Effects of Microstructure, Mechanical and Physical Properties on Machinability of Graphite Cast Irons
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Procedures
2.1. Tractor front Bracket Castings
2.2. Performance Testing and Microstructure Observations
2.2.1. Mechanical and Physical Properties and Microstructure
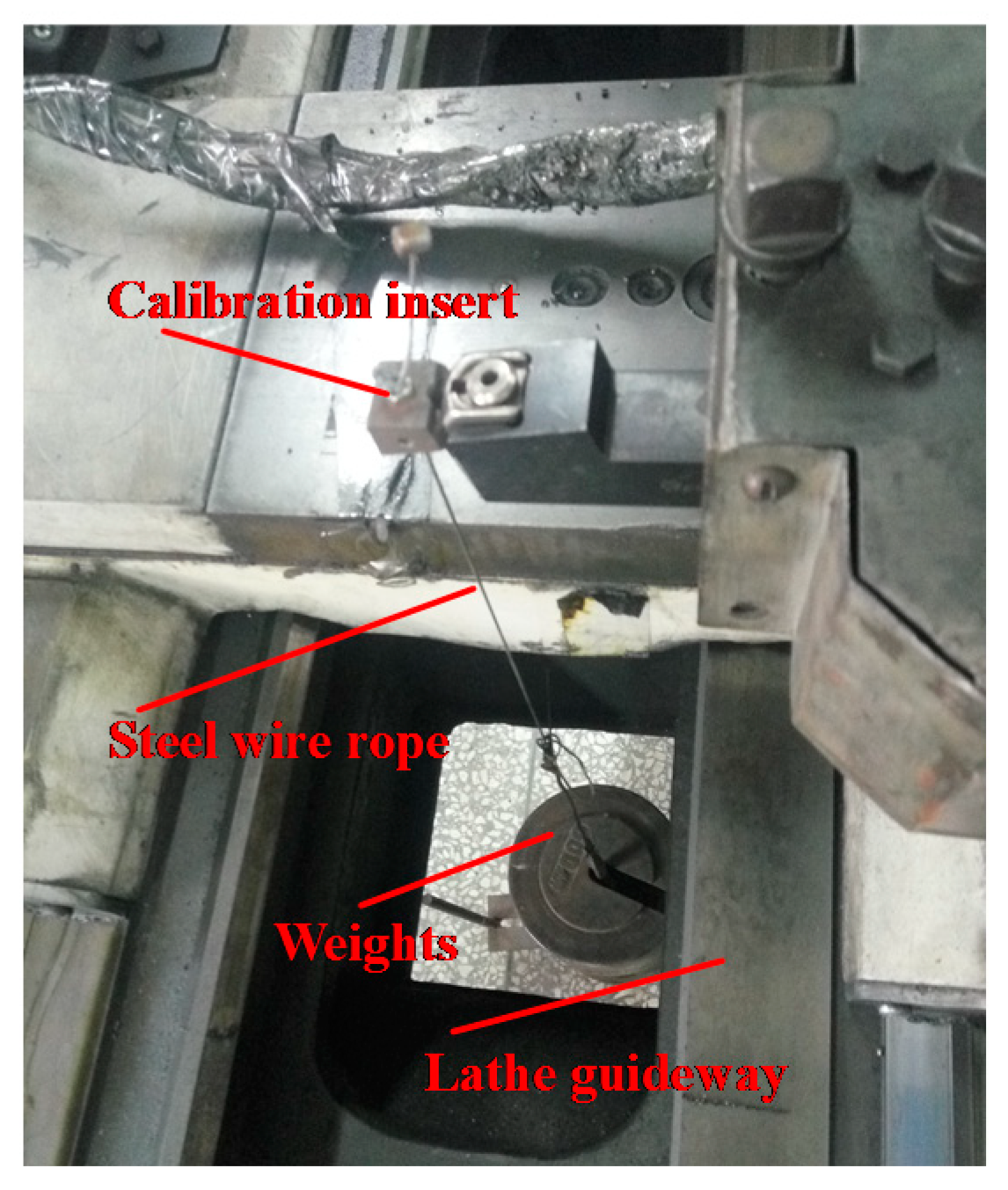
2.2.2. Turning Tests
2.2.3. Drilling Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure Effects on Mechanical Properties
3.2. Microstructure and Physical Properties Effects on Turning and Drilling Ability
3.2.1. Chips Shape
3.2.2. The Roughness of Turning Bar Surface and Drilling Hole Internal Surface
3.2.3. Insert and Bit Temperature during Turning and Drilling
3.2.4. Turning and Drilling Load
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ezugwu, E.O.; Wang, Z.M. Titanium alloys and their machinability—A review. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 1997, 68, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günay, M.; Korkut, I.; Aslan, E.; Seker, U. Experimental investigation of the effect of cutting tool rake angle on main cutting force. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2005, 166, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayyar, V.; Kaminski, J.; Kinnander, A.; Nyborg, L. An experimental investigation of machinability of graphitic cast iron grades; flake, compacted and spheroidal graphite iron in continuous machining operations. Procedia Cirp 2012, 1, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seker, U.; Hasirci, H. Evaluation of machinability of austempered ductile irons in terms of cutting forces and surface quality. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2006, 173, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.Z.; Li, Z.L.; Xiong, Y.; Li, F.J.; Ren, F.Z.; Volinsky, A.A. Effect of microstructure and mechanical properties on cutting force of different cast irons with similar tensile strength. China Foundry 2019, 16, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tooptong, S.; Park, K.H.; Kwon, P. A comparative investigation on flank wear when turning three cast irons. Tribol. Int. 2018, 120, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, M.; Ortner, H.M.; Flege, S.; Reuter, U.; Ensinger, W. Analytical investigations concerning the wear behaviour of cutting tools used for the machining of compacted graphite iron and grey cast iron. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2008, 26, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, J.A.G.; Sales, W.F.; Guesser, W.L.; Machado, Á.R. Machinability of rectangular bars of nodular cast iron produced by continuous casting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2018, 98, 2505–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, L.R.M.; Diniz, A.E. Effect of the gray cast iron microstructure on milling tool life and cutting force. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. 2013, 35, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, M.; Rohollah, G.; Carsten, B. Effects of workpiece microstructure, mechanical properties and machining conditions on tool wear when milling compacted graphite iron. Wear 2018, 410, 190–201. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, M.B.; Naves, V.T.G.; De Melo, J.D.B.; De Andrade, C.L.F.; Guesser, W.L. Analysis of wear of cemented carbide cutting tools during milling operation of gray iron and compacted graphite iron. Wear 2011, 271, 2426–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.Z.; Li, F.J.; Liu, W.M.; Ma, Z.H.; Tian, B.H. Effect of inoculating addition on machinability of gray cast Iron. J. Rare Earth 2009, 27, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, A.; El Mansori, M. Drilling performance of green austempered ductile iron (ADI) grade produced by novel manufacturing technology. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2012, 59, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, J.; Rafal, K.; Tomasz, T. Operational tests of wear dynamics of drills made of low-alloy high-speed Hs2-5-1 steel. Eksploat. Niezawodn. 2016, 18, 271–277. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wu, W.W. Investigation of drilling machinability of compacted graphite iron under dry and minimum quantity lubrication. Metals 2019, 9, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Lacalle, L.N.L.; Lamikiz, A.; Sanchez, J.A.; de Bustos, I.F. Simultaneous measurement of forces and machine tool position for diagnostic of machining tests. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2005, 54, 2329–2335. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, F.Z.; Zhang, D.W.; Volinsky, A.A. Experimental investigation of the cutting force measurements in machinability evaluations of metals. J. Test. Eval. 2014, 42, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar]
- Hernando, J.C.; Elfsberg, J.; Ghassemali, E.; Dahle, A.K.; Diószegi, A. The effect of coarsening of primary austenite on the ultimate tensile strength of hypoeutectic compacted graphite Fe-C-Si alloys. Scr. Mater. 2019, 168, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhao, Y.C.; Chen, J.P. Relationship between cutting machining properties of graphite-containing cast irons and their structures. Mod. Cast Iron 2005, 25, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Ju, J.; Fu, H.G.; Ma, S.Q.; Lin, J.; Lei, Y.P. Effect of chromium content on microstructure, hardness, and wear resistance of as-cast Fe-Cr-B alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 6428–6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchely, M.F.; Gutierrez, J.C.; Leon, L.M.; Toro, A. The effect of microstructure on abrasive wear of hardfacing alloys. Wear 2005, 259, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. Effects of raw material proportioning on pearlitic lamellar spacing and hardness of ductile iron. Foundry 2011, 60, 397–400. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Song, R.B.; Li, Y.P.; Yang, F.Q.; Wu, C.J.; Wang, Z.Y. Influence of nodularizing and inoculation treatment on the microstructure characteristic and mechanical property of lower bainite cast iron. J. Mech. Eng. 2015, 51, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carazo, F.D.; Giusti, S.M.; Boccardo, A.D.; Godoy, L.A. Effective properties of nodular cast-iron: A multi-scale computational approach. Comp. Mater. Sci. 2014, 82, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.Z.; Cui, L.K.; Shi, W.P.; Xiong, Y.; Wei, S.Z. Drilling-ability evaluation for grey cast iron and ductile iron front brackets. Acta Metrol. Sin. 2018, 39, 842–846. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Barrero, S.; Fernández-Larrinoa, J.; Azkona, I.; López de Lacalle, L.N.; Polvorosa, R. Enhanced performance of nanostructured coatings for drilling by droplet elimination. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 31, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Material | C | Si | Mn | Cr | S | P | Mg | Rare Earths | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HT250 | Design | 3.15–3.3 | 1.6–1.8 | 0.8–1 | 0.2–0.3 | ≤0.12 | ≤0.10 | - | - |
