Abstract
The study aimed to analyze the recovery period of the anodized 316L biomedical stainless steel (BSS) mini-implant through its implantation on femur of rabbit model. The 316L BSS mini-implant was modified by an electrochemical anodization approach with different voltages. The anodized samples were characterized via field-emission scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffractometry, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The biocompatibility was assessed by cell culture assay. The anodized mini-implant was implanted on rabbit’s femur then evaluated histologically after 4 and 8 weeks. Analytical results indicated that the topography of the anodized mini-implant at 5 V for 5 min consisted of a dual (micro/nano) porous structure. Oxide film of Cr2O3 was formed on the surface of anodized mini-implant after anodizing with 5 V for 5 min. In vitro cell culture assay revealed that fibroblast cells (NIH-3T3) on the anodized samples were more firmly attached as compared with the control sample. Moreover, histological analysis demonstrated that the anodized mini-implant improved bone recovering at 4 weeks after implantation. Thus, this study suggests that the anodized 316L BSS mini-implant could be a potential choice as anchorage device for effective and efficient orthodontic treatment.
1. Introduction
The concept of osseointegration, which was first introduced by Branemark et al., has led to increased interest in evaluating the use of dental implants not only as a replacement for missing teeth but also in improving orthodontic therapy as anchorage [1,2,3,4]. In general, dental implants are not feasible in orthodontic treatment due to their larger size; thus, they require a larger space which has the potential to damage the roots of the surrounding teeth and require complex surgical procedures [2,3,5]. Thus, mini-implants are present as a solution to overcome this problem [5,6,7]. In addition, mini-implants can be used for various prosthodontic treatments by stabilizing dentures and surgical guides in implant placement [4]. Mini-implants differ from dental implants from a physical point of view to their response to the surrounding tissue [5]. The temporary use of mini-implants allows this device to only rely on mechanical retention, partial osseointegration, and does not even require osseointegration until the mini-implant is removed [2,8,9,10,11]. However, good osseointegration is needed in certain conditions, such as inadequate bone conditions and in the case of diabetic patients [8,10].
In orthodontic treatment, the needed anchorage is helpful to avoid unwanted tooth movement [12,13]. Meanwhile, the presence of mini-implants during treatment has the potential to be lost due to fractures and loose screws [3,14]. Therefore, the stability of the mini-implant becomes an essential factor during orthodontic treatment. The modified mini-implant surface was reported more stable during its use [10]. The stability of the mini-implant is associated with its adaptation to the surrounding bone tissue or bone-implant contact [8]. In the meantime, the healing or recovery time before orthodontic loading affects the stability of the mini-implant [4]. The recovery time for the appropriate mini-implant is not clear. Immediately loading orthodontic force has been reported to destabilize the primary mini-implant [5]. Immediately and delay loading also revealed that no significant difference was found in its effect on the stability of the mini-implant [2]. Another study indicated that delayed loading would increase the stability of mini-implants [5]. However, appropriate recovery time is needed to make the orthodontic treatment effective and efficient [2].
It is well known that 316L biomedical stainless steel (BSS) has been extensively used in orthodontic mini-implants and orthopedic bone plates due to its various advantages including: lower cost, good fracture toughness, excellent manufacture properties, acceptable biocompatibility, and the most anti-corrosion when in direct contact with biological fluids [15,16,17]. Nevertheless, 316L BSS may still trigger inflammatory and immune responses due to local corrosion issues and the release of various ions such as Ni, Cr, and Mo [18]. Hence, numerous surface treatment techniques for 316L BSS such as ion implantation, anodization, thermal oxidation, chemical or physical vapor deposition, plasma treatment, laser, and polymer coating applications are performed to increase biocompatibility, which is the success of the biomaterial in its application [18,19,20]. Anodizing is quite a popular and widely used surface treatment method for 316L BSS because of its satisfactory advantages, including simple handling technology, cost-effectiveness, and great osseointegration potential through the growth of self-ordered tunneling nanotubes [19,21]. Meanwhile, our latest research [22] found that the anodized 316L BSS with a dual (micro/nano) porous surface exhibited great potential to enhance osteoblast-like cell adhesion ability. The anodized oxide surface played a key role to promote osteoblast-like cells ingrowth into the dual porous structure, which offered cell adhesion ability for increasing the stability of implants. Accordingly, the anodized 316L BSS with a dual (micro/nano) porous oxide layer is a promising biomaterial to be used as a mini-implant for orthodontic treatment applications. On the basis of the improvement of 316L BSS mini-implants, the present study further investigated the influence of anodization on fibroblasts behavior in the animal model and proposed the mechanism justifying the effect of anodization.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Preparation
In this study, the polished 316L BSS discs (Φ 15 mm × 1.2 mm) and machined mini-implants (Φ 2 mm × 10 mm) were adopted as substrates, and the chemical compositions of the 316L BSS are shown in Table 1. Before anodization, the substrates received ultrasonic cleaning in acetone, ethanol, and were rinsed in deionized water. Hereafter, a mixture solution of nitric acid (4%) and hydrofluoric acid (2%) was used to etch the substrates at 25 °C for 30 s, and the substrates were ultrasonically cleaned with deionized water. Subsequently, the substrates were modified with different voltages (0.5, 1, 3, and 5 V for 5 min) through anodization in 1 M sulfuric acid (98% H2SO4) and 1 M nitric acid (85% HNO3) solution at 25 °C under a constant current. The platinum counter electrode was adopted in the present treatment. The distance between the platinum electrode and substrate was 40 mm. For comparison, the unmodified 316L BSS was used as a control in this study.

Table 1.
Chemical compositions of the 316L BSS.
2.2. Surface and Microstructure Characterization
The surface morphology of the anodized mini-implant was observed using a JEOL JSM-6500F field-emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM, Tokyo, Japan) at accelerating voltage of 20 kV. The X-ray diffractometer (XRD; Rigaku 2200, Tokyo, Japan) supplied with Cu Kα1 was used to recognize the phase and crystallinity of the anodized mini-implant operated at voltage of 50 kV and a current of 250 mA. The diffraction peaks of XRD spectrum were matched with Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards (JCPDS) card. The chemical analysis was performed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS; PHI 1600, Waltham, MA, USA) with monochromatized Mg Kα radiation under voltage of 250 W, and angle analyzer of 54.7° parallel to the X-ray beam. The argon ion was employed to rid the sample surface at 3 kV for 5 min before analysis.
2.3. Cell Behavior Analysis
After previous study using an osteoblast cell line [22], the fibroblast cell line (NIH-3T3ATCC CRL-1658, Bioresource Collection and Research Center, Hsinchu, Taiwan) was applied to assess additional cellular responses of the investigated samples in the present study. Before analysis, the samples were sterilized by ethylene oxide (3M 8XL, 3M, Saint Paul, MN, USA). After the sterilization process, the sterilized samples were placed in 24-well plates. Subsequently, the cells (5 × 104/mL) cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM; Gibco, Taiwan) containing 10% fetal bovine serum and 0.1% antibiotic (penicillin/streptomycin) were seeded onto the investigated samples, and incubated at standard culture conditions with 5% CO2 and temperature of 37 °C for 12 h and 24 h, respectively. Hereafter, the cells on the investigated samples were fixed in 2% glutaraldehyde at 25 °C for 1 h, washed twice in phosphate buffer saline, and dried in an oven at 30 °C. The attachment and morphology of NIH-3T3 cells on the investigated samples were analyzed via the JEOL JSM-6500F FE-SEM operated at 25 kV.
