Use of Multi-Anionic Sodium Tripolyphosphate to Enhance Dispersion of Concentrated Kaolin Slurries in Seawater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Rheological Characterization
2.2. Particle Size Distribution
2.3. Zeta Potential
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Yield Stress of Kaolin Slurries
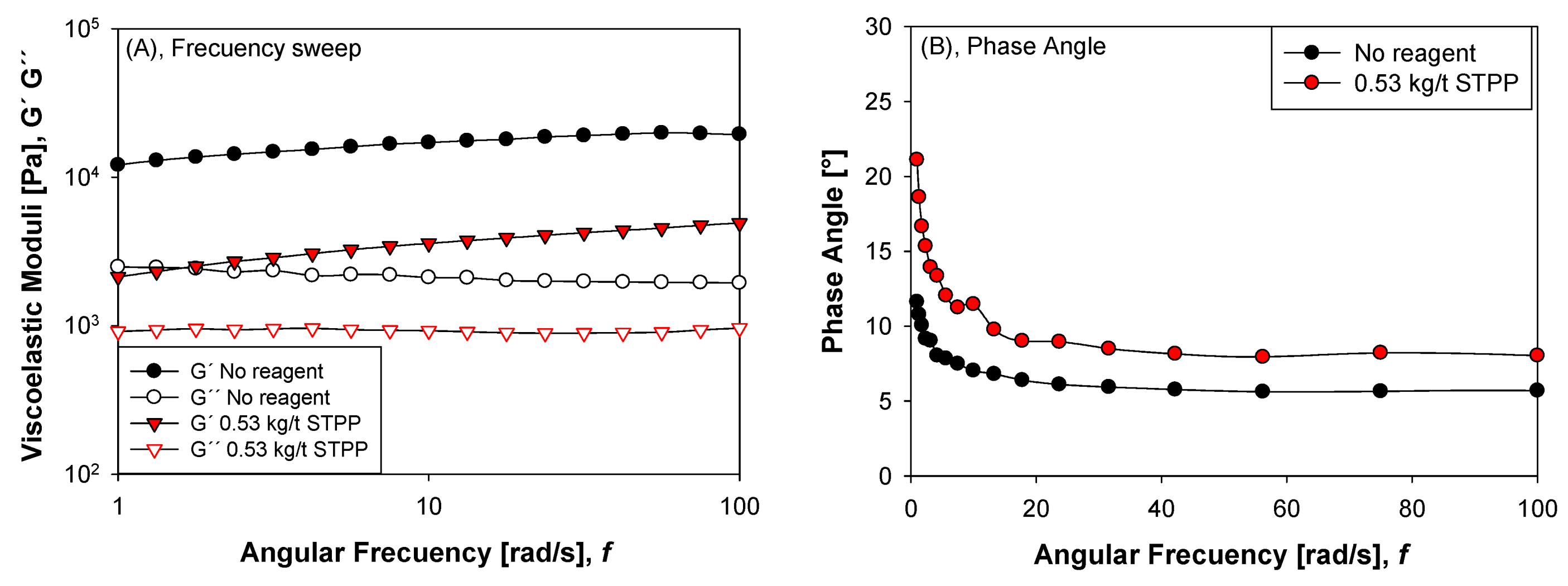
3.2. Viscoelasticity by Oscillatory Rheology
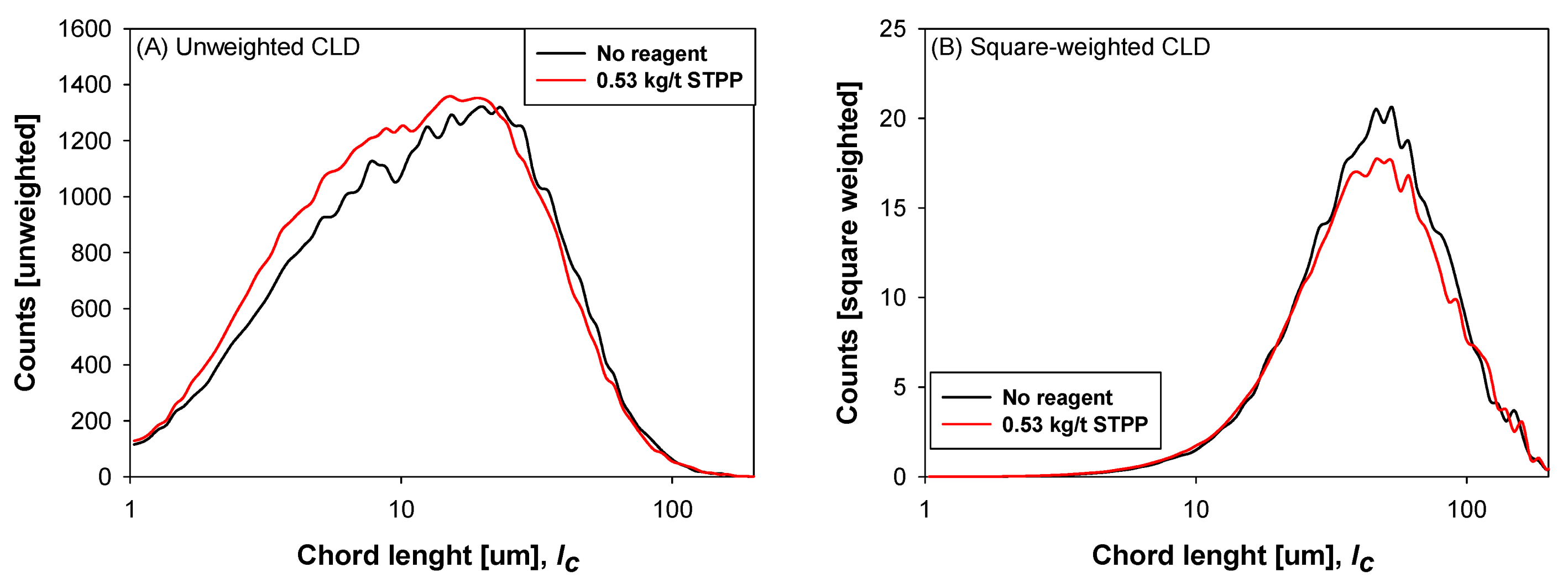
3.3. Chord Length Distribution
3.4. Zeta Potential
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klein, B.; Hallbom, D.J. Modifying the rheology of nickel laterite suspensions. Miner. Eng. 2002, 15, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, N.; Forster, J.; Bobicki, E.R. Slurry rheology in mineral processing unit operations: A critical review. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 2102–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofrá, F.; Boger, D.V. Environmental rheology for waste minimisation in the minerals industry. Chem. Eng. J. 2002, 86, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boger, D.V. Rheology and the Minerals Industry. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2000, 20, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.D.; Boger, D.V. Application of rheology to solving tailings disposal problems. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1998, 54, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihle, C.F.; Kracht, W. The relevance of water recirculation in large scale mineral processing plants with a remote water supply. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kretser, R.; Scales, P.J.; Boger, D.V. Improving clay-based tailings disposal: Case study on coal tailings. AIChE J. 1997, 43, 1894–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisternas, L.A.; Gálvez, E.D. The use of seawater in mining. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2018, 39, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, J.S.; Castro, S.; Gutierrez, L. Flotation in Seawater. Mining Metall. Explor. 2019, 36, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeldres, R.I.; Arancibia-Bravo, M.P.; Reyes, A.; Aguirre, C.E.; Cortes, L.; Cisternas, L.A. The impact of seawater with calcium and magnesium removal for the flotation of copper-molybdenum sulphide ores. Miner. Eng. 2017, 109, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellón, C.I.; Piceros, E.C.; Toro, N.; Robles, P.; López-Valdivieso, A.; Jeldres, R.I. Depression of pyrite in seawater flotation by guar gum. Metals 2020, 10, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paredes, Á.; Acuña, S.M.; Toledo, P.G. AFM study of pyrite oxidation and xanthate adsorption in the presence of seawater salts. Metals 2019, 9, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reyes, C.; Álvarez, M.; Ihle, C.F.; Contreras, M.; Kracht, W. The influence of seawater on magnetite tailing rheology. Miner. Eng. 2019, 131, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafe, M.; Klauber, C.; McFarlane, A.J. Clays in the Minerals Processing Value Chain; Grafe, M., Klauber, C., McFarlane, A.J., Robinson, D.J., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; ISBN 9781316661888. [Google Scholar]
