Study of Heat Source Model and Residual Stress Caused by Welding in GMAW of Al Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experiments
2.1. Characteristics of Each Type of Aluminum Alloy
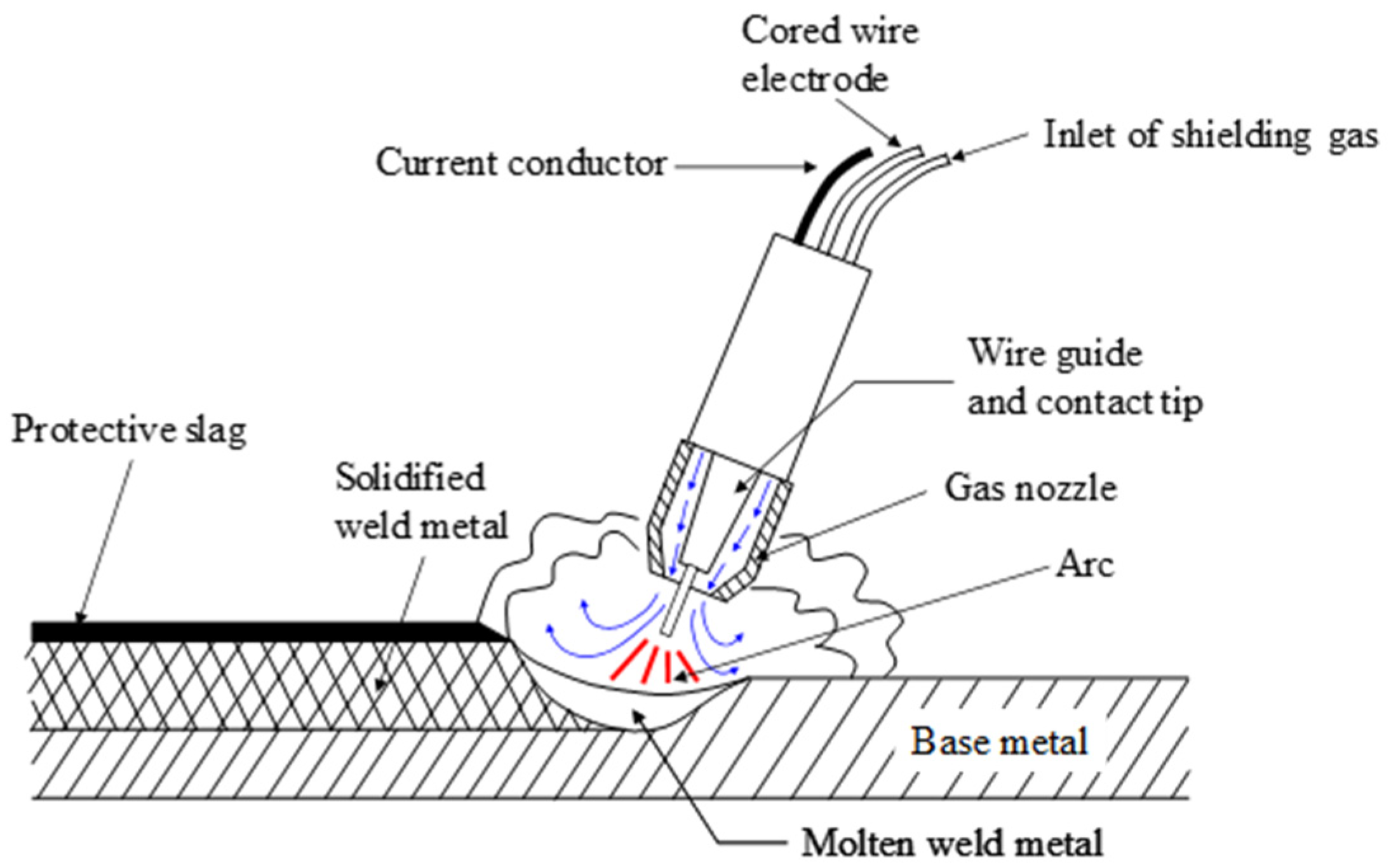
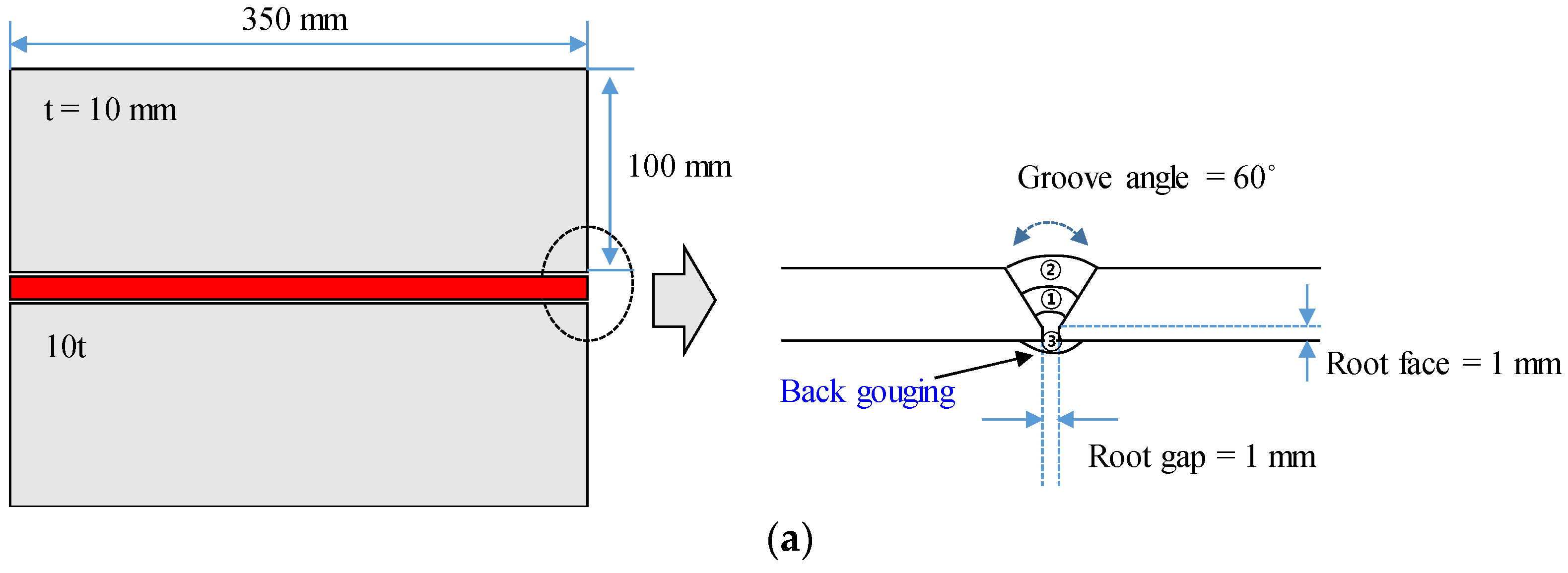
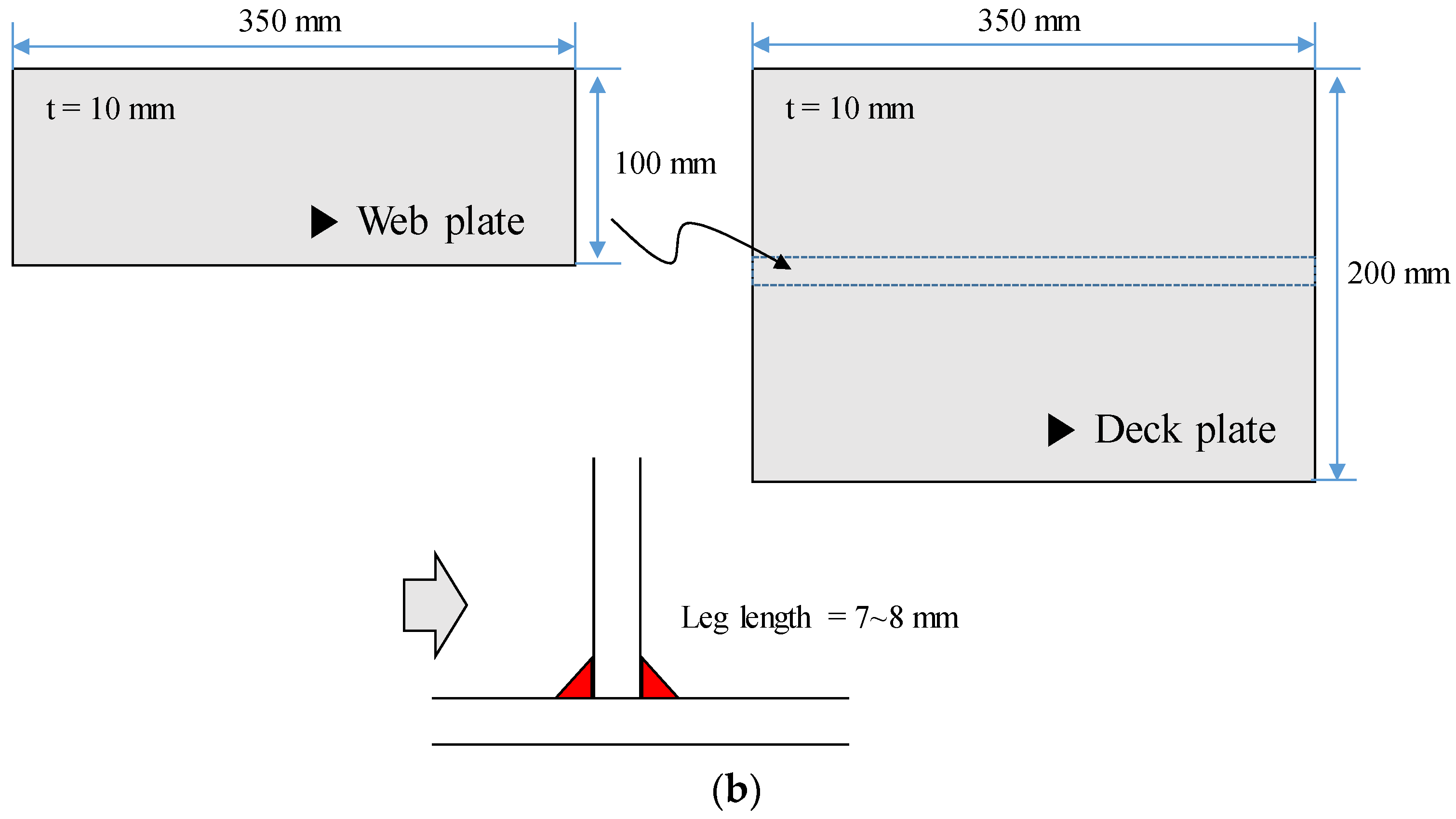
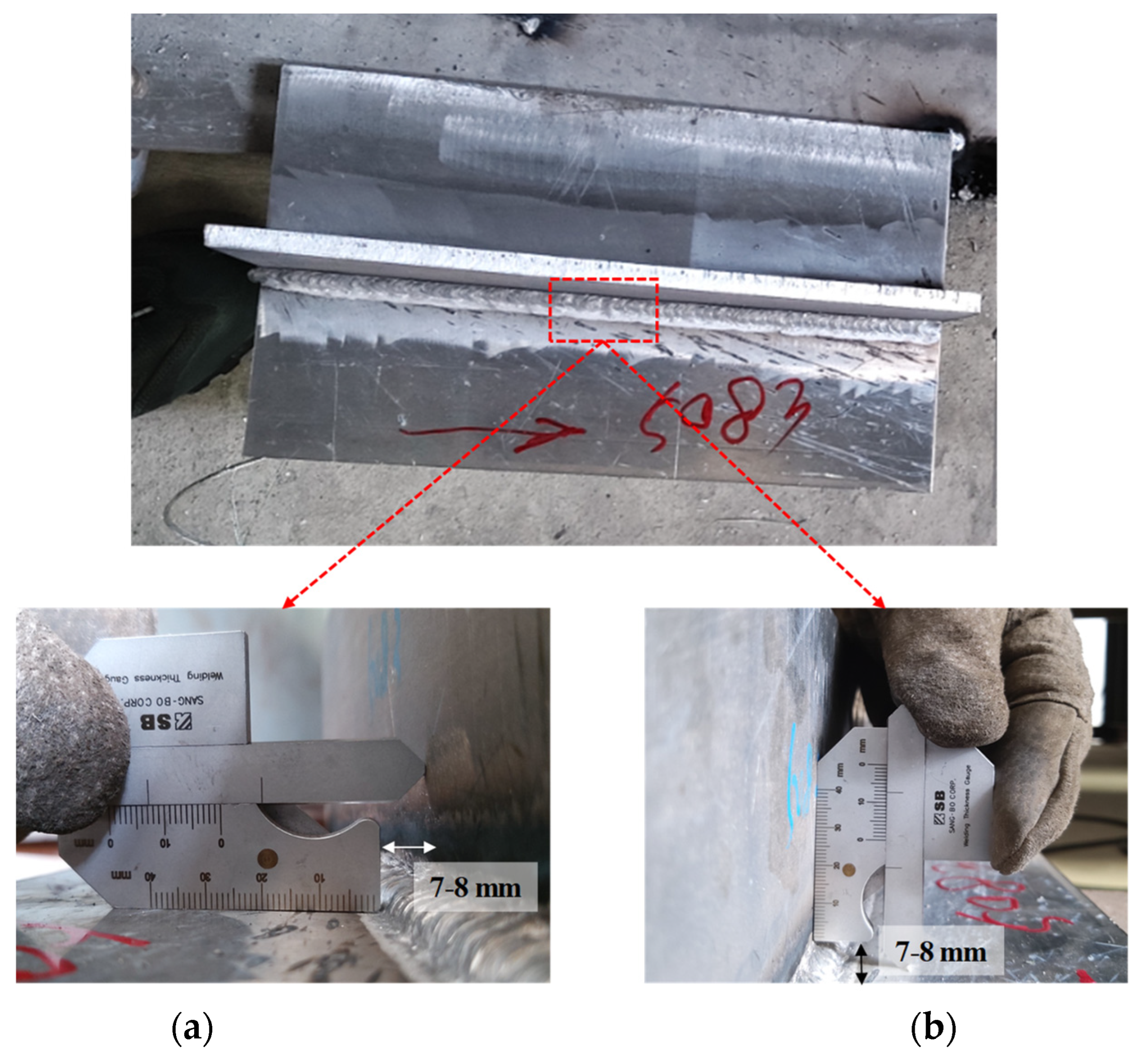
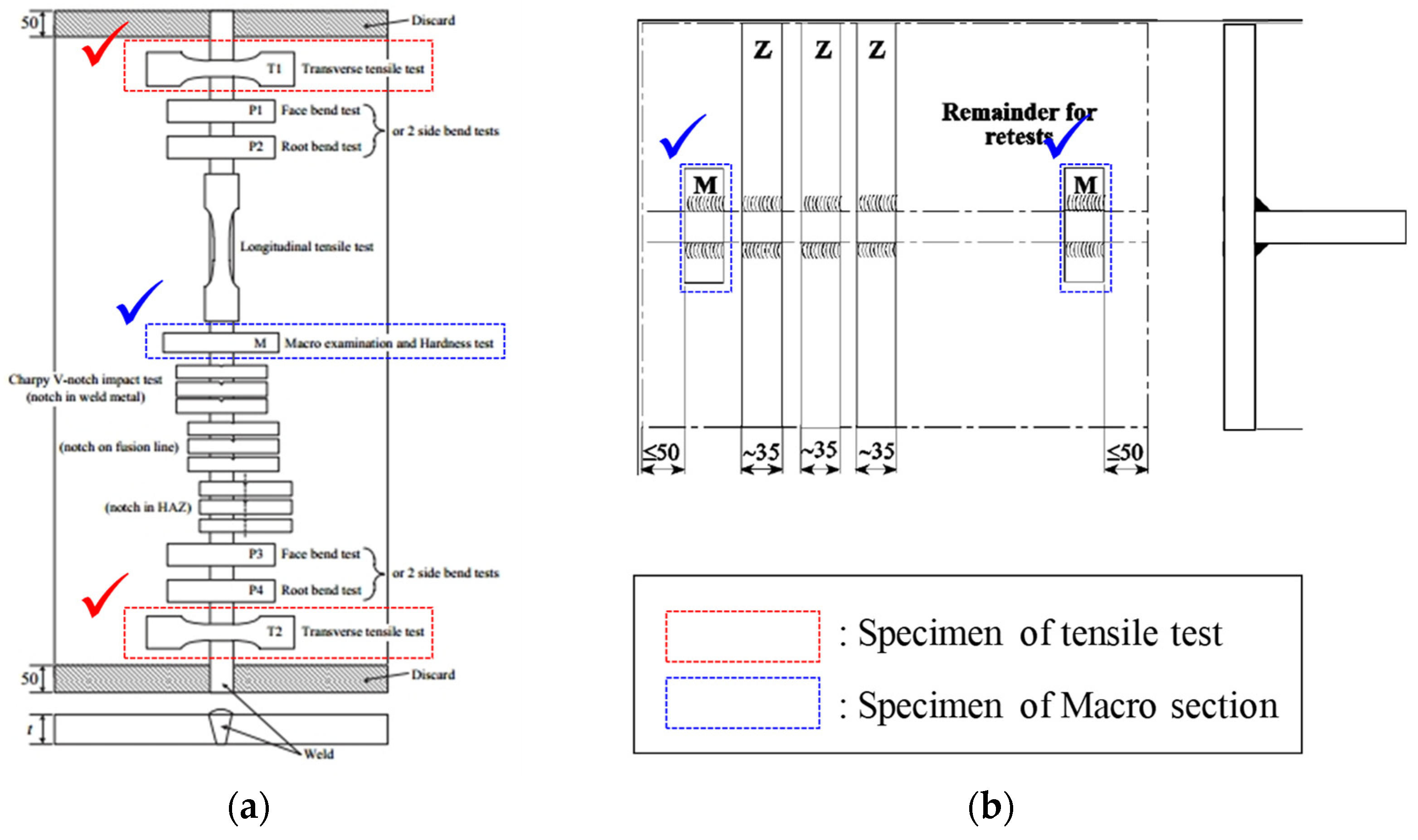
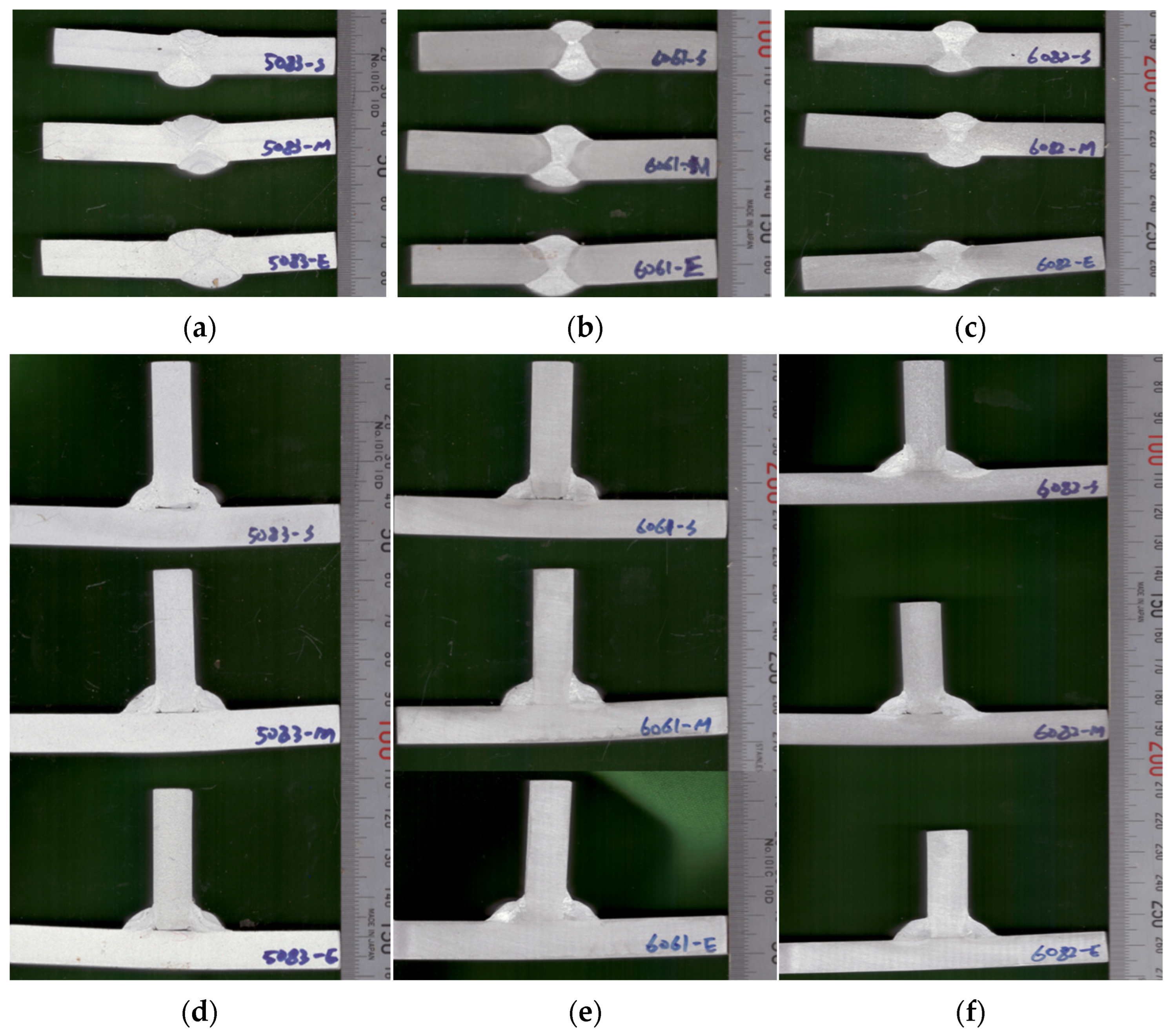
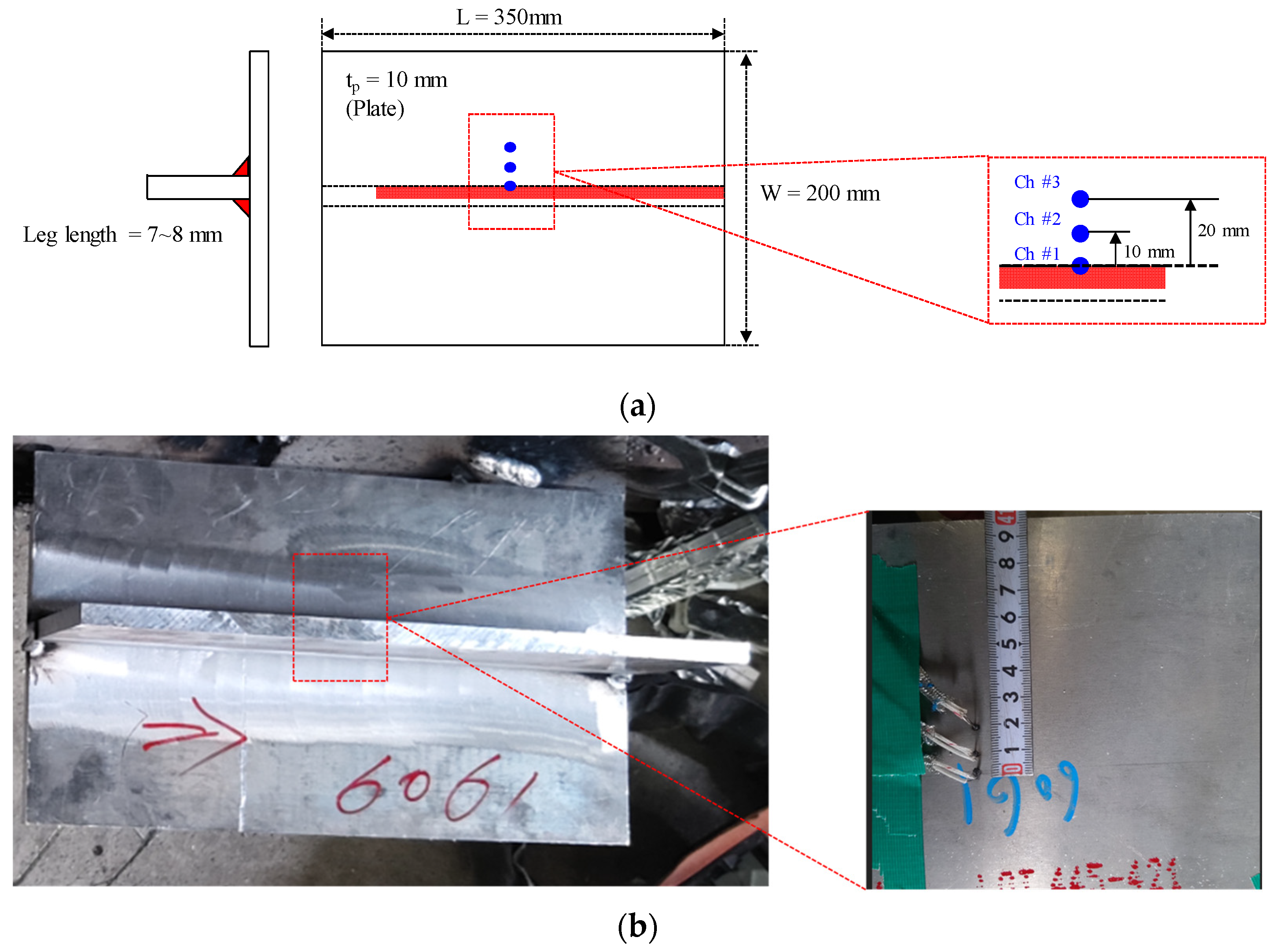
2.2. Specimen Testing Using GMAW
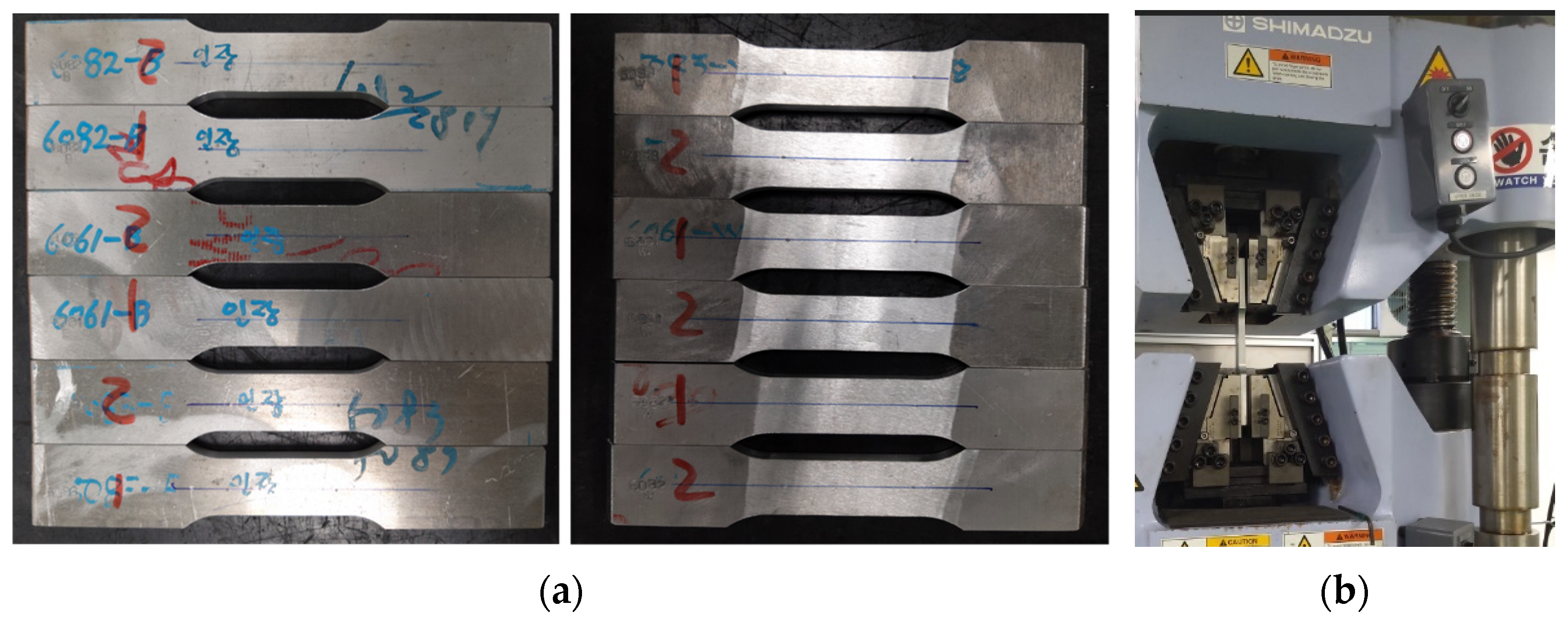
2.3. Mechanical Property Testing for Al Alloys
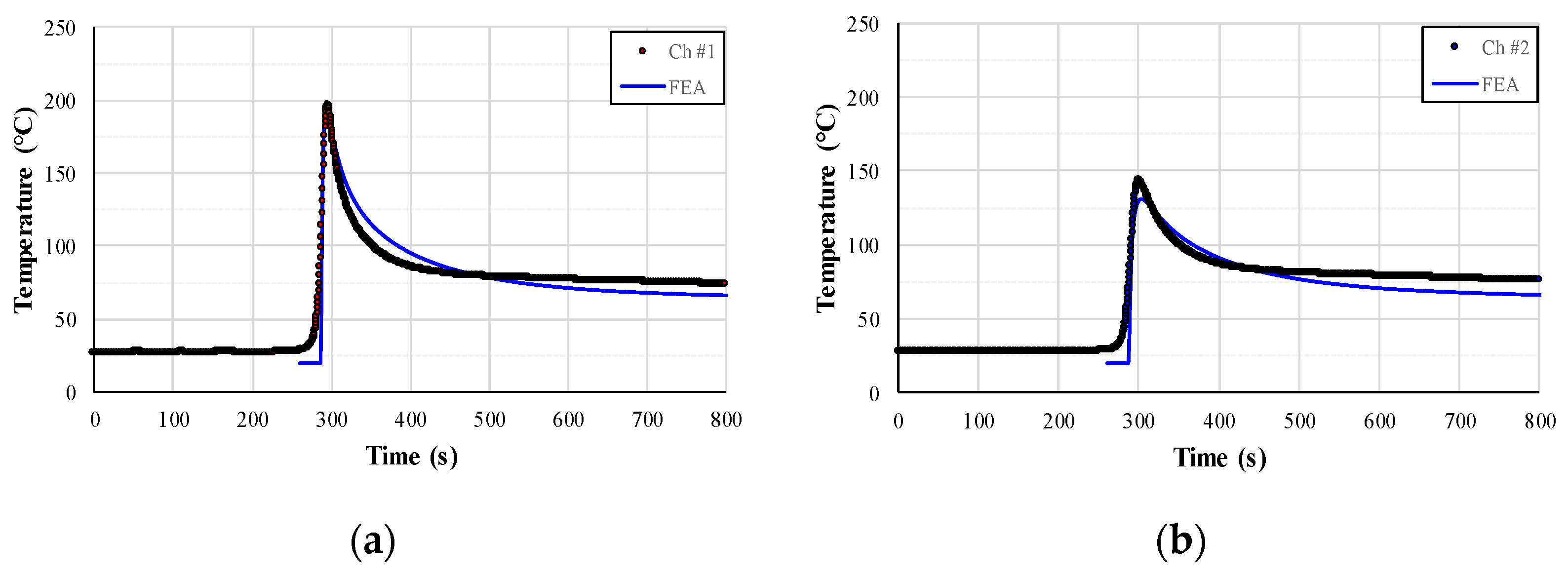
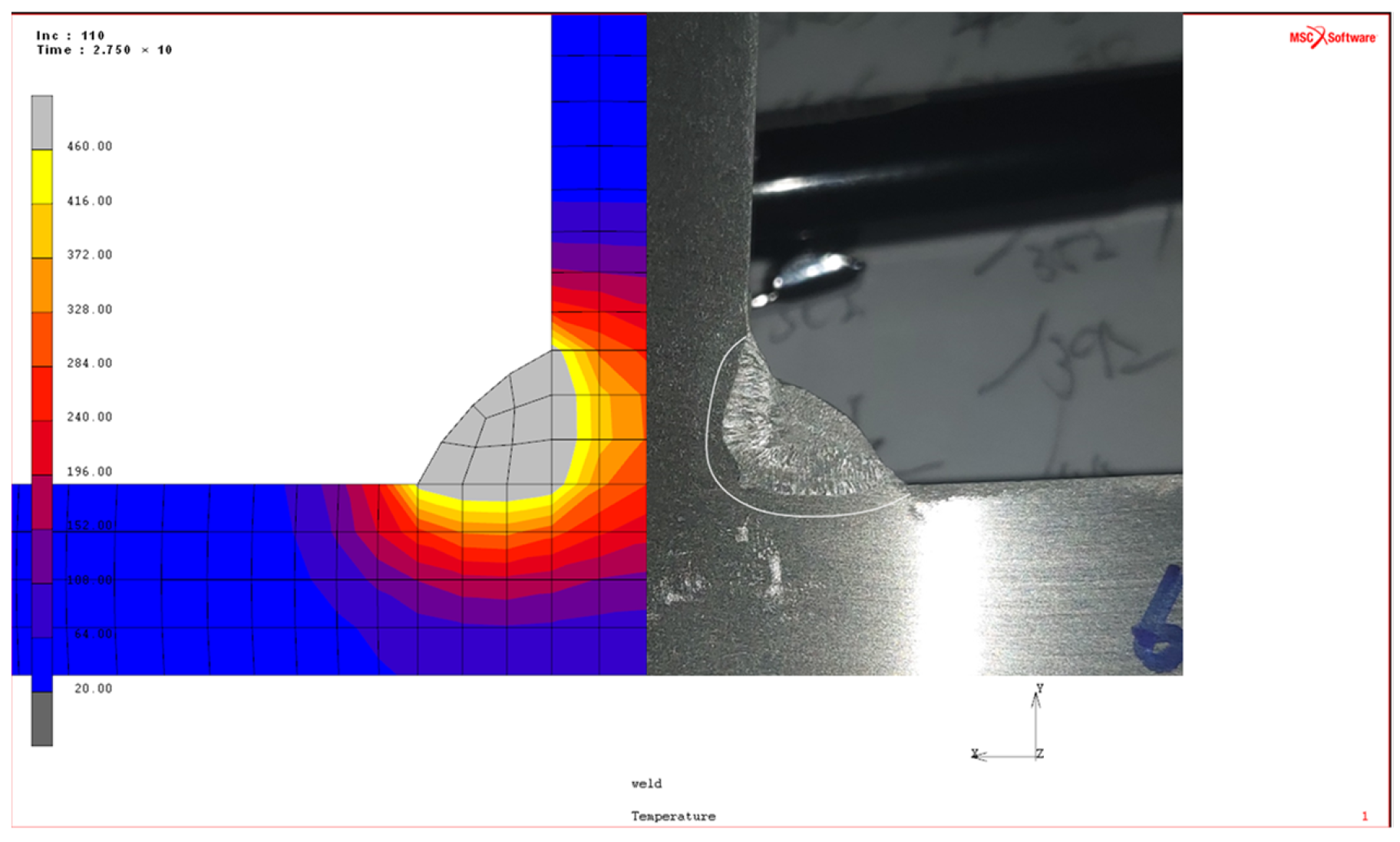
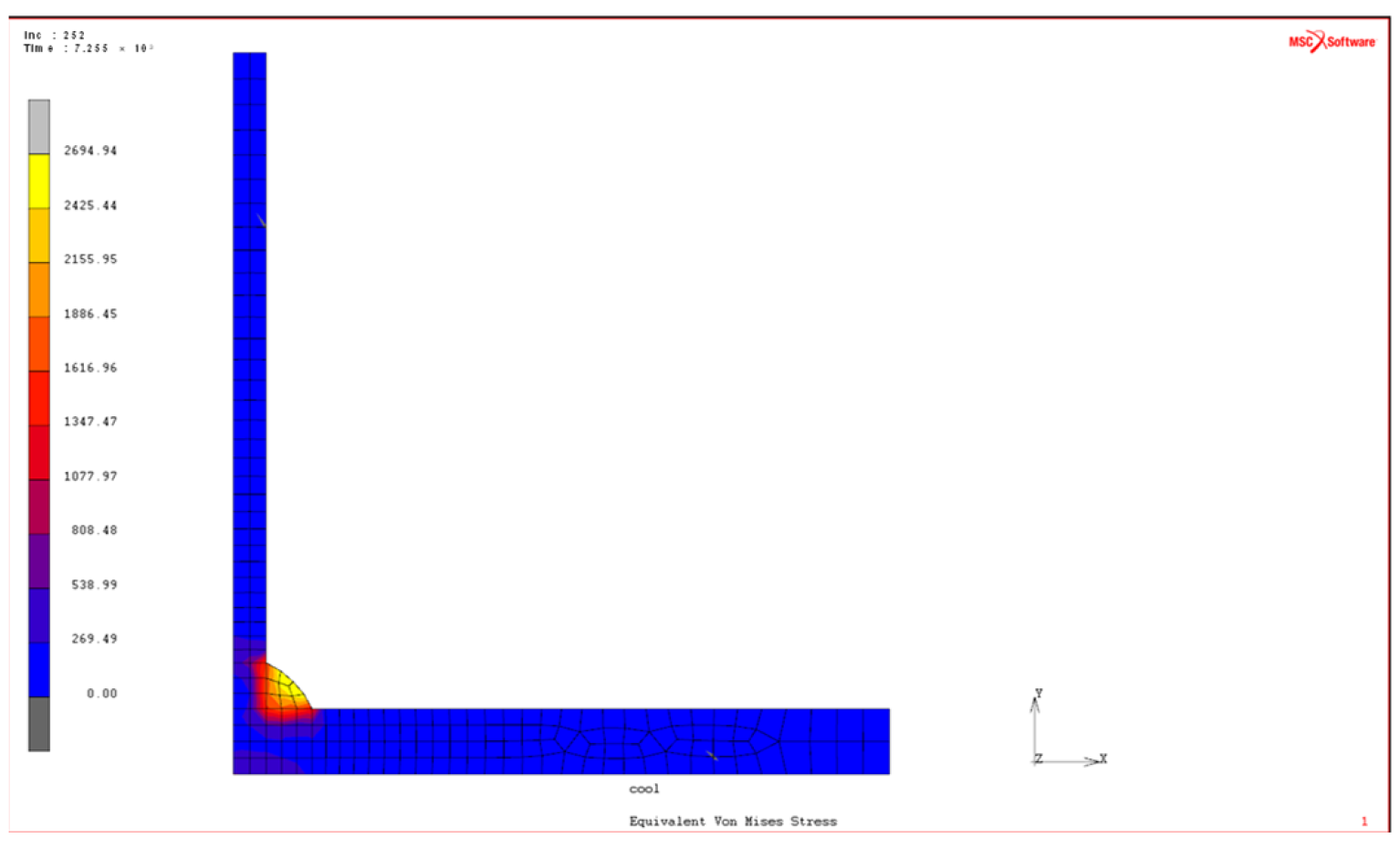
3. FE Analysis and Verification of Weld-Induced Residual Stresses
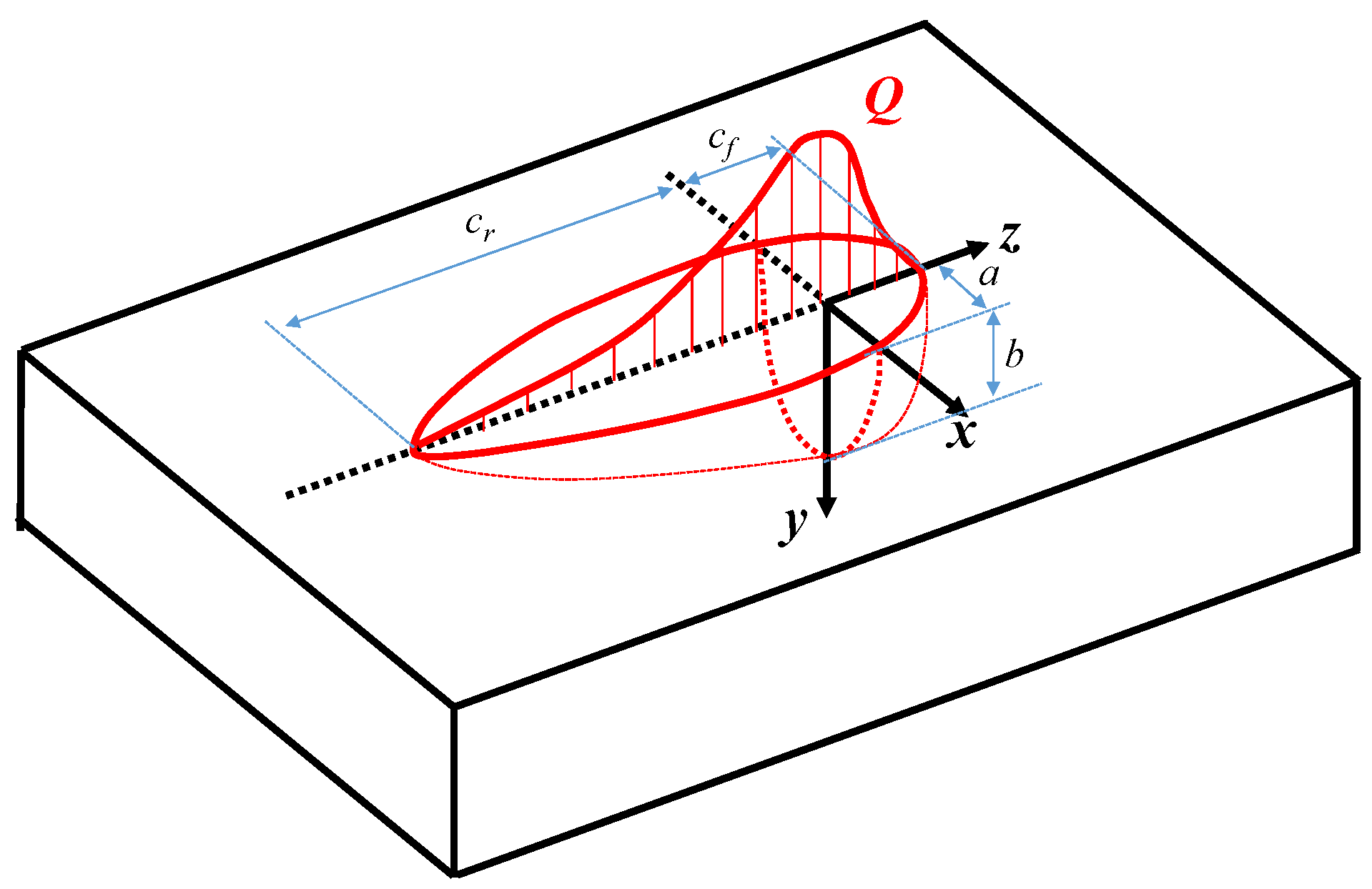
3.1. Definition of GMAW Heat Source Model of Al Alloy
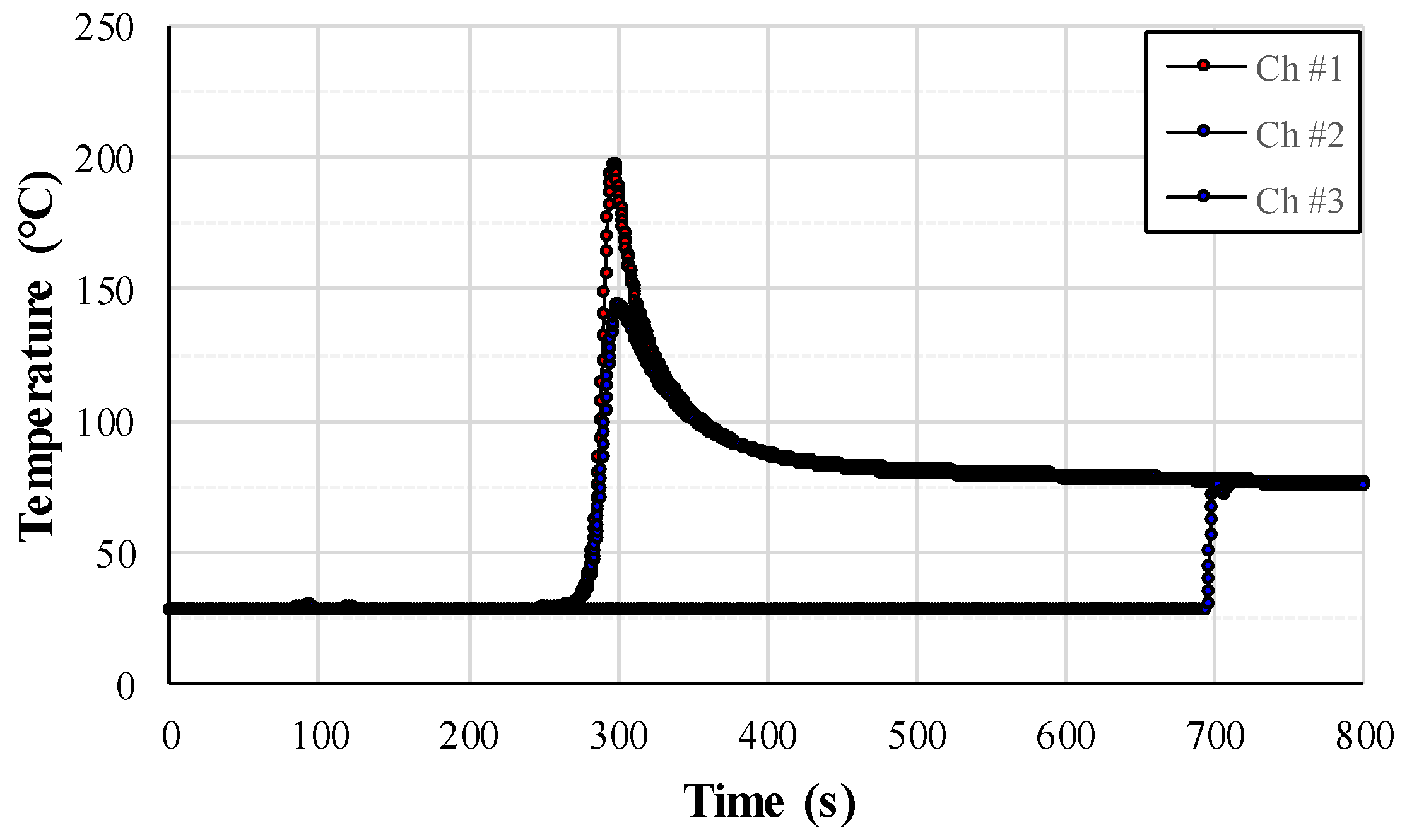
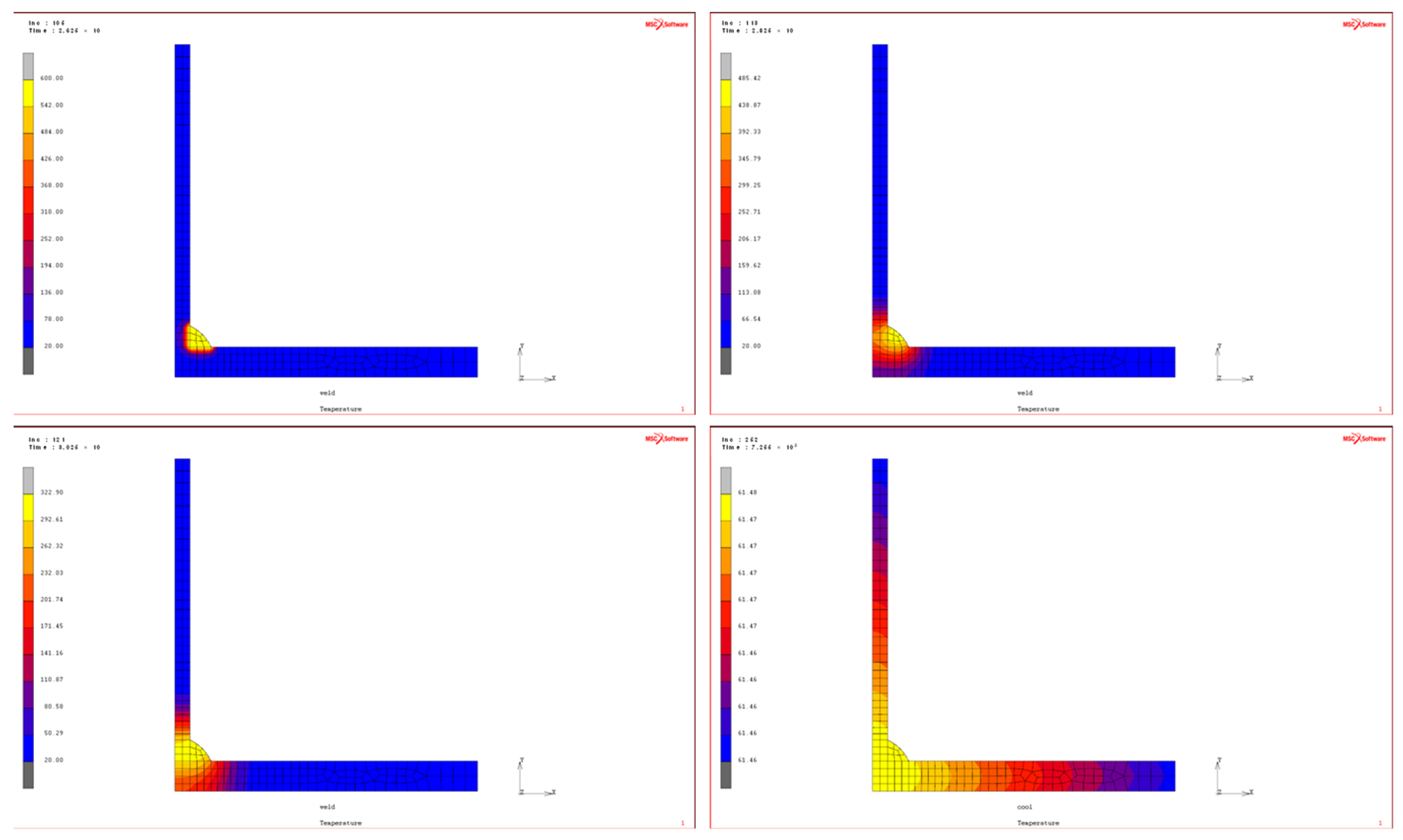
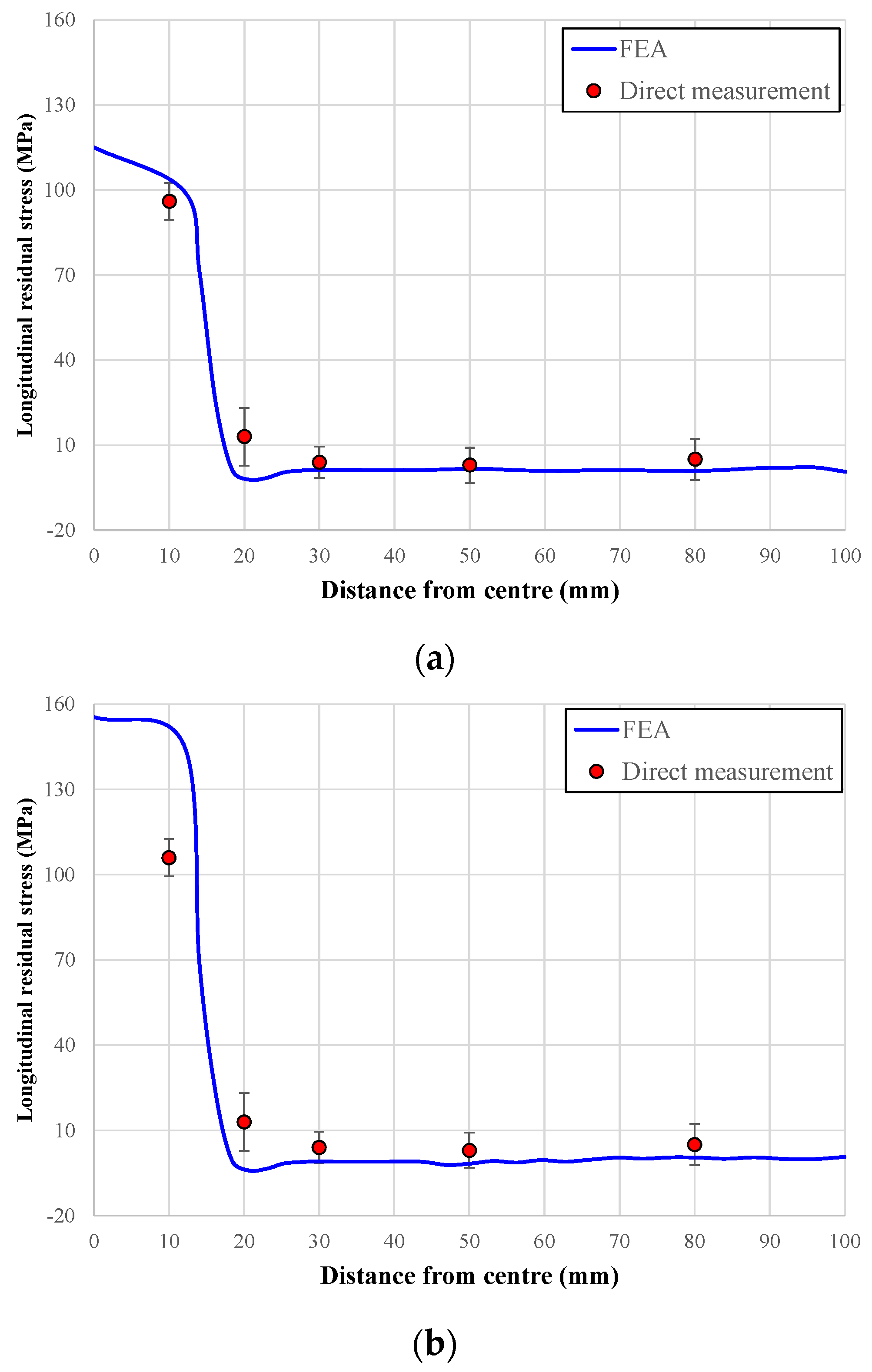
3.2. FE Analysis of Welding-Induced Residual Stress
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masubuchi, K. Analysis of Welded Structures: Residual Stresses, Distortion and Their Consequences, 1st ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.S.; Davidson, P.C.; Chapman, J.C.; Dowling, P.J. Strength and Stiffness of Ships’ Plating under in-Plane Compression and tension. Trans RINA Lond. 1988, 130, 277–296. [Google Scholar]
- Ueda, Y. Computational Welding Mechanics (A volume of Selected Papers in the Commemoration of the Retirement from Osaka University); Joining and Welding Research Institute, Osaka University: Osaka, Japan, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Paik, J.K.; Thayamballi, A.K.; Ryu, J.Y.; Jang, J.H.; Seo, J.K.; Park, S.W.; Seo, S.K.; Andrieu, C.; Cojeen, H.P.; Kim, N.I. The statistics of weld induced initial imperfections in aluminum stiffened plate structures for marine applications. Int. J. Marit. Eng. 2006, 148, 19–63. [Google Scholar]
