Assessment of the Generalization Ability of the ASTM E900-15 Embrittlement Trend Curve by Means of Monte Carlo Cross-Validation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. The ASTM E900-15 ETC
2.2. Programming Tools
2.3. The Method of Maximum Likelihood
- (1)
- is an approximately unbiased estimator for θ;
- (2)
- The variance of is nearly as small as the variance that could be obtained with any other estimator;
- (3)
- has an approximate normal distribution.
2.4. Resampling
2.5. Strategy of the Analysis
3. Results
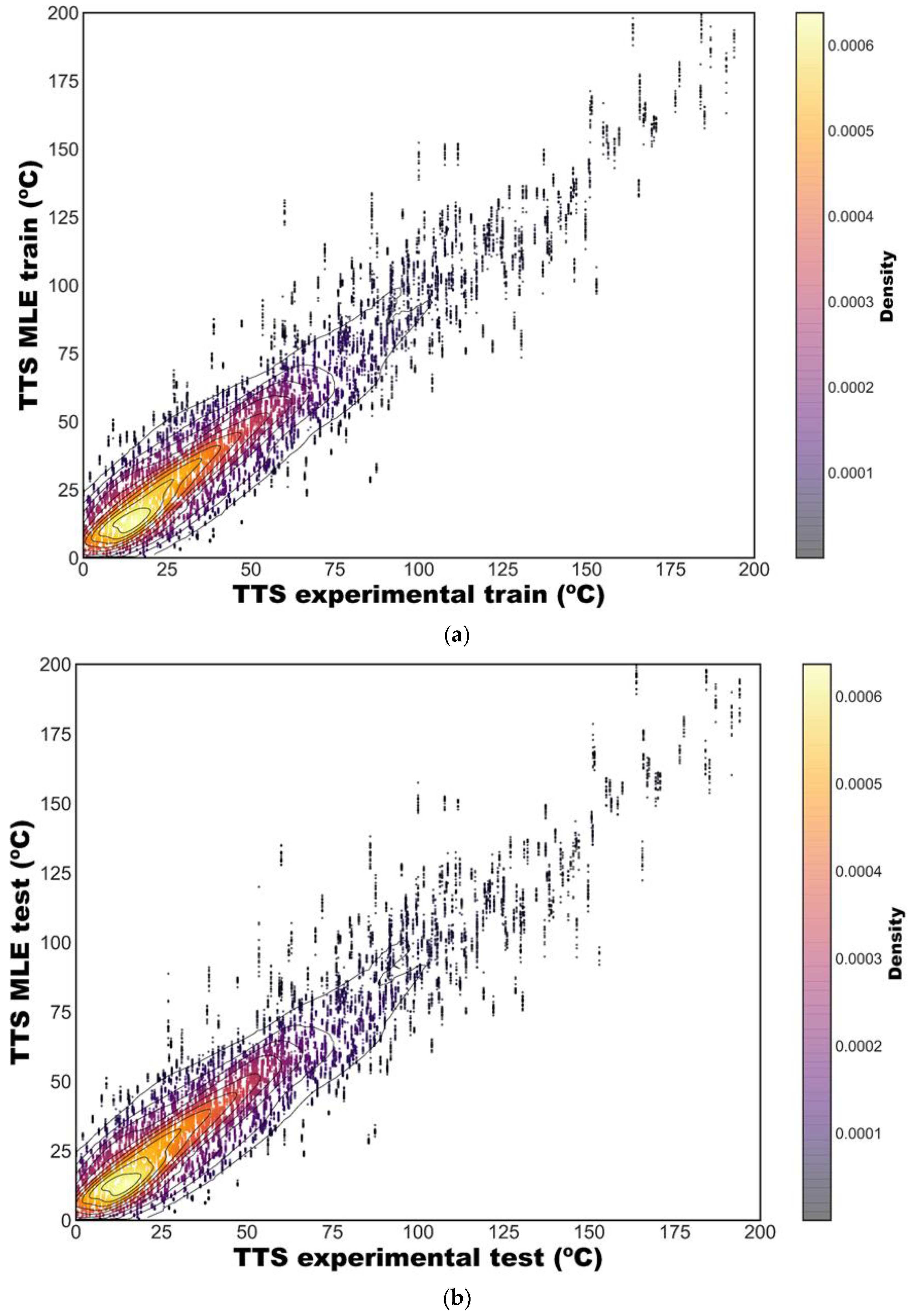
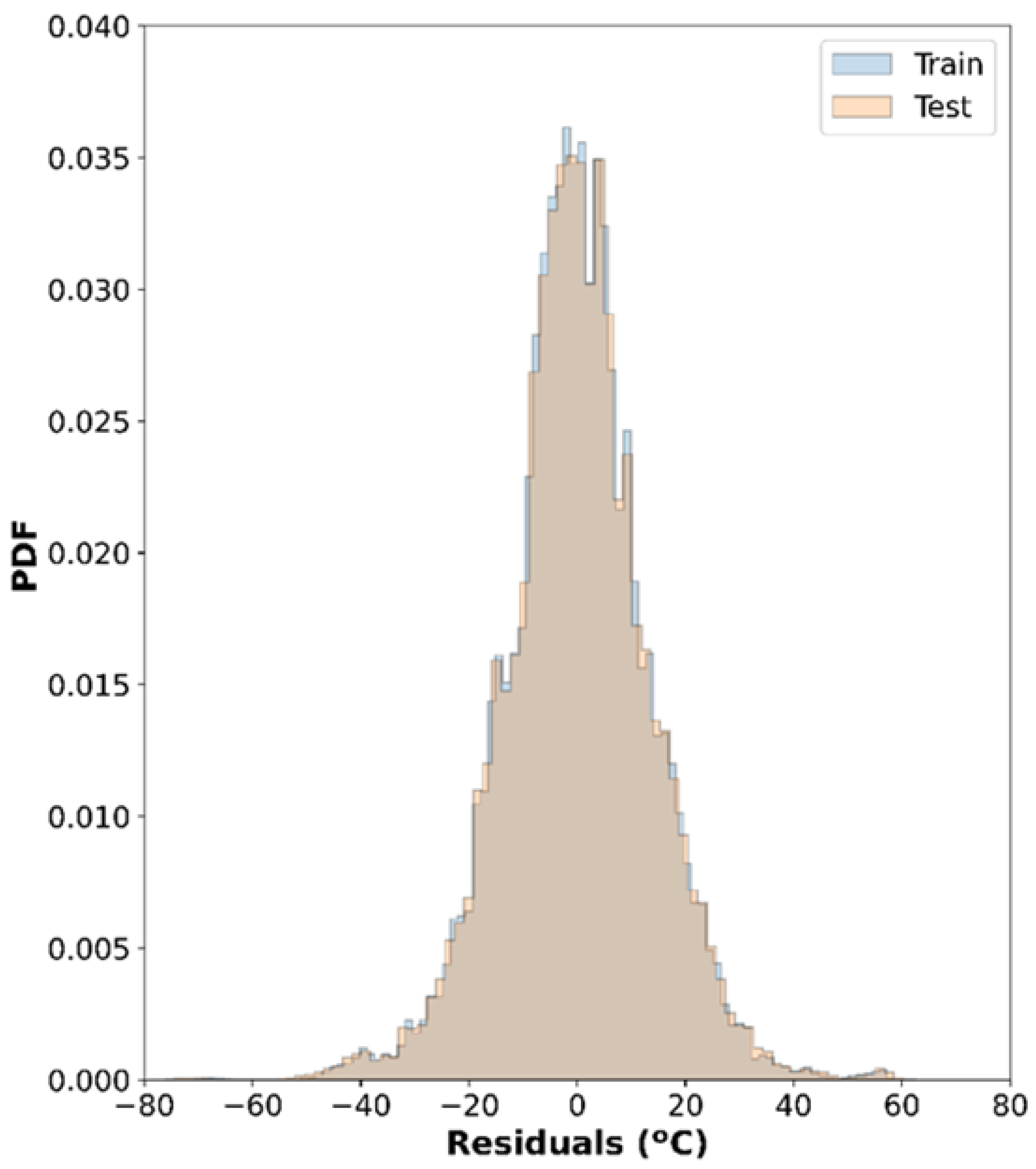
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Inferential Statistics
3.3. Assessment of Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- USNRC. Regulatory Guide 1.99 (Revision 2): Radiation Embrittlement of Reactor Vessel Materials; USNRC: Washington, DC, USA, 1998.
