Surface Morphology Analysis of Laser Shock Peened 20CrMnTi Steel: A Statistical Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Preparation
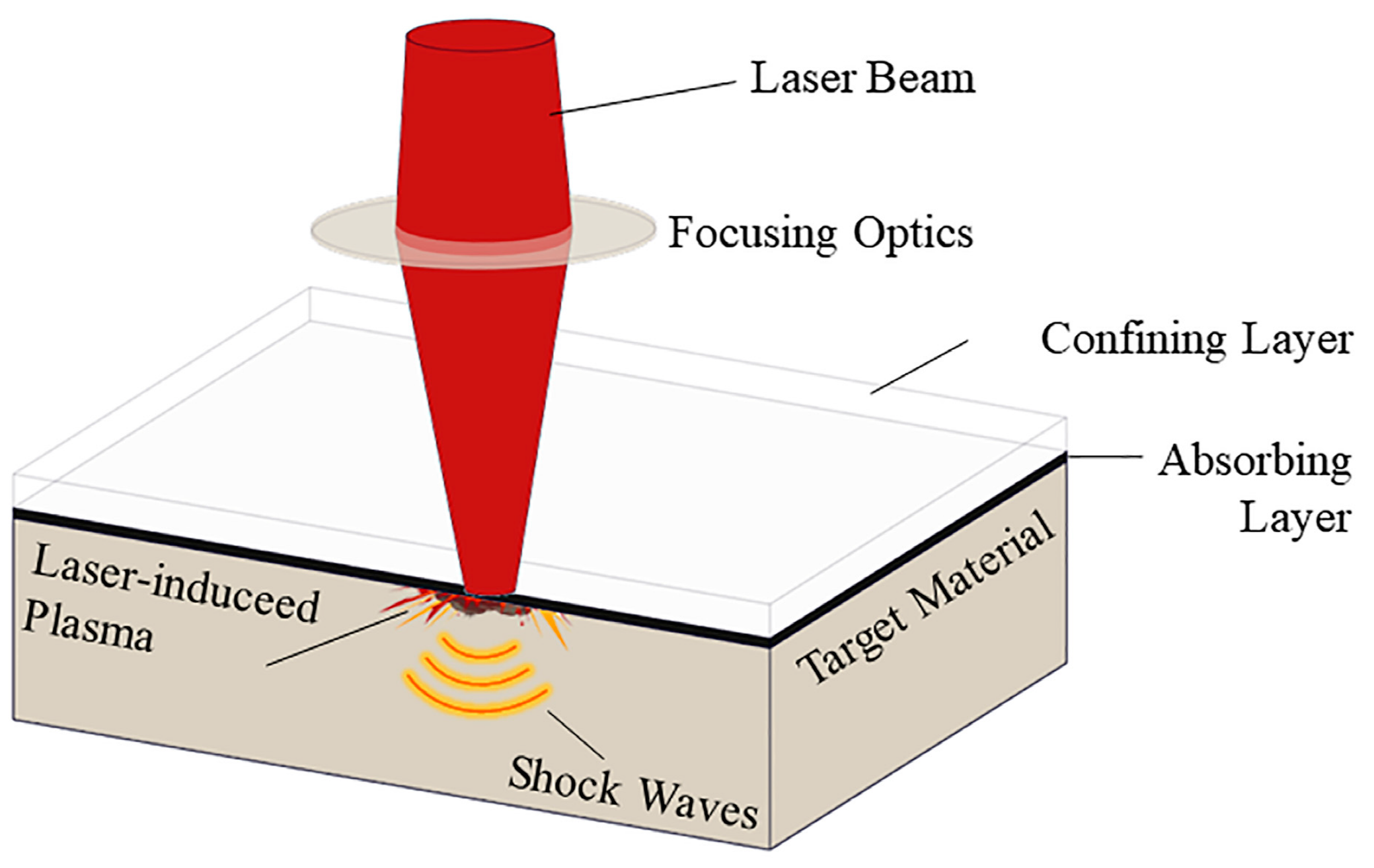
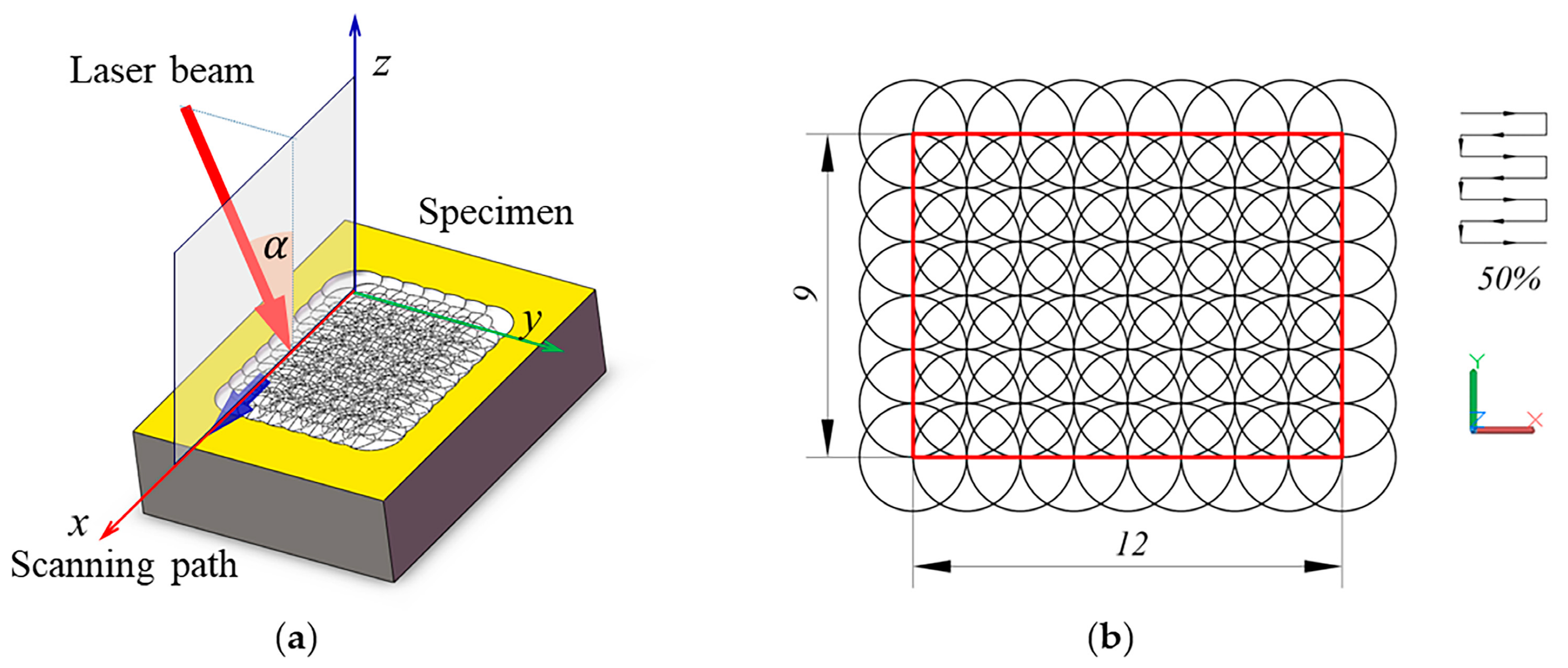
2.2. LSP Experiments