- Paik, J.K. Characteristics of welding induced initial deflections in welded aluminum plates. Thin-Walled Struct. 2007, 45, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.K. Mechanical Collapse Testing on Aluminum Stiffened Panels for Marine Applications; Ship Structure Committee: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Paik, J.K.; Andrieu, C.; Cojeen, H.P. Mechanical Collapse Testing on Aluminum Stiffened Plate Structures for Marine Applications. Mar. Technol. SNAME News 2008, 45, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.K.; Kim, B.J.; Sohn, J.M.; Kim, S.H.; Jeong, J.M.; Park, J.S. On buckling collapse of a fusion-welded aluminum stiffened plate structure: An experimental and numerical study. J. Offshore Mech. Arct. Eng. 2012, 134, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Vhanmane, S.; Bhattacharya, B. Estimation of ultimate hull girder strength with initial imperfections. Ships Offshore Struct. 2008, 3, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luís, R.M.; Soares, C.G.; Nikolov, P.I. Collapse strength of longitudinal plate assemblies with dimple imperfections. Ships Offshore Struct. 2008, 3, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, G.; Yordan, G.; Soares, C.G. Effect of weld shape imperfections on the structural hot-spot stress distribution. Ships Offshore Struct. 2011, 6, 145–159. [Google Scholar]
