Competition for Nucleation and Grain Initiation during Solidification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Heterogeneous Nucleation and Grain Initiation
2.1. Recent Advances in Heterogeneous Nucleation
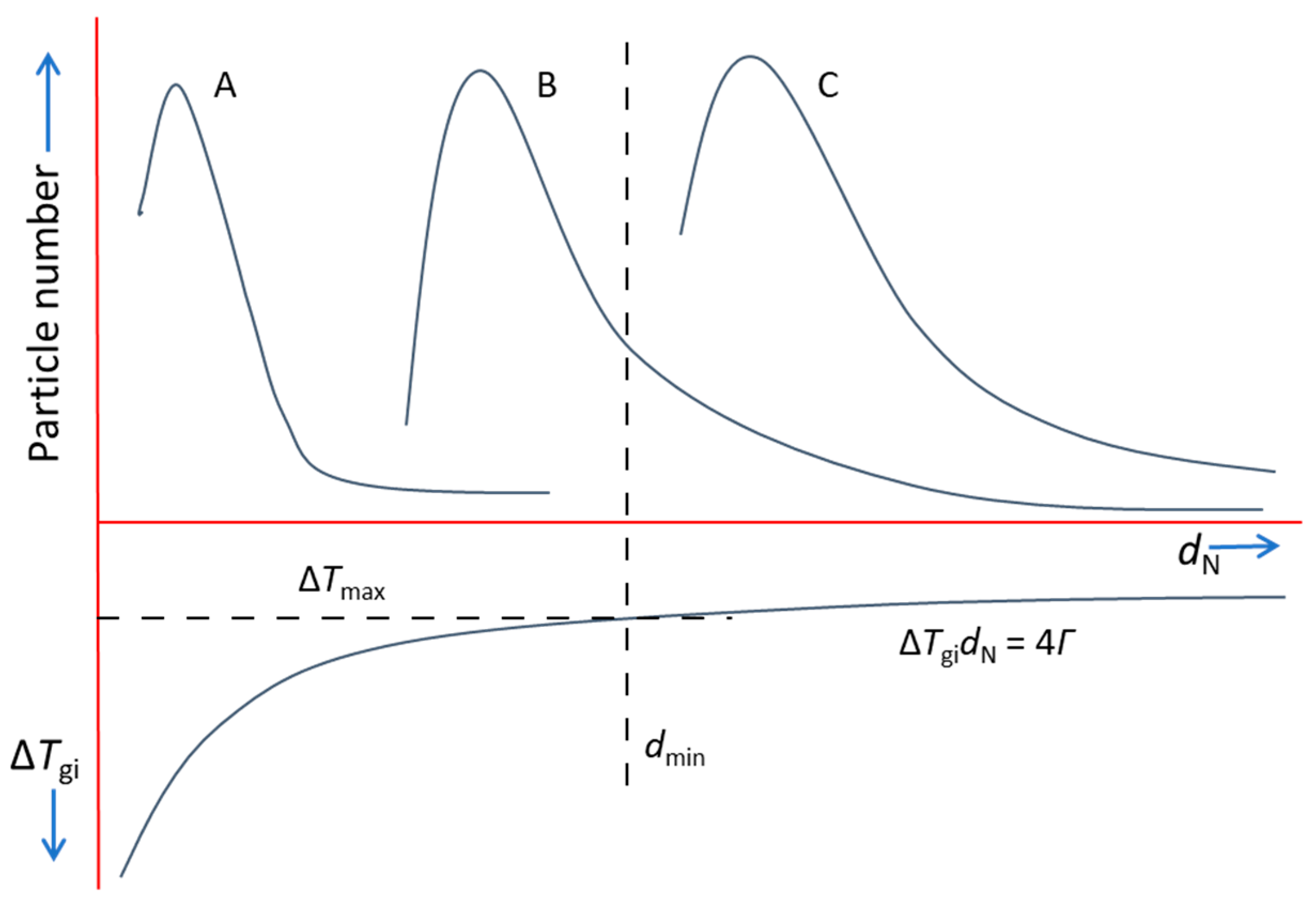
2.2. Grain Initiation during Solidification
