Effect of Cavitation Peening on Fatigue Properties in Friction Stir Welded Aluminum Alloy AA5754
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
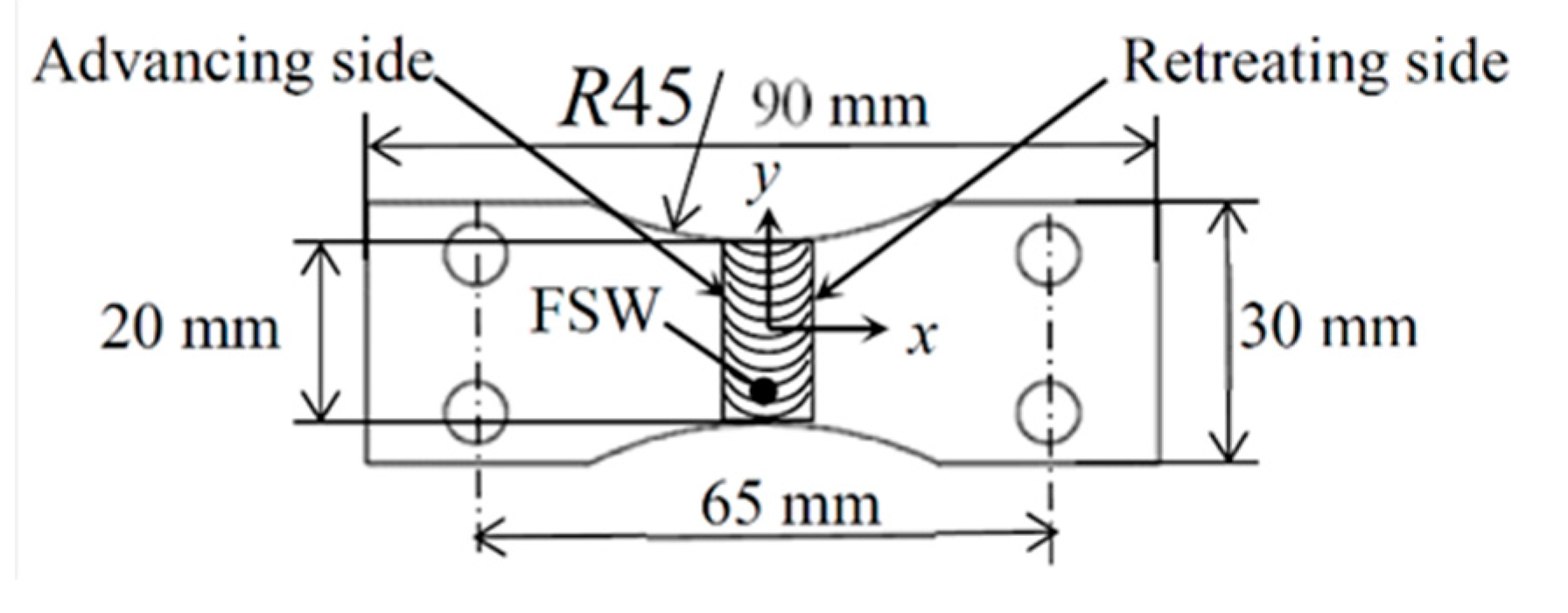
2.1. Friction Stir Welded Aluminum Alloy AA5754
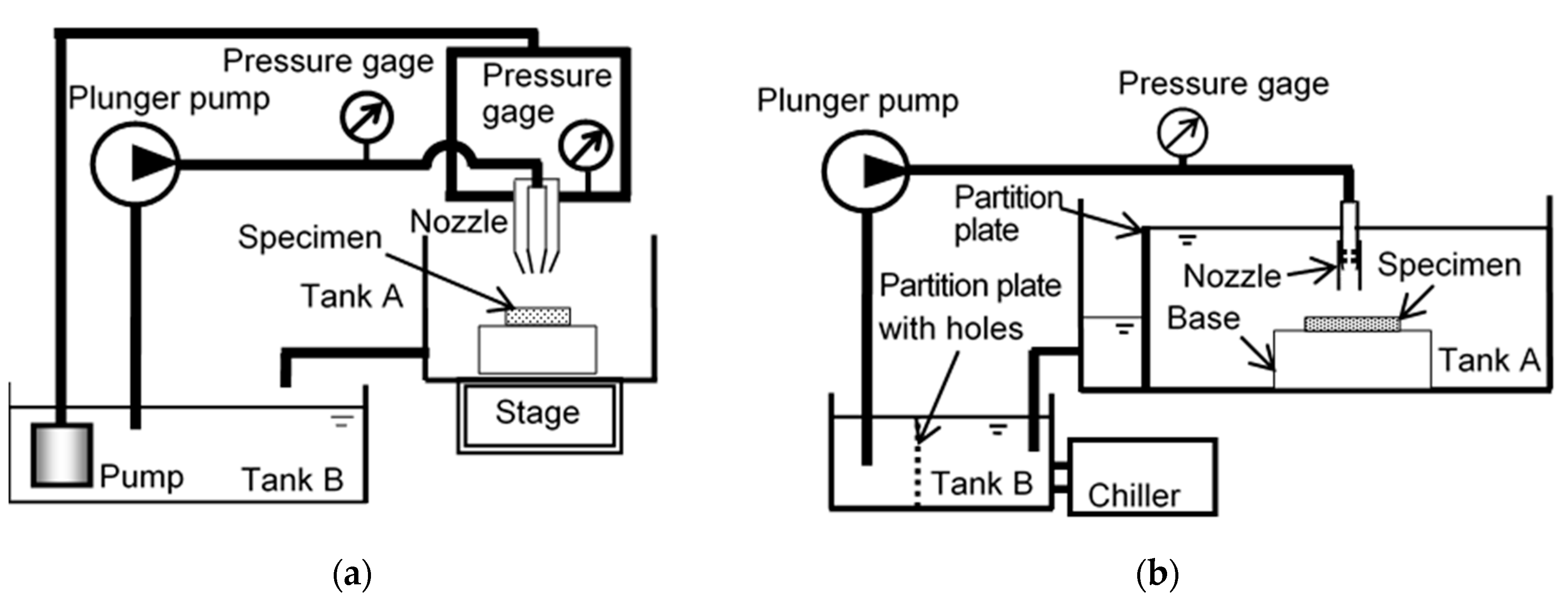
2.2. Cavitation Peening Using a Cavitating Jet in Air and Water
2.3. Evaluation of Fatigue Properties and Surface Characteristics
3. Results
3.1. Aspect of Cavitation Peened Surface
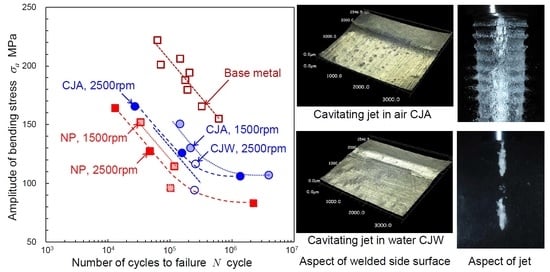
3.2. Improvement of Fatigue Properties of FSWed AA5754 by Cavitation Peening
3.3. Introduction of Compressive Residual Stress by Cavitation Peening
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Cavitation peening using a cavitating jet in air (CJA) and a cavitation jet in water (CJW) can improve fatigue properties of FSWed AA5754. The fatigue properties treated by CJA are better than those treated by CJW, as the surface roughness of CJA is smaller than that of CJW.
- (2)
- The fatigue life at σa = 150 MPa can be more than doubled by CJA and CJW compared with non-peened FSWed specimen. CJA and CJW can also improve the fatigue strength at N = 105 more than 1.2 times compared with non-peened FSWed specimen.
- (3)
- Cavitation peening using CJA can introduce compressive residual stress into both surfaces of the welded side and the root side of the FSWed part.
- (4)
- In the present FSW condition, the surface residual stress of the FSWed specimen near the center part of the root side and boundary of FSW of the welded side reveals tension.
- (5)
- The fatigue life at σa = 150 MPa and the fatigue strength at N = 105 of tested FSW specimen were 3–5% and 53–59% of bulk sheet, respectively. In the present condition, the fatigue properties of FSWed specimen joining at a rotational speed of 1500 rpm were better than those of 2500 rpm.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, W.M.; Nicholas, E.D.; Needham, J.C.; Murch, M.G.; Temple-Smith, P.; Dawes, C.J. Improvements relating to friction stir welding. Eur. Pat. Specif. 1991, 615, B1. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, W.M.; Threadgill, P.L.; Nicholas, E.D. Feasibility of friction stir welding steel. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 1999, 4, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Y. Friction stir processing technology: A review. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2008, 39, 642–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandan, R.; DebRoy, T.; Bhadeshia, H. Recent advances in friction-stir welding—Process, weldment structure and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2008, 53, 980–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, K.; Ramulu, M. Friction stir welding of titanium alloys: A review. Mater. Des. 2018, 141, 230–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabibbo, M.; Paoletti, C.; Ghat, M.; Forcellese, A.; Simoncini, M. Post-FSW cold-rolling simulation of ECAP shear deformation and its microstructure role combined to annealing in a fswed aa5754 plate joint. Materials 2019, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabibbo, M.; Forcellese, A.; Santecchia, E.; Paoletti, C.; Spigarelli, S.; Simoncini, M. New approaches to friction stir welding of aluminum light-alloys. Metals 2020, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, W.M.; Nicholas, E.D. Friction stir welding for the transportation industries. Mater. Des. 1997, 18, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun, T.; Soutis, C. Recent developments in advanced aircraft aluminium alloys. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas, M.; Gerlich, A.P. Joining of automotive sheet materials by friction-based welding methods: A review. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2018, 21, 130–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.S.; Ma, Z.Y. Friction stir welding and processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2005, 50, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoncini, M.; Ciccarelli, D.; Forcellese, A.; Pieralisi, M. Micro-and macro-mechanical properties of pinless friction stir welded joints in AA5754 aluminium thin sheets. Proc. CIRP 2014, 18, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.H.; Chen, D.L.; Ma, Z.Y. Microstructure and low-cycle fatigue of a friction-stir-welded 6061 aluminum alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 41, 2626–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.F.; Liu, J.H.; Chen, D.L.; Luan, G.H. Low-cycle fatigue of a friction stir welded 2219-T62 aluminum alloy at different welding parameters and cooling conditions. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 74, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.X.; Wu, C.S.; Gao, S. Effect of ultrasonic vibration on fatigue performance of AA2024-T3 friction stir weld joints. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 29, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Gao, J.; Li, Q.C. Fatigue of friction stir welded aluminum alloy joints: A review. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthayakumar, M.; Balasubramanian, V.; Rani, A.M.A.; Hadzima, B. Effects of welding on the fatigue behaviour of commercial aluminum AA-1100 joints. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Recent Advances in Materials & Manufacturing Technologies, Dubai, UAE, 28–29 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chehreh, A.B.; Gratzel, M.; Bergmann, J.P.; Walther, F. Effect of corrosion and surface finishing on fatigue behavior of friction stir welded EN AW-5754 aluminum alloy using various tool configurations. Materials 2020, 13, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Torzewski, J.; Grzelak, K.; Wachowski, M.; Kosturek, R. Microstructure and low cycle fatigue properties of AA5083 H111 friction stir welded joint. Materials 2020, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, P.J. Residual stress and its role in failure. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2007, 70, 2211–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.J.; Oosterkamp, L.D.; Browne, P.A.; Hughes, D.J.; Kang, W.P.; Withers, P.J.; Vaughan, G.B.M. Synchrotron X-ray residual strain scanning of a friction stir weld. J. Strain Anal. Eng. Des. 2001, 36, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.; Steuwer, A.; Preuss, M.; Withers, P.J. Microstructure, mechanical properties and residual stresses as a function of welding speed in aluminium AA5083 friction stir welds. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 4791–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prime, M.B.; Gnaupel-Herold, T.; Baumann, J.A.; Lederich, R.J.; Bowden, D.M.; Sebring, R.J. Residual stress measurements in a thick, dissimilar aluminum alloy friction stir weld. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 4013–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas, M.; Gharghouri, M.A.; Bhakhri, V.; Klassen, R.J.; Gerlich, A.P. Assessing residual stresses in friction stir welding: Neutron diffraction and nanoindentation methods. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 3733–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhong, H.L.; Li, S.C.; Zhao, H.J.; Chen, J.Q.; Qi, L. Microstructure, mechanical properties and fatigue crack growth behavior of friction stir welded joint of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 135, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, R.; Jata, K.V.; Sadananda, K. Residual stress effects on near-threshold fatigue crack growth in friction stir welds in aerospace alloys. Int. J. Fatigue 2003, 25, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Wu, Y.X.; Gong, H. Prediction of temperature and residual stress distributions in friction stir welding of aluminum alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 106, 3301–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamleh, O.; Rivero, I.V.; Lyons, J. Evaluation of surface residual stresses in friction stir welds due to laser and shot peening. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2007, 16, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamleh, O. Effects of peening on mechanical properties in friction stir welded 2195 aluminum alloy joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 492, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamleh, O. A comprehensive investigation on the effects of laser and shot peening on fatigue crack growth in friction stir welded AA 2195 joints. Int. J. Fatigue 2009, 31, 974–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamleh, O.; DeWald, A. An investigation of the peening effects on the residual stresses in friction stir welded 2195 and 7075 aluminum alloy joints. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 4822–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Wu, Y.X.; Gong, H.; Chen, D.; Guo, X.D. Effect of shot peening on redistribution of residual stress field in friction stir welding of 2219 aluminum alloy. Materials 2020, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyama, H. Surface mechanics design of metallic materials on mechanical surface treatments. Mech. Eng. Rev. 2015, 2, 14–00192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamleh, O.; Lyons, J.; Forman, R. Laser peening and shot peening effects on fatigue life and surface roughness of friction stir welded 7075-T7351 aluminum. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2007, 30, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulstaar, M.A.; Al-Fadhalah, K.J.; Wagner, L. Microstructural variation through weld thickness and mechanical properties of peened friction stir welded 6061 aluminum alloy joints. Mater. Charact. 2017, 126, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Yang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cai, M. Improvement of very high cycle fatigue properties in an AA7075 friction stir welded joint by ultrasonic peening treatment. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2017, 40, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Liu, Z.P.; Zhai, X.; Yan, Z.F.; Wang, W.X.; Liaw, P.K. Incredible improvement in fatigue resistance of friction stir welded 7075-T651 aluminum alloy via surface mechanical rolling treatment. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 124, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baisukhan, A.; Nakkiew, W. Sequential effects of deep rolling and post-weld heat treatment on surface integrity of AA7075-T651 aluminum alloy friction stir welding. Materials 2019, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, Y.; Masaki, K.; Gushi, T.; Sano, T. Improvement in fatigue performance of friction stir welded A6061-T6 aluminum alloy by laser peening without coating. Mater. Des. 2012, 36, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, T.; Eimura, T.; Kashiwabara, R.; Matsuda, T.; Isshiki, Y.; Hirose, A.; Tsutsumi, S.; Arakawa, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Masaki, K.; et