- Khedmati, M.R.; Pedram, M.; Rigo, P. The effects of geometrical imperfections on the ultimate strength of aluminium stiffened plates subject to combined uniaxial compression and lateral pressure. Ships Offshore Struct. 2012, 9, 88–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teresa, M.; Craig, F. Effect of weld-induced imperfections on the ultimate strength of an aluminium patrol boat determined by the ISFEM rapid assessment method. Ships Offshore Struct. 2013, 9, 218–235. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.J.R.; Elwi, A.E.; Grodin, G.Y.; Kulak, G.L. Material testing and residual stress measurements in a stiffened steel plate. In Strength and Stability of Stiffened Plate Components; Ship Structure Committee: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kenno, S.Y.; Das, S.; Kennedy, J.; Rogge, R.; Gharghouri, M. Distributions of residual stresses in stiffened plates with one and two stiffeners. Ships Offshore Struct. 2010, 5, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kenno, S.Y.; Das, S.; Rogge, R.B.; Gharghouri, M.A. Changes in residual stresses caused by an interruption in the weld process of ships and offshore structures. Ships Offshore Struct. 2016, 12, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.S.; Hyun, C.M.; Paik, J.K. Full-scale measurements of welding-induced initial deflections and residual stresses in steel-stiffened plate structures. Int. J. Marit. Eng. 2018, 160, A397–A412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.S.; Hyun, C.M.; Paik, J.K. An empirical formulation for predicting welding-induced biaxial compressive residual stresses on steel stiffened plate structures and its application to thermal plate buckling prevention. Ships Offshore Struct. 