Abstract
Metals stability and corrosion resistance are very important factors that influence the possibility of their applications. In order to study and foresee the behavior of metals during various applications in all kinds of conditions and media, numerous approaches and techniques are developed and applied. Among those techniques, electrochemical measurements nowadays have a dominant role since they are proved to be highly efficient, reliable, fast, relatively low-cost, and easy regarding the preparation and execution of measurements. Besides that, they also provide quite a good amount of data regarding the effect and the mechanism of the reactions that metals interact in. Metals corrosion is reduced by various methods, one of the most frequently used ones is the application of corrosion inhibitors. Usually, organic compounds are studied as potential corrosion inhibitors, and at the moment the focus is on the effect on the environment. Hence, environmentally friendly and non-toxic inhibitors are important research topics. Purines, since they are the group of bioorganic compounds found in numerous biochemical structures such as DNA and RNA, present a very interesting possible solution and are studied as inhibitors of corrosion for copper, steel, aluminum, etc., as well as for some metal alloys. Data obtained and available up until the present are presented and discussed in this review.
1. Introduction
Metals corrosion significantly contributes to metal loss and the need for replacement of metallic parts and presents potentially a big problem regarding the reliability of metallic vessels, pipes, reactors, and tanks. There are many ways of possible prevention such as alloying, coating, and application of inhibitors either by pretreatment or addition into the corrosive media [1]. Depending on the planned metal application, the way the inhibitor is introduced that fits best is determined. To make a proper inhibitor choice, besides literature survey, theoretical approach, and comparison, it is essential to make proper tests and conduct experimental studies. Numerous techniques are developed, tested, and introduced into corrosion studies; however, electrochemical measurements are one of the most often applied and provide fast, reliable, and exhaustive data. Usually, authors use electrochemical techniques such as different polarization techniques, i.e., potentiodynamic polarization, potentiostatic polarization, cyclic voltammetry, and several others such as polarization resistance determination, electrochemical noise, etc. Open circuit measurements, as the first step in the experimental process, allow presumptions regarding the state of the surface. For instance, a shift of the potential in the positive or negative direction can indicate if some protective layer forms in the presence of organic compounds, or under tested conditions corrosion processes are favored. Potentiodynamic polarization techniques allow the determination of the current density changes, and accompanying processes that take place on the metal surfaces. Current peaks in cyclic voltammetry curves indicate electrochemical reactions and the formation of oxidation or reduction products. In the vicinity of the corrosion potential using the Tafel extrapolation method, it is possible to calculate corrosion current density. Corrosion current density is further used for the calculation of the inhibition efficiency values. The behavior described by potentiostatic measurements is very similar, just that the correlation that is studied is not potential–current, instead it is time–current at a steady potential value. The lower the values of current density, the higher the values of inhibition efficiency. Polarization resistance increase, on the other hand, is directly correlated with the increase in inhibition efficiency. Electrochemical noise measurements are interesting as a noninvasive method that can provide data regarding the mechanism and kinetics of the corrosion processes by monitoring fluctuations of potential and current. Antonijević and Radovanović [2] noticed that, among various other techniques, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) can be used as a method of characterization of protective films formed on copper surfaces. Changes in the structure of the surface layer on the metal induce changes in the parameters, such as impedance and phase angle, so their increase indicates the formation of a layer that protects the surface. According to several review papers published regarding corrosion inhibitors and with special attention devoted to the eco-friendly corrosion inhibitors, they are now quite numerous [3,4,5,6], and purine derivatives present an important class of alkaloids studied as corrosion inhibitors [7]. Xanthines are bioorganic compounds that are a very common constituent of numerous foods and drinks, such as coffee, tea, cocoa, chocolate, etc. Adenine is part of DNA and RNA, purine is found in the metabolic processes in living organisms, and derivatives can be found in pharmaceuticals used for viral treatments [8]. On the other hand, these compounds also have the ability to react and form complexes with metals. The structure of the formed complex depends on the form of metal as well as the form of organic molecules, which, among others, varies with the pH value of the media [9,10]. Inhibitor molecules can be found in the form of a neutral molecule (INH), deprotonated anion (IN), and protonated cation (INH2). The structures of all the organic compounds mentioned in the text are provided in the Supplementary material in Table S1.
According to the data available in the literature, back in 1979, research by Vasseghi and Nobe [11] showed that purine and aminopurine have the potential to inhibit corrosion of iron in sulfuric acid. In 1985, Abdel Aal and Wahdan [12] studied purine as an inhibitor of corrosion of steel in HClO4 solution. Until now, they have been tested as corrosion inhibitors for numerous metals and alloys such as steel [13,14], aluminum [15,16], tin, indium, both pure and in the form of alloys [17,18], titanium [19], Mg alloys [20,21], copper [22,23,24,25], brass [26], nickel [27], and alloys such as Sn-Ag alloy [28] and CoCrMo alloy [29]. Purine compounds exhibit an inhibiting effect toward metal corrosion in various aqueous media but also in hydrocarbon media such as highly refined naphthenic mineral base oil [30]. Due to their origin and characteristics, these compounds are considered potential inhibitors of corrosion of metallic biomaterials in real or simulated body fluids [25,31,32,33,34].
The broad area of possible applications and the characterization of these compounds as environmentally friendly and non-toxic indicate that they should receive adequate attention. In the following text, available data were obtained by electrochemical methods, regarding the application of purine and derivatives as inhibitors of corrosion of copper and brass, steel, and other metals.
2. Discussion
2.1. Copper and Alloys
2.1.1. Chloride Media
The purine compound structure is based on the imidazole and pyrimidine ring, whereas various derivatives contain additional functional groups. According to the survey of literature, most of the research included purine (PU) or adenine (AD), and a significant amount of attention was also dedicated to xanthine compounds, especially caffeine and theophylline, Table S1. The molecular structures of purine and adenine are presented in Figure 1.
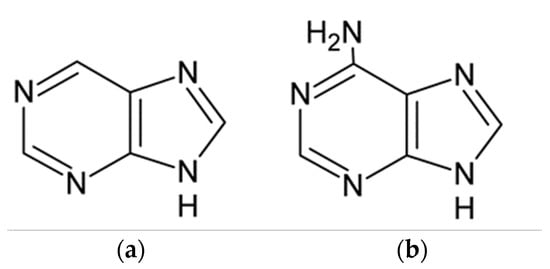
Figure 1.
Molecular structure of (a) purine and (b) adenine.
After a few papers published in the 1980s and 1990s, increasing attention has been devoted to the application of purine and adenine as corrosion inhibitors in the last 15 years. Scendo [22,23,35,36,37] studied their effects on corrosion of copper in different solutions, and in the meantime, other research groups made their contributions, so until now they are studied as copper corrosion inhibitors in solutions containing various corrosive species such as chloride [22,23], sulfate [35,36,38], and nitrate [37]. The studies included electrochemical methods, and the results indicated that these compounds behave as copper corrosion inhibitors.
Scendo [22] used the linear potential sweep technique and, based on the analysis of the data obtained in the Tafel region, it is concluded that corrosion potential shifts towards positive values and current density decreases in solutions containing purine which, according to the changes in Tafel slopes, behaves as a mixed-type inhibitor. He also noticed an increase in polarization resistance and inhibition efficiency with concentration that is connected with the surface coverage increase. According to the electrochemical quartz microbalance in the presence of purine, an increase in the mass of copper specimens is observed due to the adsorption of purine molecules as explained by reactions [22]:
CuCl2− + PUH ↔ (Cu−PU)ads + H+ + 2Cl−
The results can be seen in Table 1 and the mechanism of purine action mechanism is described via formation of adsorbed protective layer on metal surface.

Table 1.
Copper corrosion inhibition efficiency obtained by purine compounds.
Scendo [23] further used the same techniques to analyze the effect of adenine on copper corrosion. Polarization data lead to the conclusion that adenine is a mixed-type inhibitor in this case and the effect increases with its concentration. Electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance showed a mass increase due to adsorption of adenine according to the mechanism described for purine adsorption. The protective layer contains [Cu-C5H4N5]ads, but corrosive species still have the ability to penetrate it to a certain extent. According to the results of these studies, a mechanism of interaction between inhibitor and copper in chloride solution can be proposed, assuming that the dominant form is a neutral molecule. Variations of the mechanism, based on the form in which copper is found, are as follows [22,23]:
Cu + INH − e− ↔ [Cu-IN]ads + H+
CuClads + INH ↔ [Cu-IN]ads + Cl− + H+
nCuCl2− + nINH ↔ (Cu-IN)n + nH+ + 2nCl−
[Cu-IN]ads + (Cu-IN)n ↔ [(Cu-IN)m]ads, where m = n + 1.
