Abstract
In today’s world, efficiency and margin of safety are prime considerations for any applications. To address such parameters in aerospace or high-tech consumer products, there are still limitations in terms of capabilities from a material perspective. Aluminium 7075 is predominantly used as a combination material in these applications, but it has many drawbacks such as early wear/friction, low fatigue life cycle, high weight ratios, high deformation and stresses. To overcome these key issues, many reinforcements have been used to date. However, the results are not so convincing with respect to tribological applications, and the aforementioned issues still persist. In the current work, a novel hybrid composite comprising Aluminium 7075 as substrate and the reinforcement of silicon carbide and aluminium oxide at varying combinations of 3 to 9% in steps of 3% and a constant percentage of 5% were added, respectively. The exhaustive work focuses on extracting the mechanical, tribological and physical properties of a hybrid composite. Furthermore, a microcharacterisation study of these combinations was carried out using FE-SEM and EDX. In a continuation to this simulation, a study was performed using ANSYS Workbench to identify a suitable gear application with real-time loading conditions. The observed results show a tensile strength of 366 MPa for 6%SiC, hardness of 93 VHN and wear rate of 0.00025 mm3/Nm for the 9%SiC combination.
1. Introduction
Metal matrix composites (MMCs), as the name demonstrates, have a metal material as a matrix. Matrices in these composites can be aluminium, magnesium, titanium, etc. The reinforcements selected could be silicon carbide, aluminium oxide, boron carbide, carbon fibre, glass fibre, etc. These composites are primarily used to give points of interest over their monolithic counter parts. The main advantages include higher mechanical strength, low material density. The advancement of high-quality and high-strength aluminium is the essential necessity of aviation and automobile industry. The noted uses of aluminium include electronic packaging, aircraft structures, internal combustion engine components and power transmission towers. It is also encouraged in the preparation of a variety of recreational products [1]. Hybrid aluminium MMCs assisted with granular ceramics play a significant part in advanced engineering materials having exceptional properties of high hardness and fatigue strength, less weight and better wear resistance. Specially, these are replacing ferrous established materials in the automotive, defence, and aviation sectors [2]. Mechanical properties such as strength, hardness, wear and fatigue resistance are upgraded when aluminium is impregnated with different particle reinforcements when compared to natural homogeneity. The fatigue behaviour of aluminium MMCs is demonstrated to be better because of low crack propagation rates when contrasted with their unreinforced materials [3]. The higher strength, lower density, excellent corrosion resistance, good thermal properties, creep resistance and good fatigue behaviour of aluminium 7075 alloy has been broadly utilised in the aviation industry [1,4,5]. Composites with more than one reinforcement are called hybrid composites. The behaviour of hybrid composites is a weighed sum of the individual additives in which there may be an extra-favourable balance between the inherent benefits and drawbacks [6]. The contact stress analysis of the aluminium metal matrix composite comes nearer to steel material and is better than polymer material [7]. The performance of the aluminium metal matrix composite matches with mild steel material [8]. For the same contact stress condition, aluminium metal matrix composites have 45% less mass reduction compared to structural steel material. Consequently, it tends to be suggested for all sorts of light weight applications [9]. The structural model evaluated using the aluminium MMCs using computer-assisted analysis proved to obtain higher efficiency and ease of manufacturing [10]. Through simulation results, it tends to be demonstrated that aluminium composite gears give 60% lesser weight contrasted with steel gears [11]. Aluminium matrix reinforced with silicon carbide can be used in the manufacturing of power-transmitting elements such as gears [12]. In this present investigation, aluminium 7075 reinforced with silicon carbide and aluminium oxide are produced through a stir-casting process, and the mechanical and tribological properties are studied. Aluminium MMCs that yield optimum mechanical and tribological properties will be selected as gear material. A further simulation analysis of aluminium matrix composite spur gears is carried out.
2. Materials and Methods
The aluminium 7075 hybrid composite material is fabricated with a stir-casting process. Silicon carbide with varying weight percentages of 3%, 6%, 9% and aluminium oxide with a fixed weight percentage of 5% will be added as reinforcements. Commercially available aluminium 7075 ingots were used as a matrix material. Aluminium 7075 was supplied by Bharat Aerospace Metals, Mumbai. Micro-sized aluminium oxide and silicon carbide were used as the reinforcement for the aluminium metal matrix composite. Aluminium 7075 alloy was melted in a mild steel crucible at a temperature of 750 °C. After melting and degassing by adding hexachloroethane tablets, molten metal was stirred with the help of a zirconium-coated mild steel stirrer at 400 rpm for a duration of 15 min. At the time of stirring, aluminium oxide and silicon carbide were added, which were preheated at 250 °C. Lastly, the composite material was poured into the already heated metal mould. The aluminium 7075 along with various weight percentages of hybrid composites were produced, and test specimens were machined as per ASTM standards.
3. Experimental Methods
3.1. Hardness Test
The cast samples were exposed to a Vickers hardness test to discover the hardness values. The Vickers hardness test was performed in accordance with ASTM E92 (Fuel instruments and Engineers pvt. Ltd., Yadrav, India) at room temperature. The diameter and length of the test specimen were 20 mm and 20 mm, respectively. A load of 5 kgf was applied utilising diamond tip indenter for a dwell time of 10 s. On each specimen, three readings were taken, and the average of three readings was considered as the VHN for that specimen.
3.2. Tensile Test
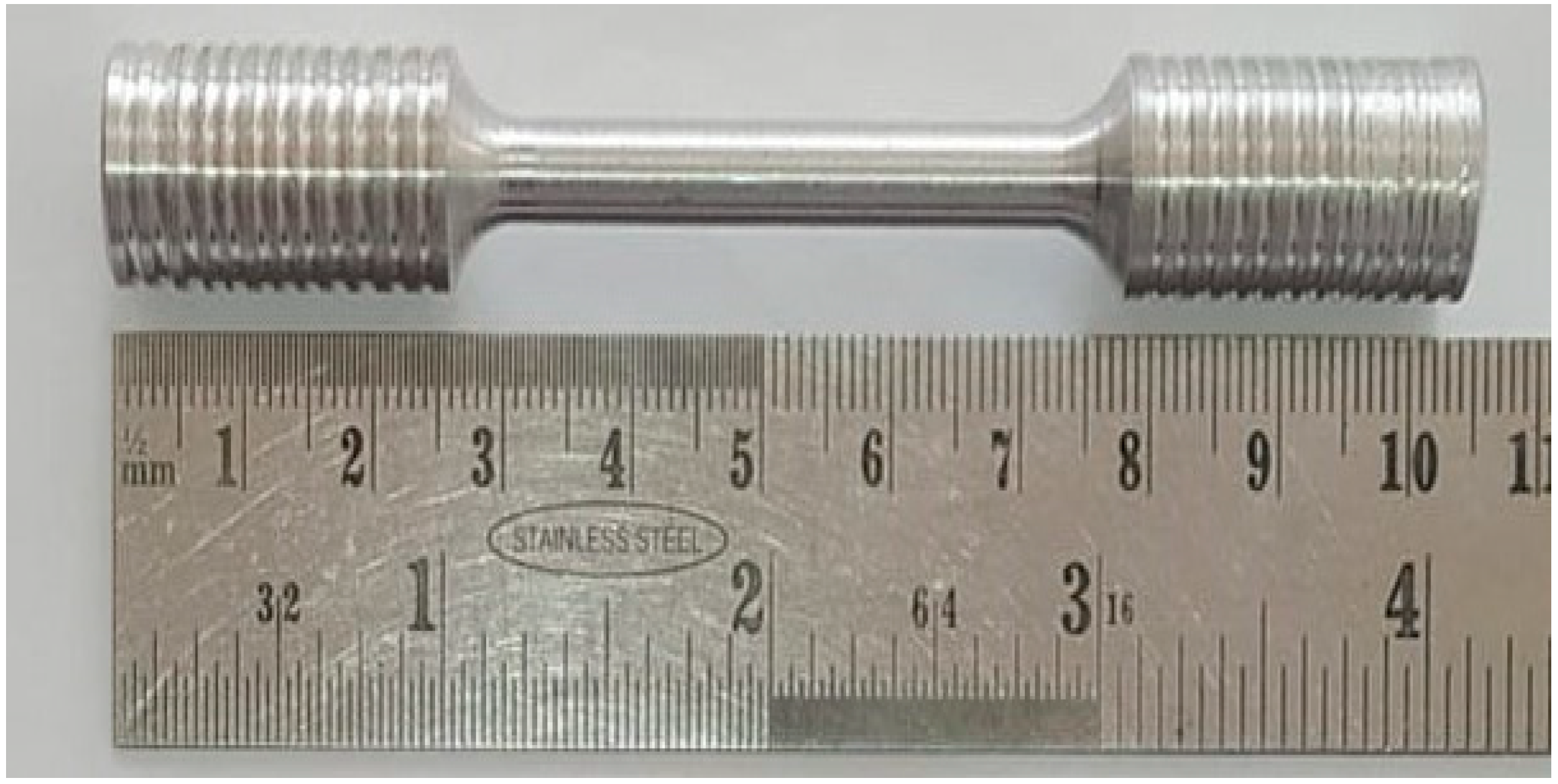
A tensile test was carried to check the tensile properties, percentage of elongation and ultimate tensile strength of aluminium 7075 without reinforcements and with reinforcements. The figure shows the tensile specimen as per ASTM D3552-17 (Fuel instruments and Engineers pvt. Ltd., Yadrav, India). Specimens were prepared from cast aluminium MMCs, as shown in Figure 1. A tensile test was carried on round specimens with a diameter 6 of mm and gauge length of 25 mm by using a universal testing machine of 100 kN capacity. The results after testing were quantified based on average values of three samples. The average strain rate was observed as 0.1355 s−1.

Figure 1.
Tensile test specimen as per ASTM D3552-17.
3.3. Wear Test
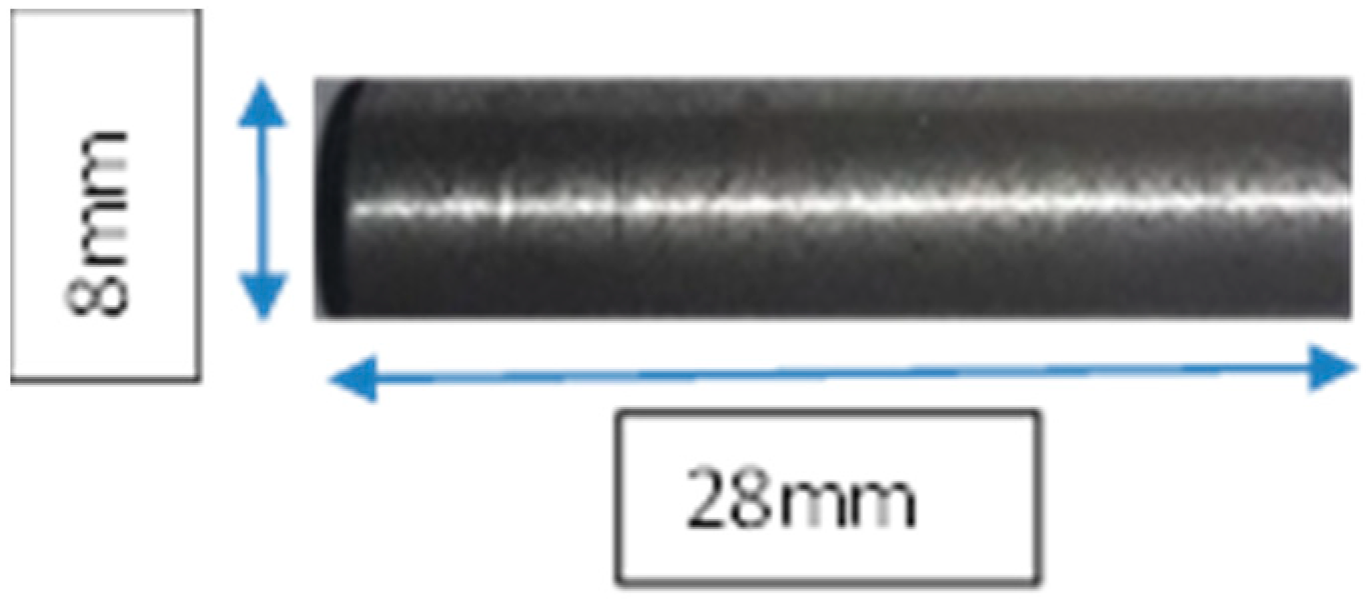
Wear tests for dry sliding conditions were carried with a pin-on-disc apparatus (Magnum, Bengaluru, India). The specimens were tested for different loads and disc radius at a constant speed of 450 rpm. The wear test specimen is shown in Figure 2. It has a diameter of 8 mm and length of 28 mm.

Figure 2.
Wear test specimen.