- Eason, E.D.; Odette, G.R.; Nanstad, R.K.; Yamamoto, T. A Physically Based Correlation of Irradiation-Induced Transition Temperature Shifts for RPV Steels; Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2007.
- ASTM E900-15e2; Standard Guide for Predicting Radiation-Induced Transition Temperature Shift in Reactor Vessel Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- Hashimoto, Y.; Nomoto, A.; Kirk, M.; Nishida, K. Development of new embrittlement trend curve based on Japanese surveillance and atom probe tomography data. J. Nucl. Mater. 2021, 553, 153007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreño, D.; Serrano, M.; Kirk, M.; Sainz-aja, J.A. Prediction of the Transition-Temperature Shift Using Machine Learning Algorithms and the Plotter Database. Metals 2022, 12, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guido, S.; Müller, A. Introduction to Machine Learning with Python. A Guide for Data Scientists; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Newton, MA, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1449369415. [Google Scholar]
- Geron, A. Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn and TensorFlow; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Newton, MA, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1491962299. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Deep Learning with Python; Manning Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1617294433. [Google Scholar]
- Adjunct for ASTM E900-15; Technical Basis for the Equation used to Predict Radiation-Induced Transition Temperature Shift in Reactor Vessel Materials. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- The 2018 Top Programming Languages-IEEE Spectrum. Available online: https://spectrum.ieee.org/the-2018-top-programming-languages (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Stack Overflow Developer Survey. 2019. Available online: https://insights.stackoverflow.com/survey/2019/ (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Montgomery, D.C.; Runger, G.C. Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994; Volume 19, ISBN 0471204544. [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen, P.; Gommers, R.; Oliphant, T.E.; Haberland, M.; Reddy, T.; Cournapeau, D.; Burovski, E.; Peterson, P.; Weckesser, W.; Bright, J.; et al. SciPy 1.0: Fundamental algorithms for scientific computing in Python. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nelder, J.A.; Mead, R. A Simplex Method for Function Minimization. Comput. J. 1965, 7, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M. Direct search methods: Once scorned, now respectable. In Proceedings of the Numerical analysis: Proceedings of the 1995 Dundee Biennial Conference in Numerical Analysis; Griffiths, D., Watson, G., Eds.; Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1996; pp. 191–208. [Google Scholar]
- Cawley, G.C.; Talbot, N.L.C. On over-fitting in model selection and subsequent selection bias in performance evaluation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 2079–2107. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, M.; Johnson, K. Applied Predictive Modeling; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4614-6848-6. [Google Scholar]
- Dubitzky, W.; Granzow, M.; Berrar, D.P. (Eds.) Fundamentals of Data Mining in Genomics and Proteomics; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; ISBN 978-0-387-47508-0. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, A.V.; Duflo, E. Chapter 1—An Introduction to the “Handbook of Field Experiments.” In Handbook of Field Experiments; Banerjee, A.V., Duflo, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 1–24. ISSN 2214-658X. [Google Scholar]
- Lumley, T.; Diehr, P.; Emerson, S.; Chen, L. The importance of the normality assumption in large public health data sets. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2002, 23, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch’s t-test-Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Welch%27s_t-test (accessed on 22 January 2022).