Adsorption of purine and adenine is attributed to the formation of the Cu-N bonds or interactions of π electrons of aromatic rings with Cu or electrostatic interactions enhanced by adsorption of negatively charged chloride ions. A more detailed adsorption mechanism is provided later based on new theoretical findings. A comparison of the inhibition efficiency values obtained under the same conditions using purine and adenine, Table 1, showed that overall, adenine provided a better inhibition effect than purine. This fact indicates that the introduction of the amino group leads to an improvement of inhibition characteristics. Also, the inhibition properties of guanine toward copper corrosion in an acidic chloride solution (0.1 M HCl, pH 2) at different temperatures were investigated [42]. The electrochemical and weight loss methods reveal that due to the adsorption of guanine on the copper surface, the attack of aggressive Cl− ions is hindered. Hence, the corrosion rate was reduced. This study showed good inhibitory properties of guanine at 298 K, as well as at 313 K, and 333 K (Table 1). According to the surface-enhanced Raman spectra (SERS) of the copper surface at open circuit potential, the first step in the inhibition mechanism is the chemisorption of a neutral molecule of guanine leading to the formation of a Cu(I)Guanine protective layer. The extracted caffeine from black tea was studied as a copper corrosion inhibitor in a neutral chloride solution [40]. The data collected by electrochemical measurements (Table 1) show good inhibitory properties of caffeine for copper. It was concluded that caffeine is a cathodic type of inhibitor in neutral chloride solutions. Furthermore, the authors had done quantum chemical and molecular dynamic simulations to explain the interactions between inhibitor molecules and the copper surface. Taking into consideration the electron density of caffeine and calculated values for EHOMO (−5.513 eV), ELUMO (−1.947 eV), and ΔE (3.566 eV), it was expected to have a flat-lying adsorption orientation of caffeine on the metal surface via noncovalent interaction. This orientation allows for greater copper coverage and thus provides corrosion protection. Guo et al. [39] studied copper corrosion in more complex chloride media such as alkaline artificial seawater. They chose guanine (G), adenine (A), and hypoxanthine (I), Table S1, as potential corrosion inhibitors. For the study, they applied electrochemical methods such as open circuit potential measurement (OCP), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and potentiodynamic polarization. The analysis of the EIS data, presented in Figure 2, is enabled by the performance of the CNLS (complex non-linear least squares) simulation [43,44,45,46,47]. Behavior during OCP measurements indicated the formation of an adsorbed inhibitor layer. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, Figure 2, showed that the carbonyl group introduced in purine enhances inhibition efficiency to a greater extent than the amino group, so the efficiency followed the order I > G > A. It is concluded that as the radius of the capacitive arc increases with time and there is no diffusion, I and G form a protective compact layer of adsorbed molecules. However, for adenine, the situation is a bit different, indicating an adsorbed layer that only provides protection and diminishes diffusion to a certain extent. According to the potentiodynamic polarization results, all tested inhibitors provide corrosion inhibition and prevent the formation of cuprous oxide. They are all mixed-type inhibitors, whereas G and A influence cathodic processes to a greater extent. Maximum inhibition efficiency is obtained at concentration of 0.1 g/l for I and G and 0.2 g/l for A. The adsorption of the molecules can be explained by the Langmuir adsorption isotherm, and the corresponding values of equilibrium constant and Gibbs free energy of adsorption indicate mixed physical and chemical adsorption and the superior inhibiting effect of I. Theoretical calculations were in agreement with experimental results and adsorption energy of I on Cu(110) surface has the lowest value, also the orientation of molecules on the surface is proposed, and it is parallel for G and I, and adenine is adsorbed inclined to the copper surface. Once more the difference between G and I on the one side and A on the other is accentuated.
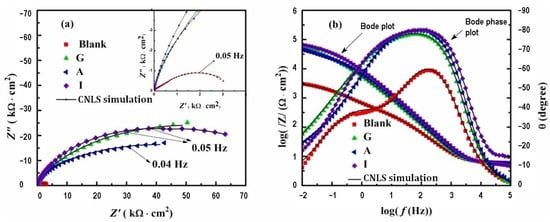
Figure 2.
EIS of copper in alkaline artificial seawater without and with various inhibitors of 0.1 g/L: (a) Nyquist plots, (b) Bode plots. Reprinted with permission from ref. [39]. Copyright 2022 Elsevier.
Corrosion of copper in synthetic seawater is also studied by Petrović Mihajlović et al. [25]. The results of the potentiodynamic polarization study can be seen in Figure 3. In order to investigate the effect of the increase in molecular size and weight of the inhibitor and the introduction of functional groups into its structure, Figure 4, structurally similar compounds imidazole, purine, adenine, and 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP), Table S1, were tested. As usual, the increasing complexity of the molecule structure is assumed to lead to the increase in inhibition efficiency that can be obtained by that compound. In this case, that hypothesis is true, and the inhibition efficiency followed the trend: imidazole < purine < adenine < 6-benzylaminopurine. The increase in inhibitor concentration and the addition of amino and benzyl group into the purine molecule led to the decrease in current density and increase in inhibition efficiency.
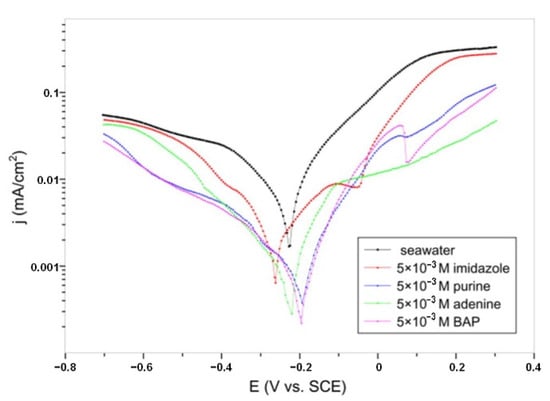
Figure 3.
The potentiodynamic polarization curves of copper recorded in blank seawater and seawater containing 5 × 10−3 M imidazole, purine, adenine, and 6-benzylaminopurine, respectively. Reprinted with permission from ref. [25]. Copyright 2022 Elsevier.
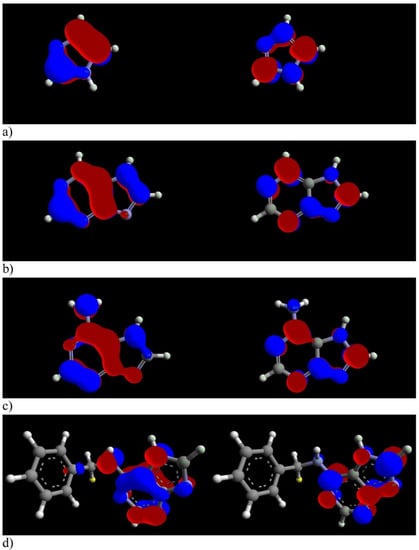
Figure 4.
Distribution of HOMO (left) and LUMO (right) of (a) imidazole, (b) purine, (c) adenine and (d) 6-benzylaminopurine. Reprinted with permission from ref. [25]. Copyright 2022 Elsevier.
However, at higher potential values, it is noticed that adenine provided the most reliable protection. The interaction between the tested compounds and copper in seawater is also observed by OCP measurements. The results lead to the assumption that they influence both cathodic and anodic processes on the copper surface, since no clear trend in the potential shift could be determined. They act via adsorption on the copper surface and several adsorption isotherms are tested: Langmuir, Freundlich, kinetic-thermodynamic, Temkin and Flory–Huggins, and Langmuir adsorption isotherm proved to be the best fit. Some more details regarding the interaction between the compounds and copper surface can be seen from quantum chemical calculations. Optimized structures and distributions of HOMO and LUMO can be seen in Figure 4. The lower value of ΔE (ΔE = ELUMO − EHOMO) and a decrease in global hardness (η) or an increase in dipole moment (μ) indicate that it can be expected that the compound should be considered a better corrosion inhibitor.
Further study of the metal-inhibitor interactions regarding the studied compounds was conducted by Kumar et al. [48] using density functional theory (DFT) and reactive force fields (ReaxFF). The adsorption of imidazole, purine, adenine, and 6-benzylaminopurine on the Cu (111) surface was simulated as well as the interactions of the surface with molecules of inhibitors. All applied quantum chemical calculations provided results that were in good agreement with each other as well as with experimental findings. It is concluded that all these compounds adsorb on the Cu (111) surface, but the mechanisms differ. According to the charge distribution, adenine adsorbs via electrostatic and van der Waal’s interactions. On the other hand, imidazole, purine, and 6-benzylaminopurine form Cu-N covalent bonds alongside weak van der Waal’s and H-Cu interactions. The energy corresponding to the interaction of inhibitors with the Cu surface increases from imidazole towards 6-benzylaminopurine. The mode of adsorption is also different for adenine in comparison with other compounds, i.e., the adenine molecule is oriented parallel to the surface while other compounds show a perpendicular orientation.
Previously, authors Yan et al. [49] conducted theoretical calculations, quantum chemical calculations, and molecular dynamic simulation, and concluded that the inhibition efficiency of three purine derivatives that adsorb parallel to the surface follows the order adenine < 2-amino-6-thiol-9H-purine < 2,6-dithiol-9H-purine, Table S1. However, these results also had to be proved, by agreement, with the experimental findings. Besides, Hadisaputra et al. [50] tried to explain the ability of caffeine and its derivatives (theophylline and theobromine) to protect copper from dissolution using theoretical density functional theory (DFT), and Monte Carlo simulation studies. The molecular structure of the used methylxanthines is illustrated in Figure 5. The applied software enabled calculation and comparison of several parameters corresponding to the three tested compounds, i.e., the energy of the highest occupied (EHOMO) and the lowest unoccupied (ELUMO) molecular orbitals, the electron affinity (A), the ionization potential (I), the absolute electronegativity (χ), softness (σ), hardness (η) and the fraction of electron transferred (ΔN). According to the EHOMO values (caffeine > theobromine > theophylline), caffeine should provide the best protection compared to theophylline and theobromine. This is accompanied by a change in the values of ionization potential. Based on the Monte Carlo simulation, the authors showed the most stable low energy adsorption configuration of the tested xanthines in the Cu (111)/100H2O system. According to the determined length (<3.50 A) of the shortest active side bond of the inhibitor with copper, it is assumed that a protective layer is formed on the metal surface through electron transfer between the inhibitor and d orbitals of copper and van der Waal’s interactions. Moreover, the adsorption energy distribution of caffeine, theobromine, and theophylline confirmed that caffeine should provide the highest degree of protection, followed by theobromine and theophylline.
Figure 5.
Molecular structure of methylxanthines.
Ogunyemi et al. [51] included quite a broad selection of the purine derivatives in the theoretical calculations. They studied the structure and characteristics of 2,6-dithiopurine, 2,6-diaminopurine, caffeine, xanthine, hypoxanthine, adenine, adenosine, guanine, guanosine, theophylline, ally-theophylline, and propargyl-theophylline, Table S1. Quantum chemical parameters calculated were energies of the highest occupied (EHOMO) and the lowest unoccupied (ELUMO) molecular orbital, the difference between ELUMO and EHOMO (ΔE), ionization potential (IP), and the electron affinity (EA), absolute hardness (η) and absolute electronegativity (χ), number of transferred electrons (ΔN), electrophilicity index (ω), polarizability (α), and dipole moment (μ). Those values were compared with the inhibition efficiency values found in the literature and obtained by experimental work. However, there is no strict and consistent correlation between those parameters and inhibition efficiencies. Mulliken population density analysis and Fukui indices were also obtained and presented. Quantitative structure-property relationships (QSPRs) were used to predict the theoretical inhibition efficiency and the following model that combines some quantum chemical parameters [51]:
%IE = −170 + 66.0 × η − 20.64 × ELUMO + 1.2 × α
Provided good correlation with the experimental data as can be seen in Table 2:

Table 2.