3.4. Coefficient of Friction
The coefficient of friction was examined during the wear test with respect to load and reinforcement.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Hardness Test
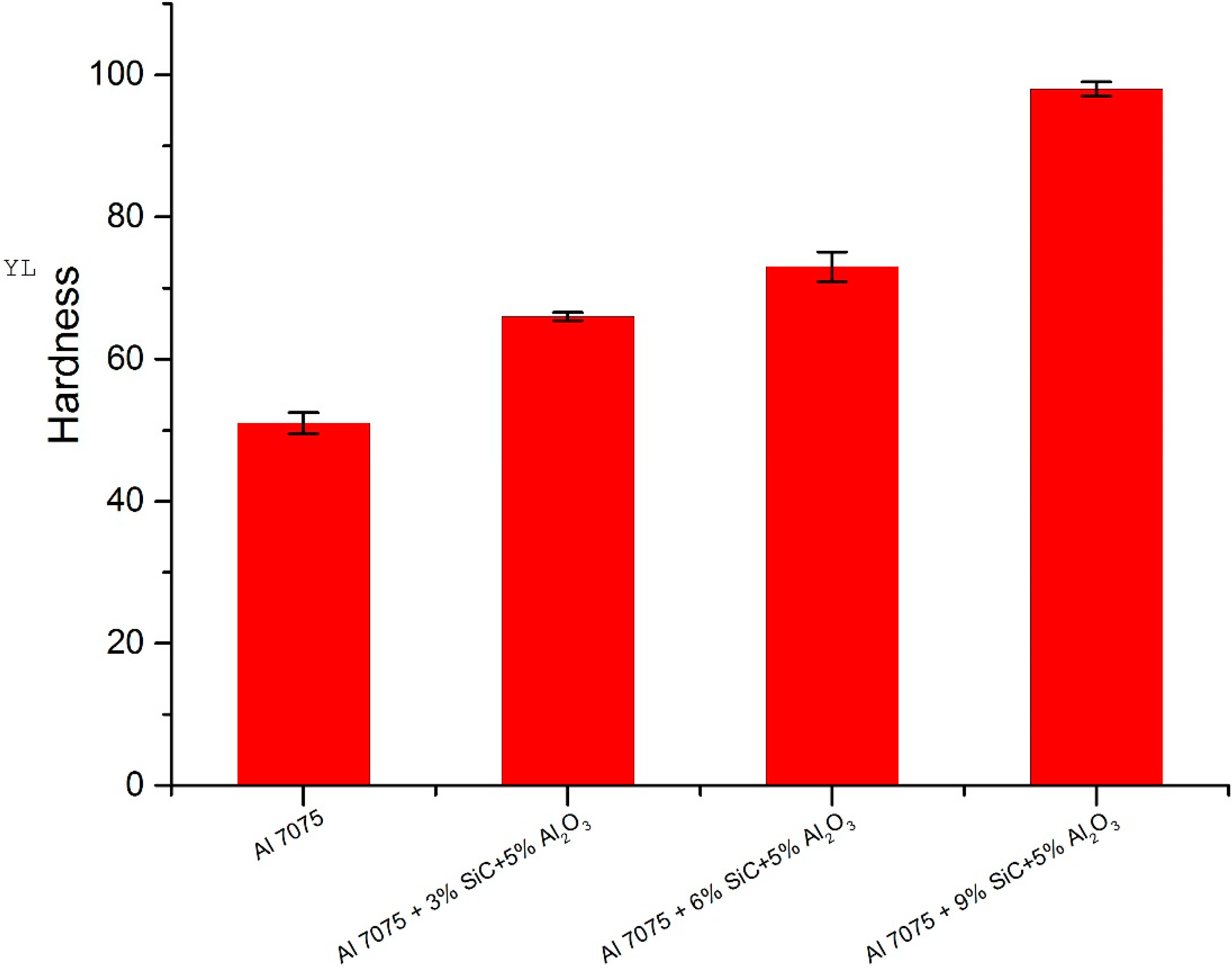
The outcomes of Vickers hardness values are shown in Figure 3. The test outcomes confirm that the Vickers hardness values of the hybrid MMCs are higher in comparison with their unreinforced counterpart, and furthermore, the hardness numbers increase as the reinforcement ratio increases. The addition of Al2O3 and SiC particles upgrade hardness as these particles are more hard than aluminium, which provide their intrinsic property of hardness compared to a soft matrix. It is noted that the availability of reinforcements in an aluminium matrix block the shift of disruptions, which finally boosts the strength and hardness of hybrid composites, as shown in Figure 3.
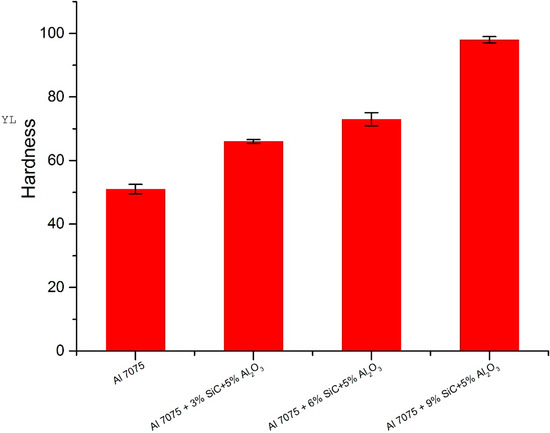
Figure 3.
Vickers hardness number vs. different composite materials.
Three readings are taken for each specimen, and the mean value is considered. Hardness has increased by an amount of 48% due to the addition of 9% SiC and 5% Al2O3 to aluminium alloy. Table 1 shows the different kinds of composite materials with Vickers hardness numbers.

Table 1.
VHN for different composite materials.
4.2. Tensile Strength Test
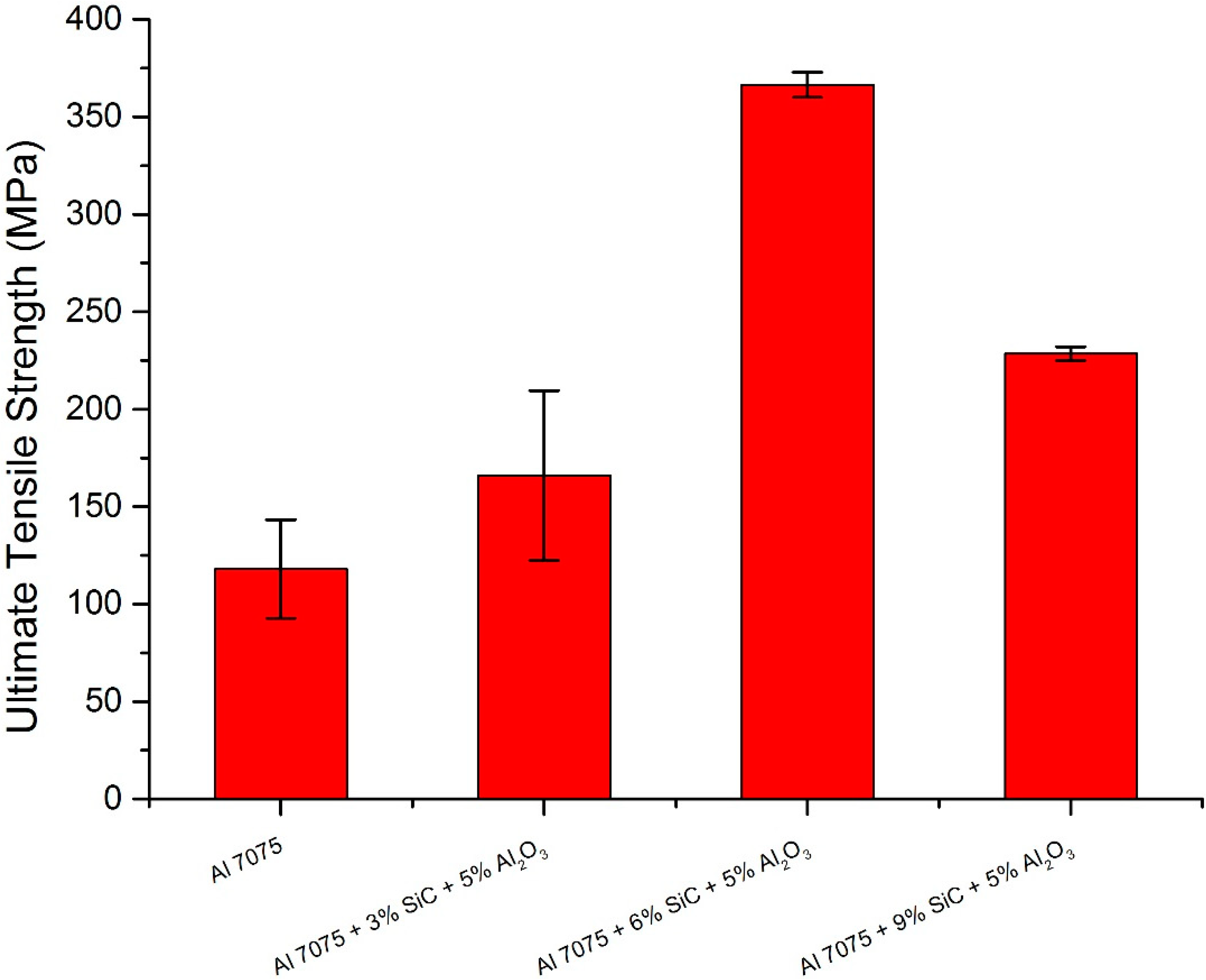
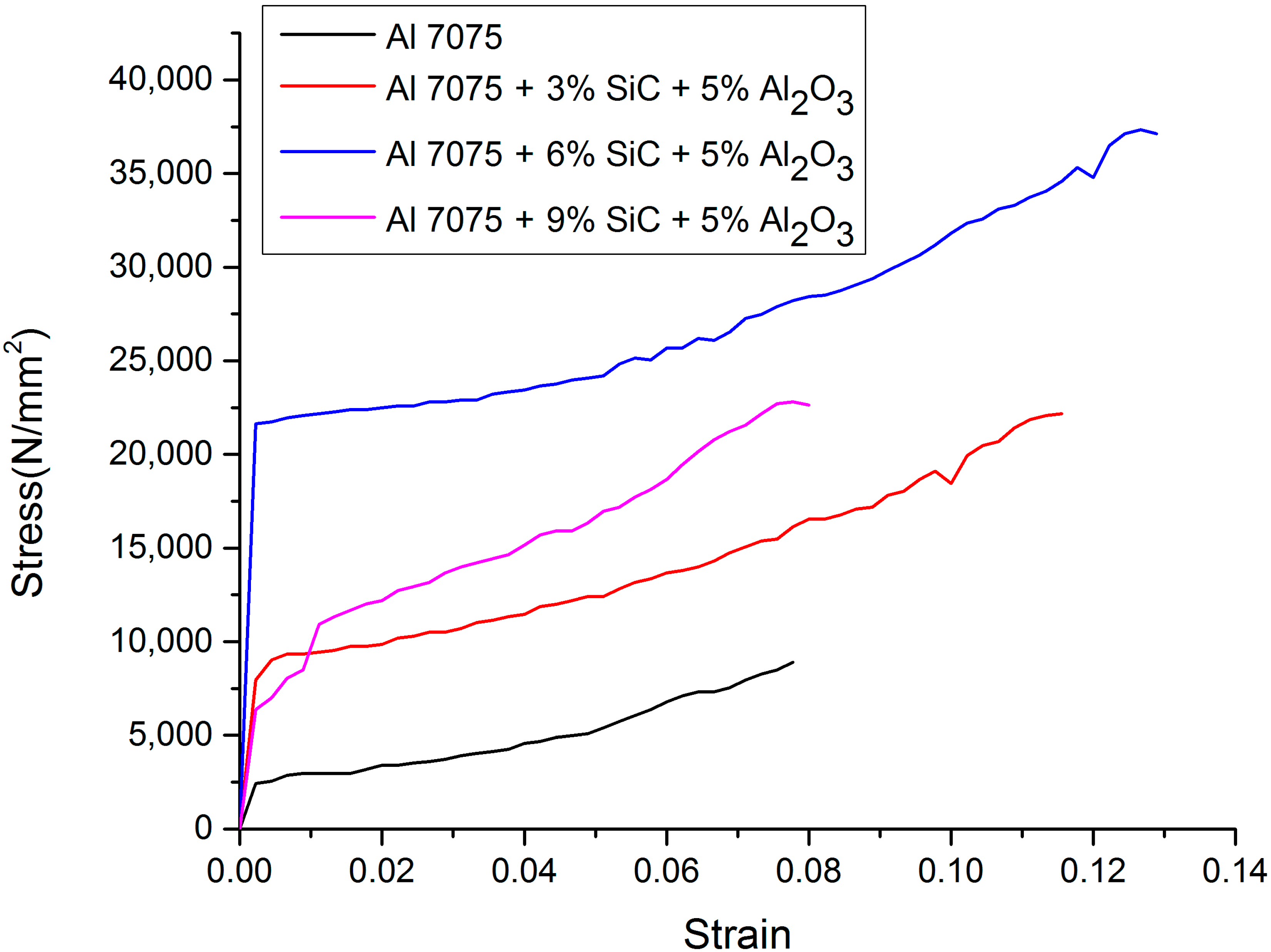
Figure 4 shows the results of tensile tests for different weight fractions of reinforcements of SiC and Al2O3. Table 2 presents the ultimate tensile strength of unreinforced aluminium 7075 and reinforced aluminium 7075 with SiC and Al2O3. From the results, it is observed that with the increase in the addition of reinforcements, the ultimate tensile strength increases up to an addition of 6% SiC and 5% Al2O3, but with further addition, i.e., at 9% SiC and 5% Al2O3, the ultimate tensile strength decreases. The increase in ultimate tensile strength was up to 67.79%. The increase in ultimate tensile strength could be due to the existence and equal distribution of reinforcement. The integrated reinforcement acts as an obstacle to dislocation movements. A further increase in particle volume percentage leads to a decrease in ultimate tensile strength, which is due to increased agglomeration and porosity. The agglomeration of particles makes the material weaker and hence leads to a reduction in tensile strength [6]. Figure 5 shows the stress–strain curve for unreinforced aluminium 7075 and reinforced aluminium 7075 with SiC and Al2O3. From the curve, it is clear that a hybrid combination of 6% SiC and 5% Al2O3 provides more ductility and strength to the material compared to its unreinforced counterpart, but with further addition, i.e., at 9% SiC and 5% Al2O3, a reduction in ductility is observed. This seems to be associated with hard particles distribution and percolation, as previously reported.