3. Competition for Nucleation
4. Competition for Grain Initiation
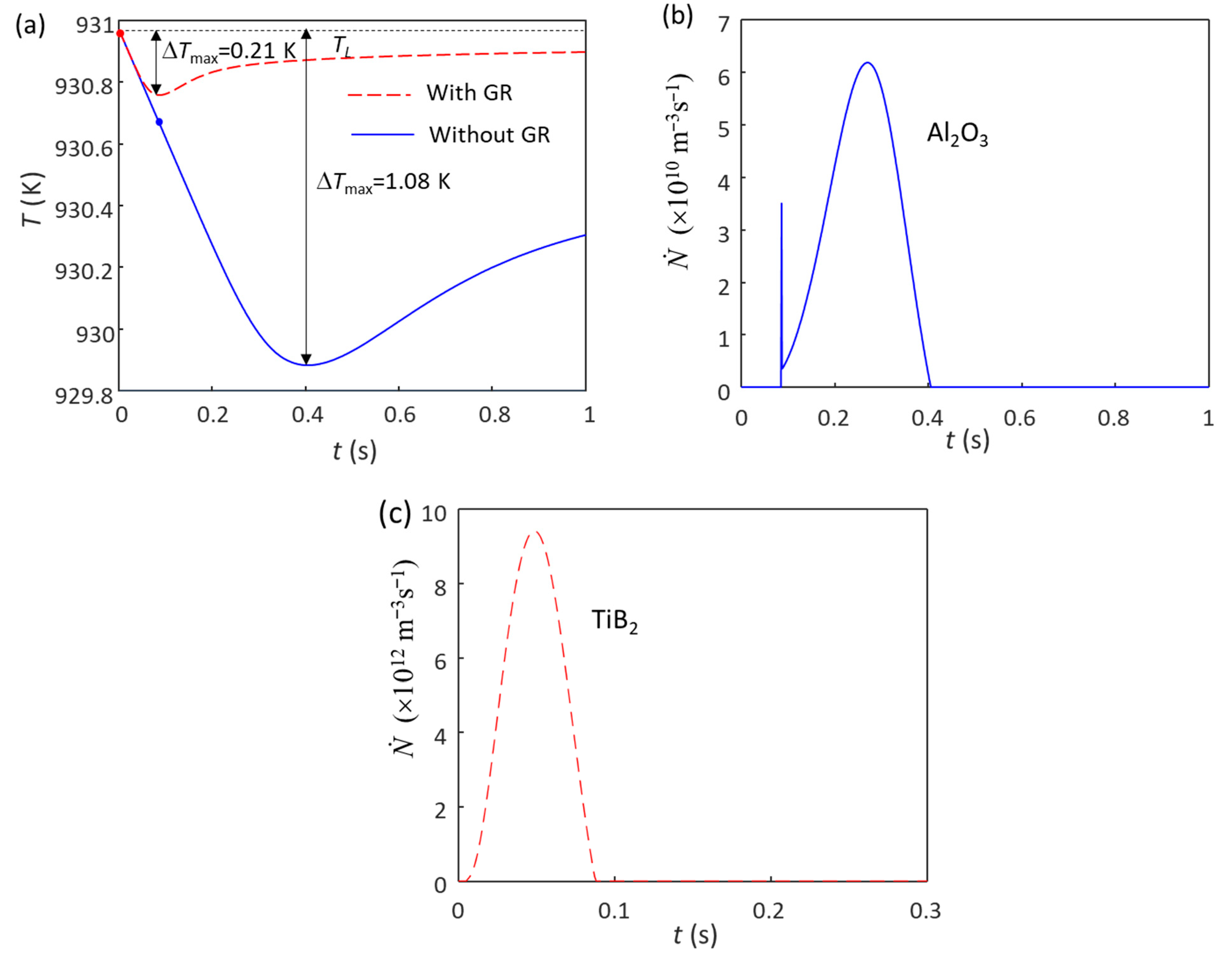
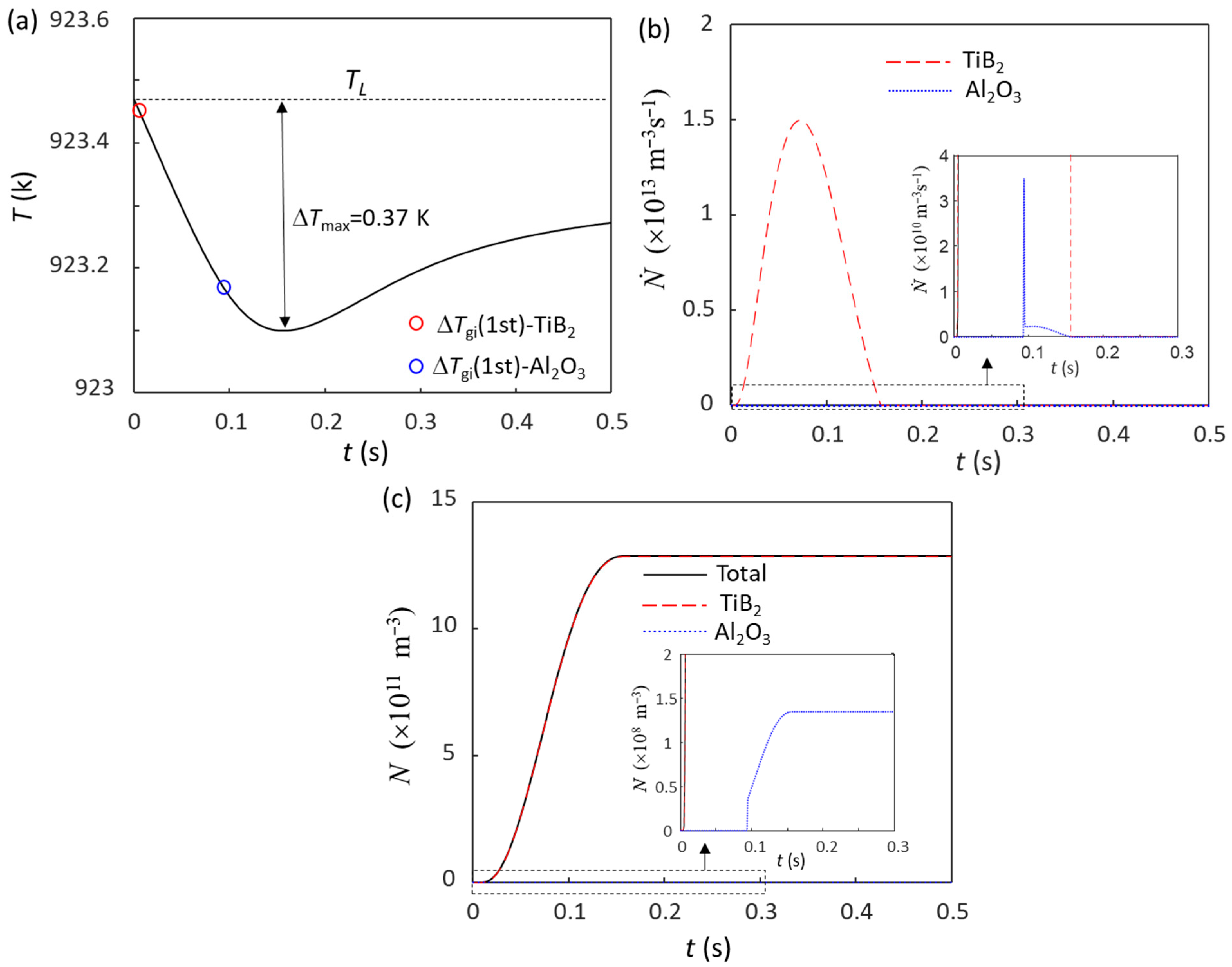
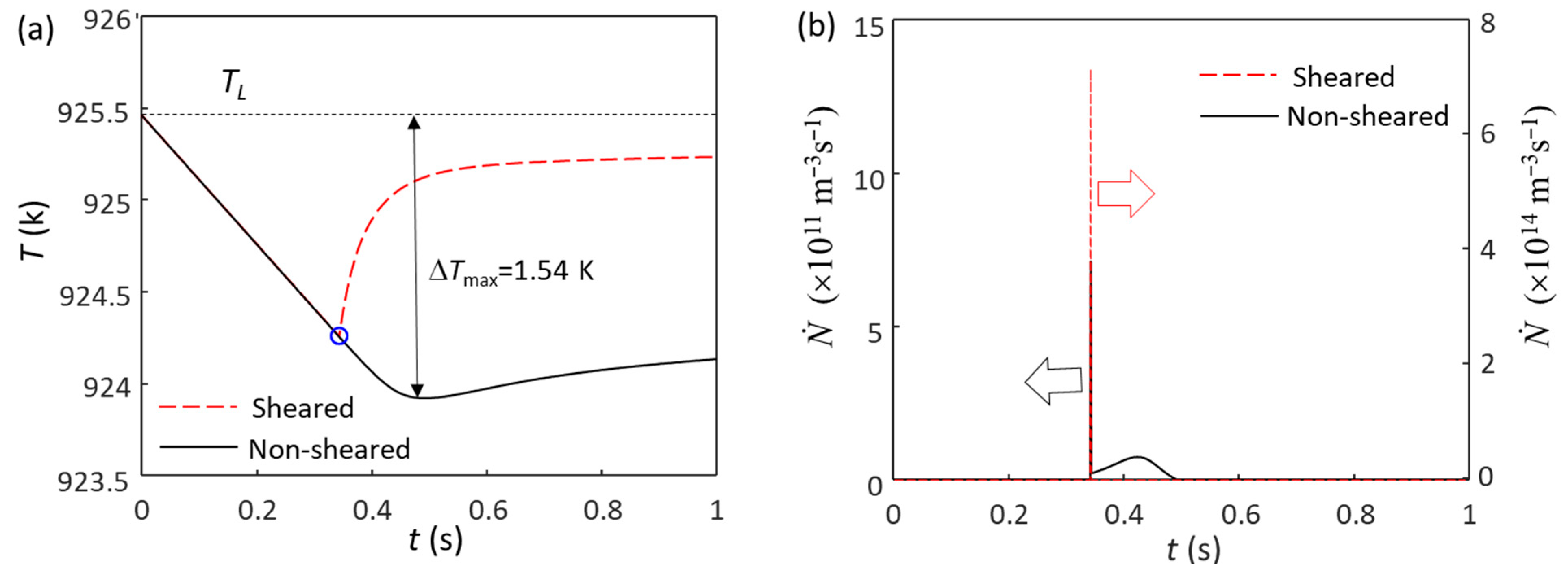
4.1. Competition for Grain Initiation between Potent TiB2 and Al2O3 Particles in Al Alloys
