Why Color Matters—Proposing a Quantitative Stability Criterion for Laser Beam Processing of Metals Based on Their Fundamental Optical Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Evaluation of the Optical and Thermo-Physical Properties
2.2. Experimental Setup
3. Results
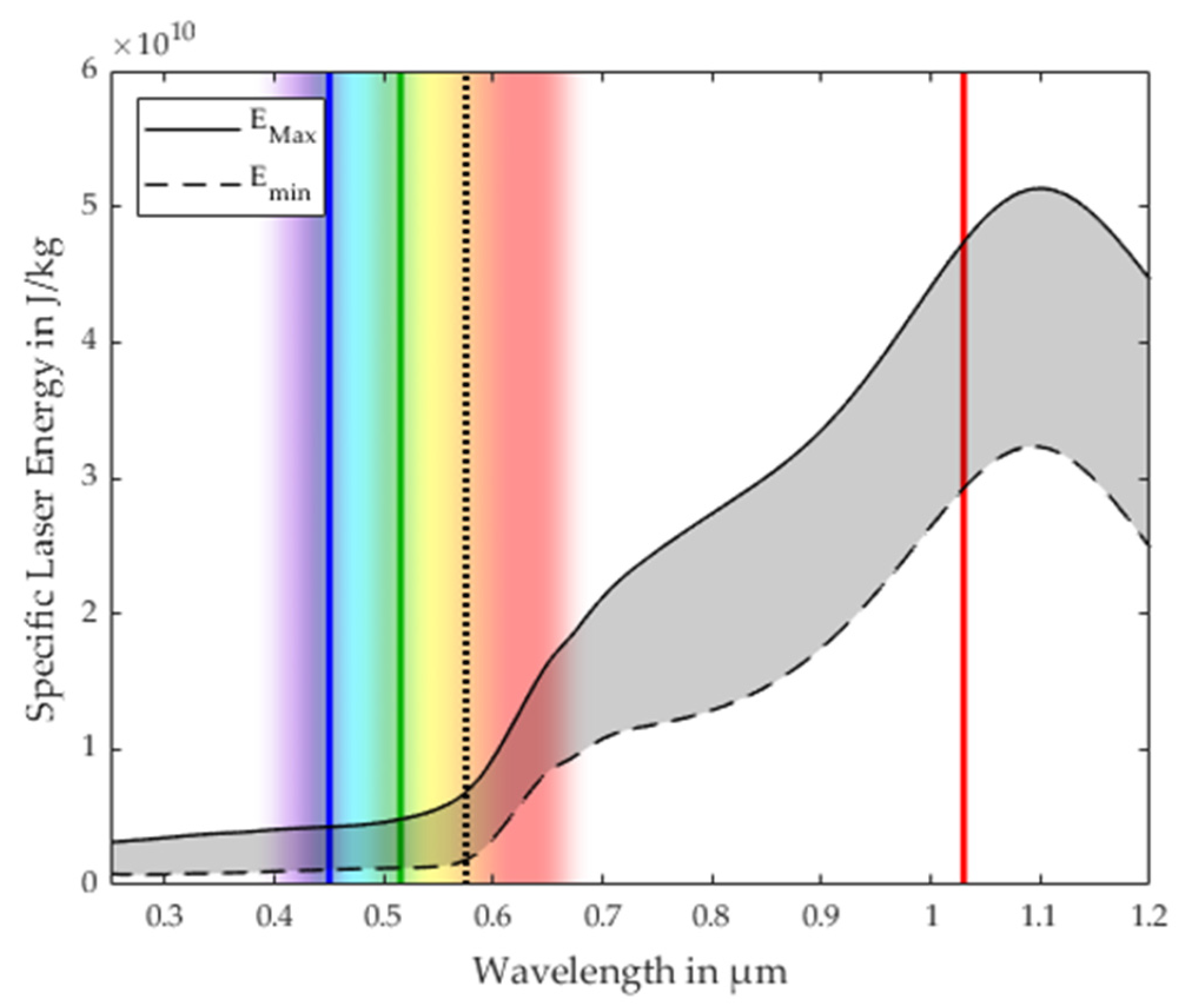
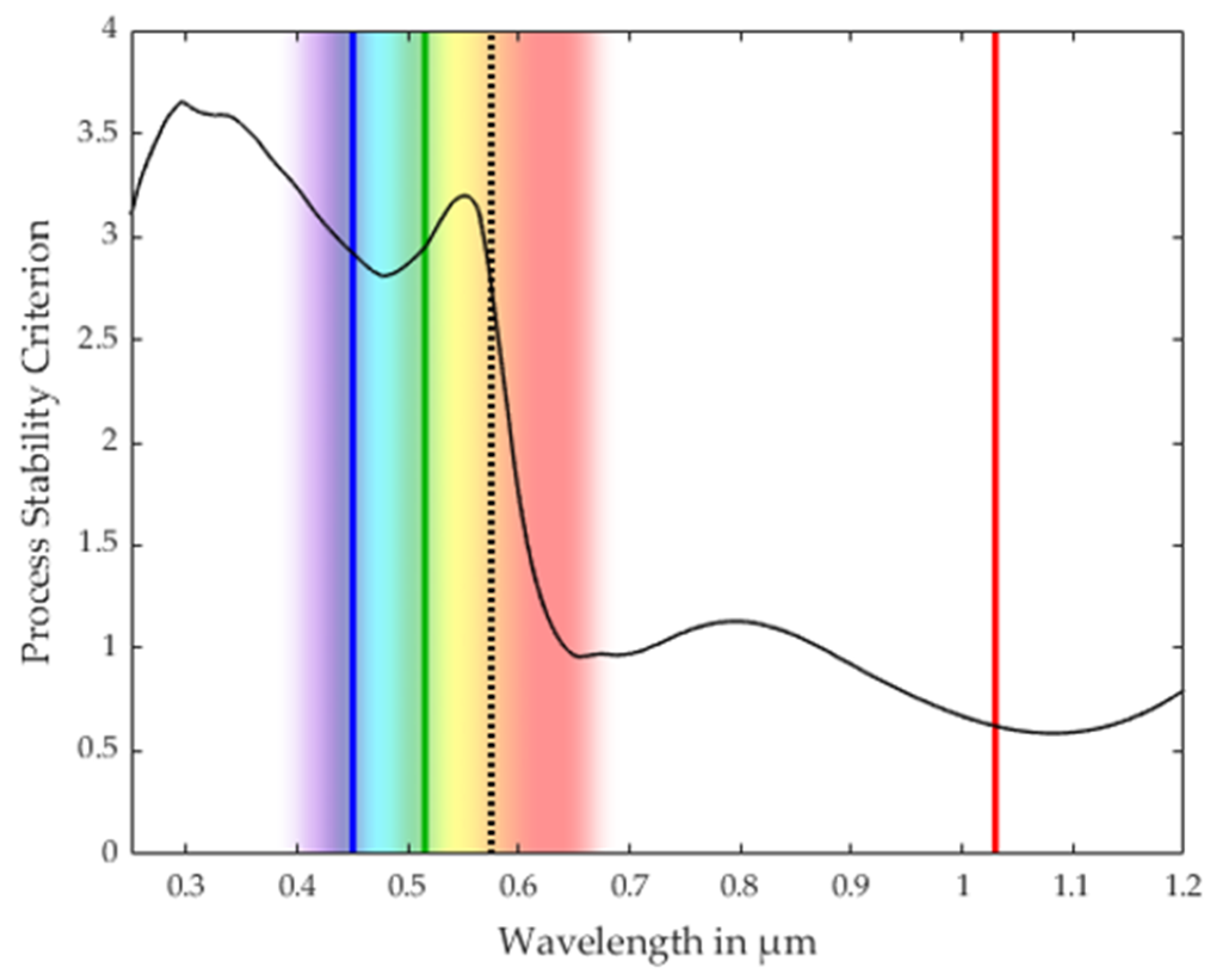
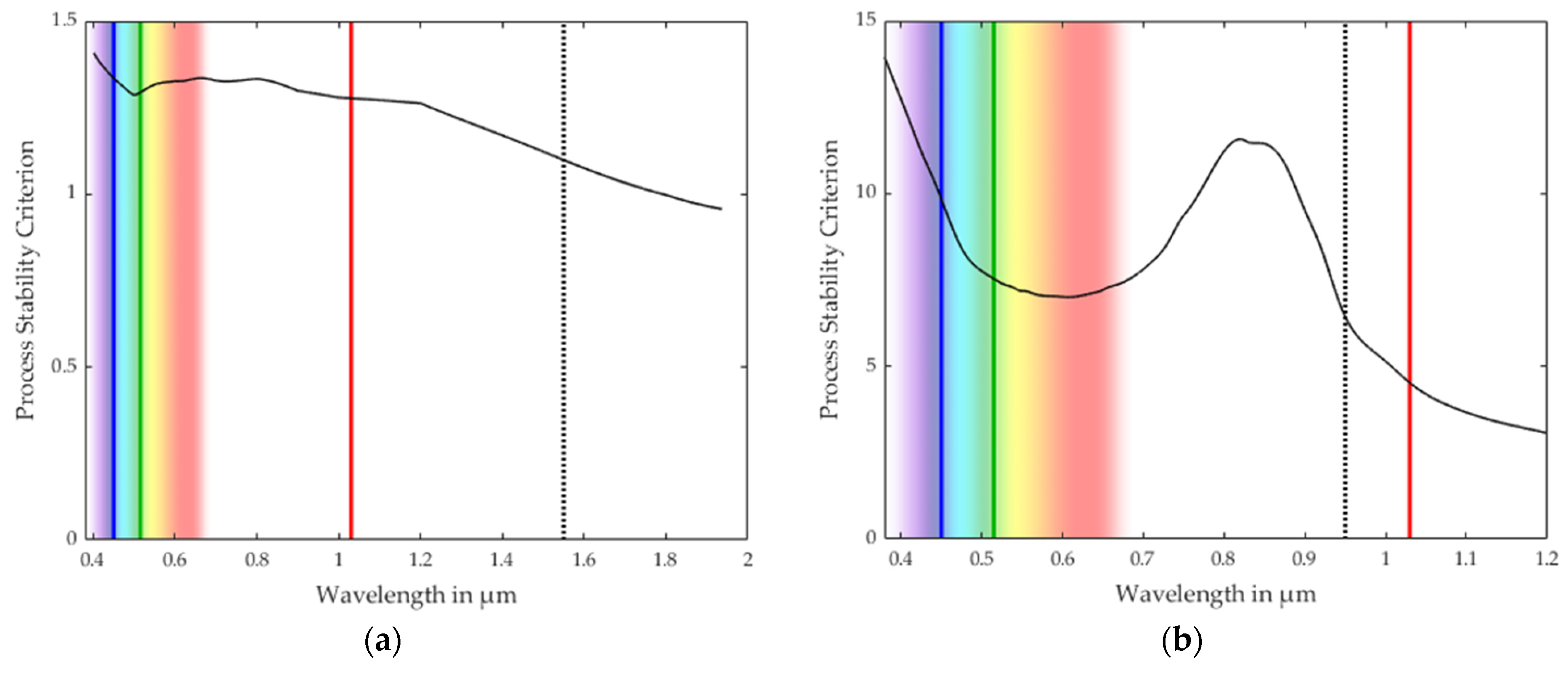
3.1. Process Stability Criterion
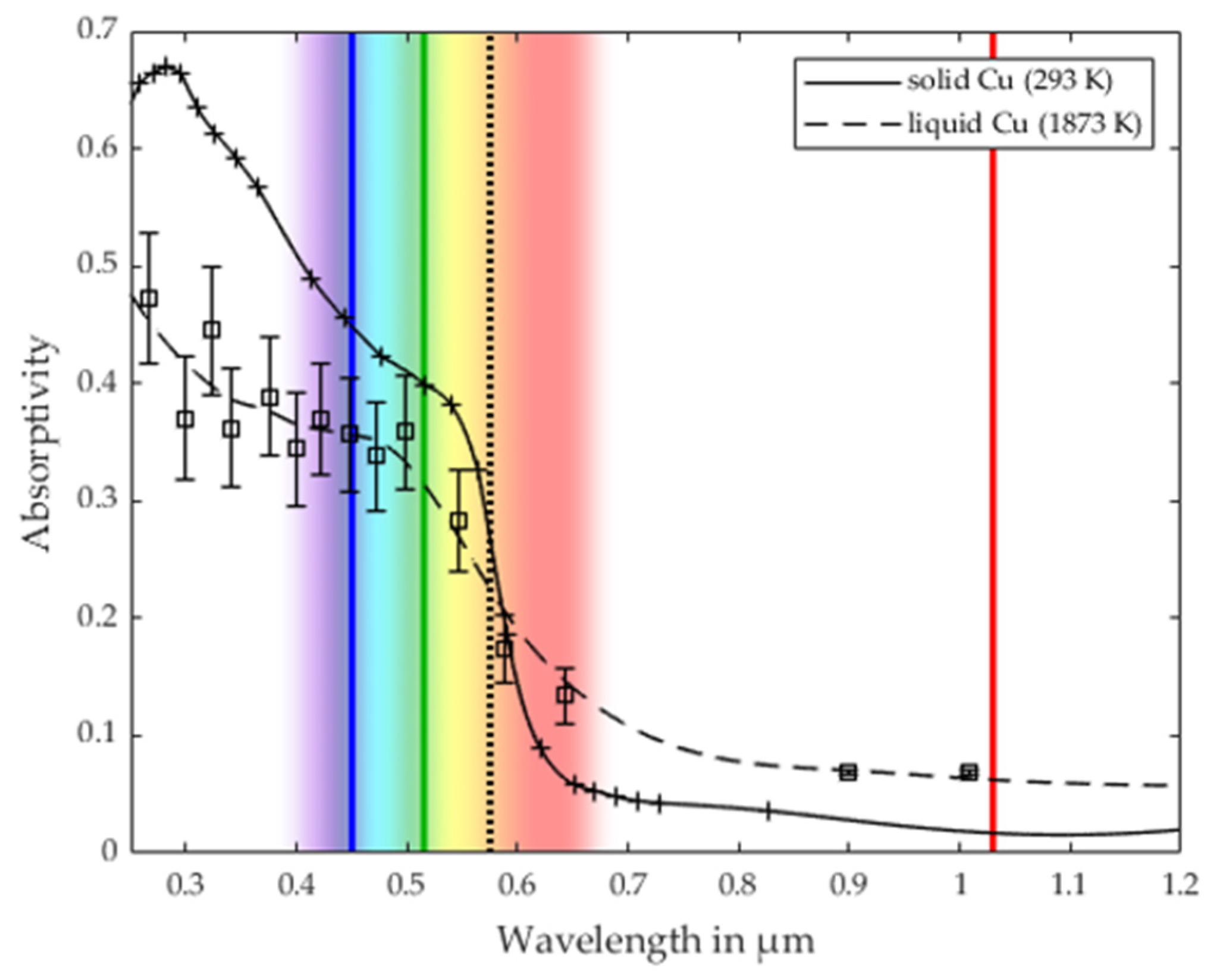
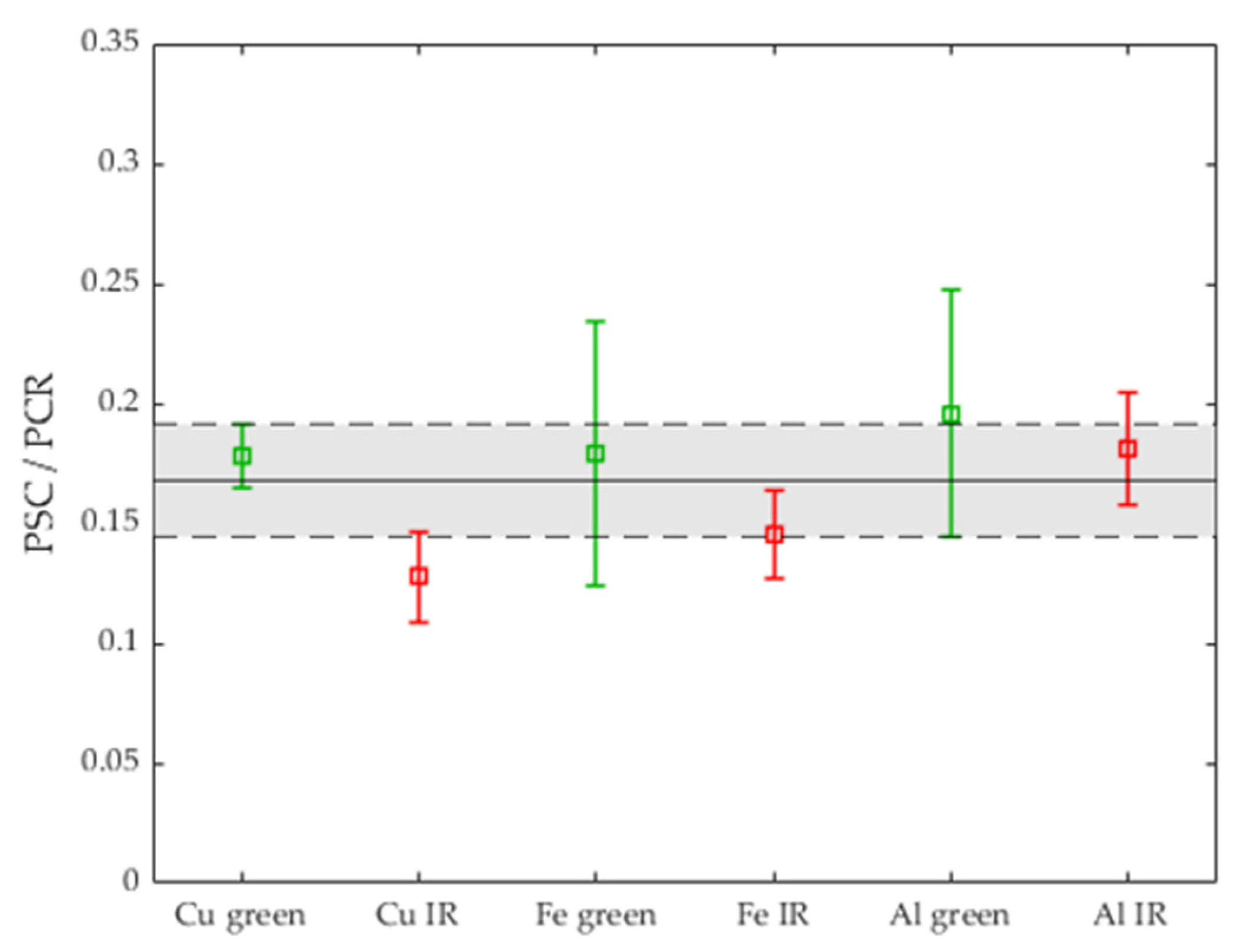
3.2. Validation of the Process Stability Criterion for Copper
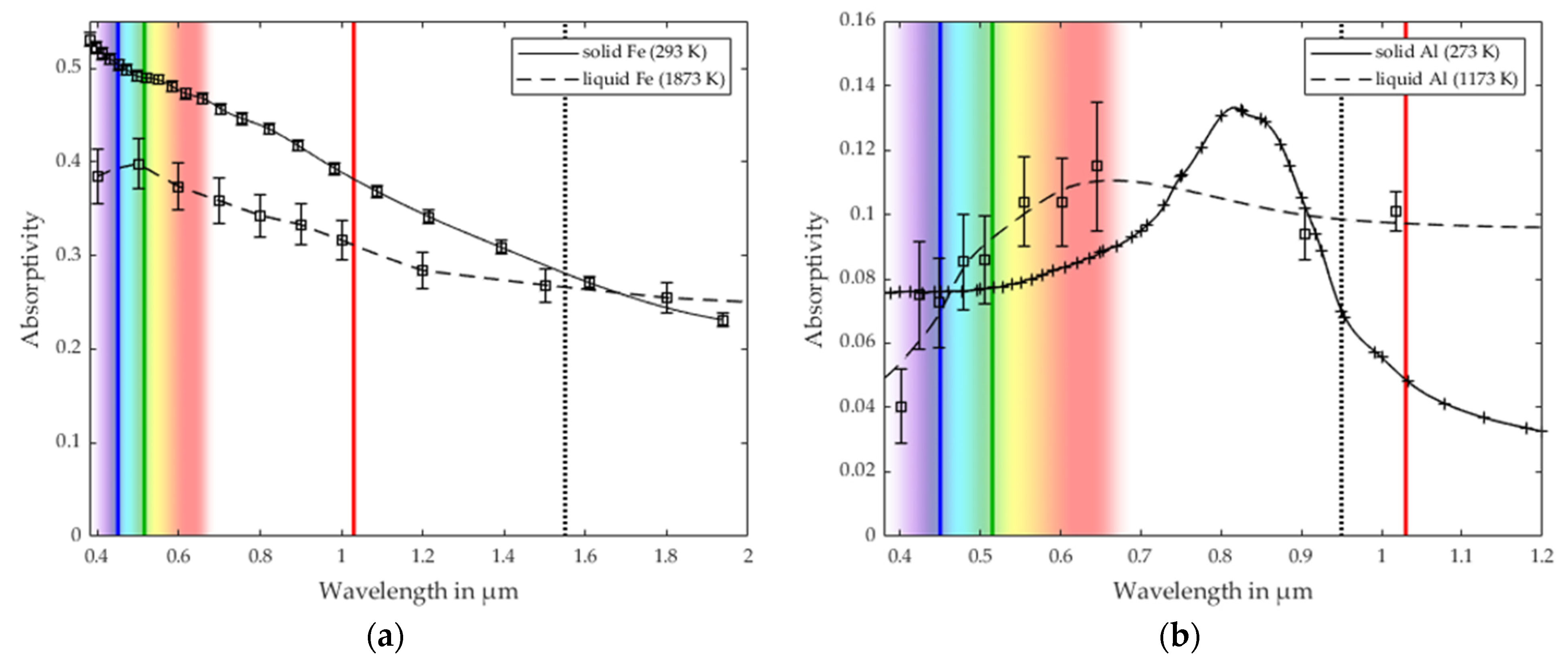
3.3. Comparison with the Process Stability Criterion of Iron and Aluminum
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hügel, H.; Graf, T. Laser in der Fertigung: Grundlagen der Strahlquellen, Systeme, Fertigungsverfahren; Springer: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2014; ISBN 3834818178. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M.; Zäh, M.; Li, L.; Duflou, J.; Overmeyer, L.; Vollertsen, F. Advances in macro-scale laser processing. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 2018, 67, 719–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A.F. Fresnel absorption of 1μm- and 10μm-laser beams at the keyhole wall during laser beam welding: Comparison between smooth and wavy surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 3354–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, A.; Weber, R.; Heider, A.; Graf, T. Forced