High Temperature Behavior of Al-7Si-0.4Mg Alloy with Er and Zr Additions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
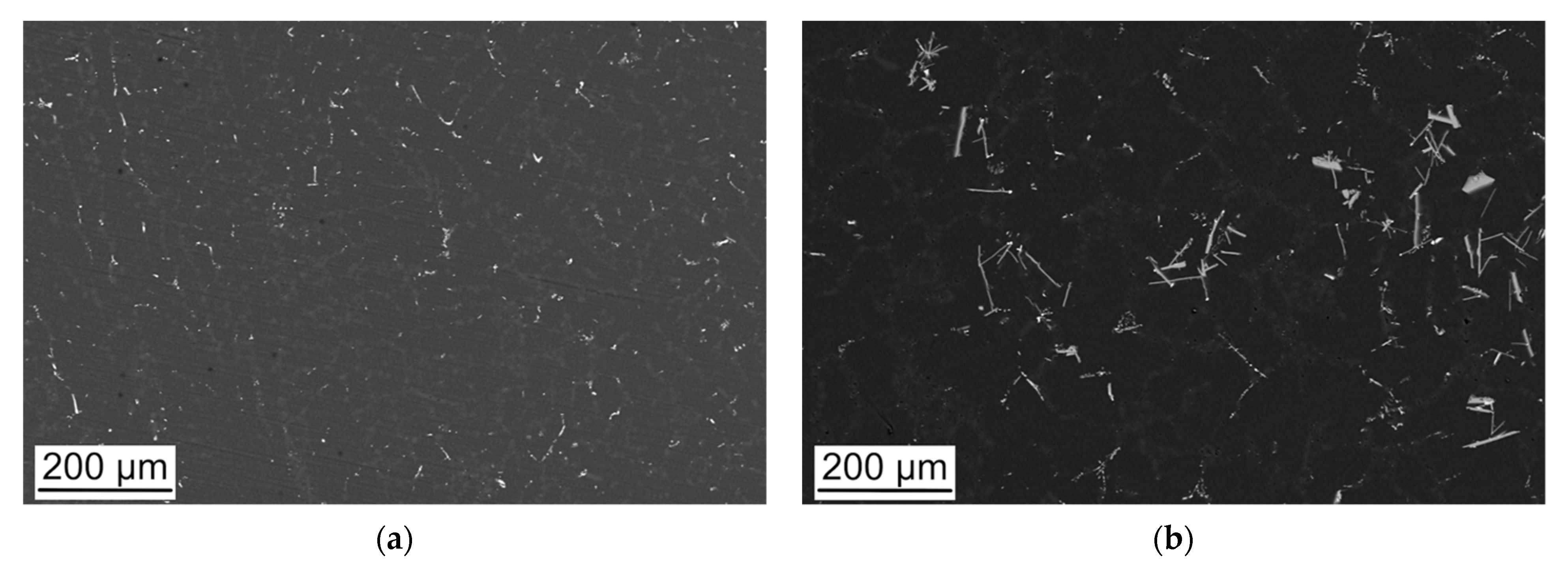
3.1. Alloy Microstructure
3.2. Creep Tests at 300 °C
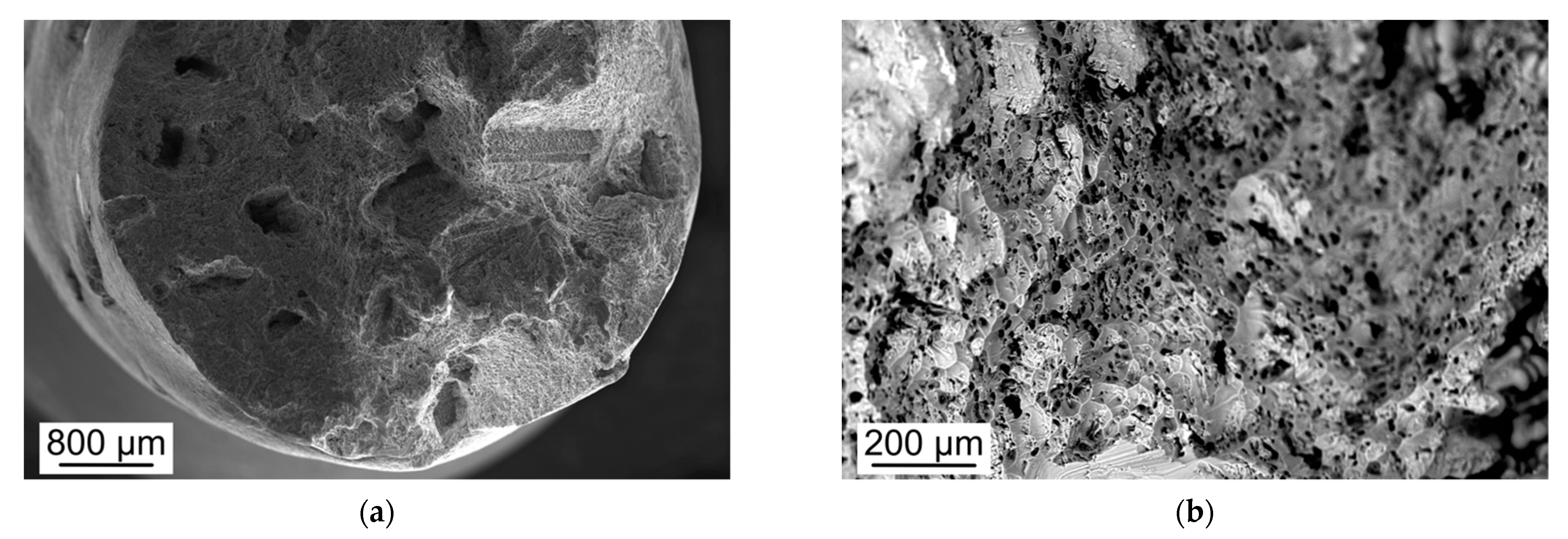
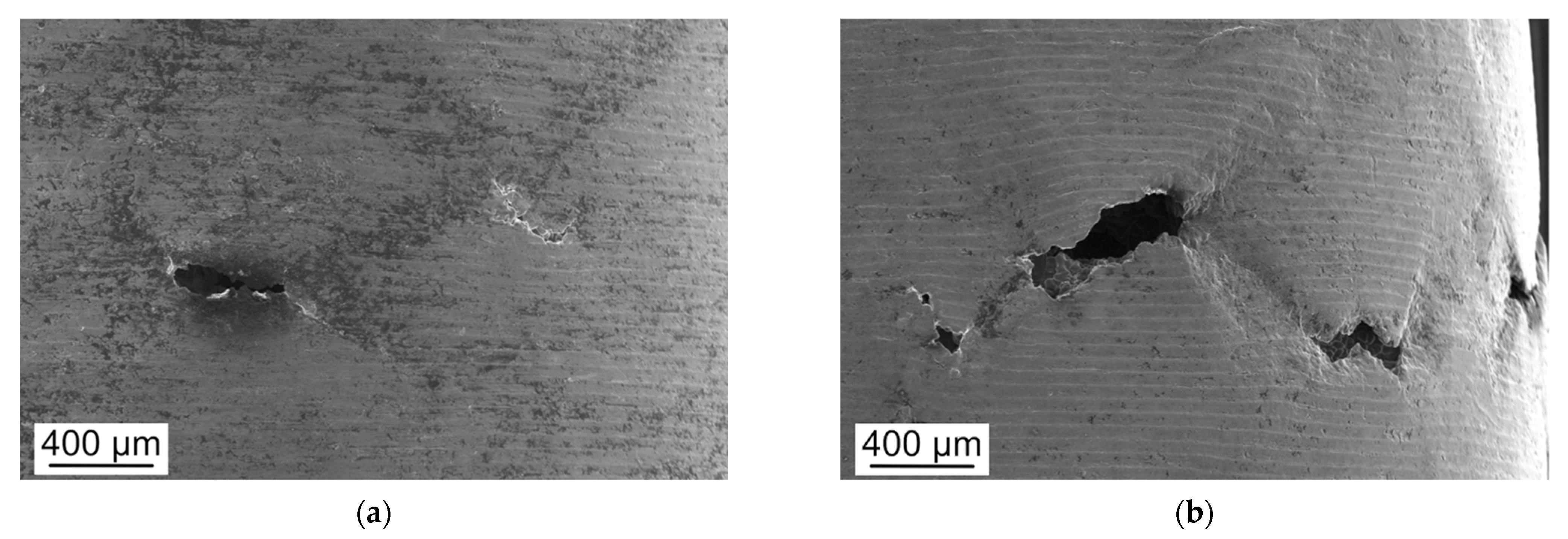
3.3. Fractographic Analyses
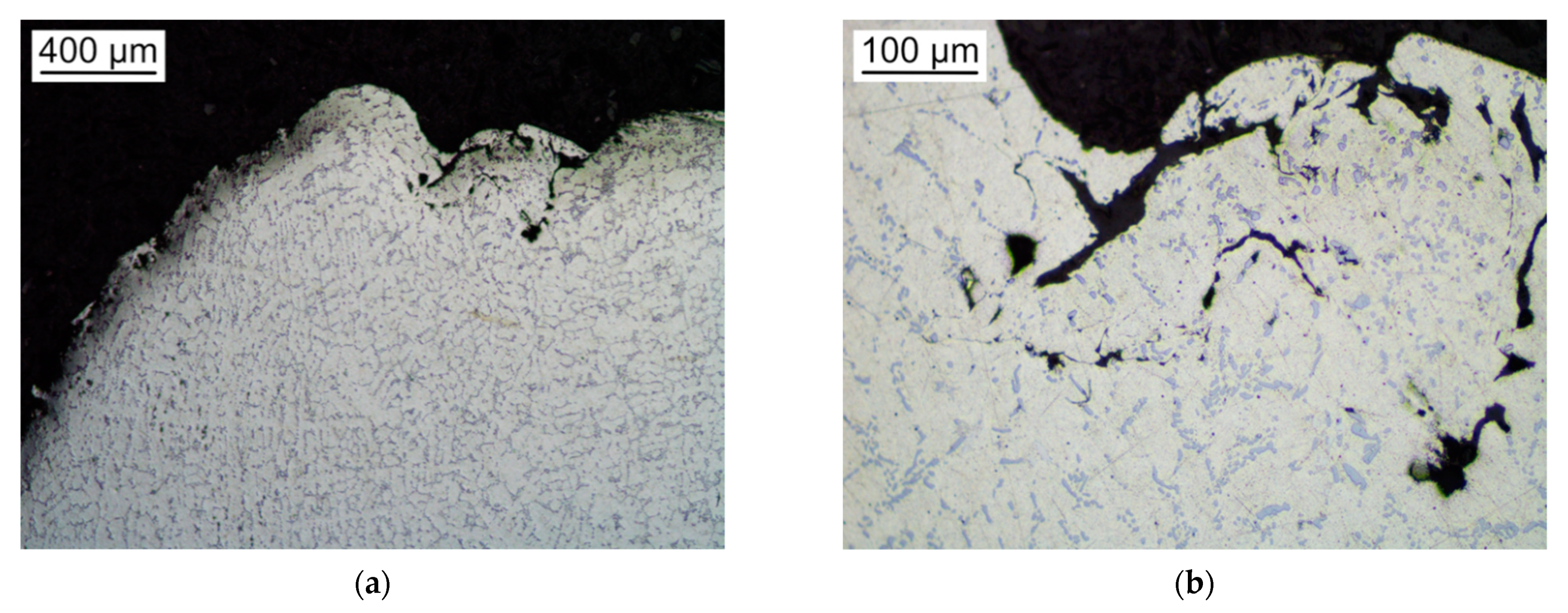
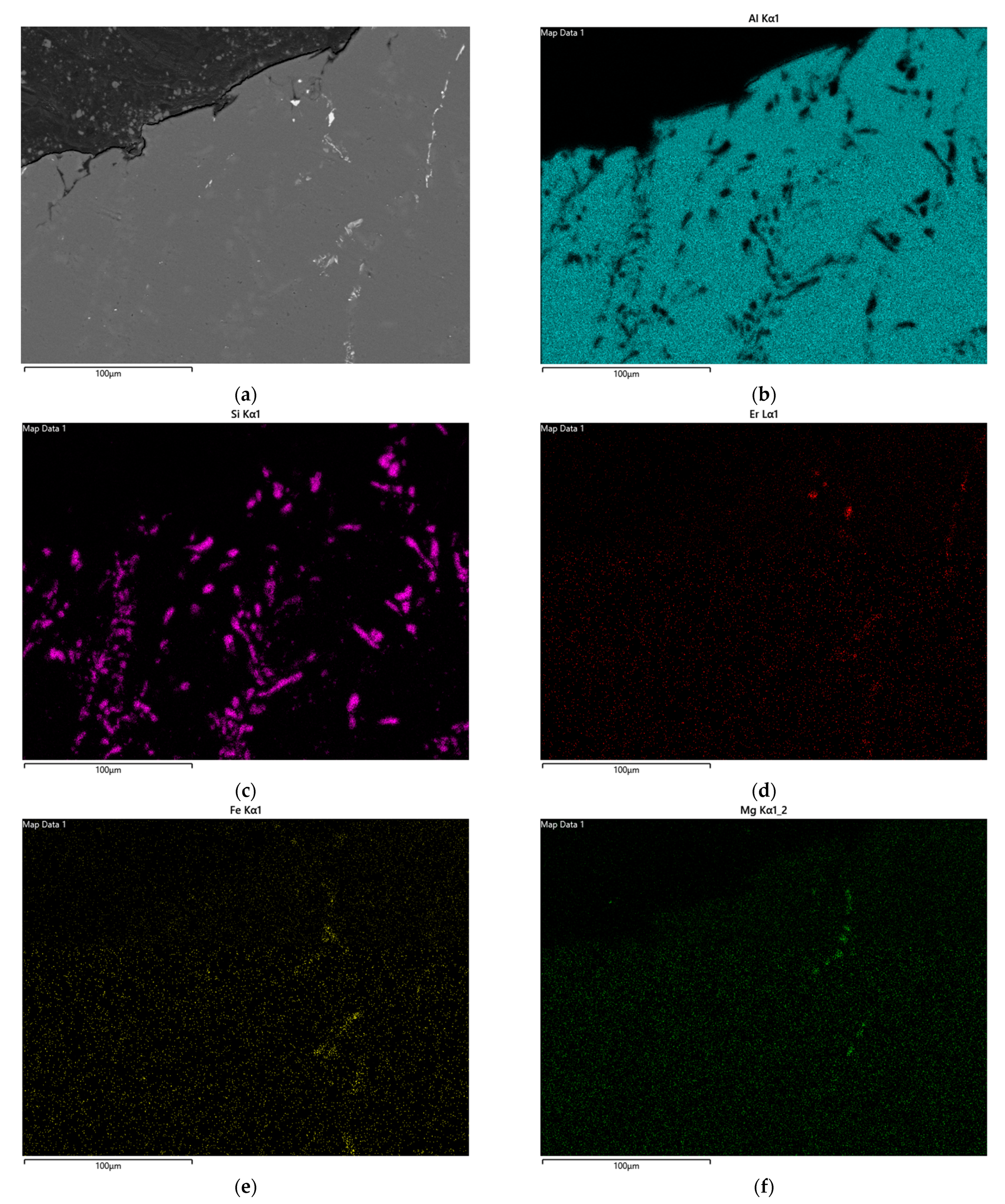
3.4. Metallographic Analyses of Specimens Aged at 300 °C
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
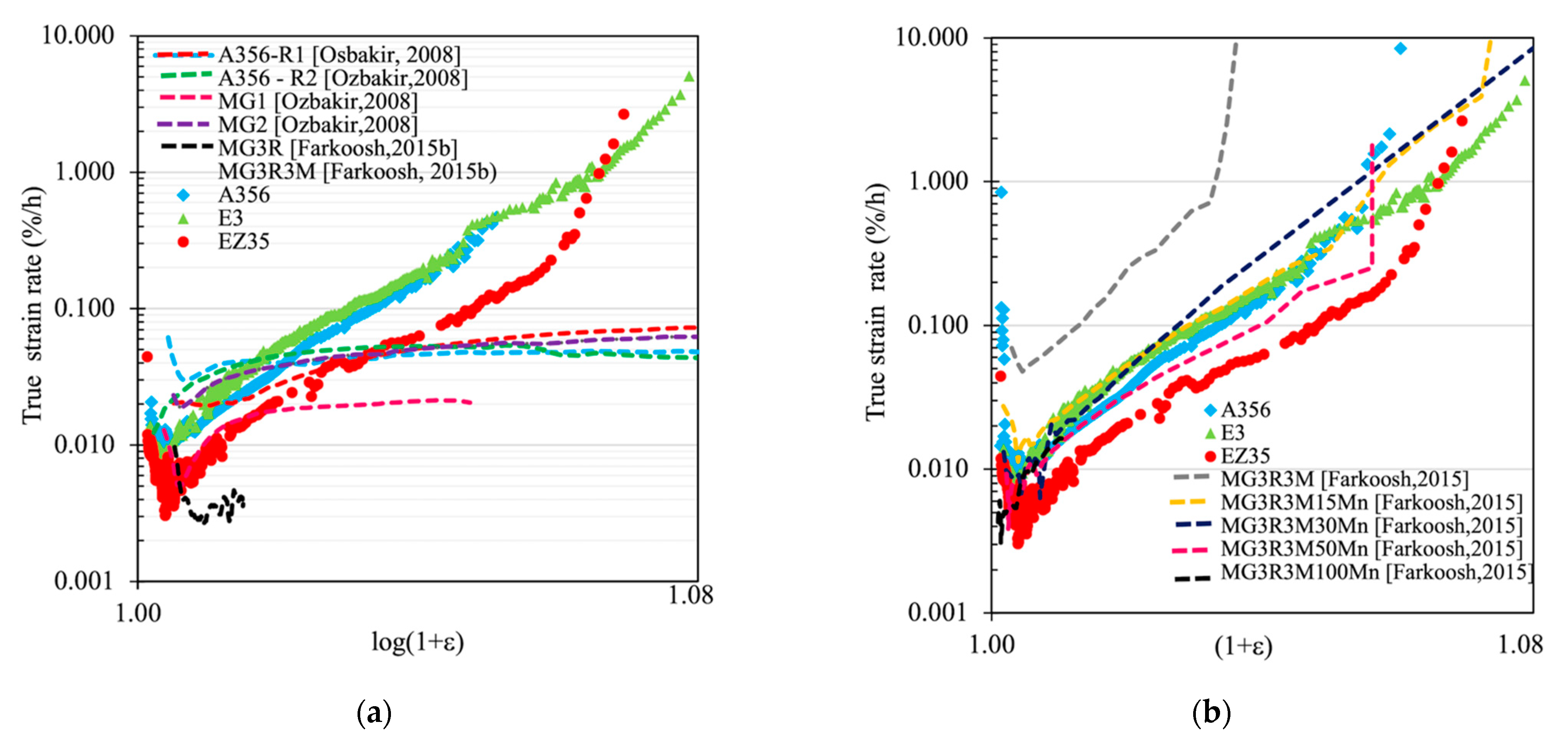
- The minimum creep strain rate at 300 °C decreased from the A356 to E3 and EZ35 alloy, corresponding to the greater amount of strengthening particles;
- The analysis of creep strain rate, performed on a true strain rate vs. (1 + e) plot in order to compare creep curves in tension and in compression, shows that the strain rate increased continuously during the