Comparison of the experimental and calculated values of inhibition efficiency for purine derivatives. Data from [51].
2.1.2. Sulfate and Other Media
Sulfate ions are also known as aggressive species that promote copper corrosion. Hence, studies are being conducted focused on the possibility of using purine compounds as inhibitors of copper corrosion in solutions containing these ions. Electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance experiments, potentiodynamic polarization measurements, and chronoamperometry were used to study the effects of purine and adenine on the corrosion of copper in nearly neutral sulfate solutions [35]. The cathodic reaction in neutral sulfate solution is:
2H2O + 2e− ↔ H2 + 2OH−
While without an inhibitor, the anodic reaction mechanism includes the following reactions. Firstly, dissolution occurs:
Cu − e− ↔ Cu+surf
When passivation takes place, copper oxides and hydroxides are formed and copper oxidizes from Cu(I) to Cu(II) that is built in the surface layer.
2Cu + H2O − 2e− ↔ Cu2O + 2H+
Cu2O + H2O − 2e− ↔ 2CuO + 2H+
Cu2O + 3H2O − 2e− ↔ 2Cu(OH)2 + 2H+
In these reactions, H+ ions are released that decrease the pH value and further promote dissolution. However, in sulfate solution in the presence of an inhibitor, copper ions react with inhibitor molecules adsorbed on the electrode surface, forming a protective layer according to the equation:
Cu+ + INHads ↔ (Cu-IN)ads + H+
But, according to the literature data [35], at higher potential, further oxidation of copper occurs:
Cu+surf − e− ↔ Cu2+sol
Due to adsorption of purine and adenine on a copper surface, current density decreases, which are proved by both potentiodynamic and potentiostatic polarization. Electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance measurements proved the adsorption since the mass loss is considerably lower in the presence of inhibitors. The effect gets more pronounced with the increase in concentration, and the best results are obtained in the solution containing 1 × 10−2 M adenine. Following this study, Scendo [36] studied the spontaneous dissolution of copper in nearly neutral and acidic sulfate solutions and the effects of purine and adenine on that process. The results are in good agreement, but one should bear in mind that the inhibitor molecule is dominantly protonated, in acidic solutions, and adsorbs directly on the Cu surface [36]:
Cu + INH2+ − e− ↔ [Cu-IN]ads + 2H+
Adenine is, in this case, also more efficient. All the values of inhibition efficiency obtained by the application of purine compounds on copper, which are summarized in Table 1, and based upon the analysis of the ones corresponding to sulfate solutions several conclusions can be made. It is obvious that possible inhibition efficiency depends on the pH value. The highest values of inhibition efficiency are obtained in neutral media, whereas they also provide good protection in acidic [35] and weakly alkaline media [38]. Their adsorption is described by the Langmuir adsorption isotherm [23,26,35,36,37,38]. Purine and adenine influence cathodic and anodic reactions, so they are classified as mixed-type inhibitors. The same conclusions are reached in acidic NaNO3 solutions [37], where both compounds inhibited copper corrosion, but adenine to a greater extent. The results of chronoamperometric measurements confirmed that both compounds added to the solution led to a decrease in current values as a result of the formation of a compact protective layer on the surface.
Radovanovic et al. [26] used potentiodynamic polarization and chronoamperometry measurements to prove that purine can inhibit brass corrosion in sulfate solutions as well. According to the electrochemical measurements results presented in Figure 6 and Table 1, purine showed better corrosion protection in weakly alkaline solutions. The effect is also due to the adsorption of purine on the electrode surface. Adsorption leads to the blocking of the surface-active sites and inhibition of both anodic and cathodic processes. Protective layer formation is observed in the data collected by chronoamperometry as well.
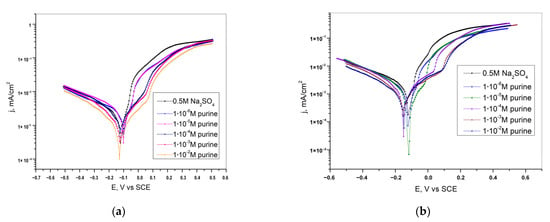
Figure 6.
Polarization curves of brass in (a) neutral and (b) alkaline 0.5 M Na2SO4 with the addition of purine. Scan rate 1 mV/s. Reprinted from [26].
Three xanthine derivatives (caffeine, theobromine, and theophylline) were examined as inhibitors of copper corrosion in an aerated 0.1 M H2SO4 solution [41]. Researchers concluded that caffeine protects copper, while theobromine and theophylline accelerate the corrosion rate under these conditions. Potentiodynamic polarization curves of copper indicated that caffeine reduced densities of both anodic and cathodic current. The lower cathodic current density is due to the blocking of cathodic active sites on the copper surface. On the other side, the decrease in current density in the anode part of the curve is because of the formation of Cu2+-caffeine complex that is adsorbed on the metal surface. The wettability surface analysis confirmed the formation of a hydrophobic protective layer preventing copper dissolution. The authors [41] tested Langmuir, Temkin, and Frumkin adsorption isotherms to see which one would be the best fit for the obtained data. It is concluded that caffeine adsorption on the surface of copper in sulfuric acid solution can be described by the Temkin adsorption isotherm.
Some studies are conducted in order to test the suitability of application of purine compounds in more specific conditions. For instance, Zeng et al. [24] studied the ability of adenine (AD) to protect copper from corrosion in chemical mechanical polishing. The open circuit potential measurements revealed an increase in potential values with the increase in adenine concentration. This is attributed to the formation of a dense layer on the surface and the shift of the oxidation reactions towards higher potentials. Potentiodynamic polarization measurements were conducted in the reference slurry containing 1 wt % glycine and 0.3 wt % H2O2 without and with the addition of adenine. According to the behavior of the Tafel slopes in the presence of adenine, the authors assumed that AD had a major influence on the anodic reaction. The inhibitory effect was explained by the molecular adsorption of AD on the surface of Cu, Cu2O, and CuO described by the following reaction mechanism, with the participation of the intermediary hydroxyl radical (OH*) species [24]:
2Cu + H2O2 = Cu2O + H2O
Cu2O + H2O2 = 2CuO + H2O
Cu + H2O2 = Cu+ + OH− + OH*
Cu+ + OH* = Cu2+ + OH−
CuO + H2O = Cu(OH)2
Cu(OH)2 = Cu2+ + 2OH−
Cu2+ + 2H2NCH2COO− = (H2NCH2COO)2Cu
Hara et al. [52] showed that adenine and hypoxanthine are able to protect copper from corrosion during annealing that produces conditions of high temperature and humidity. Their actions are compared to benzotriazole (BTA, Table S1) and it is concluded that they can efficiently inhibit copper oxidation with no environmental impact and that their protective layers are thinner than BTA. On the other hand, Jakeria et al. [53] tried to use adenine as an inhibitor of corrosion of copper in palm biodiesel, but BTA was more efficient.
2.1.3. Physiological Media
Besides all the previously described applications, the characteristics of purine compounds that classify them as non-toxic inspired investigations for potential applications in human organisms. Alvarez et al. [31] used purine solutions for pretreatment of copper surfaces in order to test their suitability to decrease “burst release” of copper used in intrauterine birth control devices. The authors chose synthetic uterine fluid (SUF) as a test medium that mainly contains chlorides, and smaller amounts of bicarbonates, and phosphates. According to the potentiodynamic and potentiostatic measurements, pretreatment in chloride solution containing 0.01 or 0.001 M purine provided excellent inhibition efficiency. The increase in immersion time provides significant improvement when a lower concentration is used, whereas in the presence of 0.01 M the effect is very small. The following study [32] included 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) and pterin (PT), Table S1. The action of those compounds includes complex adsorption reactions including inhibitors as well as chloride ions and water molecules [32]:
Cu(PT)ad + Cl−→Cu(Cl)ad + PT + e−
Cu(6-MP)ad + Cl−→Cu(Cl)ad + 6-MP + e−
Cu + H2O↔Cu(OH)ad + H+ + e−
Cu + Cl−↔Cu(Cl)ad + e−
As a result, copper release is optimized in order to provide a continuous contraception effect. Alonso et al. [33] devoted more attention to the process of purine adsorption on the surface of copper and its application as a pretreatment in order to reduce copper “burst release”. They used quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) to directly monitor mass change due to potential purine adsorption and a voltamperometric technique to record cathodic polarization curves to observe the effect of pretreatment. It is interesting to note that a greater increase in mass is noticed in the presence of chloride ions, and in the presence of a lower concentration of purine. The authors proposed an explanation including different reaction mechanisms. In the presence of a lower concentration of purine and chloride ions, the formation of Cu(I) is favored, and PU molecules replace adsorbed chlorides, forming a Cu(I)-purine complex. The presence of a high concentration of purine leads to blocking of the surface and purine adsorbs on the pure copper surface. The difference in the composition of the layer formed on the copper surface is confirmed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) measurements. In the presence of a high purine concentration, 1 × 10−2 M − 1 × 10−3 M, purine chemisorption on the pure copper surface occurs, and (Cu(0)-PU)ads forms. When the purine concentration is lower, such as 1 × 10−4 M, [Cu(I)-PU]ads forms and there are also compounds of copper and chlorine.
