Effect of Mn Substitution Fe on the Formability and Magnetic Properties of Amorphous Fe88Zr8B4 Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
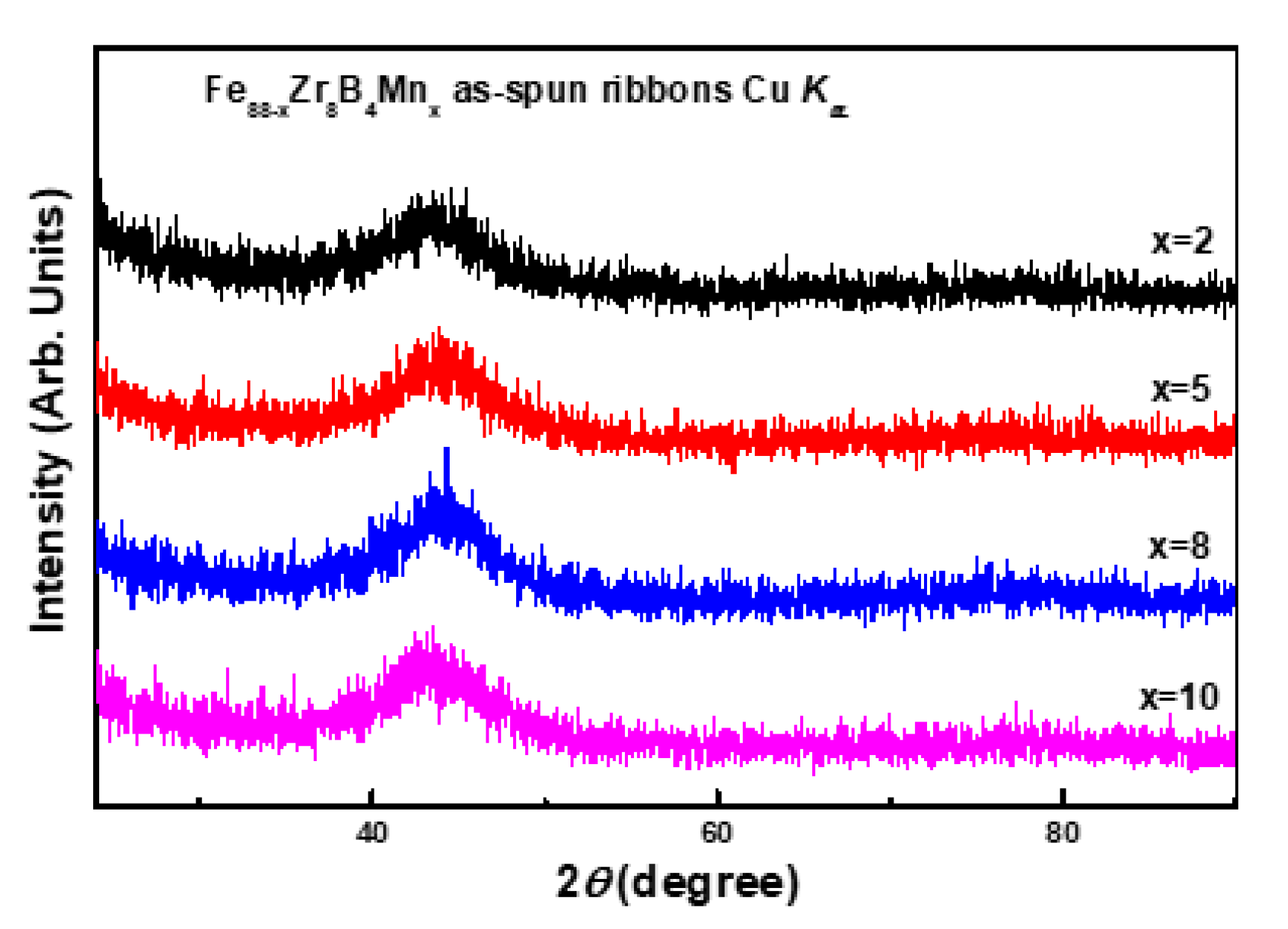
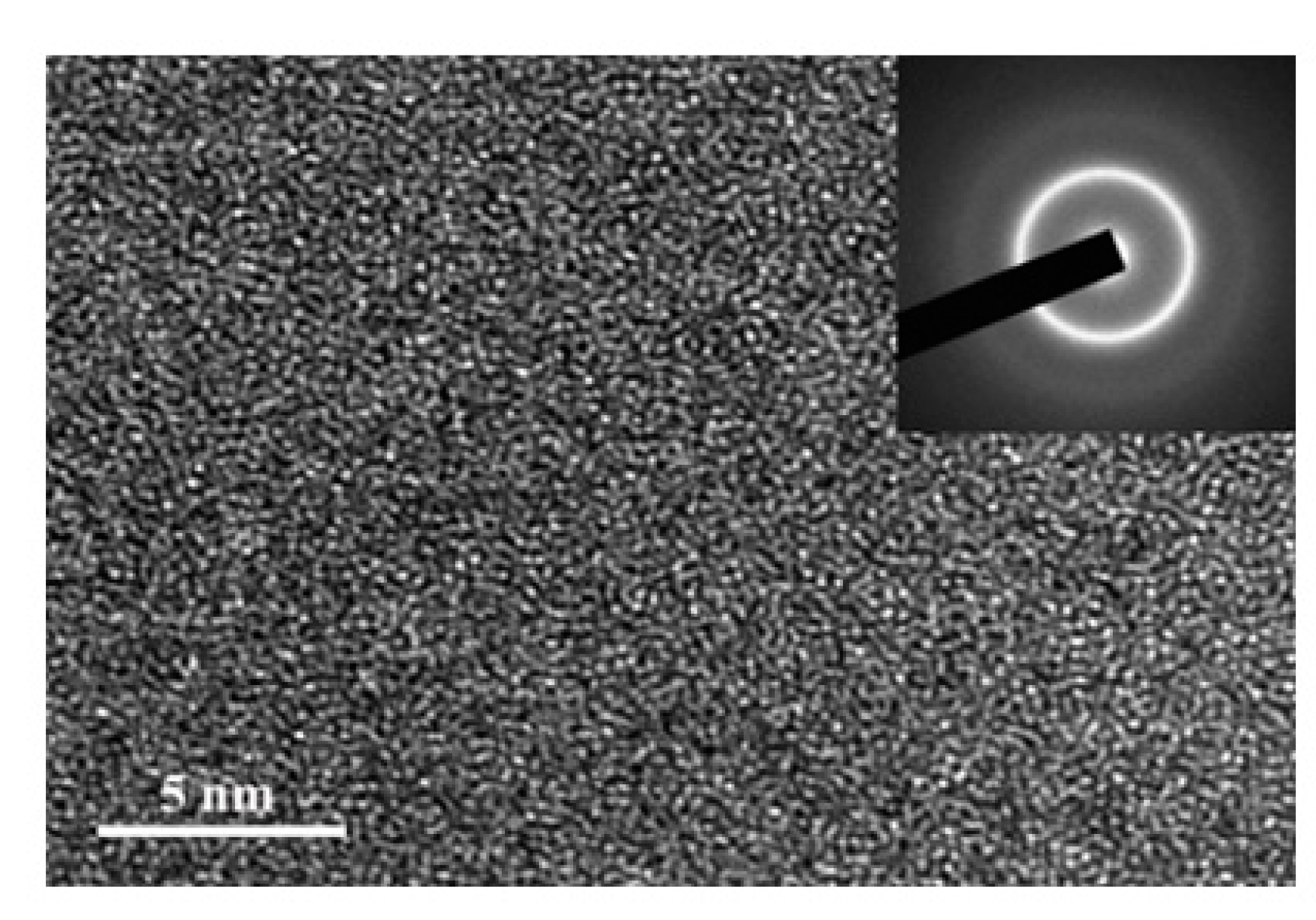
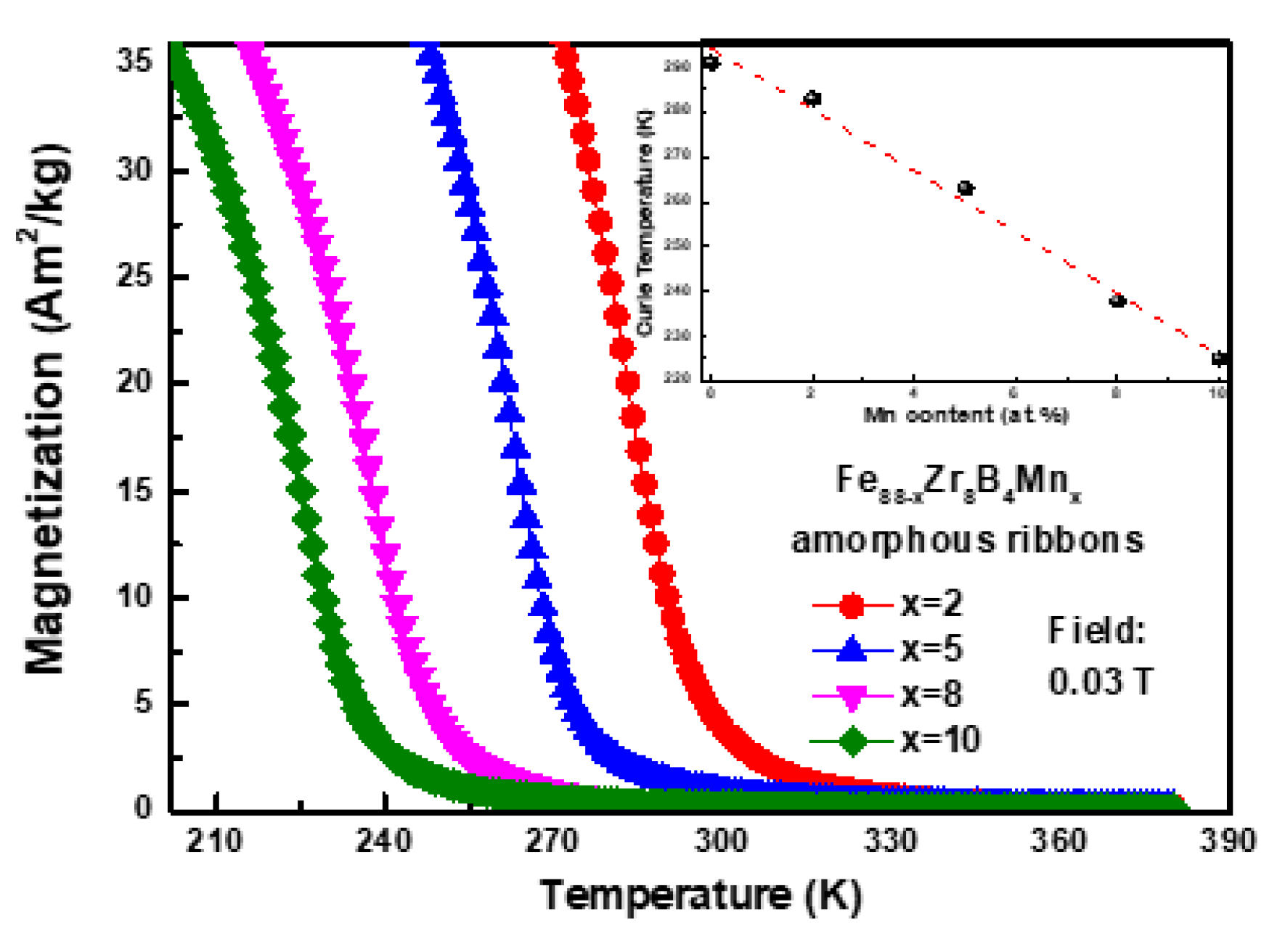
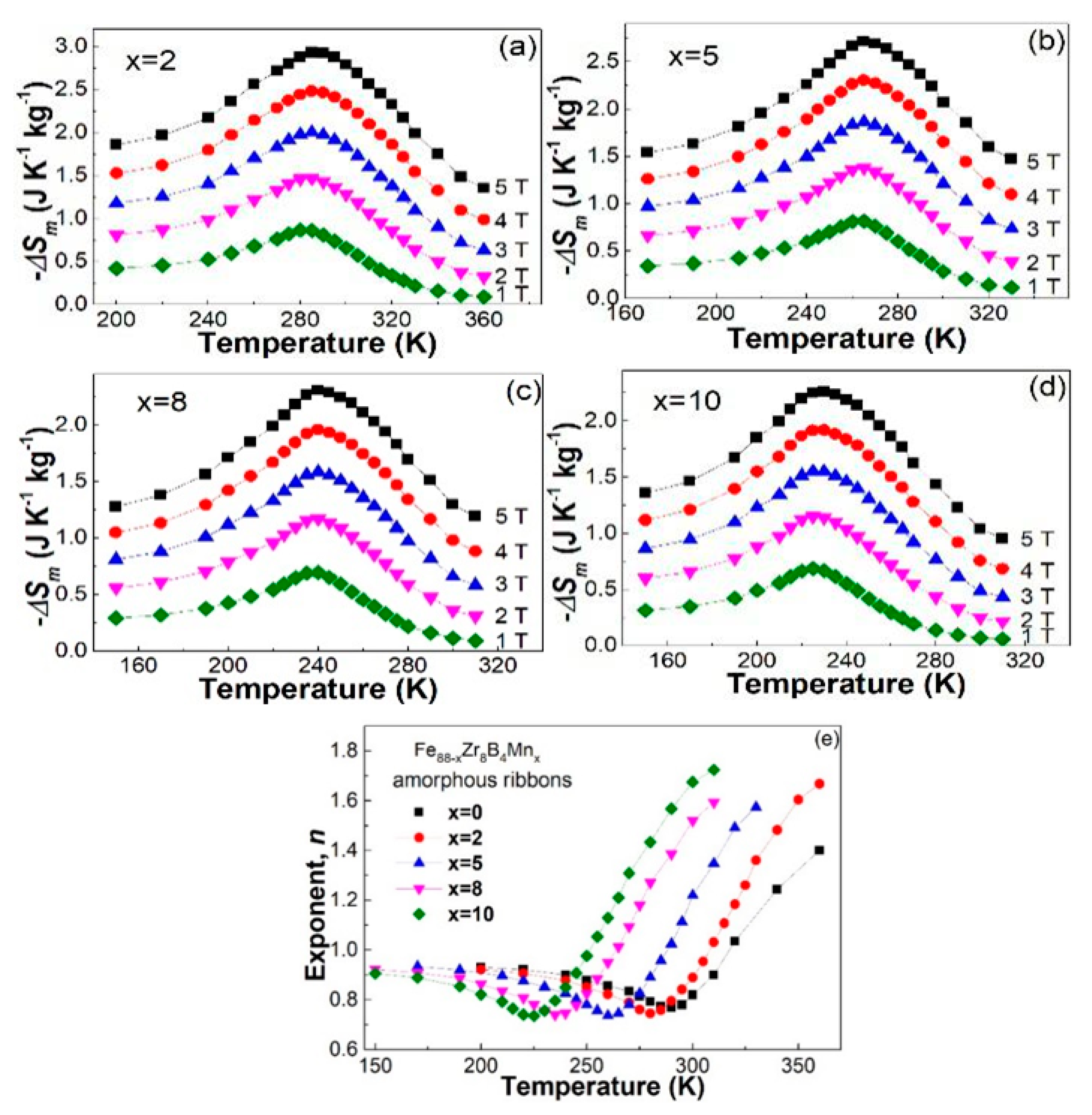
3.1. Descriptive of the Experimental Results
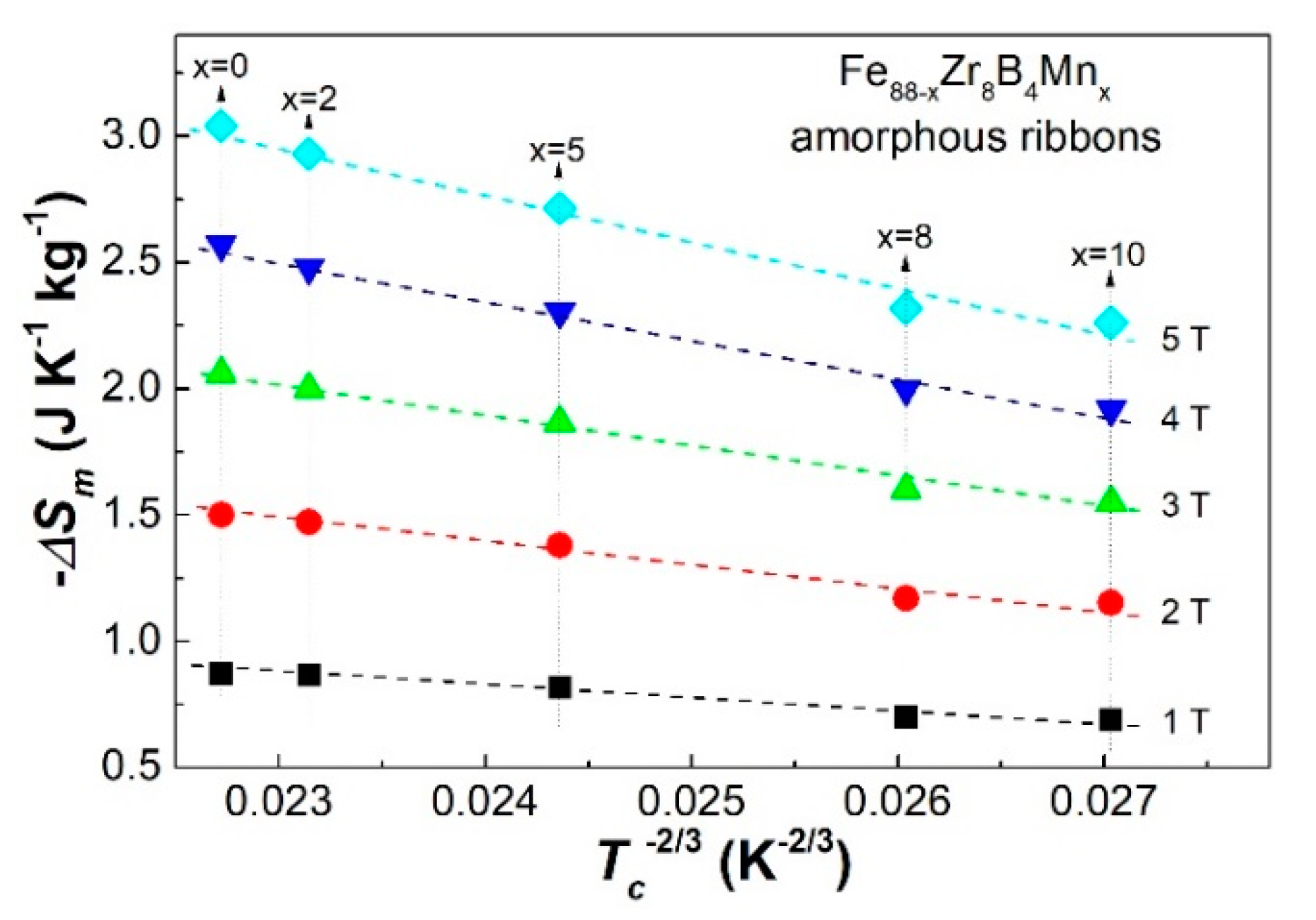
3.2. Discussion
3.3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, L.; Chen, Z.-G.; Dargusch, M.; Zou, J. High Performance Thermoelectric Materials: Progress and Their Applications. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1701797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, V.; Blázquez, J.S.; Ipus, J.J.; Law, J.Y.; Moreno-Ramírez, L.M.; Conde, A. Magnetocaloric effect: From materials re-search to refrigeration devices. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 93, 112–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, N.A.; von Ranke, P.J. Theoretical aspects of the magnetocaloric effect. Phys. Rep. 2010, 489, 89–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tishin, A.M.; Spichkin, Y.I. The Magnetocaloric Effect and Its Applications; CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group, LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pecharsky, V.K.; Gschneidner, K.A. Giant Magnetocaloric Effect in Gd5(Si2Ge2). Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 4494–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.G.; Sun, J.R.; Hu, F.X.; Zhang, H.W.; Cheng, Z.H. Recent Progress in Exploring Magnetocaloric Materials. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4545–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balli, M.; Fruchart, D.; Gignoux, D. Optimization of La(Fe,Co)13−xSix based compounds for magnetic refrigeration. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2007, 19, 236230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegus, O.; Bao, L.-H.; Song, L. Phase transitions and magnetocaloric effects in intermetallic compounds MnFeX (X = P, As, Si, Ge). Chin. Phys. B 2013, 22, 037506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planes, A.; Mañosa, L.; Acet, M. Magnetocaloric effect and its relation to shape-memory properties in ferromagnetic Heusler alloys. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 233201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phan, M.-H.; Yu, S.-C. Review of the magnetocaloric effect in manganite materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 308, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidelli, M.; Orekhov, A.; Bassi, A.L.; Terraneo, G.; Djemia, P.; Abadias, G.; Nord, M.; Béché, A.; Gauquelin, N.; Verbeeck, J.; et al. Novel class of nanostructured metallic glass films with superior and tunable mechanical properties. Acta Mater. 2021, 213, 116955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Wang, W.H. Magnetocaloric effect in rare earth-based bulk metallic glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 495, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Xie, H.; Li, D.; Xia, L.; Yu, P. Microstructure and its effect on magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of the Co50Gd50-xFex glassy ribbons. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2020, 533, 119935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ding, D.; Xia, L.; Chan, K.C. Achieving tailorable magneto-caloric effect in the Gd-Co binary amorphous alloys. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 035302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, B.; Liu, X.; Li, D.; Yu, P.; Xia, L. Effect of Ni substitution on the formability and magnetic properties of a Gd50Co50 amorphous alloy. Chin. Phys. B 2020, 29, 056401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.Y.; Gan, L.H.; Chan, K.C.; Ding, D.; Xia, L. Achieving a table-like magnetic entropy change across the ice point of wa-ter with tailorable temperature range in Gd-Co-based amorphous hybrids. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 723, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.L.; Zhao, D.Q.; Bai, H.Y.; Wang, W.H.; Pan, M.X. Room temperature table-like magnetocaloric effect in amorphous Gd50Co45Fe5 ribbon. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 055004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zhong, X.; Franco, V.; Montemayor, R.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, D. Table-like magnetocaloric effect of Fe88−xNdxCr8B4 composite materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 390, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.S.; Zhang, J.Z.; Wen, L.; Yu, P.; Xia, L. Outstanding magnetocaloric effect of Fe88−xZr8B4Smx (x = 0, 1, 2, 3) amorphous alloys. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astro. 2018, 61, 056121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.H.; Ma, L.Y.; Tang, B.Z.; Ding, D.; Xia, L. Effect of Co substitution on the glass forming ability and magnetocaloric effect of Fe88Zr8B4 amorphous alloys. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2017, 60, 076121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Zhang, J.Z.; Xia, L. Effect of boron on the magneto-caloric effect in Fe91−xZr9Bx (x = 3, 4, 5) amorphous alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 13948–13955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bi, X. The role of Zr and B in room temperature magnetic entropy change of FeZrB amorphous alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 262501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.; Gurram, M.; Reddy, A.; Perumal, A.; Saravanan, P.; Srinivasan, A. Enhanced soft magnetic properties and mag-netocaloric effect in B substituted amorphous Fe–Zr alloy ribbons. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 2010, 175, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, V.; Borrego, J.M.; Conde, C.F.; Conde, A.; Stoica, M.; Roth, S. Refrigerant capacity of FeCrMoCuGaPCB amor-phous alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 083903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franco, V.; Blázquez, J.S.; Conde, A. The influence of Co addition on the magnetocaloric effect of Nanoperm-type amor-phous alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 064307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidelli, M.; Gravier, S.; Blandin, J.