constant load test of about one order of magnitude due to the actual increase of true stress and to a high apparent power-law index. Comparisons with literature data confirm this behavior and correlate it to the presence of nanoscale strengthening particles that could be modeled as threshold stress-behavior;
- The above analysis of creep strain rate for a single specimen can be carried out up to the onset of damage (in tension creep) or barreling (in compression creep). Specifically, in tension creep tests the strain level at which the onset of creep damage occurs could reduce significantly as the microstructural features related to it becoming more critical (high aspect ratio or in higher volume fractions);
- The analysis of the overall tensile creep behavior should take into account, in addition to the minimum creep strain rate, also the final damage, causing a final increase of the strain rate up to the final fracture. As a result, the alloy EZ35, characterized by finer dendritic grains, globular eutectic Si and by high amount of stable coarse Zr-rich intermetallics, mostly in the intradendritic position, displays the onset of creep damage at about 5.5% strain and good ductility indexes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, S.K.; Roy, H.; Mondal, A.K.; Dutta, K. Damage Assessment of A356 Al Alloy under Ratcheting–Creep Interaction. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 2877–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C. High temperature mechanical properties of Al–Si–Mg–(Cu) alloys for automotive cylinder heads. Mater. Trans. 2013, 54, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, S.; Allard, L.F.; Rodriguez, A.; Watkins, T.R.; Shyam, A. Comparative Evaluation of Cast Aluminum Alloys for Automotive Cylinder Heads: Part I—Microstructure evolution. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 48, 2529–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caceres, C.H.; Davidson, C.J.; Griffiths, J.R.; Wang, Q.G. The effect of Mg on the microstructure and mechanical behavior of Al-Si-Mg casting alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1999, 30, 2611–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marioara, C.D.; Andersen, S.J.; Zandbergen, H.W.; Holmestad, R. The Influence of Alloy Composition on Precipitatesof the Al-Mg-Si System. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Gariboldi, E. Prediction of the yield strength and microstructure of a cast Al-Si-Mg alloy by means of physically-based models. Metall. Ital. Int. J. Ital. Assoc. Metall. 2017, 109, 5–14. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/da87/55f77d332b16830fb2f28d91e0ce9c4089f4.pdf?_ga=2.137556403.2019131743.1585306164-1529008527.1567347920 (accessed on 27 April 2021).