2.4. Implantation Procedure
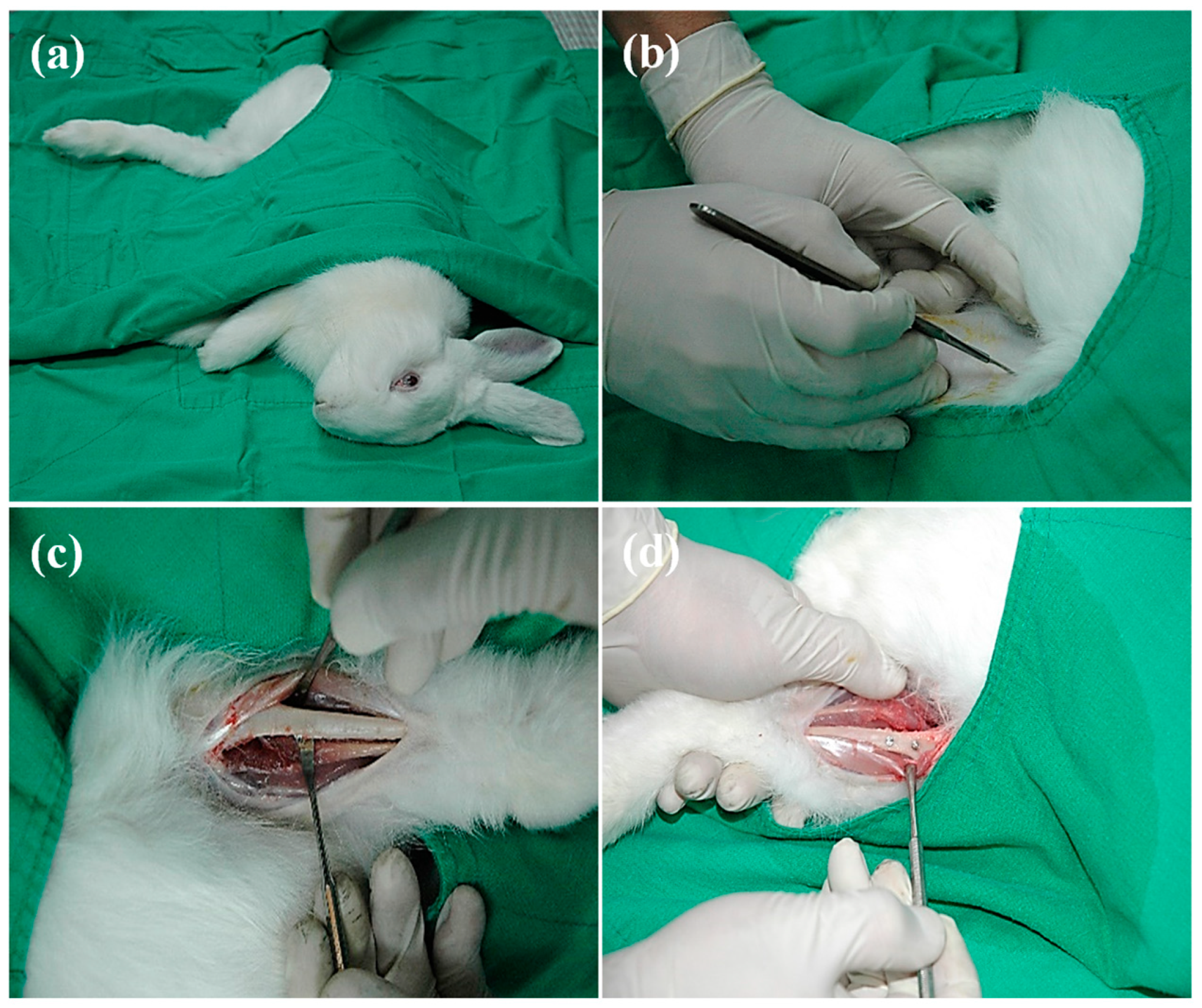
All protocols involving animals were in accordance with the guidelines of the advisory committee for laboratory animal center of Taipei medical university (project identification code: LAC-2013-0180). Studies were carried out on 12 male New Zealand white rabbits with a mean weight of 3.5 ± 0.5 kg from the Livestock Research Institute (Tainan, Taiwan). Rabbits were kept under controlled environmental conditions (22 ± 2 °C, 75 ± 5% relative humidity, 12-h dark/12-h light cycle) and had free access to standard rabbit chow and water. The animals were randomly separated into two groups according to the implant material: 6 rabbits for anodized 316L mini-implants and 6 rabbits for control mini-implants. These two material groups were further divided into different subgroups with an implantation time of 4 and 8 weeks. Surgery was performed under general anesthesia (Figure 1a), which was initiated with ketamine hydrochloride (10 mg kg−1, Ketamin 10%, CP-Pharma Partner, Burgdorf, Germany) and medetomidin (0.125 mg kg−1, Domito, Pfizer Pharma, Berlin, Germany) and maintained with isoflurane (2.5–3.5 vol.% oxygen, 0.5–1.0 L min−1, Isoba, Essex Pharma, Munich, Germany). The rabbits were anaesthetized with 35 mg/kg Ketamin and 5 mg/kg Xsilazin. The surgical sites were disinfected with povidone iodine and were injected with local anesthesia (lidocaine 2% + 1:100,000 epinephrine). A longitudinal incision was performed (Figure 1b), subcutaneous tissue was dissected to expose the left femur bone (Figure 1c), and implanted with anodized implant and control-implant (Figure 1d). The wound was dressed at the end of the procedure. Cephalotin (40 mg/kg) was given 30 min preoperatively and intramuscularly twice daily for 48 h postoperatively.
Figure 1.
Implantation procedure in a rabbit model: (a) general anesthesia; (b) longitudinal incision; (c) tissue dissection, and (d) the femur area implanted with the investigated mini-implants.
2.5. Hystopathological Evaluation
The rabbits were euthanized with an overdose of intravenous Pentothal Sodium 100 mg/kg at week 4 and week 8 after implantation. The femurs and mini-implants were removed and dissected free of soft tissue. The specimens were rinsed in distilled water, and immediately fixed with 10% formalin for 2 weeks. The fixed-specimens were decalcified with Plank Rychlo decalcifier (Muto Pure Chemicals Co., LTD, Tokyo, Japan) for 2 weeks. The decalcified-specimens were washed in distilled water, dehydrated, embedded, trimmed, stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H & E), and examined via a digital image capture pathology scanner (Aperio CS model, Leica Biosystems, Bualo Grove, IL, USA) under different magnifications.