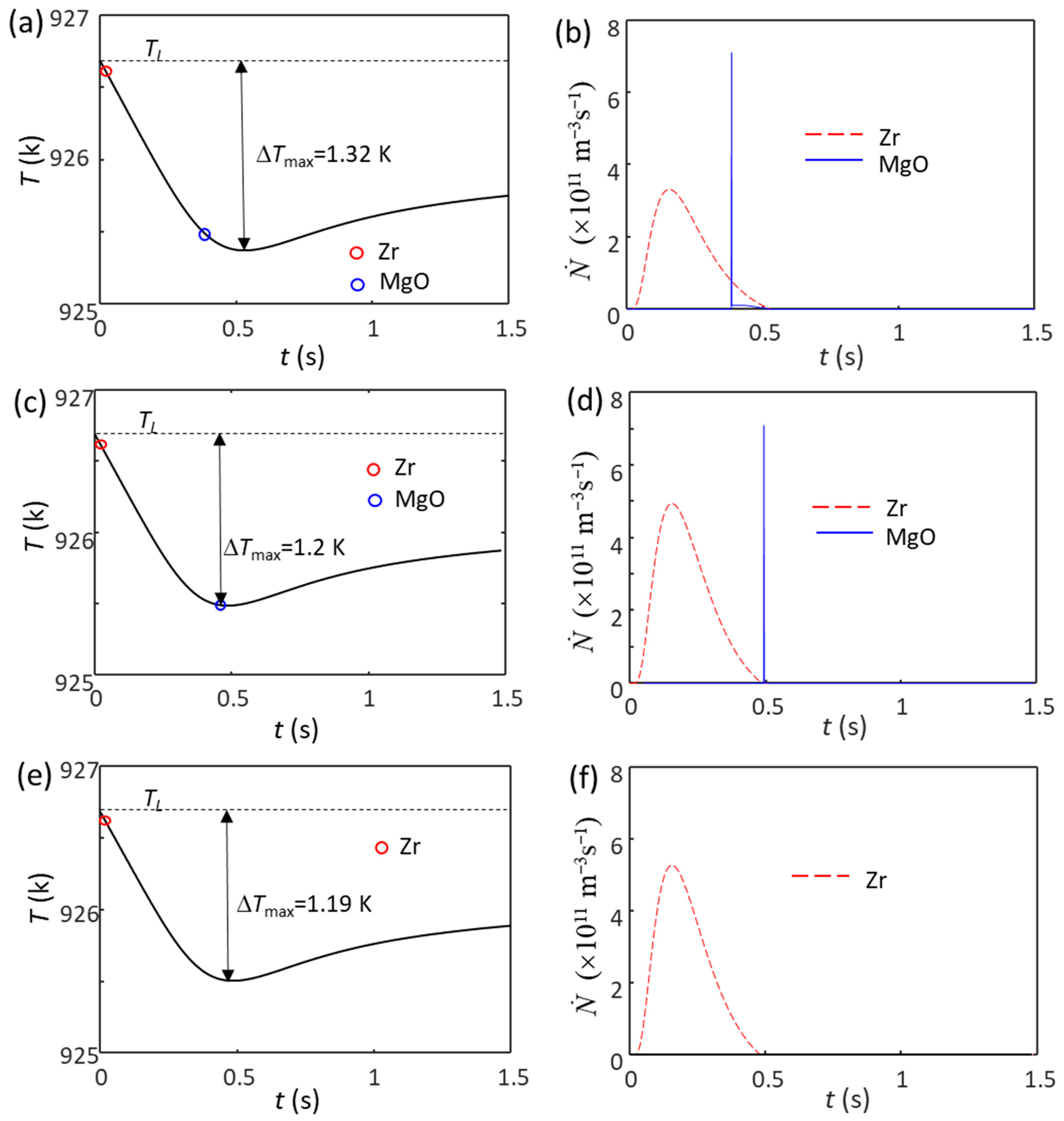
4.2. Competition for Grain Initiation between Zr and MgO Particles in Mg Alloys
5. General Discussion
- when ΔTn(1) < ΔTmax < ΔTn(2), only Type 1 particles participate in nucleation;
- when ΔTn(2) < ΔTmax < ΔTn(1), only Type 2 particles participate in nucleation;
- when ΔTn(1) < ΔTn(2) < ΔTmax, both Type 1 and Type 2 particles participate in nucleation; Type 1 particles nucleate first, followed by Type 2 particles; and
- when ΔTn(2) < ΔTn(1) < ΔTmax, both Type 1 and Type 2 particles participate in nucleation; Type 2 particles nucleate first, followed by Type 1 particles.
6. Summary
- (1)
- The competition for heterogeneous nucleation is governed by , which states that nucleation occurs first on nucleant particles with the smallest nucleation undercooling and then on particles with progressively smaller nucleation undercoolings until recalescence.
