Characterization of Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zones in Al and Ti-Deoxidized Offshore Steels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Heat Treatments
2.2. Mechanical Testing
2.3. Microstructural Characterization
2.3.1. Non-Metallic Inclusion Characterization
2.3.2. Prior Austenite Reconstruction
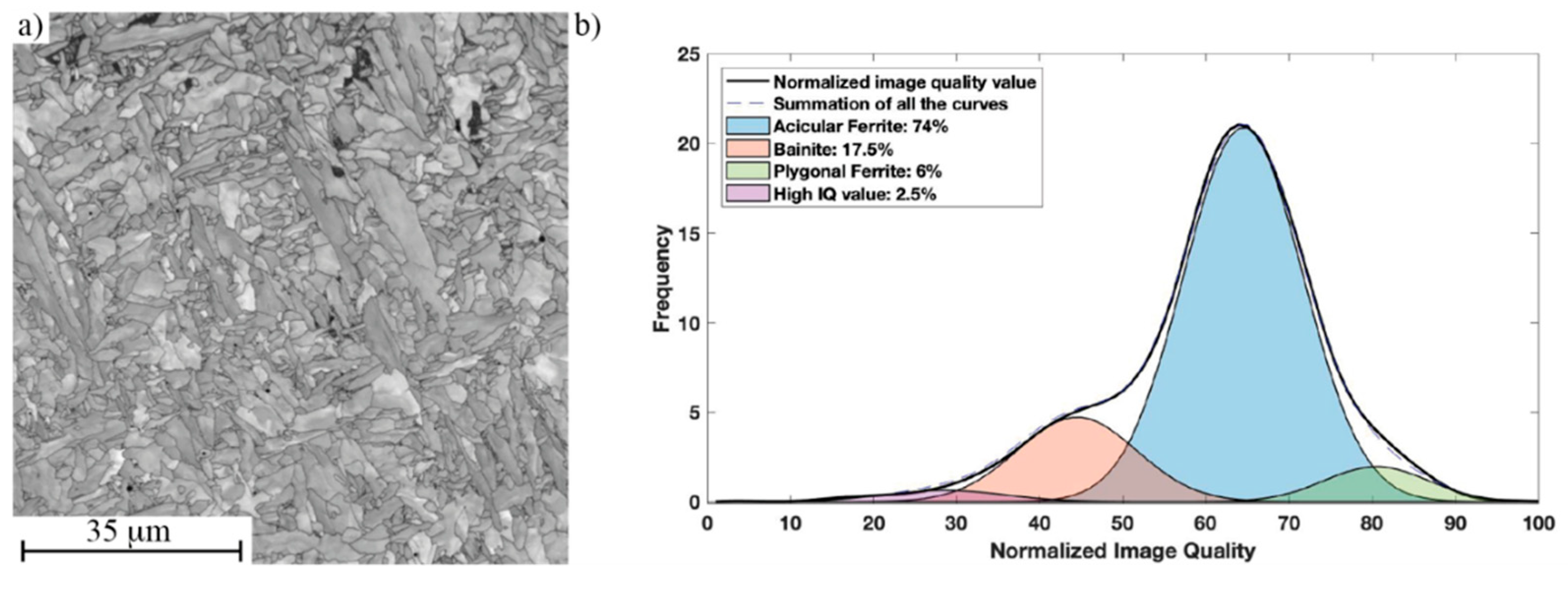
2.3.3. IQ Analysis
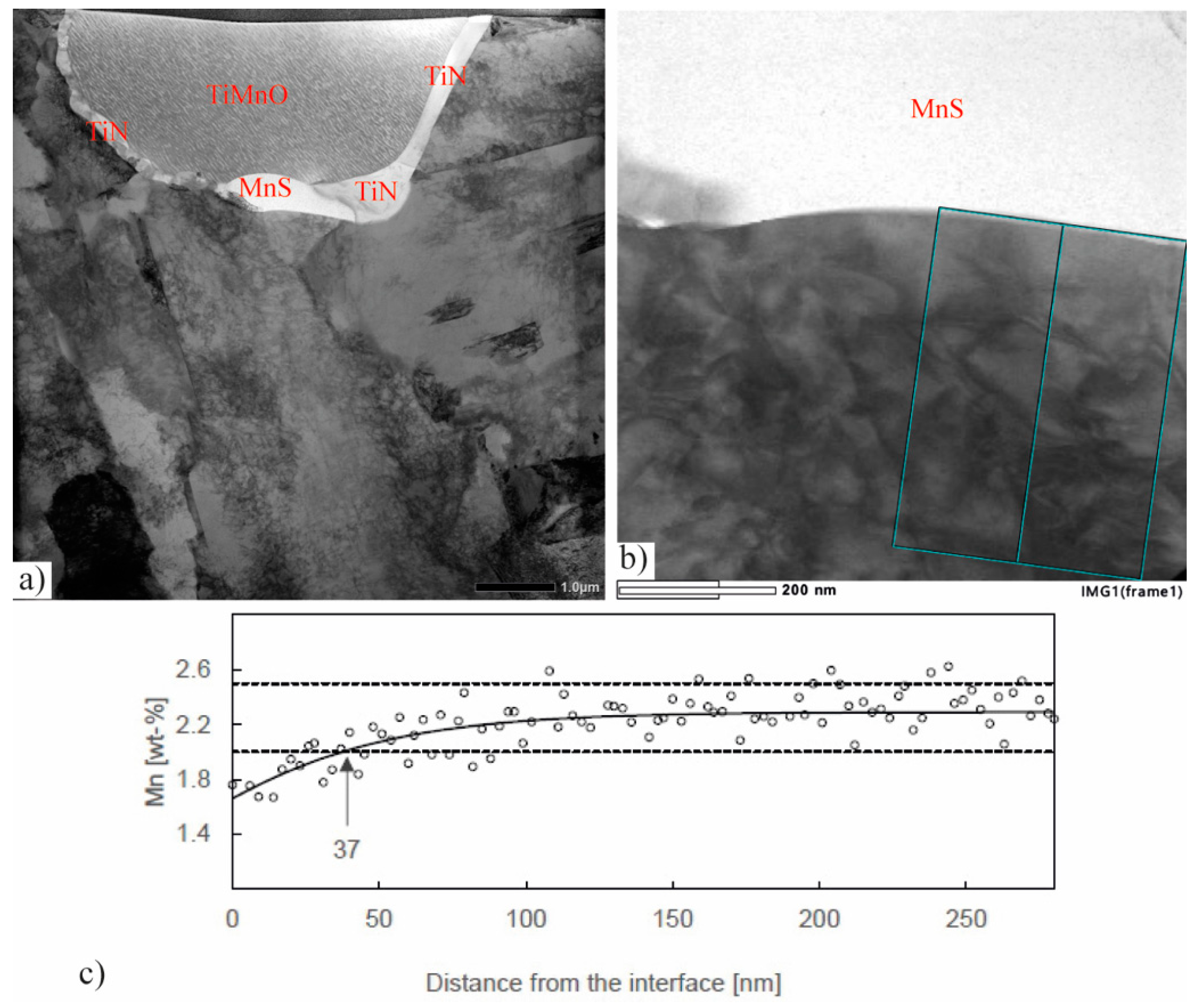
2.3.4. Mn Depletion around Inclusions
2.4. Modelling
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Inclusions
3.1.1. Size Distribution
3.1.2. Inclusion Types
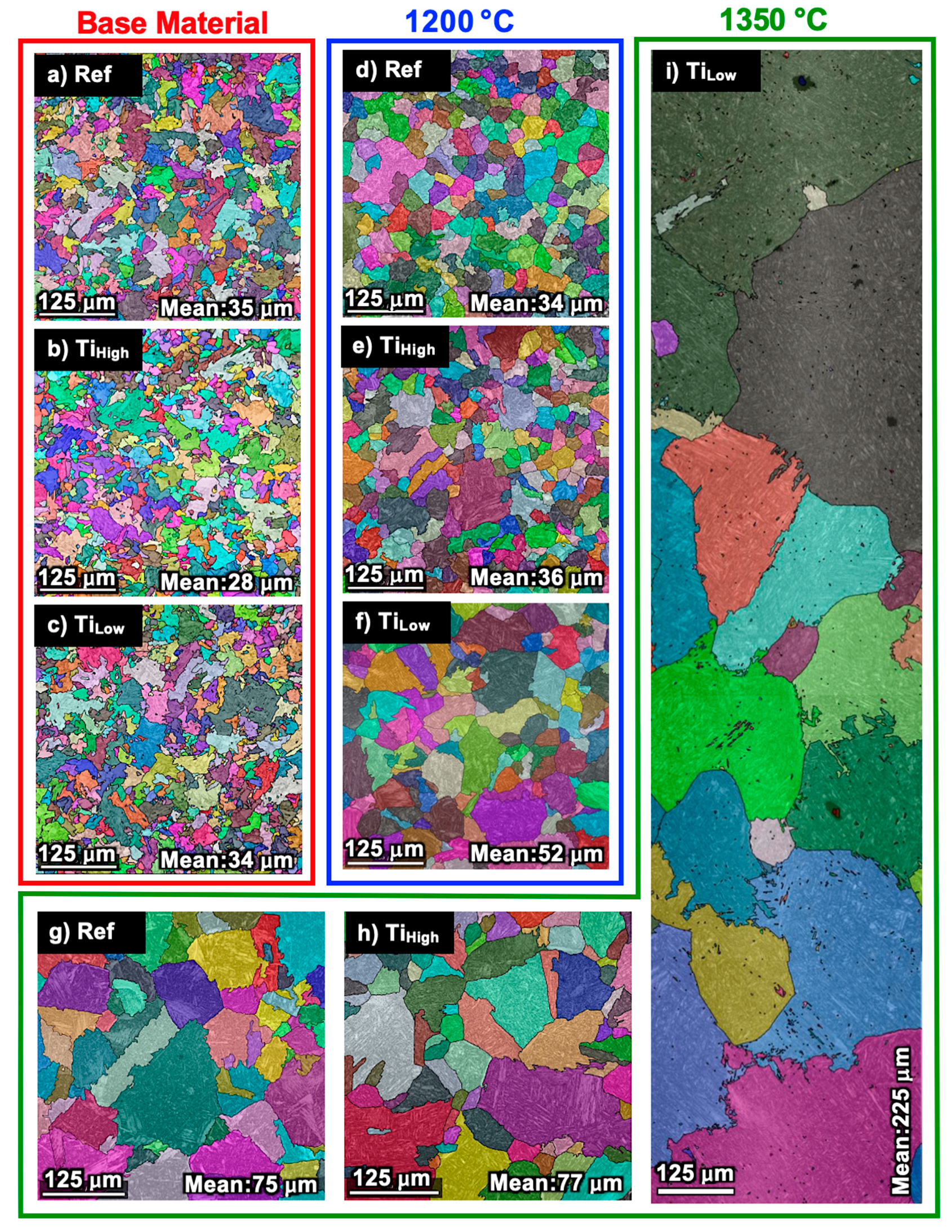
3.2. Growth of Prior Austenite Grain Size
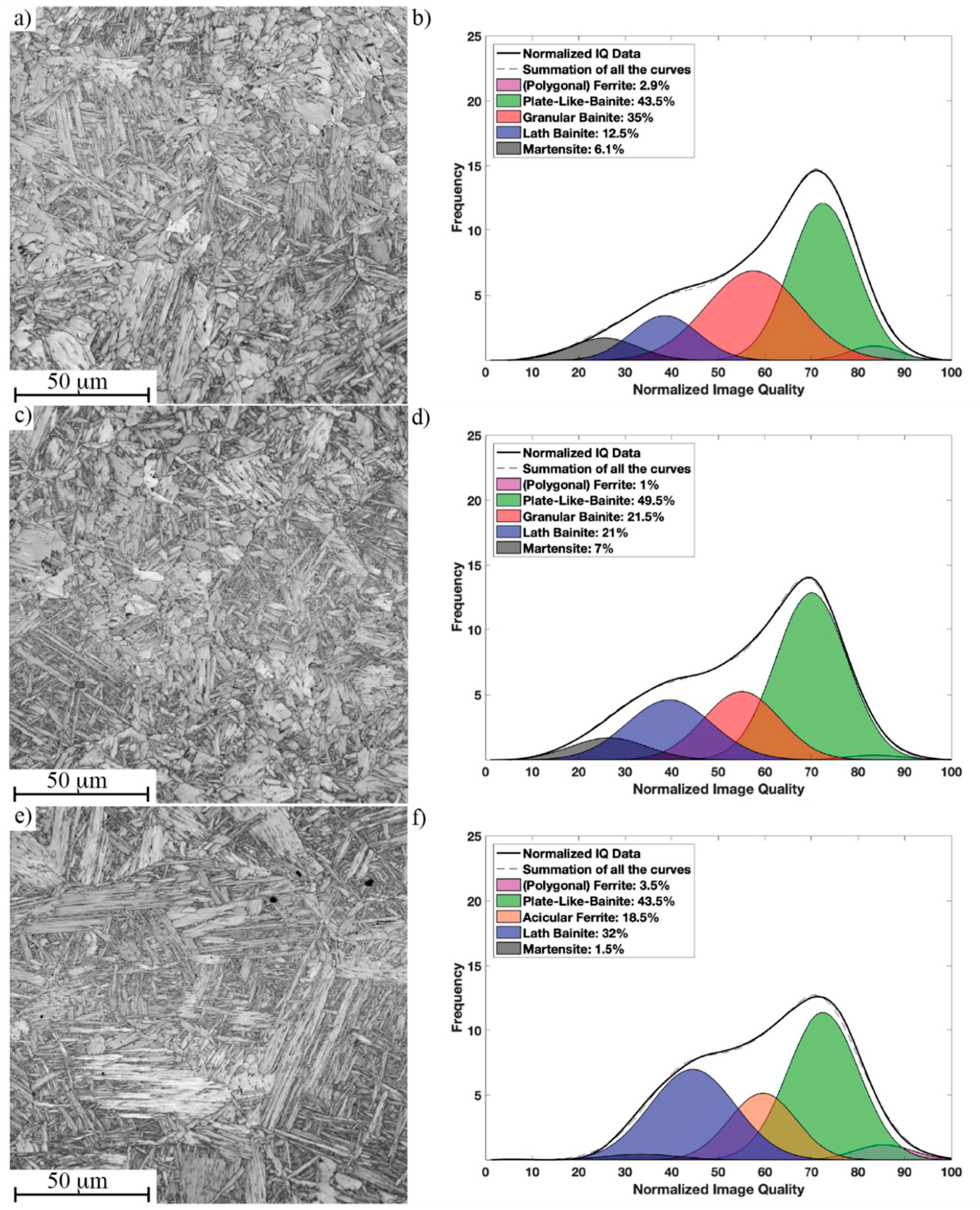
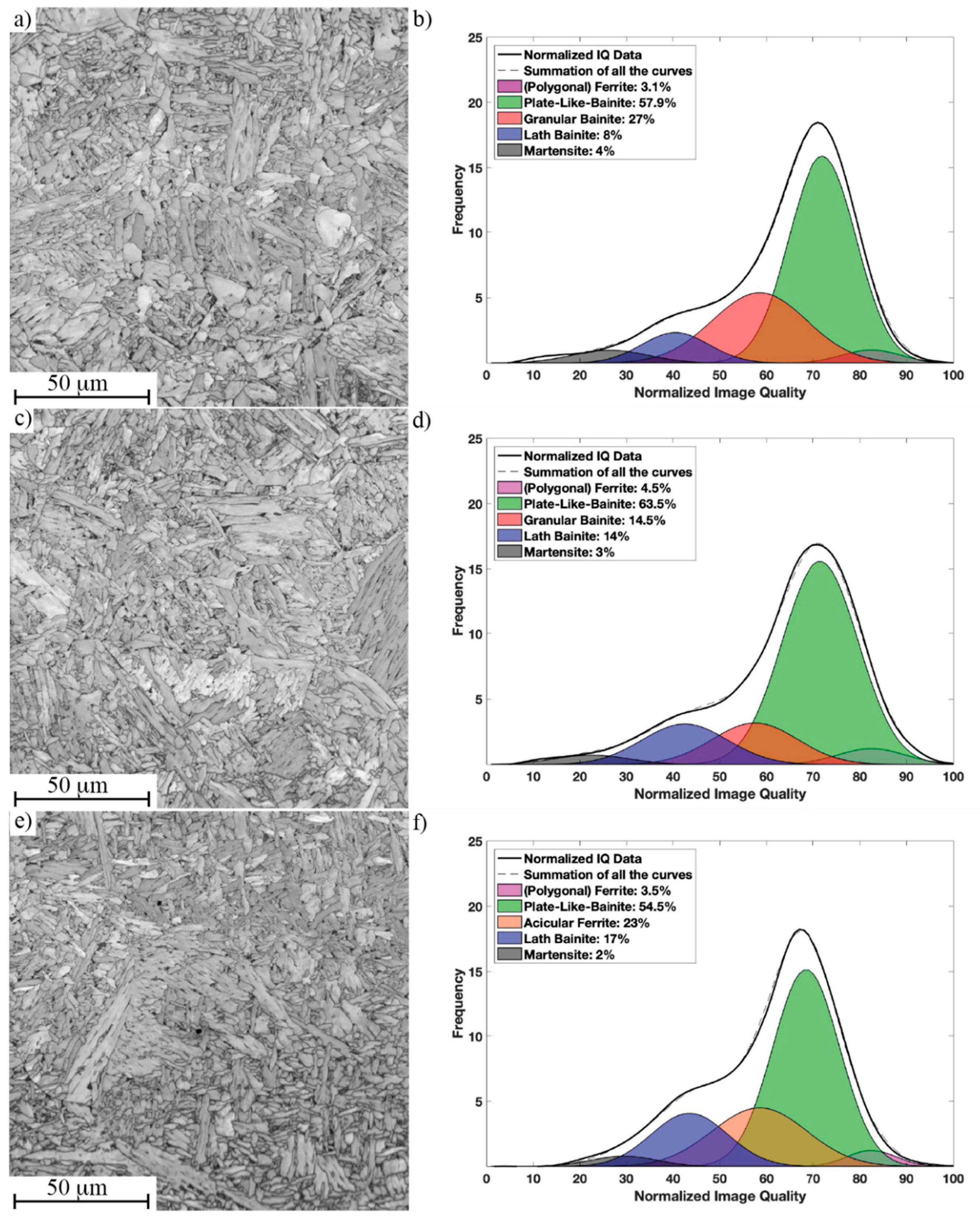
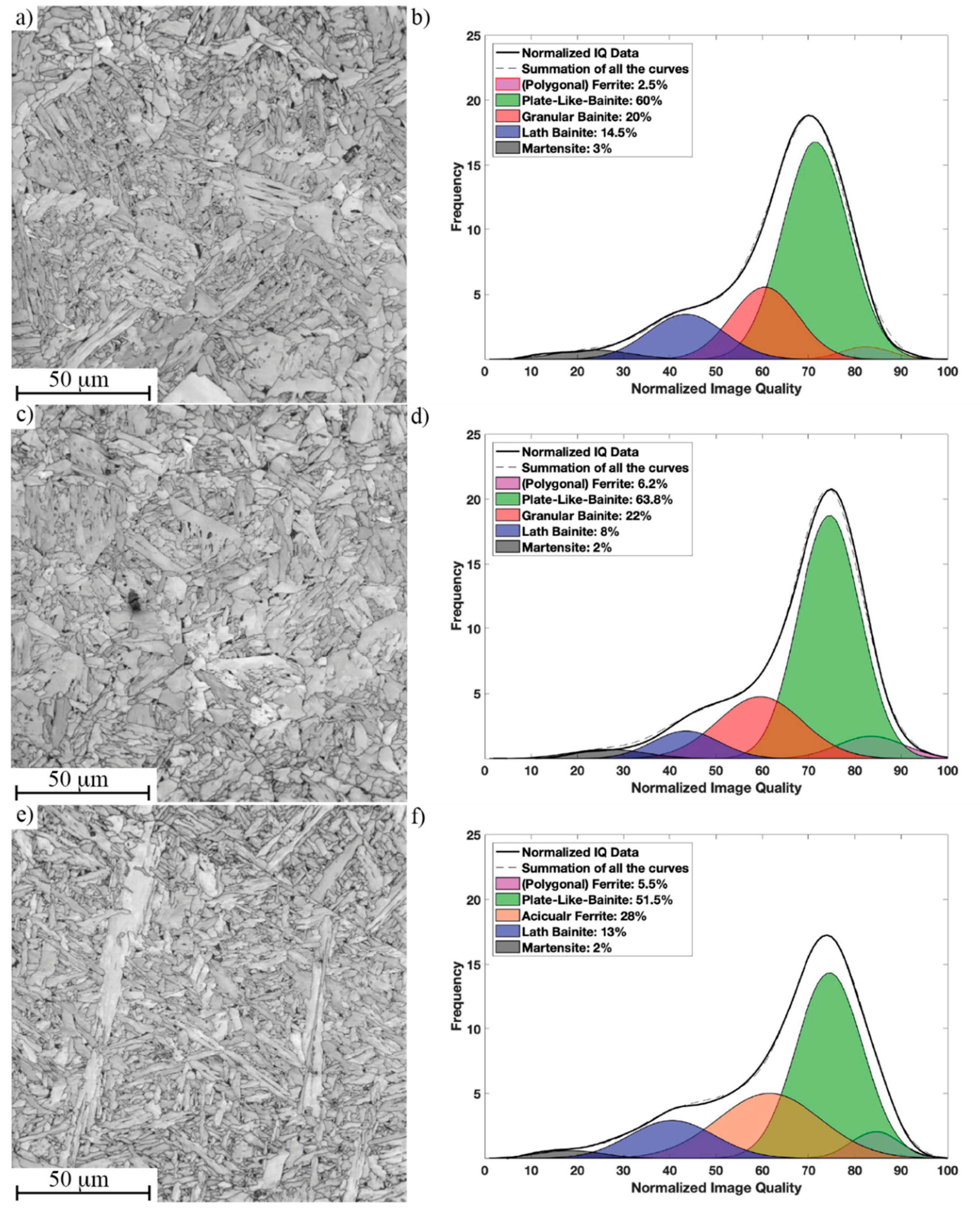
3.3. Microstructure of Simulated CGHAZ with Different Cooling Rates
3.4. TEM Studies of Mn Depletion around Inclusions
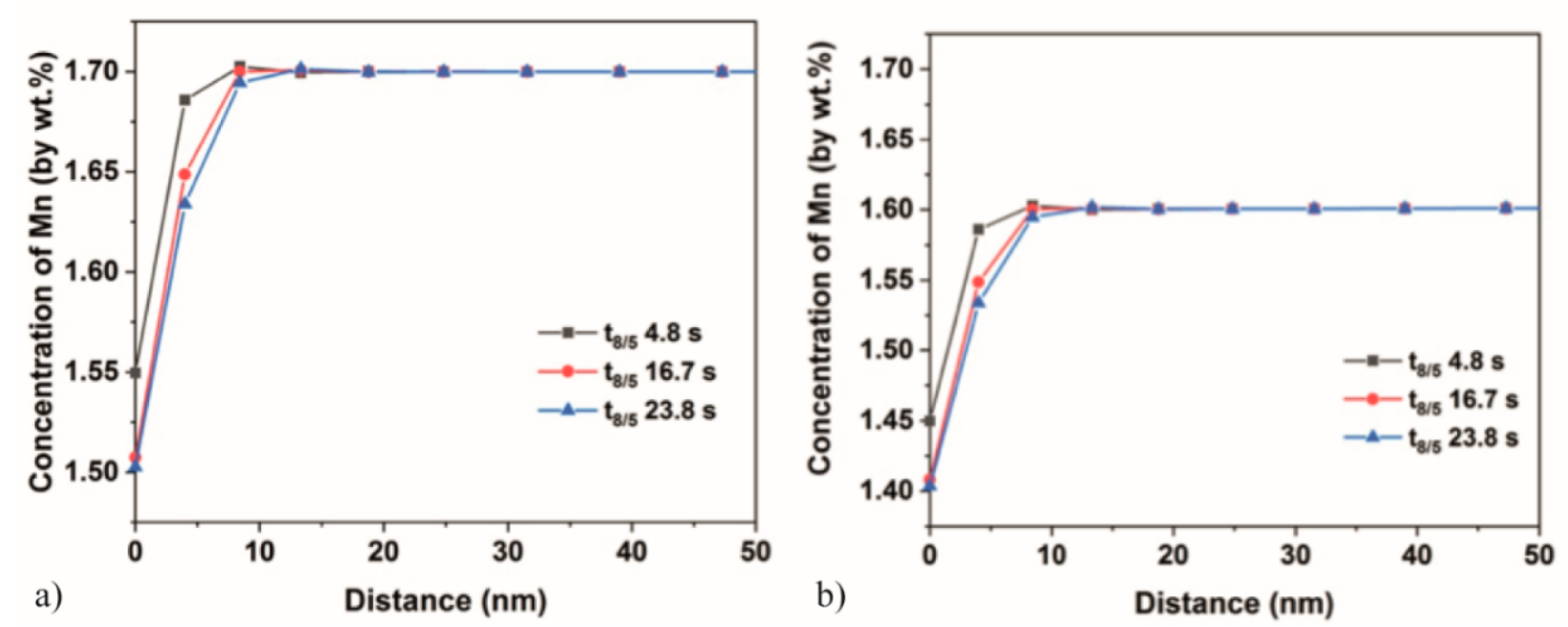
3.5. DICTRA Simulations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Willms, R. High strength steel for steel constructions. Nord. Steel Constr. Conf. Malmo Swed. 2009, 597–604. [Google Scholar]
- SFS. SFS-EN 10225: Weldable Structural Steels For Fixed Offshore Structures. Technical Delivery Conditions; Suomen Standardoimisliitto SFS: Helsinki, Finland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, L.; Qiu, C.; Zhao, D.; Gao, X.; Du, L. Microstructural characteristics and toughness of the simulated coarse grained heat affected zone of high strength low carbon bainitic steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 529, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Schino, A. Analysis of heat treatment effect on microstructural features