- Gariboldi, E.; Lemke, J.N.; Rovatti, L.; Baer, O.; Timelli, G.; Bonollo, F. High-Temperature Behavior of High-Pressure Diecast Alloys Based on the Al-Si-Cu System: The Role Played by Chemical Composition. Metals 2015, 8, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Liu, K.; Chen, X.-G. Improved elevated temperature properties in Al-13%Si piston alloys by Mo addition. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yao, J.-Y.; Sweet, L.; Easton, M.; Taylor, J.; Robinson, P.; Parson, N. Influences of Nickel and Vanadium Impurities on Microstructure of Aluminum Alloys. JOM 2013, 65, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shi, Z.; Li, H.; Lin, Y.; Li, N.; Gong, T.; Zhang, R.; Liu, H. Effects of Holmium Additions on Microstructure and Properties of A356 Aluminum Alloys. Metals 2018, 8, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baraderani, B.; Raiszadeh, R. Precipitation hardening of cast Zr-containing A356 aluminium alloy. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramod, S.L.; Prasada Rao, A.K.; Murty, B.S.; Bakshi, S.R. Effect of Sc addition on the microstructure and wear properties of A356 alloy and A357-TiB2 in situ composite. Mater. Des. 2015, 78, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Z.M.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, R.Y. Effects of erbium modification on the microstructure and mechanical properties of A356 aluminum alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 626, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilaqua, W.L.; Stadtlander, A.R.; Froehlich, A.R.; Braga Lemos, G.V.; Reguly, A. High-temperature mechanical properties of cast Al-Si-Cu-Mg alloy by combined additions of cerium and zirconium. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 026532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.; Morini, L.; Ceschini, L.; Seifeddine, S. The role of transition metal additions on the ambient and elevated temperature properties of Al-Si alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 693, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipling, D.E.; Dunand, D.C.; Seldman, D.N. Criteria for developing castable, creep-resistant aluminium-based alloys—A review. Z. Metallkunde 2006, 97, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Liu, K.; Chen, X.G. Precipitation behavior of dispersoids and elevated-temperature properties in Al–Si–Mg foundry alloy with Mo addition. J. Mater. Res. 2019, 34, 3071–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morri, A.; Ceschini, L.; Messieri, S.; Cerri, E.; Toschi, S. Mo Addition to the A354 (Al–Si–Cu–Mg) Casting Alloy: Effects on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties at Room and High Temperature. Metals 2018, 8, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tocci, M.; Donnini, R.; Angella, G.; Gariboldi, E.; Pola, A. Tensile Properties of a Cast Al-Si-Mg Alloy with Reduced Si Content and Cr Addition at High Temperature. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 7097–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolley, A.; Radmilovic, V.; Dahmen, U. Segregation in Al3(Sc,Zr) precipitates in Al-Sc-Zr alloys. Scr. Mater. 2005, 52, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, C.B.; Seidman, D.N. Temporal evolution of the nanostructure of Al(Sc,Zr) alloys: Part II-coarsening of Al3(Sc1-xZrx) precipitates. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 5415–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Du, K.; Huang, Z.Y.; Huang, H.; Nie, Z.R.; Ye, H.Q. Deformation-induced dissolution and growth of precipitates in an Al-Mg-Er alloy during high-cycle fatigue. Acta Mater. 2014, 81, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Bin, J.; Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Lu, X. Precipitation evolution and coarsening resistance at 400 °C of Al microalloyed with Zr and Er. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.P.; Gao, K.Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, W.; Nie, Z.R. Precipitation evolution in Al-Er-Zr alloys during aging at elevated temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 574, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth-Morrison, C.; Dunand, D.C.; Seidman, D.N. Coarsening resistance at 400 °C of precipitation-strengthened Al–Zr–Sc–Er alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 7029–7042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzak, W.; Amirkhiz, B.S.; Niewczas, M. Structure and properties of cast Al-Si Based alloy with Zr-V-Ti additions and its evaluation of high-temperature performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 595, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Jiang, F.; Ai, F.; Yan, H. Effects of rare earth Er additions on microstructure development and mechanical properties of die-cast ADC12 aluminum alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 538, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, M.H.; Doty, H.W.; Valtierra, S.; Samuel, F.H. Mechanical performance of Zr-Containing 354-type Al-Si-Cu-Mg cast alloy: Role of additions and heat treatment. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 18, 5715819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, F.-S.; Zhang, W.-W.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, D.-T.; Yang, C. Effect of zirconium on microstructures and mechanical properties of squeeze-cast Al-5.0Cu-0.4Mn-0.1Ti-0.1RE alloy. J. Cent. South Univ. 2017, 24, 2231–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Gariboldi, E.; Morri, A. Influences of different Zr additions on the microstructure, room and high temperature mechanical properties of an Al-7Si-0.4Mg alloy modified with 0.25%Er. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 713, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-C.; Chou, C.-Y.; Lee, S.-L.; Lin, C.-K.; Lin, J.-C.; Lim, S.W. Effect of trace La addition on the microstructures and mechanical properties of A356 (Al-7Si-0.35Mg) aluminum alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 487, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy-Yii, S.L.; Kurniawan, D. Effect of rare earth addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Si alloys: An overview. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 845, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.G.; Samuel, A.M.; Doty, H.W.; Valtierra, S.; Samuel, F.H. Effect of Solidification Rate and Rare Earth Metal Addition on the Microstructural Characteristics and Porosity Formation in A356 Alloy. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 5086418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altenbach, H.; Kozhar, S.; Naumenko, K. Modelling creep damage of an aluminium-silicon eutectic alloy. Int. J. Damage Mech. 2012, 22, 683–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rashno, S.; Ranjbar, K.; Reihanian, M. Impression creep characterization of cast Al-7Si-0.3 Mg alloy. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 0865e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiresgandari, B.; Nami, B.; Shahmiri, M.; Abed, A. Effect of Mg and semi solid processing on microstructure and impression creep properties of A356 alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 2518–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkoosh, A.R.; Pekguleryuz, M. The effects of manganese on the Τ-phase and creep resistance in Al–Si–Cu–Mg–Ni alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 582, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hess, D.; Yan, X.; Caron, F. Evaluation of a New High Temperature Casting Aluminium for cylinder head applications. In Proceedings of the 122nd Metalcasting Congress, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 3–5 April 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Farkoosh, A.R.; Grant Chen, X.; Pekguleryuz, M. Interaction between molybdenum and manganese to form effective dispersoids in an Al–Si–Cu–Mg alloy and their influence on creep resistance. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 627, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garat, M. Optimization of aluminium cylinder head alloy of the AlSi7Cu3Mg type reinforced by additions of peritectic elements. Inter. Met. 2011, 5, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Allard, L.F.; Rodriguez, A.; Porter, W.D.; Shyam, A. Comparative Evaluation of Cast Aluminum Alloys for Automotive Cylinder Heads: Part II—Mechanical and Thermal Properties. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 2543–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidani, M.; Larouche, D. Application of cast Al–Si alloys in internal combustion engine components. Int. Mater. Rev. 2014, 59, 132–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.J.; Maijer, D.M.; Dancoine, L. Constitutive behaviour of as-cast A356. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 548, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, C.Y.; Kang, C.-S.; Cho, J.-I.; Oh, I.-H.; Kim, Y.-C. Effect of microstructure on mechanical properties for A356 casting alloy. Int. J. Cast. Met. Res. 2008, 21, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Gariboldi, E.; Morri, A. Er addition to Al-Si-Mg-based casting alloy: Effects on microstructure, room and high temperature mechanical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 708, 1234–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Buzolin, R.H.; Gariboldi, E.; Rovatti, L.; Vallant, R.; Sommitsch, C. Effects of Er and Zr Additions on the As-Cast Microstructure and on the Solution-Heat-Treatment Response of Innovative Al-Si-Mg-Based Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 1000–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6892-2:2018. Metallic Materials-Tensile Testing—Part 2: Method of Test at Elevated Temperature; The International Organization for Standardization Publishing: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 204:2018. Metallic Materials—Uniaxial Creep Testing in Tension-Method of Test; The International Organization for Standardization Publishing: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rasband, W.S. ImageJ, Version 2.0.0-rc-69/1.52i, Distribution Fiji. 2018. Available online: https://imagej.net/Welcome (accessed on 29 March 2021).
- Colombo, M.; Albu, M.; Gariboldi, E.; Hofer, F. Microstructural changes induced by Er and Zr additions to A356 alloy investigated by thermal analyses and STEM observations. Mater. Charact. 2020, 161, 11011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkoosh, A.R.; Chen, X.G.; Pekgureryuz, M. Dispersoid strengthening of a high temperature Al-Si-Cu-Mg alloy via Mo addition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 620, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbakir, E. Development of Aluminum Alloys for Diesel-Engine Applications. Master’s Thesis, McGill University, Montréal, QC, Canada, December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rashno, S.; Reihanian, M.; Ranjbar, K. Tensile and creep properties of Al-7Si-0.3Mg alloy with Zr and Er addition. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 36, 1603–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Breton, F. Evaluation of New AlSiCuMg Cast Aluminium Alloys for Automotive Cylinder Heads. In Proceedings of the 2020 AFS 124th Metalcasting Congress, Cleveland, OH, USA, 21–23 April 2020; Available online: http://afsinc.s3.amazonaws.com/2020%20Proceedings/2020-018_lm.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2021).
- Griffiths, S.; Croteau, J.R.; Rossell, M.D.; Erni, R.; De Luca, A.; Vo, N.Q.; Dunand, D.C.; Leinenbach, C. Coarsening- and creep resistance of precipitation-strengthened Al–Mg–Zr alloys processed by selective laser melting. Acta Mater. 2020, 188, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigarelli, S.; Paoletti, C. A new model for the description of creep behaviour of aluminium-based composites reinforced with nanosized particles. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 112, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermo-Calc Software; Version 2020b with TCAL5.1 Al-Alloys Database; Thermo-Calc Software: Stockholm, Sweden, 2020.
