Normalizing Effect of Heat Treatment Processing on 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Manufactured by Powder Bed Fusion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. 17-4 PH SS Powder
2.2. Part Fabrication by L-PBF
2.3. Post-Heat Treatment Procedures
2.4. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
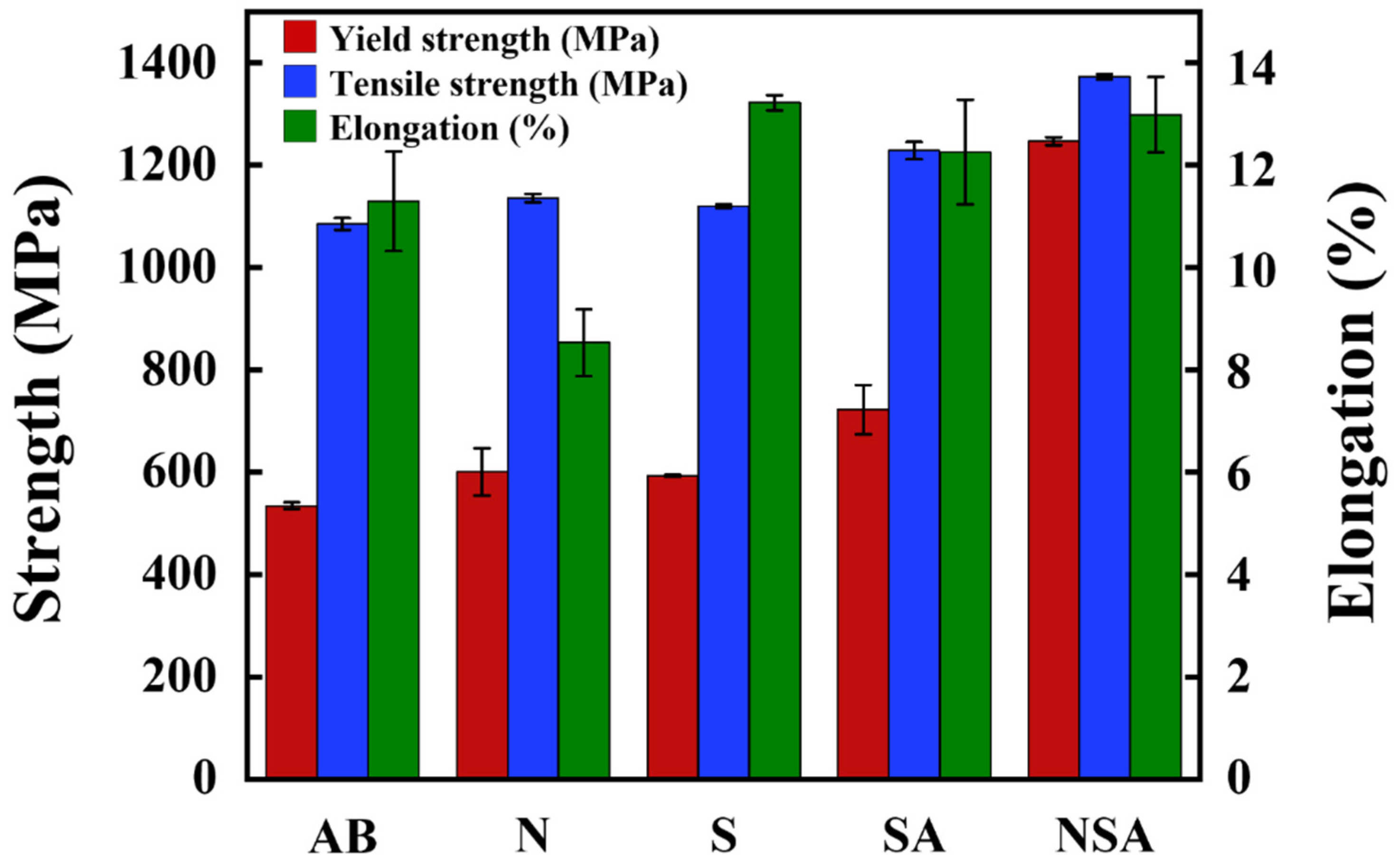
3.1. Mechanical Properties
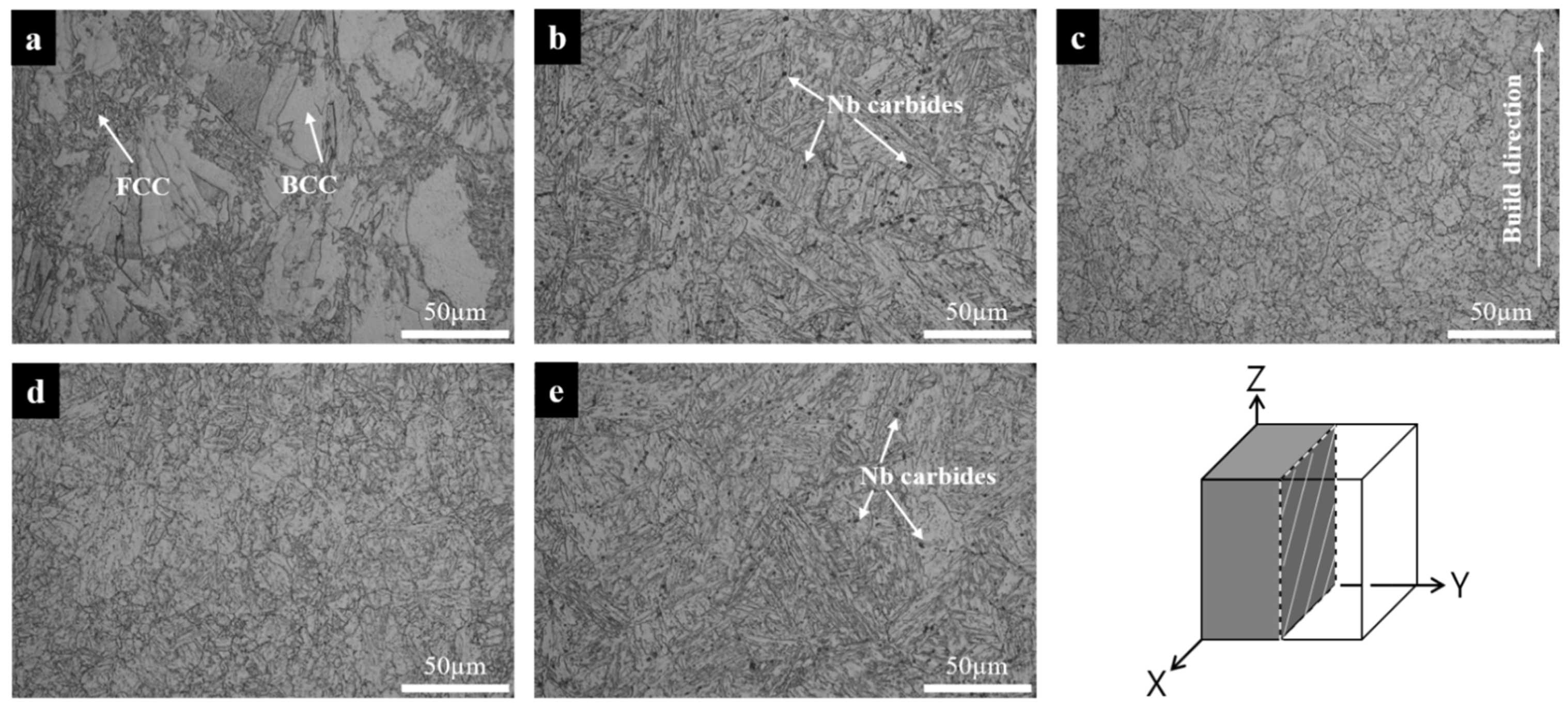
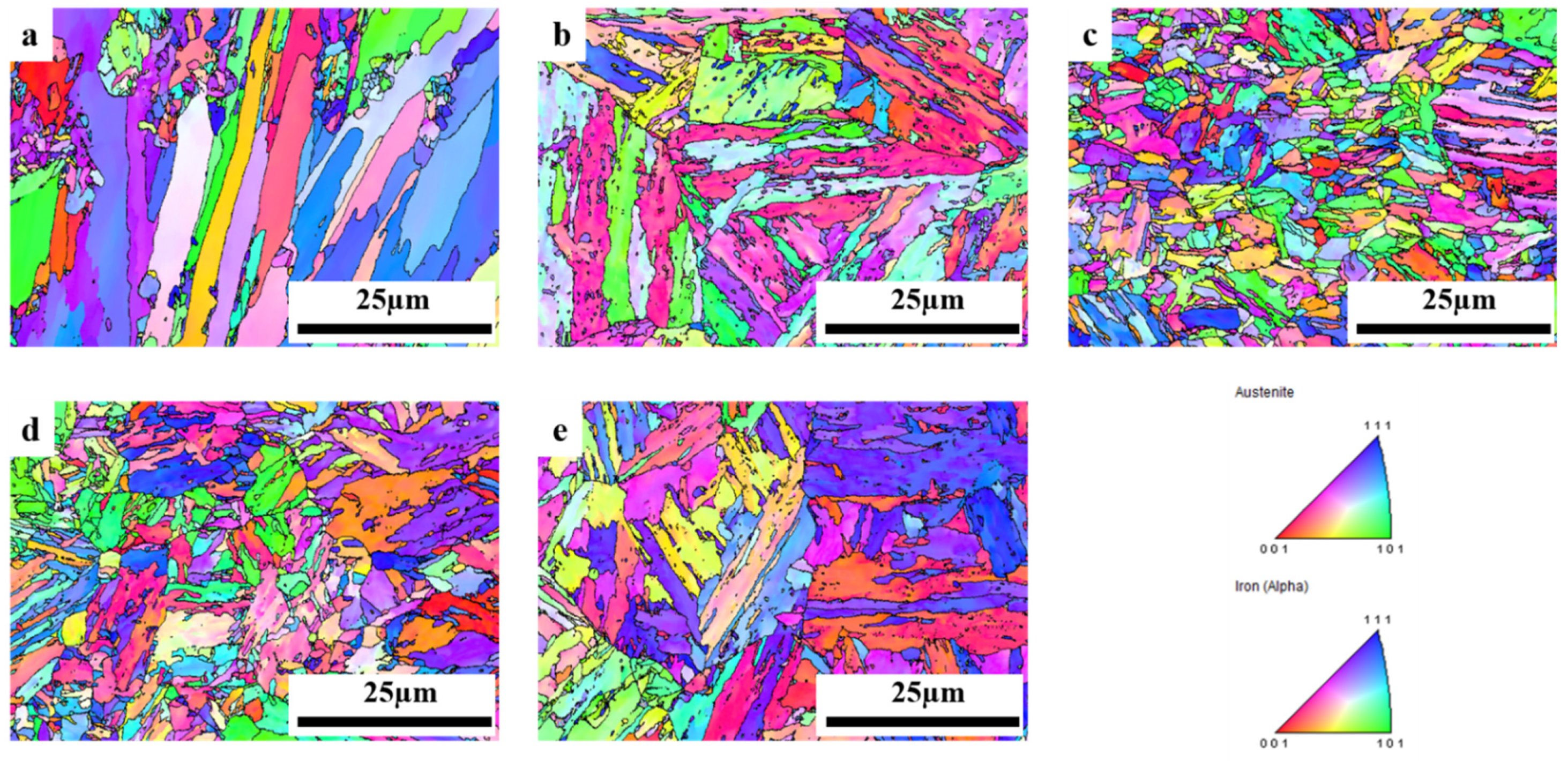
3.2. XRD Patterns and Optical Micrography Images