evolution in a micro-alloyed martensitic steel. Acta Met. Slovaca 2016, 22, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loder, D.; Michelic, S.K.; Bernhard, C. Acicular Ferrite Formation and Its Influencing Factors—A Review. J. Mater. Sci. Res. 2017, 6, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, D.S.; Karasev, A.V.; Jönsson, P.G. On the Role of Non-metallic Inclusions in the Nucleation of Acicular Ferrite in Steels. ISIJ Int. 2009, 49, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Terasaki, H.; Komizo, Y. In situ observation of the formation of intragranular acicular ferrite at non-metallic inclusions in C–Mn steel. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, H.; Ohkita, S.; Matsuda, S.; Yamamoto, K. Improvement of HAZ in HSLA steel by Introducing finely dispersed Ti-Oxide. Weld. Res. Suppl. 1987, 66, 301–309. [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen, R. Improvement of Weld HAZ Toughness at Low Heat Input by Controlling the Distribution of MA Constituents; University of Oulu: Oulu, Finland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Haaland, D.; Van Der Eijk, C.; Grong, Ø. The role of interactive particles in steel. In Proceedings of the International Symposium “Safety in Application of High Strength Steel”, Trondheim, Norway, 1–2 July 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Mabuchi, H.; Uemori, R.; Fujioka, M. The Role of Mn Depletion in Intra-Granular Ferrite Transformation in the Heat Affected Zone of Welded Joints with Large Heat Input in Structural Steels. ISIJ Int. 1996, 36, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Jang, J.; Park, J.H.; Lee, C. Influence of Ti on non-metallic inclusion formation and acicular ferrite nucleation in high-strength low-alloy steel weld metals. Met. Mater. Int. 2014, 20, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.