Oxidation Behavior of an Austenitic Steel (Fe, Cr and Ni), the 310 H, in a Deaerated Supercritical Water Static System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
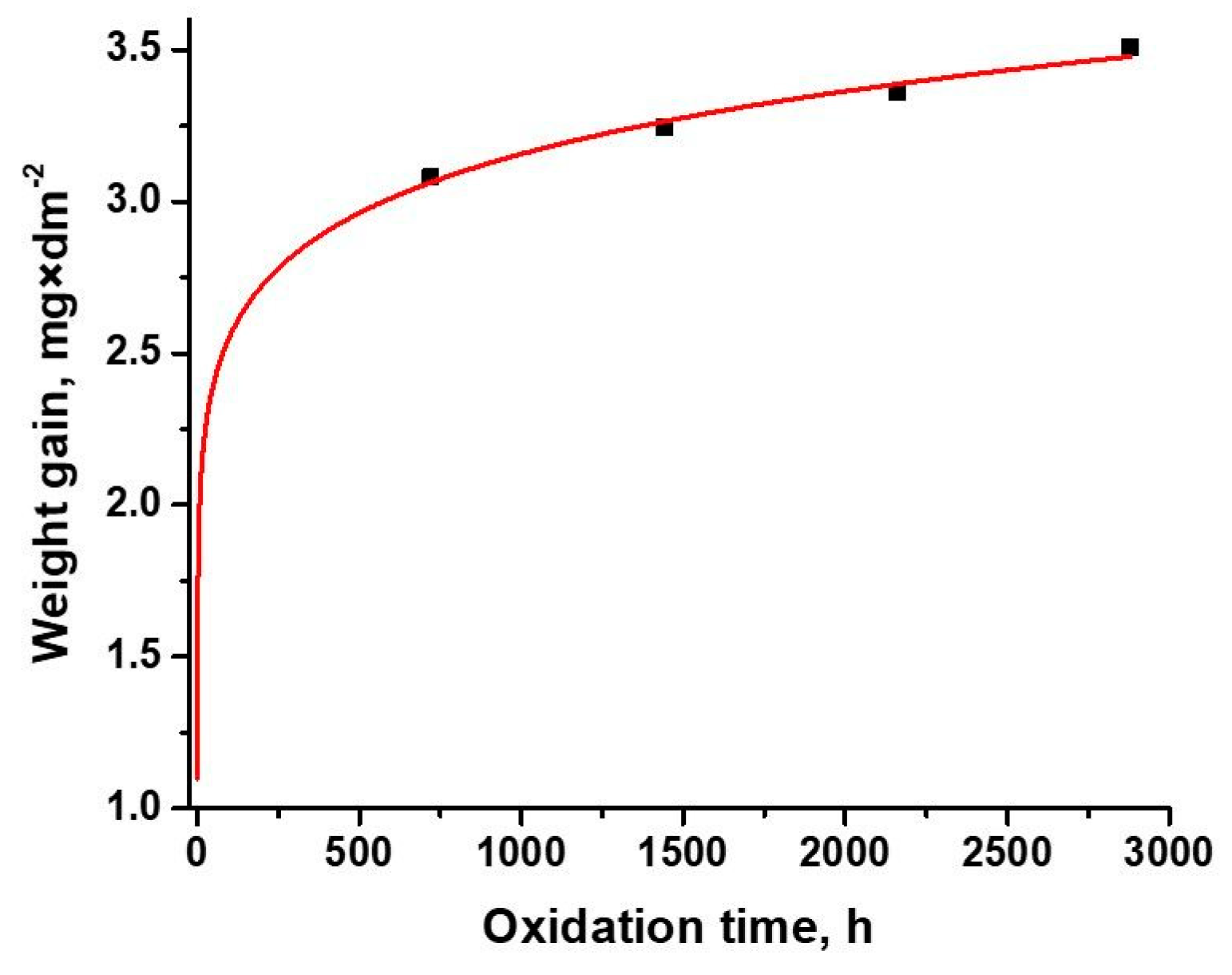
3.1. Oxidation Kinetics
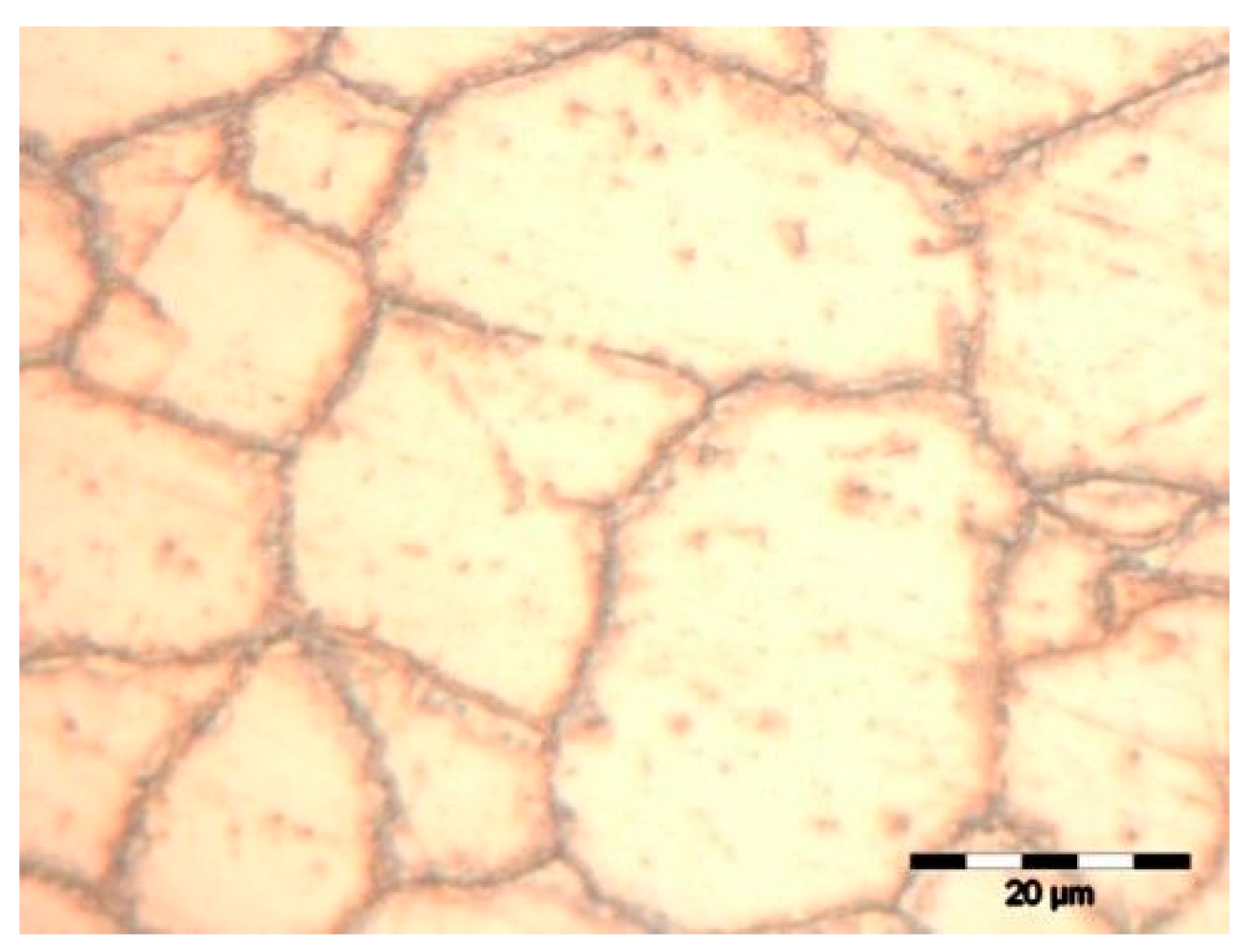
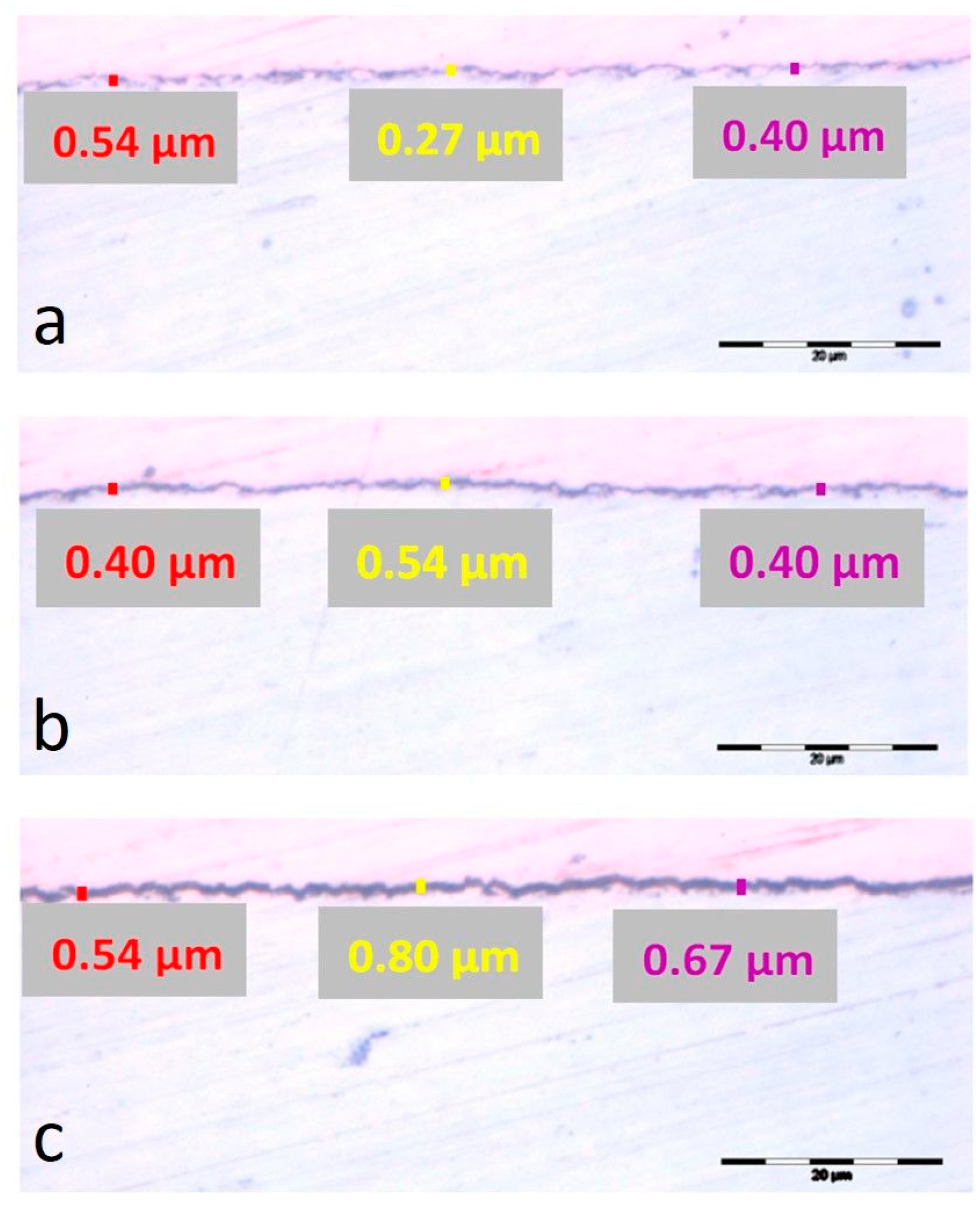
3.2. Metallographic Analysis (Optical Microscopy)
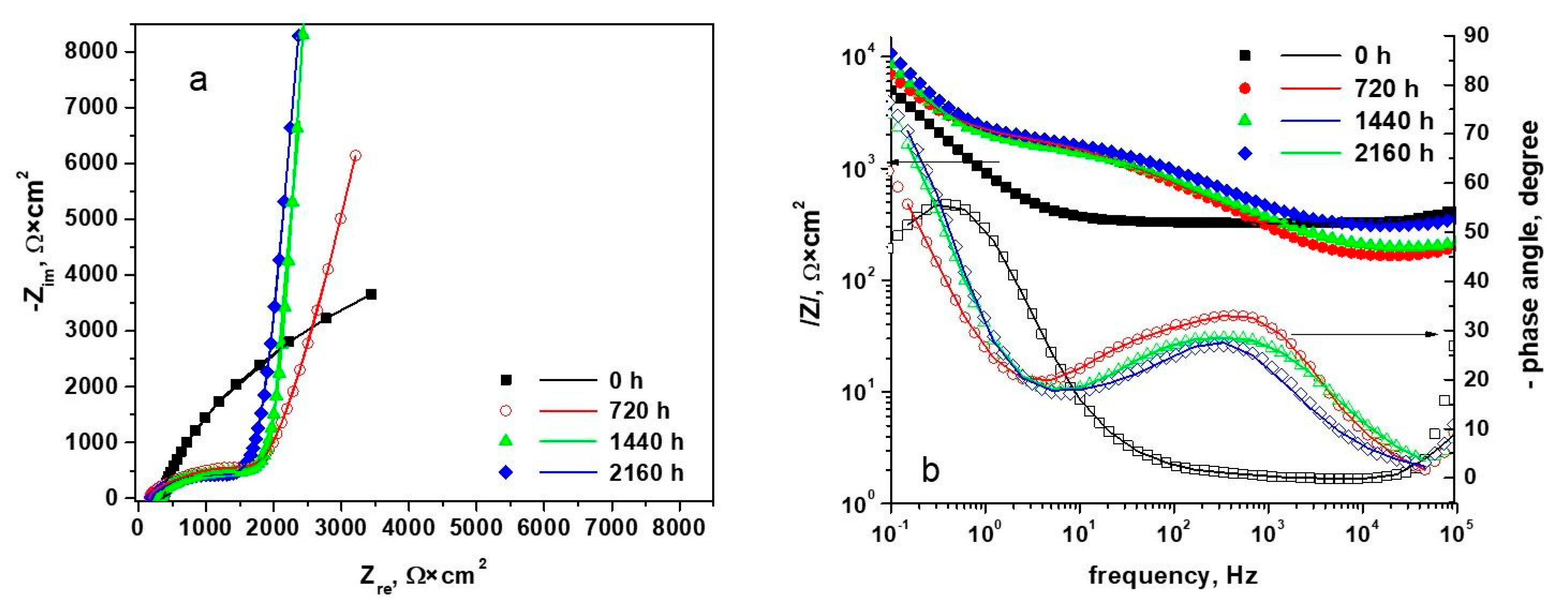
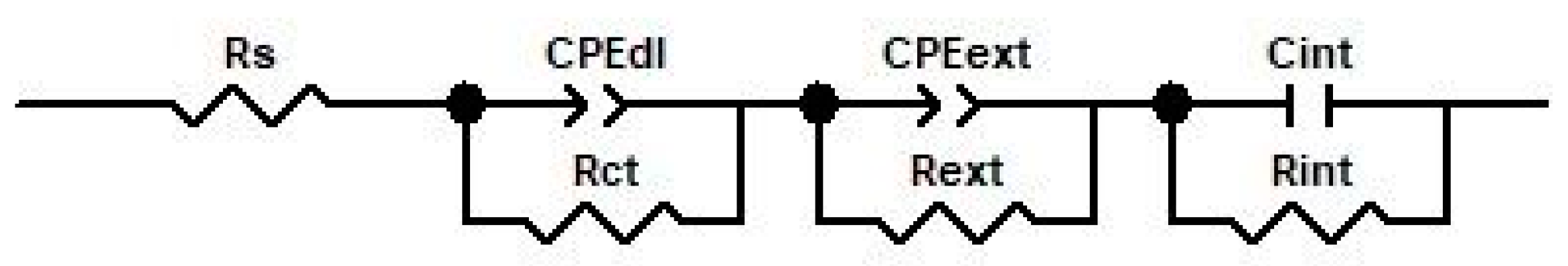
3.3. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
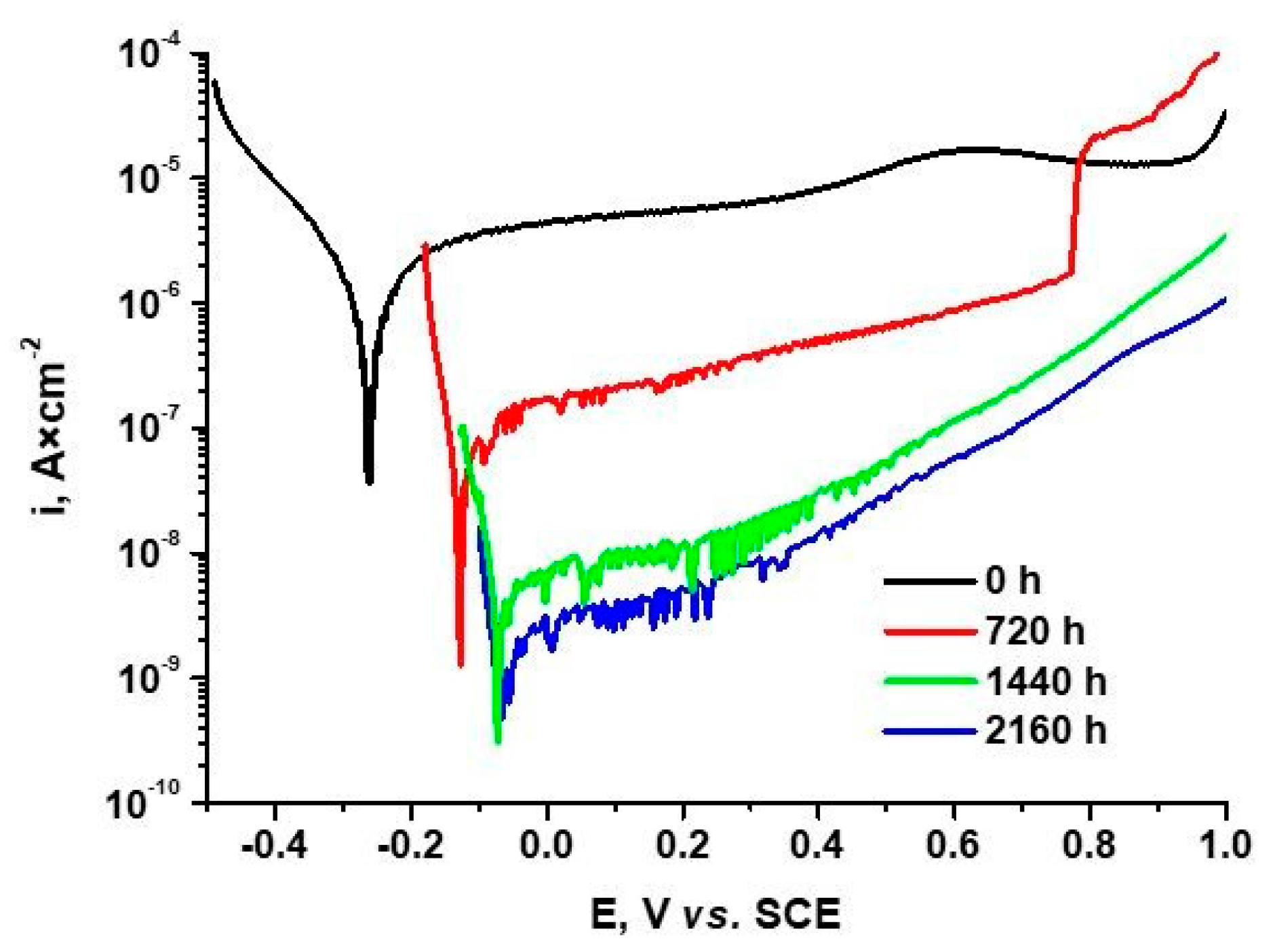
3.4. Potentiodynamic Polarization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohammadi, T.; Huang, X. Effect of Al and Ti addition on performance of stainless steel 310 in supercritical water. Corros. Eng. Sci. Techn. 2014, 50, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US DOE. Nuclear Energy Research Advisory Committee. Generation IV International Forum, A Technology Roadmap for Generation IV Nuclear Energy System; Technical Report; U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2002; pp. 1–18. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buongiorno, J.; Corwin, W.; MacDonald, P.; Mansur, L.; Nanstad, R.; Swindeman, R.; Rowcliffe, A.; Was, G.; Wilson, D.; Wright, I. The Supercritical Water Reactor (SCWR) Survey of Materials Experience and R&D Needs to Assess Viability; INEEL/EXT-0300693 Rev.1; Idaho National Laboratory: Idaho Falls, ID, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Corwin, W.R. U.S. Generation IV reactor integrated materials technology program. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2006, 38, 591–618. [Google Scholar]
- Fulger, M.; Mihalache, M.; Ohai, D.; Fulger, S.; Valeca, S.C. Analyses of oxide films grown on AISI 304L stainless steel and Incoloy 800HT exposed to supercritical water. J. Nucl. Mater. 2011, 415, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yang, Q.; Guzonas, D. Performance of Chemical Vapor Deposition and Plasma Spray-Coated Stainless Steel 310 in Supercritical Water. J. Nucl. Eng. Radiat. Sci. 2016, 2, 021011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, K.L.; Charit, I. Structural Materials for Gen-IV Nuclear Reactors: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Nucl. Mater. 2008, 383, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapping, R.L. Materials performance in CANDU reactors: The first 30 years and the prognosis for life extension and new designs. J. Nucl. Mater. 2008, 383, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zheng, W.; Yang, L. A review of irradiation effects on mechanical properties of candidate SCWR fuel cladding alloys for design considerations. CNL Nuclear Rev. 2016, 5, 309–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, F.; Ducu, M.C.; Fulger, M.; Negrea, D.A. Investigation of oxidation behavior of 304l and 310s steels with potential application in supercritical water-cooled nuclear reactors. Rev. Chim. 2020, 71, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzonas, D.A.; Wills, J.S.; McRae, G.A.; Sullivan, S.; Chu, K.; Heaslip, K.; Stone, M. Corrosion-Resistant Coatings for Use in a Supercritical Water CANDU Reactor. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power System-Water Reactors, The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 14–18 August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Was, G.S.; Ampornrat, P.; Gupta, G.; Teysseyre, S.; West, E.A.; Allen, T.R.; Sridharan, K.; Tan, L.; Chen, Y.; Ren, X.; et al. Corrosion and stress corrosion cracking in supercritical water. J. Nucl. Mater. 