deep-penetration welding with low-power second-harmonic assistance of cw copper welding with 1 μm wavelength. Phys. Procedia 2010, 5, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haubold, M.; Ganser, A.; Eder, T.; Zäh, M.F. Laser welding of copper using a high power disc laser at green wavelength. Procedia CIRP 2018, 74, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, S.; Ramsayer, R.; Poprawe, R. Process Studies on Laser Welding of Copper with Brilliant Green and Infrared Lasers. Phys. Procedia 2011, 12, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poprawe, R. Lasertechnik für die Fertigung: Grundlagen, Perspektiven und Beispiele für den Innovativen Ingenieur; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; ISBN 3540214062. [Google Scholar]
- Pricking, S.; Baumann, F.; Zaske, S.; Dold, E.; Kaiser, E.; Killi, A. Progress in green disk laser development for industrial high power applications. In Solid State Lasers XXX: Technology and Devices, Proceedings of the SPIE LASE 2021, Online Only, 6–12 March 2021; Clarkson, W.A., Shori, R.K., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2021; Volume 11664, ISBN 9781510641631. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, E.; Dold, E.-M.; Killi, A.; Zaske, S.; Pricking, S. Application benefits of welding copper with a 1 kW, 515 nm continuous wave laser. In Proceedings of the 10th CIRP Conference on Photonic Technologies LANE 2018, Fürth, Germany, 3–6 September 2018; Schmidt, M., Vollertsen, F., Dearden, G., Eds.; Bayerisches Laserzentrum GmbH: Erlangen, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- König, H.; Lell, A.; Ali, M.; Stojetz, B.; Eichler, C.; Peter, M.; Löffler, A.; Strauss, U.; Baumann, M.; Balck, A.; et al. Blue 450 nm high power semiconductor continuous wave laser bars exceeding rollover output power of 80 W. In High-Power Diode Laser Technology XVI, Proceedings of the SPIE LASE 2018, San Francisco, CA, USA, 27 January–1 February 2018; Zediker, M.S., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; Volume 10514, ISBN 978-1-510615-13-7. [Google Scholar]
- Baumann, M.; Balck, A.; Malchus, J.; Chacko, R.V.; Marfels, S.; Witte, U.; Dinakaran, D.; Ocylok, S.; Weinbach, M.; Bachert, C.; et al. 1000 W blue fiber-coupled diode-laser emitting at 450 nm. In High-Power Diode Laser Technology XVII, Proceedings of the SPIE LASE 2019, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–7 February 2019; Zediker, M.S., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019; Volume 10900, p. 3. ISBN 9781510624429. [Google Scholar]
- Zediker, M.S.; Fritz, R.D.; Finuf, M.J.; Pelaprat, J.M. Laser welding components for electric vehicles with a high-power blue laser system. J. Laser Appl. 2020, 32, 22038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Miyagi, M.; Okamoto, S. Fundamental study on welding properties of 515 nm green laser. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Congress on Laser Materials Processing, Laser Microprocessing and Nanomanufacturing, San Diego, CA, USA, 19–23 October 2014; Laser Institute of America, Ed.; Laser Institute of America: Orlando, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 458–462, ISBN 978-1-940168-02-9. [Google Scholar]
- Engler, S. Laserstrahlschweißen von Kupferwerkstoffen Mit Brillanten Strahlquellen im Infraroten und Grünen Wellenlängenbereich. Ph.D. Thesis, RWTH Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Britten, S.W.; Schmid, L.; Molitor, T.; Rütering, M. Blue high-power laser sources for processing solutions in e-mobility and beyond. Procedia CIRP 2020, 94, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, H.-J.; Gudat, W.; Kunz, C. Optical Constants from the Far Infrared to the X-ray Region: Mg, Al, Cu, Ag, Au, Bi, C, and Al2O3. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1975, 65, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otter, M. Optische Konstanten massiver Metalle. Z. Physik 1961, 161, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otter, M. Temperaturabhängigkeit der optischen Konstanten massiver Metalle. Z. Physik 1961, 161, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenreich, H.; Philipp, H.R. Optical Properties of Ag and Cu. Phys. Rev. 1962, 128, 1622–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.B.; Christy, R.W. Optical Constants of the Noble Metals. Phys. Rev. B 1972, 6, 4370–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comins, N.R. The optical properties of liquid metals. Philos. Mag. 1972, 25, 817–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, J.N. Infra-red measurements of the optical constants of liquid silver. Philos. Mag. 1960, 5, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, Y.; Wada, T. Effect of Temperature upon the Reflectivity of Copper, Silver and Gold. Sci. Pap. Inst. Phys. Chem. Res. 1934, 25, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Beaglehole, D. Optical properties of copper and gold in the vacuum ultra-violet. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1965, 85, 1007–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, H.-J.; Gudat, W.; Kunz, C. Optical Constants from the Far Infrared to the X-ray Region: Mg, Al, Cu, Ag, Au, Bi, C, and Al2O3. DESY SR-74/4. 1974. Available online: https://refractiveindex.info/download/data/1974/Hagemann%201974%20-%20DESY%20report%20SR-74-7.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2022).
- Johnson, P.; Christy, R. Optical constants of transition metals: Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, and Pd. Phys. Rev. B 1974, 9, 5056–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spisz, E.W.; Weigand, A.J.; Bowman, R.L.; Jack, J.R. Solar Absorptances and Spectral Reflectances of 12 Metals for Temperatures Ranging from 300 to 500 K; NASA TN D-5353; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1969.