-H.; Cho, Y.; Chung, S.; Shim, J.-D.; Lee, D. Nucleation of intragranular ferrite at Ti2O3 particle in low carbon steel. Acta Mater. 1999, 47, 2751–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Farrar, R.A. Role of non-metallic inclusions in formation of acicular ferrite in low alloy weld metals. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1996, 12, 237–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, M. Nucleation of phase transformations at intragranular inclusions in steel. Met. Mater. 1998, 4, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseki, T.; Ohkita, S.; Yurioka, N. Thermodynamic study of inclusion formation in low alloy steel weld metals. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 1997, 2, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, Y.; Saito, N.; Tsuzuki, T.; Tokunaga, Y.; Okamoto, K. Improvement in HAZ Toughness of Steel by TiN-MnS Addition. ISIJ Int. 1994, 34, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Uhm, S.; Lee, C.; Lee, J.; An, Y. Effects of Inclusions and Microstructures on Impact Energy of High Heat-Input Submerged-Arc-Weld Metals. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2005, 127, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thewlis, G. Transformation kinetics of ferrous weld metals. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1994, 10, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaro, F.J.; Krauklis, P.; Easterling, K.E. Formation of acicular ferrite at oxide particles in steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1989, 5, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.-S.; Shim, J.-H.; Suh, J.-Y.; Oh, Y.-J.; Cho, Y.W.; Shim, J.-D.; Lee, D.N. Inoculated acicular ferrite microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 319–321, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Matsuda, S.; Haze, T.; Chijiiwa, R.; Mimura, H. A Newly Developed Ti-Oxide Bearing Steel Having High HAZ Toughness. In Residual and Unspecified Elements in Steel; Melilli, A.S., Nisbett, E.G., Eds.; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1989; pp. 266–284. ISBN 978-0-8031-5097-3. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Kang, J.; Wang, G.; Misra, D.; Yuan, G. Relationship Between Impact Toughness and Microstructure for the As-Rolled and Simulated HAZ of Low-Carbon Steel Containing Ti-Ca Oxide Particles. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 2927–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatarvas, T. Evolution of Inclusion Population in Calcium Treated Ultra-High Strength Steels: Novel Applications of Sample Data Treatment; University of Oulu: Oulu, Finland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nyyssönen, T.; Isakov, M.; Peura, P.; Kuokkala, V.-T. Iterative Determination of the Orientation Relationship Between Austenite and Martensite from a Large Amount of Grain Pair Misorientations. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 2587–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyyssönen, T.; Peura, P.; Kuokkala, V.-T. Crystallography, Morphology, and Martensite Transformation of Prior Austenite in Intercritically Annealed High-Aluminum Steel. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 6426–6441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaheri, V.; Nyyssönen, T.; Grande, B.; Porter, D. Computational design of a novel medium-carbon, low-alloy steel microalloyed with niobium. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 2978–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaheri, V.; Kolli, S.; Grande, B.; Porter, D. Insight into the induction hardening behavior of a new 0.40% C microalloyed steel: Effects of initial microstructure and thermal cycles. Mater. Charact. 2019, 149, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdjumow, G.; Sachs, G. Uber den Mechanismus der Stahlhärtung. Z. Phys. 1930, 64, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaheri, V.; Pohjonen, A.; Asperheim, J.I.; Ivanov, D.; Porter, D. Physically based modeling, characterization and design of an induction hardening process for a new slurry pipeline steel. Mater. Des. 2019, 182, 108047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeArdo, A.J.; Garcia, C.I.; Cho, K.; Hua, M. New Method of Characterizing and Quantifying Complex Microstructures in Steels. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2010, 25, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.-O.; Helander, T.; Höglund, L.; Shi, P.; Sundman, B. Thermo-Calc & DICTRA, computational tools for materials science. Calphad 2002, 26, 273–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Song, B. Intragranular Ferrite Formation Mechanism and Mechanical Properties of Non-quenched-and-tempered Medium Carbon Steels. Steel Res. Int. 2008, 79, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.L.; Breen, A.J.; Trimby, P.; Proust, G.; Ringer, S.P.; Cairney, J.M. An automated method of quantifying ferrite microstructures using electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) data. Ultramicroscopy 2014, 137, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Al | Nb | V | Ti | N | O | Others | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref | 0.05 | 0.01 | 1.6 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.037 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.016 | 0.006 | 0.0023 | Cr, Mo, Cu, |
| Tihigh | 0.05 | 0.03 | 1.7 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.027 | 0.006 | 0.0080 | Ni in equal |
| Tilow | 0.05 | 0.23 | 1.7 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.016 | 0.008 | 0.0047 | proportions |
| Inclusion Type | Combined Class | Ref 16.7 s (<3 µm) | Ref 16.7 s (all) | TiHigh 16.7 s (<3 µm) | TiHigh 16.7 s (all) | TiLow 16.7 s (<3 µm) | TiLow 16.7 s (all) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | Al2O3 containing oxides | 2.2 | 3.6 | – | – | – | – |
| Al2O3 MnO | Al2O3 containing oxides | 0.2 | 0.2 | – | – | – | – |
| Al2O3 MnO MnS | Al2O3 containing complex | 0.1 | 0.1 | – | – | – | – |
| Al2O3 MnO MnS TiN | Al2O3 containing complex | 1.8 | 1.8 | – | – | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Al2O3 MnO TiN | Al2O3 containing complex | 4.4 | 4.6 | – | – | – | – |
| Al2O3 MnO TiOx | Al2O3 containing oxides | – | – | – | – | 0.7 | 1.1 |
| Al2O3 MnO TiOx MnS | Al2O3 containing complex | 0.1 | 0.1 | – | – | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Al2O3 MnO TiOx MnS TiN | Al2O3 containing complex | 0.1 | 0.1 | – | – | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| Al2O3 MnO TiOx TiN | Al2O3 containing complex | 1.3 | 1.3 | – | – | 0.6 | 1.0 |
| Al2O3 MnS | Al2O3 containing complex | 1.2 | 2.5 | – | – | – | – |
| Al2O3 MnS TiN | Al2O3 containing complex | 4.5 | 6.3 | – | – | – | – |
| Al2O3 TiN | Al2O3 containing complex | 9.5 | 13.5 | – | – | – | – |