There is also research focused on the possibility on inhibiting copper corrosion in simulated blood plasma (BM3) using adenine (AD), and 2,6-diaminopurine (DAP) [34], Table S1. Cyclic voltammetry, open circuit potential measurements, potentiodynamic polarization, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy were the basis of the study that was substantiated by theoretical and surface analysis. The appearance of synergistic action of the mentioned inhibitors with potassium sorbate (PS) was also investigated (Figure 7). Potassium sorbate was chosen since it is a food additive and preservative often used, and hence it is safe to introduce into the human organism [54,55]. Chronoamperometric measurements were included in pretreatment conducted in BM3 solution containing 1 × 10−3 M AD/DAP + 1 mass% PS at the potential of 0.000 V vs. SCE for 10 min. Linear voltammetry results show a decrease in the corrosion current density, indicating the inhibiting effect of adenine, 2,6-diaminopurine, and their combination with potassium sorbate. Cyclic voltammetry results show that current peaks corresponding to the reactions of copper oxidation are diminished, and in some cases, there was a shift of peak potential in the positive direction. In the presence of 0.01 M purine compounds, peaks are completely lost due to organic molecules adsorption that protects the copper surface from oxidation [23,25,33]. It is proposed that at lower potentials Cu(I)-AD/Cu(I)-DAP complexes form and at higher potential complexes Cu(II)-AD/Cu(II)-DAP [25,56]. EIS results show that the process is controlled by charge-transfer and diffusion through the surface layer that in the presence of AD or DAP inhibits copper oxidation, which is in diagrams illustrated as the increase in semicircle diameter and impedance values. The adsorption of inhibitor molecules on the copper surface was also confirmed by scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDS). The adsorption according to the Langmuir adsorption isotherm based on the Gibbs free energy of adsorption and the distribution of the highest occupied and lowest unoccupied molecular orbitals indicates physical adsorption of AD and DAP.
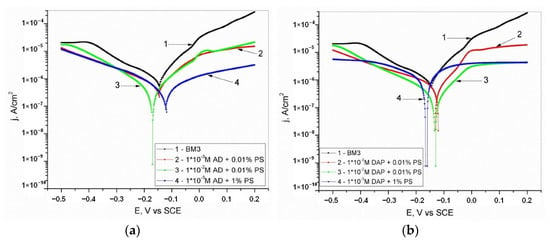
Figure 7.
Potentiodynamic polarization curves of copper recorded in BM3 solution with the addition of (a) adenine and potassium sorbate or (b) 2,6-diaminopurine and potassium sorbate, scan rate 1 mV/s. Reprinted from [34].
2.2. Steel and Iron
2.2.1. Chloride Media
In addition to copper, purine, and purine derivatives have also been tested as steel corrosion inhibitors. Numerous researchers have conducted their investigations in chloride medium [13,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64].
Yan et al. [57] performed experiments using purine derivatives (adenine, guanine, 2,6-dithiopurine, 2,6-diaminopurine, and 6-thioguanine, Table S1) to decrease the dissolution of mild steel in HCl solution. The obtained results are summarized in Table 3. Besides electrochemical methods, the authors utilized quantum chemical studies to explain the inhibition properties of these compounds. It was concluded that inhibition efficiency depends on the concentration of purine derivatives and the change of trend of inhibition efficiency follows the order: 2,6-dithiopurine > 6-thioguanine > 2,6-diaminopurine > adenine > guanine. The trend of changing the energy gap (ΔE) of compounds was in correlation with the obtained inhibition efficiencies, which implies the strong interaction of inhibitor molecules with the steel surface. There was no agreement on the degree of protection with other quantum chemical parameters, which is explained by the physical adsorption of purines. The proposed model for adsorption is the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. Further, in the research by Cruz-Gonzalez et al. [58] other purine derivatives (adenine, guanine, adenosine, and guanosine, Table S1) as inhibitors of steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid were tested in the concentration range between 5 and 200 ppm. The optimal concentration was 25 ppm since a further increase in concentration only slightly increased the IE. Based on the gathered results by Scendo et al. [59] and Scendo and Trela [60], the authors pointed out that purine and adenine behave as stainless-steel corrosion inhibitors in acidic chloride solutions. Inhibition efficiency increased with inhibitor concentration due to increased surface coverage by adsorbed adenine/purine molecules. Jiang et al. [13] investigated 6-furfurylaminopurine (FAP) and N-benzylaminopurine (N-BAP), Table S1, as inhibitors of corrosion of mild steel in HCl solution. They provided vast data regarding surface analysis and theoretical calculations using quantum chemical calculations based on density functional theory (DFT) to analyze molecule parameters. Geometry, Frequency, Non-covalent, eXtended Tight Binding (GFN-xTB) method was used to study adsorption modes, Figure 8, and molecular dynamics simulations to observe corrosive species diffusion, however, the real proof of their inhibiting activity is provided by electrochemical analysis. According to the EIS measurements results presented by Nyquist and Bode plots, capacitive loop diameters increase, as well as the impedance modulus, and phase angle peaks broaden in the presence of purine derivatives. All of these changes are manifestations of the inhibitive effect of tested compounds. The way to observe those changes via calculated values is through the fitting procedure of experimental data using equivalent circuits and obtained values of polarization resistance that increase as the surface protection increases. A very interesting derivative of adenine and amino acid alanine, Adenine-L-Alanine ramification (ALAR), Table S1, can be a very efficient inhibitor of corrosion of steel in hydrochloric acid, according to Hu et al. [61].
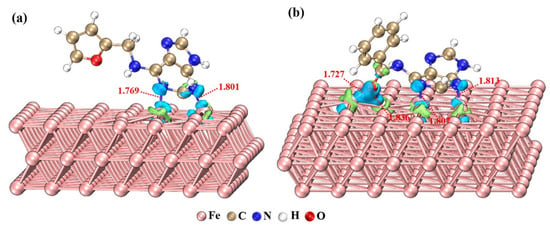
Figure 8.
Optimized adsorption geometries and electron density difference distribution for the adsorption of the purine derivatives on Fe (110) surface: (a) FAP, (b) N-BAP. (The blue and green isosurfaces depict electron deficiency and electron accumulation, respectively. The unit of all indicated bond lengths is Angstrom). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.) Reprinted with permission from ref. [13]. Copyright 2022 Elsevier.
Purine and adenine-based drugs are interesting compounds that could be utilized as potential corrosion inhibitors. Tenvir ([(9-[(R) 2 [[bis [ [(isopropoxycarbonyl) oxy] methoxy] phosphinyl] methoxy] propyl] adenine fumarate)], Table S1), an antiviral drug that is an adenine derivative, is studied as potential inhibitor of mild steel corrosion in 1 M HCl [62]. EIS results indicated an increase in charge transfer resistance and a decrease in capacitance that is attributed to the adsorption of Tenvir molecules on the interface steel surface/hydrochloric acid. Potentiodynamic polarization results are in good agreement with EIS results, and according to them, Tenvir acts as a mixed-type inhibitor by decreasing the surface available for reaction by blocking surface-active sites. The mild steel surface covered by Tenvir molecules is detected in SEM analysis. Further, Verma et al. [63] applied a DFT study in order to evaluate three purine-based medicines as potential inhibitors of corrosion of mild steel in HCl. They used 2-amino-9-((2-hydroxyethoxy)methyl)-3H-purin-6(9H)-one (Acyclovir), ((1S,4R)-4-(2-amino-6-(cyclopropylamino)-9H-purin-9-yl)cyclopent-2-en-1-yl)methanol (Abacavir) and (R)-(((1-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)propan-2- yl)oxy)methyl)phosphonic acid (Tenofovir), Table S1, and the trend of the increase in inhibition efficiency is expected to be Tenofovir < Acyclovir < Abacavir. Further, adenine and guanine were utilized as low carbon steel corrosion inhibitors in NaCl solution [64]. Electrochemical techniques revealed better inhibition properties of guanine than adenine due to the presence of more heteroatoms. Based on the Nyquist diagram and the obtained parameters, the presence of inhibitors leads to an increase in the charge transfer resistance (Rct) and a decrease in the double layer capacitance (Cct) in relation to the blank solution. These results were explained by the adsorption of purine derivatives on the inner Helmholtz plane of low carbon steel, which blocks the active sites and interferes with the charge transfer process. The dissolution of low carbon steel in the presence of guanine has been studied at different immersion times (0.5–12 h) in the temperature range of 305 to 325 K. The highest inhibition efficiency of 1 × 10−3 M guanine, Table S1, was achieved after 2 h of immersion time (98%). Further increases in time have led to a decrease in the inhibition efficiency of guanine. Also, the authors demonstrated that the dissolution of low carbon steel in chloride solution with the addition of guanine was reduced at a higher temperature (Table 3). The experimental results of Kassou et al. [59] were used in the study of Tüzün and Kaya [65] in order to find a correlation between the inhibition efficiency values and molecule characteristics obtained by quantum chemical calculations. The conclusion is that the parameters such as chemical hardness, global softness, and energy gap can give a good indication regarding the choice and design of potential inhibitors.
Due to the presence of heteroatoms in the molecular structure and their non-toxicity, methylxanthines, Table S1, are interesting as corrosion inhibitors for steel. In order to study inhibition properties of caffeine and theophylline for grey cast iron in 3 wt % NaCl, Espinoza Vázquez et al. [14] conducted electrochemical experiments using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and potentiodynamic polarization techniques. Additionally, the synergistic effect of xanthines and coating (Paraloid B-72) was examined in a saline medium. Better protection of gray cast iron was observed when a combination of xanthines and Paraloid B-72 was applied (Table 3). Nyquist diagrams of gray cast iron in NaCl solutions with caffeine/theophylline and Paraloid B-72, Figure 9, show a trend of increasing semicircular diameter as the inhibitor concentration increases, which is an indicator of better protection of the electrode surface achieved.
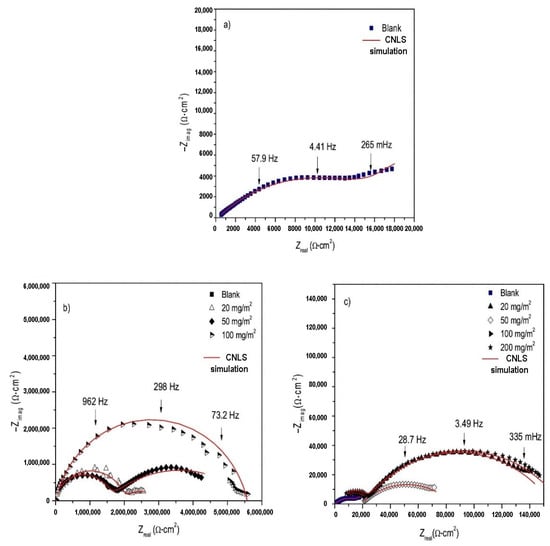
Figure 9.
Nyquist diagram (a) without coating, and in function of (b) theophylline and (c) caffeine concentrations with Paraloid B-72 coating of gray cast iron immersed in 3% NaCl. Reprinted with permission from ref. [14]. Copyright 2022 Elsevier.