- Wasserstein, R.L.; Lazar, N.A. The ASA’s Statement on p-Values: Context, Process, and Purpose. Am. Stat. 2016, 70, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amrhein, V.; Greenland, S.; McShane, B. Retire statistical significance. Nature 2019, 567, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mehta, D. Highlight negative results to improve science. Nature 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters in “M” (Equations (4)–(6)) | Value | Parameters in “B” (Equations (2) and (3)) | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| B_Weld | 9.190 × 10−1 | CuMAX | 2.800 × 10−1 |
| B_Plate | 1.080 | CuMIN | 5.300 × 10−2 |
| B_Forge | 1.011 | M_Weld | 9.680 × 10−1 |
| B_Const | 1.894 × 10−12 | M_Plate | 8.190 × 10−1 |
| B_Exp | 5.695 × 10−1 | M_Forge | 7.380 × 10−1 |
| B_Texp | −5.470 | M_slope | 1.139 × 102 |
| B_Pconst | 9.000 × 10−2 | M_Maxslope | 6.126 × 102 |
| B_Pexp | 2.160 × 10−1 | M_lnMinFlu | 4.500 × 1020 |
| B_Niconst | 1.660 | M_Texp | −5.450 |
| B_Niexp1 | 8.540 | M_Pconst | 1.000 × 10−1 |
| B_Niexp2 | 3.900 × 10−1 | M_Pexp | −9.800 × 10−2 |
| B_Mnexp | 3.000 × 10−1 | M_Niconst | 1.680 × 10−1 |
| - | - | M_Niexp1 | 5.800 × 10−1 |
| - | - | M_Niexp2 | 7.300 × 10−1 |
| Set | Mean (°C) | RMSE (°C) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Train set | 1.3 × 10−3 | 13.22 | 0.877 |
| Test set | 2.6 × 10−2 | 13.53 | 0.871 |
| Δ (%) | N/A | 2.34 | −0.68 |
| Mean | SD | 2.5% | 25% | 50% | 75% | 97.5% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuMAX | 2.765 × 10−1 | 1.071 × 10−2 | 2.532 × 10−1 | 2.734 × 10−1 | 2.772 × 10−1 | 2.836 × 10−1 | 2.921 × 10−1 |
| CuMIN | 5.415 × 10−2 | 2.193 × 10−3 | 4.880 × 10−2 | 5.299 × 10−2 | 5.418 × 10−2 | 5.539 × 10−2 | 5.765 × 10−2 |
| M_Weld | 9.740 × 10−1 | 1.579 × 10−1 | 6.515 × 10−1 | 8.781 × 10−1 | 9.747 × 10−1 | 1.071 | 1.290 |
| M_Plate | 7.924 × 10−1 | 1.276 × 10−1 | 5.305 × 10−1 | 7.153 × 10−1 | 7.939 × 10−1 | 8.708 × 10−1 | 1.046 |
| M_Forge | 7.462 × 10−1 | 1.258 × 10−1 | 4.938 × 10−1 | 6.686 × 10−1 | 7.465 × 10−1 | 8.242 × 10−1 | 9.983 × 10−1 |
| M_slope | 1.156 × 102 | 18.70 | 78.57 | 1.042 × 102 | 1.152 × 102 | 1.267 × 102 | 1.546 × 102 |
| M_Maxslope | 6.274 × 102 | 1.000 × 102 | 4.290 × 102 | 5.663 × 102 | 6.251 × 102 | 6.837 × 102 | 8.304 × 102 |
| M_lnMinFlu | 4.212 × 1020 | 7.031 × 1019 | 2.983 × 1020 | 3.707 × 1020 | 4.109 × 1020 | 4.781 × 1020 | 5.503 × 1020 |
| M_Texp | −4.968 | 6.024 × 10−1 | −6.174 | −5.355 | −4.978 | −4.575 | −3.763 |
| M_Pconst | −2.034 × 10−2 | 1.073 × 10−1 | −1.250 × 10−1 | −1.248 × 10−1 | −3.974 × 10−2 | 5.518 × 10−2 | 2.107 × 10−1 |
| M_Pexp | −1.669 × 10−1 | 4.227 × 10−2 | −2.490 × 10−1 | −1.942 × 10−1 | −1.679 × 10−1 | −1.408 × 10−1 | −7.904 × 10−2 |