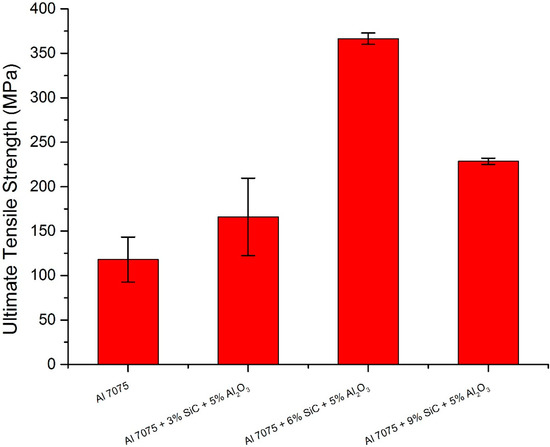
Figure 4.
Ultimate tensile strength vs. different composite materials.

Table 2.
Ultimate tensile strength for different composite materials.
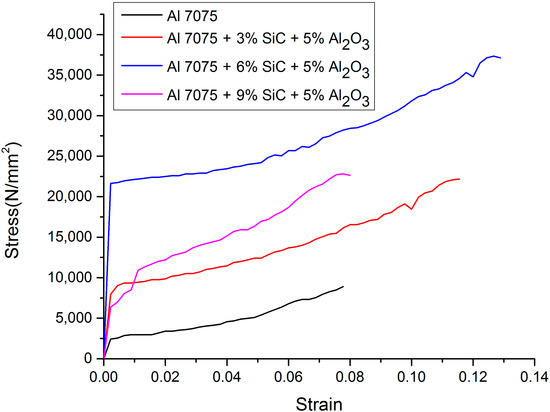
Figure 5.
Stress vs. strain for different composite materials.
4.3. Wear Test
Effect of Reinforcements
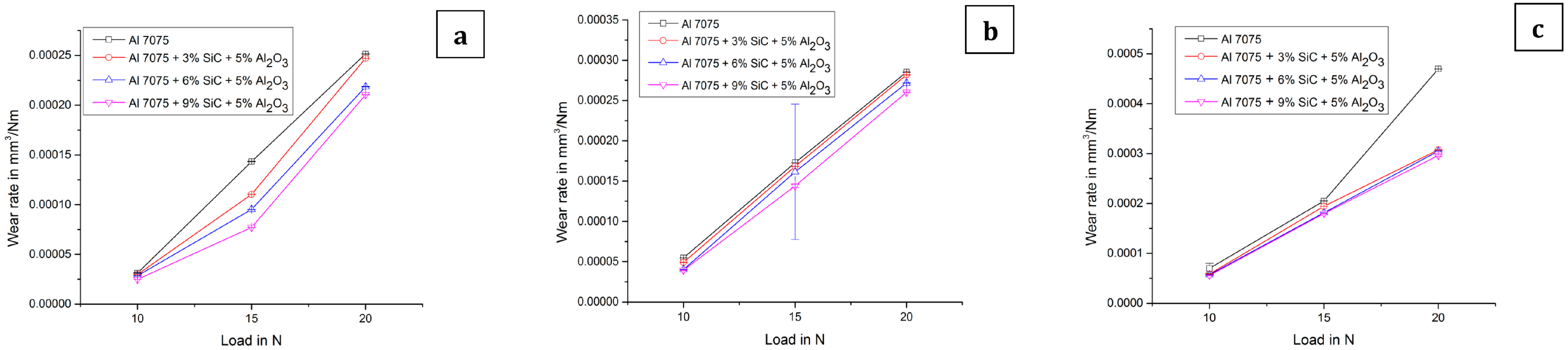
The response of reinforcements on wear rate at different values of loads is shown in Figure 6a–c. It shows that the maximum wear rate was detected for aluminium 7075 alloy and was decreased with the increase in percentage of silicon carbide and aluminium oxide. This shows that the presence of reinforcement decreases the wear rate. The percentage of aluminium oxide was restricted to 5% because a further increase in aluminium oxide could have increased the wear rate [2]. A 5% inclusion of SiC and Al2O3 in Al7075 resulted in a wear rate of 0.165mm3/Nm at 20N load and sliding distance of 282 m [3], whereas the current work for the composition of 6% SiC and 5% Al2O3 in Al7075 depicted 0.21 mm3/Nm at 20 N load and a sliding distance of 154 m. An increase in sliding distance with constant load will promote a higher wear rate. The percentage of SiC in the Al7075 hybrid composite increases the wear rate due to its ceramic material behaviour. The effect of load on different hybrid composites is shown in Figure 6a–c. It shows that for all the composite materials, the wear rate increases with increase in load [13]. The observed wear rate is 0.00025 mm3/Nm, and it is least for all the cases.
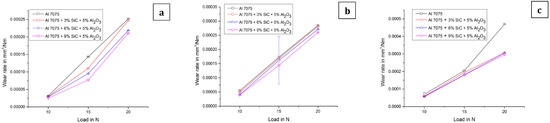
Figure 6.
(a) Wear graph (for sliding radius 20 mm and sliding distance 154 m). (b) Wear graph (for sliding radius 40 mm and sliding distance 503 m). (c) Wear graph (for sliding radius 60 mm and sliding distance 754 m).
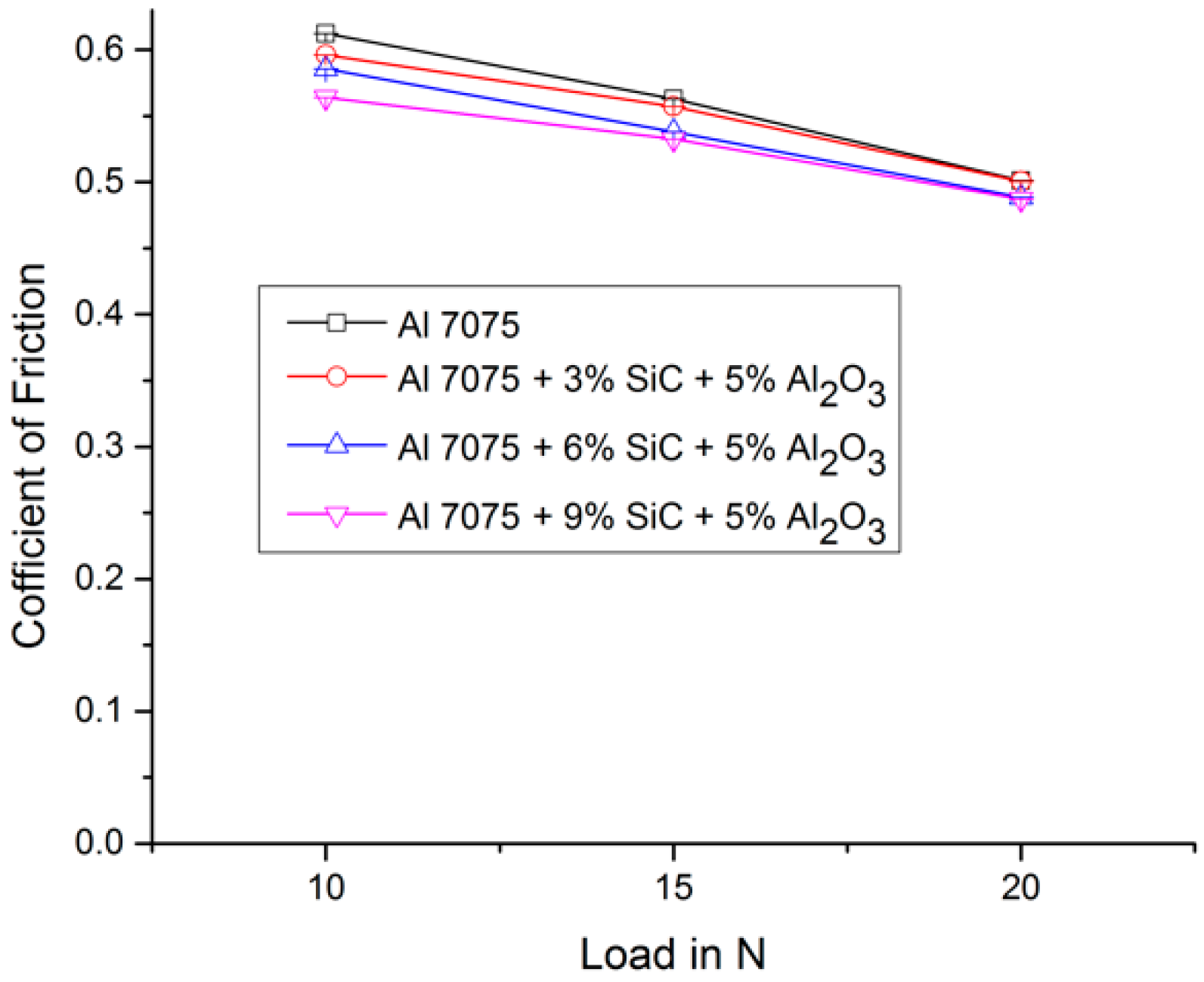
4.4. Coefficient of Friction
Figure 7 and Table 3 show the variations of coefficient of friction along with load and reinforcement. It is seen that as the load increases, the coefficient of friction decreases, and also, as the reinforcement increases, the coefficient of friction decreases. The decrease in coefficient of friction is mainly due to the softening of material and due to the increase in applied load, which increases the heat between the contact surfaces [14,15].
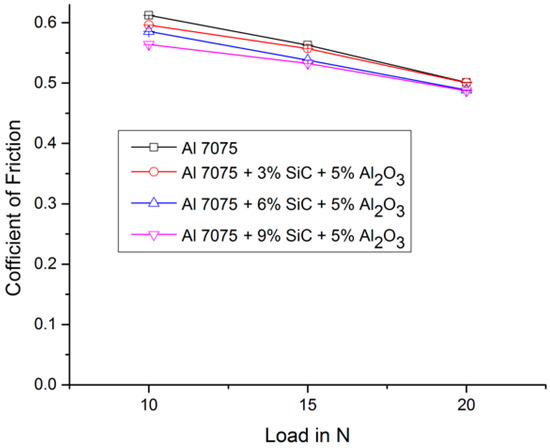
Figure 7.
Variation of coefficient of friction for different aluminium 7075 MMCs and loads.

Table 3.
Coefficient of friction for different aluminium 7075 MMCs and loads.
5. Microcharacterisation Study
5.1. EDAX Analysis
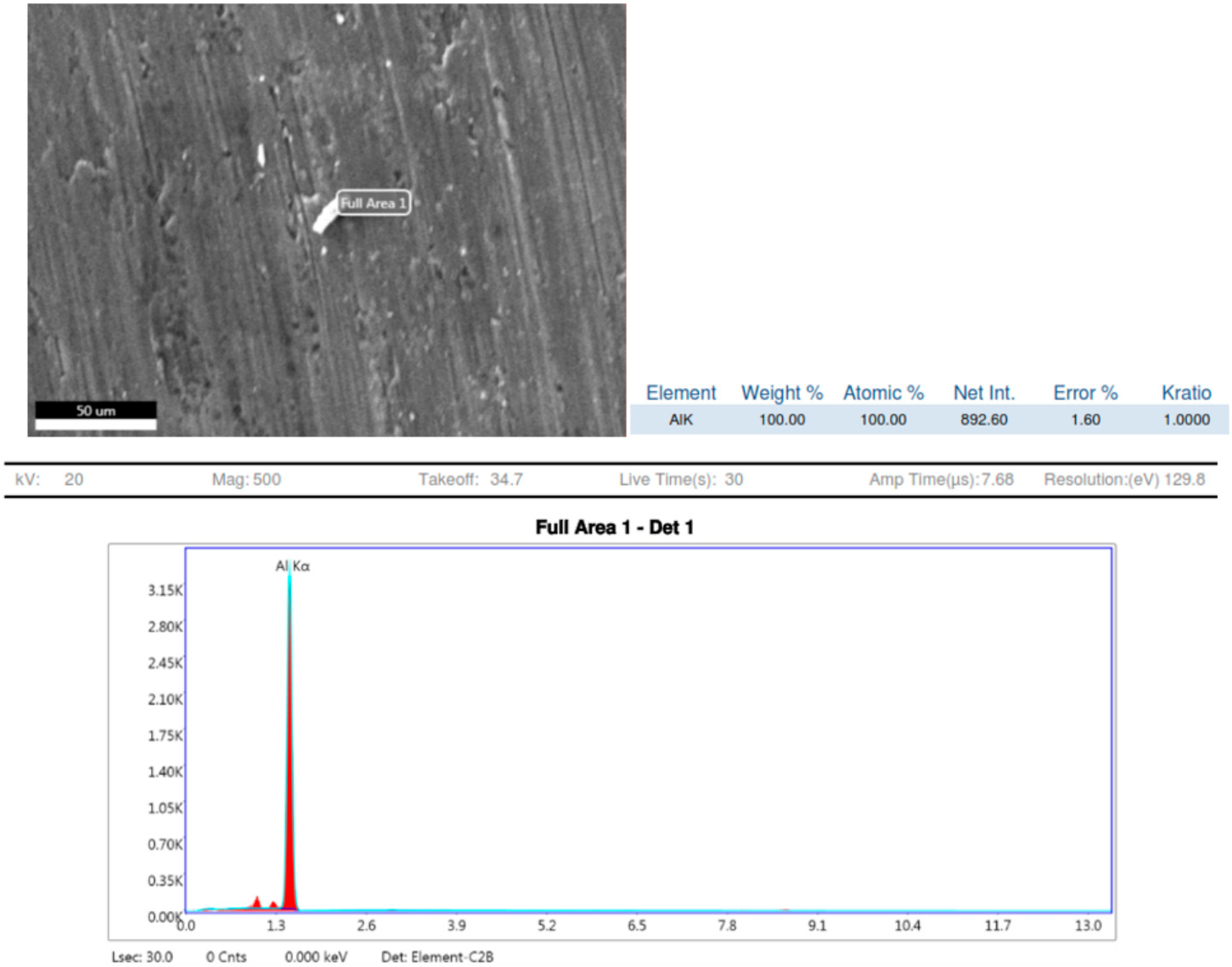
To discover the chemical composition of the hybrid composite, energy dispersive X-ray (EDAX) spectroscopy measurements are carried out in the SEM on specimens (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany). The EDAX profile for the same is shown in Figure 8.