2019, 14, S18–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.S.; Noh, S.H.; Lee, D.H.; Seo, D.H.; Paik, J.K. Direct measurements, numerical predictions and simple formula estimations of welding-induced biaxial residual stresses in a full-scale steel stiffened plate structure. Structures 2020, 29, 2094–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, D. The theory of moving sources of heat and its application to metal treatments. Trans ASME 1946, 68, 849–866. [Google Scholar]
- Pavelic, V.; Tanbakuchi, R.; Uyehara, O.A.; Myers, P.S. Experimental and computed temperature histories in gas tung-sten-arc welding of thin plates. Weld J. 1969, 48, 295–305. [Google Scholar]
- Eager, T.W.; Tasi, N.S. Temperature fields produced by travelling distributed heat source. Weld J. 1983, 12, 346–354. [Google Scholar]
- Wahab, M.A.; Painter, M.J.; Davies, M.H. The prediction of the temperature distribution and weld pool geometry in the gas metal arc welding process. J. Mater. Process Technol. 1998, 77, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, S.; Kumar, P.V.; Raj, B.; Bose, M.S.C. Temperature distribution during multipass welding of plates. Int. J. Press Vessels Pip. 1998, 75, 891–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, R.T.C.; Szekely, J.; Westhoff, R.C. On the calculation of the free surface temperature of gas-tungsten-arc weld pools from first principles. Metall. Trans. 1992, 23, 357–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Ohta, A.; Matsuoka, K.; Suzuki, N.; Maeda, Y. Analytical solutions for transient temperature of semi-infinite body subjected to 3-D moving heat sources. Weld J. 1999, 78, 265–274. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.G.; Tsai, H.L.; Na, S.J. Heat transfer and fluid flow in a partially or fully penetrated weld pool in gas tungsten arc welding. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 2001, 44, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Chaudhary, A.K.; Arora, N.; Mishra, B.K. Estimation of heat source model parameters for twin-wire submerged arc welding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2009, 45, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpei, T.; Chelladurai, H.; Ansari, M.Z. Experimental investigation and numerical analyses of residual stresses and distortions in GMA welding of thin dissimilar AA5052-AA6061 plates. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 25, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, E.S.; Park, J.Y.; Choi, J. MIG Welding Optimization of Muffler Manufacture by Microstructural Change and Thermal Deformation Analysis. J. Weld. Join. 2017, 35, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aleo, V. Effect of Welding on the Width of Heat Affected Zone of Aluminum Alloys. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Windsor, Windsor, ON, Canada, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sel, H.; Awang, M.; Md, A.I.; Ismailc, E.R.; Ahmadi, Z.A. Evaluation of properties and FEM model of the friction welded mild steel-Al6061-alumina. Mater. Res. 2013, 16, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Type | Series | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Non-heat-treatable | 1xxx | pure metal Al(>99.0%) |
| 3xxx | Al-Mn series alloys | |
| 4xxx | Al-Si series alloys | |
| 5xxx | Al-Mg series alloys | |
| Heat-treatable | 2xxx | Al-Cu series alloys |
| 6xxx | Al-Mg-Si series alloys | |
| 7xxx | Al-Si-Mg series alloys |
| Type | Dimension (L × W × t) | Al 5083 H321 | Al 6061 T6 | Al 6082 T6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Butt specimen | 350 × 100 × 10 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Fillet specimen | (plate) 350 × 200 × 10 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| (web) 350 × 100 × 10 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Total | 4 | 4 | 4 | |
