Influence of Specimen Surface Roughness on Hydrogen Embrittlement Induced in Austenitic Steels during In-Situ Small Punch Testing in High-Pressure Hydrogen Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
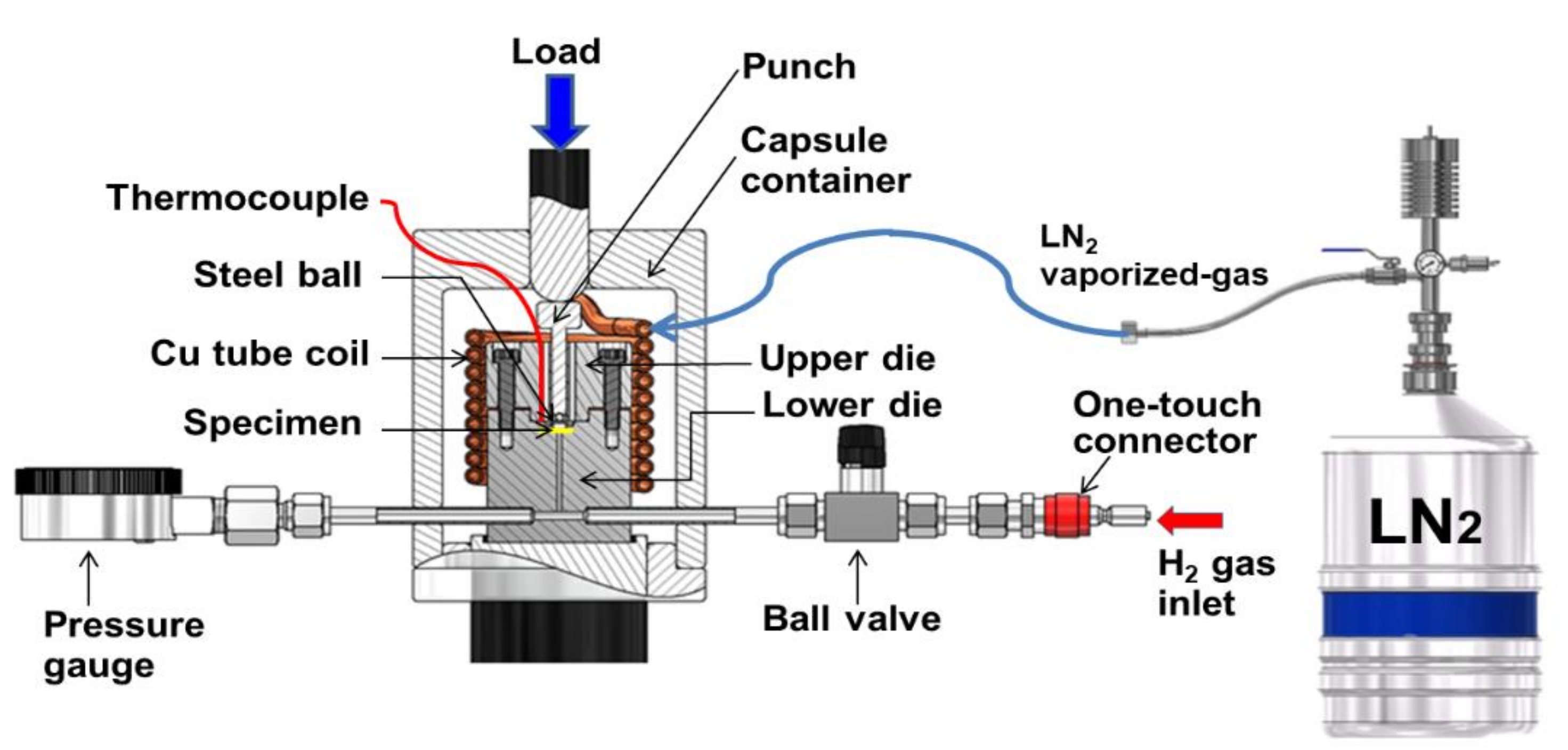
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Specimens
2.2. Experimental Procedure
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
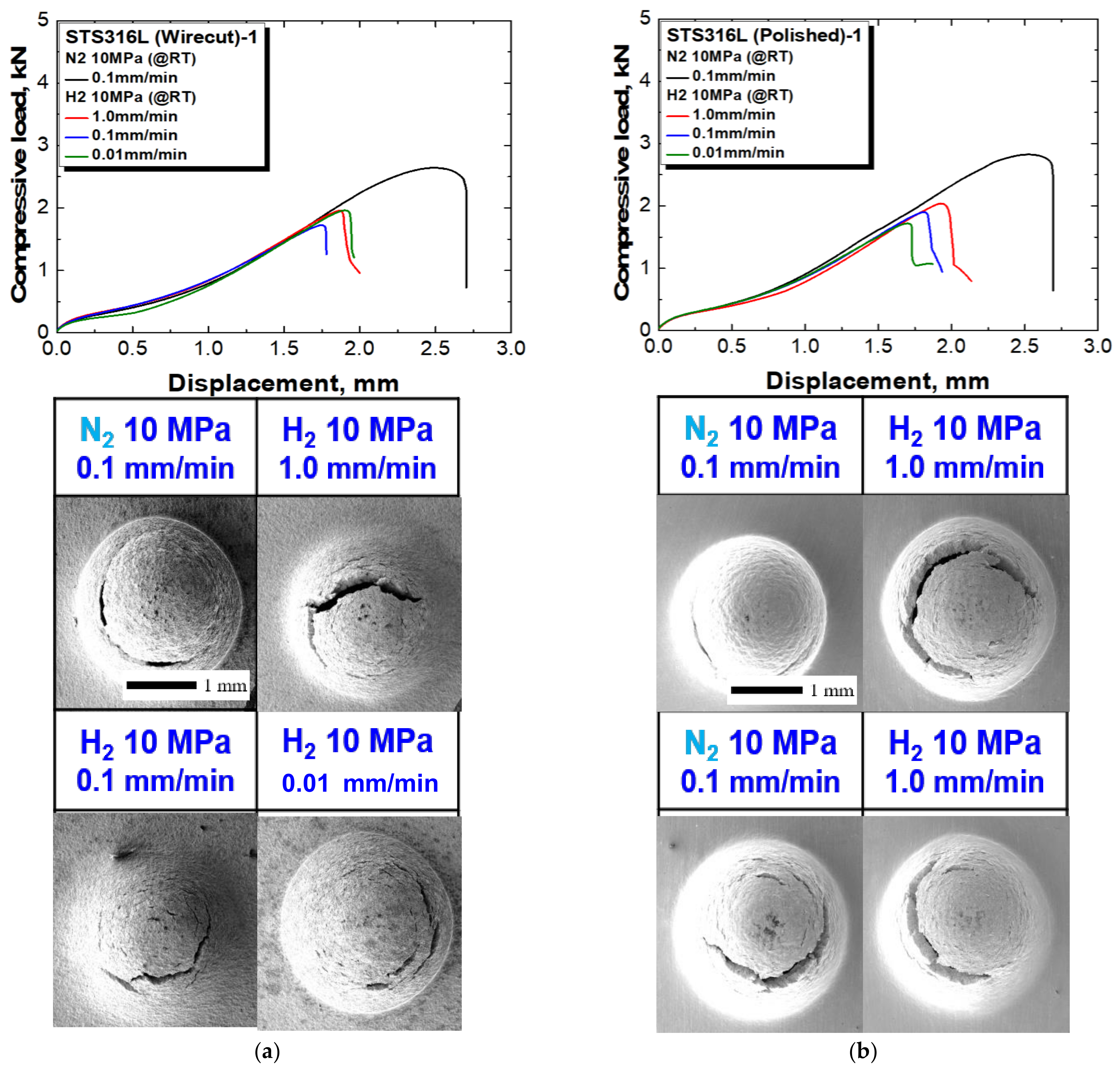
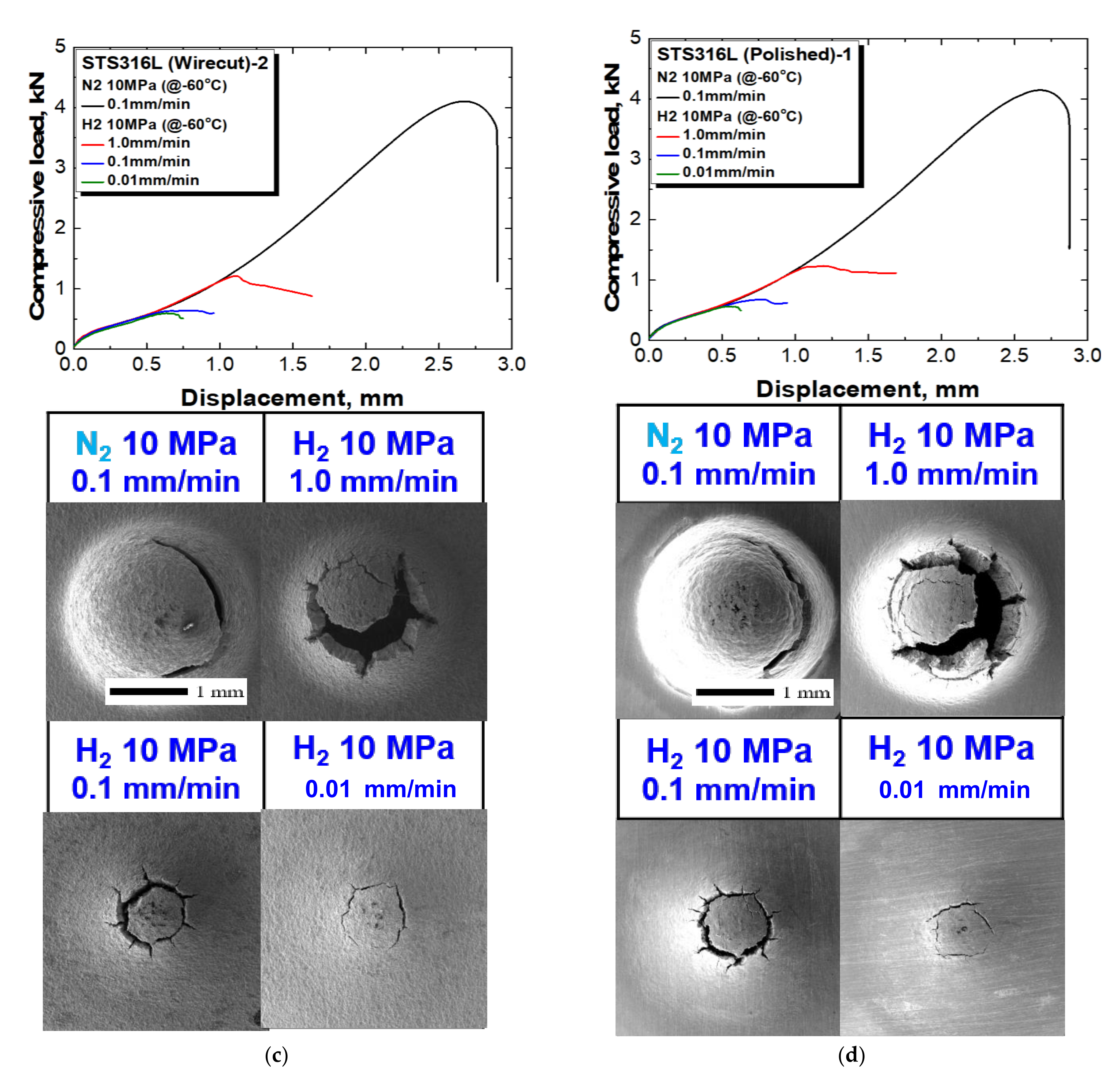
3.1. Qualitative Investigation of Surface Roughness Effect on HE Behaviors
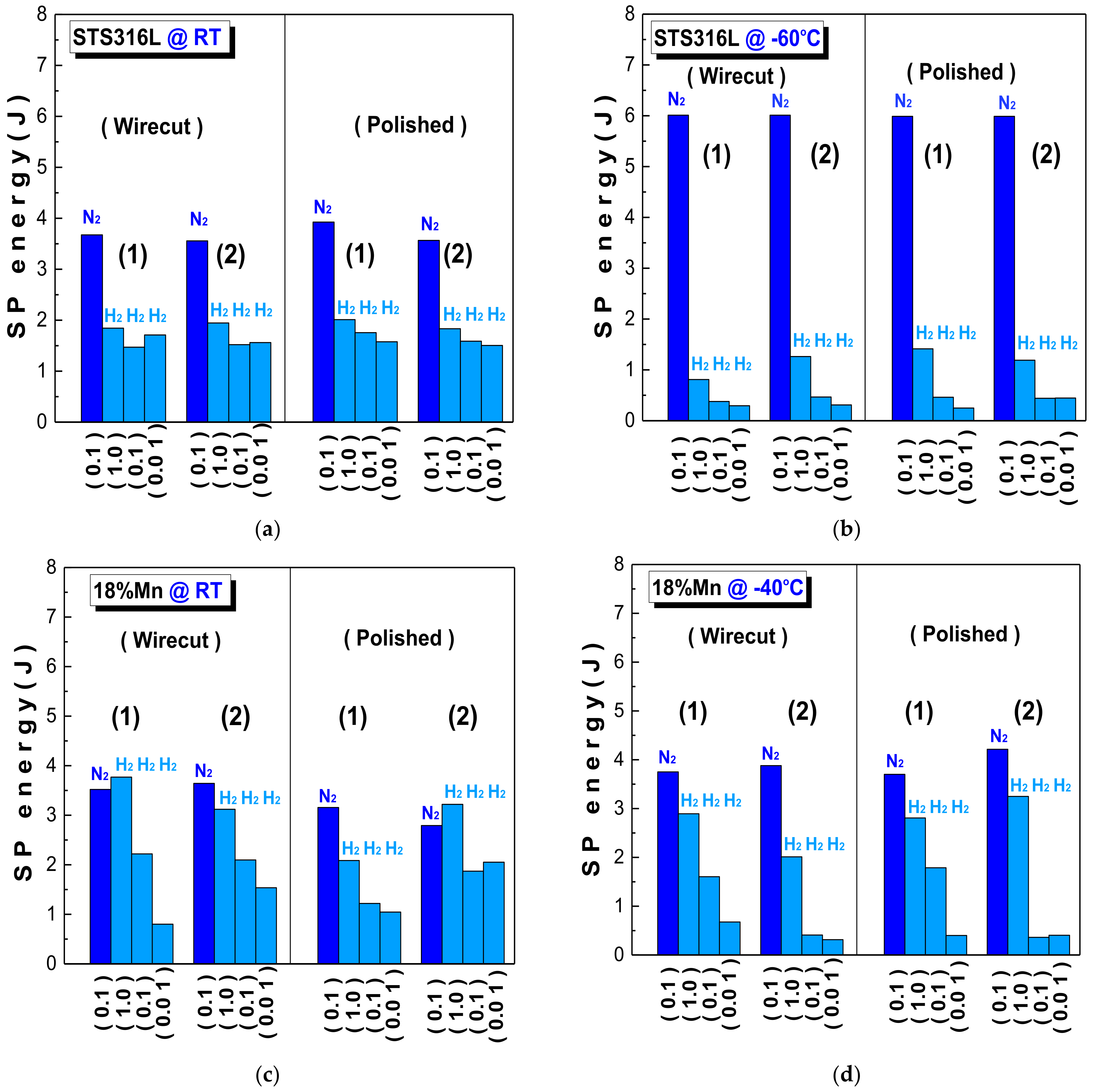
3.2. Surface Roughness Effect on Quantitative Evaluation of HE Susceptibility
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagumo, M.; Takai, K. The predominant role of strain-induced vacancies in hydrogen embrittlement of steels: Overview. Acta Mater. 2019, 165, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wen, M.; Imade, M.; Fukuyama, S.; Yokogawa, K. Effect of nickel equivalent on hydrogen gas embrittlement of austenitic stainless steels based on type 316 at low temperatures. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 3414–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michler, T.; Lee, Y.; Gangloff, R.R.; Naumann, J. Influence of macro segregation on hydrogen environment embrittlement of SUS 316L stainless steel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 3201–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Marchi, C.; Michler, T.; Nibur, K.A.; Somerday, B.P. On the physical differences between tensile testing of type 304 and 316 austenitic stainless steels with internal hydrogen and in external hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 