3.3. Phase Analysis
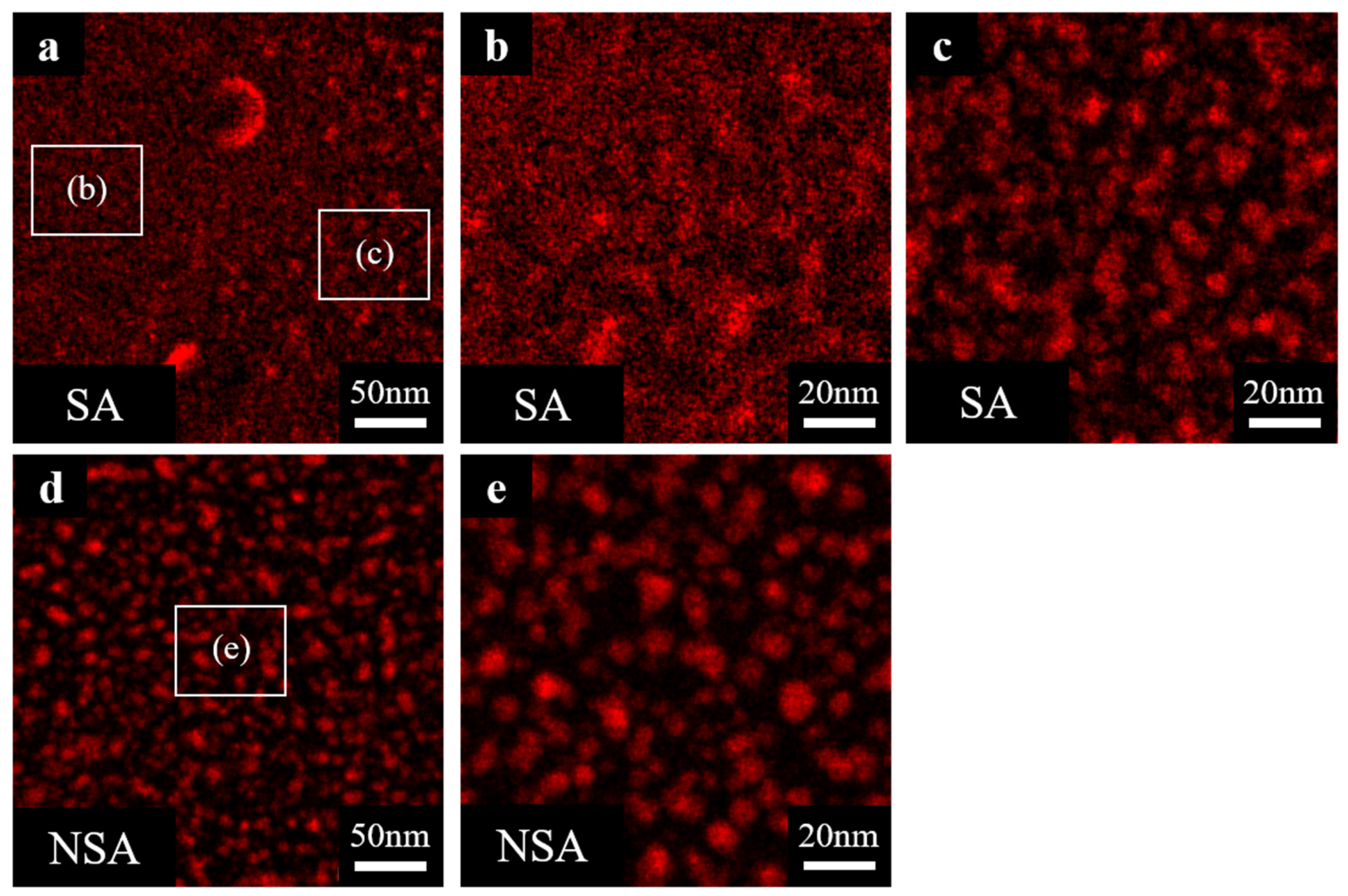
3.4. Cu Precipitation
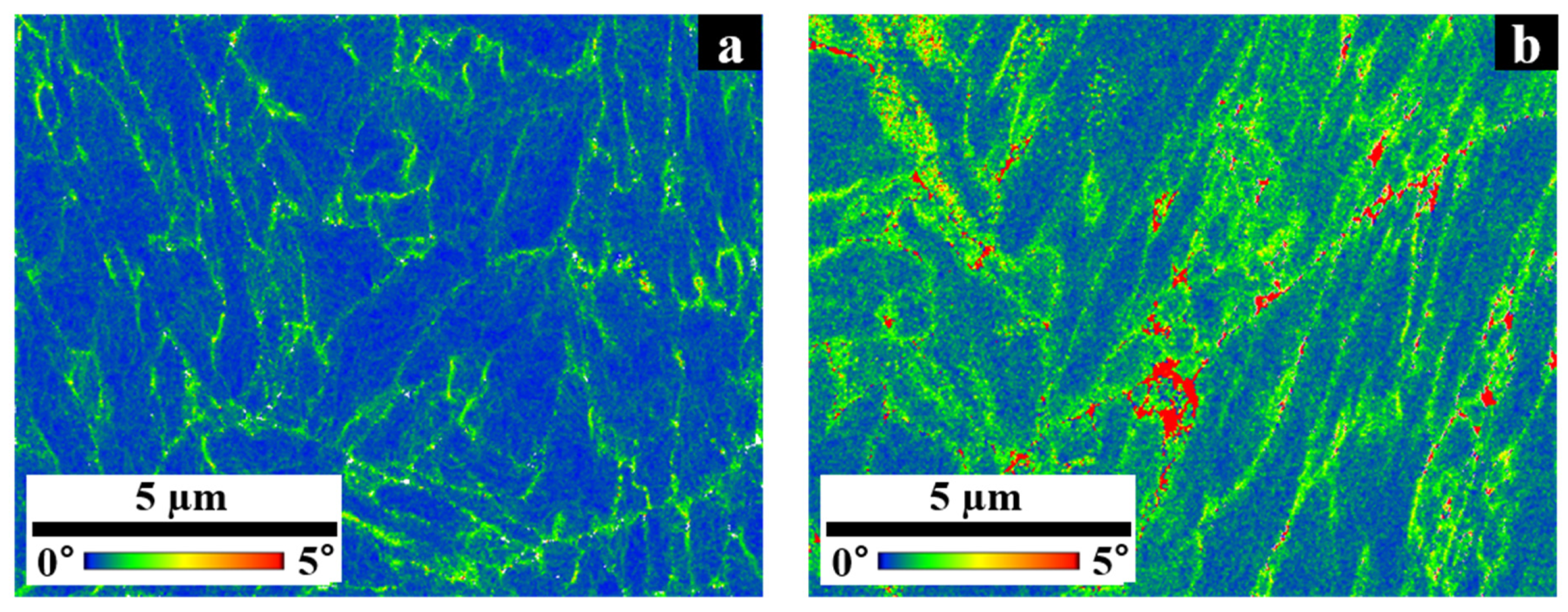
3.5. Effects of Normalizing Treatment
4. Conclusions
- Significant differences in the mechanical properties of 17-4 PH SS were observed among the various HTs. Compared to the conventional method, the NSA treatment condition resulted in superior mechanical properties that met the ASTM-693 (H900) industrial standard. The yield strength and elongation of the resulting 17-4 PH SS were 1264 MPa and 12.9%, respectively.