al. Femtosecond laser peening of 2024 aluminum alloy without a sacrificial overlay under atmospheric conditions. J. Laser Appl. 2017, 29, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima, T.; Sano, T.; Hirose, A.; Tsutsumi, S.; Masaki, K.; Arakawa, K.; Hori, H. Femtosecond laser peening of friction stir welded 7075-T73 aluminum alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 262, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasoh, A.; Watanabe, K.; Sano, Y.; Mukai, N. Behavior of bubbles induced by the interaction of a laser pulse with a metal plate in water. Appl. Phys. A 2005, 80, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyama, H. Comparison between the improvements made to the fatigue strength of stainless steel by cavitation peening, water jet peening, shot peening and laser peening. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 269, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyama, H.; Lichtarowicz, A.; Momma, T.; Williams, E.J. A new calibration method for dynamically loaded transducers and its application to cavitation impact measurement. J. Fluids Eng. 1998, 120, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyama, H.; Sekine, Y.; Saito, K. Evaluation of the enhanced cavitation impact energy using a PVDF transducer with an acrylic resin backing. Measurement 2011, 44, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyama, H. Key factors and applications of cavitation peening. Inter. J. Peen. Sci. Technol. 2017, 1, 3–60. [Google Scholar]
- Soyama, H. Cavitation peening: A review. Metals 2020, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyama, H. Cavitating jet: A review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, K.; Hirano, K.; Mochizuki, M.; Kurosawa, K.; Saito, H.; Hayashi, E. Improvement of residual stress on material surface by water jet peening. Zairyo 1996, 45, 734–739. [Google Scholar]
