Recovery of Pure Pd(II) from Spent Electroplating Solutions by Solvent Extraction with Ionic Liquids from Sulfuric Acid Leaching Solution of Cemented Pd
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of Ionic Liquids
2.3. Experimental Procedure and Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
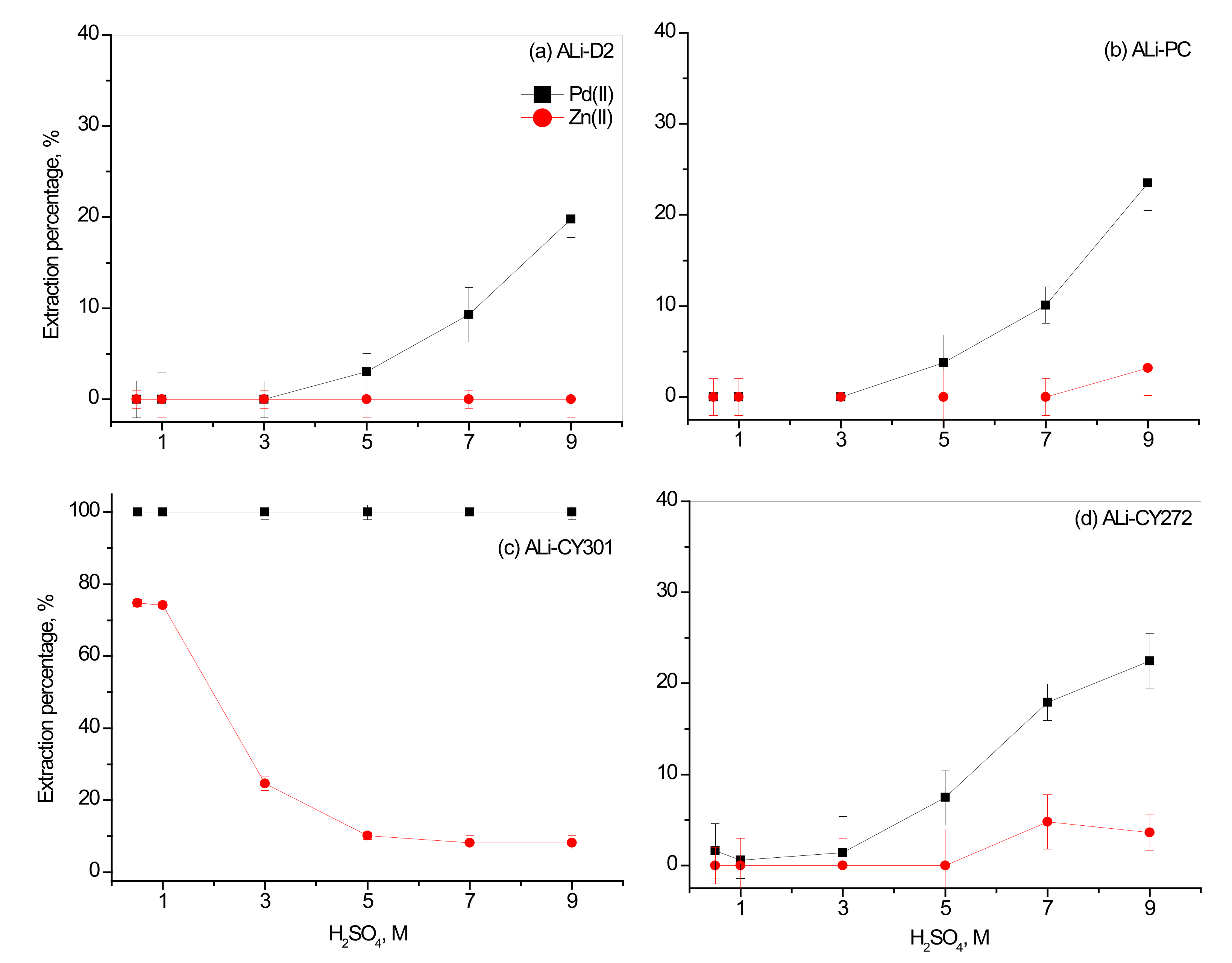
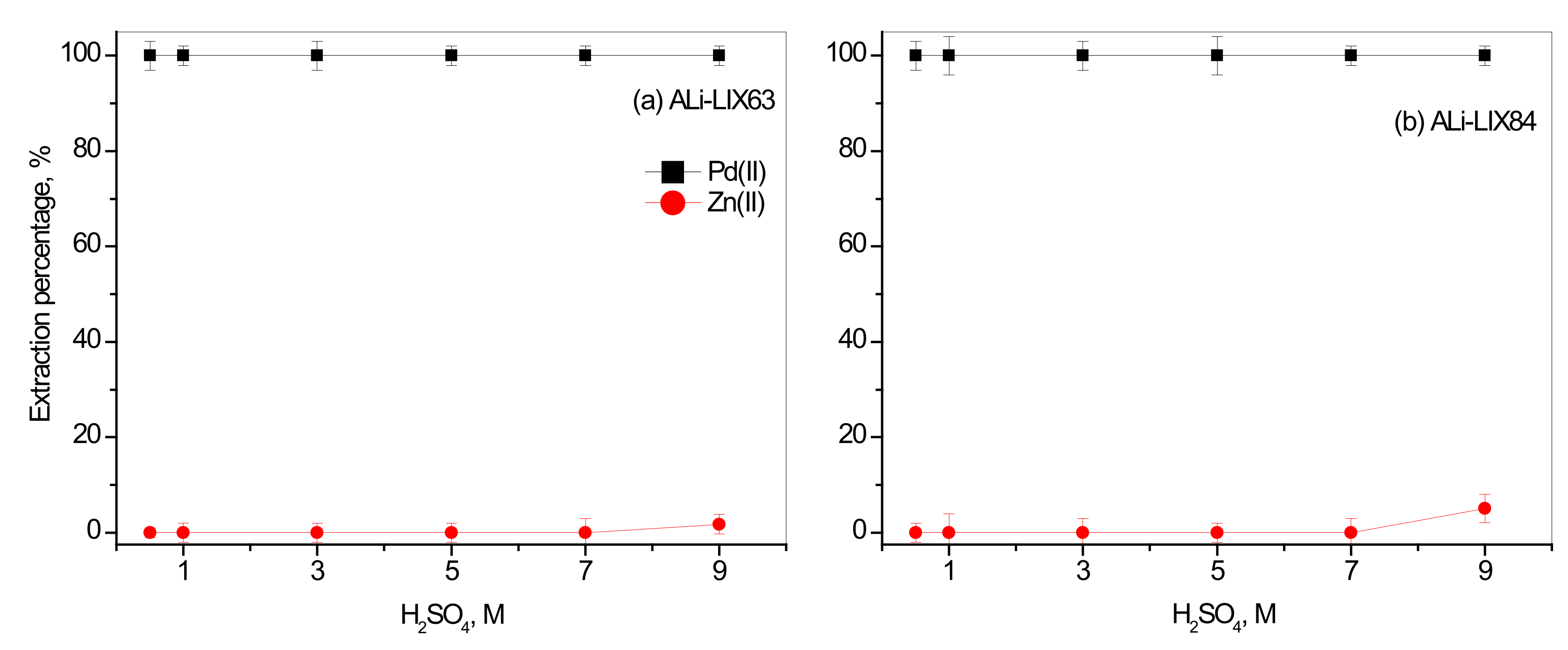
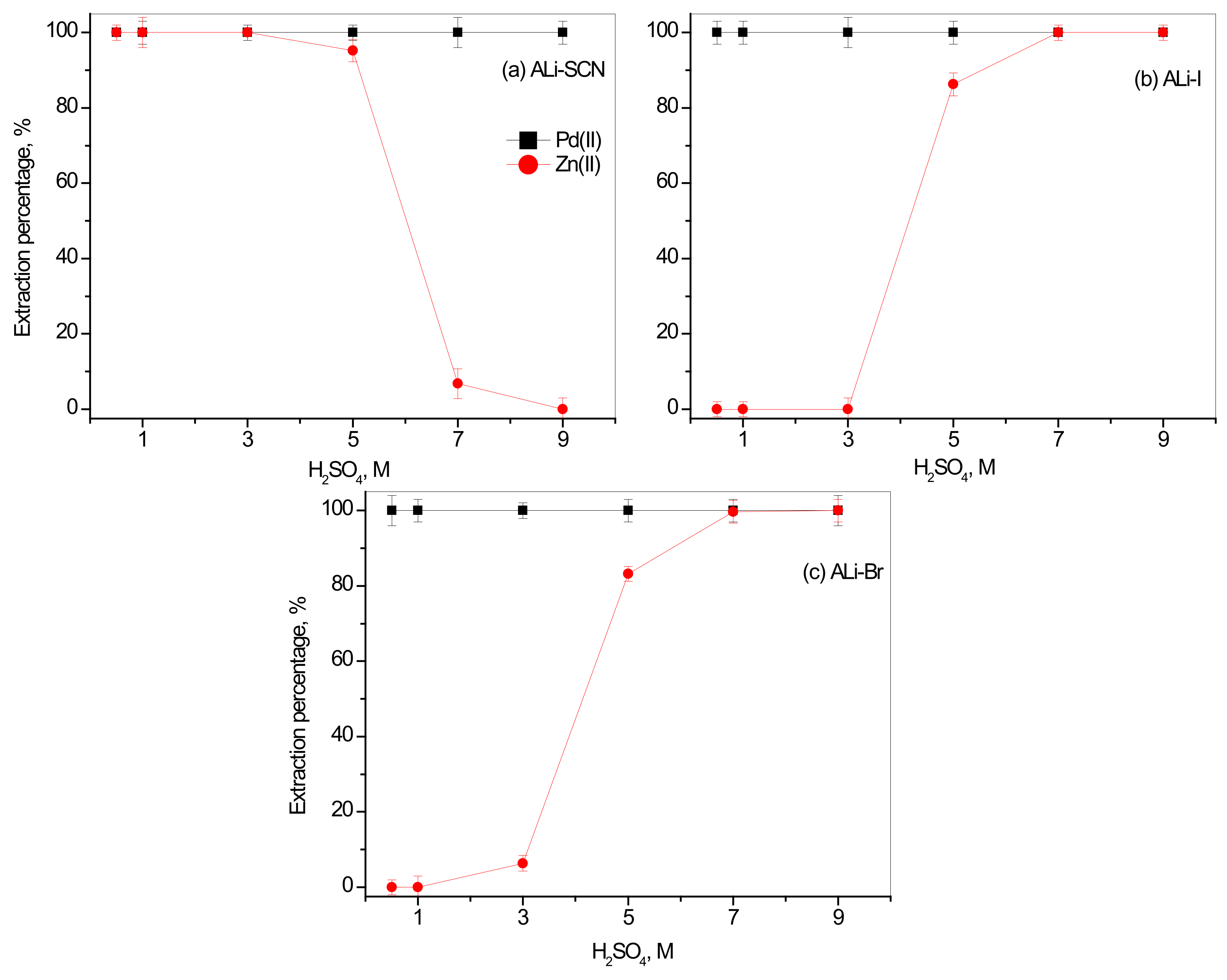
3.1. Effect of H2SO4 Concentration on the Separation of Pd(II) over Zn(II)
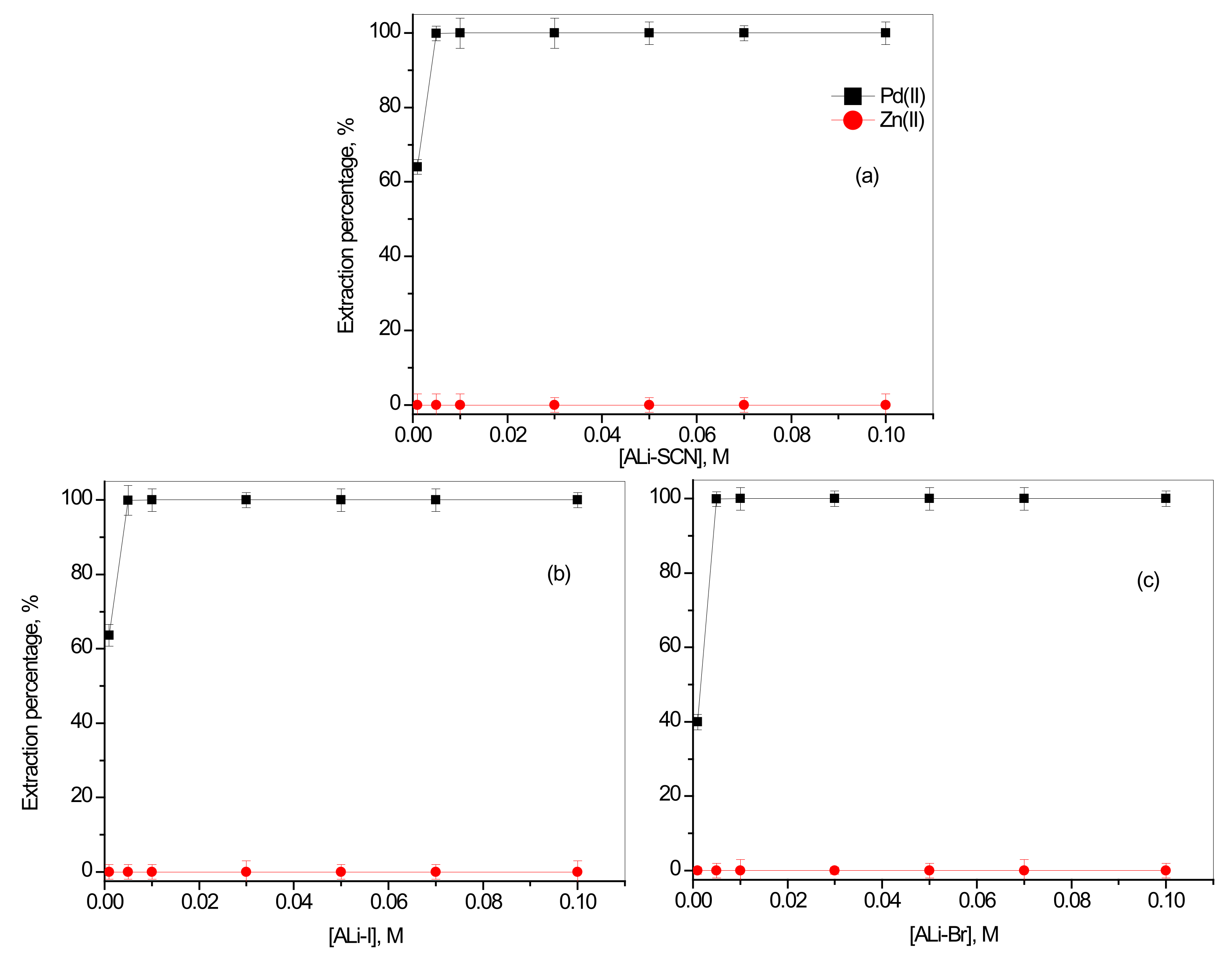
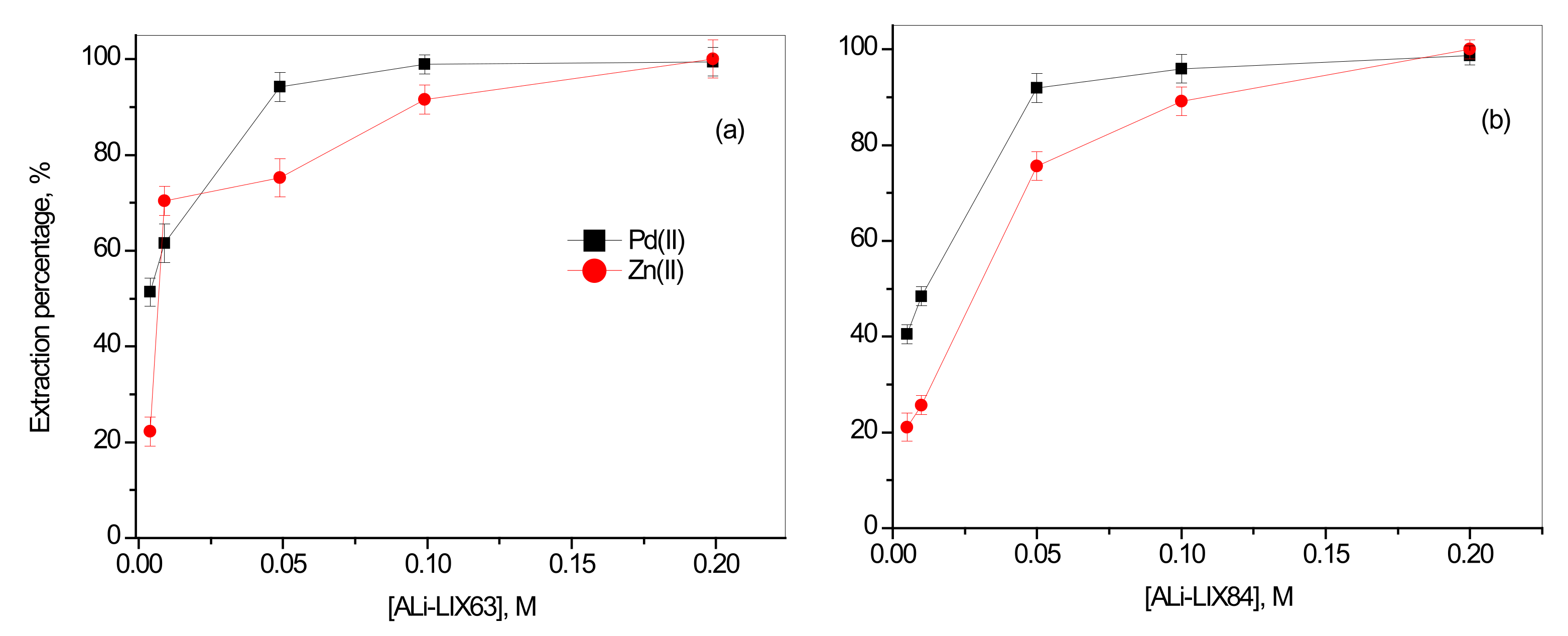
3.2. Effect of Synthesized ILs Concentration on the Separation of Pd(II) over Zn(II)
3.2.1. Effect of Concentration of Synthesized ILs with Organic Anions
3.2.2. Effect of Concentration of Synthesized ILs with Inorganic Anions
3.3. Stripping of Pd(II)
3.3.1. Preliminary Stripping Experiments
3.3.2. Stripping of Pd(II) from Loaded Organic Phase of Synthesized ILs with Organic Anions
3.3.3. Stripping of Pd(II) from Loaded Organic Phase of Synthesized ILs with Inorganic Anions
3.4. The Separation of Pd(II) over Zn(II) from Real Leaching Solution of Cemented Pd
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antler, M. The Application of Palladium in Electronic Connectors Continuing Studies result in Growing use. Platin. Met. Rev. 1982, 26, 106–117. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.J.; Nguyen, V.N.H.; Lee, M.S. Leaching of a Mixture of Palladium and Zinc Metal Using Hydrochloric and Sulfuric Acid Solutions. Korean J. Met. Mater. 2021, 59, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Sonu, C.H.; Lee, M.S. Separation of Pt(IV), Pd(II), Rh(III) and Ir(IV) from concentrated hydrochloric acid solutions by solvent extraction. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 164, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, H.T.; Lee, M.S. Separation of Pd(II) and Pt(IV) from hydrochloric acid solutions by solvent extraction with Cyanex 301 and LIX 63. Miner. Eng. 2018, 115, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Singh, I. Extraction and separation of platinum, palladium and rhodium using Cyanex 923 and their recovery from real samples. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 134–135, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.R.; Raju, B.; Lee, J.-Y.; Park, H.K. Process for the separation and recovery of palladium and platinum from spent automobile catalyst leach liquor using LIX 84I and Alamine 336. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 180, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovira, M.; Cortina, J.L.; Amaldos, J.; Sastre, A.M. Recovery and separation of platinum group metals using impregnated resins containing alamine 336. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 1998, 16, 1279–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreier, G.; Edtmaier, C. Separation of Ir, Pd and Rh from secondary Pt scrap by precipitation and calcination. Hydrometallurgy 2003, 68, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Riaño, S.; Binnemans, K. Separation of precious metals by split-anion extraction using water-saturated ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 8375–8388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieszyńska, A.; Wisniewski, M. Selective extraction of palladium(II) from hydrochloric acid solutions with phosphonium extractants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 80, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crundwell, F.K.; Moats, M.; Ramachandran, V.; Robinson, T.G.; Davenport, W.G. Extractive Metallurgy of Nickel, Cobalt and Platinum Group Metals; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rane, M.; Venugopal, V. Study on the extraction of palladium(II) and platinum(IV) using LIX 84I. Hydrometallurgy 2006, 84, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, Z.-D. Solvent extraction and separation of palladium(II) and platinum(IV) from hydrochloric acid medium with dibutyl sulfoxide. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.P.; Carvalho, G.; Costa, M.C.; Da Costa, A.M.R.; Nogueira, C. Recovery of Platinum and Palladium from Chloride Solutions by a Thiodiglycolamide Derivative. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2013, 32, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swain, B.; Jeong, J.; Kim, S.-K.; Lee, J.-C. Separation of platinum and palladium from chloride solution by solvent extraction using Alamine 300. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, M. Solvent extraction in hydrometallurgy. In Solvent Extraction Principles and Practice, 2nd ed.; Rydberg, J., Cox, M., Musikas, C., Choppin, G.R., Eds.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 455–505. [Google Scholar]
- Onghena, B.; Valgaeren, S.; Hoogerstraete, T.V.; Binnemans, K. Cobalt(ii)/nickel(ii) separation from sulfate media by solvent extraction with an undiluted quaternary phosphonium ionic liquid. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 35992–35999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Sonu, C.H.; Lee, M.S. Separation of platinum(IV) and palladium(II) from concentrated hydrochloric acid solutions by mixtures of amines with neutral extractants. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 32, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayl, A. Extraction and separation of Co(II) and Ni(II) from acidic sulfate solutions using Aliquat 336. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.; Azra, N.; Iqbal, M.; Lee, M.S. Synthesis of succinimide based ionic liquids and comparison of extraction behavior of Co(II) and Ni(II) with bi-functional ionic liquids synthesized by Aliquat336 and organophosphorus acids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 238, 116496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.N.H.; Lee, M.S. Separation of Co(II), Ni(II), Mn(II) and Li(I) from synthetic sulfuric acid leaching solution of spent lithium ion batteries by solvent extraction. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, J.S. Solvent Extraction of Cobalt(II) and Nickel(II) by a Quaternary Ammonium Thiocyanate. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1982, 17, 1697–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, C.; Oates, C.; Monhemius, A.; Plant, J. Complexation of platinum, palladium and rhodium with inorganic ligands in the environment. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2008, 8, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, T.; Elding, L.I.; Meľnikov, M.Y.; Feldman, V.I.; Kristjánsdóttir, Á.G.; Matsson, O.; Mikkelsen, K.V.; Senning, A. Equilibria, Kinetics and Mechanism for Complex Formation between Hydrogen Sulfate/Sulfate and Palladium(II). Hydrolysis of Tetraaquapalladium(II). Acta Chem. Scand. 1998, 52, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsuta, S.; Yoshimoto, Y.; Okai, M.; Takeda, Y.; Bessho, K. Selective Extraction of Palladium and Platinum from Hydrochloric Acid Solutions by Trioctylammonium-Based Mixed Ionic Liquids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 12735–12740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kubota, F.; Baba, Y.; Kamiya, N.; Goto, M. One Step Effective Separation of Platinum and Palladium in an Acidic Chloride Solution by Using Undiluted Ionic Liquids. Solvent Extr. Res. Dev. Jpn. 2014, 21, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, K.; Takao, K.; Suzuki, T.; Mori, T.; Arai, T.; Ikeda, Y. Extraction of Pd(ii), Rh(iii) and Ru(iii) from HNO3 aqueous solution to betainium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ionic liquid. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 5648–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuny, A.; Coll, M.; Sastre, A.M. Use of methyltrioctyl/decylammonium bis 2,4,4-(trimethylpentyl)phosphinate ionic liquid (ALiCY IL) on the boron extraction in chloride media. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 97, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.N.; Nguyen, V.N.H.; Liu, Y.; Lee, M.S. Analysis of the interaction in the mixture of organophosphorus acids and Aliquat 336 through the measurement of dielectric constant and viscosity. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 315, 113738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, C.J.; Gans, P.R.; Kriek, J. Complexation of palladium(II) with thiocyanate—A spectrophotometric investigation. J. Coord. Chem. 2014, 67, 1520–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elding, L. Palladium(II) halide complexes. I. Stabilities and spectra of palladium(II) chloro and bromo aqua complexes. Inorganica Chim. Acta 1972, 6, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elding, L. Stabilities of platinum(II) chloro and bromo complexes and kinetics for anation of the tetraaquaplatinum(II) ion by halides and thiocyanate. Inorganica Chim. Acta 1978, 28, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elding, L.I.; Olsson, L.-F. Stabilities, solubility, and kinetics and mechanism for formation and hydrolysis of some palladium(II)and platinum(II) iodo complexes in aqueous solution. Inorganica Chim. Acta 1986, 117, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, J.R.; Prince, H. Zinc: Inorganic and Coordination Chemistry. Based in part on the article Zinc: Inorganic and Coordination Chemistry by Reg H. Prince which appeared in the Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry, First Edition. In Encyclopedia of Inorganic and Bioinorganic Chemistry, 1st ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, B.K. The extraction of some base metal ions by cyanex 30l cyanex 302 and their binary extractant mixtures with aliquat 336. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 1992, 10, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, D.; Depuydt, D.; Binnemans, K. Overview of the Effect of Salts on Biphasic Ionic Liquid/Water Solvent Extraction Systems: Anion Exchange, Mutual Solubility, and Thermomorphic Properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 6747–6757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveichuk, Y.V.; Rakhman’ko, E.M.; Yasinetskii, V.V. Thiocyanate complexes of d metals: Study of aqueous solutions by UV, visible, and IR spectrometry. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 60, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiromitsu, M.; Tatsuya, S. Stability and Extractability of Zinc (II) Thiocyanate complexes in several solvent extraction systems. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1971, 44, 3347–3352. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.N.H.; Lee, M.S. Solvent extraction of Hydrochloric Acid Using Commercial Extractants and Synthesized Ionic Liquids. J. Korean Inst. Resour. Recycl. 2020, 29, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Landini, D.; Maia, A.; Rampoldi, A. Stability of quaternary onium salts under phase-transfer conditions in the presence of aqueous alkaline solutions. J. Org. Chem. 1986, 51, 3187–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbaix, M. Atlas of Electrochemical Equilibria in Aqueous Solutions; Pergamon Press: London, UK, 1966; pp. 359–591. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, T.; Nakamura, T.; Fujimatsu, T. Extraction of bivalent Manganese, Cobalt, Copper, Zinc, and Cadmium from hydrochloric acid solutions by long-chain alkyl quaternary ammonium chloride in various organic solvents. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1981, 54, 2656–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
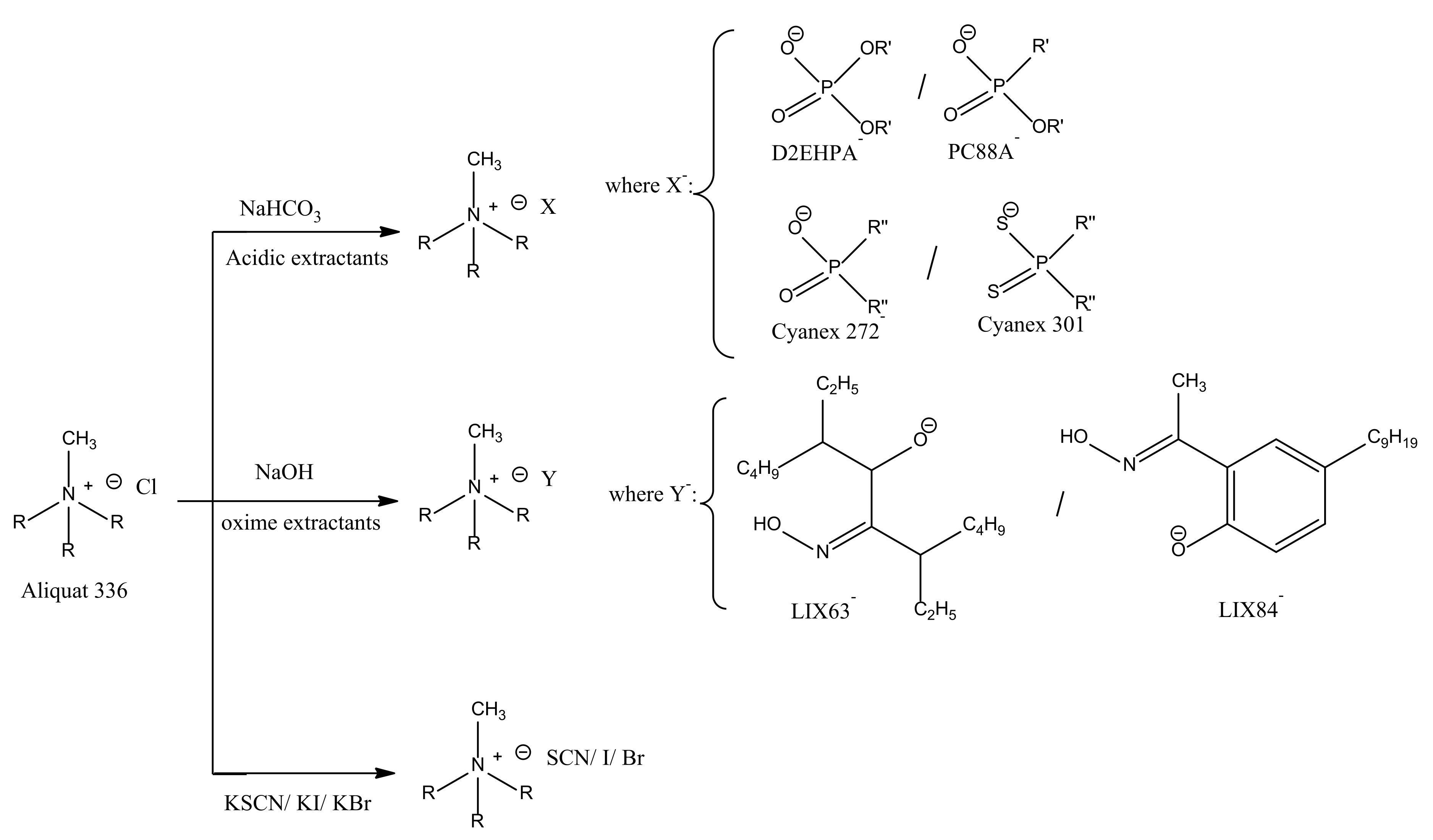
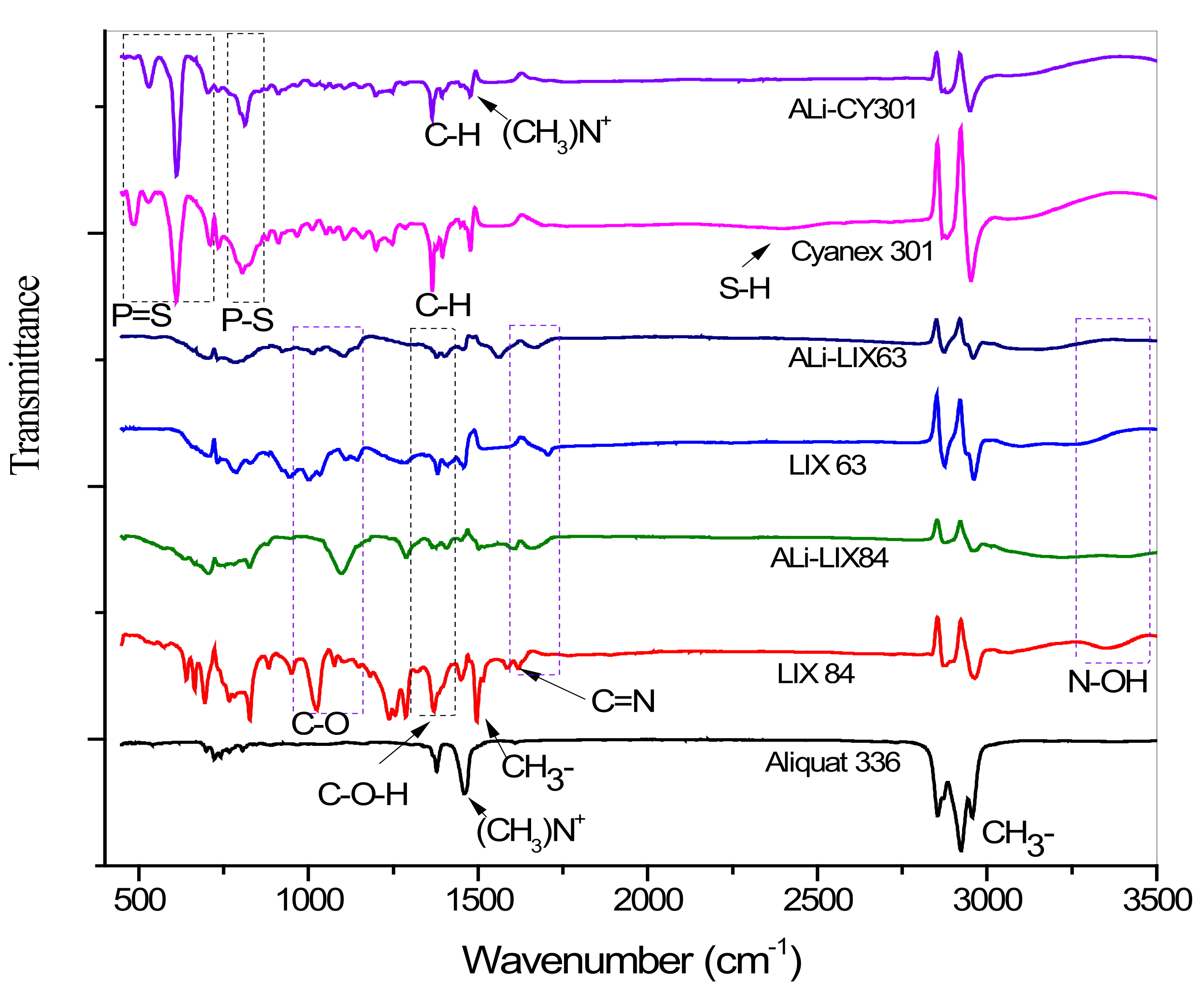

| Extractant | C–O (cm−1) | C–O–H (cm−1) | C=N (cm−1) | N–O–H (cm−1) | P–S (cm−1) | P=S (cm−1) | S–H (cm−1) | C–H (cm−1) | (CH3)+N (cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aliquat 336 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1378 | 1463.6 | |
| LIX 84 | 1025.6 | 1375 | 1620 | 3370 | - | - | - | - | - |
| LIX 63 | 998 | 1382 | 1706 | 3370 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cyanex 301 | - | - | - | - | 804 | 608 | ≈2500 | 1365 | - |
| ALi–LIX84 | 1096 | 1409 | 1620 | 3370 | - | - | - | - | - |
| ALi–LIX63 | 1014 | 1377 | 1668 | 3370 | - | - | - | - | 1463.6 |
| ALi–CY301 | - | - | - | - | 814 | 613.9 | - | 1365 | 1479.7 |
| Reaction | logK | Reaction | logK |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pd2+ + Cl− = PdCl+ | 4.47 | Pd2+ + 2SCN− = Pd(SCN)2o | 15.46 |
| Pd2+ + 2Cl− = PdCl2o | 7.74 | Pd2+ +3SCN− = Pd(SCN)3− | 21.94 |
| Pd2+ + 3Cl− = PdCl3− | 10.2 | Pd2+ + 4SCN− = Pd(SCN)42− | 27.42 |
| Pd2+ + 4Cl− = PdCl42− | 11.5 | Zn2+ + Cl− = ZnCl+ | 0.43 |
| Pd2+ + Br− = PdBr+ | 5.17 | Zn2+ + 2Cl− = ZnCl2o | 0.61 |
| Pd2+ + 2Br− = PdBr2o | 9.42 | Zn2++ 3Cl− = ZnCl3− | 0.5 |