3. Results
3.1. Microstructural and Chemical Bonding Features
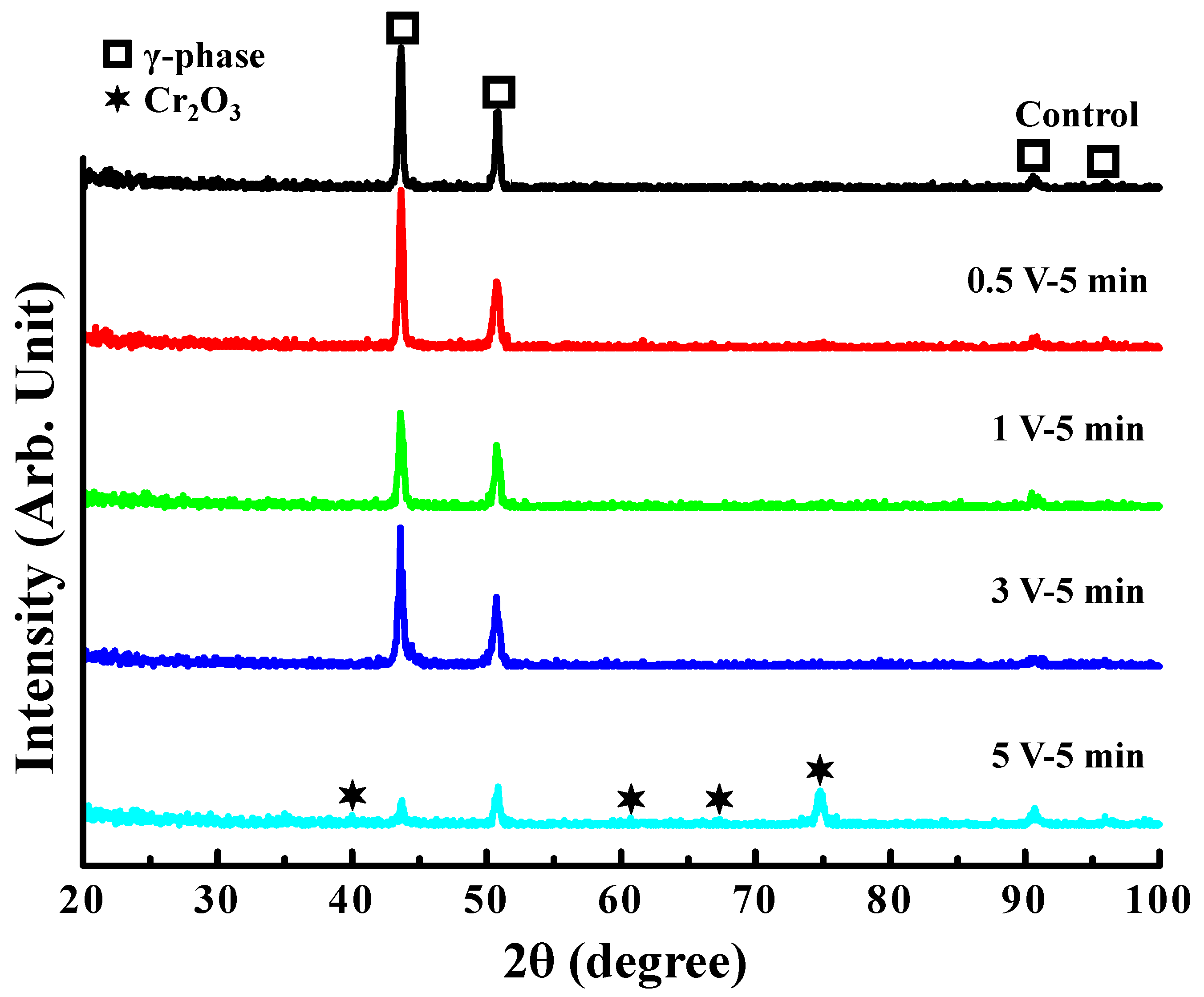
Figure 2 presents the XRD spectra for control and anodized sample at various modified voltages for 5 min. Clearly, the control and anodized samples (0.5 V, 1 V, and 3 V) presented the typical reflection peaks of austenite (γ) phase. No other precipitate compounds were found on the surface of these investigated samples. However, it was found that the reflection peaks corresponding to chromium oxide (Cr2O3) were detected on the anodized sample at 5 V for 5 min.
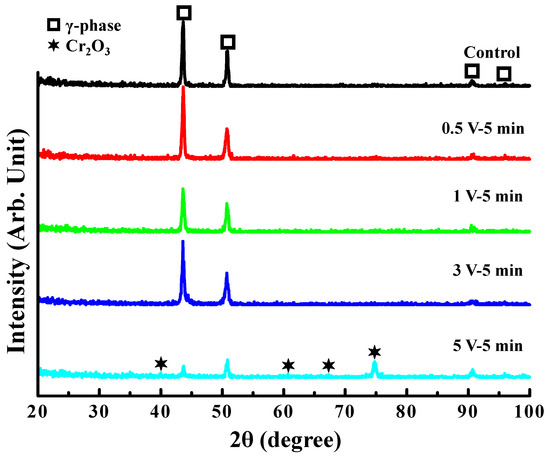
Figure 2.
The XRD spectra of control and anodized sample at 0.5, 1, 3, and 5 V for 5 min.