9736–9745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamabe, J.; Takakuwa, O.; Matsunaga, H.; Itoga, H.; Matsuoka, S. Hydrogen diffusivity and tensile-ductility loss of solution-treated austenitic stainless steels with external and internal hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 13289–13299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. Standard Test Method for Determination of Susceptibility of Metals to Embrittlement in Hydrogen Containing Environments at High Pressure, High Temperature, or Both; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, P.; Liu, P.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J. Development of high pressure gaseous hydrogen storage technologies. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, H.; Yoshikawa, M.; Kondo, R.; Yamabe, J.; Matsuoka, S. Slow strain rate tensile and fatigue properties of Cr–Mo and carbon steels in a 115 MPa hydrogen gas atmosphere. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 5739–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michler, T.; Yukhimchuk, A.A.; Naumann, J. Hydrogen environment embrittlement testing at low temperatures and high pressures. Corrosion. Sci. 2008, 50, 3519–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, T. Evaluation of hydrogen embrittlement by internal high-pressure hydrogen environment in specimen. J. Jpn. Inst. Metals Mater. 2008, 72, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogata, T. Influence of high pressure hydrogen environment on tensile and fatigue properties of stainless steels at low temperature. AIP Conf. Proc. 2012, 1435, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- García, T.E.; Arroyo, B.; Rodriguez, C.; Belzunce, F.; Álvarez, A.Z. Small punch test methodologies for the analysis of the hydrogen embrittlement of structural steels. Theoret. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2016, 86, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komazaki, S.; Koyama, A.; Misawa, T. Effect of morphology of copper precipitation particles on hydrogen embrittlement behavior in Cu-added ultralow carbon steel. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 2213–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Committee for Standardization. Small Punch Test Method for Metallic Materials—Part B: A Code of Practice for Small Punch Testing for Tensile and Fracture Behavior; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- García, T.E.; Rodríguez, C.; Belzunce, F.J.; Cuesta, I.I. Effect of hydrogen embrittlement on the tensile properties of CrMoV steels by means of the small punch test. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 664, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komazaki, S.; Sugimoto, T.; Hasegawa, Y.; Kohno, K. Damage evaluation of a welded joint in a long-term service exposed boiler by using a small punch creep test. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, H.S.; Bae, K.O.; Baek, U.B.; Nahm, S.H. Establishment of an in-situ small punch test method for characterizing hydrogen embrittlement behaviors under hydrogen gas environments and new influencing factor. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 23472–23483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.S.; Kim, K.H.; Baek, U.B.; Nahm, S.H. Development of evaluation technique for hydrogen embrittlement behavior of metallic materials using in-situ SP testing under pressurized hydrogen gas conditions. Trans. Korean Soc. Mech. Eng. A 2011, 35, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization. Transportable Gas Cylinders—Compatibility of Cylinder and Valve Materials with Gas Contents—Part 4: Test Methods for Selecting Steels Resistant to Hydrogen Embrittlement; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.S.; Yeo, J.H.; Custodio, N.A.; Baek, U.B.; Nahm, S.H. Evaluation of material compatibility for hydrogen applications using performance factors obtained by in-situ SP test. In Proceedings of the ASME 2020 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference, Virtual, 3 August 2020. PVP2020-21241. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, K.O.; Shin, H.S.; Baek, U.B. Quantitative evaluation of hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility in various steels for energy use using an in-situ small punch test. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 20107–20118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kentish, P. Stress corrosion cracking of gas pipelines—Effect of surface roughness, orientations and flattening. Corros. Sci. 2007, 44, 2521–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroga, L.R.; Marcolino, G.F.; Santos, M.; Rodrigues, G.; Santos, C.E.; Brito, P. Influence of machining parameters on surface roughness and susceptibility to hydrogen embrittlement of austenitic stainless steels. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 29027–29033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharyya, S.G.; Khandelwal, A.; Kain, V.; Kumar, A.; Samajdar, J. Surface working of 304L stainless steel: Impact on microstructure, electrochemical behavior and SCC resistance. Mater. Charact. 2012, 72, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, T.; Ono, Y. Influence of roughness of inner surface of simple mechanical testing method to evaluate influence of high pressure hydrogen gas. In Proceedings of the ASME 2019 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, 14–19 July 2019. PVP2019-93492. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, M.D.; Connolly, S.; Gorley, M.; Wynne, B.P.; Surrey, E. Influence of surface finish on small punch testing of 9Cr Eurofer-97 steel. J. Test. Eval. 2020, 48, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization. Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Profile Method—Terms, Definitions and Surface Texture Parameters; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Karthik, V.; Kasiviswanathan, K.V.; Raj, B. Miniaturized Testing of Engineering Materials; Taylor & Francis: Oxfordshire, UK, 2016; pp. 66–78. [Google Scholar]




| Material | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 wt% Mn steel | 0.62 | - | 17.98 | 0.02 | 0.02 | - | - | - | Bal. |
| STS316L steel | 0.013 | 0.47 | 0.66 | 0.03 | 0.004 | 16.65 | 10.11 | 2.06 | Bal. |
| Material | Yield Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18 wt% Mn steel | 498 | 1070 | 50.2 |
| STS316L steel | 229 | 568 | 63.5 |
| Surface Roughness | STS316L Steel | 18 wt% Mn Steel | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ra (μm) | Rmax (μm) | Ra (μm) | Rmax (μm) | |
| Wirecutted (as-received) | 2.88 ± 0.195 | 17.68 ± 1.011 | 2.40 ± 0.160 | 14.46 ± 0.424 |