The protective ability of caffeine extracted from tea leaves on mild steel was shown in the work of Hamidon and Husin [66]. Researchers incorporated extracted caffeine into hybrid sol-gel coatings and applied them to the surface of mild steel. The corrosion behavior of such prepared samples was investigated in 3.5 wt % NaCl. The results obtained by potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements showed improved corrosion resistance of mild steel when a hybrid sol-gel with caffeine was used compared to the hybrid sol-gel as an inhibitor. Increasing the concentration of caffeine in the hybrid sol-gel coating also provides higher inhibition efficiency. According to the changing trend, in the value of Tafel slopes, caffeine is classified, in this system, as a mixed-type inhibitor. The wettability analysis of bare (θwater = 59.74°) and coated mild steel (θwater = 96.41°) implied the hydrophobic character of hybrid sol-gel containing caffeine, is in good correlation with results achieved by electrochemical measurements.
Espinoza-Vazquez and Rodríguez-Gomez [67] investigated and confirmed the inhibitor ability of caffeine against corrosion of low carbon steel in both 3% NaCl and 3% NaCl + CO2 solutions. Before potentiodynamic polarization measurements and EIS measurements, OCP was monitored until the steady-state was achieved. In a neutral chloride solution, water molecules on the low carbon steel surface could be displaced by caffeine following the reaction:
Org + H2Oads → Orgads + H2O
When CO2 is present in NaCl solution, the corrosion mechanism is different. Due to the CO2 gas, the solution becomes acidic, and the steel surface becomes positively charged, allowing the adsorption of Cl- ions. Under these conditions, caffeine is in cationic form and could interact with Cl- ions to form (FeCl−-inhibitor+)ads protective film.
Electrochemical techniques and quantum chemical calculations were used to examine the inhibitory effect of theobromine on mild steel corrosion in 1 M HCl [68]. The temperature used for experiments was 308 K. Due to the presence of heteroatoms in the molecular structure of theobromine such as N and O atoms, as well as delocalized π-electrons of aromatic rings, it reduces the corrosion rate by controlling both cathodic and anodic reactions. The corrosion rate decreased as the inhibitor concentrations increased. All research methods used in this study have shown that the highest efficiency of inhibition was 90% (Table 3). In a further investigation, Espinoza-Vázquez et al. [69] applied electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in order to evaluate the inhibition efficiency obtained by caffeine, theophylline, allyl- theophylline, and propargyl-theophylline, Table S1, in 1 M HCl. It was concluded that caffeine provided the best protection, followed by propargyl derivative of theophylline. It is assumed that the advantage is a result of a different adsorption mechanism since these two compounds are chemisorbed while theophylline and its allyl derivative are physisorbed.
Espinoza-Vázquez et al. [70] synthetized five theophylline-triazole compounds (Comp 3–7-((1-benzyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl) methyl)-1,3-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6–dione; Comp 4–7-((1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl) methyl)-1,3-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione; Comp 5–7-((1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl) methyl)-1,3-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione; Comp 6–7-((1-(4-bromobenzyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl) methyl)-1,3-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione; Comp 7–7-((1-(4-iodobenzyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl) methyl)-1,3-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione), Table S1, and tested them as corrosion inhibitors for steel (API 5L X52) in 1 M HCl solution. The inhibition efficiency was concentration-dependent and was highest at a concentration of 50 ppm for all compounds studied. The results obtained by potentiodynamic polarization measurements classify these compounds as mixed-type inhibitors with a significant effect on the cathodic reaction. According to the thermodynamic analysis and the calculated Gibbs free adsorption energy, compounds 3, 6, and 7 are chemisorbed on the steel surface, while the adsorption of compounds 4 and 5 includes both physical and chemical processes. The process of adsorption can be described by the Langmuir adsorption isotherm.
2.2.2. Sulfate and Other Media
In addition to the chloride medium, sulfuric acid was used for corrosion testing of steel in the presence of purine and its derivatives. The ability of adenine to inhibit the corrosion of low carbon steel in a 4.0 M H2SO4 solution was tested using electrochemical and weight loss methods [71]. Additionally, the aim of the study was to investigate the synergistic effect between adenine and iodide ions. The archived data showed that adenine alone, as with iodide ions, interferes with both anodic and cathodic reactions. The authors explained that the corrosion process of low carbon steel was inhibited by the adsorption of protonated molecules of adenine on the positively charged steel surface. It is enabled through interactions between the delocalized π-electrons of the pyrimidine and imidazole rings as well as the partial negative charges of N-1, N-3, and N-7 atoms and the metal surface. In the presence of iodide ions, the first adsorption of I- ions occurs on the positively charged surface, which allows further adsorption of adenine in cationic form through electrostatic interactions. The binary inhibitory system of adenine and iodide ions provides better protection for low carbon steel compared to adenine (Table 3). The calculated synergistic parameter was higher than 1.0, indicating the co-adsorption between iodide anions and adenine cations [71]. In the research of Bagga et al. [72] the effect of the extract of Ficus racemosa on the corrosion of mild steel in sulfuric acid was studied. The conclusion of the study was that the inhibiting effect is a result of the synergistic action of numerous chemical constituents of the extract, among which purine nucleosides are found.

Table 3.
Steel corrosion inhibition efficiency obtained by purine and xanthine compounds.
Table 3.
Steel corrosion inhibition efficiency obtained by purine and xanthine compounds.
| Inhibitor | Concentration | Medium | IE % | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caffeine Theophylline | 200 ppm | 3 wt % NaCl | 57.4 EIS/77.4 PP 39.9 EIS/65.3 PP | [14] |
| Caffeine + Paraloid B-72 Theophylline + Paraloid B-72 | 200 mg m−2 | 86.4 EIS 99.7 EIS | ||
| Hybrid sol-gel + caffeine | 100 ppm | 3.5 wt % NaCl | 84.22 EIS | [66] |
| 88.79 PP | ||||
| Caffeine | 50 pm | 3 wt % NaCl | 82.7 EIS | [67] |
| 3 wt % NaCl + CO2 low carbon steel | 94.7 EIS | |||
| Theobromine | 1.0 g dm−3 | 1 M HCl mild steel | 90.0 WL,PP,EIS (308 K) | [68] |
| Adenine | 1 × 10−3 M | 200 ppm NaCl low carbon steel | 82 PP/83 EIS (305 K); 95 EIS (315 K); 88 EIS (325 K) | [64] |
| Guanine | 91 PP/93 EIS (305 K) | |||
| Guanine Adenine 2,6-dithiopurine 2,6-diaminopurine 6-thioguanine | 1 × 10−3 M | 1 M HCl mild steel | 68.3 PP/67.8 EIS 69.6 PP/69.9 EIS 85.9 PP/85.4 EIS 73.5 PP/70.9 EIS 77.9 PP/78.4 EIS | [57] |
| Comp 3 | 50 ppm | 1 M HCl steel API 5L X52 | 91.7 EIS/86.9 PP | [70] |
| Comp 4 | 86.9 EIS/87.0 PP | |||
| Comp 5 | 94.0 EIS/71.0 PP | |||
| Comp 6 | 91.8 EIS/93.5 PP | |||
| Comp 7 | 90.9 EIS/88.2 PP | |||
| Caffeine | 20 ppm | 1 M HCl steel API 5L X70 | 96.4 EIS | [69] |
| Theophylline | 88.6 EIS | |||
| Propargyl-theophylline | 91.0 EIS | |||
| Allyl-theophylline | 74.6 EIS | |||
| Caffeine | 50 ppm | 95.4 EIS | ||
| Theophylline | 90.6 EIS | |||
| Propargyl-theophylline | 90.0 EIS | |||
| Allyl-theophylline | 79.1 EIS | |||
| PVPO-TiO2-Adenine | 800 ppm | 1 M H2SO4 carbon steel 303 K | 83.50 WL/87.53 PP/92.18 EIS | [73] |
| 7-(ethylthiobenzimidazolyl) theophylline (7-ETBT) | 2 × 10−3 M | 1 M HCl mild steel | 90.73 WL/87.06 PP | [74] |
| FAP N-BAP | 0.8 × 10−3 M | 1 M HCl mild steel | 93.5 PP 97.7 PP | [13] |
| Adenine | 10 × 10−3 M | 1.1 M Cl- (NaCl, HCl) pH 1.5 25 °C 304 austenic stainless steel | 85 PP | [60] |
| Tenvir | 400 ppm | 1 M HCl mild steel | 96.05 WL/94.0 EIS/94.27 PP | [62] |
| Adenine Guanine Adenosine Guanosine | 25 ppm | 1 M HCl steel API 5L X52 | 91 EIS 88 EIS 94 EIS 93 EIS | [58] |
| Adenine KI | 5 × 10−2 M | 4 M H2SO4 low carbon steel | 83 EIS 75 EIS | [71] |
| Adenine + KI | 5 × 10−2 M + 1 × 10−3 M | 88 EIS |
EIS—electrochemical impedance spectroscopy; PP—potentiodynamic polarization measurements; WL—weight loss. Comp 3–7-((1-benzyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl) methyl)-1,3-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6–dione; Comp 4–7-((1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl) methyl)-1,3-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione; Comp 5–7-((1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl) methyl)-1,3-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione; Comp 6–7-((1-(4-bromobenzyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl) methyl)-1,3-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione; Comp 7–7-((1-(4-iodobenzyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl) methyl)-1,3-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione.
Saini et al. [73] formed an adenine-containing hybrid material (HM) using Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) Oxime (PVPO) and TiO2 (PVPO-TiO2-Adenine). This hybrid material was used to inhibit corrosion of carbon steel in sulfuric acid. The results of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy as well as potentiodynamic polarization results unequivocally proved that it provided good protection of steel against corrosion in sulfuric acid. Those results are in good agreement with weight loss, SEM, atomic force microscopy (AFM) results, and quantum chemical calculations. Based on all those results, the proposed mechanism includes adsorption on copper surface via high density electron centers, in a configuration where one ring lies flat on the surface whereas others have different orientations in space and the hydrophobic part is facing the media.
2.3. Other Metals
Besides numerous studies dedicated to corrosion of copper and steel that included purine compounds as potential inhibitors, there is research focused on several other metals and alloys, such as aluminum, magnesium, tin, indium, etc. The obtained inhibition efficiencies are summarized in Table 4. Analysis of the data presented in Table 4 leads to the conclusion that purines can be classified as corrosion inhibitors for a broad range of materials.

