Recent Advances in Magnetostrictive Tb-Dy-Fe Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Grain Orientation and Properties of Directionally Solidified Tb-Dy-Fe Alloys
2.1. Grain Growth and Orientation Control during Directional Solidification Process
2.2. <111>-Oriented Tb-Dy-Fe Alloys Prepared by Directional Solidification in Magnetic Fields
3. Effects of Substitute Elements on Magnetostriction of Tb-Dy-Fe Alloys
3.1. Alloy System Containing Other Rare-Earth Elements
3.1.1. Pr
3.1.2. Nd
3.1.3. Ho
3.2. Alloy System Containing Other Elements
4. Mechanical Properties of Tb-Dy-Fe Alloys
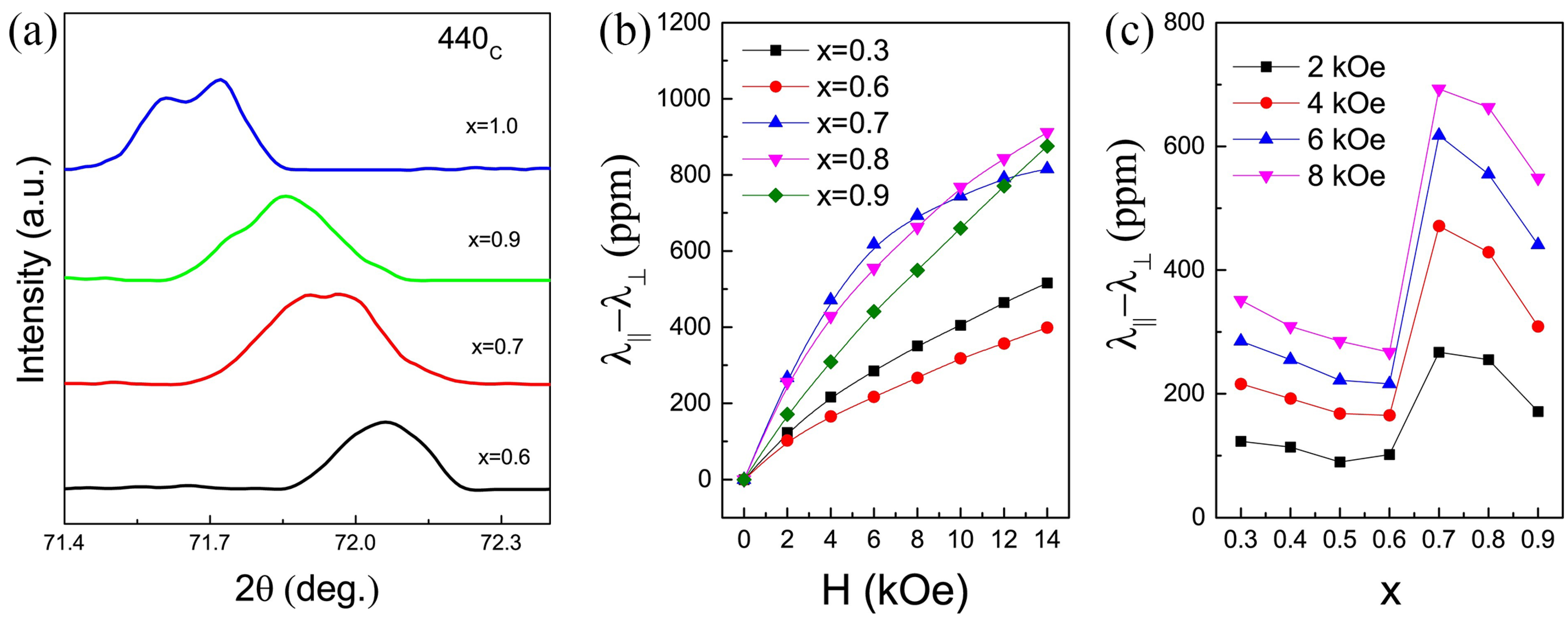
5. Structural Origin and Magnetic Morphotropic Phase Boundary (MPB) of Tb-Dy-Fe Alloys
6. Progress on Tb-Dy-Fe Giant Magnetostrictive Composites
6.1. Polymer-Banded Tb-Dy-Fe Composite
6.2. Sintered Tb-Dy-Fe Material Composited with Dy-Cu Alloys
7. Progress in Application of Tb-Dy-Fe Alloys
7.1. Tb-Dy-Fe Giant Magnetostrictive Thin Film
7.2. Application in Microsensors and Other Devices
8. Summary and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clark, A.E. Magnetic and Magnetoelastic Properties of Highly Magnetostrictive Rare Earth-Iron Laves Phase Compounds. AIP Conf. Proc. 1974, 18, 1015–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.; Crowder, D. High temperature magnetostriction of TbFe2 and Tb0.27Dy0.73Fe2. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1985, 21, 1945–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.Z.; Gao, X.X. Magnetostrictive Materials; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.Z.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, M.C.; Gao, X.X.; Wang, Z.C.; Shi, Z.H. Giant magnetostrictive materials of Tb-Dy-Fe alloy with [110] axial alignment. Prog. Nat. Sci. 1998, 6, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Jiang, C.; Xiao, F.; Xu, H. Magnetostriction of Tb0.36Dy0.64(Fe1−xCox)2 (x = 0-0.20) <112>-oriented crystals. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 414, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, M.C.; Gao, X.X.; Zhou, S.Z. Effect of two-steps heat treatment on the mechanical properties and magnetostriction of <110> oriented TbDyFe giant magnetostrictive material. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 416, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.J.; Zhang, Z.D. Progress in bulk MgCu2-type rare-earth iron magnetostrictive compounds. Chin. Phys. B 2013, 22, 077507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Zhang, T.L.; Wang, J.M.; Jiang, C.B. Giant Magnetostrictive Materials and Their Applications. Mater. China 2012, 31, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.B.; Liu, J.J.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, J.; Du, J.; Si, P.Z. Structural, magnetic and magnetostrictive properties of Laves-phase compounds TbxHo0.9−xNd0.1Fe1.93 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.40). Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 148, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wun-Fogle, M.; Restorff, J.B.; Clark, A.E. Hysteresis and magnetostriction of TbxDyyHo1-x-yFe1.95 [112] dendritic rods. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 6253–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.J.; Busbridge, S.C.; Wang, B.W.; Zhang, Z.D.; Zhao, X.G. Structure and magnetic and magnetostrictive properties of (Tb0.7Dy0.3)0.7Pr0.3(Fe1−xCox)1.85 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.6). IEEE Trans. Magn. 2001, 37, 3025–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.H.; Jiang, C.B.; Xu, H.B. Magnetostriction and electrical resistivity of Si doped Tb0.3Dy0.7Fe1.95 oriented crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 192507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.E. Chapter 7 Magnetostrictive Rare Earth-Fe2 Compounds. In Handbook of Ferromagnetic Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1980; Volume 1, pp. 531–589. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Bao, H.X.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Y.; Ren, X.B.; Song, X.P.; Matsushita, Y.; Katsuya, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Kobayashi, K. ChemInform Abstract: Structural Changes Concurrent with Ferromagnetic Transition. Chin. Phys. B 2013, 22, 046101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.R.; Song, X.P.; Yang, S.; Deng, J.K.; Wang, Y. Monte Carlo Simulation on the Magnetization Rotation near Magnetic Morphotropic Phase Boundary; SPIE: Shenzhen, China, 2012; Volume 8409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Bao, H.; Chao, Z.; Yu, W.; Gao, J. Large Magnetostriction from Morphotropic Phase Boundary in Ferromagnets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 197201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fohtung, E. Magnetostriction Fundamentals. In Encyclopedia of Smart Materials; Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute: Troy, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Zhou, C.; Chang, K.; Wang, B.; Shi, Q.; Chen, K.; Chen, Y.-S.; Ren, Y.; Yang, S. Local structure study on magnetostrictive material Tb1−xDyxFe2. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 127, 235102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.Z.; Liu, J.H.; Jiang, C.B.; Xu, H.B. Control of solid-liquid interface morphology and radial composition distribution: TbDyFe single crystal growth. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 621, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palit, M.; Banumathy, S.; Singh, A.K.; Pandian, S.; Chattopadhyay, K. Crystallography of solid-liquid interface and evolution of texture during directional solidification of Tb0.3Dy0.7Fe1.95 alloy. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palit, M.; Banumathy, S.; Singh, A.K.; Pandian, S.; Chattopadhyay, K. Orientation Selection and Microstructural Evolution in Directionally Solidified Tb0.3Dy0.7Fe1.95. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, D.Z.; Liu, J.H.; Jiang, C.B.; Xu, H.B. Correlation between Growth Twinning and Crystalline Reorientation of Faceted Growth Materials during Directional Solidification. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 3092–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.B.; Zhou, S.S.; Zhang, M.C.; Run, W. The preferred orientation, microstructure and magnetostriction in directionally solidified TbDyFe alloys. Acta Metall. Sin. 1998, 34, 164–170. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, D.Z.; Zhang, T.L.; Jiang, C.B.; Xu, H.B. Preferred orientation transition mechanism of faceted-growth materials with FCC structure: Competitive advantage depends on 3D microstructure morphologies. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 741, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.H.I.; Guo, M.; Vleugels, J.; Van der Biest, O.; Blanpain, B. Strong static magnetic field processing of metallic materials: A review. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2012, 16, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fautrelle, Y.; Ren, Z.M.; Li, X.; Nguyen-Thi, H.; Mangelinck-Noel, N.; Salloum, A.; Zhong, Y.B.; Kaldre, I.; Bojarevics, A. Thermoelectric magnetic force acting on the solid during directional solidification under a static magnetic field. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 1331–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.F.; Liu, T.; Dong, M.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Q. Magnetic domain structure, crystal orientation, and magnetostriction of Tb0.27Dy0.73Fe1.95 solidified in various high magnetic fields. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 401, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.F.; Liu, T.; Chai, S.W.; Dong, M.; Wang, Q. Influence of magnetic flux density and cooling rate on orientation behavior of Tb0.27Dy0.73Fe1.95 alloy during solidification process. Acta Phys. Sin. Chin. Ed. 2016, 65, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.L.; Liu, T.; Dong, M.; Guo, X.Y.; Yuan, S.; Wang, Q. Enhanced magnetostriction of Tb–Dy–Fe via simultaneous <111>-crystallographic orientation and -morphological alignment induced by directional solidification in high magnetic fields. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 053903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, T.; Wang, K.; Gao, P.F.; Liu, Y.; He, J.C. Progress on High Magnetic Field-Controlled Transport Phenomena and Their Effects on Solidification Microstructure. ISIJ Int. 2014, 54, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, M.; Liu, T.; Guo, X.Y.; Liu, Y.R.; Dong, S.L.; Wang, Q. Enhancement of mechanical properties of Tb0.27Dy0.73Fe1.95 alloy by directional solidification in high magnetic field. Mat. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2020, 785, 139377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.F.; Liu, T.; Dong, M.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, Q. Magnetostrictive gradient in Tb0.27Dy0.73Fe1.95 induced by high magnetic field gradient applied during solidification. Funct. Mater. Lett. 2016, 09, 1650003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.F. Evolution of Microstructure and Magnetostrictive Performance of Tb0.27Dy0.73Fe1.95 Alloy Solidified in High Magnetic Field Gradients. Ph.D. Dissertation, Northeastern University, Boston, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Gao, P.F.; Dong, M.; Xiao, Y.B.; Wang, Q. Effect of cooling rate on magnetostriction gradients of Tb0.27Dy0.73Fe1.95 alloys solidified in high magnetic field gradients. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 056216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, W.J.; Liu, J.J.; Li, D.; Liu, W.; Zhao, X.G.; Zhang, Z.D. Direct experimental evidence for anisotropy compensation between Dy3+ and Pr3+ ions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 122506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.G.; Chen, Z.Y.; Wang, L.; Hu, C.C.; Pan, Q.; Shi, D.N. Synthesis and magnetostrictive properties of Pr1−xDyx(Fe0.8Co0.2)1.93cubic Laves compounds. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 056207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.B.; Zheng, W.G.; Cui, Y.; Shi, Y.G.; Shi, D.N. Structural, Magnetic, and Magentostrictive Properties of Dy1−x(Tb0.2Pr0.8)xFe1.93 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.5) Compounds. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 2017, 31, 2217–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.G.; Tang, S.L.; Wang, R.L.; Su, H.L.; Han, Z.D.; Lv, L.Y.; Du, Y.W. High-pressure synthesis of giant magnetostrictive PrxTb1−xFe1.9 alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 202503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.G.; Tang, S.L.; Zhai, L.; Huang, H.B.; Wang, R.L.; Yu, J.Y.; Du, Y.W. Composition anisotropy compensation and magnetostriction in Pr(Fe1−xCox)1.9 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.5) cubic Laves alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 212507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.G.; Tang, S.L.; Lv, L.Y.; Fan, J.Y. Magnetic and magnetostrictive properties in high-pressure synthesized Dy1−xPrxFe1.9 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) cubic Laves alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 506, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.B.; Liu, Y.D.; Kan, C.X.; Shi, Y.G.; Shi, D.N. Structure and magnetostriction in (Tb0.2Pr0.8)xDy1−xFe1.93 Laves compounds synthesised by high-pressure annealing. Mater. Res. Bull. 2019, 112, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.C.