- Du, Y.; Chang, Y.A.; Huang, B.; Gong, W.; Jin, Z.; Xu, H.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Xie, F.-Y. Diffusion coefficients of some solutes in fcc and liquid Al: Critical evaluation and correlation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 363, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Tang, K.; Marioara, C.D.; Andersen, S.J. Modeling over-ageing in Al-Mg-Si alloys by a multi-phase CALPHAD-coupled Kampmann-Wagner Numerical model. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chomsaeng, N.; Haruta, M.; Chairuangsri, T.; Kurata, H.; Isoda, S.; Shiojiri, M. HRTEM and ADF-STEM of precipitates at peak-ageing in cast A356 aluminium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 496, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, K.; Wen, S.; Huang, H.; Nie, Z.; Zhou, D. The study on the coarsening process and precipitation strengthening of Al3Er precipitate in Al-Er binary alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 610, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wen, S.P.; Gao, K.Y.; Wang, W.; Nie, Z.R. Age hardening behavior and corresponding microstructure of dilute Al-Er-Zr alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 2849–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manente, A.; Timelli, G. Optimizing the Heat Treatment Process of Cast Aluminium Alloys. In Recent Trends in Processing and Degradation of Aluminium Alloys; Ahmad, Z., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2011; pp. 197–220. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/books/recent-trends-in-processing-and-degradation-of-aluminium-alloys/optimizing-the-heat-treatment-process-of-cast-aluminium-alloys (accessed on 27 April 2021).