| Actual | 3.26 | 1.80 | 0.83 | 0.17 | 0.055 | 0.03 | - | - | |
| QT450 | Design | 3.6–4 | 2.7–3 | ≤0.35 | - | ≤0.035 | ≤0.07 | 0.035–0.055 | 0.02–0.04 |
| Actual | 3.55 | 2.93 | 0.26 | - | 0.018 | 0.031 | 0.055 | 0.02 | |
| Material | Graphite Shape and Content, vol.% | Graphite Length or Diameter, mm | Pearlite Content, vol.% | Tensile Strength, MPa | Brinell Hardness, HB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HT250 | Flake, 100 | 0.12–0.25 | 45–55 | 191 | 163 |
| QT450 | Sphere, 90 | 0.03–0.06 | <5 | 420 | 141 |
| Materials | Turning | Drilling | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth 2 mm | Depth 3 mm | Φ 14.5 mm Bit | Φ 19 mm Bit | |
| HT250 | 34.2 | 40.9 | 20.4 | 50.3 |
| QT450 | 34.6 | 36.4 | 29.6 | 89.5 |
| Material | Insert | Φ 14.5 mm Bit | Φ 19 mm Bit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 1500, | n = 800, | n = 240, | n = 200, | |||
| t = 2 | t = 3 | v = 0.27 | v = 0.5 | v = 0.42 | v = 0.5 | |
| HT250 | 87 | 116 | 98 | 89 | 86 | 92 |
| QT450 | 93 | 114 | 126 | 102 | 105 | 124 |
| Material | 323 K | 423 K | 473 K | 573 K |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HT250 | 49 | 46 | 44 | 41 |
| QT450 | 31 | 33 | 34 | 36 |
| Material | Cutting Depth of 2 mm | Cutting Depth of 3 mm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Deviation | Average | Deviation | |
| HT250 | 964 | 40 | 1415 | 58 |
| QT450 | 882 | 31 | 1192 | 37 |
| Material | Turning | Boring |
|---|---|---|
| v = 30, f = 0.2, t = 1.5 | v = 30, f = 0.3, t = 1.5 | |
| FGI | 615 | 790 |
| CGI | 700 | 920 |
| SGI | — | 940 |
| Material | Measuring Project | Φ 14.5 mm Bit | Φ 19 mm Bit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 1500, v = 0.27 | N = 800, V = 0.5 | n = 240, v = 0.42 | N = 200, V = 0.5 | ||
| HT250 | Relative torque, % | 16 | 7 | 5 | 6 |
| Relative feed force, % | 62 | 59 | — | — | |
| QT450 | Relative torque, % | 15 | 8 | 5 | 6 |
| Relative feed force, % | 63 | 61 | — | — | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, J.; Ren, F.; Li, F.; Cui, L.; Xiong, Y.; Volinsky, A.A. Effects of Microstructure, Mechanical and Physical Properties on Machinability of Graphite Cast Irons. Metals 2020, 10, 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020285
Ren J, Ren F, Li F, Cui L, Xiong Y, Volinsky AA. Effects of Microstructure, Mechanical and Physical Properties on Machinability of Graphite Cast Irons. Metals. 2020; 10(2):285. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020285
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Jiangzhuo, Fengzhang Ren, Fengjun Li, Linkai Cui, Yi Xiong, and Alex A. Volinsky. 2020. "Effects of Microstructure, Mechanical and Physical Properties on Machinability of Graphite Cast Irons" Metals 10, no. 2: 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020285
APA StyleRen, J., Ren, F., Li, F., Cui, L., Xiong, Y., & Volinsky, A. A. (2020). Effects of Microstructure, Mechanical and Physical Properties on Machinability of Graphite Cast Irons. Metals, 10(2), 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10020285