- Ordal, M.A.; Long, L.L.; Bell, R.J.; Bell, S.E.; Bell, R.R.; Alexander, R.W.; Ward, C.A. Optical properties of the metals Al, Co, Cu, Au, Fe, Pb, Ni, Pd, Pt, Ag, Ti, and W in the infrared and far infrared. Appl. Opt. 1983, 22, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.C. Optical properties of liquid metals at high temperatures. Philos. Mag. 1969, 20, 1115–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordal, M.A.; Bell, R.J.; Alexander, R.W.; Long, L.L.; Querry, M.R. Optical properties of fourteen metals in the infrared and far infrared: Al, Co, Cu, Au, Fe, Pb, Mo, Ni, Pd, Pt, Ag, Ti, V, and W. Appl. Opt. 1985, 24, 4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D.W.; Hunter, W.R. Comments on the Optical Constants of Metals and an Introduction to the Data for Several Metals. In Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids I; Palik, E.D., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 275–367. ISBN 0125444206. [Google Scholar]
- Babar, S.; Weaver, J.H. Optical constants of Cu, Ag, and Au revisited. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dold, B.; Mecke, R. Optische Eigenschaften von Edelmetallen, Übergangsmetallen und deren Legierungen im Infrarot. Optik 1965, 22, 435–446. [Google Scholar]
- Shiles, E.; Sasaki, T.; Inokuti, M.; Smith, D.Y. Self-consistency and sum-rule tests in the Kramers-Kronig analysis of optical data: Applications to aluminum. Phys. Rev. B 1980, 22, 1612–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.Y.; Shiles, E.; Inokuti, M. The Optical Properties of Metallic Aluminum. In Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids I; Palik, E.D., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 369–408. ISBN 0125444206. [Google Scholar]
- Mathewson, A.G.; Myers, H.P. Optical absorption in aluminium and the effect of temperature. J. Phys. F Met. Phys. 1972, 2, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalenskii, A.V.; Zvekov, A.A. Temperature dependences of the optical properties of aluminum nanoparticles. Tech. Phys. Lett. 2017, 43, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liljenvall, H.G.; Mathewson, A.G.; Myers, H.P. The temperature dependence of the optical constants of aluminium. Solid State Commun. 1971, 9, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Nordine, P.C. Optical properties of liquid aluminum in the energy range 1.2–3.5 eV. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 47, 11780–11787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Nordine, P.C. Analysis of the optical properties of liquid aluminum. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 48, 4130–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, L.X.; Klepeis, J.E.; Streitz, F.H. Calculation of optical absorption in Al across the solid-to-liquid transition. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havstad, M.A.; McLean, W.; Self, S.A. Apparatus for the measurement of the optical constants and thermal radiative properties of pure liquid metals from 0.4 to 10 μm. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1993, 64, 1971–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dausinger, F. Strahlwerkzeug Laser: Energieeinkopplung und Prozesseffektivität; Teubner: Stuttgart, Germany, 1995; ISBN 3-519-06217-8. [Google Scholar]
- Akashev, L.A.; Kononenko, V.I. Optical Properties of Liquid Aluminum and Al-Ce Alloy. High Temp. 2001, 39, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüttner, B. Optical properties of polyvalent metals in the solid and liquid state: Aluminium. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1994, 6, 2459–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, L.G.; Tangherlini, F.R. Optical Constants of Silver, Gold, Copper, and Aluminum. II. The Index of Refraction n. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1954, 44, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Yugawa, K.J.; Nordine, P.C. Optical properties of liquid nickel and iron. Phys. Rev. B 1997, 55, 8201–8206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, J.H.; Colavita, E.; Lynch, D.W.; Rosei, R. Low-energy interband absorption in bcc Fe and hcp Co. Phys. Rev. B 1979, 19, 3850–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shvarev, K.M.; Gushchin, V.S.; Baum, B.A. Effect of Temperature on the Optical Properties of Iron. High Temp. 1978, 16, 441–446. [Google Scholar]
- Seban, R.A. The Emissivity of Transition Metals in the Infrared. J. Heat Transf. 1965, 87, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gushchin, V.S.; Shvarev, K.M.; Baum, B.A.; Gel’d, P.V. Influence of composition on optical properties and electronic characteristics of Fe-Ni alloys at high temperatures. Sov. Phys. J. 1978, 21, 882–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, J.H.; Krafka, C.; Lynch, D.W.; Koch, E.E. Optical Properties of Metals, Pt. 1: The Transition Metals; Fachinformationszentrum Energie, Physik, Mathematik: Karlsruhe, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Moravec, T.J.; Rife, J.C.; Dexter, R.N. Optical constants of nickel, iron, and nickel-iron alloys in the vacuum ultraviolet. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 3297–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D.W.; Hunter, W.R. An Introduction to the Data for Several Metals. In Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids II.; Palik, E.D., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998; pp. 341–420. ISBN 0-12-544422-2. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, J.H.; Krafka, C.; Lynch, D.W.; Koch, E.E. Optical Properties of Metals. Pt. 2: Noble Metals, Aluminium, Scandium, Yttrium, the Nalthanides and the Actinides (0.1 Hv 500 ev); Fachinformationszentrum Energie, Physik, Mathematik: Karlsruhe, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, H.E.; Silver, M.; Ashley, E.J. Infrared Reflectance of Aluminum Evaporated in Ultra-High Vacuum. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1963, 53, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endriz, J.G.; Spicer, W.E. Study of Aluminum Films. I. Optical Studies of Reflectance Drops and Surface Oscillations on Controlled-Roughness Films. Phys. Rev. B 1971, 4, 4144–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvarev, K.M.; Gushchin, V.S.; Baum, B.A.; Gel’d, V.P. Optical Constants of Iron Alloys with Carbon in the Temperature Interval 20–1600 °C. High Temp. 1979, 17, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- DIN Deutsches Institut für Normung e., V. Grundlagen der Meßtechnik b—Teil 3: Auswertung von Messungen Einer Einzelnen Meßgröße, Meßunsicherheit; Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 1996; (DIN 1319-3:1996-05). [Google Scholar]