| Welding Parameter | Current (A) | Voltage (V) | Speed (cm/min) | Heat Input (kJ/cm) | Leg Length (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPS Condition | 145.6–218.4 | 23.5–31.7 | 30.1–45.1 | 6–8 | 4.2–8.4 |
| Real Condition | 210 | 25 | 39.6 | 7.8 | 7.5 |
| Welding Parameter | Number of Pass | Current (A) | Voltage (V) | Speed (cm/min) | Heat Input (kJ/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPS Condition | #1 | 132.2–184.8 | 19–25.8 | 22.4–33.6 | 5.6–9.3 |
| #2 | 128–192 | 19–25.8 | 28.9–43.32 | 5.9–8.8 | |
| Back gouging | |||||
| #3 | 124–186 | 19–25.8 | 22.1–33.1 | 5.6–9.4 | |
| Real Condition | #1 | 150 | 23 | 28 | 9 |
| #2 | 160 | 22 | 30 | 7.04 | |
| Back gouging | |||||
| #3 | 155 | 23 | 25 | 8.57 | |
| Si (%) | Fe (%) | Cu (%) | Mn (%) | Mg (%) | Cr (%) | Ni (%) | Zn (%) | Ti (%) | Others | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Each | Total | |||||||||||
| Actual | 0.19 | 0.36 | 0.029 | 0.66 | 4.79 | 0.083 | 0.0081 | 0.11 | 0.016 | - | - | |
| Limit | Min. | - | - | - | 0.40 | 4.00 | 0.050 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Max. | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.10 | 1.00 | 4.90 | 0.25 | - | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.050 | 0.15 | |
| Si (%) | Fe (%) | Cu (%) | Mn (%) | Mg (%) | Cr (%) | Ni (%) | Zn (%) | Ti (%) | Others | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Each | Total | |||||||||||
| Actual | 0.69 | 0.43 | 0.22 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 0.17 | 0.0098 | 0.048 | 0.017 | - | - | |
