Craniofacial Reconstruction with Personalized Lightweight Scaffold Fabricated Using Electron-Beam Additive Manufacturing
Abstract
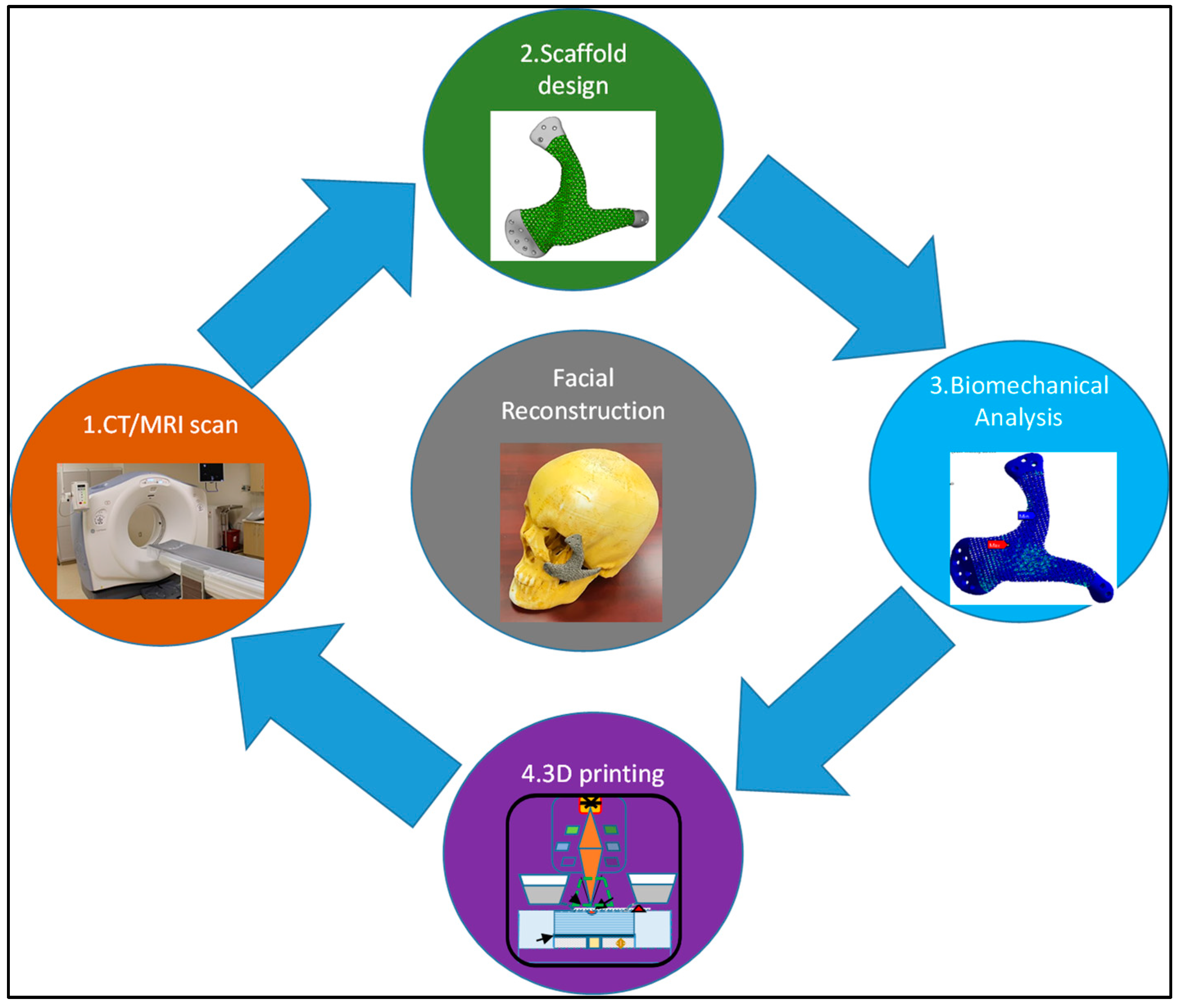
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CT/MRI Scan
2.2. Implant Design Customization
2.3. EBAM Fabrication
2.4. Compression Test
3. Finite Element Analysis
3.1. Material Properties
3.2. Boundary Conditions
3.3. Mesh Creation and Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanasono, M.M. Reconstructive Surgery for Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Adv. Med. 2014, 2014, 795483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, W.; Choi, W.S.; Wong, M.C.-M.; Powcharoen, W.; Zhu, W.; Tsoi, J.K.-H.; Chow, M.; Kwok, K.-W.; Su, Y. Three-Dimensionally Printed Patient-Specific Surgical Plates Increase Accuracy of Oncologic Head and Neck Reconstruction Versus Conventional Surgical Plates: A Comparative Study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chu, P.K.; Ding, C. Surface Modification of Titanium, Titanium Alloys, and Related Materials for Biomedical Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2004, 47, 49–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pilliar, R.M. Modern Metal Processing for Improved Load-Bearing Surgical Implants. Biomaterials 1991, 12, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niinomi, M. Recent Research and Development in Metallic Materials for Biomedical, Dental and Healthcare Products Applications. Mater. Sci. Forum 2007, 539–543, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Viteri, V.S.; Fuentes, E. Titanium and Titanium Alloys as Biomaterials; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Arabnejad, S.; Johnston, B.; Tanzer, M.; Pasini, D. Fully Porous 3D Printed Titanium Femoral Stem to Reduce Stress-Shielding Following Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Orthop. Res. 2017, 35, 1774–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, G.; Pandit, A.; Apatsidis, D. Fabrication Methods of Porous Metals for Use in Orthopaedic Applications. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2651–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghouse, S.; Reznikov, N.; Boughton, O.R.; Babu, S.; Ng, K.C.G.; Blunn, G.; Cobb, J.P.; Stevens, M.M.; Jeffers, J.R.T. The Design and In Vivo Testing of a Locally Stiffness-Matched Porous Scaffold. Appl. Mater. Today 2019, 15, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In Vivo Testing of Porous Ti-25Nb Alloy Serving as a Femoral Stem Prosthesis in a Rabbit Model. Available online: https://www.spandidos-publications.com/10.3892/etm.2016.3472 (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- Moiduddin, K.; Hammad Mian, S.; Alkindi, M.; Ramalingam, S.; Alkhalefah, H.; Alghamdi, O. An In Vivo Evaluation of Biocompatibility and Implant Accuracy of the Electron Beam Melting and Commercial Reconstruction Plates. Metals 2019, 9, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Liang, H.; Gao, C.; Peng, S.; Shen, L.; Shuai, C. Additive Manufacturing of Bone Scaffolds. Int. J. Bioprint. 2018, 5, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcam, A.B. Electron Beam Melting—EBM Process, Additive Manufacturing. Available online: http://www.arcam.com/technology/electron-beam-melting/ (accessed on 7 July 2017).
- Chua, C.K.; Wong, C.H.; Yeong, W.Y. Standards, Quality Control, and Measurement Sciences in 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-0-12-813490-0. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer, F. The Use of Finite Element Analysis to Enhance Research and Clinical Practice in Orthopedics. J. Knee Surg. 2016, 29, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albogha, M.H.; Takahashi, I. Generic Finite Element Models of Orthodontic Mini-Implants: Are They Reliable? J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 3751–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, R.; Antonov, M.; Kollo, L.; Holovenko, Y.; Prashanth, K.G. Mechanical Behavior of Ti6Al4V Scaffolds Filled with CaSiO3 for Implant Applications. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Materialise Mimics. Available online: https://www.materialise.com/en/medical/software/mimics (accessed on 6 July 2019).