- (2)
- The competition for grain initiation occurs only on those particles that have participated in heterogeneous nucleation and is governed by , which states that, among all the solid particles, the largest solid particles initiate grains first, followed by grain initiation on progressively smaller ones regardless of the type of nucleant particles from which the solid particles originated.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kelton, K.F.; Greer, A.L. (Eds.) Nucleation in Condensed Matter: Applications in Materials and Biology; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- McCartney, D.G. Grain refining of Al and its alloys using inoculants. Int. Mater. Rev. 1989, 34, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, M.; StJohn, D. Grain refinement of aluminum alloys: Part I. The nucleant and solute paradigms—A review of the literature. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1999, 30, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, B.S.; Kori, S.A.; Chakraborty, M. Grain refinement of aluminium and its alloys by heterogeneous nucleation and alloying. Int. Mater. Rev. 2002, 47, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, M.A.; Qian, M.; Prasad, A.; StJohn, D.H. Recent advances in grain refinement of light metals and alloys. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2016, 20, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, K.D.; Birbilis, N. Effect of grain size on corrosion: A review. Corrosion 2010, 66, 075005–075005-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwinski, F. (Ed.) Magnesium Alloys—Design, Processing and Properties; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Eskin, D.G.; Tzanakis, I.; Wang, F.; Lebon, G.S.B.; Subroto, T.; Pericleous, K.; Mi, J. Fundamental studies of ultrasonic melt processing. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2019, 52, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaroszewski, M.; Thomas, S.; Rane, A.V. (Eds.) Advanced Materials for Electromagnetic Shielding: Fundamentals, Properties, and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Dong, A.; Gao, J.; Damoah, L.N.W. Application of electromagnetic (EM) separation technology to metal refining processes: A review. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2014, 45, 2153–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Pan, F. A review on electromagnetic shielding magnesium alloys. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2021, 9, 1906–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xia, M.; Arumuganathar, S. Enhanced heterogeneous nucleation in AZ91D alloy by intensive melt shearing. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 4891–4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.T.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Z. Mechanisms of enhanced heterogeneous nucleation during solidification in binary Al-Mg alloys. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 1528–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Z.; Xia, M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, G.; Patel, J.B.; Bian, Z.; Bayandorian, I.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.T.; Scamans, G.M. Melt conditioning by advanced shear technology (MCAST) for refining solidification microstructures. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2009, 22, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Zuo, Y.B.; Jiang, B. A new technology for treating liquid metals with intensive melt shearing. Mater. Sci. Forum 2011, 690, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.B.; Yang, X.; Mendis, C.L.; Fan, Z. Melt conditioning of light metals by application of high shear for improved microstructure and defect control. JOM 2017, 69, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Zuo, Y.B.; Jiang, B. Apparatus and Method for Liquid Metals Treatment. International Patent Application No. PCT/GB2011/051744, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, Y.; Qiu, D.; Jiang, B.; Pan, F.; Zhang, M.X. Current research progress in grain refinement of cast magnesium alloys: A review. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 619, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, T.; Zhou, X.R.; Thompson, G.E.; Pennycook, T.; Hashimotob, T. Grain refining mechanism in the Al/Al-Ti-B system. Acta Mater. 2015, 84, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engh, T.A. (Ed.) Principles of Metal Refining; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Sin, S.L.; Elsayed, A.; Ravindran, C. Inclusions in magnesium and its alloys: A review. Inter. Mater. Rev. 2013, 58, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Fan, Z. Characterization of AlN inclusion particles formed in commercial purity aluminum. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 2519–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, Z.; Mendis, C.L. Effects of native AlN particles on heterogeneous nucleation in an Al-3Fe alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2021, 52, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakke, P.; Karlsen, D.O. Inclusion assessment in magnesium and magnesium base alloys. SAE Trans. 1997, 106, 314–326. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J. (Ed.) Castings, 2nd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Dash, K.; Galano, M.L.; O’Reilly, K.A.Q. Oxidation studies of Al alloys: Part II Al-Mg alloy. Corr. Sci. 2019, 155, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirak, A.R.; Divandari, M.; Boutorabi, S.M.A.; Campbell, J. Oxide film characteristics of AZ91 magnesium alloy in casting conditions. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2007, 20, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, G.; Øvrelid, E.; Tranell, G.; Fenstad, J.; Gjestland, H. Characterisation of the surface films formed on molten magnesium in different protective atmospheres. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 332, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balart, M.J.; Fan, Z. Surface oxidation of molten AZ91D magnesium alloy in air. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2014, 27, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Ramasse, Q.; Fan, Z. The nature of native MgO in Mg and its alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 2957–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, Z.; Zhou, X.; Thompson, G.E. Characterisation of magnesium oxide and its interface with α-Mg in Mg-Al-based alloys. Phil. Mag. Lett. 2011, 91, 516–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, H.; Jiang, B.; Fan, Z. Mechanisms of grain refinement by intensive shearing of AZ91alloy melt. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 6526–6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.M.; Fan, Z. Prenucleation at the interface between MgO and liquid magnesium: An ab initio molecular dynamics study. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.S.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Z. Competitive heterogeneous nucleation between Zr and MgO particles in commercial purity magnesium. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 2182–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, J.W. On the equilibrium of heterogeneous substances. Am. J Sci. 1879, 16, 441–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volmer, M.; Weber, A.Z. Nucleus formation in supersaturated systems. Z. Für Phys. Chem. 1926, 119, 277–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, R.; Döring, W. Kinetic treatment of nucleation in supersaturated vapors. Ann. Phys. 1935, 24, 719–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeldovich, J.B. On the theory of new phase formation: Cavitation. Acta Physicochim. USSR 1943, 18, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kashchiev, D. Nucleation: Basic Theory with Applications; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cantor, B. Heterogeneous nucleation and adsorption. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 2003, 361, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.T.; Cantor, B. Solidification behaviour of Pb droplets embedded in a Cu matrix. Acta Metal. Mater. 1992, 40, 3339–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.T.; Cantor, B. Heterogeneous nucleation of Al2Cu in Al-Cu eutectic liquid droplets embedded in an al matrix. Acta Metal. Mater. 1994, 42, 3045–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z. An Epitaxial model for heterogeneous nucleation on potent substrates. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, H.; Fan, Z. Prenucleation induced by crystalline substrates. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 2766–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, H.; Fang, C.M.; Fan, Z. Prenucleation at the liquid/substrate interface: An overview. Metals, 2022; in progress. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.; Men, H.; Fan, Z. Atomic ordering in the liquid adjacent to an atomically rough solid surface. Comp. Mater. Sci. 2018, 153, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.M.; Men, H.; Fan, Z. Effect of substrate chemistry on prenucleation. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 6231–6242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Men, H. A molecular dynamics study of heterogeneous nucleation in generic liquid/substrate systems with positive lattice misfit. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 126501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Men, H.; Wang, Y.; Que, Z.P. A new atomistic mechanism for heterogeneous nucleation in the systems with negative lattice misfit: Creating a 2D template for crystal growth. Metals 2021, 11, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Men, H. Heterogeneous nucleation and grain initiation on a single substrate. Metals 2022, 12, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Men, H. An overview on atomistic mechanisms of heterogeneous nucleation. Metals, 2022; in progress. [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull, D.; Vonnegut, B. Nucleation catalysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1952, 44, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.L.; Bunn, A.M.; Tronche, A.; Evans, P.V.; Bristow, D.J. Modelling of inoculation of metallic melts: Application to grain refinement of Al by Al-Ti-B. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 2823–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Gao, F.; Jiang, B.; Que, Z.P. Impeding nucleation for more significant grain refinement. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quested, T.E.; Greer, A.L. The effect of the size distribution of inoculant particles on as-cast grain size in aluminium alloys. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 3859–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z. Heterogeneous nucleation, grain initiation and grain refinement of Mg-alloys. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Magnesium Alloys and Their Applications, Old Winsor, UK, 24–27 July 2018; pp. 7–17. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Gao, F. Grain initiation and grain refinement: An overview. Metals, 2022; in progress. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Gao, F.; Zhou, L.; Lu, S.Z. A new concept for growth restriction during solidification. Acta Mater. 2018, 152, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calculated from Pandat 2021 Version Software with PanMg Database. Available online: https://computherm.com/databases (accessed on 7 August 2022).