| Limit | Min. | 0.40 | - | 0.15 | - | 0.80 | 0.040 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Max. | 0.80 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 0.15 | 1.20 | 0.35 | - | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.050 | 0.15 | |
| Si (%) | Fe (%) | Cu (%) | Mn (%) | Mg (%) | Cr (%) | Ni (%) | Zn (%) | Ti (%) | Others | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Each | Total | |||||||||||
| Actual | 1.01 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 0.72 | 0.01 | - | 0.01 | 0.02 | - | - | |
| Limit | Min. | 0.7 | - | - | 0.4 | 0.6 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Max. | 1.3 | 0.50 | 0.1 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 0.25 | - | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.15 | |
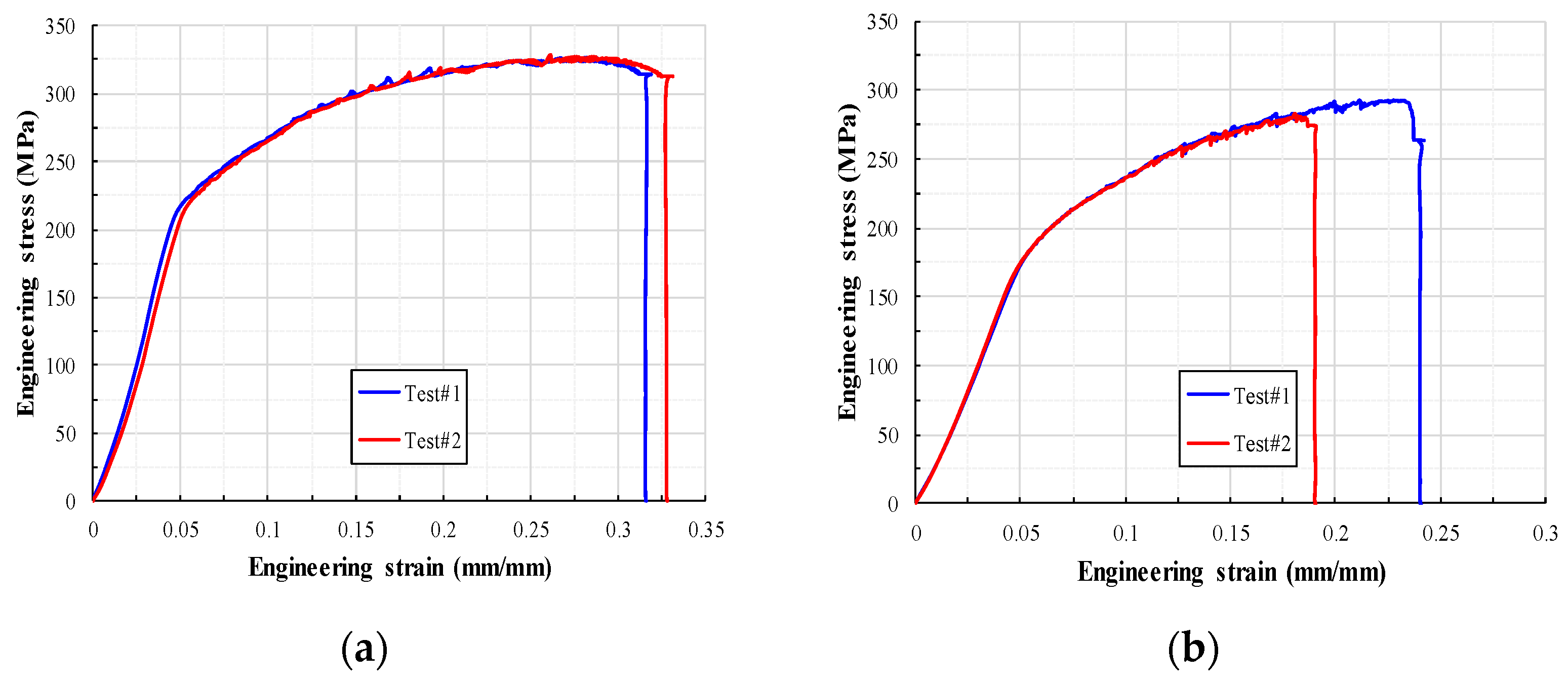
| Yield Stress (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Fracture Strain (mm/mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al 5083 H321 (Base metal) | #1 | 207.4 | 326.7 | 0.316 |
| #2 | 209.8 | 328.6 | 0.327 | |
| Al 5083 H321 (Weld metal) | #1 | 179.8 | 292.5 | 0.240 |
| #2 | 178.1 | 287.9 | 0.044 | |
| Al 6061 T6 (Base metal) | #1 | 297.4 | 325.5 | 0.289 |
| #2 | 280.4 | 327.2 | 0.301 | |
| Al 6061 T6 (Weld metal) | #1 | 187.3 | 227.4 | 0.087 |
| #2 | 180.4 | 233.4 | 0.112 | |
| Al 6082 T6 (Base metal) | #1 | 307.1 | 328.8 | 0.205 |
| #2 | 302.7 | 326.3 | 0.207 | |
| Al 6082 T6 (Weld metal) | #1 | 180.9 | 236.2 | 0.103 |
| #2 | 192.1 | 234.1 | 0.093 | |
| a (mm) | b (mm) | cf (mm) | cr (mm) | ff (-) | fr (-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 0.4 | 1.6 |