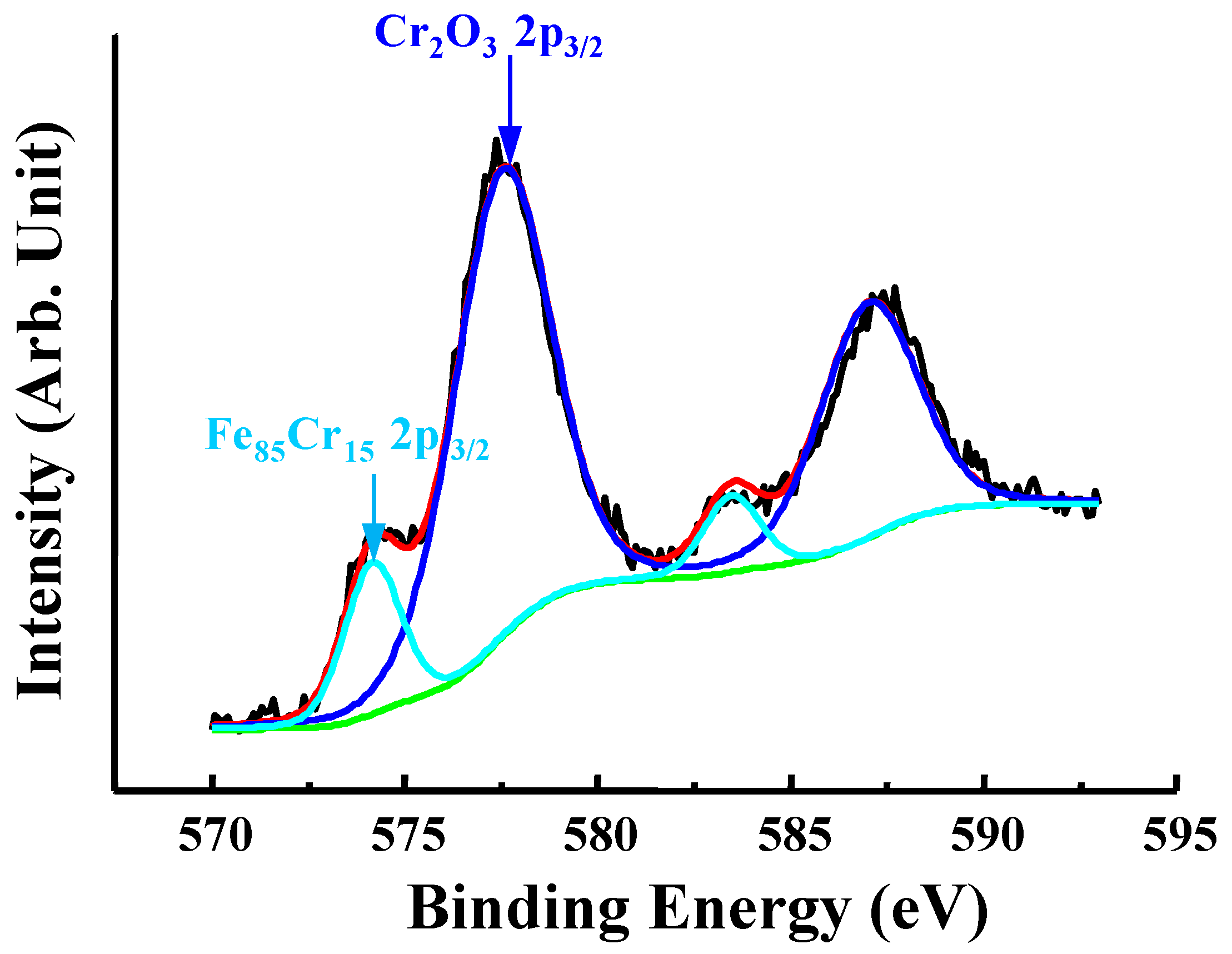
Figure 3 exhibits the XPS spectrum of Cr 2p3/2 taken from the anodized sample at 5 V for 5 min. Apparently, the main composition that formed after anodizing was chromium oxide. The presence of oxygen atoms and molecules also could be seen at interstitial sites refers to an emission peak of about 577.5 eV. It is indicated that enhancement of Cr-O bonding is formed through anodization following different voltages. Hence, it proved that the Cr2O3 oxide layer was formed on the surface of anodized sample at 5 V for 5 min. Accordingly, the microstructure of the surface of anodized sample with a voltage of 5 V was composed of γ and Cr2O3 phases.
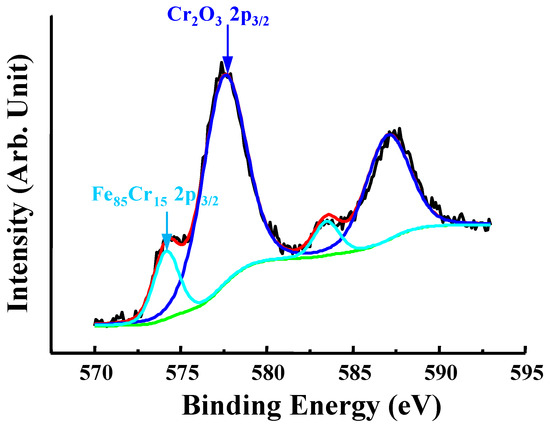
Figure 3.
The XPS spectrum of Cr 2p3/2 taken from the anodized sample at 5 V for 5 min.
3.2. Morphology of the Potential Anodized Mini-Implant
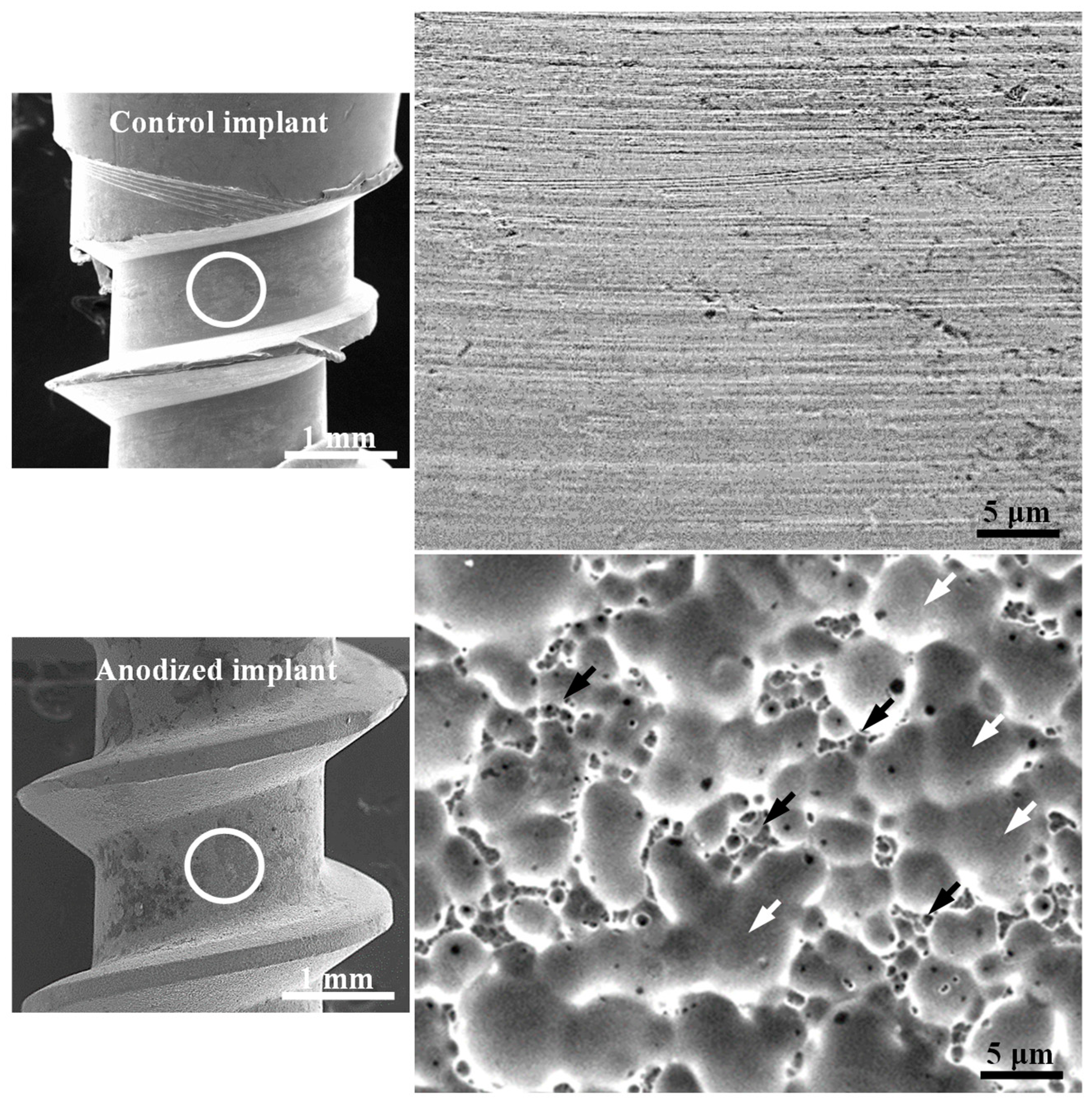
Figure 4 depicts the FE-SEM micrographs of the control mini-implant and anodized mini-implant at 5 V for 5 min. Obviously, the control implant without modification exhibited regular machining grooves. Meanwhile, the anodized surface of the mini-implant at current voltage showed the formation of a dual (micro/nano) porous oxide surface.