- Wang, S.H.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Z. Brunel University London, Uxbridge, Middlesex, UK. to be submitted.
- Wang, D.; Chang, W.; Shen, Y.; Sun, J.; Sheng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, Q. The role of lattice mismatch in heterogeneous nucleation of pure Al on Al2O3 single-crystal substrates with different termination planes. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 137, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, Z. Grain refinement of Mg alloys by Zr. to be submitted.
- Zuo, Y.B.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Z. January. Grain refinement of DC cast magnesium alloys with intensive melt shearing. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2012, 27, 012043. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Barekar, N.; El Fakir, O.; Yang, X.; Dear, J.P.; Fan, Z. Influence of intensive melt shearing on subsequent hot rolling and the mechanical properties of twin roll cast AZ31 strips. Mater. Lett. 2015, 144, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.F.; Xia, M.; Li, H.T.; Xu, J.; Granasy, L.; Scamans, G.M. Shear enhanced heterogeneous nucleation in some Mg-and Al-alloys. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2009, 22, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Parameters (Symbol, Unit) | Al-Cu | Mg-Zr |
|---|---|---|
| Partition coefficient (k) | −2.5 [58] | 4.7 [59] |
| Liquidus slope (m, K(wt.%)−1) | 0.13 [58] | 8.2 [59] |
| Heat capacity (cpv, Jm−3K−1) | 2.58 × 106 [55] | 2.59 × 106 [54] |
| Enthalpy of fusion (∆HV, Jm−3) | 9.5 × 108 [55] | 6.75 × 108 [54] |
| Diffusion coefficient (D, m2s−1) | 2.52 × 10−9 [55] | 2.7 × 10−9 [54] |
| Gibbs–Thompson coefficient (Γ, Km) | 1.42 × 10−7 [55] | 1.48 × 10−7 [54] |
| Volume (V0, m3) | 1 × 10−6 | 1 × 10−6 |
| Cooling rate (K/s) | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| N0(Zr) (m−3) | N0(MgO) (m−3) | ΔTmax (K) | N(Zr)/N | Grain Size (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 1.0 × 1014 | 1.82 | 0 | 251 |
| 1.0 × 1011 | 1.0 × 1014 | 1.32 | 97.7% | 184 |
| 1.5 × 1011 | 1.0 × 1014 | 1.2 | 99.3% | 165 |
| 1.6 × 1011 | 1.0 × 1014 | 1.19 | 100% | 162 |
| - | 1.0 × 1017 | 1.2 | 0 | 88 |
| 1.0 × 1011 | 1.0 × 1017 | 1.2 | 9.2% | 86 |
| 1.5 × 1011 | 1.0 × 1017 | 1.2 | 13.4% | 85 |
| 1.6 × 1011 | 1.0 × 1017 | 1.19 | 100% | 162 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, F.; Fan, Z. Competition for Nucleation and Grain Initiation during Solidification. Metals 2022, 12, 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12091512
Gao F, Fan Z. Competition for Nucleation and Grain Initiation during Solidification. Metals. 2022; 12(9):1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12091512
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Feng, and Zhongyun Fan. 2022. "Competition for Nucleation and Grain Initiation during Solidification" Metals 12, no. 9: 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12091512
APA StyleGao, F., & Fan, Z. (2022). Competition for Nucleation and Grain Initiation during Solidification. Metals, 12(9), 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12091512