| Al2O3 TiOx | Al2O3 containing oxides | 0.5 | 1.0 | – | – | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Al2O3 TiOx MnS | Al2O3 containing complex | 0.4 | 0.6 | – | – | – | – |
| Al2O3 TiOx MnS TiN | Al2O3 containing complex | 0.3 | 0.4 | – | – | – | – |
| Al2O3 TiOx TiN | Al2O3 containing complex | 3.0 | 3.7 | – | – | – | – |
| MnO | MnO(+MnS-TiN) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| MnO MnS | MnO(+MnS-TiN) | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| MnO MnS TiN | MnO(+MnS-TiN) | 3.6 | 3.7 | 2.8 | 3.1 | 6.9 | 7.2 |
| MnO TiN | MnO(+MnS-TiN) | 16.5 | 17.5 | 5.9 | 7.7 | 1.8 | 2.1 |
| MnO TiOx | MnO-TiOx(+TiN) | – | – | 14.6 | 33.5 | 5.5 | 14.9 |
| MnO TiOx MnS | MnO-TiOx-MnS(+TiN) | – | – | 5.2 | 9.7 | 4.7 | 6.3 |
| MnO TiOx MnS TiN | MnO-TiOx-MnS(+TiN) | – | – | 5.9 | 7.1 | 9.3 | 11.2 |
| MnO TiOx TiN | MnO-TiOx(+TiN) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 10.3 | 11.4 | 7.0 | 9.2 |
| MnS | MnS | 2.8 | 4.2 | 1.9 | 3.7 | 0.5 | 0.7 |
| MnS TiN | MnS TiN | 2.9 | 4.8 | 4.4 | 6.1 | 1.7 | 2.5 |
| TiN | TiN | 4.7 | 9.3 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.4 |
| TiOx | TiOx(+MnS-TiN) | – | – | 0.3 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 3.4 |
| TiOx MnS | TiOx(+MnS-TiN) | 0.3 | 0.3 | 1.7 | 3.3 | 1.1 | 1.3 |
| TiOx MnS TiN | TiOx(+MnS-TiN) | 0.1 | 0.1 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 1.0 | 1.3 |
| TiOx TiN | TiOx(+MnS-TiN) | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.7 |
| Grain Size | Ref 4.8 s | Tihigh 4.8 s | Tilow 4.8 s | Ref 16.7 s | Tihigh 16.7 s | Tilow 16.7 s | Ref 23.8 s | Tihigh 23.8 s | Tilow 23.8 s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (µm) | 1.54 | 1.37 | 1.22 | 1.92 | 1.73 | 2.06 | 1.84 | 2.44 | 1.61 |