| M_Niconst | −2.147 × 10−2 | 1.780 × 10−1 | −4.188 × 10−1 | −1.305 × 10−1 | 4.851 × 10−3 | 1.092 × 10−1 | 2.604 × 10−1 |
| M_Niexp1 | 4.257 × 10−1 | 1.843 × 10−1 | 1.656 × 10−1 | 2.893 × 10−1 | 3.978 × 10−1 | 5.239 × 10−1 | 8.665 × 10−1 |
| M_Niexp2 | 1.013 | 3.740 × 10−1 | 4.613 × 10−1 | 7.530 × 10−1 | 9.436 × 10−1 | 1.210 | 1.909 |
| B_Weld | 7.754 × 10−1 | 1.697 × 10−1 | 4.266 × 10−1 | 6.638 × 10−1 | 7.880 × 10−1 | 8.903 × 10−1 | 1.089 |
| B_Plate | 9.141 × 10−1 | 2.009 × 10−1 | 5.046 × 10−1 | 7.841 × 10−1 | 9.308 × 10−1 | 1.049 | 1.283 |
| B_Forge | 8.479 × 10−1 | 1.864 × 10−1 | 4.650 × 10−1 | 7.270 × 10−1 | 8.611 × 10−1 | 9.763 × 10−1 | 1.185 |
| B_Const | 1.360 × 10−12 | 4.274 × 10−13 | 6.130 × 10−13 | 1.019 × 10−12 | 1.362 × 10−12 | 1.678 × 10−12 | 2.167 × 10−12 |
| B_Exp | 5.725 × 10−1 | 5.673 × 10−3 | 5.634 × 10−1 | 5.687 × 10−1 | 5.715 × 10−1 | 5.758 × 10−1 | 5.859 × 10−1 |
| B_Texp | −5.787 | 4.408 × 10−1 | −6.715 | −6.062 | −5.782 | −5.494 | −4.938 |
| B_Pconst | 1.891 × 10−1 | 1.092 × 10−1 | 3.516 × 10−2 | 1.161 × 10−1 | 1.686 × 10−1 | 2.392 × 10−1 | 4.596 × 10−1 |
| B_Pexp | 2.957 × 10−1 | 6.033 × 10−2 | 1.957 × 10−1 | 2.557 × 10−1 | 2.890 × 10−1 | 3.279 × 10−1 | 4.343 × 10−1 |
| B_Niconst | 4.075 | 1.385 | 1.943 | 3.073 | 3.866 | 4.878 | 7.294 |
| B_Niexp1 | 9.727 | 1.912 | 6.752 | 8.415 | 9.476 | 10.71 | 14.28 |
| B_Niexp2 | 4.452 × 10−1 | 1.022 × 10−1 | 0.2749 | 0.3770 | 0.4327 | 0.5009 | 0.6821 |
| B_Mnexp | 2.191 × 10−1 | 6.646 × 10−2 | 9.460 × 10−2 | 1.743 × 10−1 | 2.185 × 10−1 | 2.621 × 10−1 | 3.562 × 10−1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreño, D.; Kirk, M.; Serrano, M.; Sainz-Aja, J.A. Assessment of the Generalization Ability of the ASTM E900-15 Embrittlement Trend Curve by Means of Monte Carlo Cross-Validation. Metals 2022, 12, 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12030481
Ferreño D, Kirk M, Serrano M, Sainz-Aja JA. Assessment of the Generalization Ability of the ASTM E900-15 Embrittlement Trend Curve by Means of Monte Carlo Cross-Validation. Metals. 2022; 12(3):481. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12030481
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreño, Diego, Mark Kirk, Marta Serrano, and José A. Sainz-Aja. 2022. "Assessment of the Generalization Ability of the ASTM E900-15 Embrittlement Trend Curve by Means of Monte Carlo Cross-Validation" Metals 12, no. 3: 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12030481
APA StyleFerreño, D., Kirk, M., Serrano, M., & Sainz-Aja, J. A. (2022). Assessment of the Generalization Ability of the ASTM E900-15 Embrittlement Trend Curve by Means of Monte Carlo Cross-Validation. Metals, 12(3), 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12030481