2007, 371, 176–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, K.; Konys, J.; Heikinheimo, L. Materials for high performance light water reactors. J. Nucl. Mater. 2004, 327, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazono, Y.; Iwai, T.; Abe, H. General corrosion properties of modified PNC1520 austenitic stainless steel in supercritical water as a fuel cladding candidate material for supercritical water reactor. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2010, 215, 012094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvig, A.; Huang, X.; Kim, D.J.; Guzonas, D. Surface oxide formation on IN625 and plasma sprayed NiCrAlY after high density and low density supercritical water testing. Mater. Corros. 2012, 65, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Materials Selection for the Canadian Supercritical Water-Cooled Nuclear Reactor Concept. JOM 2016, 68, 452–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Y.; Guzonas, D. Corrosion Assessment of Candidate Materials for Fuel Cladding in Canadian SCWR. JOM 2016, 68, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.; Chen, Y.; Tan, L.; Ren, X.; Sridharan, K. Corrosion of Candidate Materials for Supercritical Water-Cooled Reactor. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power System-Water Reactors, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 14–18 August 2005; Allen, T.R., King, P.J., Nelson, L., Eds.; TMS (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society): Pittsburgh, PA, USA; pp. 1397–1405. [Google Scholar]
- Bsat, S.; Huang, X. Corrosion Behaviour 310 Stainless Steel in Superheated Steam. Oxid. Met. 2015, 84, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Sanchez, R. Effect of water or steam pressure on the oxidation behaviour of alloy 625 and A286 at 625 °C. CNL Nucl. Rev. 2016, 5, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bsat, S.; Xiao, B.; Huang, X.; Penttilä, S. Oxidation Behaviour of Alloys 800H, 3033 and 304 in High-Temperature Supercritical Water. Oxid. Met. 2018, 89, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bsat, S.; Huang, X.; Penttila, S. Corrosion behaviour of bare and nicraly coated alloy 214 in supercritical water at 700 °C. J. Nucl. Eng. Radiat. Sci. 2018, 4, 021007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, B.; Tepylo, N.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Penttilä, S. Oxidation behavior of alumina-forming austenitic steels in superheated steam at 700 °C. J. Nucl. Eng. Radiat. Sci. 2020, 6, 031109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Briceno, D.; Castro, L.; Biazquez, F. Oxidation of stress corrosion cracking of stainless steels in SCWR. In Structural Materials for Innovative Nuclear Systems; Forschangszentrum Karlsruhe: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Radulescu, M.; Pirvan, I.; Lucan, D.; Fulger, M. The use of some electrochemical methods in the study of the superficial films formed on some carbon steel used in a CANDU NPS. In Proceedings of the 7th European Symposium on Corrosion Inhibitors, Ferrara, Italy, 17–21 September 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Hakiki, N.E.; Boudin, S.; Rondot, B.; Da Cunha Belo, M. The electronic structure of passive films formed on stainless steels. Corros. Sci. 1995, 37, 1809–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outokumpu Stainless AB Company. Inspecţion Certificate No. 1293516/18.05.2007-1.4484; Outokumpu Stainless AB Company: Dalarna, Sweden.
