Synergism between B and Nb Improves Fire Resistance in Microalloyed Steels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials & Methods
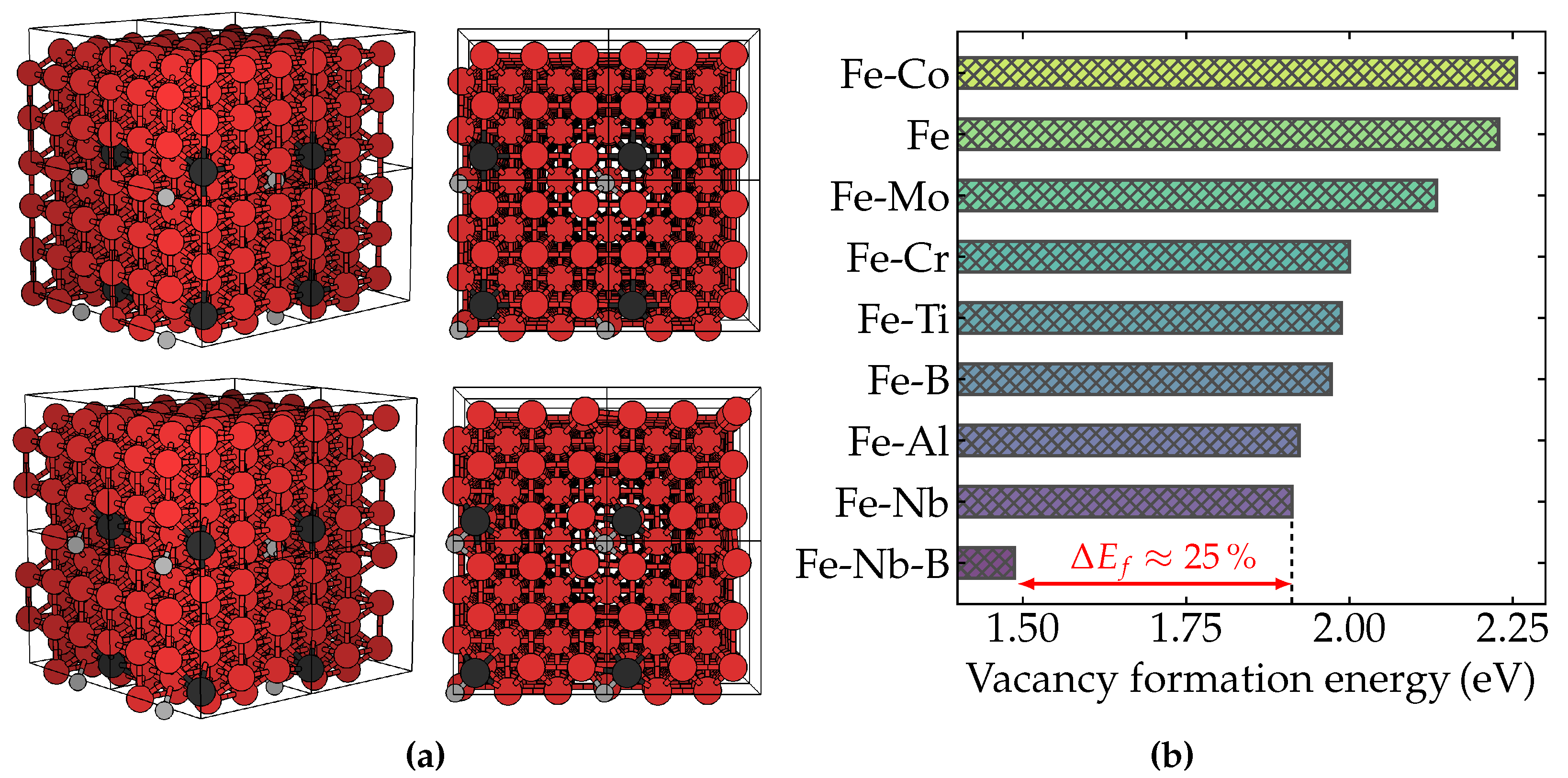
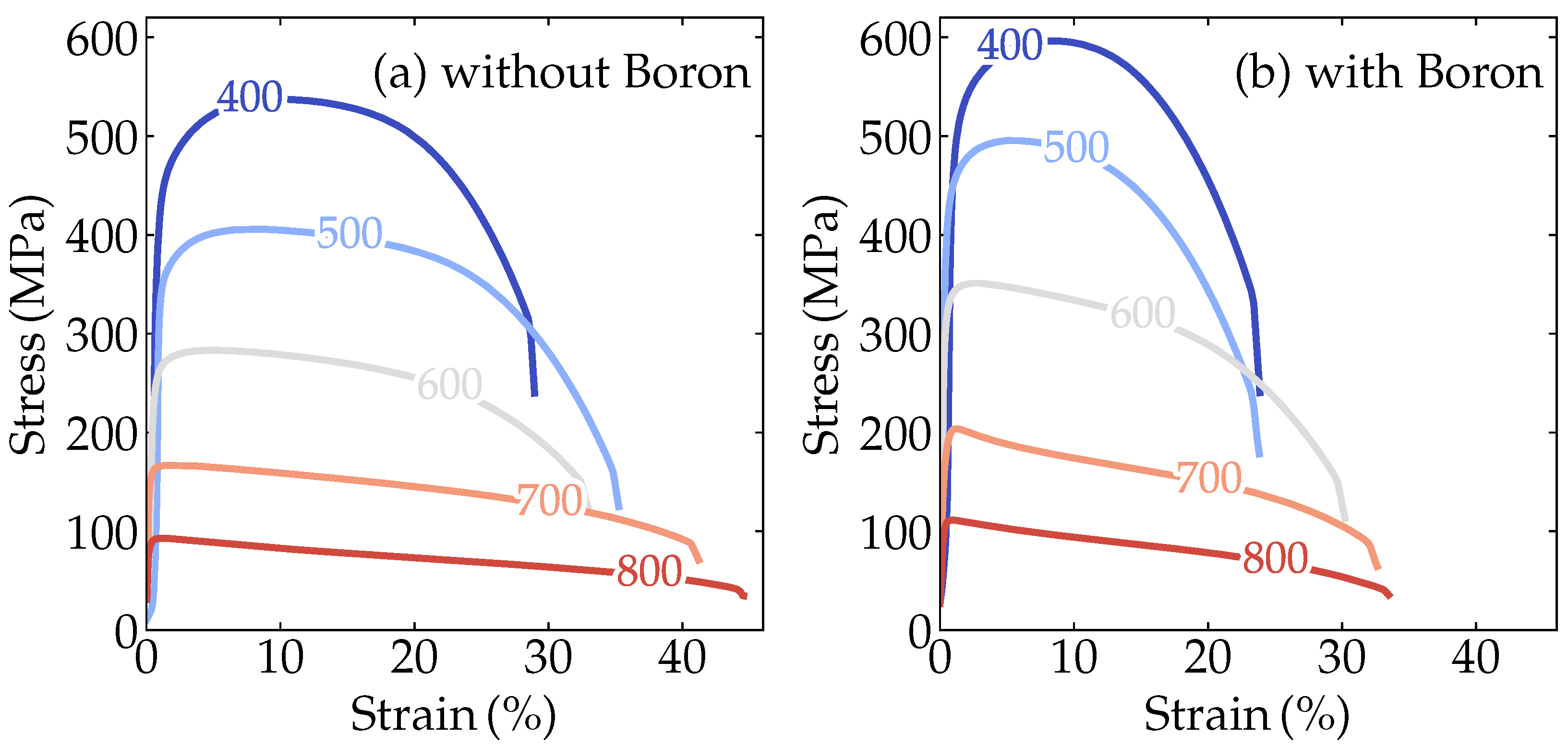
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, H.R.; Cheng, G.H. Hardenability effect of boron on carbon steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1987, 3, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, N.; Matsubara, Y.; Sakai, T.; Saito, Y. Proc. of the Int. Conf. on Martensitic Transformations (ICOMAT-92) 767, 1992. ISIJ Int. 1997, 37, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xue, X.; Yang, H. Influence of Boron on initial austenite grain size and hot deformation behavior of Boron microalloyed steels. Crystals 2015, 5, 592–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Du, L.X.; Ma, Y.N.; Sun, G.S.; Xie, H.; Misra, R. Effect of microalloying with molybdenum and boron on the microstructure and mechanical properties of ultra-low-C Ti bearing steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 640, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koley, S.; Karani, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Shome, M. Influence of Boron on Austenite to Ferrite Transformation Behavior of Low Carbon Steel Under Continuous Cooling. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 3449–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Ortlepp, I.; Bleck, W. Boron in Heat-Treatable Steels: A Review. Steel Res. Int. 2019, 90, 1900133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, G.; Goto, A.; Takayama, N.; Furuhara, T. Three-dimensional atom probe analysis of boron segregation at austenite grain boundary in a low carbon steel-Effects of boundary misorientation and quenching temperature. Scr. Mater. 2018, 154, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.P.G.A.; Barboza, M.J.R.; Goldenstein, H.; Nunes, C.A. Borocarbide coarsening and the effect of borocarbide particle size on Charpy V-notch impact properties of medium-carbon boron-containing steel. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2020, 111, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghali, S.N.; El-Faramawy, H.S.; Eissa, M.M. Influence of boron additions on mechanical properties of carbon steel. JMMCE 2012, 11, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Nyo, T.; Kaijalainen, A.; Javaheri, V.; Tervo, H.; Hannula, J.; Somani, M.; Kömi, J. Incompatible effects of B and B+ Nb additions and inclusions’ characteristics on the microstructures and mechanical properties of low-carbon steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 819, 141453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.H.; Shin, C.; Moon, J.; Jang, J.H.; Ha, H.Y.; Park, S.J.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, B.H.; Chung, J.H.; Speer, J.G.; et al. Mechanisms for improving tensile properties at elevated temperature in fire-resistant steel with Mo and Nb. Mater. Des. 2020, 194, 108882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E8/E8M-16a; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 1–30. [CrossRef]
- ASTM E21-17; Standard Test Methods for Elevated Temperature Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 1–24. [CrossRef]
- Kohn, W.; Sham, L.J. Self-consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects. Phys. Rev. 1965, 140, A1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hohenberg, P.; Kohn, W. Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. 1964, 136, B864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dal Corso, A. Pseudopotentials periodic table: From H to Pu. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2014, 95, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannozzi, P.; Baroni, S.; Bonini, N.; Calandra, M.; Car, R.; Cavazzoni, C.; Ceresoli, D.; Chiarotti, G.L.; Cococcioni, M.; Dabo, I.; et al. QUANTUM ESPRESSO: A modular and open-source software project for quantum simulations of materials. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 395502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannozzi, P.; Andreussi, O.; Brumme, T.; Bunau, O.; Nardelli, M.B.; Calandra, M.; Car, R.; Cavazzoni, C.; Ceresoli, D.; Cococcioni, M.; et al. Advanced capabilities for materials modelling with Quantum ESPRESSO. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2017, 29, 465901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzari, N.; Vanderbilt, D.; De Vita, A.; Payne, M.C. Thermal Contraction and Disordering of the Al(110) Surface. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorini, T.T.; de Freitas, B.X.; Ferreira, P.P.; Chaia, N.; Suzuki, P.A.; Joubert, J.M.; Nunes, C.A.; Coelho, G.C.; Eleno, L.T. T2 phase site occupancies in the Cr–Si–B system: A combined synchroton-XRD/first-principles study. Scr. Mater. 