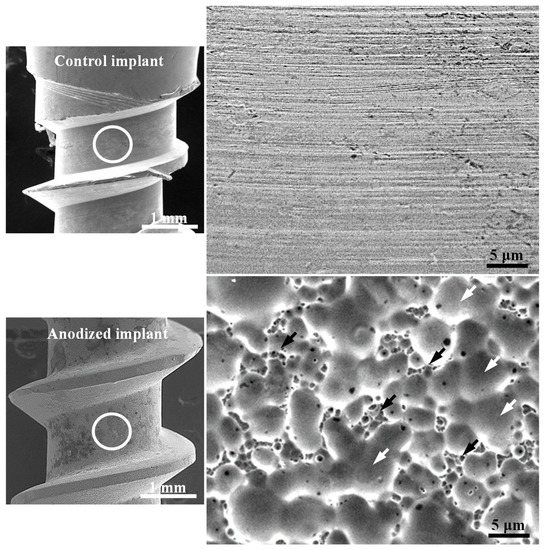
Figure 4.
FE-SEM micrographs of the control mini-implant and anodized mini-implant at 5 V for 5 min (the higher magnification micrographs were taken from the investigated implants marked as white circular area. The white and black arrows represent micropores and nanopores, respectively).
3.3. Cell Adhesion and Response
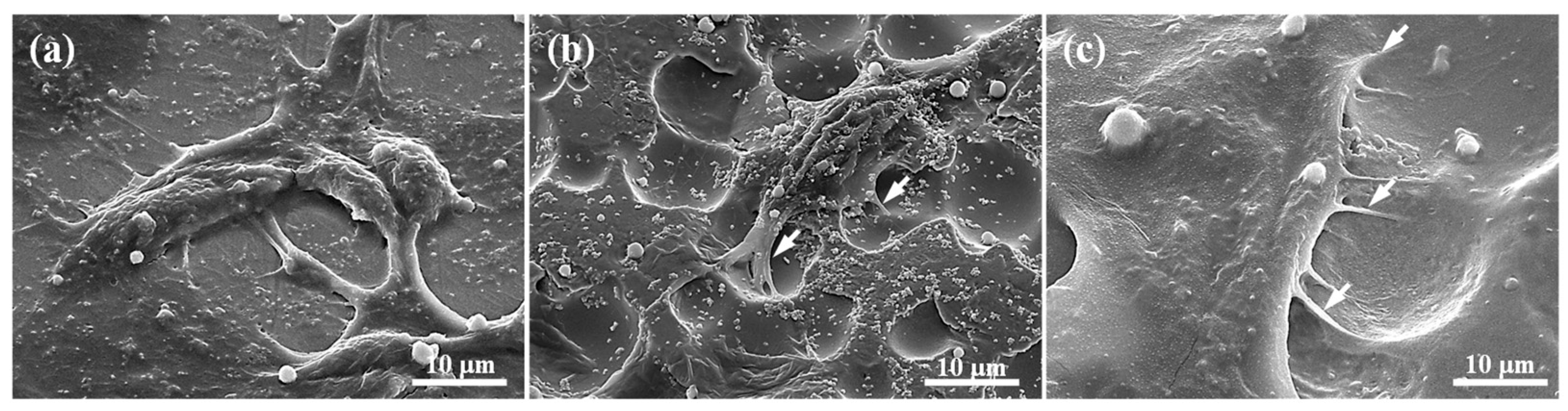
Figure 5 illustrates the FE-SEM micrographs of fibroblast cell morphology on control and anodized sample at higher modifying voltages. It is clearly seen that the fibroblast cells grow along the surface of the control and anodized samples after culturing for 24 h. However, cells appeared to be more well distributed with a strong flat patch on the anodized surface. Moreover, the filopodia of cells not only adhered flat, but also tightly grabbed the porous structure as pointed by arrows. This characteristic of cell adhesion and response revealed that the anodized surface possessed good biocompatibility.

Figure 5.
The FE-SEM micrographs of fibroblast cell morphology for 24 h incubation on the investigated samples: (a) control, (b) anodized at 3 V for 5 min, and (c) anodized at 5 V for 5 min.