Table 4.
Corrosion inhibition efficiency obtained by purine and xanthine compounds.
2.3.1. Aluminum
Several studies dealt with the possibility of using purine compounds as inhibitors of aluminum corrosion in different media, and the obtained inhibition efficiencies are summarized in Table 4. Weight loss and electrochemical measurements were utilized to study the inhibitory properties of theophylline anhydrous towards aluminum in a 2.0 M hydrochloric acid solution [15]. In the investigated concentration range of theophylline from 5 × 10−6 M to 5 × 10−4 M, both chemical and electrochemical techniques indicated that the corrosion rate of aluminum was decreased in relation to the blank solution. The inhibition efficiency of 99.99% was achieved at a theophylline concentration of 1 × 10−4 M, Table 4. The cathodic Tafel slope changed in the presence of the inhibitor while the anodic Tafel slope did not, indicating that theophylline can be classified as a cathodic type of inhibitor. The adsorption study pointed out the spontaneous adsorption of theophylline and the formation of a stable layer on the metal surface.
Further, the ability of theophylline to protect aluminum from deterioration was examined in 1 M NaOH [75]. In this study, it is interesting that the expired drug theophylline was used. In the concentration of 2.5%, theophylline exhibited 90%, and 91% of protection based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and potentiodynamic polarization measurements, respectively. Scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy confirmed the formation of a theophylline protective film on the aluminum surface that diminishes its corrosion rate.
Adenine (AD), guanine (GU), and hypoxanthine (HYP), Table S1, were studied as potential inhibitors of aluminum corrosion in hydrochloric acid solution [16]. The authors used weight loss along with electrochemical methods such as potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The experimental results are complemented by quantum chemical calculations. EIS results showed that these purine compounds adsorb on the aluminum surface, leading to an increase in charge transfer resistance and a decrease in capacitance because their molecules replace water molecules on the surface. Guanine and hypoxanthine influenced the cathodic part of potentiodynamic curves, whereas adenine acted as a mixed-type inhibitor. Adsorption is a result of electrostatic interactions of purine compounds molecules with the surface of aluminum, whereas they can form a multi-molecular layer and occupy more than one active site, which indicates the occurrence of physisorption. Several adsorption isotherms are used in order to find the best fit, i.e., Flory–Huggins, Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin, and El Awardy et al. The conclusion is that Flory–Huggins, Langmuir, and El Awardy et al. models described the adsorption of AD, GU, and HYP on aluminum.
The effect of purine on the protection of aluminum against corrosion in an acidic environment in 1 M deaerated H3PO4 solution under different conditions was investigated as well [76]. The measurements were conducted using the polarization and impedance measurements, which were complemented with EDX examinations of the electrode surface. The addition of purine to the blank solution did not lead to significant protection of the Al electrode surface, but therefore the addition of I- ions significantly improved the efficiency of corrosion inhibition. As already known, purine is an organic base that in an acidic medium can be found in protonated form. In that case, there is an equilibrium between the cation and the neutral molecule. Interaction between the positively charged electrode surface and protonated purine form results in weak adsorption. Hence, under described conditions, purine provides little inhibition efficiency (≈55%). Iodide ions are strongly adsorbed on the surface of the metal and obviously help the physical adsorption of purine on the surface of the Al electrode, which is reflected in increasing the efficiency of inhibition, whose value reaches ≈94%.
2.3.2. Magnesium
Zoubi et al. [20] applied an advanced surface modification method, i.e., low temperature-interfacial plasma electrolysis (LT-PE) that results in plasma-assisted electrochemical reaction (PAE) on the metal surface. This represents one of the most versatile wet-coating systems used to achieve a surface of significant corrosion resistance of metallic materials. The surface treatment of the AZ31 magnesium alloy was performed in a silicate-based electrolyte which contains melamine (MEL), adenine (AD) and, N·N·N′.N′-tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMD), Table S1. Conducted EIS and potentiodynamic polarization tests indicated that the presence of MEL and TEMD as nitrogen and carbon donors contributes to the fabrication of magnesium silicate and magnesium oxide in the compact inorganic layer. In the presence of AD, behaving as acceptor-type ions, the formation of stable organic complexes is preferred. That is the reason for a higher porosity layer to be formed in the presence of adenine. The best result regarding corrosion inhibition is observed in Table 4, with the addition of TEMD.
Magnesium can be used as a biodegradable biomaterial. That is the reason why Park et al. [21] focused on the inhibition of Mg corrosion and biodegradation by the application of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH), Table S1. According to potentiodynamic polarization curves, the treatment of Mg with NADH leads to a decrease in corrosion current density and an increase in the corrosion potential. Those results showed that the efficiency of corrosion inhibition increased with NADH concentration. The mechanism of NADH action is illustrated in Figure 10.
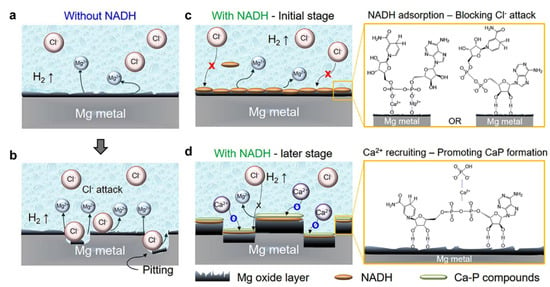
Figure 10.
Schematic illustrations of the role of NADH in the corrosion of Mg: (a,b) conventional corrosion of Mg in the absence of NADH. Here, Cl− ions attack and dissolve Mg oxides formed on the Mg surface. (c,d) Corrosion of Mg in the presence of NADH. At the initial stage of corrosion (c), NADH self-adsorbs onto Mg oxides and blocks Clf ions from dissolving Mg oxides. At the late stages of corrosion (d), self-adsorbed NADH recruits Ca2+ ions to form stable Ca-P compounds on Mg oxides. Reprinted from [21].
2.3.3. Titanium, Tin, Indium, Nickel, and Alloys: CoCrMo and Sn-Ag Alloy
Titanium is one of the common biomaterials, so its stability and behavior in physiological fluids are of great significance. Potentiodynamic polarization curves of titanium in artificial blood plasma (BM3) and in the presence of adenine are presented in Figure 11 [19]. Open circuit potential measurements are also performed and reveal that in the presence of adenine, a protective layer is formed which passivates the titanium surface and prevents further corrosion. According to the OCP and potentiodynamic polarization curves, it can be seen that adenine acts like a cathodic corrosion inhibitor in BM3 solution. Adenine adsorbs on the Ti surface and passive layer formation occurs at a more negative potential in regard to blank BM3 solution. Interaction between the titanium surface and an adenine molecule occurs via the N atom. In aggressive media, a certain amount of TiO2 dissolves, which leads to the reaction of adenine and metal surface, forming a complex. This complex provides protection from the aggressive ions in the solution. Potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy results are in good agreement. Current density decreases, while capacitive loop and phase angle increase with the addition of adenine. This statement is supported by the calculated values of the efficiency of inhibition presented in Table 4.
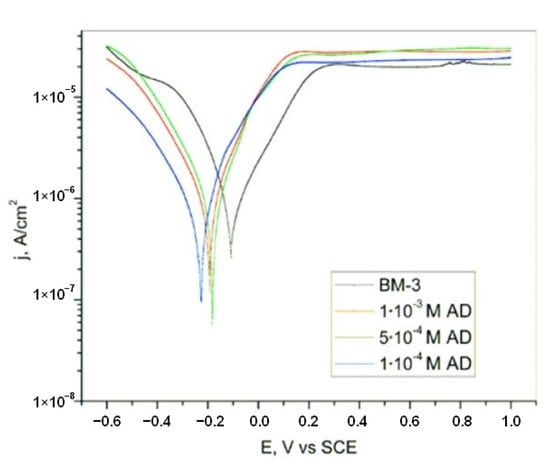
Figure 11.
Potentiodynamic polarization curves of titanium in BM3 solution without and with the addition of different concentrations of adenine. Immersion time was 30 min. Reprinted from [19].
Another medically important material, CoCrMo [77,78,79,80], was the focus of the study conducted by Romas et al. [29]. These authors studied caffeine (1,3,7-trimethyl xanthine) as an inhibitor of corrosion of CoCrMo alloy in artificial saliva using electrochemical methods. The open circuit potential tests were performed in artificial saliva solution at different temperatures in the presence of different amounts of caffeine. The observed shift of the OCP to the higher values in the presence of an inhibitor over time indicates the formation of the protective layer on the CoCrMo surface. The results indicated that it adsorbs on the surface of the alloy according to the Langmuir adsorption isotherm and inhibits anodic current. The influence of temperature on the inhibitory effect was also investigated, and the results showed that the corrosion rate increases with increasing temperature because the high temperature blocks the inhibitory activity of caffeine. Besides, caffeine as a corrosion inhibitor for nickel in 3.5%NaCl solution was tested using different electrochemical techniques, including electrochemical noise analysis, open circuit potential measurements, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and linear voltammetry [27]. The achieved results demonstrated good inhibitory properties of caffeine, with the highest inhibition efficiency over 95%. Inhibition of nickel corrosion in chloride solution occurs due to a complex mechanism including adsorption of caffeine molecules, charge transfer, and electrostatic bonding between the metal surface and inhibitor molecules.
El-Sayed et al. [17,18] studied the effect of adenine and adenosine on the corrosion of tin, indium, and their alloys. They chose 0.5 M HCl [17] and 0.5 M HClO4 [18] solutions as test media. The results of potentiodynamic polarization studies are very interesting since it is concluded that these compounds inhibit corrosion of pure tin and indium in both media, and also act as catalysts of cathodic and anodic processes in the case of their alloys in HClO4 solution, Table 4. Both effects become more distinct with the increase in concentration. The adsorption of adenine and adenosine on the surfaces of tin, indium, and their alloys are described by the Frumkin adsorption isotherm [17,18].