| Pd2+ + 3Br− = PdBr3− | 12.72 | Zn2+ + 4Cl− = ZnCl42− | 0.2 |
| Pd2+ + 4Br− = PdBr42− | 14.94 | Zn2+ + Br− = ZnBr+ | −0.57 |
| Pd2+ + I− = PdI+ | 6.08 | Zn2+ + I− = ZnI+ | −1.50 |
| Pd2+ + 2I− = PdI2o | 22.00 | Zn2+ + SCN− = ZnNSC+ | 0.90 |
| Pd2+ + 3I− = PdI3− | ≈25.80 | Zn2+ + 2SCN− = Zn(NSC)2o | 0.70 |
| Pd2+ + 4I− = PdI42− | 28.30 | Zn2+ +3SCN− = Zn(NSC)3− | 0.60 |
| Pd 2+ + SCN− = PdSCN+ | 8.14 | Zn2+ + 4SCN− = Zn(NSC)42− | 0.30 |
| Stripping Agent | Loaded Organic Phase, Stripping Percentage (%S) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALi–C301 | ALi–LIX63 | ALi–LIX84 | ALi–I | ALi–Br | ALi–SCN | |
| 5% NH3 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 2.1 | 89.7 | 100.0 | 5.0 |
| 0.1 M HCl | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 2.4 | 0.0 |
| 0.1 M H2SO4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 0.5 M thioure | 0.5 | 2.9 | 2.2 | 2.5 | 9.0 | 1.1 |
| 0.1 M HCl + 0.5 M thioure | 0.8 | 13.5 | 14.1 | 11.4 | 17.9 | 1.2 |
| 0.1 M H2SO4 + 0.5 M thioure | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.6 |
| Stripping Agent | Pd(II) Stripping Percentage (%S) | Stripping Agent | Pd(II) Stripping Percentage (%S) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALi–LIX63 | ALi–LIX84 | ALi–LIX63 | ALi–LIX84 | ||
| 0.1 M HCl + 0.5 M thiourea | 13.5 | 14.1 | 0.5 M HCl + 0.1 M thiourea | 81.8 | 100 |
| 0.5 M HCl + 0.5 M thiourea | 100 | 100 | 0.5 M HCl + 0.2 M thiourea | 91.0 | 100 |
| 1 M HCl + 0.5 M thiourea | 100 | 100 | 0.5 M HCl + 0.3 M thiourea | 94.1 | 100 |
| 3 M HCl + 0.5 M thiourea | 65.3 | 65.9 | 0.5 M HCl + 0.4 M thiourea | 96.9 | 100 |
| 5 M HCl + 0.5 M thiourea | 34.4 | 45.0 | 0.5 M HCl + 0.5 M thiourea | 100 | 100 |
| Stripping Agent NH3, M | Loaded Organic Phase, %S | |
|---|---|---|
| ALi–I | ALi–Br | |
| 0.5 | 91.4 | 100 |
| 1 | 89.6 | 100 |
| 2 | 88.5 | 100 |
| 3 | 86.5 | 100 |
| IL Extractant | [H2SO4], M | Extraction Percentage (%E) | Stripping Agents | Stripping Percentage (%S) | Separation Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 M ALi–D2 | 9 | Pd: 19.8 Zn: 0 | - | - | Low extraction percentage Complete separation |