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, X.X.; Huang, H.B.; Shi, Y.G.; Chen, L.Q. Ultrasensitive magnetostrictive responses at the pre-transitional rhombohedral side of ferromagnetic morphotropic phase boundary. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 56, 1713–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.C.; Shi, Y.G.; Shi, D.N.; Zhou, X.G.; Fan, J.Y.; Lv, L.Y.; Tang, S.L. Optimization on magnetic transitions and magnetostriction in TbxDyyNdz(Fe0.9Co0.1)1.93 compounds. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 143906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Pan, Z.B.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.R.; Song, X.H.; Ren, W.J. Large magnetostriction and direct experimental evidence for anisotropy compensation in Tb0.4−xNdxDy0.6(Fe0.8Co0.2)1.93 Laves compounds. Mater. Lett. 2014, 137, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.Y.; Liu, J.J.; Pan, Z.B.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, X.C.; Liu, L.D.; Du, J.; Si, P.Z. Magnetostriction of TbxDy0.9−xNd0.1(Fe0.8Co0.2)1.93 compounds and their composites (0.20 ≤ x ≤ 0.60). J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 582, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.G.; Tang, S.L.; Huang, Y.J.; Lv, L.Y.; Du, Y.W. Anisotropy compensation and magnetostriction in TbxNd1−xFe1.9 cubic Laves alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 142515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jammalamadaka, S.N.; Markandeyulu, G.; Balasubramaniam, K. Magnetostriction and anisotropy compensation in TbxDy0.9−xNd0.1Fe1.93 (0.2 ≤ x ≤ 0.4). Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 242502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.B.; Liu, J.J.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, X.; Song, X.H.; Zhang, Z.R.; Ren, W.J. Structural, magnetic and magnetoelastic properties of Laves-phase Tb0.3Dy0.6Nd0.1(Fe1−xCox)1.93 compounds (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.40). Intermetallics 2015, 64, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Shi, Y.G.; Wang, L.; Pan, Q.; Li, H.F.; Shi, D.N. Structure and magnetic properties of melt-spun Tb0.2Nd0.8(Fe0.8Co0.2)1.9 compound. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 656, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Magnetostrictive Properties in (Pr,Nd)Modulated Laves Compounds. Master Dissertation, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.G.; Wang, L.; Zheng, W.G.; Chen, Z.Y.; Shi, D.N. Effects of Co substitution for Fe on the structural and magnetostrictive properties of melt-spun Tb0.2Nd0.8Fe1.9 ribbons. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 433, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, A.; Li, Y.B.; Mi, J.W.; Zuo, W.L.; Ghani, A.; Dai, Z.Y.; Yao, K.K.; Hao, C.X.; Yaseen, M.; Saeed, A. Spin configuration, magnetic and magnetostrictive properties of Tb0.27Dy0.73−xNdxFe2 compounds. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 249, 122951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lv, Y.; Li, G.; Huang, W.M.; Sun, Y.; Cui, B.Z. The magnetostriction and its ratio to hysteresis for Tb-Dy-Ho-Fe alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 7282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.W.; Cao, S.Y.; Huang, W.M.; Sun, Y.; Weng, L.; Zhao, Z.Z. Phase Relationship and Magnetostriction of Tb-Dy-Ho-Fe Alloys. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.B.; Liu, J.J.; Si, P.Z.; Ren, W.J. Magnetostriction of Laves Tb0.1Ho0.9−xPrx (Fe0.8Co0.2)1.93 alloys. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 77, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wang, B.M.; Huang, W.M.; Yan, J.W. High frequency magnetic properties of polymer-bonded Tb-Dy-Ho-Fe fiber composites. Ferroelectrics 2018, 530, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wang, B.W.; Cao, S.Y.; Xiao, J. Effect of Ho Doping and Annealing on Magnetostrictive Properties of Tb-Dy-Ho-Fe/Epoxy Composites. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 55, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.W.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.X. Fabrication, magnetostriction properties and applications of Tb-Dy-Fe alloys: A review. China Foundry 2016, 13, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, N.J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.W.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.X. Effect of Co, Cu, Nb, Ti, V on magnetostriction and mechanical properties of TbDyFe alloys. Intermetallics 2018, 100, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.B.; Ma, T.Y.; Xu, H.B. A kind of wide operating temperature range giant magnetostrictive alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 449, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.Y.; Jiang, C.B.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H.B. The Co-doped Tb0.36Dy0.64Fe2 magnetostrictive alloys with a wide operating temperature range. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 292, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zeng, Y.Y.; Chang, T.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, A.Z.; Liu, S.Y.; Tian, F.H.; Zhang, Y.; Song, X.P.; Yang, S. Ferromagnetic and magnetostrictive properties of Tb0.3Dy0.7(Co1−xFex)2 alloys. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 58, 050921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, P.; Abell, J.S.; Pitman, K.C. Phase relationships in the Tb-Dy-Fe ternary system. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 67, 4998–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.J.; Abell, J.S.; Hwang, A.M.H. Defects in Terfenol-D crystals. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1991, 99, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, D.T.; Verhoeven, J.D.; McMasters, O.D.; Spitzig, W.A. Strength of Terfenol-D. J. Appl. Phys. 1989, 65, 3712–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Tang, H.J.; Zhang, M.C.; Gao, X.X.; He, J.P.; Zhou, S.Z. Effect of heat treatment on the mechanical properties of <110> oriented TbDyFe giant magnetostrictive material. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 413, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.W.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.X. Effect of Nb on magnetic and mechanical properties of TbDyFe alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 449, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.W.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.X. Effect of copper on magnetostriction and mechanical properties of TbDyFe alloys. J. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.G.; Li, J.H.; Bao, X.Q.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Gao, X.X. Improvement of bending strength via introduced (Dy,Tb)Cu phase at grain boundary on giant magnetostrictive Tb-Dy-Fe alloy by diffusing Dy-Cu alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 826, 153959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ren, X. Noncubic crystallographic symmetry of a cubic ferromagnet: Simultaneous structural change at the ferromagnetic transition. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 014407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergstrom, R., Jr.; Wuttig, M.; Cullen, J.; Zavalij, P.; Briber, R.; Dennis, C.; Garlea, V.O.; Laver, M. Morphotropic phase boundaries in ferromagnets: Tb1−xDyxFe2 alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett 2013, 111, 017203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, S.; Liao, X.; Gao, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, D.; Song, X. Simulation study on exchange interaction and unique magnetization near ferromagnetic morphotropic phase boundary. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2017, 29, 445802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atzmony, U.; Dariel, M.P.; Dublon, G. Spin-orientation diagram of the pseudobinary Tb1−xDyxFe2 Laves compounds. Phys. Rev. B 1977, 15, 3565–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.Y.; Liu, X.L.; Pan, X.W.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Yan, M.; Li, H.Y.; Fang, M.X.; Ren, X.B. Local rhombohedral symmetry in Tb0.3Dy0.7Fe2 near the morphotropic phase boundary. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 192407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.H.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.D.; Wang, Z.L.; Liu, D.M.; Ren, Y.; Chang, T.T.; Zhang, R. In-situ studies of low-field large magnetostriction in Tb1−xDyxFe2 compounds by synchrotron-based high-energy x-ray diffraction. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 658, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, C.C.; Yang, T.N.; Huang, H.B.; Hu, J.M.; Wang, J.J.; Shi, Y.G.; Shi, D.N.; Chen, L.Q. Phase-field simulation of domain structures and magnetostrictive response in Tb1−xDyxFe2 alloys near morphotropic phase boundary. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 141908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.C.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, T.N.; Li, W.; Chen, L.Q. Phase-field simulation of magnetic microstructure and domain switching in (Tb0.27Dy0.73)Fe2 single crystal. AIP Adv. 2021, 11, 015207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, C.E.; Marchant, G.A.; Staunton, J.B. Spin Orientation and Magnetostriction of Tb1−xDyxFe2 from First Principles. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2020, 14, 014091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhajjar, R.; Law, C.T.; Pegoretti, A. Magnetostrictive polymer composites: Recent advances in materials, structures and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 97, 204–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.Y.; Or, S.W.; Chan, H.L.W. Large Magnetostriction in Epoxy-Bonded Terfenol-D Continuous-Fiber Composite with [112] Crystallographic Orientation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2006, 42, 3111–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, K.K.; Henry, C.P.; Altin, G.; Carman, G.P. Crystallographically Aligned Terfenol-D/Polymer Composites for a Hybrid Sonar Device. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2006, 83, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.F.; Qi, M.; Guan, X.C.; Li, J.H.; Ou, J.P. Magnetostrictive properties of titanate coupling agent treated Terfenol-D composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 1205–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Zhang, T.L.; Jiang, C.B. Cut-off frequency of magnetostrictive materials based on permeability spectra. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 1933–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Zhang, T.L.; Jiang, C.B.; Xu, H.B. Grain-<111>-oriented anisotropy in the bonded giant magnetostrictive material. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 102501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleta, J.; Lewandowski, D.; Mech, R. Magnetostriction of field-structural composite with Terfenol-D particles. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2015, 15, 897–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.L.; Liu, J.J.; Shen, W.C.; Ding, Q.L.; Wang, M.K.; Du, J.; Si, P.Z. Magnetomechanical behavior of Tb0.2Dy0.8−xPrx(Fe0.8Co0.2)1.93/epoxy pseudo-1-3 particulate composites. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.C.; Zhang, T.L.; Wu, Y.Y.; Jiang, C.B. High-performance magnetostrictive composites with large particles volume fraction. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 805, 1266–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Liu, J.; Ding, Q.; Wang, M.; Pan, Z. Textured Orientation and Dynamic Magnetoelastic Properties of Epoxy-Based TbxDy0.7−xPr0.3(Fe0.9B0.1)1.93 Particulate Composites. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 2020, 33, 3857–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Zhang, T.L.; Meng, H.; Zhou, X.M.; Jiang, C.B. A study on laminated structures in Terfenol-D/Epoxy particulate composite with enhanced magnetostriction. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 243909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.G.; Li, J.H.; Bao, X.Q.; Liu, M.; Gao, X.X. Improvement of mechanical properties of magnetostrictive Tb-Dy-Fe alloys via preparing sintered material with low-melting Dy-Cu alloy binder. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 895, 162572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arout Chelvane, J.; Sherly, A.; Palit, M.; Talapatra, A.; Mohanty, J. Magnetic anisotropy and magnetostrictive properties of sputtered Tb-Dy-Fe-Co thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 8989–8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panduranga, M.K.; Lee, T.; Chavez, A.; Prikhodko, S.V.; Carman, G.P. Polycrystalline Terfenol-D thin films grown at CMOS compatible temperature. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 056404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.H.; Chang, W.C.; Anbalagan, A.K. Anomalous X-ray scattering study on oxidized TbxDy1−xFe2-y thin films: Influence of thermal annealing on the oxide composition. Radiat. Phys. Chemistry 2020, 175, 108915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panduranga, M.K.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Schneider, J.D.; Lee, T.; Klewe, C.; Chopdekar, R.; Shafer, P.; N’Diaye, A.T.; Arenholz, E.; Candler, R.N.; et al. Single magnetic domain Terfenol-D microstructures with passivating oxide layer. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 528, 167798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, H.; Sakamoto, K.; Inomata, N.; Toda, M.; Toan, N.V.; Ono, T. Magnetostrictive Performance of Electrodeposited TbxDy1−xFey Thin Film with Microcantilever Structures. Micromachines 2020, 11, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.Q.; Niu, R.; Peng, Z.D.; Li, H.; Luo, Y.M.; Zhou, T.J.; Dong, C.H. A Current Sensor Based on Capillary Microresonator Filled with Terfenol-D Nanoparticles. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2021, 33, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, W.; Jia, Y.N.; Fan, S.Y.; Liang, Y. Sensitivity Improvement of TbDyFe Thin-Film Coated Saw-Based Current Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2019 14th Symposium on Piezoelectrcity, Acoustic Waves and Device Applications (Spawda19), Shijiazhuang, China, 11–14 January 2019; pp. 519–522. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.L.; Sun, H.Y.; Sang, L.W.; Imura, M.; Koide, Y.; Koizumi, S.; Liao, M.Y. Integrated TbDyFe Film on a Single-Crystal Diamond Microelectromechanical Resonator for Magnetic Sensing. Phys. Status Solidi-Rapid Res. Lett. 2021, 15, 2100352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakon, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Komori, T. Rotation angle sensing system using magnetostrictive alloy Terfenol-D and permanent magnet. Sens. Actuators A 2021, 321, 112588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.L.; Li, K.S.; Luo, Y.; Yu, D.B.; Wang, Z.L.; Wu, G.Y.; Xie, J.J.; Tang, Z.F. Magnetostrictive properties and detection efficiency of TbDyFe/FeCo composite materials for nondestructive testing. J. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, M.C.; Sinha, S. Design and analysis of magnetostrictive sensors for wireless temperature sensing. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2021, 92, 014901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, N.; Jasenek, J.; Cervenova, J.; Usakova, M. Magnetic Optical FBG Sensors Using Optical Frequency-Domain Reflectometry. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, N.; Jasenek, J.; Cervenova, J. The Influence of Magnetic Field Applied on Fiber Bragg Gratings. Aip. Conf. Proc. 2018, 1996, 020024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanja, J.M.; Dai, Y.T.; Zhou, X.; Liu, B.; Yang, M.H.; Dai, J.X. Femtosecond Laser Ablated FBG Multitrenches for Magnetic Field Sensor Application. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2015, 27, 1717–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.H.; Qiao, X.G.; Rong, Q.Z.; Sun, A. Fiber-optic magnetic field sensor using a phase-shifted fiber Bragg grating assisted by a TbDyFe bar. Sens. Actuators A 2017, 261, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H. A mechanical amplifier based high-finesse fiber-optic Fabry-Perot interferometric sensor for the measurement of static magnetic field. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 125106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




















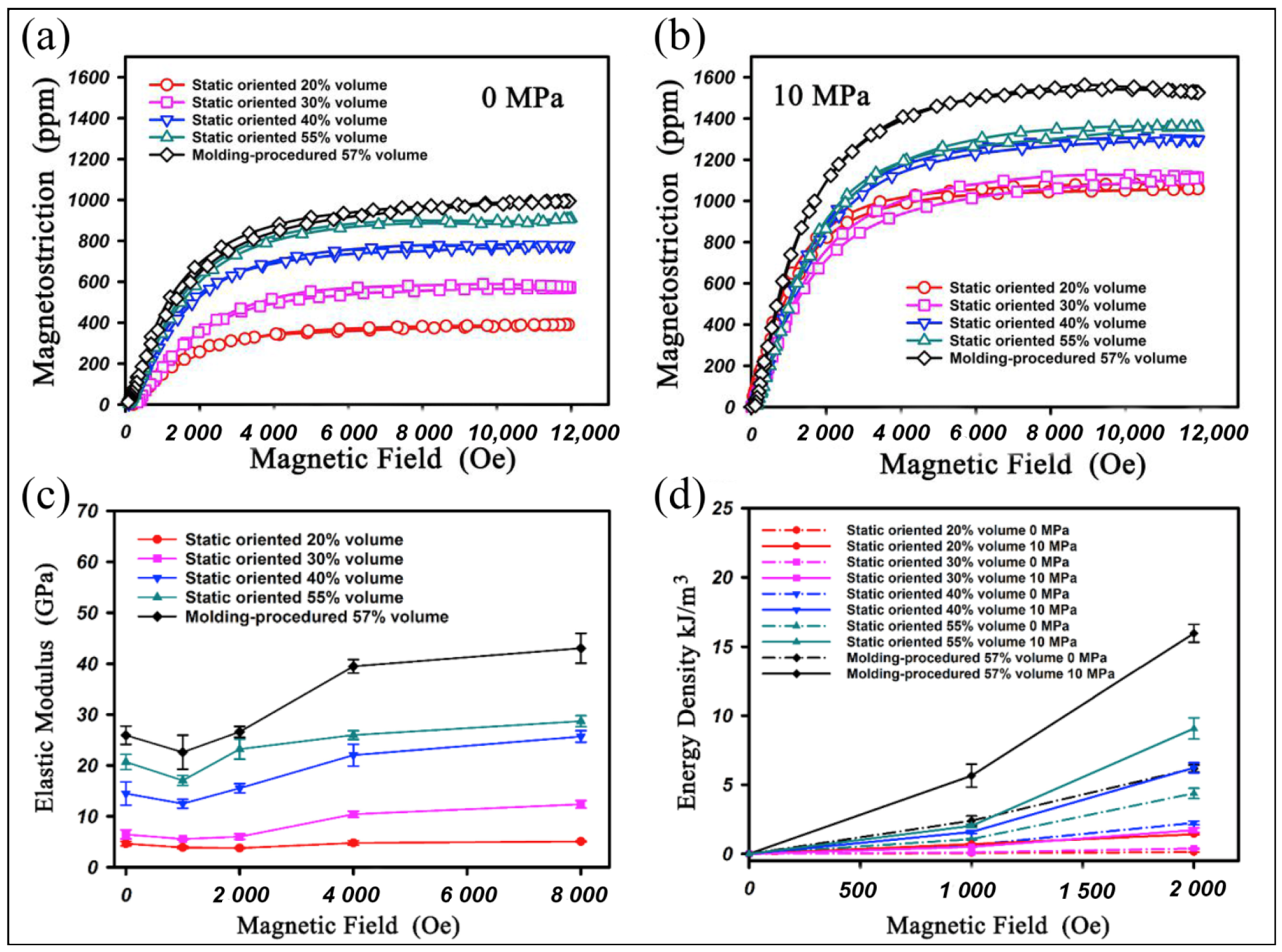





| Composite | Orientation | Preparation | Magnetostrictive Particle Morphology | Magnetostrictive Particle Size | Particle Content | Magnetostriction or Comments | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tb0.3Dy0.7Fe1.9/epoxy | <111> | 8000 Oe magnetic field curing | Particles; pseudo-1–3 chain structure | >300 μm | 40 vol% | 1358 ppm (at 17 MPa) | [84] |
| Tb0.3Dy0.7Fe1.92/epoxy | - | 8000 Oe magnetic field curing | - | 200–300 μm | 40 vol% | Cut-off frequency is 6800 kHz; loss factor is only 4.3% of that for the monolithic Tb-Dy-Fe alloy (at 10 kHz and 10 mT) | [83] |
| Tb0.4Dy0.5Nd0.1(Fe0.8Co0.2)1.93/epoxy | <111> | 10 kOe magnetic field curing | Particles; pseudo-1–3 chain structure | ≤150 μm | 20 vol% | 390 ppm (λa is 650 ppm at 6 kOe) | [45] |
| Terfenol-D/epoxy | <112> | 1885 Oe magnetic field curing | Powder, particle; pseudo-1–3 chain structure | 5–300 μm | 70 vol% | 720 ppm (at 9 MPa) | [85] |
| (Tb0.15Ho0.85Fe1.9)0.31 + (Tb0.3Dy0.7Fe1.9)0.69/epoxy | Pressure curing molding | Particles; pseudo-1–3 chain structure | 75–180 μm | 94 wt% | 605 ppm | [57] | |
| Tb0.25Dy0.45Ho0.30Fe1.9/epoxy | <110> | 120 ℃ bonding molding | <110> staple fiber | 0.8 mm × 0.8 mm ×12 mm | 90 vol% | 220 kA/M saturated magnetic field; 5 kA/M coercivity; the total loss at 20 kHz is 115 W/m3 | [56] |
| Tb0.2Dy0.55Pr0.25(Fe0.8Co0.2)1.93/epoxy | <110> | 8042 Oe magnetic field curing | Particles; pseudo-1–3 chain structure | 75–150 µm | 30 vol% | 110 ppm (λ||, at 80 kA/m); 580 ppm (λa, at 950 kA/m) | [86] |
| Tb0.5Dy0.5Fe1.95/epoxy | <111> | Two-step method with 10 kOe dynamic magnetic orientation | Lamellar structure | 100–200 µm | 57 vol% | 1500 ppm | [87] |
| TbxDy0.7−xPr0.3(Fe0.9B0.1)1.93/epoxy | <111> | 8042 Oe magnetic field curing | Particles; pseudo-1–3 chain structure | 60–150 μm | 30 vol% | d33~2.2 nm/A (Hbias~80 kA/m) | [88] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.; Gong, J.; Bao, X.; Gao, X. Recent Advances in Magnetostrictive Tb-Dy-Fe Alloys. Metals 2022, 12, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12020341
Yang Z, Li J, Zhou Z, Gong J, Bao X, Gao X. Recent Advances in Magnetostrictive Tb-Dy-Fe Alloys. Metals. 2022; 12(2):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12020341
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zijing, Jiheng Li, Zhiguang Zhou, Jiaxin Gong, Xiaoqian Bao, and Xuexu Gao. 2022. "Recent Advances in Magnetostrictive Tb-Dy-Fe Alloys" Metals 12, no. 2: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12020341
APA StyleYang, Z., Li, J., Zhou, Z., Gong, J., Bao, X., & Gao, X. (2022). Recent Advances in Magnetostrictive Tb-Dy-Fe Alloys. Metals, 12(2), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12020341