-J.; Pardoen, T.; Raskin, J.-P.; Mompiou, F. Compositional-induced structural change in ZrxNi100−x thin film metallic glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 615, S348–S351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, D. Under what conditions can a glass be formed? Contemp. Phys. 1969, 10, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.P.; Liu, C.T. Glass Formation Criterion for Various Glass-Forming Systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 115505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Calculations of Amorphous-Forming Composition Range for Ternary Alloy Systems and Analyses of Stabilization of Amorphous Phase and Amorphous-Forming Ability. Mater. Trans. 2001, 42, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trhlík, M.; De Moor, P.; Erzinkyan, A.L.; Gurevich, G.M.; Parfenova, V.P.; Schuurmans, P.; Severijns, N.; Vanderpoorten, W.; Vanneste, L.; Wouters, J. Antiferromagnetic coupling between the Mn and Fe nearest neighbours in ferromagnetic Mn:Pt-10 at.% Fe. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1992, 4, 9181–9190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.K. On a generalized approach to first and second order magnetic transitions. Phys. Lett. 1964, 12, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.Y.; Franco, V.; Moreno-Ramírez, L.M.; Conde, A.; Karpenkov, D.Y.; Radulov, I.A.; Skokov, K.; Gutfleisch, O. A quantitative criterion for determining the order of magnetic phase transitions using the magnetocaloric effect. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belo, J.H.; Amaral, J.S.; Pereira, A.M.; Amaral, V.S.; Araújo, J.P. On the Curie temperature dependency of the magneto-caloric effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 242407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
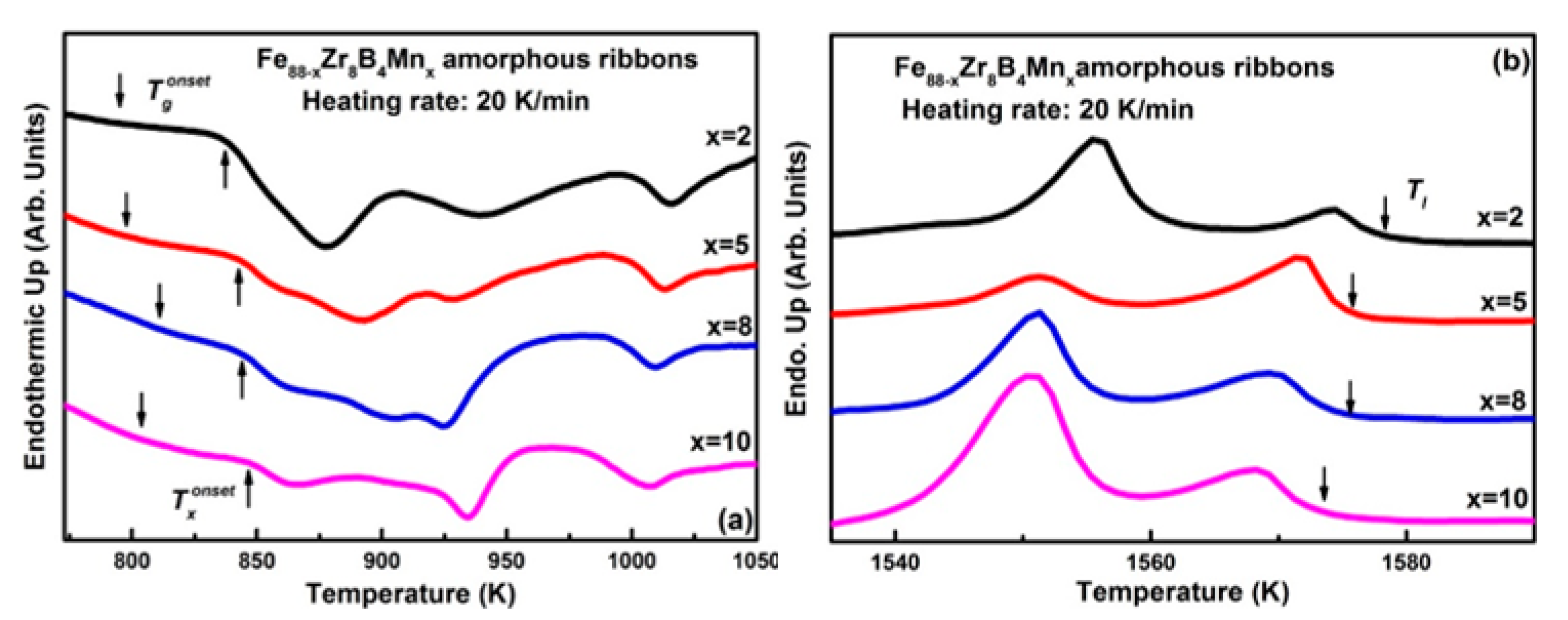


| Fe88−xZr8B4Mnx | Tg (K) | Tx (K) | Tl (K) | Trg | γ | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x = 0 | 787 | 840 | 1611 | 0.489 | 0.350 | [19] |
| x = 2 | 794 | 837 | 1578 | 0.503 | 0.353 | Present work |
| x = 5 | 797 | 842 | 1575 | 0.506 | 0.355 | |
| x = 8 | 811 | 843 | 1575 | 0.515 | 0.353 | |
| x = 10 | 806 | 847 | 1573 | 0.512 | 0.356 |
| Fe88−xZr8B4Mnx | Tc (K) | −ΔSmpeak (J·kg−1·K−1) | n | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 T | 2 T | 3 T | 4 T | 5 T | ||||
| x = 0 | 291 | 0.87 | 1.5 | 2.06 | 2.57 | 3.04 | 0.769 | [19] |
| x = 2 | 283 | 0.867 | 1.471 | 1.999 | 2.480 | 2.931 | 0.745 | Present work |