| 0.1 M ALi–CY272 | 5 | Pd: 7.5 Zn: 0 | - | - | Low extraction percentage Complete separation |
| 0.1 M ALi–PC | 7 | Pd: 10 Zn: 0 | - | - | As above |
| 0.001 M ALi–CY301 | 7–9 | Pd: 100 Zn: 0 | Aqua regia diluted 1.5 times | 90.6 | High extraction percentage of Pd(II) but control of IL concentration to low is necessary to avoid co-extraction of a small amount of Zn(II). High separation |
| 0.005 M ALi–LIX63 | 0.5–9 | Pd: 100 Zn: 0 | Mixture of 0.5 M HCl and 0.5 M Thiourea | 100 | High extraction and stripping percentage Complete separation |
| 0.005 M ALi–LIX84 | 0.5–9 | Pd: 100 Zn: 0 | Mixture of 0.5 M HCl and 0.1 M Thiourea | 100 | As above |
| 0.005 M ALi–I | 0.5–3 | Pd: 100 Zn: 0 | 0.5 M NH3 | 91.4 | As above |
| 0.005 M ALi–Br | 0.5–1 | Pd: 100 Zn: 0 | 0.5 M NH3 | 100 | As above |
| 0.005 M ALi–SCN | 9 | Pd: 100 Zn: 0 | 1 M NH4Cl and 5%NH3 | 98.4 | As above |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, V.-N.; Song, S.-J.; Lee, M.-S. Recovery of Pure Pd(II) from Spent Electroplating Solutions by Solvent Extraction with Ionic Liquids from Sulfuric Acid Leaching Solution of Cemented Pd. Metals 2021, 11, 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11081320
Nguyen V-N, Song S-J, Lee M-S. Recovery of Pure Pd(II) from Spent Electroplating Solutions by Solvent Extraction with Ionic Liquids from Sulfuric Acid Leaching Solution of Cemented Pd. Metals. 2021; 11(8):1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11081320
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Viet-NhanHoa, Si-Jeong Song, and Man-Seung Lee. 2021. "Recovery of Pure Pd(II) from Spent Electroplating Solutions by Solvent Extraction with Ionic Liquids from Sulfuric Acid Leaching Solution of Cemented Pd" Metals 11, no. 8: 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11081320
APA StyleNguyen, V.-N., Song, S.-J., & Lee, M.-S. (2021). Recovery of Pure Pd(II) from Spent Electroplating Solutions by Solvent Extraction with Ionic Liquids from Sulfuric Acid Leaching Solution of Cemented Pd. Metals, 11(8), 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11081320