2.3. Surface Morphology Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Morphology in the Single-Point Impact
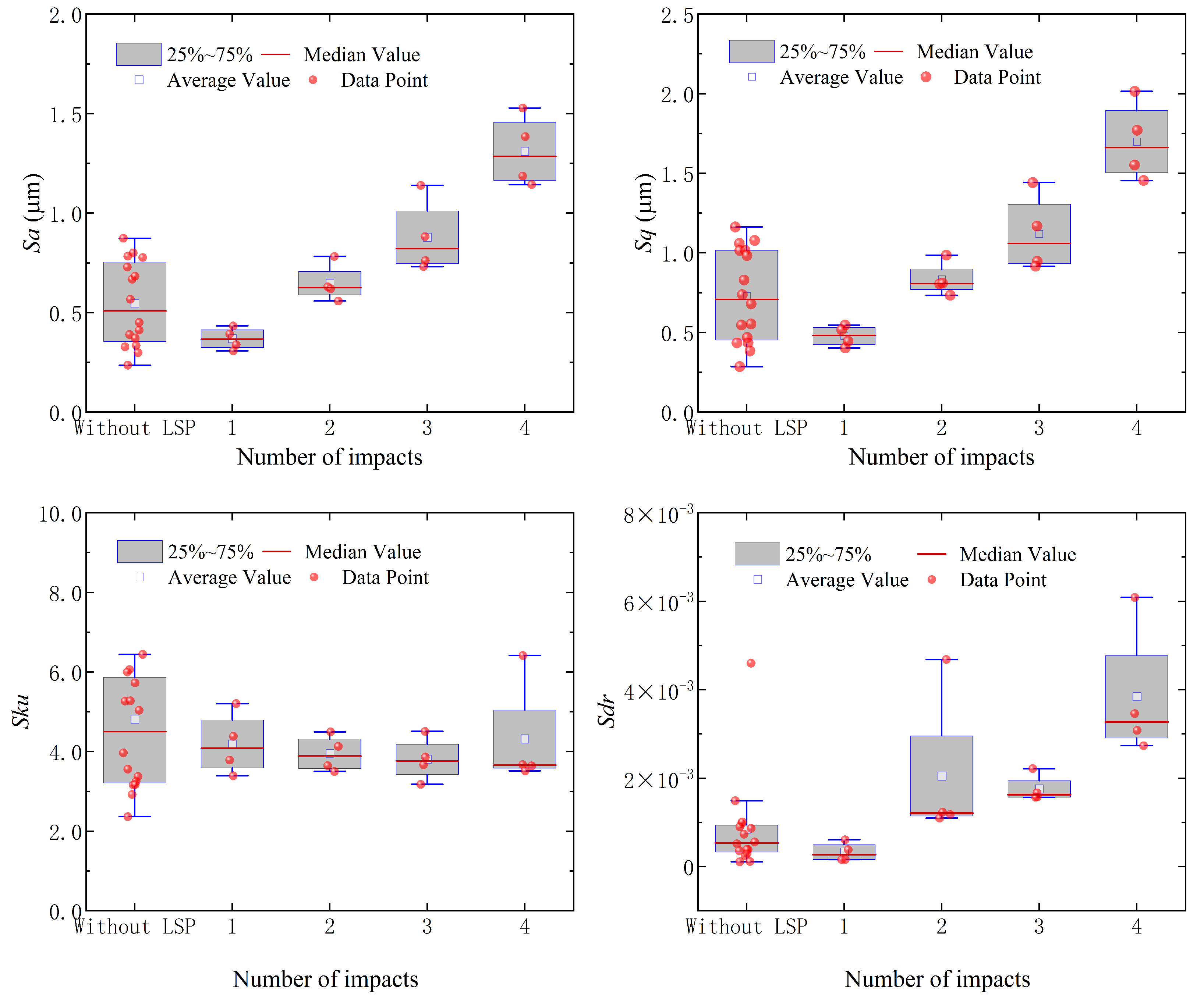