- Fattah-al Hosseini, A.; Taheri Shoja, S.; Heydari Zebardast, B.; Mohamadian Samim, P. An electrochemical impedance spectroscopic study of the passive state on AISI 304 stainless steel. Int. J. Electrochem. 2011, 152143, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morcillo, M.; Chico, B.; Díaz, I.; Cano, H.; de la Fuente, D. Atmospheric corrosion data of weathering steels. A review. Corros. Sci. 2013, 77, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Xiao, K.; Fang, X.; Xiong, Z.; Wei, L.; Zhu, P.; Li, X. Oxidation behavior of 316L austenitic stainless steel in high temperature air with long-term exposure. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 066517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnamian, Y.; Mostafaei, A.; Kohandehghan, A.; Zahiri, B.; Zheng, W.; Guzonas, D.; Chmielus, M.; Chen, W.; Luo, J.L. Corrosion behavior of alloy 316L stainless steel after exposure to supercritical water at 500 °C for 20,000 h. J. Supercritic. Fluid 2017, 127, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakan, U. Oxidation Behavior of Very High Temperature Reactor (VHTR) Candidate Materials: 316L Stainless Steel, Alloy 617, and Incoloy-800H. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Missouri, Columbia, MI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E 112-96. Standard Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Cicek, V. Corrosion Engineering; Martin Scrivener, Phillip Carmical: Beverly, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes, A.M.P.; Ferreira, M.G.S.; Rondot, B. Study of passive films formed on AISI 304 stainless steel by impedance measurements and photoelectrochemistry. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1990, 137, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudalia, M.; Guenbour, A.; Bellaouchou, A.; Fernandez-Domene, R.M.; Garcia-Anton, J. Corrosion behaviour of a highly alloyed austenitic Alloy UB6 in contaminated phosphoric acid. Int. J. Corros. 2013, 363826, 363826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olasunkanmi, J.A. Surface Defects Characterization and Electrochemical Corrosion Studies of TiAlN, TiCN and AlCrN PVD Coatings. Materials and Processes of Sustainable Energetics KAYM09. Master’s Thesis, Tallinn University of Technology, Tallinn, Estonia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lakatos-Varsányi, M.; Falkenberg, F.; Olefjord, I. The influence of phosphate on repassivation of 304 stainless steel in neutral chloride solution. Electrochim. Acta 1998, 43, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.H.; Hong, J.H.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, H.Y.; Han, J.G. Effect of Si addition to CrN coatings on the corrosion resistance of CrN/stainless steel coating/substrate system in a deaerated 3.5 wt% NaCl solution. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 9518–9523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Feng, Y.P.; Chen, S.; Wan, Q.L.; Zhu, J.F. Electrochemical characterization of AlTiN, AlCrN and AlCrSiWN coatings. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2015, 53, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.H.; Le, D.P.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, S.K.; Van Vinh, P. Corrosion behavior of TiN, TiAlN, TiAlSiN thin films deposited on tool steel in the 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 3544–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William Grips, V.K.; Barshilia, H.C.; Selvi, V.E.; Rajam, K.S. Electrochemical behavior of single layer CrN, TiN, TiAlN coatings and nanolayered TiAlN/CrN multilayer coatings prepared by reactive direct current magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 2006, 514, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Alloying Elements, [wt. %] | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | N | Fe |
| 0.063 | 0.71 | 1.61 | 0.016 | 0.001 | 24.13 | 19.03 | 0.04 | 54.34 |