- Jeldres, R.I.; Piceros, E.C.; Wong, L.; Leiva, W.H.; Herrera, N.; Toledo, P.G. Dynamic moduli of flocculated kaolinite sediments: Effect of salinity, flocculant dose, and settling time. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2018, 296, 1935–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombácz, E.; Szekeres, M. Surface charge heterogeneity of kaolinite in aqueous suspension in comparison with montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 34, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Liu, J.; Clode, P.; Leong, Y.K. Microstructure and rheology of bentonite slurries containing multiple-charge phosphate-based additives. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 169, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, E.J.; Leong, Y.K.; Liu, Y.; Fourie, A.B.; Fahey, M. Differences in the rheology and surface chemistry of kaolin clay slurries: The source of the variations. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 3817–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeldres, R.I.; Jeldres, M. Rheological perspectives of clay-based tailings in the mining industry. In Clay Science and Technology; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Güngör, N. Effect of the adsorption of surfactants on the rheology of Na-bentonite slurries. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 75, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztekin, N.; Alemdar, A.; Güngör, N.; Erim, F.B. Adsorption of polyethyleneimine from aqueous solutions on bentonite clays. Mater. Lett. 2002, 55, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunç, S.; Duman, O. The effect of different molecular weight of poly(ethylene glycol) on the electrokinetic and rheological properties of Na-bentonite suspensions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 317, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöberg, M.; Bergström, L.; Larsson, A.; Sjöström, E. The effect of polymer and surfactant adsorption on the colloidal stability and rheology of kaolin dispersions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1999, 159, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, D.; Lagaly, G. Influence of anions on the rheological properties of clay mineral dispersions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2001, 19, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahnoun, R.D.; Charfi, A.; Bouaziz, J. Effect of K3PO4, K2HPO4, KH2PO4 and H3PO4 as dispersing agents on the rheological behaviour of kaolin suspensions. Trans. Indian Ceram. Soc. 2014, 73, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Hernández, F.-J.; Páez-Flor, N.-M.; Gómez-Merino, A.-I.; Sánchez-Luque, F.-J.; Delgado-García, R.; Goyos-Pérez, L. The Influence of high-concentration Na hexametaphosphate dispersant on the rheological behavior of aqueous kaolin dispersions. Clays Clay Miner. 2016, 64, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M. The dispersive effect of sodium hexametaphosphate on kaolinite in saline water. Clays Clay Miner. 2012, 60, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, A.; Rojas, A.; Gutierrez, L.; Laskowski, J.S. Sodium hexametaphosphate and sodium silicate as dispersants to reduce the negative effect of kaolinite on the flotation of chalcopyrite in seawater. Miner. Eng. 2018, 125, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, A.; Kirichek, A.; Chassagne, C. Yield stress measurements of mud sediments using different rheological methods and geometries: An evidence of two-step yielding. Mar. Geol. 2020, 427, 106247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, J.D.G.; Ramos-Tejada, M.M.; Arroyo, F.J.; González-Caballero, F. Rheological