Heakal and Fekry [28] examined adenine as a corrosion inhibitor for Sn-Ag alloy in 1.5 M nitric acid solution, utilizing electrochemical methods and quantum chemical calculations. The observed increase in the open circuit potential values in the inhibitor-free solution shows that the alloy surface was self-protected by the formation of a passivated film. Moreover, in the presence of the inhibitor, a positive shift of the OCP values is connected with the adsorption of the adenine molecule on the surface of the Sn-Ag alloy. It was shown that adenine can hinder both anodic and cathodic corrosion reactions due to the adsorption of inhibitor molecules on the Sn-Ag alloy surface. The adsorption of adenine on the alloy surface obeys the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. Adenine provides better protection against corrosion as its concentration increases. Theoretical calculations were in good correlation with electrochemical results.
3. Conclusions
Due to the importance of protecting metals and alloys from corrosion processes, this review summarizes the results of the inhibition efficiency of bioorganic compounds, including purine and purine compounds, as well as methylxanthines. For that purpose, electrochemical methods are important for testing the ability of various organic compounds to protect metals against corrosion. These methods stand out for their rate in obtaining data, low cost, and reliability. Copper and its alloys, different types of steel, titanium, aluminum, and magnesium are included in this paper. The mechanism of dissolution and inhibition of these metals and alloys in chloride, sulfate, and physiological media is presented. Based on the presented results, bioorganic compounds could be used as corrosion inhibitors. The mode of their action includes adsorption on the surface of metals that is frequently described by the Langmuir adsorption isotherm but also, in some cases, Temkin, Frumkin, Flory–Huggins, and El Awardy isotherms provided the best fit. Their effectiveness depends on parameters such as the medium tested, the type of metal, the range of investigated concentrations, and the temperature, which should be taken into account when choosing a potential inhibitor. The highest values of inhibition efficiency are obtained in chloride solutions. Different purine compounds showed better effect on different metals. For instance, nickel corrosion was efficiently inhibited by caffeine, aluminum corrosion by theophylline, steel corrosion by caffeine, adenine, and theophylline in combination with Paraloid B-72, and copper corrosion by adenine, 6-benzylaminopurine, hypoxanthine and pretreatment with purine. The increase in inhibitor concentration leads to the increase in inhibition efficiency with a few exemptions, for instance, caffeine on CoCrMo alloy in artificial saliva, guanine, and hypoxanthine on copper in artificial seawater, etc. Corrosion processes are generally favored by increased temperature. However, purine compounds provide satisfactory protection in the range up to approximately 330 K. The results presented and discussed in the manuscript are obtained from scientific papers, and they are all from research conducted on a laboratory scale. In order to make a suggestion about a larger scale application, further studies and economic calculations would be necessary.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/met12071150/s1, Table S1: Structures of the used organic compounds.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Ž.Z.T. and M.B.P.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.B.P.M. and Ž.Z.T.; writing—review and editing, M.B.R., A.T.S. and M.M.A.; supervision, M.M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Ministry of Education, Science and Technological development of the Republic of Serbia, grant number 451-03-68/2022-14/200131.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tasić, Ž.Z.; Petrović Mihajlović, M.B.; Radovanović, M.B.; Antonijević, M.M. New trends in corrosion protection of copper. Chem. Pap. 2019, 73, 2103–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonijević, M.M.; Radovanović, M.B. Methods for Characterization of Protective Films on the Copper Surface—A Review. Zaštita Mater. Mater. Prot. 2010, 2, 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, M. Corrosion protection with eco-friendly inhibitors. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 2, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonijević, M.M.; Petrović, M.B. Copper Corrosion Inhibitors. A review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2008, 3, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Petrović Mihajlović, M.B.; Antonijević, M.M. Copper Corrosion Inhibitors. Period 2008-2014. A Review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 1027–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Quraishi, M.A.; Chauhan, D.S.; Saji, V.S. Heterocyclic biomolecules as green corrosion inhibitors. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 341, 117265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Ebenso, E.E.; Quraishi, M.A. Alkaloids as green and environmental benign corrosion inhibitors: An overview. Int. J. Corros. Scale Inhib. 2019, 8, 512–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clercq, E. The acyclic nucleoside phosphonates from inception to clinical use: Historical perspective. Antivir. Res. 2007, 75, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Martín, A.; del Pilar Brandi-Blanco, M.; Matilla-Hernández, A.; El Bakkali, H.; Nurchi, V.M.; González-Pérez, J.M.; Castiñeiras, A.; Niclós-Gutiérrez, J. Unravelling the versatile metal binding modes of adenine: Looking at the molecular recognition patterns of deaza- and aza-adenines in mixed ligand metal complexes. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 2814–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choquesillo-Lazarte, D.; del Pilar Brandi-Blanco, M.; García-Santos, I.; María González-Pérez, J.; Castiñeiras, A.; Niclós-Gutiérrez, J. Interligand interactions involved in the molecular recognition between copper(II) complexes and adenine or related purines. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2008, 252, 1241–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasseghi, S.; Ken, N. Effect of substituted purines on the corrosion behavior of iron. Corrosion 1979, 35, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Aal, M.S.; Wahdan, M.H. Effect of c-content and microstructure of steel on the inhibiting action of purine and benzo(f)quinoline in HClO4 solution. In Proceedings of the 6th European Symposium on Corrosion Inhibitors, 133rd Manifestation of the European Federation of Corrosion, Ferrara, Italy, 16–20 September 1985; pp. 345–357. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, B.; Xiong, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, G. Purine derivatives as high efficient eco-friendly inhibitors for the corrosion of mild steel in acidic medium: Experimental and theoretical calculations. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 323, 114809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza Vázquez, A.; Figueroa, A.; Sánchez Molina, D.; Rodríguez-Gómeza, F.J.; Angeles Beltrán, D. Effects of corrosion inhibition with xanthines in gray cast iron protection with Paraloid B-72 in a saline medium. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 154, 106200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.N.; Megahed, H.E.; Asmaa Ali, I.; El-Etre, M.A. Application of Theophylline Anhydrous as Inhibitor for Acid Corrosion of Aluminum. Egypt. J. Chem. 2017, 60, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eddy, N.O.; Momoh-Yahaya, H.; Oguzie, E.E. Theoretical and experimental studies on the corrosion inhibition potentials of some purines for aluminum in 0.1M HCl. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.-R.; Shaker, A.M.; Abd El-Lateef, H.M. Corrosion inhibition of tin, indium and tin–indium alloys by adenine or adenosine in hydrochloric acid solution. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.R.; Mohran, H.S.; Abd El-Lateef, H.M. Effect of some nitrogen-heterocyclic compounds on corrosion of tin, indium, and their alloys in HClO4. Monatsh. Chem. 2012, 143, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanović, M.B.; Tasić, Ž.Z.; Simonović, A.T.; Petrović Mihajlović, M.B.; Antonijević, M.M. Corrosion Behavior of Titanium in Simulated Body Solutions with the Addition of Biomolecules. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 12768–12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Zoubi, W.; Putri, R.A.K.; Sunghun, B.; Ko, Y.G. Molecular structures in the inorganic-metal interactions for optimizing electrochemical performance. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 326, 115344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Park, M.; Seo, H.; Han, H.-S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Koo, D.; Kim, K.; Cha, P.-R.; Edwards, J.; Kim, Y.-W.; et al. A new corrosion-inhibiting strategy for biodegradable magnesium: Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scendo, M. The effect of purine on the corrosion of copper in chloride solutions. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scendo, M. The influence of adenine on corrosion of copper in chloride solutions. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; Zhao, H.; Luo, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Ma, T.; Wang, W. Roles and mechanistic analysis of adenine as a green inhibitor in chemical mechanical polishing. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2021, 51, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović Mihajlović, M.B.; Radovanović, M.B.; Tasić, Ž.Z.; Antonijević, M.M. Imidazole based compounds as copper corrosion inhibitors in seawater. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 225, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanović, M.B.; Simonović, A.T.; Petrović, M.B.; Milić, S.M.; Antonijević, M.M. Influence of Purine on Brass Behavior in Neutral and Alkaline Sulphate Solutions. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 11796–11810. [Google Scholar]
- Ebadi, M.; Basirun, W.J.; Leng, S.Y.; Mahmoudian, M.R. Investigation of Corrosion Inhibition Properties of Caffeine on Nickel by Electrochemical Techniques. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 8052–8063. [Google Scholar]