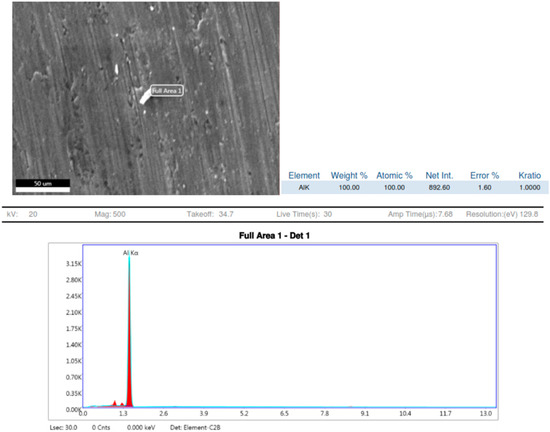
Figure 8.
EDX sample 1.
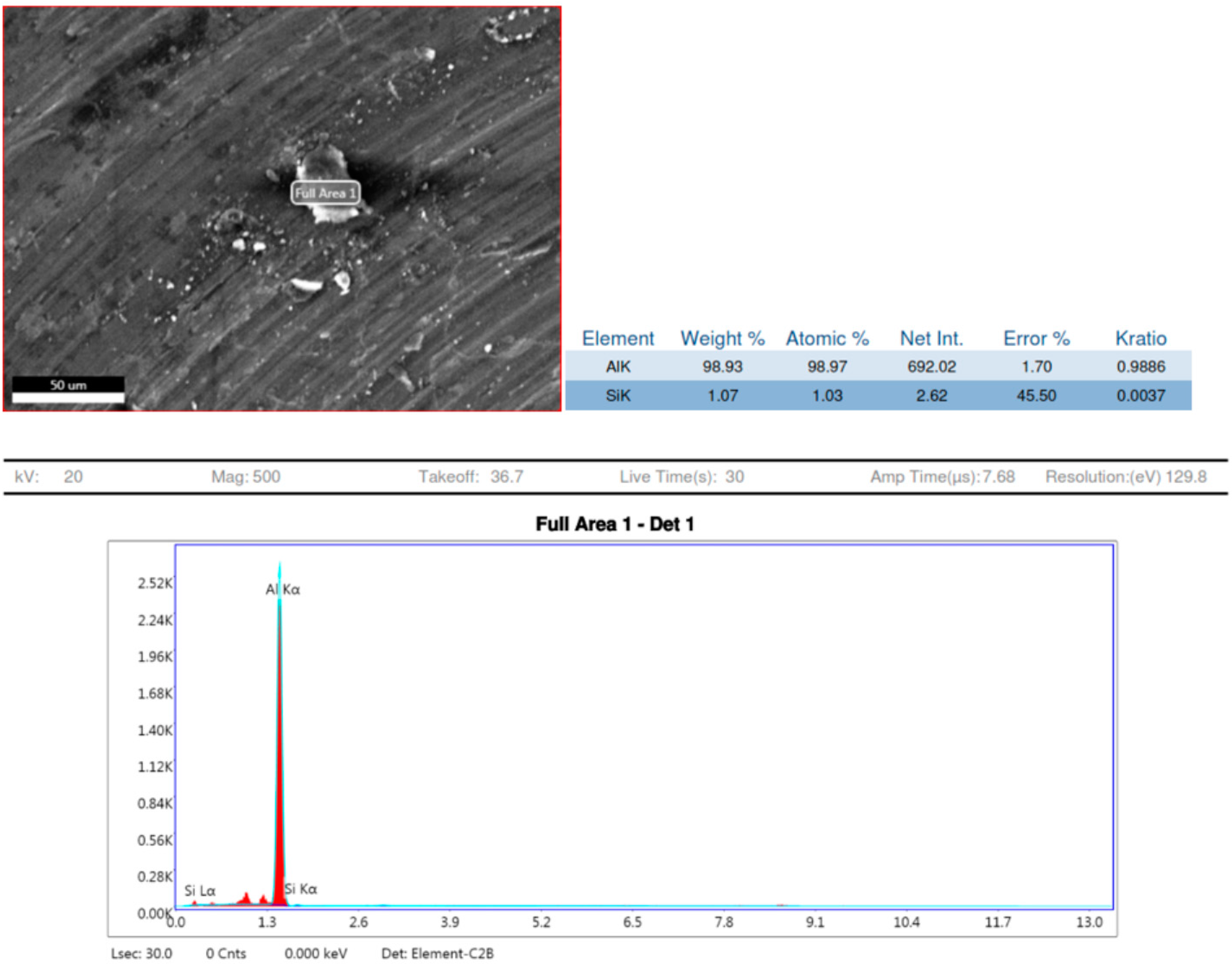
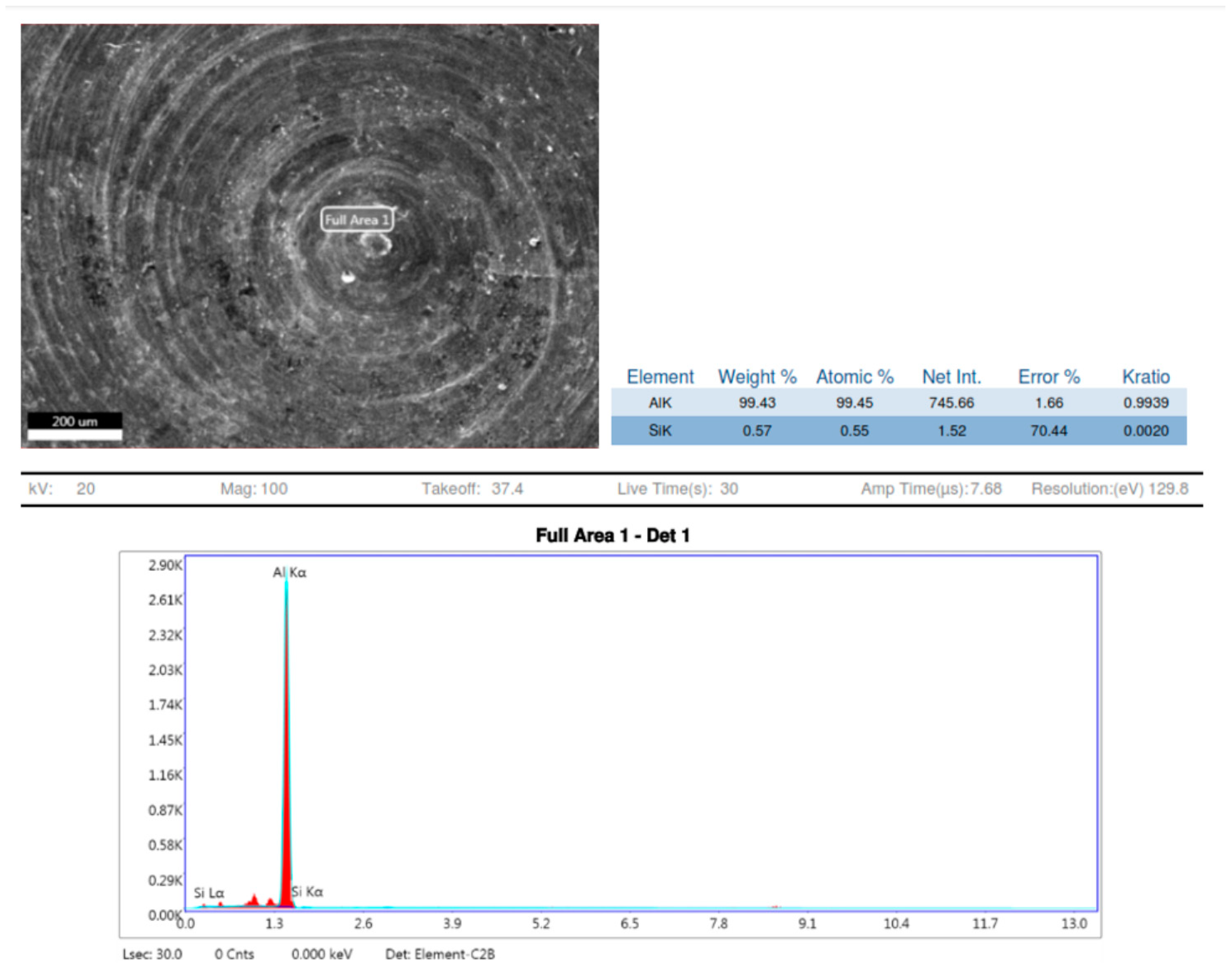
Observations based on the studies about the nucleation of multi phases after stir casting and the continuation of it in heat treatment of 7075 aluminium alloys have shown that as shown Figure 9 and Figure 10, the aluminium Kα is the major key player with 98.93 to 100% weight constituents. After slow cooling during the annealing process, chemical elements such as Magnesium (Mg), Copper (Cu) and Iron (Fe) form a laminar structure. However, if sudden cooling is subjected, these elements cluster together to form precipitates, or an agglomeration of intermetallic phases may result in dimensions larger than 1 μm [16]. Precipitations with dimensions between 1 and 10 μm cause stress concentration zones around them and result in mis-orientation and grain boundaries breakdown. This phenomenon initiates the nucleation of micro-cracks. The number of micro-cracks is proportional to the number of stress fields, corroborating to the material fatigue strength [17,18].
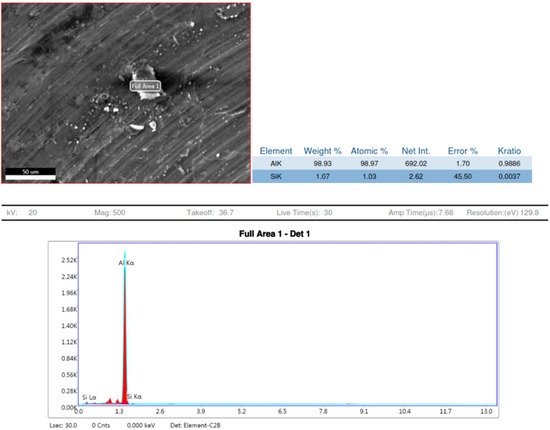
Figure 9.
EDX sample 2.
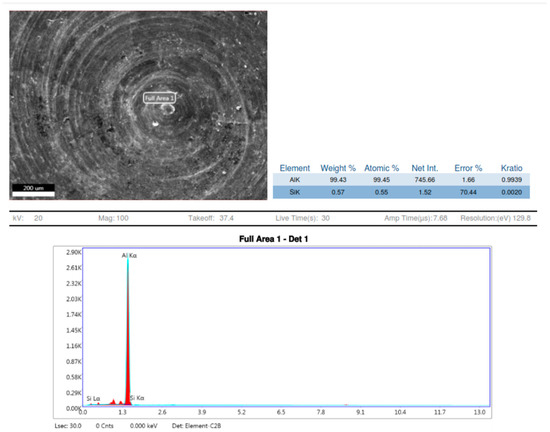
Figure 10.
EDX sample 3.
5.2. Scanning Electron Microscope Analysis
Specimens were developed from different composite combinations to carry out a metallographic study of hybrid composites. To confirm the uniform distribution of reinforcements in matrix material, SEM analysis was be conducted for this required procedure.
