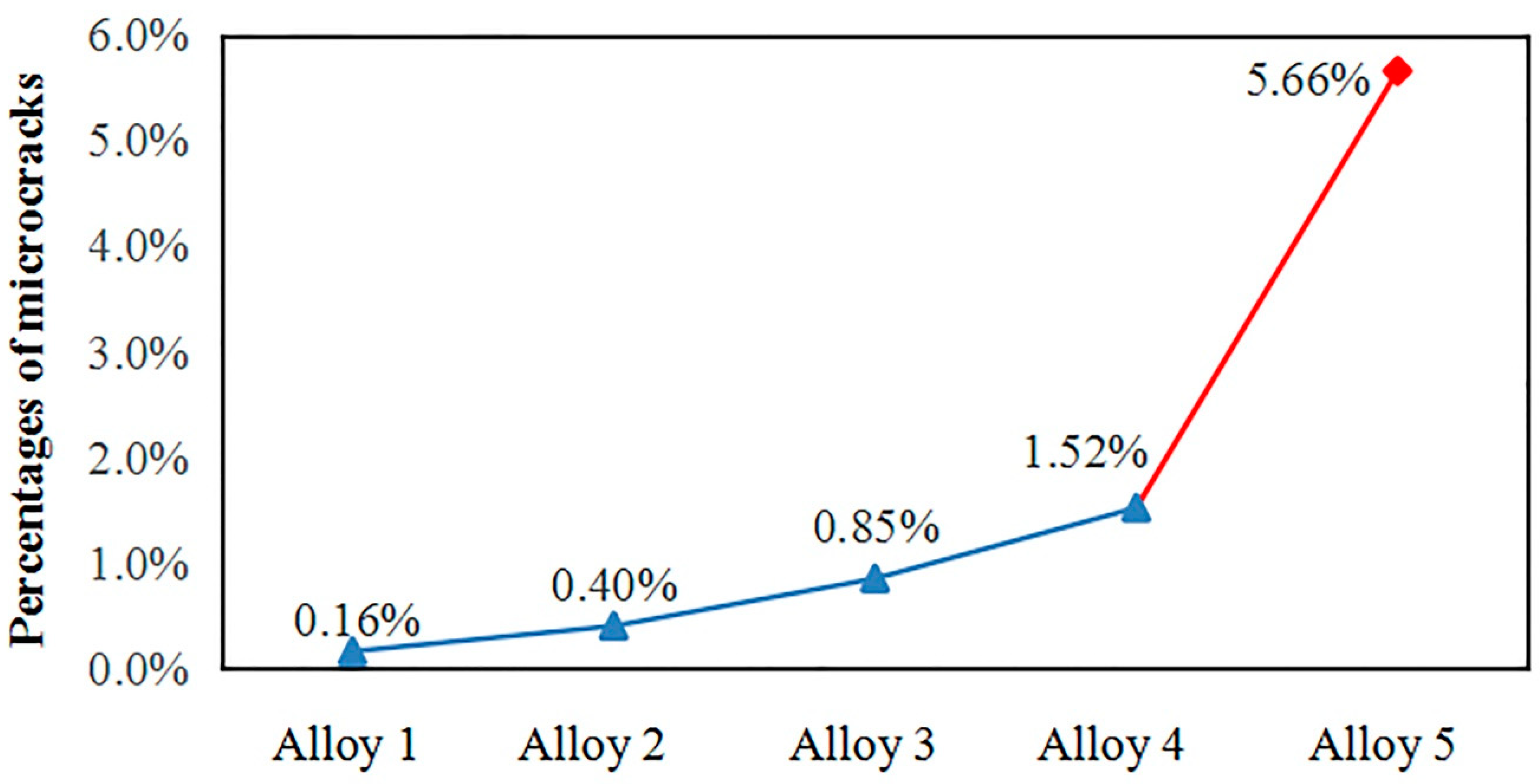
3.1. Circular-Patch Welding Test
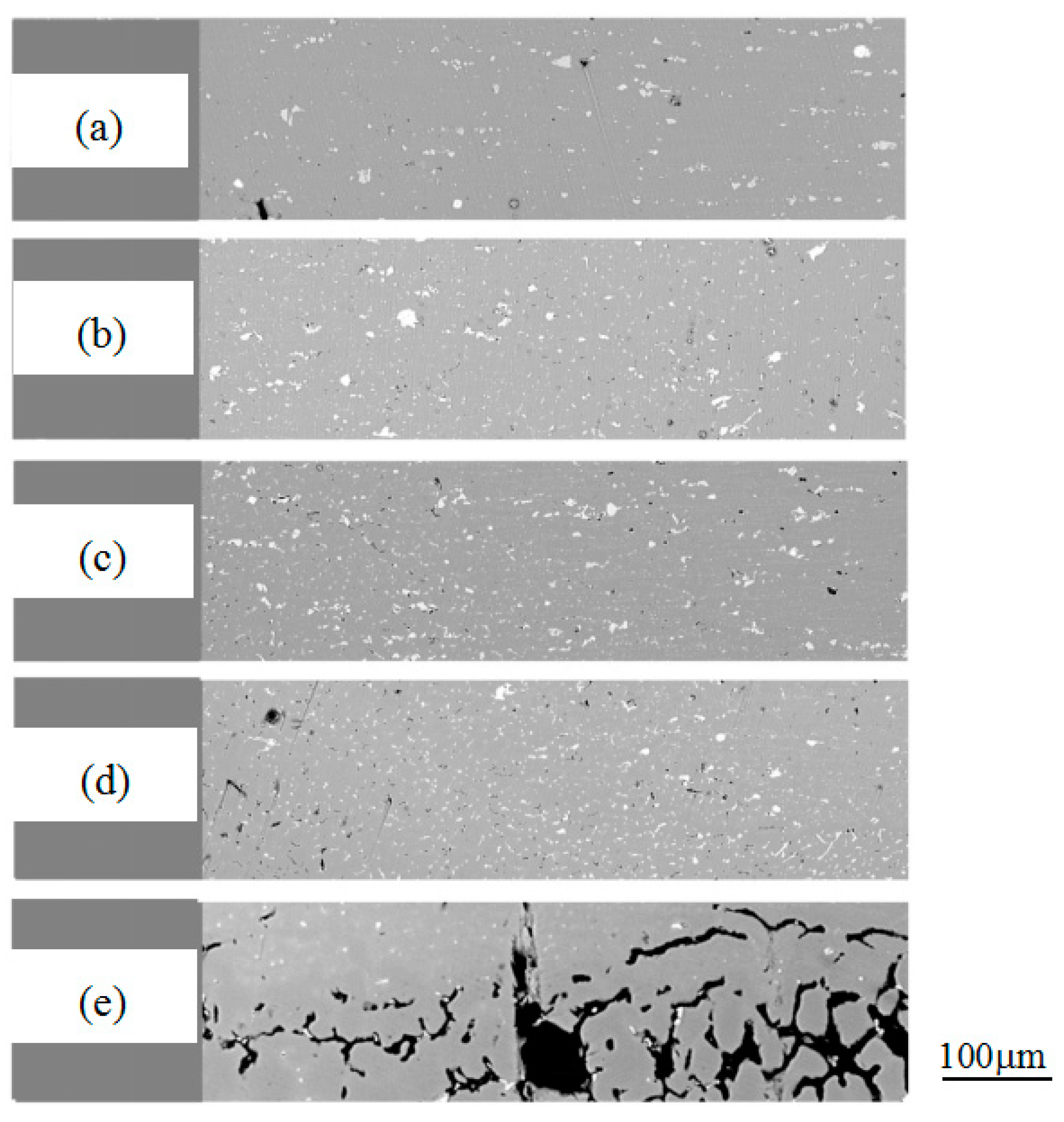
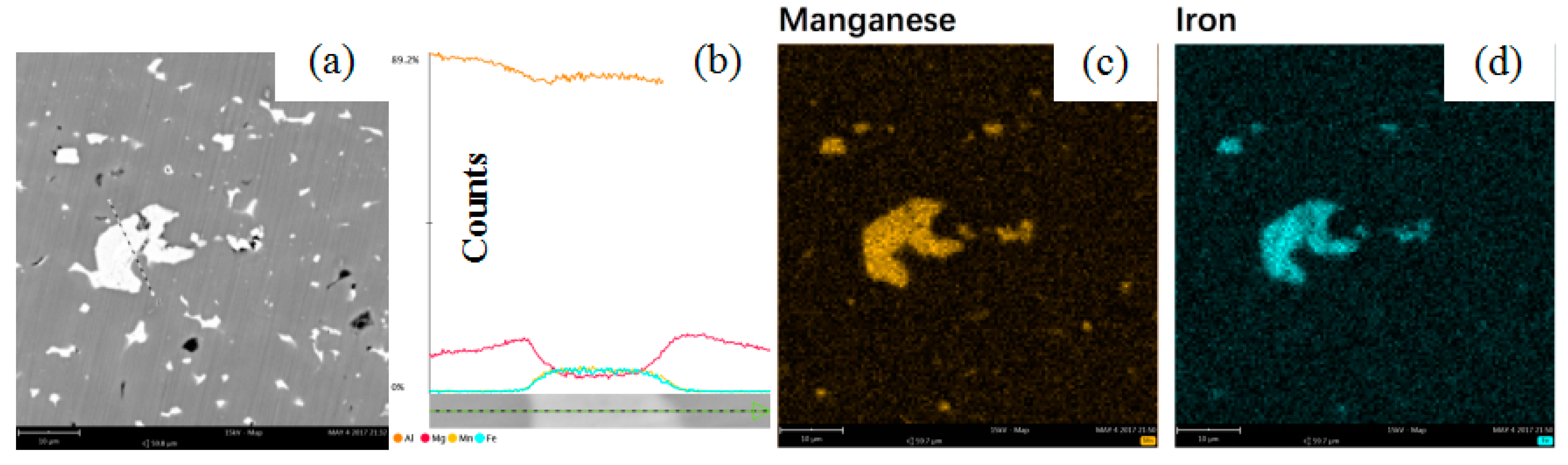
3.2. Microstructure Observation
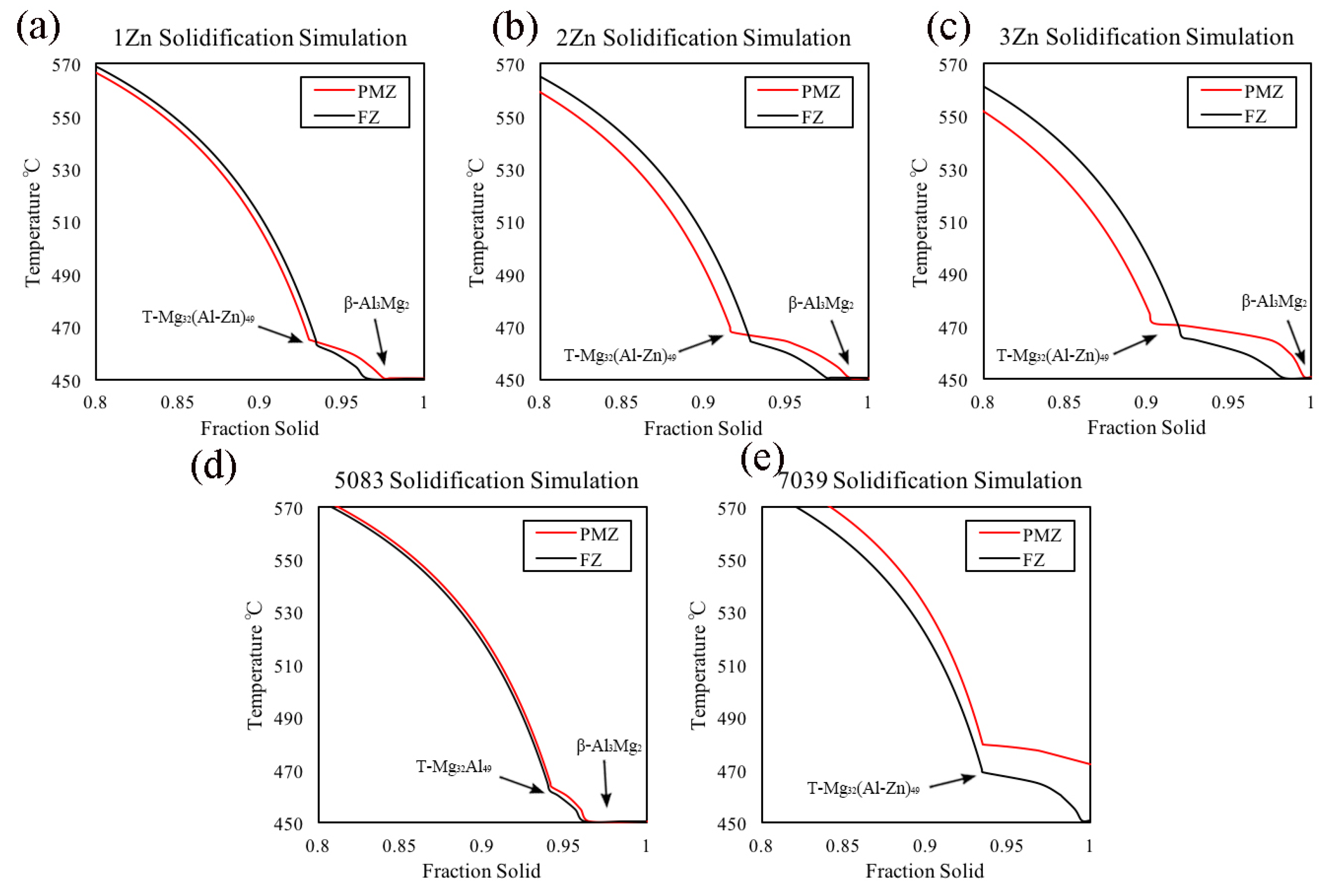
3.3. Non-Equilibrium Simulation during Solidification
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The liquation cracking susceptibility of this new Al-Mg-Zn alloy system with a Zn/Mg ratio below 1.0 is lower than traditional 7××× series alloys with a Zn/Mg ratio above 1.0. Only micro-cracks exist in the novel Al-Mg-Zn alloy system.
- (2)
- The main reason for the suppression of liquation cracking tendency compared with 7××× series alloys is that this novel Al-Mg-Zn alloy system will result in a smaller difference between the fraction solids of FZ and PMZ during the terminal solidification stage, thus leading to a narrower crack healing disparity between these two areas. The PMZ in these alloys has enough liquid to heal micro-cracks caused by concentrating stresses.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mondolfo, L.F. Aluminum Alloys: Structure and Properties; Butterworths: London, UK, 1976; pp. 651–657. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, S. Welding Metallurgy, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, P.; Vazque, L.; Ruiz, N.; Rodriguez, P.; Magana, A.; Niklas, A.; Santos, F. Comparison of hot cracking susceptibility of TIG and laser beam welded alloy 718 by varestraint testing. Metals 2019, 9, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yan, B. Effects of cerium on weld solidification crack sensitivity of 441 ferritic stainless steel. Metals 2019, 3, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, G.; Gao, H.; Amirthalingam, M.; Hermans, M. Study of solidification cracking susceptibility during laser welding in an advanced high strength automotive steel. Metals 2018, 8, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.C.; Chen, T.C.; Shiue, R.K.; Tsay, L.W. Liquation cracking in the heat-affected zone of IN738 superalloy weld. Metals 2018, 8, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Chen, J.T.; Shiue, R.K.; Tsay, L.W. The evolution of cast microstructures on the HAZ liquation cracking of Mar-M004 weld. Metals 2018, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kou, S. Crack susceptibility of binary aluminum alloys during solidification. Acta Mater. 2016, 110, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S. A simple index for predicting the susceptibility to solidification cracking. Weld. J. 2015, 94, 374–388. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Cao, G.; Kou, S. Liquation cracking in partial penetration aluminium welds: Assessing tendencies to liquate, crack and backfill. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2013, 9, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Kou, S. Predicting and reducing liquation-cracking susceptibility based on temperature vs. fraction solid. Weld. J. 2006, 85, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, S. Solidification and liquation cracking issues in welding. JOM 2003, 55, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhuang, L.; Zhang, J. Improved age-hardening response and altered precipitation behavior of Al-5.2Mg-0.45Cu-2.0Zn (wt%) alloy with pre-aging treatment. J. Alloy Compd. 2017, 691, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Zhang, D.; He, Z.; Zhuang, L.; Zhang, J. Enhanced and accelerated age hardening response of Al-5.2Mg-0.45Cu (wt%) alloy with Zn addition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 666, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Ma, Q.; Zhuang, L.; Zhang, J. Effects of Cu addition on the precipitation hardening response and intergranular corrosion of Al-5.2Mg-2.0Zn (wt.%) alloy. Mater. Charact. 2016, 122, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Liu, P.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhuang, L. Precipitation hardening behavior and microstructure evolution of Al–5.1Mg–0.15Cu alloy with 3.0Zn (wt%) addition. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 3846–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Zhang, D.; Ding, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhuang, L. Solute clustering and precipitation of Al-5.1Mg-0.15Cu-xZn alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 759, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Zhang, D.; Cui, H.; Zhuang, L.; Zhang, J. Mechanical properties, intergranular corrosion behavior and microstructure of Zn modified Al–Mg alloys. J. Alloy Compd. 