| Kinetic Equation | k | n | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| y = 0.051 × t0.564 | 0.051 | 0.564 | 0.9953 |
| Sample Oxidized for | Elements, (wt. %) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | V | Cr | Ni | O | Fe | |
| 720 h | 4.89 | 1.54 | 1.62 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 21.47 | 15.63 | 10.19 | 44.48 |
| 1440 h | 4.86 | 1.62 | 1.58 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 21.33 | 15.35 | 10.68 | 44.34 |
| 2160 h | 6.74 | 1.32 | 1.54 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 20.84 | 15.17 | 10.91 | 43.22 |
| Element Circuit | Unoxidized Sample | Oxidized Sample | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 720 h | 1440 h | 2160 h | ||
| Rs, Ω·cm2 | 331.4 | 159 | 182 | 299.7 |
| CPEdl—T, F·cm−2 | 2.608 × 10−4 | 4.39 × 10−6 | 5.25 × 10−6 | 7.54 × 10−6 |
| CPEdl—P | 0.856 | 0.882 | 0.816 | 0.767 |
| Rct, Ω·cm2 | 8810 | 265.6 | 183.1 | 641.7 |
| CPEext—T, F·cm−2 | - | 3.33 × 10−5 | 3.456 × 10−6 | 5.84 × 10−5 |
| CPEext—P | - | 0.65 | 0.602 | 0.629 |
| Rext, Ω·cm2 | - | 1757 | 1500 | 1196 |
| Cint, F·cm−2 | - | 2. 28 × 10−4 | 1. 823 × 10−4 | 1.489 × 10−4 |
| Rint, Ω·cm2 | - | 2.258 × 104 | 7.06 × 104 | 1.528 × 105 |
| Chi-squared (χ2) | 1.7 × 10−3 | 1.9 × 10−3 | 9.8 × 10−4 | 8.9 × 10−4 |
| Sample Type | Polarization Resistance from the Extrapolation of Nyquist Diagrams, (Ω*cm2) | i0 Calculated from Rp, (µA/cm2) |
|---|---|---|
| Unoxidized sample | 3.381 × 104 | 0.374 |
| Sample oxidized 720 h | 1.146 × 105 | 0.11 |
| Sample oxidized 1440 h | 1.585 × 105 | 0.0799 |
| Sample oxidized 2160 h | 2.014 × 105 | 0.0629 |
| Oxidation Time | Inner Oxide Layer Thickness, μm | Outer Oxide Layer Thickness, μm | Oxide Thickness from EIS, μm | Oxide Thickness from Gravimetric Analysis, μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 720 h | 0.949 × 10−3 | 6.976 × 10−3 | 7.925 × 10−3 | 1.96 × 10−3 |
| 1440 h | 1.202 × 10−3 | 7.149 × 10−3 | 8.351 × 10−3 | 2.06 × 10−3 |
| 2160 h | 1.488 × 10−3 | 7.333 × 10−3 | 8.821 × 10−3 | 2.13 × 10−3 |
| Sample Type | Electrochemical Parameters from Tafel Slopes | Electrochemical Parameters from Polarization Resistance Rp Values | Pi, % | P, % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecorr, mV | icorr, μA/cm2 | Vcorr, mm/year | Ecorr, mV | Rp, KΩ × cm2 | icorr, μA/cm2 | Vcorr, mm/year | - | - | |
| Unoxidized sample | −256.09 | 1.03 | 2.56 × 10−3 | −260.94 | 26.07 | 1.190 | 2.97 × 10−3 | - | - |
| Sample oxidized for 720 h | −126.62 | 5.32 × 10−2 | 1.34 × 10−4 | −127.48 | 232.93 | 6.522 × 10−2 | 1.64 × 10−4 | 94.82 | 5.48 |
| Sample oxidized for 1440 h | −63.02 | 2.62 × 10−2 | 6.54 × 10−5 | −68.16 | 612.21 | 2.187 × 10−2 | 5.47 × 10−5 | 97.45 | 0.74 |
| Sample oxidized for 2160 h | −60.69 | 1.79 × 10−2 | 4.48 × 10−5 | −57.5 | 878.59 | 1.428 × 10−2 | 3.57 × 10−5 | 98.25 | 0.27 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tudose, A.E.; Demetrescu, I.; Golgovici, F.; Fulger, M. Oxidation Behavior of an Austenitic Steel (Fe, Cr and Ni), the 310 H, in a Deaerated Supercritical Water Static System. Metals 2021, 11, 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11040571
Tudose AE, Demetrescu I, Golgovici F, Fulger M. Oxidation Behavior of an Austenitic Steel (Fe, Cr and Ni), the 310 H, in a Deaerated Supercritical Water Static System. Metals. 2021; 11(4):571. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11040571
Chicago/Turabian StyleTudose, Aurelia Elena, Ioana Demetrescu, Florentina Golgovici, and Manuela Fulger. 2021. "Oxidation Behavior of an Austenitic Steel (Fe, Cr and Ni), the 310 H, in a Deaerated Supercritical Water Static System" Metals 11, no. 4: 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11040571
APA StyleTudose, A. E., Demetrescu, I., Golgovici, F., & Fulger, M. (2021). Oxidation Behavior of an Austenitic Steel (Fe, Cr and Ni), the 310 H, in a Deaerated Supercritical Water Static System. Metals, 11(4), 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11040571