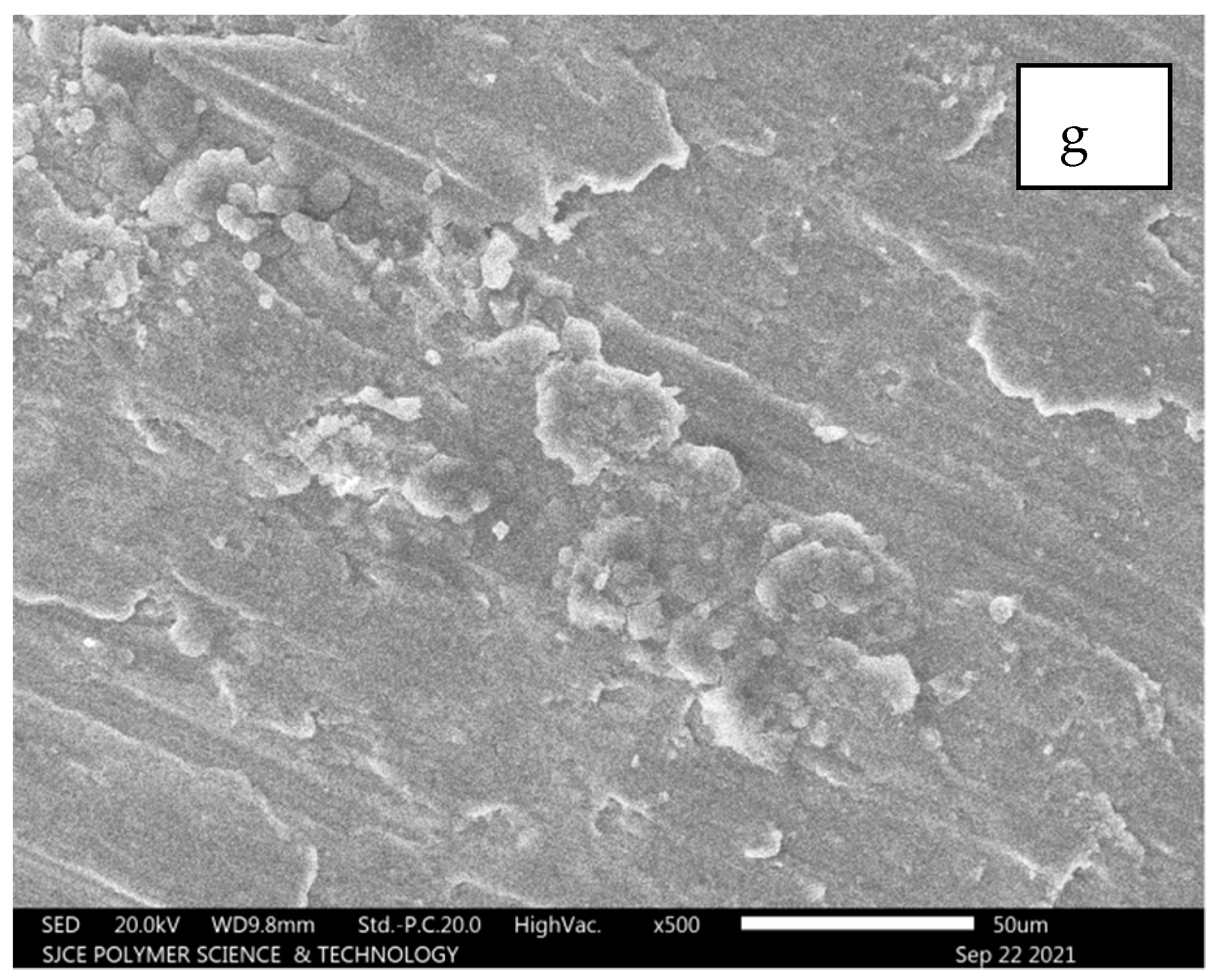
5.2.1. Al7075 + 6% SiC + 5% Al2O3
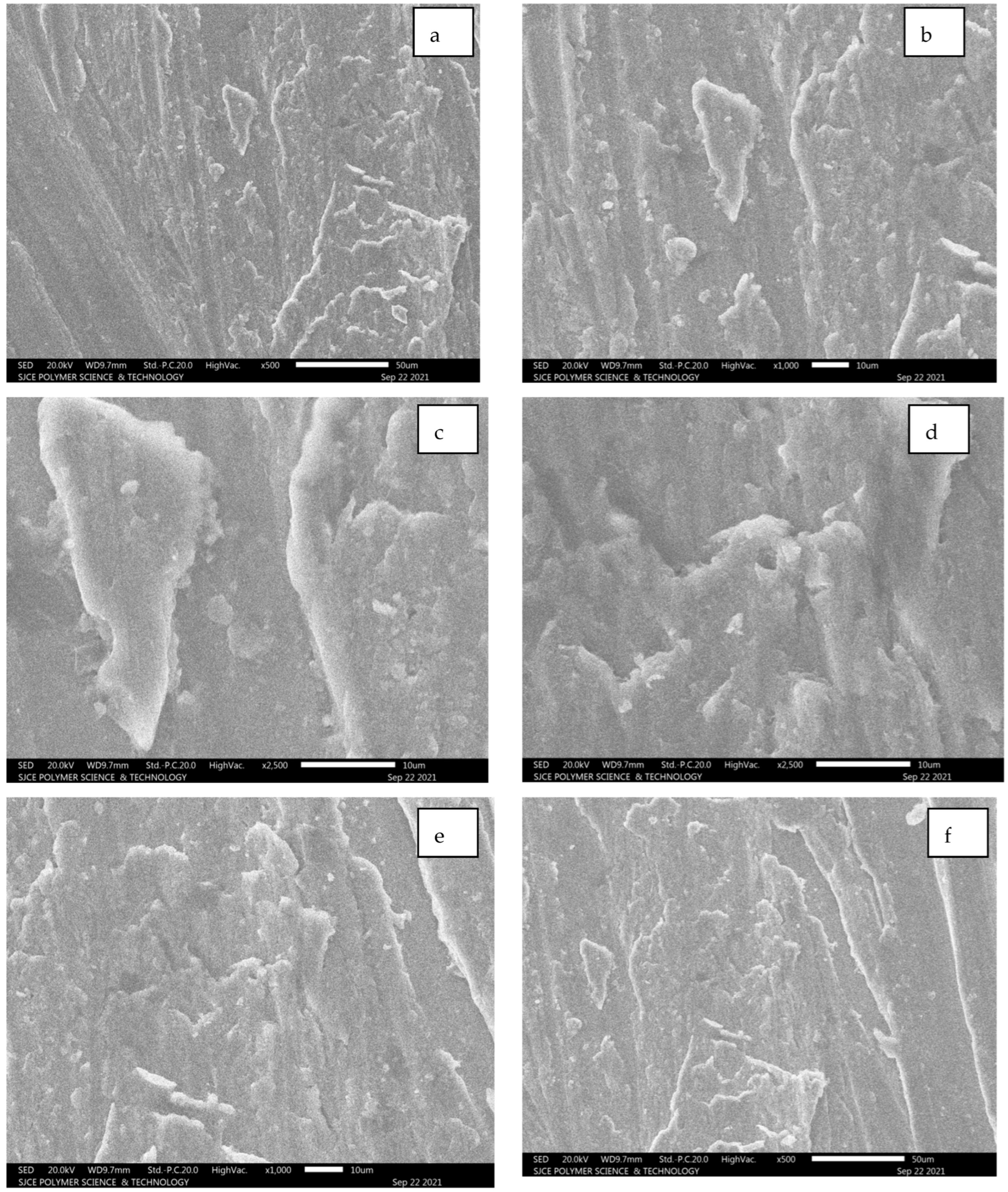
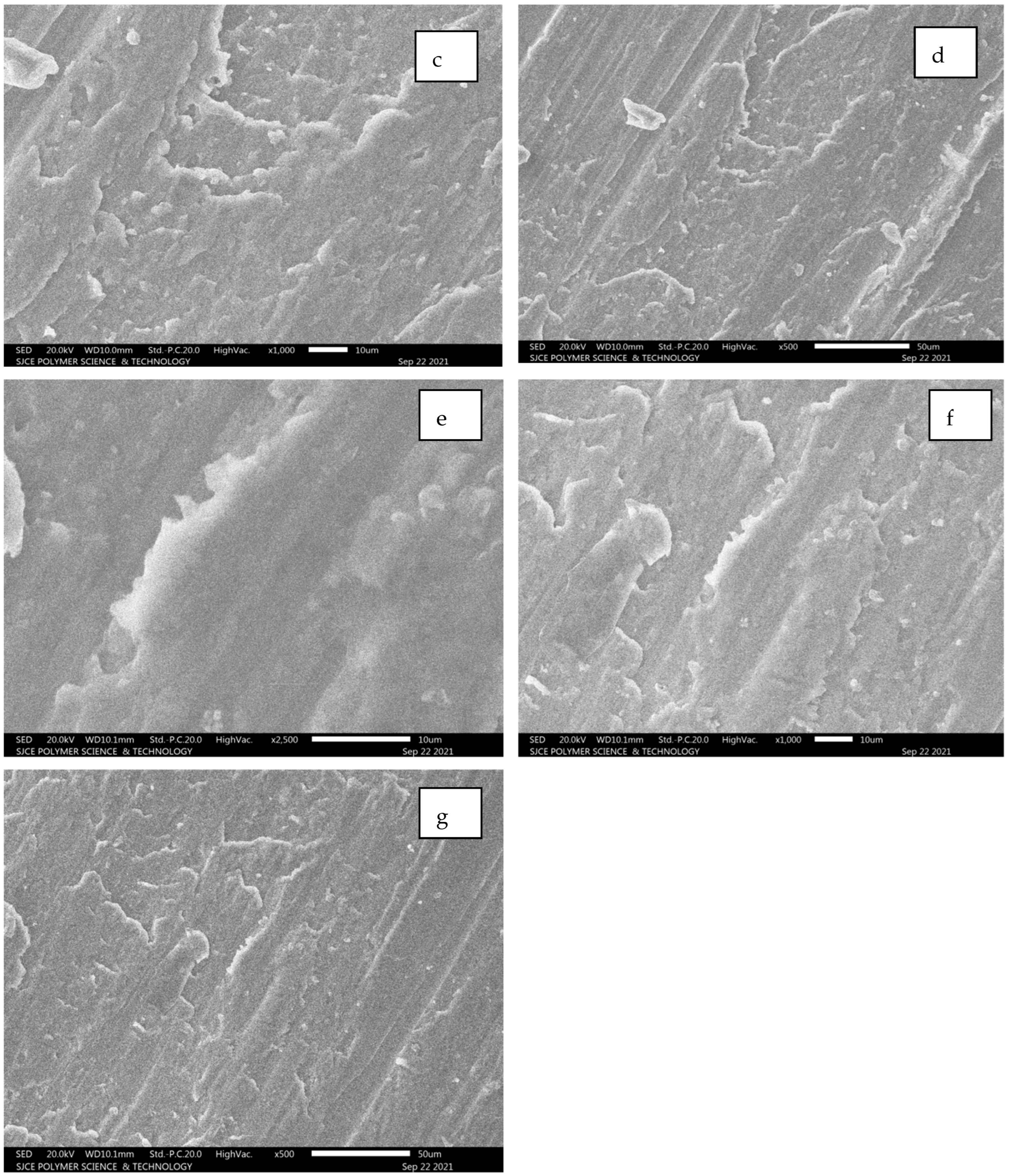
Field emission SEM extracted for Al7075 with SiC for a tensile test failed components. The failed component shows SiC patches visible in the form of a white colour along with substrate Al 7075. Figure 11c,d illustrate the white edges covered with Al7075 for the hybrid composite. Figure 11g,h demonstrate the powdered form of SiC adhered on the Al7075 substrate. The entire set of images from Figure 11a–h depicted strong cohesion among Al7075 with SiC. Furthermore, the particles pulled out during the fracture as in the case of SiC and Carbon Black (CB) particulates [19].
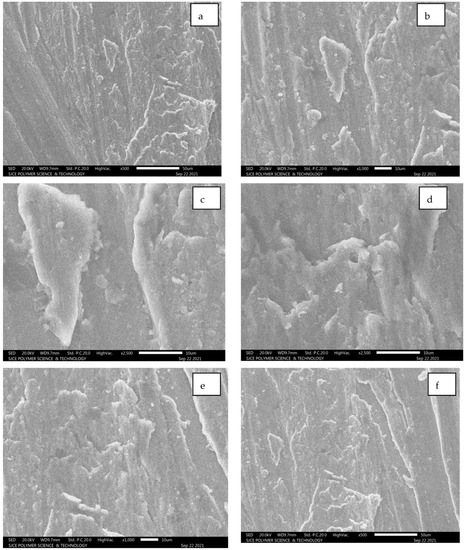
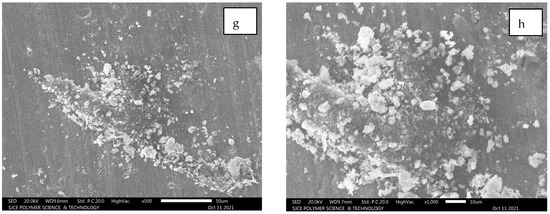
Figure 11.
(a–h): SEM images for composition of Al7075 + 6% SiC + 5% Al2O3.