- Soyama, H.; Chighizola, C.R.; Hill, M.R. Effect of compressive residual stress introduced by cavitation peening and shot peening on the improvement of fatigue strength of stainless steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 288, 116877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyama, H. Introduction of compressive residual stress using a cavitating jet in air. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2004, 126, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyama, H. High-speed observation of a cavitating jet in air. J. Fluids Eng. 2005, 127, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyama, H. Improvement of fatigue strength by using cavitating jets in air and water. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 6638–6641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, M.; Ciarapica, F.E.; D’Orazio, A.; Forcellese, A.; Simoncini, M. Sustainability analysis of friction stir welding of AA5754 sheets. Proc. CIRP 2017, 62, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalino, G.; El Mehtedi, M.; Forcellese, A.; Simoncini, M. Effect of cold rolling on the mechanical properties and formability of fswed sheets in AA5754-H114. Metals 2018, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyama, H.; Kikuchi, T.; Nishikawa, M.; Takakuwa, O. Introduction of compressive residual stress into stainless steel by employing a cavitating jet in air. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 3167–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyama, H. Enhancing the aggressive intensity of a cavitating jet by introducing a cavitator and a guide pipe. J. Fluid Sci. Technol. 2014, 9, 13–00238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyama, H. Enhancing the aggressive intensity of a cavitating jet by means of the nozzle outlet geometry. J. Fluids Eng. 2011, 133, 101301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyama, H.; Okura, Y. The use of various peening methods to improve the fatigue strength of titanium alloy Ti6Al4V manufactured by electron beam melting. AIMS Mater. Sci. 2018, 5, 1000–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.B. Two-Dimensional X-ray Diffraction; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 249–328. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. G134-17 Standard Test Method for Erosion of Solid Materials by a Cavitating Liquid Jet; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Soyama, H.; Asahara, M. Improvement of the corrosion resistance of a carbon steel surface by a cavitating jet. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1999, 18, 1953–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyama, H. Luminescence intensity of vortex cavitation in a venturi tube changing with cavitation number. Ultrason Sonochem. 2021, 71, 105389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
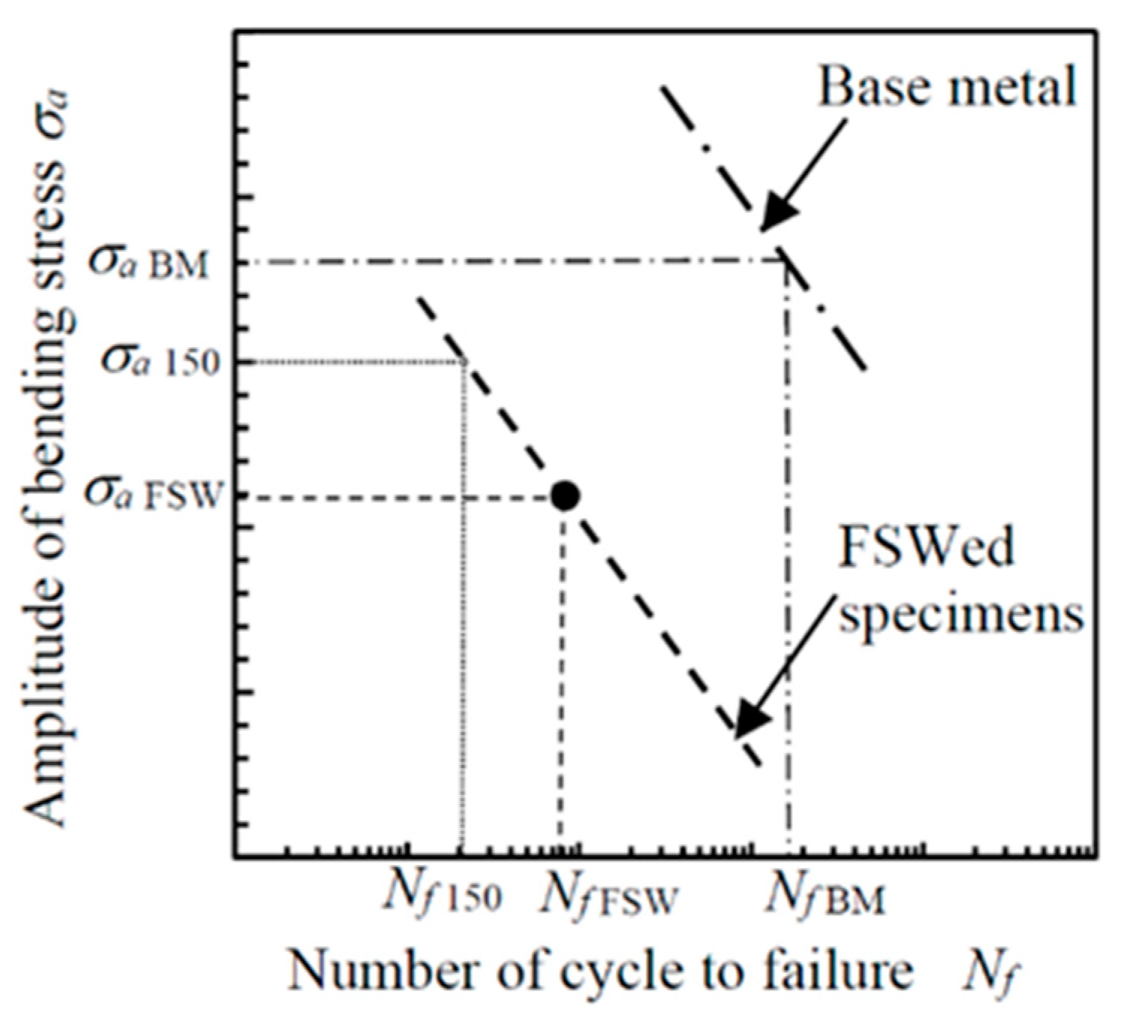
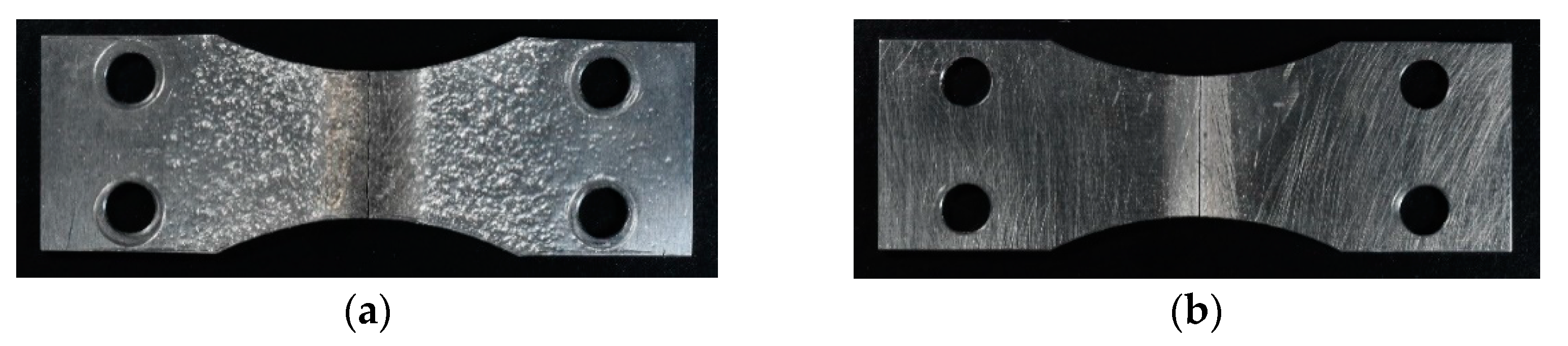
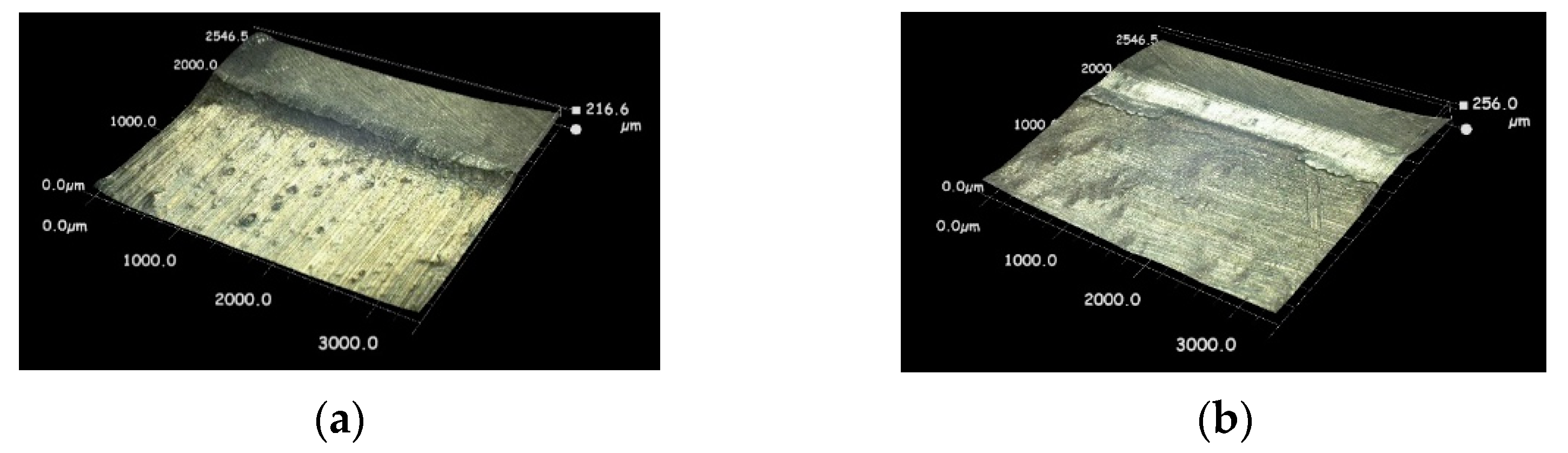

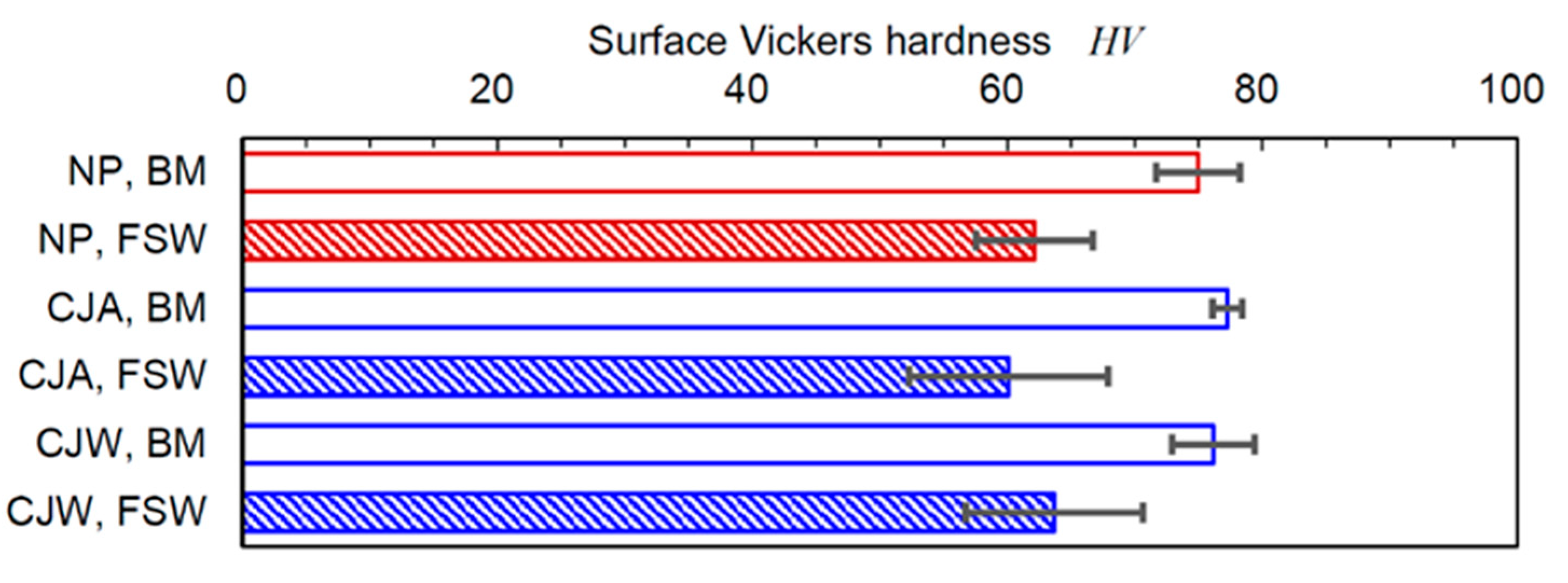
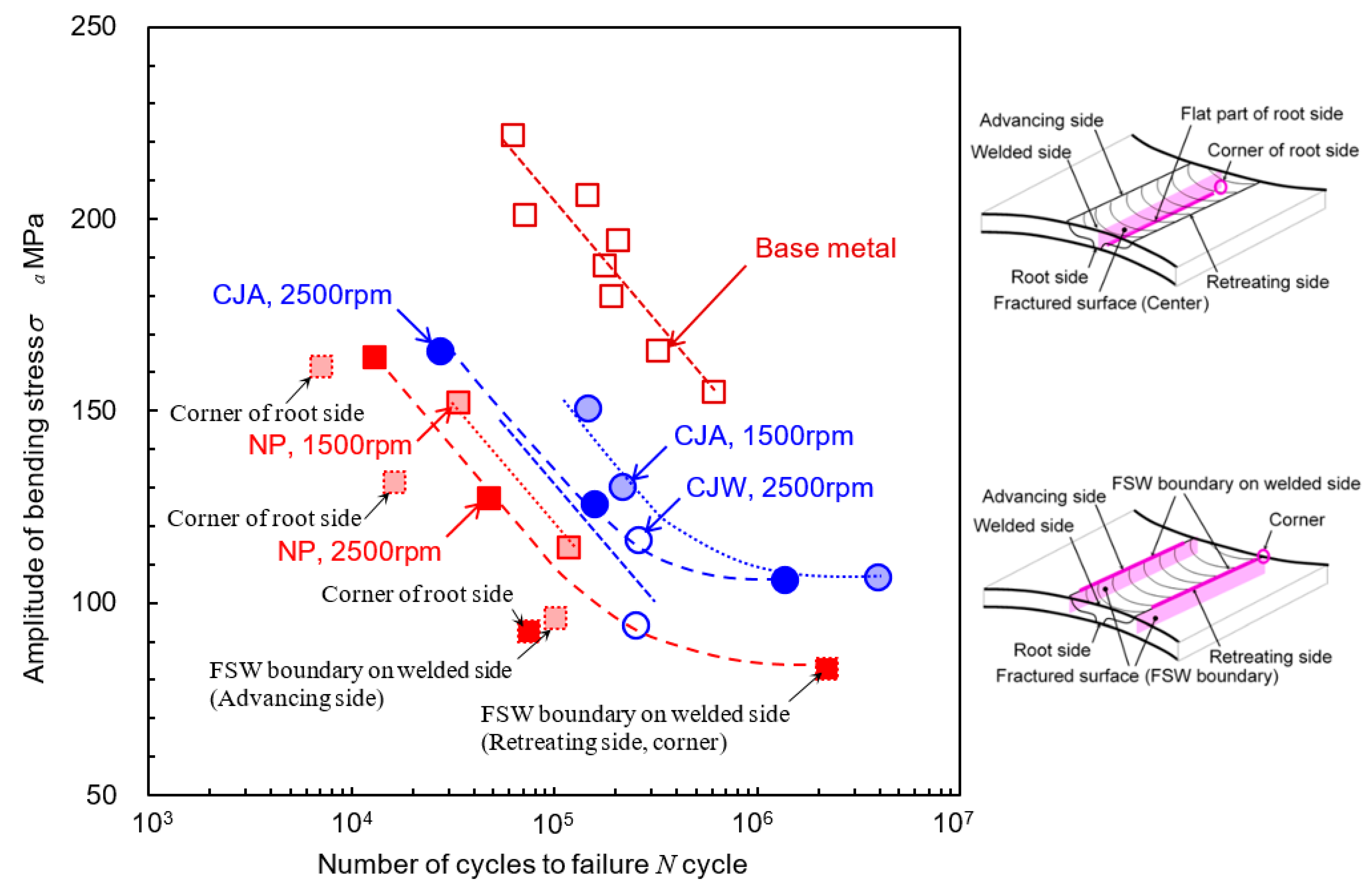
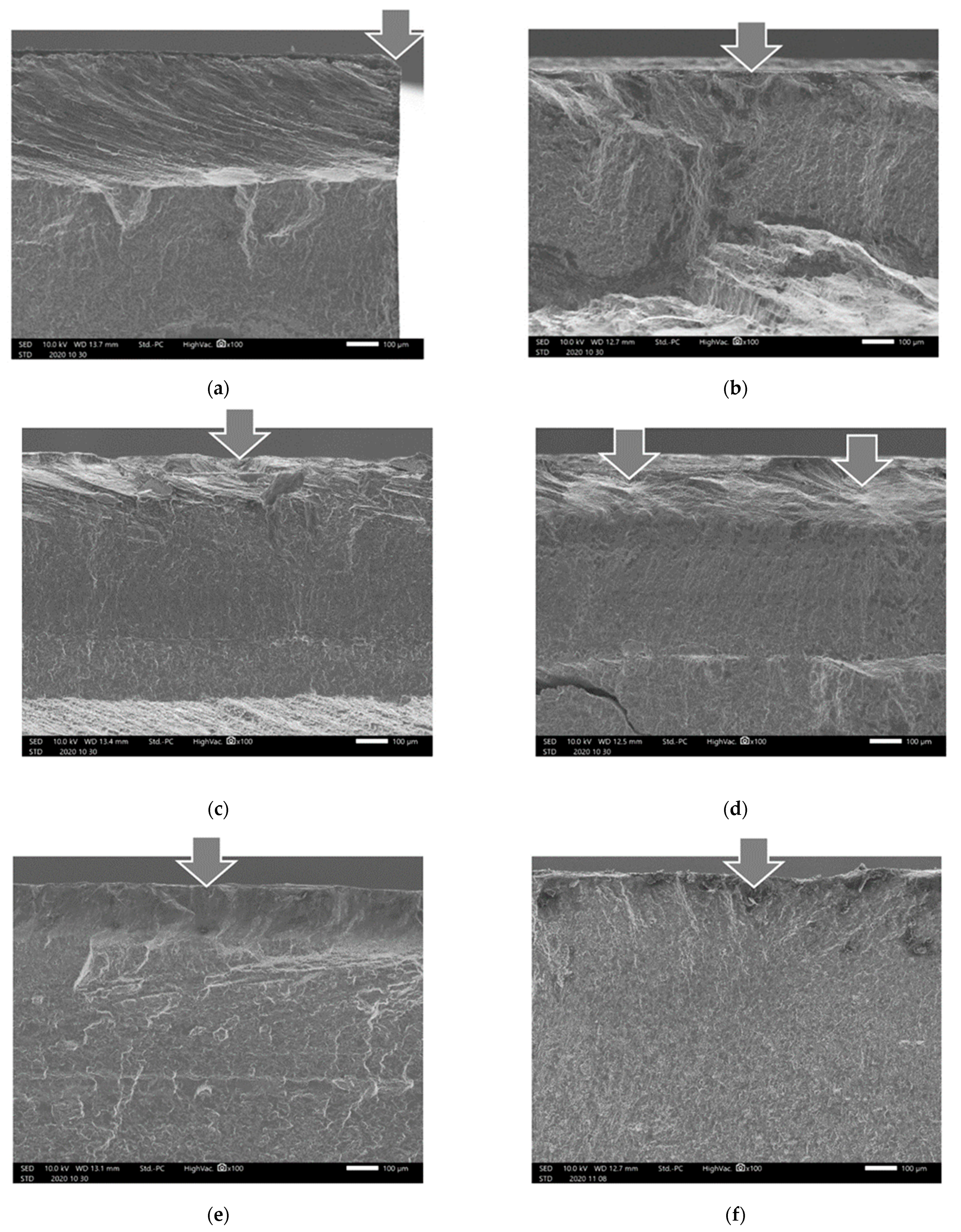
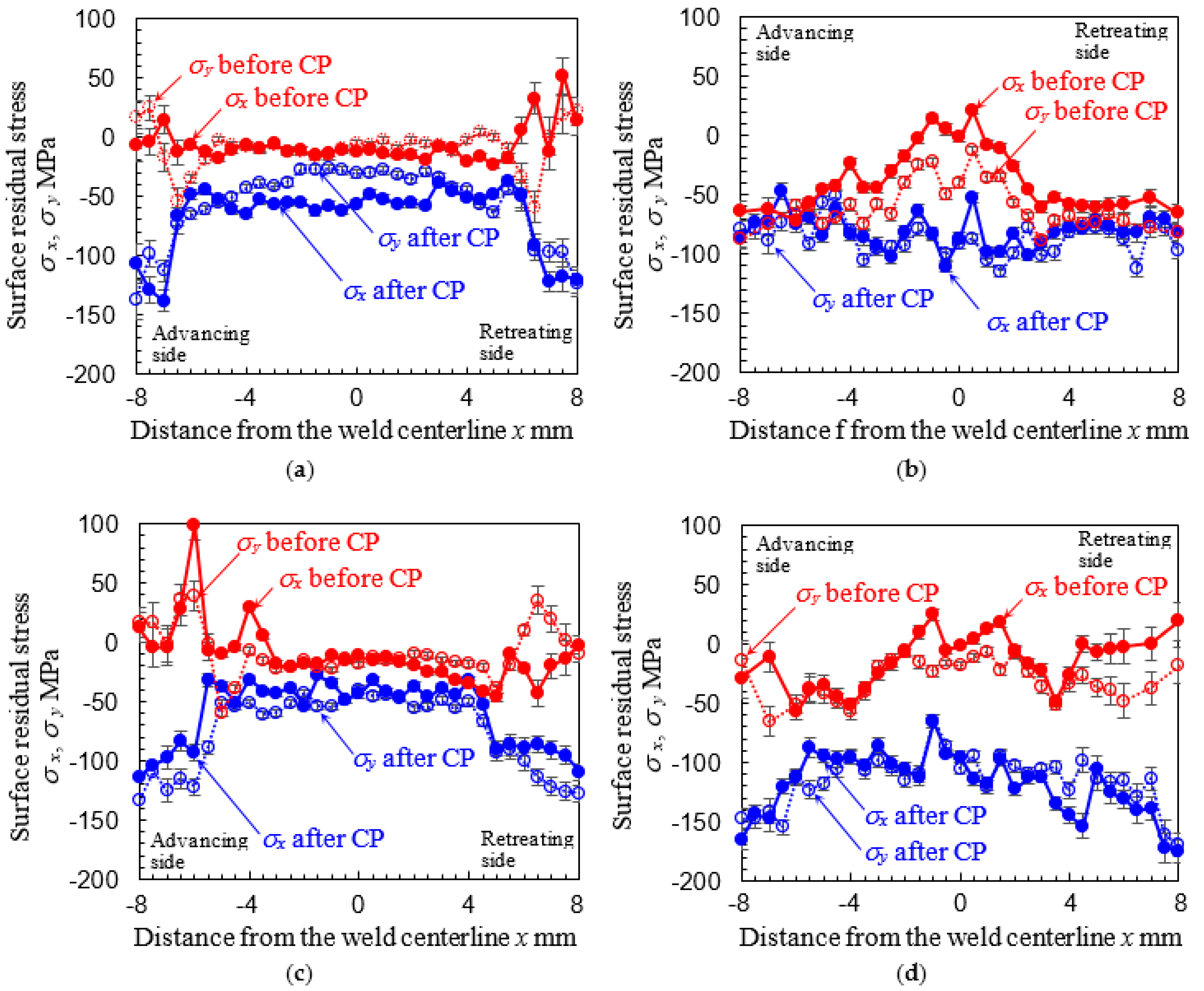
| Specimen | Peening | c2 or c3 | Nf150 (Cycle) (%) | σa at Nf = 105 (MPa) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base metal | NP | 514.7 | 7.45 × 105 | (100%) | 204.2 |
| FSW (ω = 1500 rpm) | NP | 431.2 | 3.38 × 104 | (4.54%) | 120.7 |
| CJA | 466.2 | 1.23 × 105 | (16.51%) | 155.7 | |
| FSW (ω = 2500 rpm) | NP | 418.6 | 2.10 × 104 | (2.82%) | 107.9 |
| CJA | 444.7 | 5.56 × 104 | (7.46%) | 134.2 | |
| CJW | 440.9 | 4.83 × 104 | (6.48%) | 130.4 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soyama, H.; Simoncini, M.; Cabibbo, M. Effect of Cavitation Peening on Fatigue Properties in Friction Stir Welded Aluminum Alloy AA5754. Metals 2021, 11, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010059
Soyama H, Simoncini M, Cabibbo M. Effect of Cavitation Peening on Fatigue Properties in Friction Stir Welded Aluminum Alloy AA5754. Metals. 2021; 11(1):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010059
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoyama, Hitoshi, Michela Simoncini, and Marcello Cabibbo. 2021. "Effect of Cavitation Peening on Fatigue Properties in Friction Stir Welded Aluminum Alloy AA5754" Metals 11, no. 1: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010059
APA StyleSoyama, H., Simoncini, M., & Cabibbo, M. (2021). Effect of Cavitation Peening on Fatigue Properties in Friction Stir Welded Aluminum Alloy AA5754. Metals, 11(1), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010059