- No differences in the austenite fraction were found in the XRD and EBSD results after the additional normalizing treatment. However, irregular fine-grain size and inhomogeneous distribution of the Cu precipitates that affected the mechanical properties of the 17-4 PH SS under SA conditions were observed in the OM and TEM-EDS analyses.
- The existence of a non-equilibrium ferrite phase under the SA condition was observed using KAM, and it was confirmed that the mechanical properties changed based on the differences in the precipitation behavior of the ferrite and martensite structures.
- Cu precipitation in 17-4 PH SS fabricated by L-PBF in a nitrogen environment can be stabilized by applying an additional normalizing treatment. Inhomogeneous Cu precipitation occurs in 17-4 PH SS without a normalizing step because of the mixed ferrite and martensite microstructure.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ludwigon, D.C.; HALL, A.M. The Physical Metallurgy of Precipitation-Hardenable Stainless Steels; Battelle Memorial Institute Defense Metals Information Center: Columbus, OH, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Leslie, W.C. The Physical Metallurgy of Steels; Hemisphere Publishing Corp.: Washington, DC, USA, 1981; p. 396. [Google Scholar]
- ATI Technical Data Sheet. Stainless Steel AL 17-4TM Precipitation Hardening Alloy. Available online: http://www.specialtysteelsupply.com/brochure/17-4-technical-data.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2022).
- Yoo, W.D.; Lee, J.H.; Youn, K.T.; Rhyim, Y.M. Study on the microstructure and mechanical properties of 17-4 PH stainless steel depending on heat treatment and aging time. Solid State Phenom. 2006, 118, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.D. Smooth Topological Design of Continuum Structures for Additive Manufacturing. Ph.D. Thesis, Deakin University, Melbourne, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.F. Recent advances and future trends in exploring Pareto-optimal topologies and additive manufacturing oriented topology optimization. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2020, 17, 4631–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Konovalov, S.V.; Chen, X. Research status and application of the high-entropy and traditional alloys fabricated via the laser cladding. Usp. Fiz. Met. 2020, 21, 26–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, K.; Chai, L.; Zhang, C.; Guan, H.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Sun, Q.; Li, Y. Investigation of microstructure and wear resistance of laser-clad CoCrNiTi and CrFeNiTi medium-entropy alloy coatings on Ti sheet. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 145, 107518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, J.; Yang, C.-H.; Karuppasamy, S.S. Investigation on microstructure, nanohardness and corrosion response of laser cladded colmonoy-6 particles on 316l steel substrate. Materials 2021, 14, 6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorasani, A.; Gibson, I.; Veetil, J.K.; Ghasemi, A.H. A review of technological improvements in laser-based powder bed fusion of metal printers. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 108, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zai, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Guo, W.; Wellmann, D.; Tong, X.; Tian, Y. Laser powder bed fusion of precipitation-hardened martensitic stainless steels: A review. Metals 2020, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheruvathur, S.; Lass, E.A.; Campbell, C.E. Additive manufacturing of 17-4 PH stainless steel: Post-processing heat treatment to achieve uniform reproducible microstructure. J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 2016, 68, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, P.A. Melt pool temperature and cooling rates in laser powder bed fusion. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hebert, R.J.; Aindow, M. Effect of heat treatments on microstructural evolution of additively manufactured and wrought 17-4PH stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2018, 156, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafi, H.K.; Pal, D.; Patil, N.; Starr, T.L.; Stucker, B.E. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of 17-4 precipitation hardenable steel processed by selective laser melting. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 4421–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, M.; Hono, K.; Katayama, Y. Microstructural evolution in a 17-4 PH stainless steel after aging at 400 C. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1999, 30, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabooni, S.; Chabok, A.; Feng, S.C.; Blaauw, H.; Pijper, T.C.; Yang, H.J.; Pei, Y.T. Laser powder bed fusion of 17–4 PH stainless steel: A comparative study on the effect of heat treatment on the microstructure evolution and mechanical properties. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 46, 102176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.H.; Lee, C.G.; You, Y.Z.; Lee, Y.K.; Kim, J.Y. Heat Treatment of Materials; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Baech, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Murr, L.E.; Martinez, E.; Hernandez, J.; Collins, S.; Amato, K.N.; Gaytan, S.M.; Shindo, P.W. Microstructures and properties of 17-4 PH stainless steel fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2012, 1, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, B.H.; Sun, L.; Li, R.; Hsu, T.Y. Influence of austenite grain size on γ-ε martensitic transformation temperature in Fe-Mn-Si alloys. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1995, 33, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaço, R.; Vilar, R. Stabilisation of retained austenite in laser surface melted tool steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2004, 385, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchini, L.; Vicente, N., Jr.; Lonardelli, I.; Magalini, E.; Robotti, P.; Molinari, A. Metastable austenite in 17–4 precipitation-hardening stainless steel produced by selective laser melting. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2010, 12, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBrun, T.; Nakamoto, T.; Horikawa, K.; Kobayashi, H. Effect of retained austenite on subsequent thermal processing and resultant mechanical properties of selective laser melted 17–4 PH stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2015, 81, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vunnam, S.; Saboo, A.; Sudbrack, C.; Starr, T.L. Effect of powder chemical composition on the as-built microstructure of 17-4 PH stainless steel processed by selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 30, 100876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, S.D.; Zuback, J.S.; Keist, J.S.; Palmer, T.A. Impact of composition on the heat treatment response of additively manufactured 17–4 PH grade stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 738, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auguste, P.; Mauduit, A.; Fouquet, L.; Pillot, S. Study on 17-4 PH stainless steel produced by selective laser melting. UPB. Sci. Bull. Ser. B-Chem. Mater. Sci. 2018, 80, 197–210. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Elwany, A.; Yadollahi, A.; Thompson, S.M.; Bian, L.; Shamsaei, N. Mechanical properties and microstructural characterization of selective laser melted 17-4 PH stainless steel. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2017, 23, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yadollahi, A.; Shamsaei, N.; Thompson, S.M.; Elwany, A.; Bian, L. Effects of building orientation and heat treatment on fatigue behavior of selective laser melted 17-4 PH stainless steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 94, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, X. Experimental investigation on selective laser melting of 17-4PH stainless steel. Optic. Laser Technol. 2017, 87, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasebani, S.; Ghayoor, M.; Badwe, S.; Irrinki, H.; Atre, S.V. Effects of atomizing media and post processing on mechanical properties of 17-4 PH stainless steel manufactured via selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM A693-16; Standard Specification for Precipitation-Hardening Stainless and Heat-Resisting Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Wilson, J.M.; Piya, C.; Shin, Y.C.; Zhao, F.; Ramani, K. Remanufacturing of turbine blades by laser direct deposition with its energy and environmental impact analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 80, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedzinski, M. Materials for Additive Manufacturing by Direct Energy Deposition. Master’s Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- DebRoy, T.; Wei, H.L.; Zuback, J.S.; Mukherjee, T.; Elmer, J.W.; Milewski, J.O.; Beese, A.M.; Wilson-Heid, A.; De, A.; Zhang, W. Additive manufacturing of metallic components-Process structure and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 92, 112–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doubenskaia, M.; Domashenkov, A.; Smurov, I.; Petrovskiy, P. Study of selective laser melting of intermetallic TiAl powder using integral analysis. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2018, 129, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsaei, N.; Yadollahi, A.; Bian, L.; Thompson, S.M. An overview of direct laser deposition for additive manufacturing: Part 2: Mechanical behavior, process parameter optimization and control. Addit. Manuf. 2015, 8, 12–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, H.; Huo, P.; Bai, P.; Du, W.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, W. Effect of Solution Temperature on the Microstructure and Properties of 17-4PH High-Strength Steel Samples Formed by Selective Laser Melting. Metals 2022, 12, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecki, D.J.; Siewert, T.A. WRC-1992 constitution diagram for stainless steel weld metals: A modification of the WRC-1988 diagram. Weld. J. 1992, 71, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Bhaduri, A.K.; Gill, T.P.S.; Srinivasan, G.; Sujith, S. Optimised post-weld heat treatment procedures and heat input for welding 17–4PH stainless steel. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 1999, 4, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezhadfar, P.D.; Burford, E.; Anderson-Wedge, K.; Zhang, B.; Shao, S.; Daniewicz, S.R.; Shamsaei, N. Fatigue crack growth behavior of additively manufactured 17-4 PH stainless steel: Effects of build orientation and microstructure. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 123, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, J.B.; Schultz, B.F.; Venugopalan, D.; Lopez, H.F.; Rohatgi, P.K.; Cho, K.; Kim, C.S. On the superposition of strengthening mechanisms in dispersion strengthened alloys and metal-matrix nanocomposites: Considerations of stress and energy. Met. Mater. Int. 2014, 20, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.S.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Austenite grain size and the martensite-start temperature. Scr. Mater. 2009, 60, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.C.; Hollomon, J.H.; Turnbull, D. Kinetics of the austenite → martensite transformation. J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 1949, 1, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Hwu, L.Y.; Lin, D.Y.; Lee, J.L. The relationship between alloying elements and retained austenite in martensitic stainless steel welds. Scr. Mater. 2000, 42, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

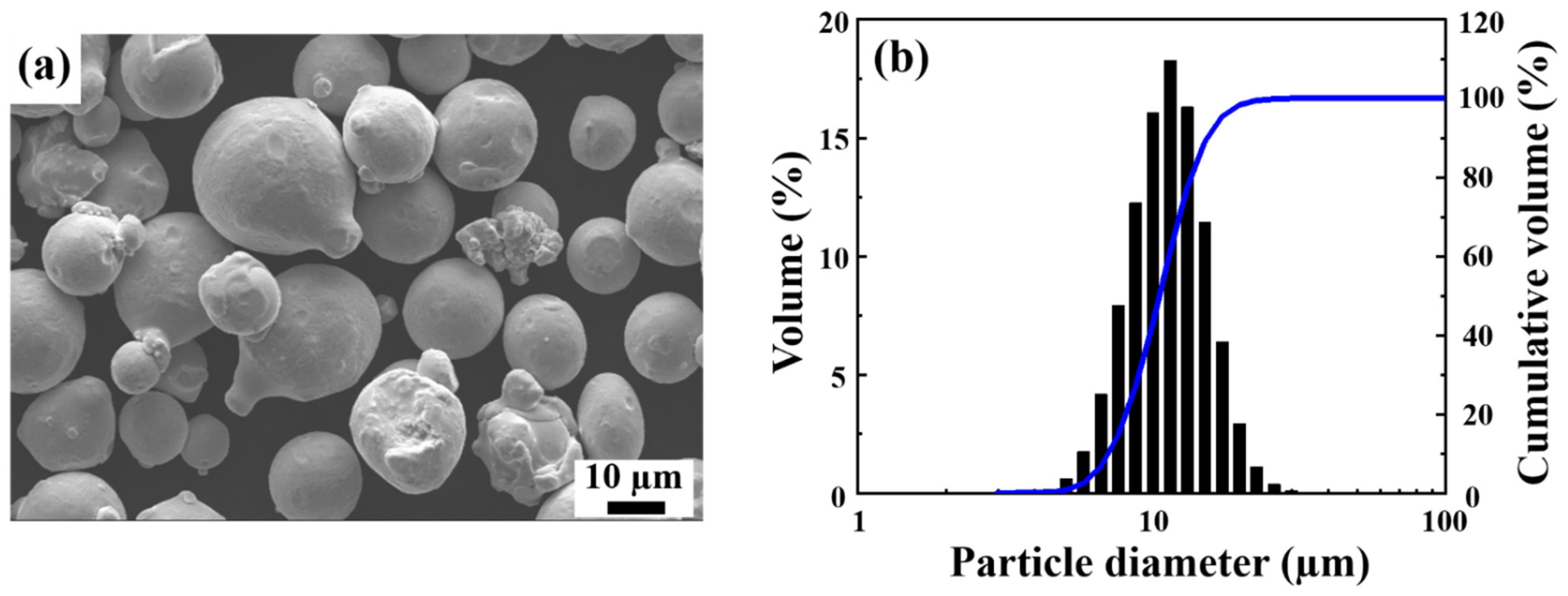
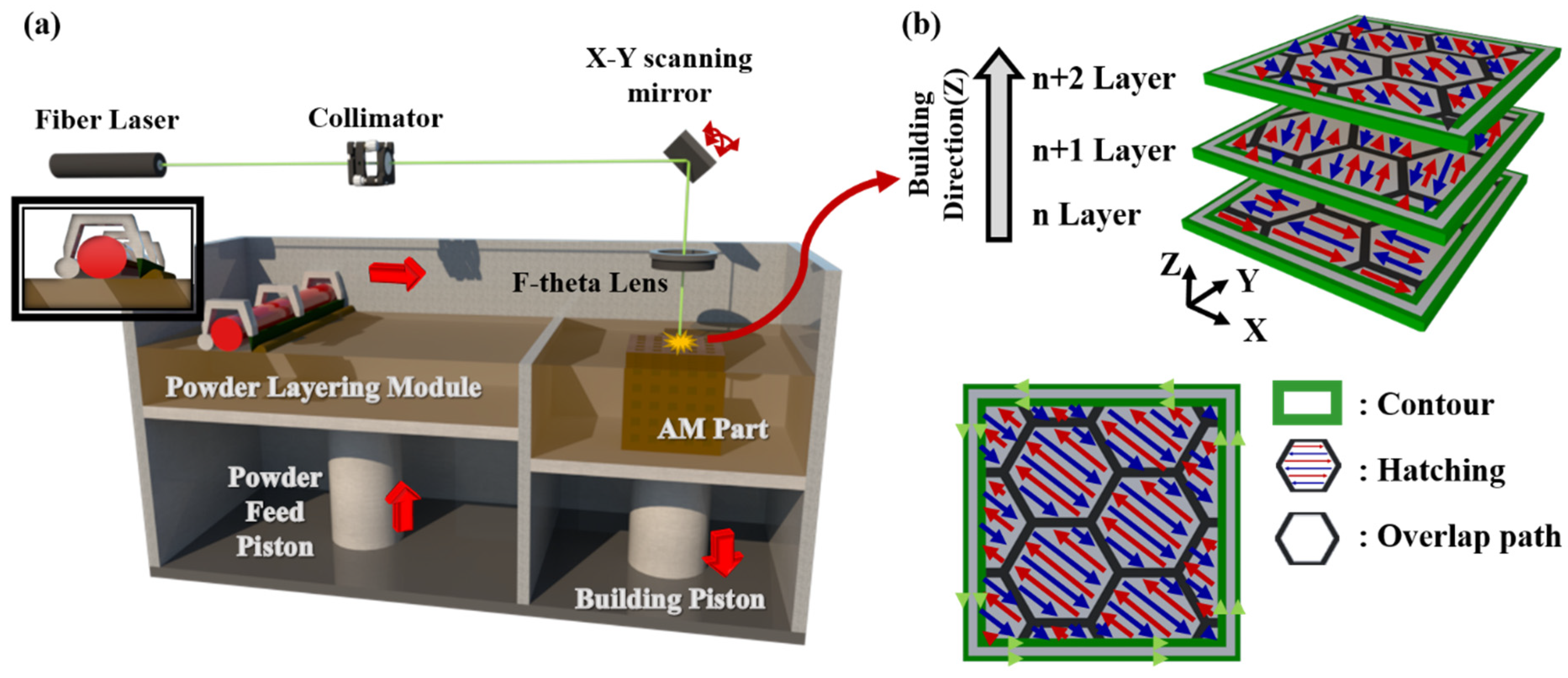


| Fe | Cr | Ni | Cu | Si | Mn | Nb | P | S | N | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bal. | 17.10 | 4.40 | 4.42 | 0.92 | 0.85 | 0.24 | 0.021 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.027 |
| Sample Name | Heat Treatment Condition |
|---|---|
| As-built (AB) | - |
| Normalizing treatment (N) | 1200 °C, 4 h + Furnace cooling |
| Solution treatment (S) | 1060 °C, 1 h + Gas cooling |
| Solution + Aging treatment (SA) | 1060 °C, 1 h + Gas cooling → 482 °C, 4 h + Air cooling |
| Normalizing + Solution + Aging treatment (NSA) | 1200 °C, 4 h + Furnace cooling → 1060 °C, 1 h + Gas cooling → 482 °C, 4 h + Air cooling |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yeon, S.-M.; Yoon, J.; Kim, T.B.; Lee, S.H.; Jun, T.-S.; Son, Y.; Choi, K. Normalizing Effect of Heat Treatment Processing on 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Manufactured by Powder Bed Fusion. Metals 2022, 12, 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12050704
Yeon S-M, Yoon J, Kim TB, Lee SH, Jun T-S, Son Y, Choi K. Normalizing Effect of Heat Treatment Processing on 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Manufactured by Powder Bed Fusion. Metals. 2022; 12(5):704. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12050704
Chicago/Turabian StyleYeon, Si-Mo, Jongcheon Yoon, Tae Bum Kim, Seung Ho Lee, Tea-Sung Jun, Yong Son, and Kyunsuk Choi. 2022. "Normalizing Effect of Heat Treatment Processing on 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Manufactured by Powder Bed Fusion" Metals 12, no. 5: 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12050704
APA StyleYeon, S.-M., Yoon, J., Kim, T. B., Lee, S. H., Jun, T.-S., Son, Y., & Choi, K. (2022). Normalizing Effect of Heat Treatment Processing on 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Manufactured by Powder Bed Fusion. Metals, 12(5), 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12050704