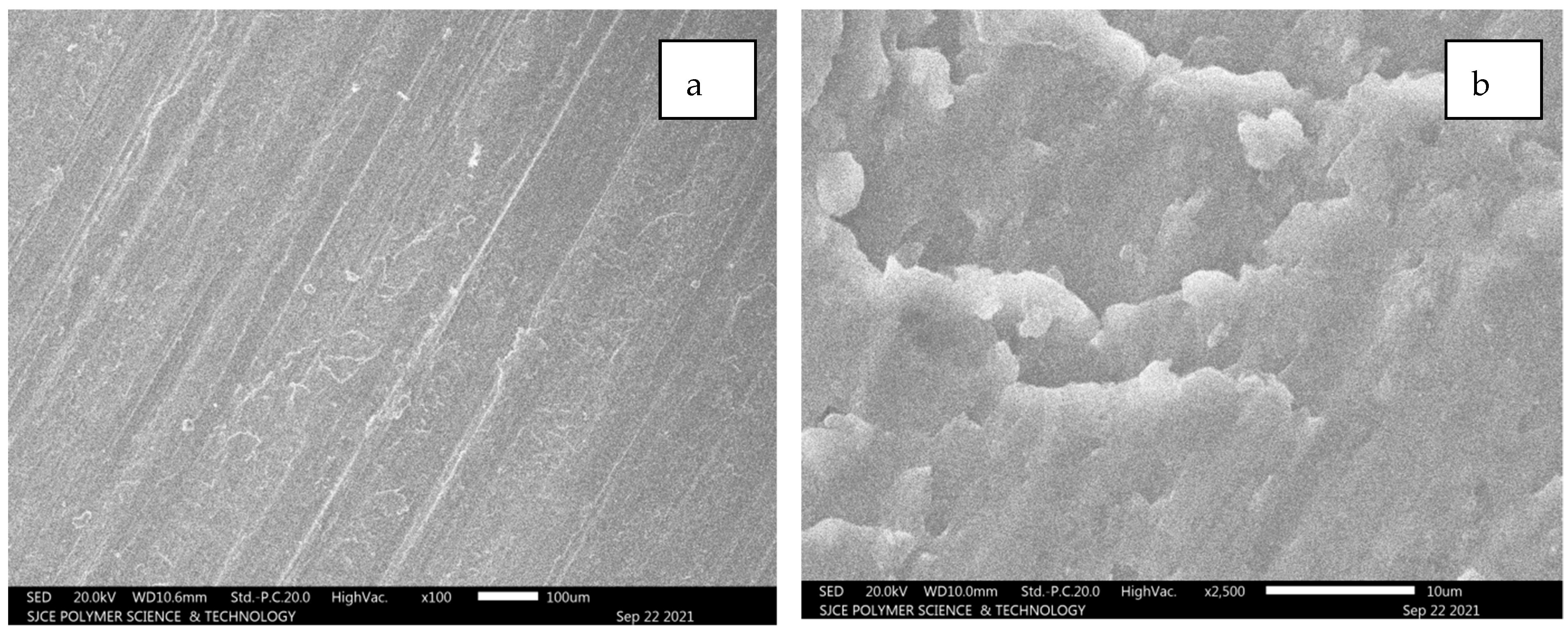
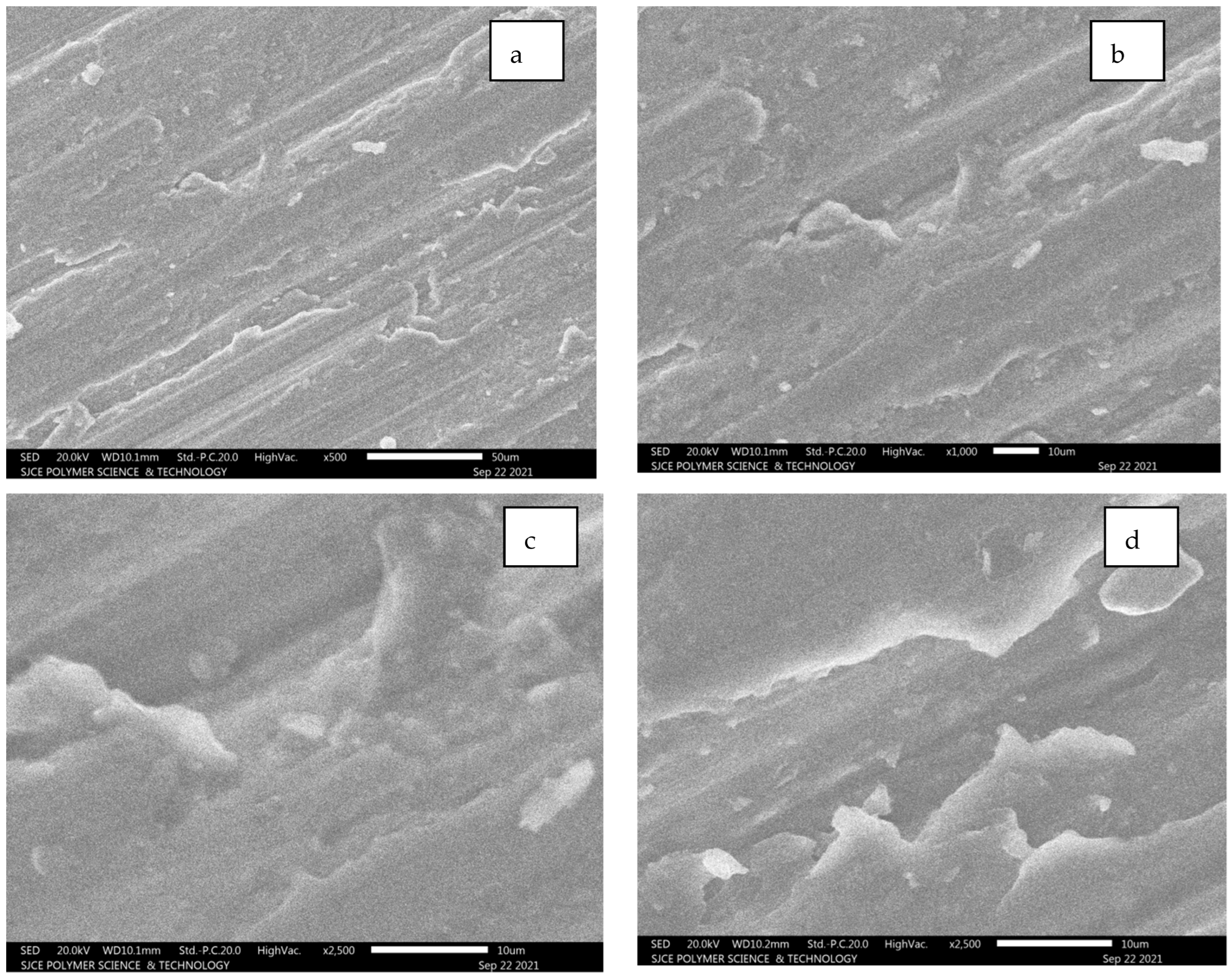
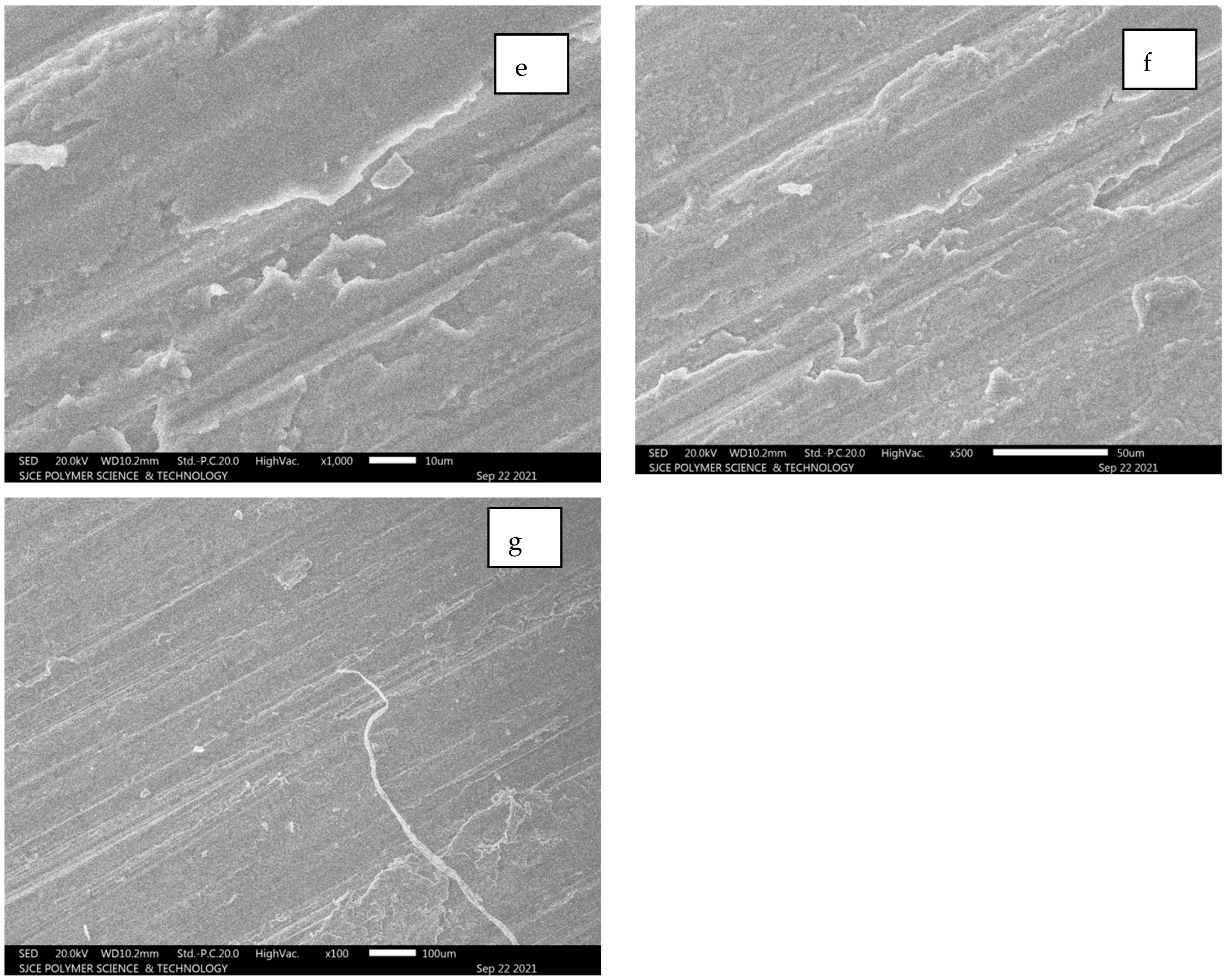
5.2.2. Al 7075 Unreinforced
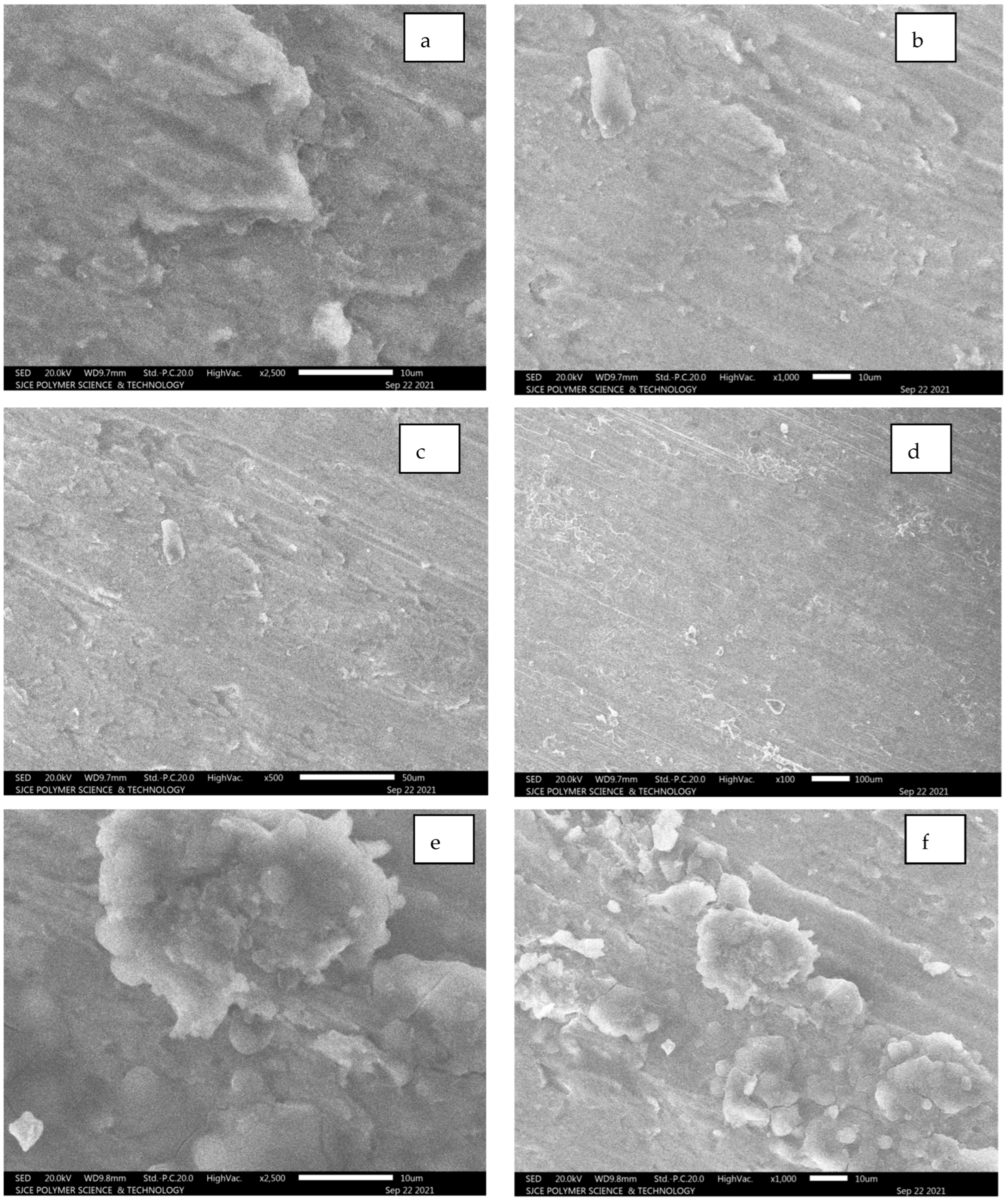
From Figure 12a–g, it is evident that longitudinal hair line cracks or line patches are clearly visible. However, these lines are developed due to a combination of SiC and alumina composition, resulting in white patches. The fracture is still not clearly identifiable as inter-granular or trans-granular behaviour. Figure 12c–f illustrates the worn surface area of the Al7075 unreinforced condition.