| Polished (#600 grit) | 0.14 ± 0.025 | 3.13 ± 0.299 | 0.11 ± 0.037 | 1.50 ± 0.419 |
| Specimen Dimension (mm) | 10 × 10 × t0.5 |
| Ball diameter (mm) | 3.0 |
| Gas purity | N2 (99.999%), H2 (99.999%) |
| Gas pressure (MPa) | 10 |
| Punch velocity (mm/min) | 1.0, 0.1, 0.01 |
| Test temperature | Room temperature and low temperatures (−60 °C for STS316L steel, −40 °C for 18 wt% Mn steel) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, H.-S.; Yeo, J.; Baek, U.-B. Influence of Specimen Surface Roughness on Hydrogen Embrittlement Induced in Austenitic Steels during In-Situ Small Punch Testing in High-Pressure Hydrogen Environments. Metals 2021, 11, 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11101579
Shin H-S, Yeo J, Baek U-B. Influence of Specimen Surface Roughness on Hydrogen Embrittlement Induced in Austenitic Steels during In-Situ Small Punch Testing in High-Pressure Hydrogen Environments. Metals. 2021; 11(10):1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11101579
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Hyung-Seop, Juho Yeo, and Un-Bong Baek. 2021. "Influence of Specimen Surface Roughness on Hydrogen Embrittlement Induced in Austenitic Steels during In-Situ Small Punch Testing in High-Pressure Hydrogen Environments" Metals 11, no. 10: 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11101579
APA StyleShin, H.-S., Yeo, J., & Baek, U.-B. (2021). Influence of Specimen Surface Roughness on Hydrogen Embrittlement Induced in Austenitic Steels during In-Situ Small Punch Testing in High-Pressure Hydrogen Environments. Metals, 11(10), 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11101579