- Davies, J.C.; Chan, H.H.L.; Jozaghi, Y.; Goldstein, D.P.; Irish, J.C. Analysis of Simulated Mandibular Reconstruction Using a Segmental Mirroring Technique. J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 47, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiduddin, K.; Mian, S.H.; Ameen, W.; Alkhalefah, H.; Sayeed, A. Feasibility Study of the Cranial Implant Fabricated without Supports in Electron Beam Melting. Metals 2021, 11, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, J. 3D Modeling, Custom Implants and Its Future Perspectives in Craniofacial Surgery. Ann. Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, F.; Klarin, J. Mechanical Properties of Trabecular Structures Produced by SLM, as a Function of the Trabecular Morphology. Master’s Thesis, Jönköping University, Jönköping, Sweden, May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Krejčí, T.; Jíra, A.; Řehounek, L.; Šejnoha, M.; Kruis, J.; Koudelka, T. Homogenization of Trabecular Structures. MATEC Web Conf. 2020, 310, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.Y.; Kim, N.; Park, J.-C.; Yoo, S.K.; Shin, D.A.; Shim, K.-W. Exploring for the Optimal Structural Design for the 3D-Printing Technology for Cranial Reconstruction: A Biomechanical and Histological Study Comparison of Solid vs. Porous Structure. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2017, 33, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, M. Design of Titanium Implants for Additive Manufacturing. In Titanium in Medical and Dental Applications; Froes, F.H., Qian, M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Biomaterials; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 203–224. ISBN 978-0-12-812456-7. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmati, S. Direct Rapid Tooling. In Comprehensive Materials Processing; Hashmi, S., Batalha, G.F., Van Tyne, C.J., Yilbas, B., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 303–344. ISBN 978-0-08-096533-8. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ahmari, A.; Nasr, E.A.; Moiduddin, K.; Anwar, S.; Kindi, M.A.; Kamrani, A. A Comparative Study on the Customized Design of Mandibular Reconstruction Plates Using Finite Element Method. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2015, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagasao, M.; Nagasao, T.; Imanishi, Y.; Tomita, T.; Tamaki, T.; Ogawa, K. Experimental Evaluation of Relapse-Risks in Operated Zygoma Fractures. Auris Nasus Larynx 2009, 36, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Saiz, E.; Rahaman, M.N.; Tomsia, A.P. Toward Strong and Tough Glass and Ceramic Scaffolds for Bone Repair. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 5461–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roohani-Esfahani, S.-I.; Newman, P.; Zreiqat, H. Design and Fabrication of 3D Printed Scaffolds with a Mechanical Strength Comparable to Cortical Bone to Repair Large Bone Defects. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, Y.; Cui, H.; Wang, X.-M. Chapter 2—Preparation and Characterization of Biomimetic Mineralized Collagen. In Mineralized Collagen Bone Graft Substitutes; Wang, X.-M., Qiu, Z.-Y., Cui, H., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Biomaterials; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019; pp. 23–60. ISBN 978-0-08-102717-2. [Google Scholar]
- Goharian, A.; Kadir, M.R.A.; Abdullah, M.R. Trauma Plating Systems: Biomechanical, Material, Biological, and Clinical Aspects; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 978-0-12-804758-3. [Google Scholar]













| Specimen | Weight (Grams) |
|---|---|
| Dode Thick | 19.80 |
| Dode Medium | 17.08 |
| Dode Thin | 13.32 |
| Materials | Youngs Modulus (MPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Yield Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cortical bone | 13,700 | 0.3 | 122 |
| Titanium scaffold (Ti6Al4V) and fixation screws | 120,000 | 0.3 | 930 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moiduddin, K.; Mian, S.H.; Elseufy, S.M.; Abdo, B.M.A.; Aboudaif, M.K.; Alkhalefah, H. Craniofacial Reconstruction with Personalized Lightweight Scaffold Fabricated Using Electron-Beam Additive Manufacturing. Metals 2022, 12, 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12040552
Moiduddin K, Mian SH, Elseufy SM, Abdo BMA, Aboudaif MK, Alkhalefah H. Craniofacial Reconstruction with Personalized Lightweight Scaffold Fabricated Using Electron-Beam Additive Manufacturing. Metals. 2022; 12(4):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12040552
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoiduddin, Khaja, Syed Hammad Mian, Sherif Mohammed Elseufy, Basem Motea Abdullah Abdo, Mohamed Kamaleldin Aboudaif, and Hisham Alkhalefah. 2022. "Craniofacial Reconstruction with Personalized Lightweight Scaffold Fabricated Using Electron-Beam Additive Manufacturing" Metals 12, no. 4: 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12040552
APA StyleMoiduddin, K., Mian, S. H., Elseufy, S. M., Abdo, B. M. A., Aboudaif, M. K., & Alkhalefah, H. (2022). Craniofacial Reconstruction with Personalized Lightweight Scaffold Fabricated Using Electron-Beam Additive Manufacturing. Metals, 12(4), 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12040552