- El-Taib Heakal, F.; Fekry, A.M. Experimental and Theoretical Study of Uracil and Adenine Inhibitors in Sn-Ag Alloy/Nitric Acid Corroding System. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, C534–C542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romas, M.; Munoz, A.; Mareci, D.; Vidal, C.; Curteanu, S.; Sutiman, D. Influence of caffeine and temperature on corrosion-resistance of CoCrMo alloy. Chem. Pap. 2014, 68, 1066–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, M.; Wiklund, P.; Leygraf, C. Bioorganic compounds as copper corrosion inhibitors in hydrocarbon media. Corros. Sci. 2012, 58, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, F.; Schilardi, P.L.; De Mele, M.F.L. Reduction of the “burst release” of copper ions from copper-based intrauterine devices by organic inhibitors. Contraception 2012, 85, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, F.; Grillo, C.; Schilardi, P.; Rubert, A.; Benítez, G.; Lorente, C.; De Mele, M.F.L. Decrease in cytotoxicity of copper-based intrauterine devices (IUD) pretreated with 6-mercaptopurine and pterin as biocompatible corrosion inhibitors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2013, 5, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, C.; Casero, E.; Román, E.; Campos, S.F.P.; De Mele, M.F.L. Effective inhibition of the early copper ion burst release by purine adsorption in simulated uterine fluids. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 189, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović Mihajlović, M.B.; Radovanović, M.B.; Simonović, A.T.; Tasić, Ž.Z.; Antonijević, M.M. Evaluation of purine based compounds as the inhibitors of copper corrosion in simulated body fluid. Results Phys. 2019, 14, 102357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scendo, M. Inhibitive action of the purine and adenine for copper corrosion in sulphate solutions. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 2985–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scendo, M. Corrosion inhibition of copper by purine or adenine in sulphate solutions. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 3953–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scendo, M. Inhibition of copper corrosion in sodium nitrate solutions with nontoxic inhibitors. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, M.B.; Simonović, A.T.; Radovanović, M.B.; Milić, S.M.; Antonijević, M.M. Influence of purine on copper behavior in neutral and alkaline sulfate solutions. Chem. Pap. 2012, 66, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Huang, H.; Liu, D. The inhibition mechanism and adsorption behavior of three purine derivatives on the corrosion of copper in alkaline artificial seawater: Structure and performance. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 622, 126644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudić, S.; Oguzie, E.E.; Radonić, A.; Vrsalović, L.; Smoljko, I.; Kliškić, M. Inhibition of copper corrosion in chloride solution by caffeine isolated from black tea. Maced. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2014, 33, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, F.S.; Giacomelli, C.; Gonçalves, R.S.; Spinelli, A. Adsorption behavior of caffeine as a green corrosion inhibitor for copper. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 2436–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.F.; Wysard, J.S.; Bandeira, M.C.E.; Mattos, O.R. Electrochemical and surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy study of Guanine as corrosion inhibitor for copper. Corros. Sci. 2021, 191, 109714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, Y.A.; Menezes, I.; Bonatti, R.S.; Bortolozo, A.D.; Osório, W.R. EIS Investigation of the Corrosion Behavior of Steel Bars Embedded into Modified Concretes with Eggshell Contents. Metals 2022, 12, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, T.; Meyer, Y.A.; Osório, W.R. The Holes of Zn Phosphate and Hot Dip Galvanizing on Electrochemical Behaviors of Multi-Coatings on Steel Substrates. Metals 2022, 12, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verissimo, N.C.; Freitas, E.S.; Cheung, N.; Garcia, A.; Osório, W.R. The effects of Zn segregation and microstructure length scale on the corrosion behavior of a directionally solidified Mg-25 wt.%Zn alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 723, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vida, T.A.; Freitas, E.S.; Cheung, N.; Garcia, A.; Osório, W.R. Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of as-cast Zn-rich Zn-Mg Alloys in a 0.06M NaCl Solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12, 5264–5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, K.; Yao, J.; Yuan, Y.; Du, B. The Laser Deposited Nickel-Aluminum Bronze Coatings on SUS630 Stainless Steel and Its Corrosion Resistance in 3.5 wt.% NaCl Solution. Metals 2022, 12, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Jain, V.; Rai, B. Imidazole derivatives as corrosion inhibitors for copper: A DFT and reactive force field study. Corros. Sci. 2020, 171, 108724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J. Theoretical evaluation of inhibition performance of purine corrosion inhibitors. Mol. Simul. 2013, 39, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadisaputra, S.; Purwoko, A.A.; Savalas, L.R.T.; Prasetyo, N.; Yuanita, E.; Hamdiani, S. Quantum Chemical and Monte Carlo Simulation Studies on Inhibition Performance of Caffeine and Its Derivatives against Corrosion of Copper. Coatings 2020, 10, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunyemi, B.T.; Latona, D.F.; Adejoro, I.A. Molecular modeling and quantitative structure–property relationships (QSPRs) of purine derivatives as corrosion inhibitor in acid medium. Sci. Afr. 2020, 8, e00336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, M.; Watanabe, D.; Kimura, C.; Aoki, H.; Sugino, T. Suppression of Cu Oxidation Using Environmentally Friendly Inhibitors under Conditions of High Temperature and High Humidity for Cu/Low-k. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 48, 04C016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakeria, M.R.; Fazal, M.A.; Haseeb, A.S.M.A. Effect of corrosion inhibitors on corrosiveness of palm biodiesel. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, A.A.; El-Kamel, R.S.; Fekry, A.M. Hydrogen evolution and quantum calculations for potassium sorbate as an efficient green inhibitor for biodegradable magnesium alloy staples used for sleeve gastrectomy surgery. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 24370–24382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasić, Ž.Z.; Antonijević, M.M.; Petrović Mihajlović, M.B.; Radovanović, M.B. The influence of synergistic effects of 5-methyl-1H-benzotriazole and potassium sorbate as well as 5-methyl-1H-benzotriazole and gelatin on the copper corrosion in sulphuric acid solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 219, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladag, N.; Trnkova, L.; Kourilova, A.; Ozsoz, M.; Jelen, F. Voltammetric study of aminopurines on pencil graphite electrode in the presence of copper ions. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Li, W.; Cai, L.; Hou, B. Electrochemical and quantum chemical study of purines as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in 1 M HCl solution. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 5953–5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Gonzalez, D.Y.; Negrón Silva, G.; Angeles Beltrán, D.; Palomar Pardavé, M.; Romero Romo, M.; Herrera Hernández, H. Adenine and guanine derivative bases of purines and their corresponding nucleosides as corrosion inhibitors in 1M hydrochloric acid. ECS Trans. 2011, 36, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scendo, M.; Trela, J.; Radek, N. Purine as an effective corrosion inhibitor for stainless steel in chloride acid solutions. Corros. Rev. 2012, 30, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scendo, M.; Trela, J. Adenine as an Effective Corrosion Inhibitor for Stainless Steel in Chloride Solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 9201–9221. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Gu, H.; Zhuang, J.; Zeng, X.; Yan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Ding, J. Synthesis and anti-corrosion performance of Adenine-L-Alanine ramification. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, G.; Verma, C.B.; Ebenso, E.E.; Quraishi, M.A. Thermodynamic and Electrochemical investigation of (9-[(R)2[[bis [[(isopropoxycarbonyl)oxy]methoxy] phosphinyl] methoxy] propyl] adenine fumarate) as Green Corrosion Inhibitor for Mild Steel in 1M HCl. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 1102–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, C.; Quraishi, M.A.; Ebenso, E.E. Adsorption and Inhibition Behavior of Purine based Drugs on Mild Steel Corrosion in Hydrochloric Acid Solution: DFT Study. Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem. 2018, 10, 98–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kassou, O.; Galai, M.; Ballakhmima, R.A.; Dkhireche, N.; Rochdi, A.; Ebn Touhami, M.; Touir, R.; Zarrouk, A. Comparative study of low carbon steel corrosion inhibition in 200 ppm NaCl by amino acid compounds. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2015, 6, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Tüzün, B.; Kaya, C. Investigation of DNA–RNA Molecules for the Efficiency and Activity of Corrosion Inhibition by DFT and Molecular Docking. J. Bio- Tribo-Corros. 2018, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidon, T.S.; Hazwan Hussin, M. Susceptibility of hybrid sol-gel (TEOS-APTES) doped with caffeine as potent corrosion protective coatings for mild steel in 3.5 wt.% NaCl. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 140, 105478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza-Vazquez, A.; Rodríguez-Gomez, F.J. Caffeine and nicotine in 3% NaCl solution with CO2 as corrosion inhibitors for low carbon steel. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 70226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmsellem, H.; Elyoussfi, A.; Steli, H.; Sebbar, N.K.; Essassi, E.M.; Dahmani, M.; El Ouadi, Y.; Aouniti, A.; El Mahi, B.; Hammouti, B. The theobromine (chocolate) as green inhibitor of mild steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid: Electrochemical and theoretical quantum studies. Der. Pharma Chem. 2016, 8, 248–256. [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza-Vázquez, A.; Rodríguez Gómez, F.J.; Martinez Cruz, I.K.; Negrón Silva, G.E.; Palomar-Pardavé, M. Determination of Inhibition Properties of Caffeine, Theophylline and Their Allylic and Propargylic Derivatives on API 5L X70 Steel Immerse in 1M HCl. ECS Trans. 2018, 84, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza-Vázquez, A.; Rodríguez-Gomez, F.J.; Martínez-Cruz, I.K.; Ángeles-Beltrán, D.; Negrón-Silva, G.E.; Palomar-Pardavé, M.; Romero, L.L.; Pérez-Martínez, D.; Navarrete-López, A.M. Adsorption and corrosion inhibition behaviour of new theophylline–triazole -based derivatives for steel in acidic medium. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 181738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Rehim, S.S.; Hazzazi, O.A.; Amin, M.A.; Khaled, K.F. On the corrosion inhibition of low carbon steel in concentrated sulphuric acid solutions. Part I: Chemical and electrochemical (AC and DC) studies. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 2258–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagga, M.K.; Gadi, R.; Yadav, O.S.; Kumar, R.; Chopra, R.; Singh, G. Investigation of phytochemical components and corrosion inhibition property of Ficus racemosa stem extract on mild steel in H2SO4 medium. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4699–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, N.; Pahuja, P.; Lgaz, H.; Chung, I.-M.; Selwal, K.; Singhal, S.; Lata, S. PVP oxime-TiO2-adenine as a hybrid material: Decent synthesis and depiction with advanced theoretical measurements for anticorrosive behavior and antibacterial potentiality. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 278, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diki, N.Y.S.; Coulibaly, N.H.; Kassi, K.F.; Trokourey, A. Mild steel corrosion inhibition by 7-(ethylthiobenzimidazolyl) theophylline. J. Electrochem. Sci. Eng. 2021, 11, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Li, L.; Li, W.; Huang, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Singh, A. Expired Drug Theophylline as Potential Corrosion Inhibitor for 7075 Aluminium Alloy in 1M NaOH Solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 1412–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.A.; Mohsen, Q.; Hazzazi, O.A. Synergistic effect of I− ions on the corrosion inhibition of Al in 1.0M phosphoric acid solutions by purine. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 114, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovljević, S.; Alar, V.; Ivanković, A. Electrochemical Behaviour of PACVD TiN-Coated CoCrMo Medical Alloy. Metals 2017, 7, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Rodriguez, M.A.L.; Laverde-Cataño, D.A.; Lozano, D.; Martinez-Cazares, G.; Bedolla-Gil, Y. Influence of Boron Addition on the Microstructure and the Corrosion Resistance of CoCrMo Alloy. Metals 2019, 9, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, R.B. Osseoconductive and Corrosion-Inhibiting Plasma-Sprayed Calcium Phosphate Coatings for Metallic Medical Implants. Metals 2017, 7, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirea, R.; Biris, I.M.; Ceatra, L.C.; Ene, R.; Paraschiv, A.; Cucuruz, A.T.; Sbarcea, G.; Popescu, E.; Badea, T. In Vitro Physical-Chemical Behaviour Assessment of 3D-Printed CoCrMo Alloy for Orthopaedic Implants. Metals 2021, 11, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).