| Temperature (°C) | Thermal Conductivity (W m−1 K−1) | Heat Capacity (J kg−1 K−1) | Density (kg m−3) | Thermal Expansion (×10−6 K−1) | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Yield Stress (MPa) | Poisson’s Ratio (-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 162 | 917 | 2703 | 22.4 | 69.7 | 277.7 | 0.33 |
| 98 | 177 | 978 | 2685 | 24.6 | 66.2 | 264.6 | |
| 201 | 192 | 1028 | 2657 | 26.6 | 59.2 | 218.6 | |
| 316 | 207 | 1078 | 2630 | 27.6 | 47.8 | 66.2 | |
| 428 | 223 | 1133 | 2602 | 29.6 | 31.7 | 17.9 | |
| 571 | 253 | 1230 | 2574 | 34.2 | 0 | 0 |
| Kinds of Material | Distance from Weld Center Line (mm) | σrx (MPa) | ±Error (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al 5083 H321 | 10 | 96 | 4.8 |
| 20 | 13 | 10.5 | |
| 30 | 4 | 12.1 | |
| 50 | 3 | 4.5 | |
| 80 | 5 | 8.2 | |
| Al 6061 T6 | 10 | 106 | 6.5 |
| 20 | 21 | 10.2 | |
| 30 | 5 | 5.5 | |
| 50 | 1 | 6.2 | |
| 80 | −5 | 7.2 | |
| Al 6082 T6 | 10 | 232 | 12.8 |
| 20 | 36 | 8.6 | |
| 30 | 8 | 14.9 | |
| 50 | 6 | 5.1 | |
| 80 | 7 | 15.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, M.-S.; Park, J.-S. Study of Heat Source Model and Residual Stress Caused by Welding in GMAW of Al Alloy. Metals 2022, 12, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12060891
Yi M-S, Park J-S. Study of Heat Source Model and Residual Stress Caused by Welding in GMAW of Al Alloy. Metals. 2022; 12(6):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12060891
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Myung-Su, and Joo-Shin Park. 2022. "Study of Heat Source Model and Residual Stress Caused by Welding in GMAW of Al Alloy" Metals 12, no. 6: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12060891
APA StyleYi, M.-S., & Park, J.-S. (2022). Study of Heat Source Model and Residual Stress Caused by Welding in GMAW of Al Alloy. Metals, 12(6), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12060891