| D80% (µm) | 14.27 | 11.20 | 8.92 | 16.43 | 19.27 | 14.75 | 21.71 | 20.71 | 17.49 |
| Performance | t8/5 = 4.8 s Microstructure/Hardness (HV10) | t8/5 = 16.7 s Microstructure/Hardness (HV10) | t8/5 = 23.8 s Microstructure/Hardness (HV10) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ref | PB-GB/231 ± 5 | PB-GB/199 ± 5 | PB-GB/190 ± 3 |
| Tihigh | PB-GB/243 ± 8 | PB-GB/210 ± 7 | PB-GB/204 ± 5 |
| Tilow | PB-LB/280 ± 11 | PB-AF/232 ± 4 | PB-AF/218 ± 5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tervo, H.; Kaijalainen, A.; Javaheri, V.; Kolli, S.; Alatarvas, T.; Anttila, S.; Kömi, J. Characterization of Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zones in Al and Ti-Deoxidized Offshore Steels. Metals 2020, 10, 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10081096
Tervo H, Kaijalainen A, Javaheri V, Kolli S, Alatarvas T, Anttila S, Kömi J. Characterization of Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zones in Al and Ti-Deoxidized Offshore Steels. Metals. 2020; 10(8):1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10081096
Chicago/Turabian StyleTervo, Henri, Antti Kaijalainen, Vahid Javaheri, Satish Kolli, Tuomas Alatarvas, Severi Anttila, and Jukka Kömi. 2020. "Characterization of Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zones in Al and Ti-Deoxidized Offshore Steels" Metals 10, no. 8: 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10081096
APA StyleTervo, H., Kaijalainen, A., Javaheri, V., Kolli, S., Alatarvas, T., Anttila, S., & Kömi, J. (2020). Characterization of Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zones in Al and Ti-Deoxidized Offshore Steels. Metals, 10(8), 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10081096