3.4. Bone Healing and Regeneration Characteristic
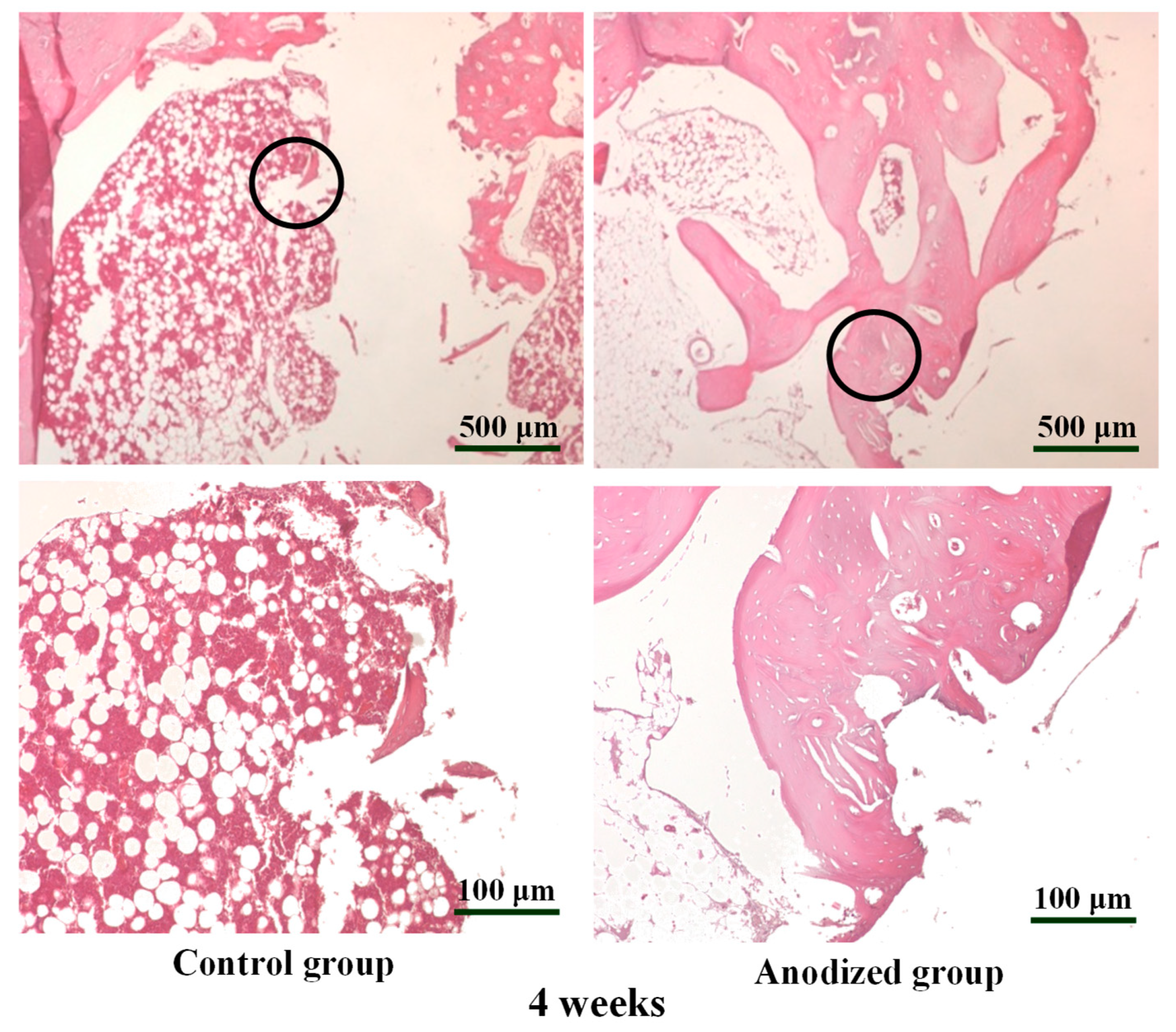
Figure 6 displays the H&E-stained bone section images of the control and anodized mini-implant (5 V) after 4 weeks from implantation. Obviously, the bone mineral density of control group exhibited a loosening bone tissue structure and anodized mini-implant group showed that the bone tissue became slightly denser in the adjacent implants.
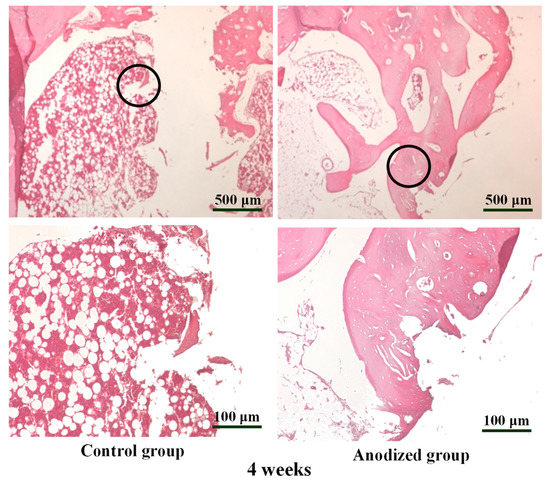
Figure 6.
The H&E-stained bone section images of the control and anodized mini-implant (5 V) after 4 weeks from implantation under different magnifications (the higher magnification images were taken from the sample marked as black circular area).
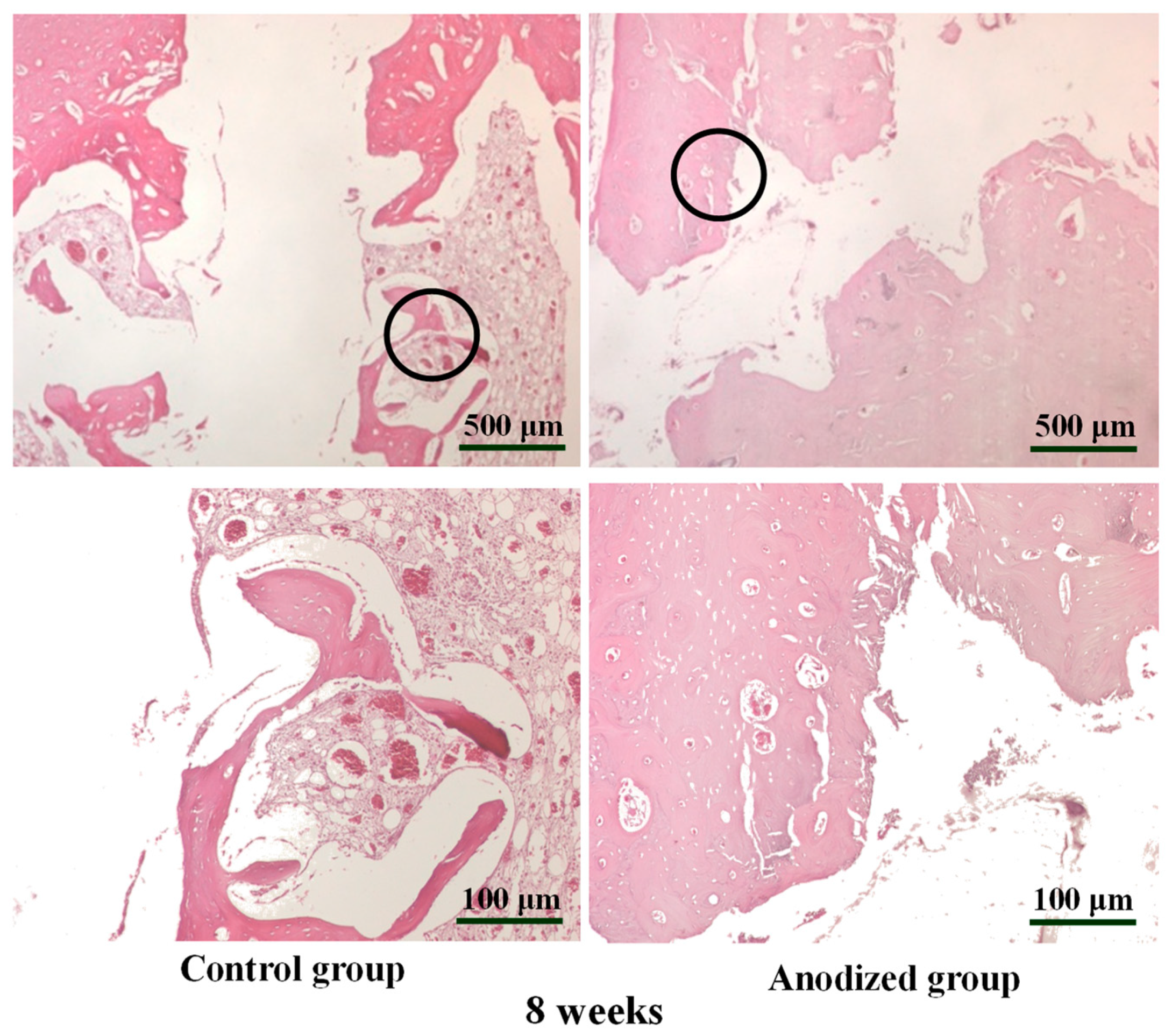
Eight weeks after implantation (Figure 7) clearly presented that the osseointegration of the control mini-implant group was similar to the situation in Figure 6. Meanwhile, the osseointegration of bone tissue in the surface anodized mini-implant group is higher than that in the control group after 8 weeks from implantation.