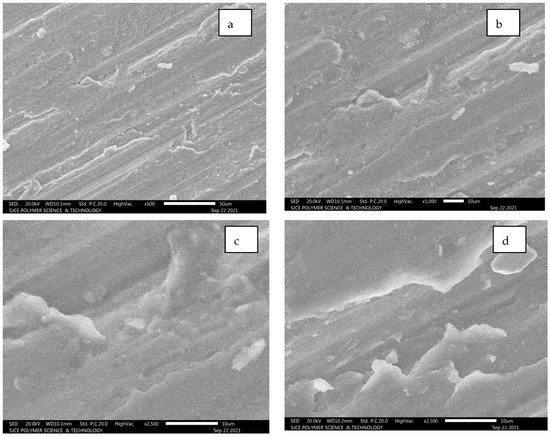
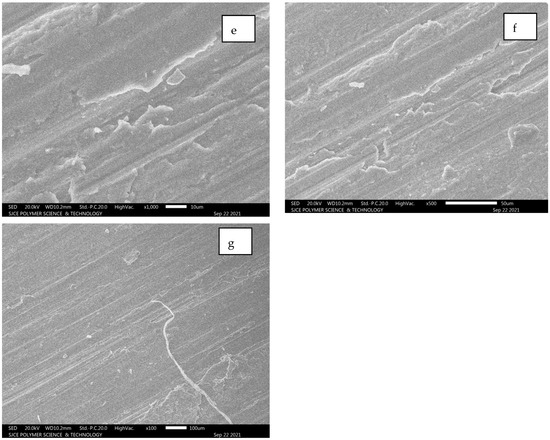
Figure 12.
(a–g): SEM images for Al 7075 unreinforced.
5.2.3. Al7075 + 3% SiC + 5% Al2O3
To introduce more clarity on the micrographs at varied locations, SEM images were captured to analyse the micro characteristic studies of the hybrid composite. Figure 13a–g illustrates the specimen fracture at the edge location.

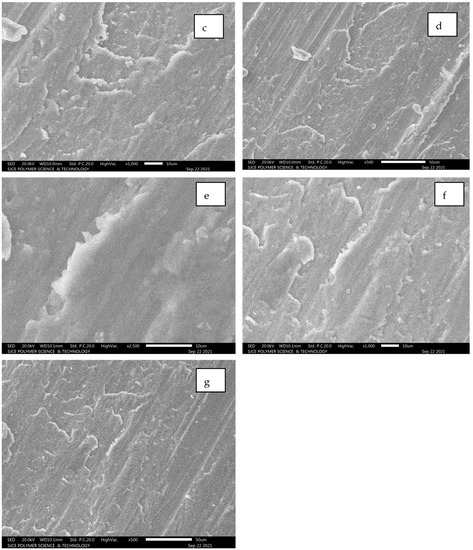
Figure 13.
(a–g): SEM images for composition of Al7075 + 3% SiC + 5% Al2O3.
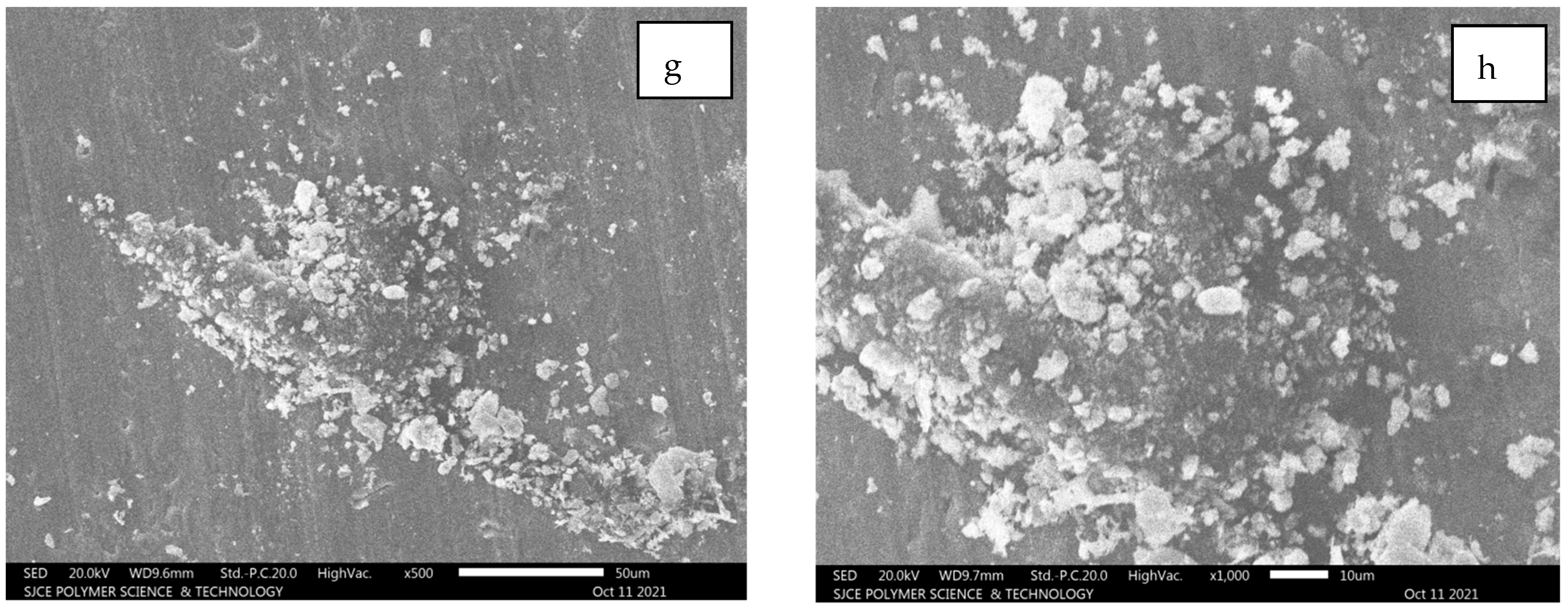
5.2.4. Al7075 + 9% SiC + 5% Al2O3
From Figure 14, it is observed that the images are captured at the mid-region of the failure, where a combination of Al 7075 with SiC and Al2O3 flakes is observed in Figure 14e.
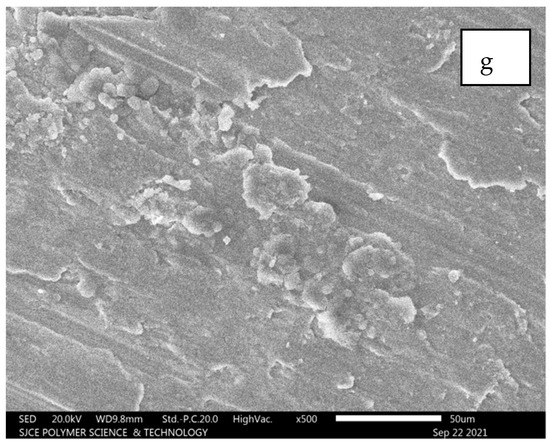
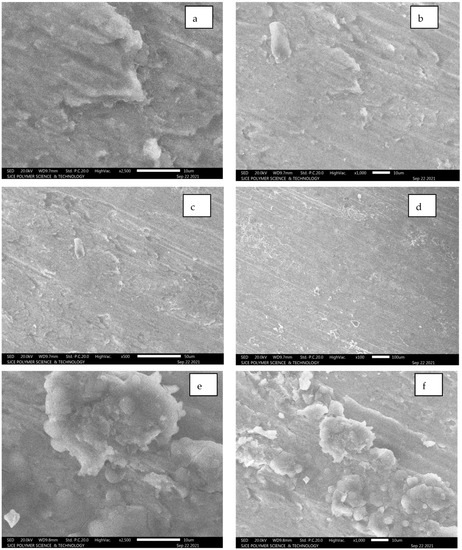

Figure 14.
(a–g): SEM images for composition of Al7075 + 9% SiC + 5% Al2O3.
6. Simulation Study
Simulation study has become an integral part of research in recent days, as it saves nearly 3/4 the time of the entire experimental work. At the same time, it will reduce the cost incurred in conducting the experiments.
Static Structural Analysis
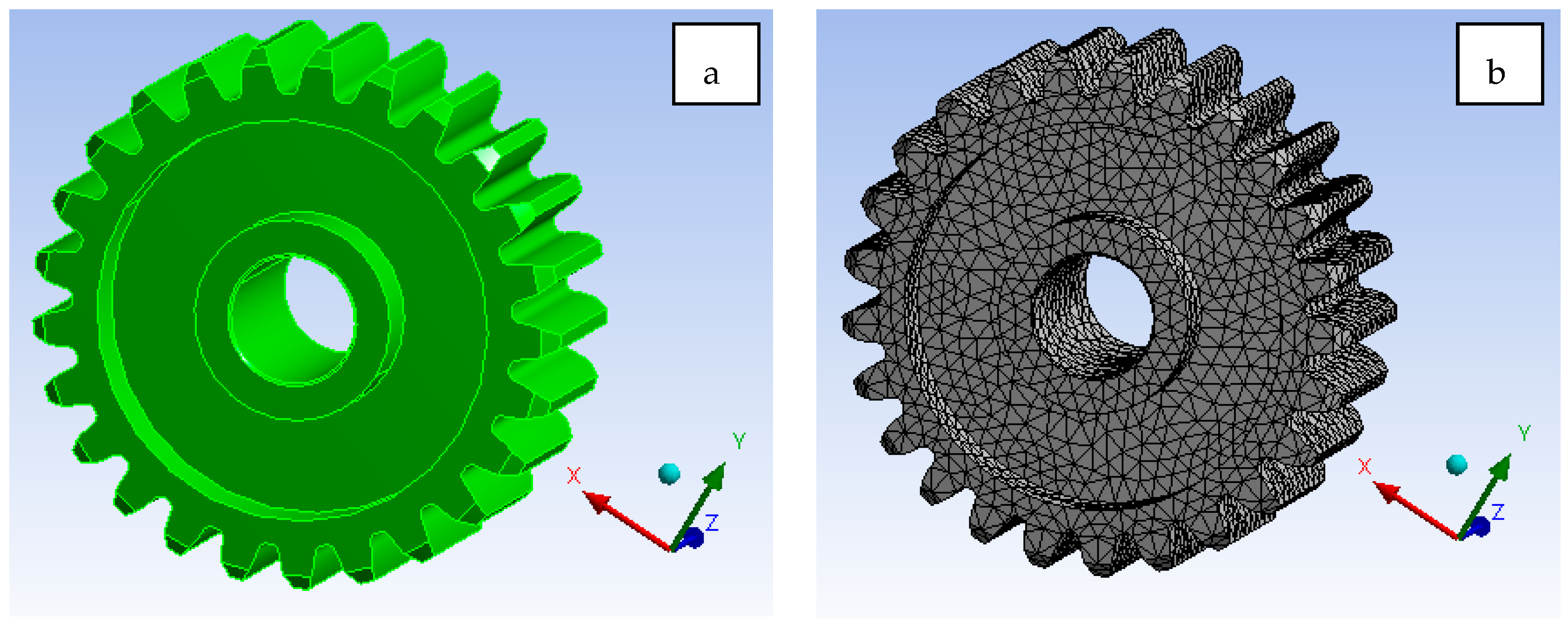
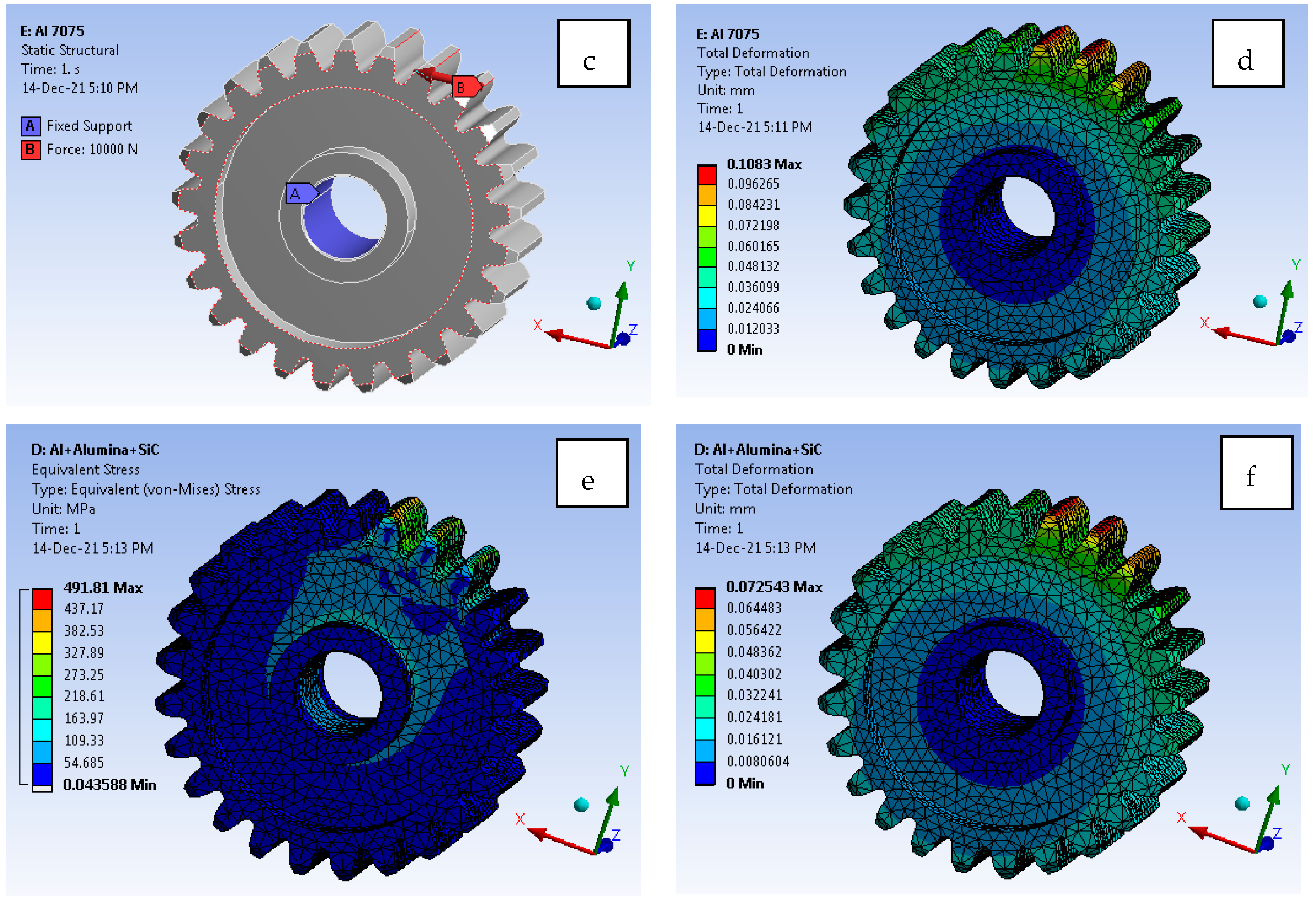
The exhaustive work focused on the development of the GEAR model, as shown in Figure 15a. As the preference given to such an application, it will reduce the wear, friction, and stress acting on the component. The effect of including alumina and SiC at an optimal percentage such as 5% and 6%, respectively, has resulted in prospective results. From Figure 15b, it can be observed that a tetrahedron 10-noded element with solid 188 [19,20,21,22,23] selected for analysis. The H-type method with element sizing and a P-Type method with element order both are considered while solving the simulation [24,25,26,27,28]. Figure 15d illustrate the Al 7075 T6 material total deformation [29,30,31,32,33,34]. From Figure 15d, it is clear that Al 7075 material alone shows 0.108 mm deformation, which is way too high in comparison to Al 7075 + Alumina + SiC as 0.0725 mm. Furthermore, optimisation is also quite feasible, as the model shows 10X better results compared with Al 7075 materials.