- Rakić, A.D.; Djurišić, A.B.; Elazar, J.M.; Majewski, M.L. Optical properties of metallic films for vertical-cavity optoelectronic devices. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dausinger, F.; Shen, J. Energy Coupling Efficiency in Laser Surface Treatment. ISIJ Int. 1993, 33, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gámez, B.; Ocaña, J.L. A theoretical method for the calculation of frequency- and temperature-dependent interaction constants applicable to the predictive assessment of laser materials processing. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2000, 33, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, D.L.; Hodgkin, V.A. Wavelength and Temperature Dependence of the Absolute Reflectance of Metals at Visible and Infrared Wavelengths. In Laser Induced Damage in Optical Materials 1980, Proceedings of the Twelfth Symposium on Optical Materials for High Power Lasers, Boulder, CO, USA, 30 September–1 October 1980; Bennett, H.E., Ed.; American Society for Testing & Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1981; pp. 190–200. ISBN 978-0-8031-4500-9. [Google Scholar]
- Minissale, M.; Pardanaud, C.; Bisson, R.; Gallais, L. The temperature dependence of optical properties of tungsten in the visible and near-infrared domains: An experimental and theoretical study. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 455601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnold, G.S. Absorptivity of several metals at 10.6 μm: Empirical expressions for the temperature dependence computed from Drude theory. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schillé, J.-P.; Guo, Z.; Saunders, N.; Miodownik, A.P. Modeling Phase Transformations and Material Properties Critical to Processing Simulation of Steels. Mater. Manuf. Processes 2011, 26, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, K.; Fabbro, R.; Muller, M. Experimental determination of temperature threshold for melt surface deformation during laser interaction on iron at atmospheric pressure. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 435402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawahito, Y.; Matsumoto, N.; Abe, Y.; Katayama, S. Laser absorption characteristics in high-power fibre laser welding of stainless steel. Weld. Int. 2013, 27, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, B. Fermi Surface and Energy Bands of Copper. Phys. Rev. 1962, 125, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, T.; Berger, P.; Weber, R.; Hügel, H.; Heider, A.; Stritt, P. Analytical expressions for the threshold of deep-penetration laser welding. Laser Phys. Lett. 2015, 12, 56002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arata, Y.; Maruo, H.; Miyamoto, I. Application of Laser Material Processing—Heat Flow in Laser Hardening; IIW Doc. IV-241-78, IIW Doc. 212-436-78; International Inst. of Welding: Genoa, Italy, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Price, D.J. The temperature variation of the emissivity of metals in the near infra-red. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1947, 59, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchi, C.; Hiernaut, J.P.; Hyland, G.J. Emissivity X Points in Solid and Liquid Refractory Transition Metals. Metrologia 1992, 29, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagran, C.; Pottlacher, G.; Rink, M.; Bauer, W. Spectral Emissivities and Emissivity X-Points of Pure Molybdenum and Tungsten. Int. J. Thermophys 2005, 26, 1001–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosei, R.; Lynch, D.W. Thermomodulation Spectra of Al, Au, and Cu. Phys. Rev. B 1972, 5, 3883–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stubbs, C.M.; Prideaux, E.B.R. A Spectro-Photometric Comparison of the Emissivity of Solid and Liquid Gold at High Temperatures with that of a Full Radiator. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1912, 87, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, H.; Ward, L. The Spectral Emissivities of Iron, Nickel and Cobalt. Proc. Phys. Soc. B 1952, 65, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, D. The Absorption of Laser Light by Rough Metal Surfaces. Ph.D. Thesis, Luleå University of Technology, Luleå, Sweden, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hummel, M.; Schöler, C.; Gillner, A. Metallographic Comparison for Laser Welding of Cu-ETP and CuSn6 with Laser Beam Sources of 515 nm and 1030 nm Wavelength. In Enhanced Material, Parts Optimization and Process Intensification; Reisgen, U., Drummer, D., Marschall, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 14–28. ISBN 978-3-030-70331-8. [Google Scholar]
- Schöler, C.; Nießen, M.; Schulz, W. Numerical Investigation of Keyhole Depth Formation in Micro Welding of Copper with 1030 nm and 515 nm Laser Radiation. In Enhanced Material, Parts Optimization and Process Intensification; Reisgen, U., Drummer, D., Marschall, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 29–39. ISBN 978-3-030-70331-8. [Google Scholar]
- Schöler, C.; Nießen, M.; Hummel, M.; Olowinsky, A.; Gillner, A.; Schulz, W. Modeling and simulation of laser micro welding. In Proceedings of the Lasers in Manufacturing Conference 2019, Munich, Germany, 24–27 June 2019; Reisgen, U., Schmidt, M., Zäh, M.F., Rethmeier, M., Eds.; German Scientific Laser Society (WLT e.V.): Munich, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, V.; Hugger, F.; Roth, S.; Schmidt, M. Influence of Temperature and Wavelength on Optical Behavior of Copper Alloys. AMM 2014, 655, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, A.; Heider, A.; Schuster, R.; Weber, R.; Graf, T. Benefits from combining laser beams with different wavelengths (green and IR) for copper welding. In Proceedings of the 29th International Congress on Applications of Lasers & Electro-Optics (ICALEO), Anaheim, CA, USA, 26–30 September 2010; Laser Institute of America, Ed.; Laser Institute of America: Orlando, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 540–546, ISBN 978-0-912035-61-1. [Google Scholar]