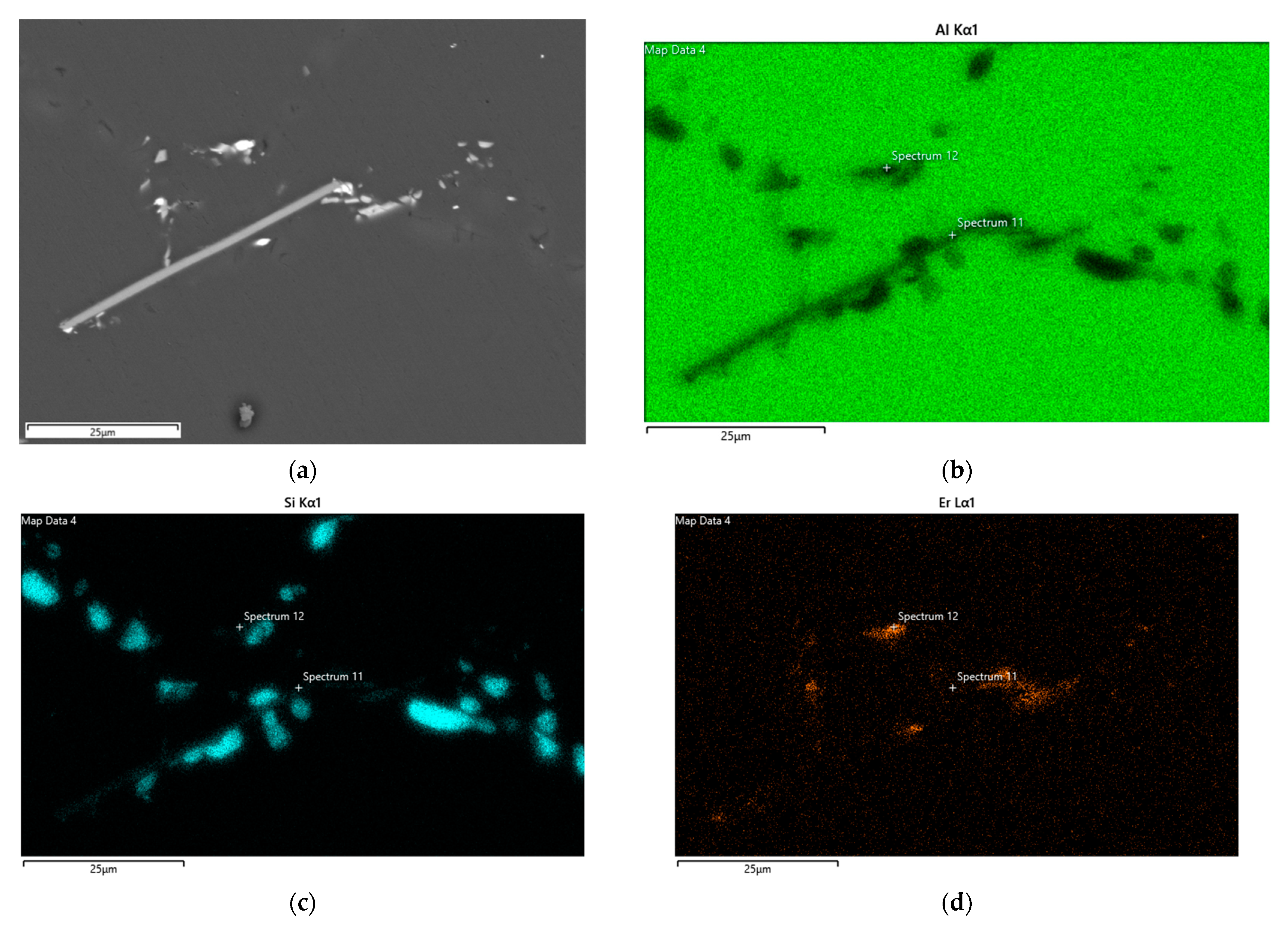
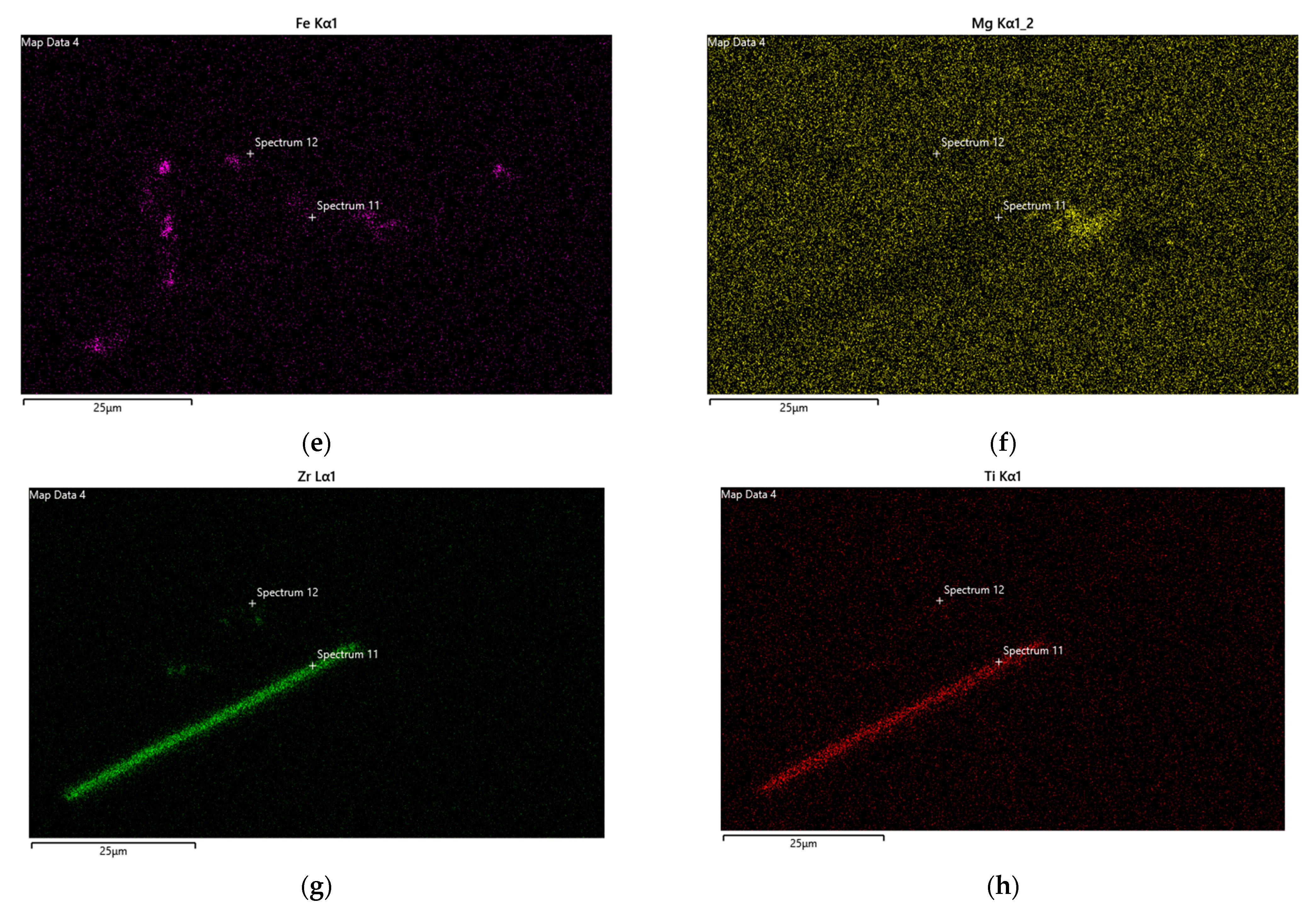
| Si | Mg | Fe | Ti | Er | Zr | Al | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A356 | 7.02 | 0.41 | 0.07 | 0.14 | - | bal | |
| E3 | 7.40 | 0.34 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.29 | - | bal |
| EZ35 | 6.66 | 0.37 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.31 | 0.49 | bal |
| Point# | Al | Si | Ti | V | Fe | Zr | Er | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | 75.58 | 8.19 | 4.57 | 0.09 | 0.47 | 10.68 | 0.43 | 100 |
| 12 | 72.63 | 11.87 | - | - | - | - | 15.49 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gariboldi, E.; Confalonieri, C.; Colombo, M. High Temperature Behavior of Al-7Si-0.4Mg Alloy with Er and Zr Additions. Metals 2021, 11, 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11060879
Gariboldi E, Confalonieri C, Colombo M. High Temperature Behavior of Al-7Si-0.4Mg Alloy with Er and Zr Additions. Metals. 2021; 11(6):879. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11060879
Chicago/Turabian StyleGariboldi, Elisabetta, Chiara Confalonieri, and Marco Colombo. 2021. "High Temperature Behavior of Al-7Si-0.4Mg Alloy with Er and Zr Additions" Metals 11, no. 6: 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11060879
APA StyleGariboldi, E., Confalonieri, C., & Colombo, M. (2021). High Temperature Behavior of Al-7Si-0.4Mg Alloy with Er and Zr Additions. Metals, 11(6), 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11060879