| x = 5 | 263 | 0.818 | 1.380 | 1.865 | 2.306 | 2.715 | 0.736 | |
| x = 8 | 238 | 0.694 | 1.172 | 1.585 | 1.960 | 2.309 | 0.740 | |
| x = 10 | 225 | 0.689 | 1.152 | 1.551 | 1.919 | 2.261 | 0.736 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Tang, B.; Ding, D.; Cui, L.; Xia, L. Effect of Mn Substitution Fe on the Formability and Magnetic Properties of Amorphous Fe88Zr8B4 Alloy. Metals 2021, 11, 1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11101577
Wang X, Wang Q, Tang B, Ding D, Cui L, Xia L. Effect of Mn Substitution Fe on the Formability and Magnetic Properties of Amorphous Fe88Zr8B4 Alloy. Metals. 2021; 11(10):1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11101577
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xin, Qiang Wang, Benzhen Tang, Ding Ding, Li Cui, and Lei Xia. 2021. "Effect of Mn Substitution Fe on the Formability and Magnetic Properties of Amorphous Fe88Zr8B4 Alloy" Metals 11, no. 10: 1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11101577
APA StyleWang, X., Wang, Q., Tang, B., Ding, D., Cui, L., & Xia, L. (2021). Effect of Mn Substitution Fe on the Formability and Magnetic Properties of Amorphous Fe88Zr8B4 Alloy. Metals, 11(10), 1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11101577