- Blom, A.; Dunias, P.; van Engen, P.; Hoving, W.; de Kramer, J. Process spread reduction of laser microspot welding of thin copper parts using real-time control. In Photon Processing in Microelectronics and Photonics II, Proceedings of the High-Power Lasers and Applications, San Jose, CA, USA, 25 January 2003; Pique, A., Sugioka, K., Herman, P.R., Fieret, J., Bachmann, F.G., Dubowski, J.J., Hoving, W., Washio, K., Geohegan, D.B., Traeger, F., et al., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2003; p. 493. [Google Scholar]
- Amorosi, S. Laser micro-spot welding of copper by real-time process monitoring. Ph.D. Thesis, École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hummel, M.; Külkens, M.; Schöler, C.; Schulz, W.; Gillner, A. In situ X-ray tomography investigations on laser welding of copper with 515 and 1030 nm laser beam sources. J. Manuf. Processes 2021, 67, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, E.; Huber, R.; Stolzenburg, C.; Killi, A. Sputter-free and Uniform Laser Welding of Electric or Electronical Copper Contacts with a Green Laser. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Photonic Technologies LANE 2014, Fürth, Germany, 8–11 September 2014; Schmidt, M., Vollertsen, F., Merklein, M., Eds.; Bayerisches Laserzentrum GmbH: Erlangen, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsayer, R.M.; Engler, S.; Schmitz, G. New approaches for highly productive laser welding of copper materials. In Proceedings of the 1st International Electric Drives Production Conference (EDPC), Nürnberg, Germany, 28–29 September 2011; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 69–73, ISBN 978-1-4577-1370-5. [Google Scholar]
- Dold, E.-M.; Kaiser, E.; Klausmann, K.; Pricking, S.; Zaske, S.; Brockmann, R. High-performance welding of copper with green multi-kW continuous wave disk lasers. In High-Power Laser Materials Processing: Applications, Diagnostics, and Systems VIII, Proceedings of the SPIE 2019, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–7 February 2019; Kaierle, S., Heinemann, S.W., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019; Volume 10911, p. 28. ISBN 9781510624641. [Google Scholar]
- Ly, S.; Rubenchik, A.M.; Khairallah, S.A.; Guss, G.; Matthews, M.J. Metal vapor micro-jet controls material redistribution in laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khairallah, S.A.; Anderson, A.T.; Rubenchik, A.; King, W.E. Laser powder-bed fusion additive manufacturing: Physics of complex melt flow and formation mechanisms of pores, spatter, and denudation zones. Acta Mater. 2016, 108, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leung, C.L.A.; Marussi, S.; Towrie, M.; del Val Garcia, J.; Atwood, R.C.; Bodey, A.J.; Jones, J.R.; Withers, P.J.; Lee, P.D. Laser-matter interactions in additive manufacturing of stainless steel SS316L and 13-93 bioactive glass revealed by in situ X-ray imaging. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 24, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, M.J.; Guss, G.; Khairallah, S.A.; Rubenchik, A.M.; Depond, P.J.; King, W.E. Denudation of metal powder layers in laser powder bed fusion processes. Acta Mater. 2016, 114, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bidare, P.; Bitharas, I.; Ward, R.M.; Attallah, M.M.; Moore, A.J. Fluid and particle dynamics in laser powder bed fusion. Acta Mater. 2018, 142, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finuf, M.; Fritz, R.; Boese, E.; Zediker, M. Metal 3d printing using high brightness blue laser systems. In High-Power Diode Laser Technology XX, Proceedings of the SPIE LASE 2022, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–27 January 2022; Zediker, M.S., Zucker, E.P., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2022; Volume 11983, p. 30. ISBN 9781510648371. [Google Scholar]
- Wagenblast, P.; Myrell, A.; Thielmann, M.; Scherbaum, T.; Coupek, D. Additive manufacturing with green disk lasers. In Laser 3D Manufacturing VII, Proceedings of the SPIE LASE 2020, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–6 February 2020; Helvajian, H., Gu, B., Chen, H., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020; Volume 11271, p. 18. ISBN 9781510633056. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, A.E.; Diwakar, P.K.; Harilal, S.S.; Hassanein, A. The role of laser wavelength on plasma generation and expansion of ablation plumes in air. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 143305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weikert, M. Oberflächenstrukturieren Mit Ultrakurzen Laserpulsen; Herbert Utz Verlag: München, Germany, 2006; ISBN 3-8316-0573-4. [Google Scholar]

| IR | ||
|---|---|---|
| Laser power | 969 W | 2986 W |
| Time span until the onset of melting | 0.03 ms ± 0.01 ms | 0.17 ms ± 0.03 ms |
| Time span until the onset of evaporation | 0.50 ms ± 0.03 ms | 1.27 ms ± 0.12 ms |
| Process stability criterion (PSC) value | 2.95 | 0.62 |
| Iron | Aluminum | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green | IR | Green | IR | |
| Laser power | 360 W | 467 W | 1049 W | 1636 W |
| Time span until the onset of melting | 0.06 ms ± 0.01 ms | 0.10 ms ± 0.01 ms | 0.02 ms ± 0.01 ms | 0.09 ms ± 0.01 ms |
| Time span until the onset of evaporation | 0.47 ms ± 0.07 ms | 0.95 ms ± 0.02 ms | 0.74 ms ± 0.06 ms | 2.34 ms ± 0.28 ms |
| Process stability criterion (PSC) value | 1.30 | 1.28 | 5.88 | 3.39 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kohl, S.; Kaufmann, F.; Schmidt, M. Why Color Matters—Proposing a Quantitative Stability Criterion for Laser Beam Processing of Metals Based on Their Fundamental Optical Properties. Metals 2022, 12, 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12071118
Kohl S, Kaufmann F, Schmidt M. Why Color Matters—Proposing a Quantitative Stability Criterion for Laser Beam Processing of Metals Based on Their Fundamental Optical Properties. Metals. 2022; 12(7):1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12071118
Chicago/Turabian StyleKohl, Stefanie, Florian Kaufmann, and Michael Schmidt. 2022. "Why Color Matters—Proposing a Quantitative Stability Criterion for Laser Beam Processing of Metals Based on Their Fundamental Optical Properties" Metals 12, no. 7: 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12071118
APA StyleKohl, S., Kaufmann, F., & Schmidt, M. (2022). Why Color Matters—Proposing a Quantitative Stability Criterion for Laser Beam Processing of Metals Based on Their Fundamental Optical Properties. Metals, 12(7), 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12071118