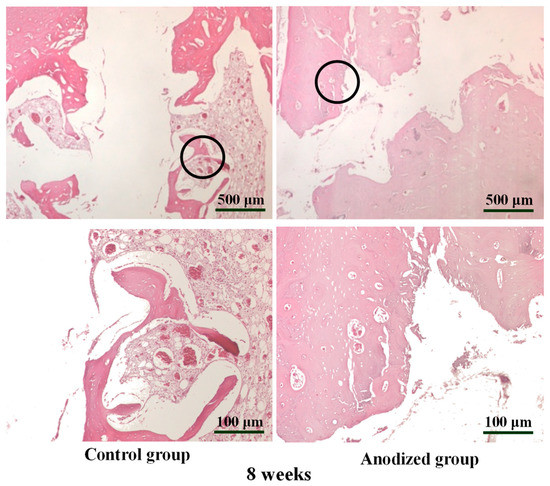
Figure 7.
The H&E-stained bone section images of the control and anodized mini-implant (5 V) after 8 weeks from implantation under different magnifications (the higher magnification images were taken from the sample marked as black circular area).
4. Discussion
The success of the mini-implant depends on its stability which is related to various mechanical factors such as design and dimensions, as well as biological factors such as bone condition and recovery time before orthodontic loading [2]. Although mini-implants without surface treatment were launched and also showed success in the application, the survival rate of mini-implants with surface modification was found to be higher than without modification [10,23,24,25]. In this study, anodization treated mini-implant produced a surface with a dual porous structure, which was able to improve the stability of the mini-implant by enhancing bone-implant contact [22,26]. The porosity of the mini-implant surface is also able to increase the resistance to fracture when force loading is applied [8].
Mini-implants are exposed to a potentially corrosive environment when inserted into the oral cavity [27,28]. Numerous internal factors such as the quality and quantity of saliva, as well as external factors such as the acidity of the food and beverages consumed by the patient, will induce the release of metal ions which have an impact on the toxicity and biocompatibility of the mini-implant [26,27]. The mini-implant formed from 316L BSS subjected to anodization with 5 V for 5 min produced a passive film on the stainless-steel surface, which is more resistant to corrosion [28,29,30]. The low carbon property of 316L BSS makes it resistant to corrosion, especially when exposed to chlorine or similar to physiological saline, but not to chloride ions and reduced sulfur compounds [30]. The results of fibroblast cell culture on anodized samples showed that the connective tissue was biocompatible, indicating that the wound healing process was not hindered when fibroblasts were activated in the inflammatory and proliferative phases [31,32,33]. In a recent study, the anodized 316L BSS also showed biocompatibility when cultured with osteoblast cells, which affected implant stability by forming partial osseointegration [22,26]. Cell adhesion and proliferation are closely related to the surface roughness obtained from the surface treated [22,26]. In this study, fibroblast cells were able to adhere and proliferate on the surface of the anodized samples. These results can be attributed to the effect of dual porous structure formation on the anodized surface, which produced the cell ingrowth into the dual porous structure for promoting cell viability [22,34].
Dental implants are closely related to bone remodeling, while bone in-growth or bone remodeling is a complex process involving not only a single cell but also several cell types in bone such as osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and fibroblasts [35]. At the beginning of bone regeneration, fibroblasts are abundant and accumulate around the osteoblasts [35]. Fibroblasts also produce a lot of extracellular matrix protein, which plays a role in regenerating bone tissue [35,36]. Moreover, fibroblasts play an important role in immune regulation and inflammatory response during wound healing, while wound healing is the first step in osseointegration [36]. Since fibroblast have many functions covering several important processes in promoting osseointegration, the present study used the fibroblast NIH-3T3 cell line for biocompatibility evaluation.
Based on the histopathological H&E staining results in this study, the anodized mini-implant has better osseointegration properties, and this phenomenon may begin at four weeks, which indicates a shorter wound healing period after implantation [37,38,39,40]. The occurrence of wound healing will support the stability of the mini-implant [1]. Faster wound healing allows for quicker loading force in the stabilized mini-implant, which leads to a reduction in orthodontic treatment time [2]. Therefore, an anodized mini-implant is a satisfactory alternative to be used as an anchorage that allows orthodontic treatment more effective and efficient. As discussed above, further experiments should be carried out to validate the present findings. Our research team is currently conducting more experiments on this study. The detailed research results on the adhesion, proliferation, and bonding the tissue to the implant can be presented in the second part of the research soon.
