Electrochemical Migration Inhibition of Tin by Disodium Hydrogen Phosphate in Water Drop Test
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Solution Preparation
2.2. Setup of Water Drop Test With and Without Na2HPO4 and ECM Measurements
2.3. Polarization Curves and Cyclic Voltammetry Measurements
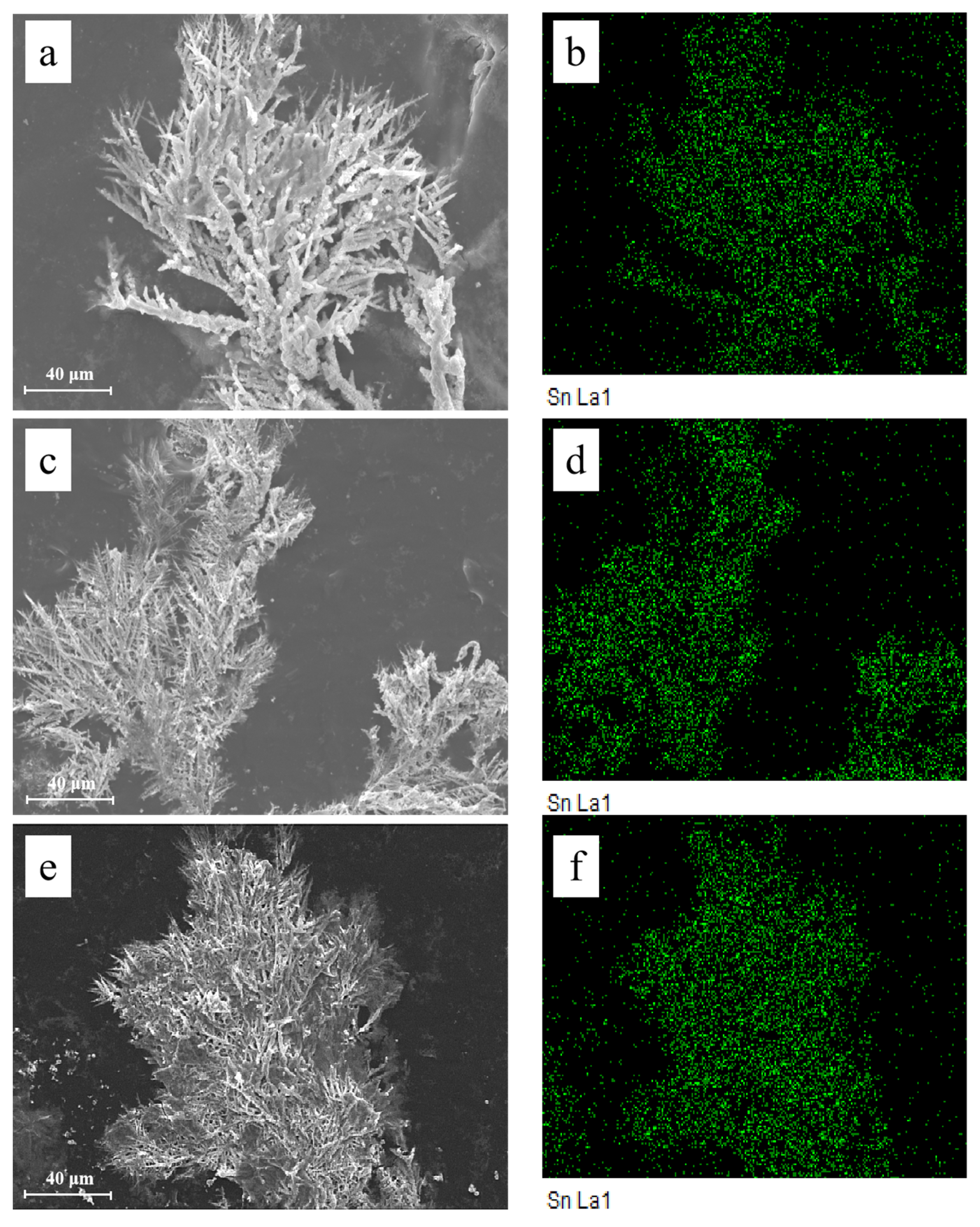
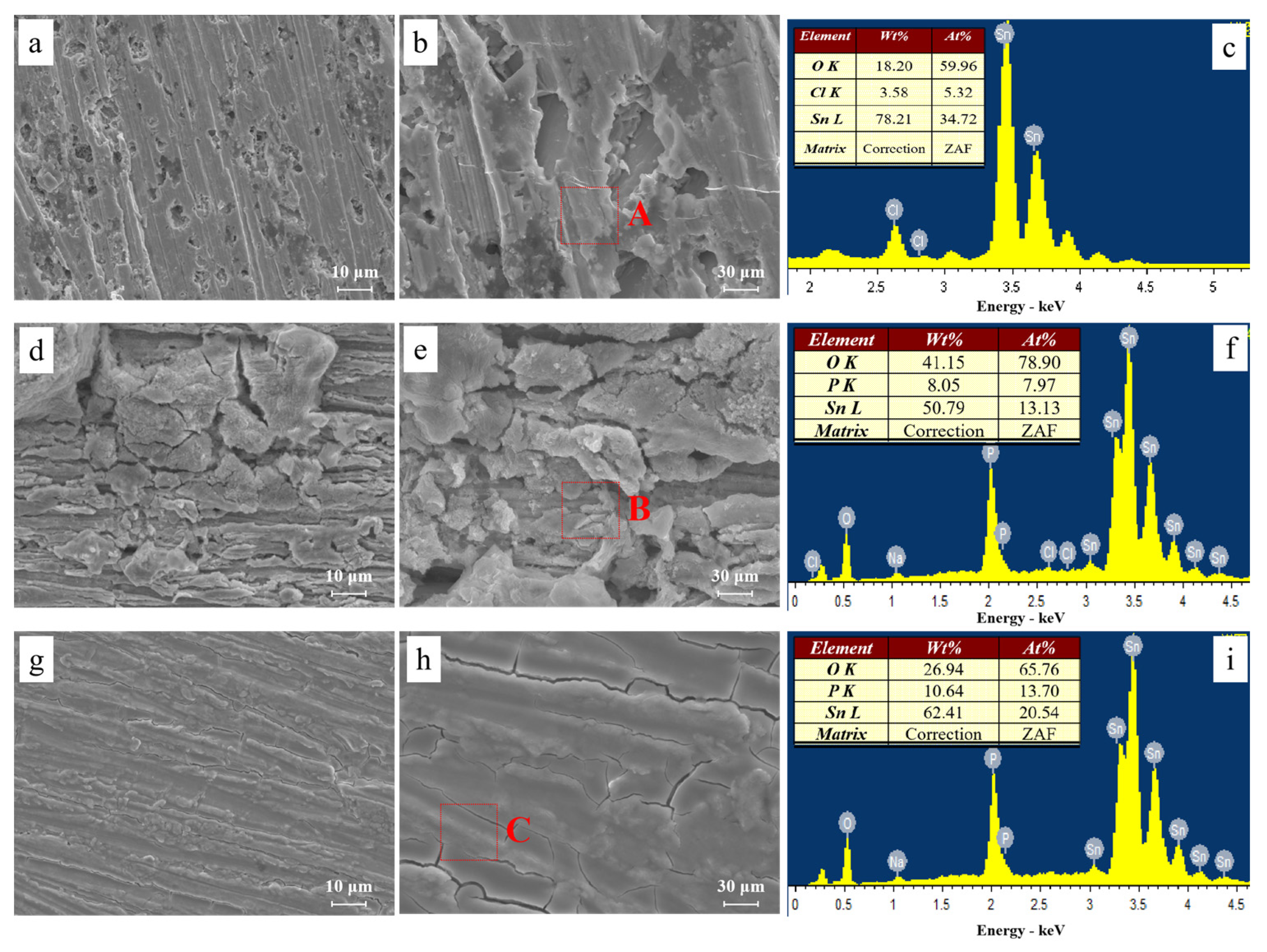
2.4. Surface Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
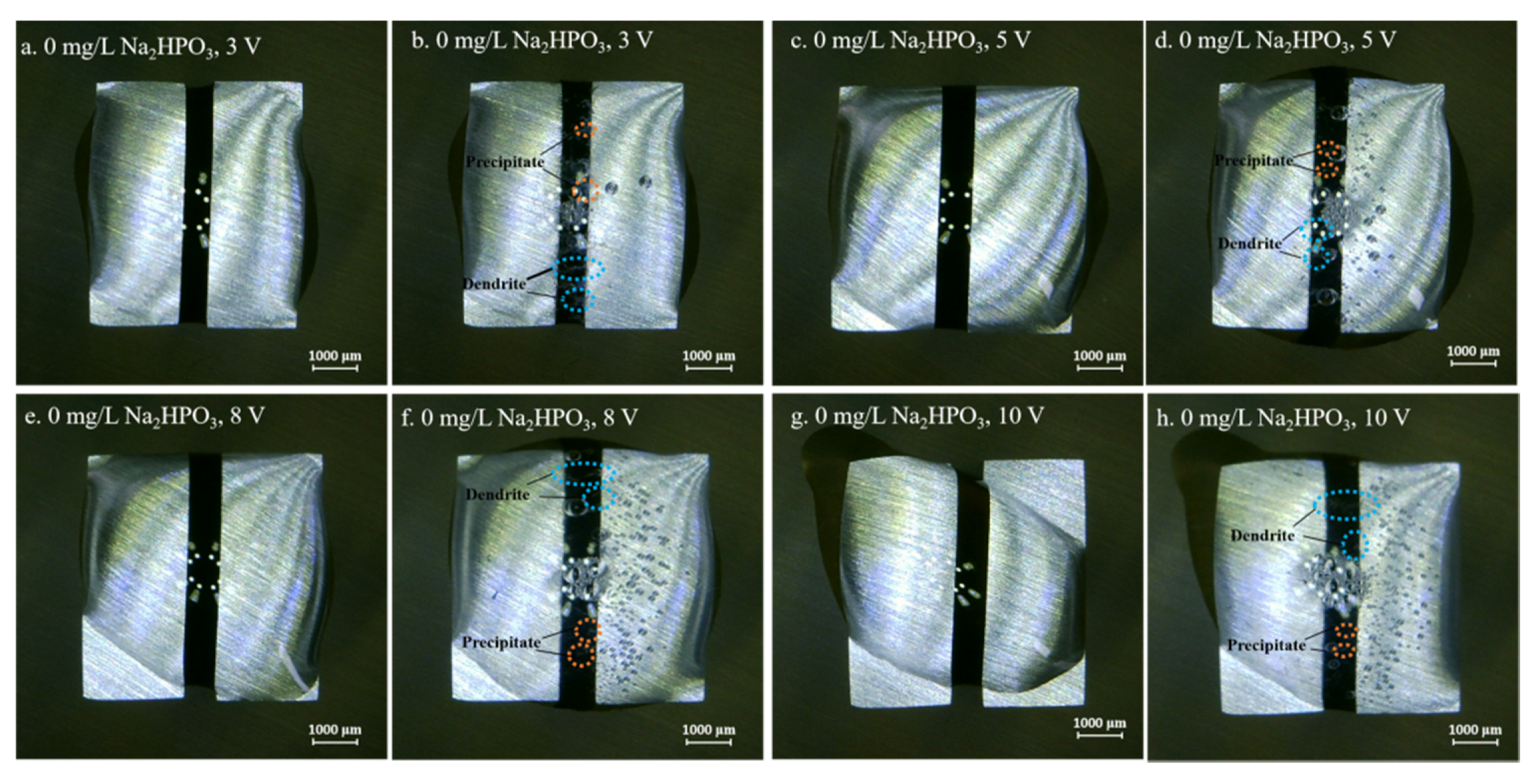
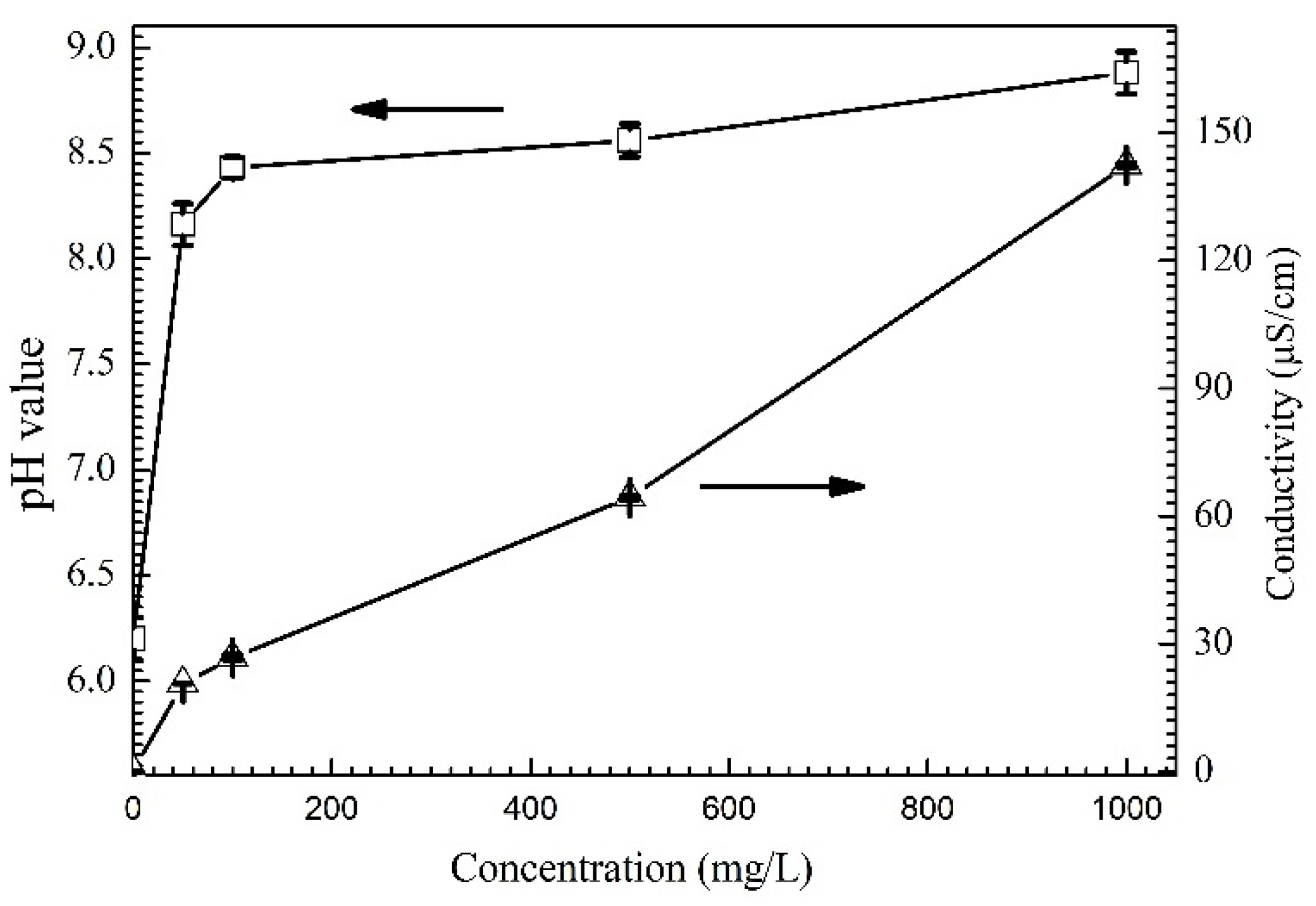
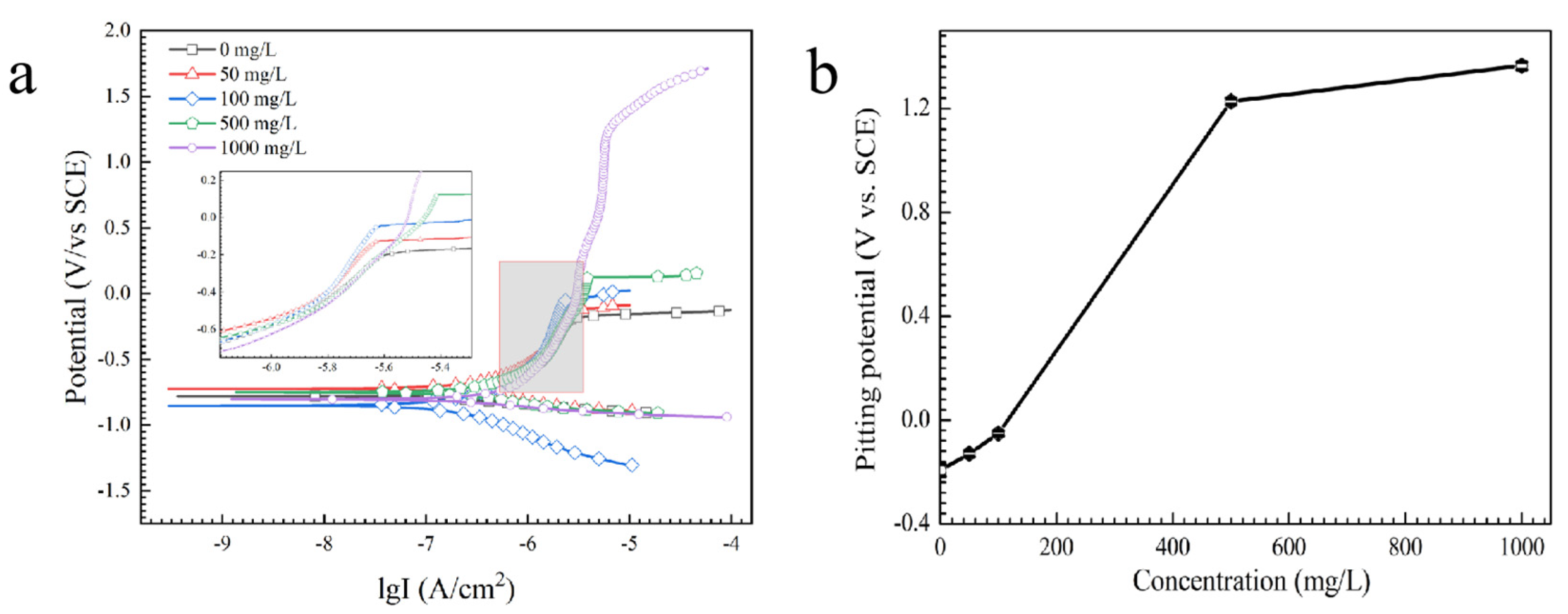
3.1. Effect of the Alert of Solution Chemistry on the Probability of the ECM of Sn
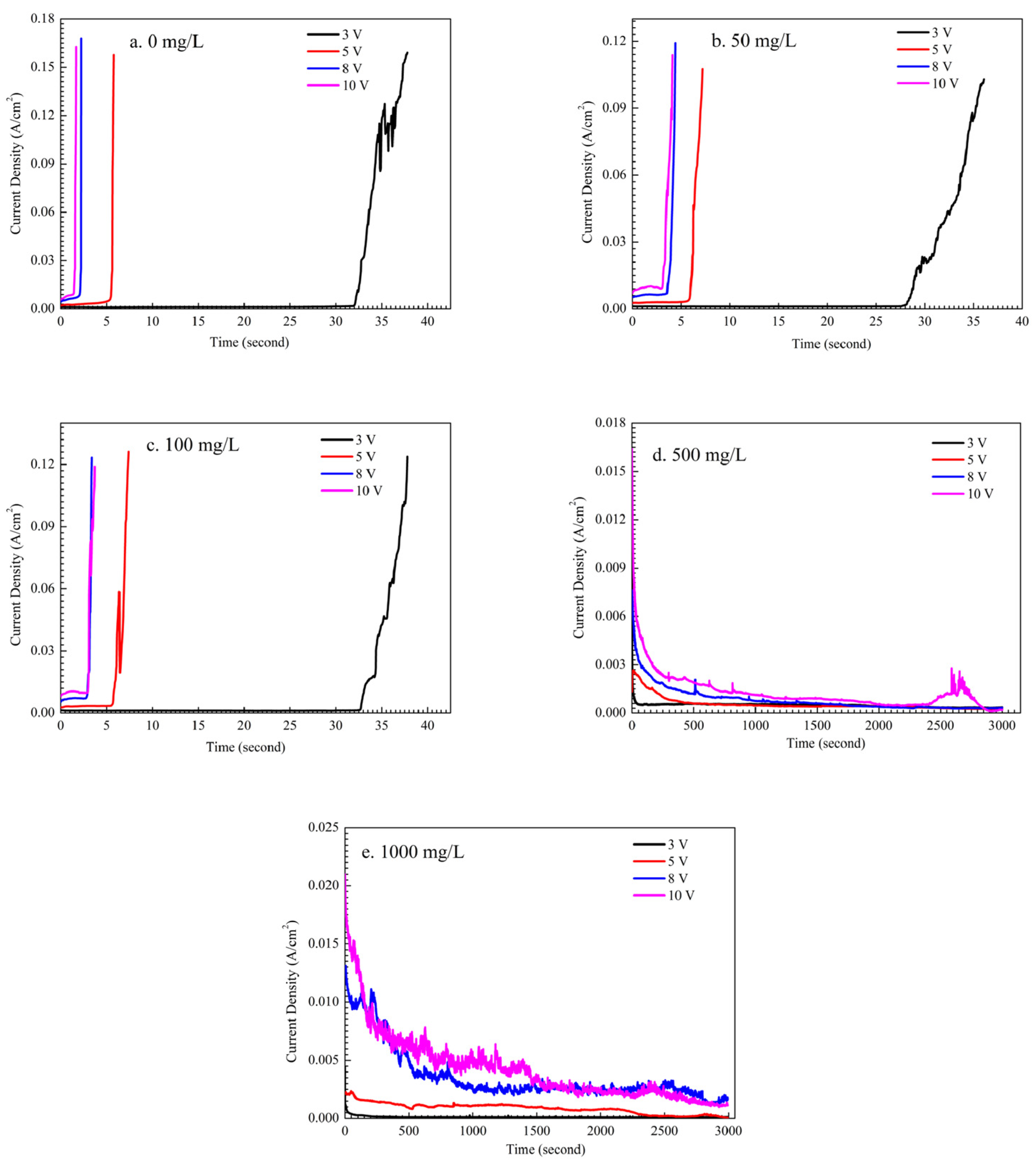
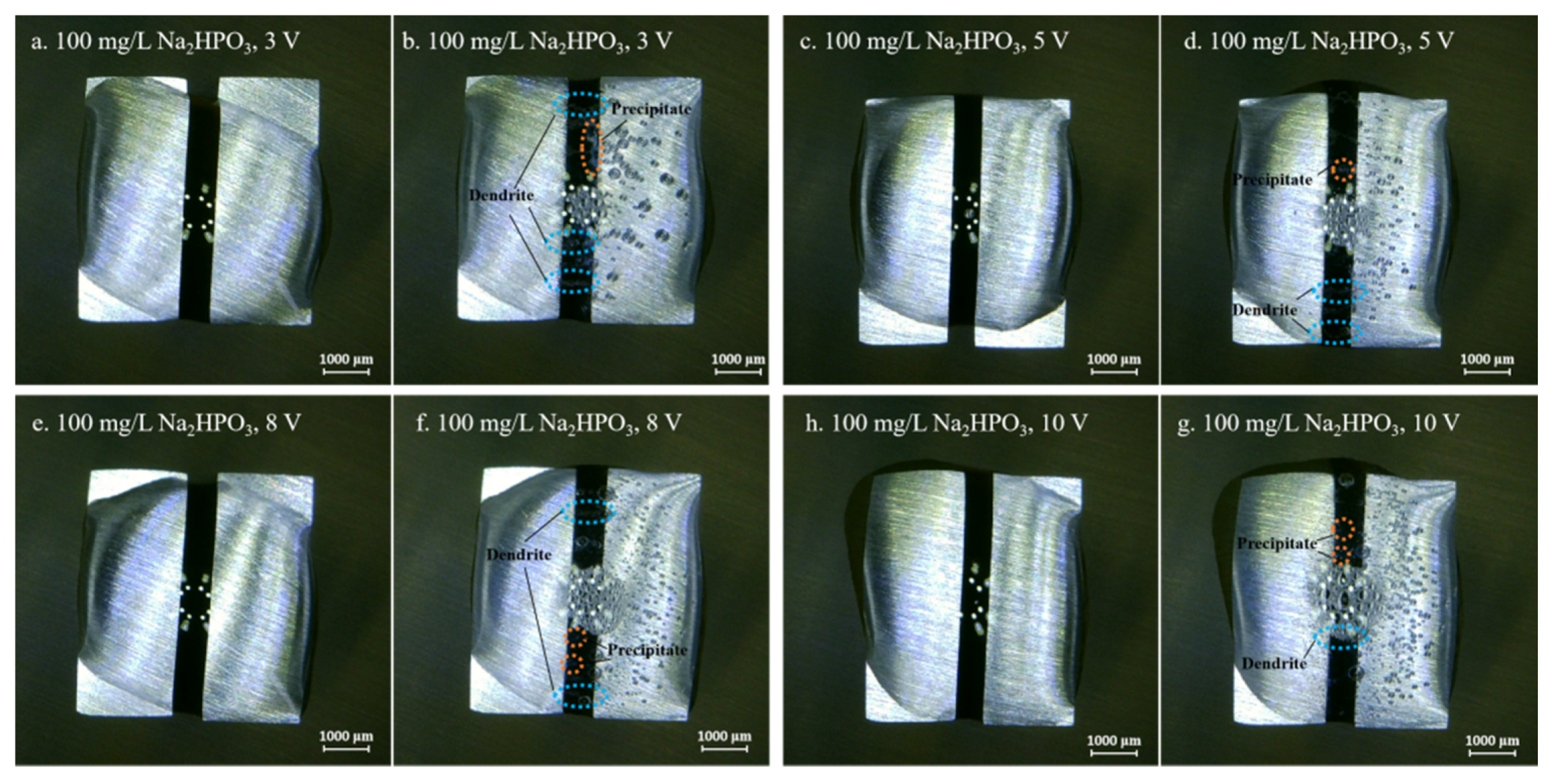
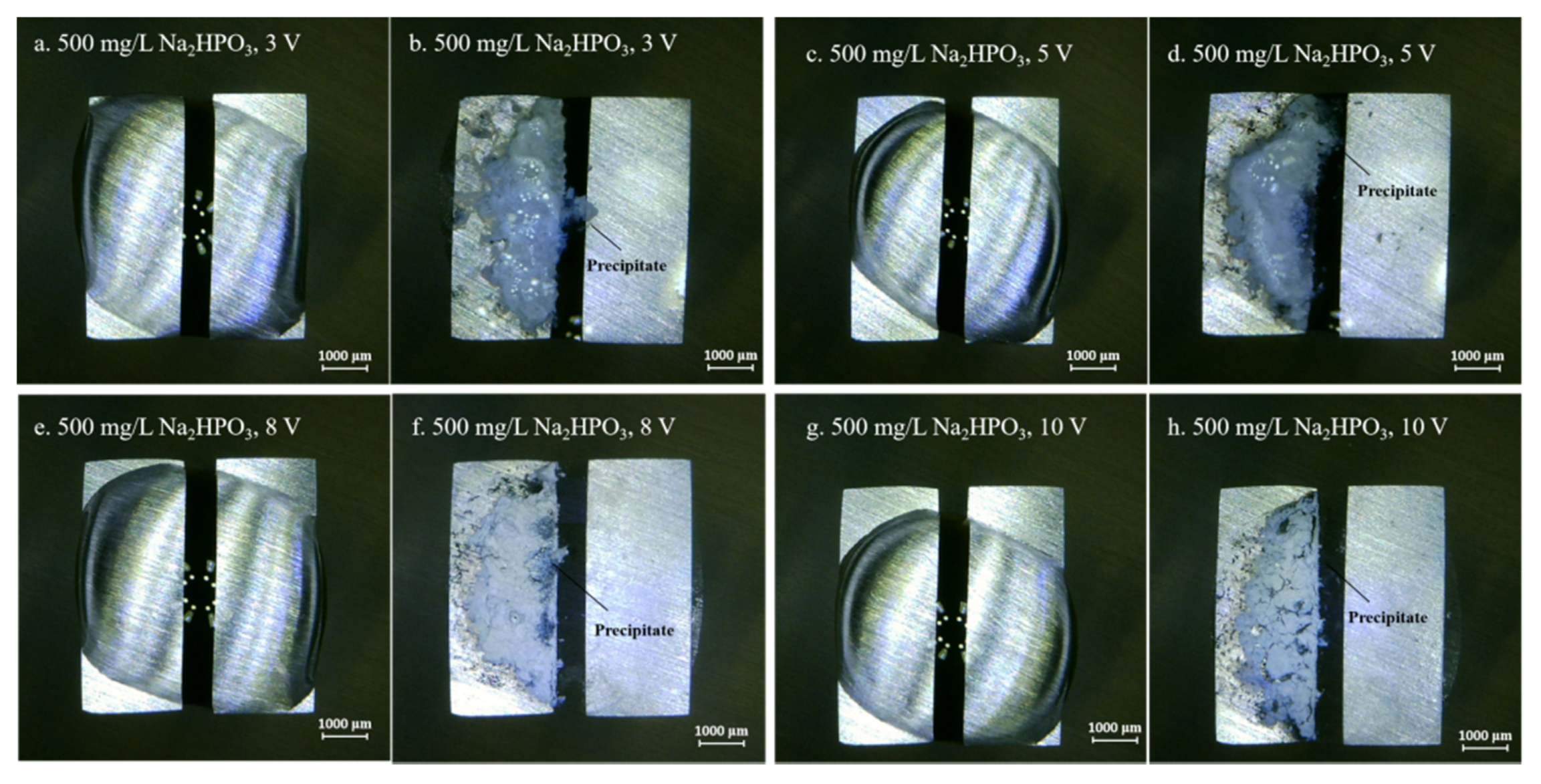
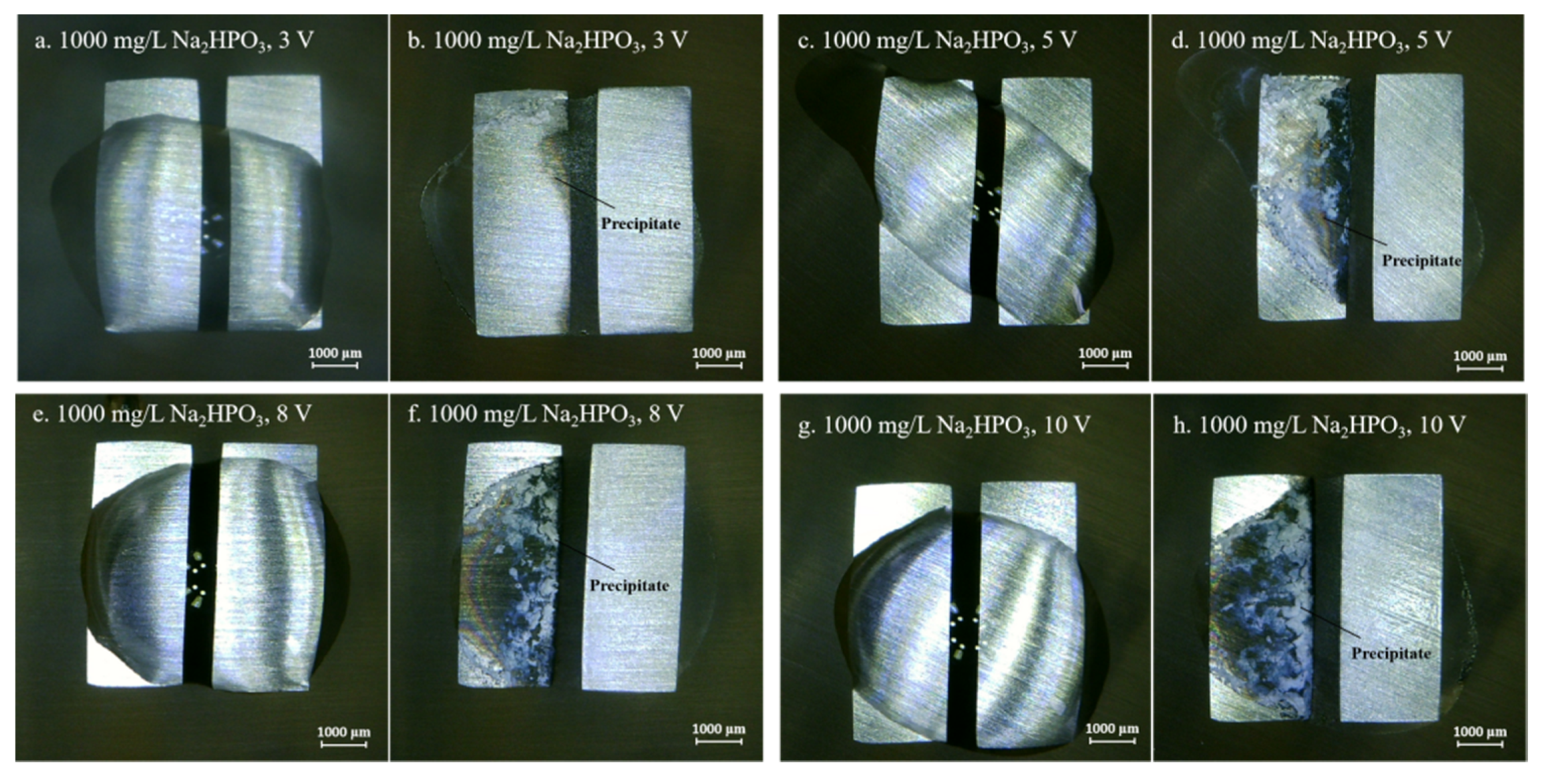
3.2. Effect of Na2HPO4 Concentration on the Probability of the ECM of Sn at Different DC Bias Voltages
3.3. Effect of Applied DC Bias Voltage on the ECM of Tin
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kyeremateng, N.; Brousse, T.; Pech, D. Microsupercapacitors as miniaturized energy-storage components for on-chip electronics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017. 12, 7–15. [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.K.; Kim, H.; Ryu, J.; Hahn, H.; Jang, S.; Joung, J.W. Inkjet printed electronics using copper nanoparticle ink. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2010, 21, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, B.; Cen, H.; Chen, Z.; Guo, X. Corrosion behavior of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu alloy under chlorine-containing thin electrolyte layers. Corros. Sci. 2018, 143, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Ma, H.; Wang, C.; Shang, S.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, H. Electrochemical migration behavior of Sn-based lead-free solder. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 14695–14702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Elshekh, H.; Yu, Z.; Yu, B.; Wang, D.; Kadhim, M.; Chen, Y.; Hou, W.; Sun, B. Effect of crystalline state on conductive filaments forming process in resistive switching memory devices. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Shen, L.; Chen, C.; Zhou, J.; Chen, L. An Arrhenius-type constitutive model to predict the deformation behavior of Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu under different temperature. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 14611–14620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Li, X.; Dong, C.; Ding, K.; Xiao, K. Electrochemical migration, whisker formation, and corrosion behavior of printed circuit board under wet H2S environment. Electrochim. Acta. 2013, 114, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gain, A.; Zhang, L. Effect of Ag nanoparticles on microstructure, damping property and hardness of low melting point eutectic tin-bismuth solder. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 15718–15730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtew, M.; Selvaduray, G. Lead-free solders in microelectronics. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2000, 27, 95–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veleva, L.; Dzib-Pérez, L.; González-Sánchez, J.; Pérez, T.R. Initial stages of indoor atmospheric corrosion of electronics contact metals in humid tropical climate: Tin and nickel. Rev. Metal. Madrid. 2007, 43, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minzari, D.; Jellesen, M.; Moller, P.; Ambat, R. On the electrochemical migration mechanism of tin in electronics. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 3366–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Liao, B.; Chen, Z.; Guo, X. Investigation of electrochemical migration of tin and tin-based lead-free solder alloys under chloride-containing thin electrolyte layers. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 9942–9949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, G.; Guo, X. In situ study the electrochemical migration of tin under unipolar square wave electric field. J. Eectrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, D495–D500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Zhang, G.; Guo, X. The effect of electrolyte layer thickness on electrochemical migration of tin. Corros. Sci. 2015, 96, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.; Xiao, K.; Dong, C.; Zou, S.; Li, X. Effects of mould on electrochemical migration behaviour of immersion silver finished printed circuit board. Bioelectrochemistry 2017, 119, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Jia, W.; Sun, R.; Chen, Z.; Guo, X. Electrochemical migration behavior of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu solder alloy under thin electrolyte layers. Surf. Rev. Lett. 2019, 26, 185–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Wang, H.; Xiao, E.; Cai, Y.; Guo, X. Recent advances in method of suppressing dendrite formation of tin-based solder alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020. Accepted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Haleem, S.M.; Abd El Wanees, S.; Abd El Aal, E.; Diab, A. Environmental factors affecting the corrosion behavior of reinforcing steel II. Role of some anions in the initiation and inhibition of pitting corrosion of steel in Ca(OH)2 solutions. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, A.; Ferreira, M.; Simões, A. Corrosion inhibition by chromate and phosphate extracts for iron substrates studied by EIS and SVET. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 1500–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Soestbergen, M.; Erich, S.; Huinink, H.; Adan, O. Dissolution properties of cerium dibutylphosphate corrosion inhibitors. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibakhshi, E.; Ghasemi, E.; Mahdavian, M. Corrosion inhibition by lithium zinc phosphate pigment, Corros. Sci. 2013, 77, 222–229. [Google Scholar]
- Etteyeb, N.; Dhouibi, L.; Takenouti, H.; Alonso, M.; Triki, E. Corrosion inhibition of carbon steel in alkaline chloride media by Na3PO4. Electrochim. Acta. 2007, 52, 7506–7512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, S.; Kassab, A. Behaviour of tin as metal-metal phosphate electrode and mechanism of promotion and inhibition of its corrosion by phosphate ions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1969, 20, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohai, L.; Vázquez, M.; Valcarce, B. Phosphate ions as corrosion inhibitors for reinforcement steel in chloride-rich environments. Electrochim. Acta. 2013, 102, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almobarak, N. Cyclic voltammetry study of passivation of tin in sodium dihydrogen phosphate solution. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2012, 48, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulmer, M.; Brown, P. Hydrolysis of dicalcium phosphate dihydrate to hydroxyapatite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 1998, 9, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Zhang, G.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Guo, X. Electrochemical migration of tin in thin electrolyte layer containing chloride ions. Corros. Sci. 2013, 74, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Wei, L.; Chen, Z.; Guo, X. Na2S-influenced electrochemical migration of tin in a thin electrolyte layer containing chloride ions. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15060–15070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medgyes, B.; Rigler, D.; Illés, B.; Harsányi, G.; Gál, L. Investigating of electrochemical migration on low-Ag lead-free solder alloys. In Proceedings of the 18th International Symposium for Design and Technology of Electronic Packaging, Alba Iulia, Romania, 25–28 October 2012; pp. 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, B.; Li, Z.; Cai, Y.; Guo, X. Electrochemical migration behavior of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu solder alloy under SO2 polluted thin electrolyte layers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 5652–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Yu, S.; Chen, L.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Z. Test methods for electrochemical migration: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 28, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Cen, H.; Chen, Z.; Guo, X. Effect of Organic Acids on the Electrochemical Migration of Tin in Thin Electrolyte Layer. Innov. Corros. Mater. Sci. (Former. Recent Pat. Corros. Sci.) 2019, 9, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Guo, X. Effect of citrate ions on the electrochemical migration of tin in thin electrolyte layer containing chloride ions. Corros. Sci. 2016, 112, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilley, W.A. Solubility of tin (II) orthophosphate and the phosphate complexes of tin (II). Inorg. Chem. 1968, 7, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, K.; Awad, S.; Kassab, A. Non-corrosive action of the tertiary phosphate ion on aluminium. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1981, 127, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavatta, L.; Iuliano, M. Formation equilibria of tin (II) orthophosphate complexes. Polyhedron 2000, 19, 2403–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, H.D.; Tissot, P. Anodic behaviour of tin in neutral phosphate solution. Corros. Sci. 1979, 19, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, S. The Corrosion and Oxidation of Metals. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1977, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, B.; Wang, H.; Wan, S.; Xiao, W.; Guo, X. Electrochemical Migration Inhibition of Tin by Disodium Hydrogen Phosphate in Water Drop Test. Metals 2020, 10, 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10070942
Liao B, Wang H, Wan S, Xiao W, Guo X. Electrochemical Migration Inhibition of Tin by Disodium Hydrogen Phosphate in Water Drop Test. Metals. 2020; 10(7):942. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10070942
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Bokai, Hong Wang, Shan Wan, Weiping Xiao, and Xingpeng Guo. 2020. "Electrochemical Migration Inhibition of Tin by Disodium Hydrogen Phosphate in Water Drop Test" Metals 10, no. 7: 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10070942
APA StyleLiao, B., Wang, H., Wan, S., Xiao, W., & Guo, X. (2020). Electrochemical Migration Inhibition of Tin by Disodium Hydrogen Phosphate in Water Drop Test. Metals, 10(7), 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10070942