and electrokinetic properties of sodium montmorillonite suspensions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 229, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benna, M.; Kbir-Ariguib, N.; Magnin, A.; Bergaya, F. Effect of pH on rheological properties of purified sodium bentonite suspensions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 218, 442–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasser, M.S.; James, A.E. The effect of electrolyte concentration and ph on the flocculation and rheological behaviour of kaolinite suspensions. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2009, 4, 430–446. [Google Scholar]
- Jeldres, R.I.; Uribe, L.; Cisternas, L.A.; Gutierrez, L.; Leiva, W.H.; Valenzuela, J. The effect of clay minerals on the process of flotation of copper ores—A critical review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 170, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeldres, M.; Robles, P.; Toledo, P.G.; Saldaña, M.; Quezada, L.; Jeldres, R.I. Improved dispersion of clay-rich tailings in seawater using sodium polyacrylate. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 612, 126015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, K.; Wilhelm, M.; Klein, C.O.; Cho, K.S.; Nam, J.G.; Ahn, K.H.; Lee, S.J.; Ewoldt, R.H.; McKinley, G.H. A review of nonlinear oscillatory shear tests: Analysis and application of large amplitude oscillatory shear (LAOS). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1697–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Phan-Thien, N.; Lee, J.B.P.; Khoo, B.C. Concentration dependence of yield stress and dynamic moduli of kaolinite suspensions. Langmuir 2015, 31, 4791–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles, P.; Piceros, E.; Leiva, W.H.; Valenzuela, J.; Toro, N.; Jeldres, R.I. Analysis of sodium polyacrylate as a rheological modifier for kaolin suspensions in seawater. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 183, 105328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| STPP Dose (kg/t) | NaOH (kg/t) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 2.19 |
| 0.10 | 1.65 |
| 0.53 | 1.24 |
| 1.00 | 1.03 |
| 3.00 | 0.69 |
| 5.00 | 0.56 |
| 7.00 | 0.27 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leiva, W.; Toro, N.; Robles, P.; Gálvez, E.; Jeldres, R.I. Use of Multi-Anionic Sodium Tripolyphosphate to Enhance Dispersion of Concentrated Kaolin Slurries in Seawater. Metals 2021, 11, 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11071085
Leiva W, Toro N, Robles P, Gálvez E, Jeldres RI. Use of Multi-Anionic Sodium Tripolyphosphate to Enhance Dispersion of Concentrated Kaolin Slurries in Seawater. Metals. 2021; 11(7):1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11071085
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeiva, Williams, Norman Toro, Pedro Robles, Edelmira Gálvez, and Ricardo Ivan Jeldres. 2021. "Use of Multi-Anionic Sodium Tripolyphosphate to Enhance Dispersion of Concentrated Kaolin Slurries in Seawater" Metals 11, no. 7: 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11071085
APA StyleLeiva, W., Toro, N., Robles, P., Gálvez, E., & Jeldres, R. I. (2021). Use of Multi-Anionic Sodium Tripolyphosphate to Enhance Dispersion of Concentrated Kaolin Slurries in Seawater. Metals, 11(7), 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11071085