5. Conclusions
The dual (micro/nano) porous structure could be generated on the 316L BSS mini- implant surface via the anodization with a voltage of 5 V. The cell response and in vivo testing results also demonstrated that the anodized surface with dual porous structure exhibited great potential to enhance cell adhesion ability and rapid recovery. Accordingly, the anodized 316L BSS mini-implant can promote the survival rate during the use as anchorage when tooth movement leads to successful orthodontic treatment.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, Y.-C.C.; Investigation, Y.-C.C. and W.-C.H.; Data curation, H.-Y.T.; Methodology, W.-C.L.; Supervision, T.S.; Resources, C.-H.L.; Validation, B.-H.H.; Writing—review and editing, M.-S.H. and K.-L.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The protocols for animal experiments were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee for Taipei Medical University under a project identification code of LAC-2013-0180.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Zheng, L.; Tang, T. Osseointegration of orthodontic micro-screws after immediate and early loading. Angle Orthod. 2010, 80, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oltramari-Navarro, P.V.; Navarro, R.L.; Henriques, J.F.; Cestari, T.M.; Francischone, C.E.; Taga, R.; McNamara, J.A., Jr. The impact of healing time before loading on orthodontic mini-implant stability: A histomorphometric study in minipigs. Arch. Oral Biol. 2013, 58, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, Z.; Wei, X.; Tang, T. The effect of varying healing times on orthodontic mini-implant stability: A microscopic computerized tomographic and biomechanical analysis. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2011, 112, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaliwal, J.S.; Albuquerque, R.F., Jr.; Murshed, M.; Feine, J.S. Osseointegration of standard and mini dental implants: A histomorphometric comparison. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2017, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramazanzadeh, B.A.; Fatemi, K.; Dehghani, M.; Mohtasham, N.; Jahanbin, A.; Sadeghian, H. Effect of healing time on bone-implant contact of orthodontic micro-implants: A histologic study. ISRN Dent. 2014, 2014, 179037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baumgaertel, S.; Razavi, M.R.; Hans, M.G. Mini-implant anchorage for the orthodontic practitioner. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 133, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchter, A.; Wiechmann, D.; Koerdt, S.; Wiesmann, H.P.; Piffko, J.; Meyer, U. Load-related implant reaction of mini-implants used for orthodontic anchorage. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2005, 16, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consolaro, A.; Romano, F.L. Reasons for mini-implants failure: Choosing installation site should be valued! Dental Press J. Orthod. 2014, 19, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynders, R.; Ronchi, L.; Bipat, S. Mini-implants in orthodontics: A systematic review of the literature. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2009, 135, 564.e1–564.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, N.H.; Kim, E.Y.; Paek, J.; Kook, Y.A.; Jeong, D.M.; Cho, I.S.; Nelson, G. Evaluation of stability of surface-treated mini-implants in diabetic rabbits. Int. J. Dent. 2014, 2014, 838356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xie, J. Comparison of the effects of mini-implant and traditional anchorage on patients with maxillary dentoalveolar protrusion. Angle Orthod. 2017, 87, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousley, R.R.; Sandler, P.J. Advances in orthodontic anchorage with the use of mini-implant techniques. Br. Dental J. 2015, 218, E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Inami, T.; Ito, K.; Kasai, K.; Tanimoto, Y. Mini-implants in the anchorage armamentarium: New paradigms in the orthodontics. Int. J. Biomater. 2012, 2012, 394121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.C.; Chang, H.H.; Chang, J.Z.; Lai, H.H.; Lu, S.C.; Chen, Y.J. Revisiting the stability of mini-implants used for orthodontic anchorage. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2015, 114, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikarakara, E.; Naher, S.; Brabazon, D. Process mapping of laser surface modification of AISI 316L stainless steel for biomedical applications. Appl. Phys. A 2010, 101, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinesi, M.; Bruni, S.; Stio, M.; Treves, C.; Bacci, T.; Borgioli, F. Biocompatibility evaluation of surface-treated AISI 316L austenitic stainless steel in human cell cultures. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 80, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stio, M.; Martinesi, M.; Treves, C.; Borgioli, F. Cultures and co-cultures of human blood mononuclear cells and endothelial cells for the biocompatibility assessment of surface modified AISI 316L austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 69, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojarad Shafiee, B.; Torkaman, R.; Mahmoudi, M.; Emadi, R.; Derakhshan, M.; Karamian, E.; Tavangarian, F. Surface modification of 316L SS implants by applying bioglass/gelatin/polycaprolactone composite coatings for biomedical applications. Coatings 2020, 10, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandracci, P.; Mussano, F.; Rivolo, P.; Carossa, S. Surface Treatments and functional coatings for biocompatibility Improvement and bacterial adhesion reduction in dental implantology. Coatings 2016, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocijan, A.; Conradi, M.; Hocevar, M. The influence of surface wettability and topography on the bioactivity of TiO2/Epoxy coatings on AISI 316L stainless steel. Materials 2019, 12, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipal, J.; Lee, T.C.; Koshy, P.; Abdullah, H.Z.; Idris, M.I. Evolution of anodised titanium for implant applications. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.-J.; Wu, C.-Y.; Huang, B.-H.; Tsai, C.-H.; Saito, T.; Ou, K.-L.; Chuo, Y.-C.; Lin, K.-L.; Peng, P.-W. Surface characteristics and cell adhesion behaviors of the anodized biomedical stainless steel. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kook, Y.A.; Jeong, D.M.; Chung, K.R.; Nelson, G. Resistance to immediate orthodontic loading of surface-treated mini-implants. Angle Orthod. 2010, 80, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.J.; Cho, I.S.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, T.W. Rotational resistance of surface-treated mini-implants. Angle Orthod. 2009, 79, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Pliska, A.; Busch, C.; Wilmes, B.; Wolf, M.; Drescher, D. Efficacy of orthodontic mini implants for en masse retraction in the maxilla: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2018, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, R.C.; Basting, R.T. In vitro study of human osteoblast proliferation and morphology on orthodontic mini-implants. Angle Orthod. 2015, 85, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, C.B.; Segurado, M.N.; Dorta, M.C.; Dias, F.R.; Lenza, M.G.; Lenza, M.A. Evaluation of cytotoxicity and corrosion resistance of orthodontic mini-implants. Dental Press J. Orthod. 2016, 21, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- do Nascimento, C.A.; Barbosa, J.A.; Montalli, V.A.M.; Micheletti, F.; Milani, R.; Pereira, V.; Caldeira, L.; Basting, R.T. Corrosion and micromorphological analysis of temporary stainless steel and titanium alloy anchorage devices. J. Bio- Tribo-Corros. 2020, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Su, H.; Dong, C.; Li, X. Passivation and electrochemical behavior of 316L stainless steel in chlorinated simulated concrete pore solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 400, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safiya, S.; Manjunath, G. Mini-implant materials: An overview. IOSR J. Dental Med. Sci. 2013, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DesJardin- Park, H.E.; Foster, D.S.; Longaker, M.T. Fibroblasts and wound healing: An update. Regen. Med. 2018, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, S. The role of the fibroblast in wound contraction and healing. Wounds 2007, 3, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Bainbridge, P. Wound healing and the role of fibroblasts. J. Wound Care 2018, 22, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.H.; Lu, Y.J.; Lan, W.C.; Ruslin, M.; Lin, H.Y.; Ou, K.L.; Saito, T.; Tsai, H.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Cho, Y.C.; et al. Surface properties and biocompatibility of anodized titanium with a potential pretreatment for biomedical applications. Metals 2021, 11, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, A.; Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xia, D.; Mao, H.; Zhao, J. Osteoblast/fibroblast coculture derived bioactive ECM with unique matrisome profile facilitates bone regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claeys, L.; Bravenboer, N.; Eekhoff, E.M.W.; Micha, D. Human fibroblasts as a model for the study of bone disorders. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Ferguson, S.J.; Beutler, T.; Cochran, D.L.; Sittig, C.; Hirt, H.P.; Buser, D. Biomechanical comparison of the sandblasted and acid-etched and the machined and acid-etched titanium surface for dental implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 60, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D.; Broggini, N.; Wieland, M.; Schenk, R.K.; Denzer, A.J.; Cochran, D.L.; Hoffmann, B.; Lussi, A.; Steinemann, S.G. Enhanced bone apposition to a chemically modified SLA titanium surface. J. Dental Res. 2004, 83, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D.N.; Nydegger, T.; Oxland, T.; Cochran, D.L.; Schenk, R.K.; Hirt, H.P.; Snetivy, D.; Nolte, L.-P. Interface shear strength of titanium implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched surface: A biomechanical study in the maxilla of miniature pigs. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 45, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmukler-Moncler, S.; Perrin, D.; Ahossi, V.; Magnin, G.; Bernard, J.P. Biological properties of acid etched titanium implants: Effect of sandblasting on bone anchorage. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2004, 11, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).