2014, 617, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Kou, S. Liquation Cracking in Full-Penetration Al-Mg-Si Welds. Weld. J. 2004, 83, 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Kou, S. Liquation Cracking in Full-penetration Al-Cu Welds. Weld. J. 2004, 84, 50–68. [Google Scholar]


| Alloy | Symbol | Mg | Zn | Zn/Mg | Mn | Cu | Cr | Ti | Zr | Fe | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base Alloys | Alloy1 | 5.0 | 0 | 0 | 0.80 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.15 |
| Alloy2 | 5.0 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.80 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.15 | |
| Alloy3 | 5.0 | 2.0 | 0.4 | 0.80 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.15 | |
| Alloy4 | 5.0 | 3.0 | 0.6 | 0.80 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.15 | |
| Alloy5 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 1.3 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 0.2 | 0.07 | - | 0.15 | 0.15 | |
| Filler Metal | 5556 | 5.1 | 0.25 | - | 0.75 | 0.1 | 0.13 | 0.13 | - | 0.4 | 0.25 |
| Polarity | DCEP (Electrode-Positive Polar) |
|---|---|
| Current | 95 A |
| Voltage | 13.3 V |
| Arc holding time | 1.0 s |
| Feeding speed | 6.1 m/min |
| Welding speed | 12 mm/s |
| Shielding gas | Argon |
| Gas flow | 17 L/min |
| Distance from workpiece | 5 mm |
| Simulated Zone | Alloy | Mg | Zn | Cu | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMZ | Alloy 1 | 5.0 | 0 | 0.15 | Bal. |
| Alloy 2 | 5.0 | 1.0 | 0.15 | ||