2021, 199, 113854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Guo, Z.; Wang, L.; Rong, Y. Carbide characterization in a Nb-microalloyed advanced ultrahigh strength steel after quenching–partitioning–tempering process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 3373–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idczak, R.; Konieczny, R.; Chojcan, J. Study of defects in Fe–Re and Fe–Mo alloys by the Mössbauer and positron annihilation spectroscopies. Solid State Commun. 2012, 152, 1924–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idczak, R.; Konieczny, R. Behaviour of vacancies in dilute Fe–Re alloys: A positron annihilation study. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 117, 1785–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Idczak, R.; Konieczny, R.; Chojcan, J. A study of defects in iron-based binary alloys by the Mössbauer and positron annihilation spectroscopies. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 103513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walp, M. Fire-Resistant Steels for Construction Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Speer, J.G.; Matlock, D.K.; Jansto, S.G. Nb-Microalloyed “Fire-Resistant” Construction Steels: Recent Progress. In Proceedings of the Value-Added Niobium Microalloyed Construction Steels Symposium CBMM and TMS, Singapore, 5–7 November 2012; pp. 133–154. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM A1077/A1077M-14; Standard Specification for Structural Steel with Improved Yield Strength at High Temperature for Use in Buildings. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 1–3. [CrossRef]
- Chijiiwa, R.; Tamehiro, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Funato, K.; Uemori, R.; Horii, Y. Development and Practical Application of Fire-Resistant Steel for Buildings. Nippon Steel Tech. Rep. 1993, 58, 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, R.; Sun, F.; Zhang, L.; Shan, A. Development and study of high-strength low-Mo fire-resistant steel. Mater. Des. 2012, 36, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Hong, S.; Park, C.; Kim, K.; Park, S. Influence of Mo on precipitation hardening in hot rolled HSLA steels containing Nb. Scr. Mater. 2000, 43, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.B.; Hong, S.G.; Park, C.G.; Park, S.H. Carbide precipitation and high-temperature strength of hot-rolled high-strength, low-alloy steels containing Nb and Mo. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2002, 33, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohrbacher, H. Synergies of Niobium and Boron Microalloying in Molybdenum Based Bainitic and Martensitic Steels. Fundam. Appl. Alloy. High Perform. Steels 2014, 1, 83–108. [Google Scholar]
- XM, W. Effect of boron addition on structure and properties of low carbon bainitic steels. ISIJ Int. 2002, 42, S38–S46. [Google Scholar]


| Alloy | B | C | Nb | Mn | N | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| with B | 0.0028 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 1.00 | 0.0029 | 0.015 |
| without B | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 1.00 | 0.0029 | 0.015 |
| Alloy | E (%) | RA (%) | UTS (MPa) | YS (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| with B | 19.6 | 75.8 | 610 | 513 |
| without B | 20.5 | 73.2 | 617 | 551 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira, P.P.; Carvalho, F.M.; Ariza-Echeverri, E.A.; Delfino, P.M.; Bauri, L.F.; Ferreira, A.M.; Braga, A.P.; Eleno, L.T.F.; Goldenstein, H.; Tschiptschin, A.P. Synergism between B and Nb Improves Fire Resistance in Microalloyed Steels. Metals 2023, 13, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13010084
Ferreira PP, Carvalho FM, Ariza-Echeverri EA, Delfino PM, Bauri LF, Ferreira AM, Braga AP, Eleno LTF, Goldenstein H, Tschiptschin AP. Synergism between B and Nb Improves Fire Resistance in Microalloyed Steels. Metals. 2023; 13(1):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13010084
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira, Pedro Pires, Felipe Moreno Carvalho, Edwan Anderson Ariza-Echeverri, Pedro Meirelles Delfino, Luiz Felipe Bauri, Andrei Marx Ferreira, Ana Paola Braga, Luiz Tadeu Fernandes Eleno, Hélio Goldenstein, and André Paulo Tschiptschin. 2023. "Synergism between B and Nb Improves Fire Resistance in Microalloyed Steels" Metals 13, no. 1: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13010084
APA StyleFerreira, P. P., Carvalho, F. M., Ariza-Echeverri, E. A., Delfino, P. M., Bauri, L. F., Ferreira, A. M., Braga, A. P., Eleno, L. T. F., Goldenstein, H., & Tschiptschin, A. P. (2023). Synergism between B and Nb Improves Fire Resistance in Microalloyed Steels. Metals, 13(1), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13010084