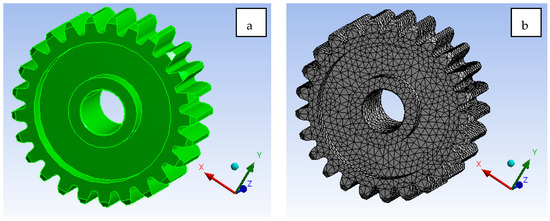
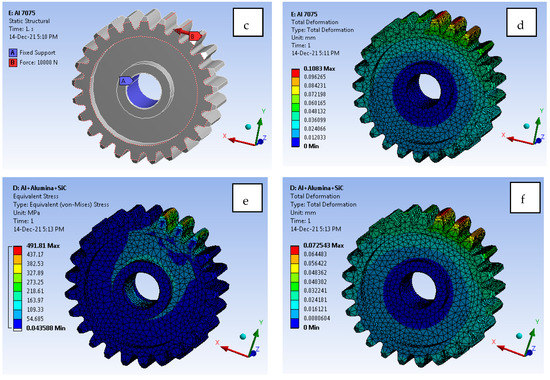
Figure 15.
(a). Geometrical model of gear (b). Mesh generation (c). Loads and boundary conditions (d). Total deformation for Al7075 T6 (e). Von mises stress for Al + Alumina + SiC (f). Total deformation for Al + Alumina + SiC.
7. Conclusions
A hybrid composite with aluminium 7075 and a varying percentage of silicon carbide and aluminium oxide reinforcements was tested using a stir-casting process. Mechanical and tribological tests were conducted to study material characterisation. Microstructural analysis confirms the presence of reinforcements and their uniform distribution in an aluminium substrate. Simulation analysis was performed using ANSYS Workbench ver 18.2 for a gear model to recommend the above said hybrid composite for gear application. Furthermore, the findings are listed below:
- (1)
- The Vickers hardness number (VHN) obtained for Al 7075 with 9% SiC and 5% Al2O3 was 98, which increased about 47% compared to unreinforced aluminium 7075.
- (2)
- The ultimate tensile strength (UTS) obtained for Al 7075 with 6% SiC and 5% Al2O3 was 366 MPa, which is 67.79% higher in comparison to unreinforced aluminium 7075. Another finding in tensile study was that for Al 7075 with 9% SiC and 5% Al2O3, the ultimate tensile strength decreased to 228.6 MPa compared to its earlier counterpart. These results of tensile test shows that hybrid composites are more advantageous compared to conventional composites.
- (3)
- The wear rate decreased with increase in reinforcements. The lowest wear rate was observed for Al 7075 with 9% SiC and 5% Al2O3. However, the findings during the wear test were with the increase in load, the sliding distance and sliding radius wear rate increased for all hybrid reinforced Al 7075 composites and unreinforced Al 7075. The coefficient of friction decreased with the increase in load for all specimens.
- (4)
- Simulation study reveals the behaviour of mechanical properties such as total deformation and von Mises stress for a given condition of Al 7075 + SiC + Alumina resulted in 30% lower deformation and unaltered stress values (as stress is not a material property) in comparison to pristine Al 7075 alloy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.H.B. and S.B.M.; methodology, S.H.B. and S.B.M.; software, A.Y.P.; validation, S.H.B. and S.B.M.; formal analysis, S.H.B. and S.B.M.; investigation, S.H.B.; resources, S.H.B.; data curation, S.H.B.; writing—review and editing, A.Y.P.; visualization, S.H.B.; supervision, S.B.M.; project administration, S.B.M.; funding acquisition, A.M.A.(Abeer Mohamed Alosaimi), A.K., M.A.H. and A.M.A. (Abdullah M. Asiri). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by [Taif University] grant number [TURSP-2020/244] and the APC was funded by [Abeer Mohamed Alosaimi].
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Taif University Researchers Supporting Project number (TURSP-2020/244), Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Roy, P.; Singh, S.; Pal, K. Enhancement of Mechanical and Tribological Properties of SiC- and CB-reinforced Aluminium 7075 Hybrid Composites Through Friction Stir Processing. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2019, 28, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryakumari, T.; Ranganathan, S. Preparation and Study the Wear Behaviour of Aluminium Hybrid Composite. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 8104–8111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, A.M.; Kaleelmulla, M. Experimental Investigations on Mechanical Behavior of Aluminium Metal Matrix Composites. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 149, 012121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moona, G.; Walia, R.S.; Rastogi, V.; Sharma, R. Parametric Optimization of Fatigue Behaviour of Hybrid Aluminium Metal Matrix Composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 21, 1441–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Chen, F.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Chenb, H.; Feng, S.; Zhao, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X. Microstructure and Microhardness of Hot Extruded 7075 Aluminum Alloy Micro-gear. J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 2015, 219, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raturi, A.; Mer, K.K.S.; Pant, P.K. Synthesis and Characterization of Mechanical, Tribological and Micro Structural Behaviour of Al 7075 Matrix Reinforced with Nano Al2O3 Particles. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 2645–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poovazhagan, L.; Kalaichelvan, K.; Rajadurai, A.; Senthilvelan, V. Characterization of Hybrid Silicon Carbide and Boron Carbide Nanoparticles-Reinforced Aluminum Alloy Composites. Procedia Eng. 2013, 64, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, Y.; Shi, Y. Contact Stress Analysis for a Pair of Aluminum Matrix Composite Helical Gear and Steel Worm. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2015, 34, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canesan, N.; Vijayarangan, S. A Static Analysis of Metal Matrix Composite Spur Gear by Three-Dimensional Finite Element Method. Comput. Struct. 1993, 46, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Nallusamy, S.; Narayanan, M.R.; Saravanan, S. Investigation on Structural Steel and Silicon Carbide Aluminum Metal Matrix Composite Spur Gears using PTC Creo and ANSYS 16.0. Mater. Des. Appl. 2018, 937, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, M.; Ashok Raj, J.; Kumar, G.S.; Akhila, R. Design and Analysis of Aluminium Matrix Composite Spur Gear. Adv. Mater. Processing Technol. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, P.B.; Utpat, A.A. Analysis of Composite Material Spur Gear Under Static Loading Condition. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 2968–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, P.B.; Utpat, A.A. Development of Aluminium Based Silicon Carbide Particulate Metal Matrix Composite for Spur Gear. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Salihi, H.A.; Mahmood, A.A.; Alalkawi, H.J. Mechanical and Wear Behavior of AA7075 Aluminum Matrix Composites Reinforced by Al2O3 Nanoparticles. Nanocomposites 2019, 5, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adediran, A.A.; Alaneme, K.K.; Oladele, I.O.; Akinlabi, E.T. Wear Characteristics of Aluminium Matrix Composites Reinforced with Si-based Refractory Compounds Derived from Rice Husks. Cogent Eng. 2020, 7, 1826634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, L.F.; Suresh, P. Wear Behavior of Aluminium Metal Matrix Composite Prepared from Industrial waste. Sci. World J. 2016, 2016, 6538345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, X.G.; Jiang, D.M.; Meng, Q.C. Evolution of Eutectic Structures in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys During Heat Treatment. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2006, 16, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.L.; Pan, J.; Hathaway, R. Fatigue Testing and Analysis: Theory and Practice. Mech. Eng. 2004, 126, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Johnson, E.A.; Shen, L.M. Effects of Heat Treatment and Strain Rate on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 6061 Al Alloy. Int. J. Damage Mech. 2015, 25, 26–41. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, V.S.; Banoo, F.; Kurahatti, R.V.; Patil, A.Y.; Raju, G.U.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Kumar, R.; Saleel, C.A. A Study of Sound Pressure Level (SPL) Inside the Truck Cabin for New Acoustic Materials: An Experimental and FEA approach. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 5949–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.Y.; Naik, A.; Vakani, B.; Kundu, R.; Banapurmath, N.R.; Roseline, M.; Krishnapillai, L.; Mathad, S.N. Next Generation Material for Dental Teeth and Denture Base Material: Limpet Teeth (LT) as an Alternative Reinforcement in Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA). J. Nano-Electron. Physics. 2021, 13, 02033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.Y.; Banapurmath, N.R.; Sumukh, E.P.; Chitwadagi, M.V.; YunusKhan, T.M.; Badruddin, I.A.; Kamangar, S. Multi-Scale Study on Mechanical Property and Strength of New Green Sand (Poly Lactic Acid) as Replacement of Fine Aggregate in Concrete Mix. Symmetry 2020, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaduti, S.C.; Sarganachari, S.G.; Patil, A.Y.; Yunus Khan, Y.T. Prediction of Injection Molding Parameters for Symmetric Spur Gear. J. Mol. Model. 2020, 26, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavagal, P.S.; Kulkarni, P.A.; Patil, N.M.; Salimath, N.S.; Patil, A.Y.; Savadi, R.S.; Kotturshettar, B.B. Cleaner Production of Edible Straw as Replacement for Thermoset Plastic. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 32, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totla, S.K.; Pillai, A.M.; Chetan, M.; Warad, C.; Vinodkumar, S.K.; Patil, A.Y.; Kotturshettar, B.B. Analysis of Helmet with Coconut Shell as the Outer Layer. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 32, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poornakanta, H.; Kadam, K.; Pawar, D.; Medar, K.; Makandar, I.; Patil, A.Y.; Kotturshettar, B.B. Optimization of Sluice Gate Under Fatigue Life Subjected for Forced Vibration by Fluid Flow. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 68, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patil, A.Y.; Banapurmath, N.R.; Shivangi, U.S. Feasibility study of Epoxy coated Poly Lactic Acid as a sustainable replacement for River sand. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 121750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaka, M.; Lavernia, E.J.; Schoenung, J.M. Particulate Reinforced Aluminum Alloy Matrix Composites—A Review on the Effect of Microconstituents. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2017, 48, 91–104. [Google Scholar]
- Bonatti, R.S.; Siqueira, R.R.; Padilha, G.S.; Bortolozo, A.D.; Osorio, W.R. Distinct Alp/Sip Composites Affecting its Densification and Mechanical Behavior. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 757, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafizpour, H.R.; Simchi, A. Investigation on Compressibility of Al–SiC Composite Powders. Powder Metall. 2018, 51, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.A.; Mohamed, F.A.; Lavernia, E.J. Particulate Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites—A Review. J. Mater. Sci. 1991, 26, 1137–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satizabal, L.M.; Caurin, H.F.; Meyer, Y.A.; Padilha, G.S.; Bortolozo, A.D.; Osorio, W.R. Distinct Heat Treatments and Powder Size Ratios Affecting Mechanical Responses of Al/Si/Cu Composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2021, 55, 3589–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallad, S.A.; Banapurmath, N.R.; Patil, V.; Ajarekar, V.S.; Patil, A.Y.; Godi, M.T.; Shettar, A.S. Graphene Reinforced Natural Fiber Nanocomposites for Structural Applications. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 376, 012072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.Y.; Hrishikesh, N.U.; Basavaraj, G.D.; Kodancha, K.G.; Chalageri, G.R. Influence of Bio-degradable Natural Fiber Embedded in Polymer Matrix, Elsevier. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 7532–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).