| Alloy 3 | 5.0 | 2.0 | 0.15 | ||
| Alloy 4 | 5.0 | 3.0 | 0.15 | ||
| Alloy 5 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 0.05 | ||
| FZ (50% delusional ratio) | Alloy 1 | 5.05 | 0.125 | 0.125 | Bal. |
| Alloy 2 | 5.05 | 0.625 | 0.125 | ||
| Alloy 3 | 5.05 | 1.125 | 0.125 | ||
| Alloy 4 | 5.05 | 1.625 | 0.125 | ||
| Alloy 5 | 4.05 | 2.125 | 0.075 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, D.; Zhao, X.; Pan, Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhuang, L. Liquation Cracking Tendency of Novel Al-Mg-Zn Alloys with a Zn/Mg Ratio below 1.0 during Fusion Welding. Metals 2020, 10, 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020222
Zhang D, Zhao X, Pan Y, Li H, Zhou L, Zhang J, Zhuang L. Liquation Cracking Tendency of Novel Al-Mg-Zn Alloys with a Zn/Mg Ratio below 1.0 during Fusion Welding. Metals. 2020; 10(2):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020222
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Di, Xin Zhao, Yanlin Pan, Hongxiang Li, Li Zhou, Jishan Zhang, and Linzhong Zhuang. 2020. "Liquation Cracking Tendency of Novel Al-Mg-Zn Alloys with a Zn/Mg Ratio below 1.0 during Fusion Welding" Metals 10, no. 2: 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020222
APA StyleZhang, D., Zhao, X., Pan, Y., Li, H., Zhou, L., Zhang, J., & Zhuang, L. (2020). Liquation Cracking Tendency of Novel Al-Mg-Zn Alloys with a Zn/Mg Ratio below 1.0 during Fusion Welding. Metals, 10(2), 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020222