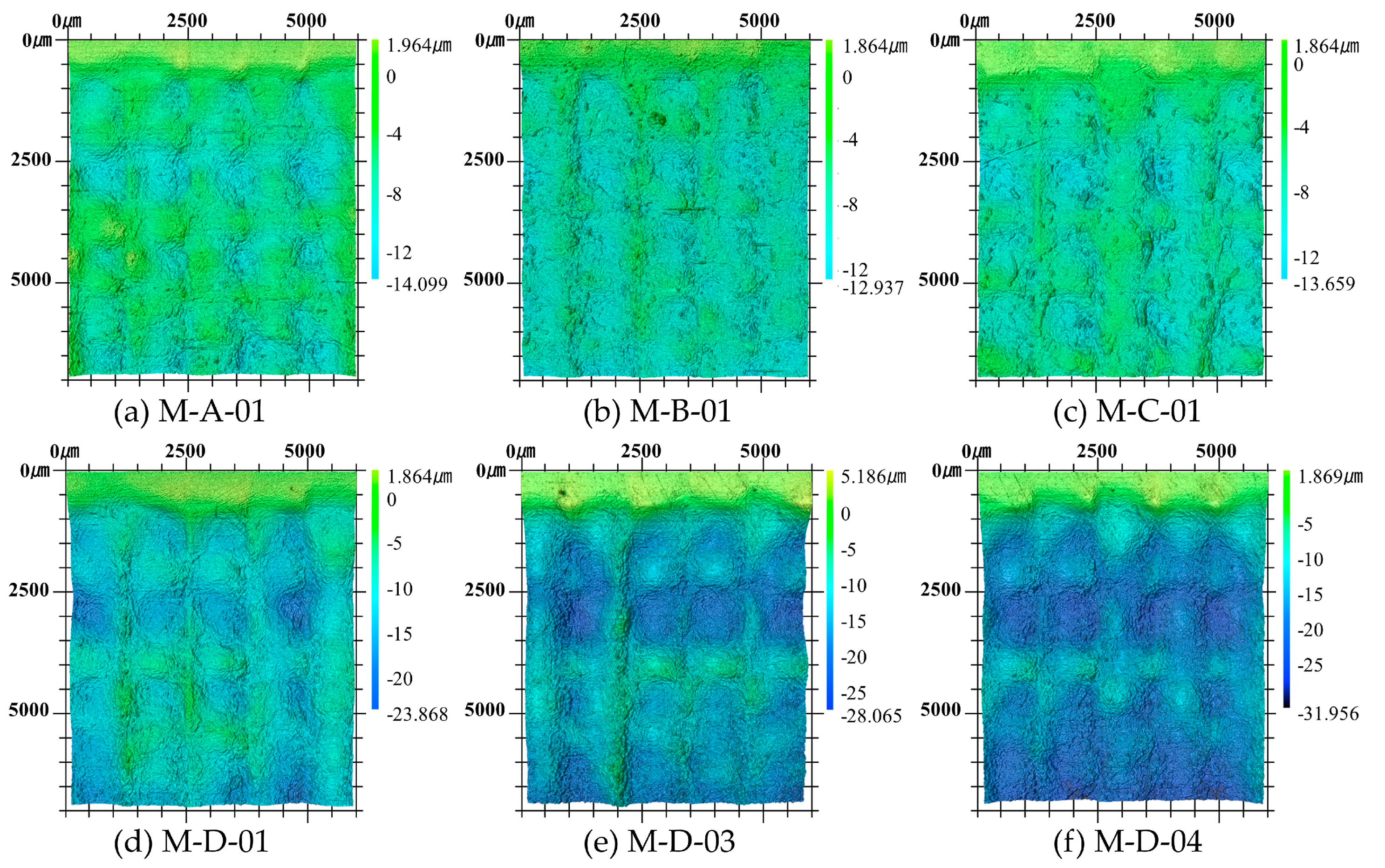
3.2. Surface Morphology in the Multiple Impacts
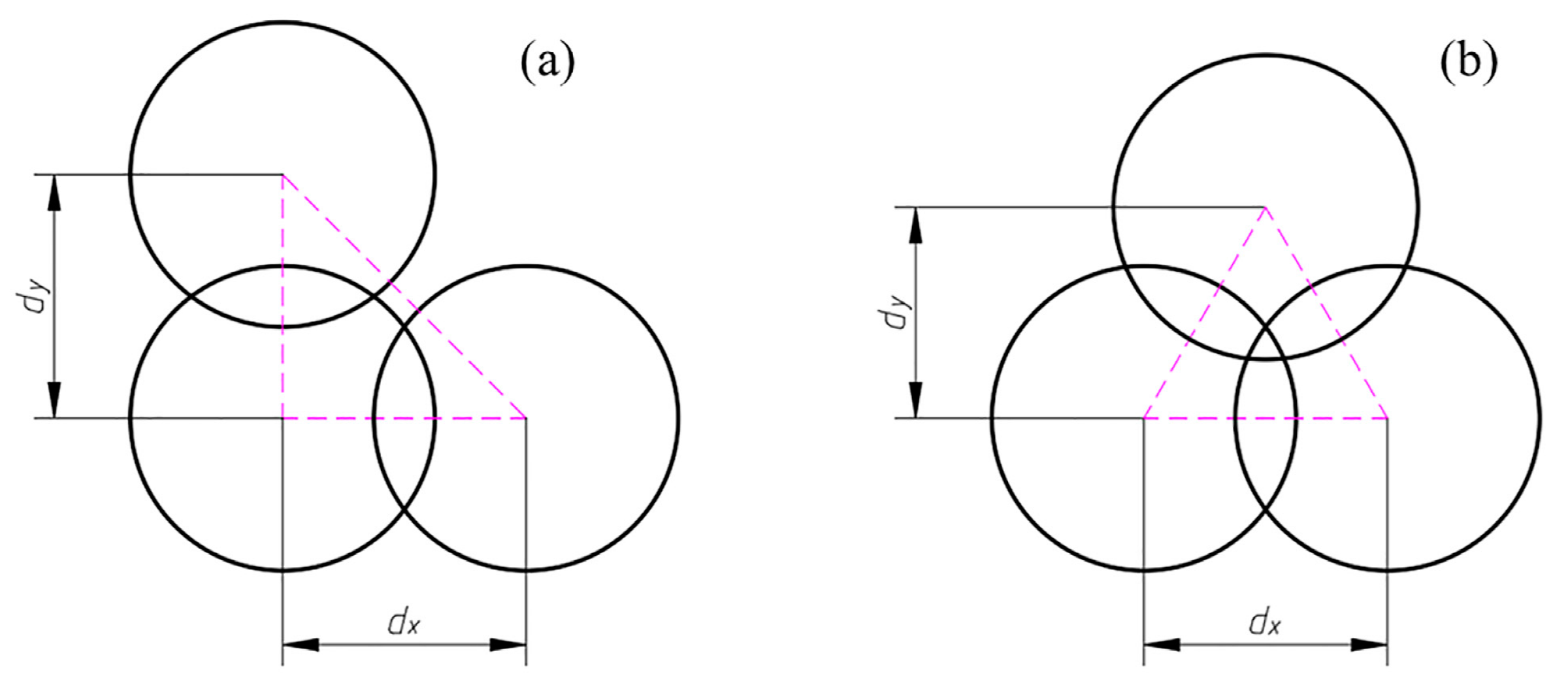
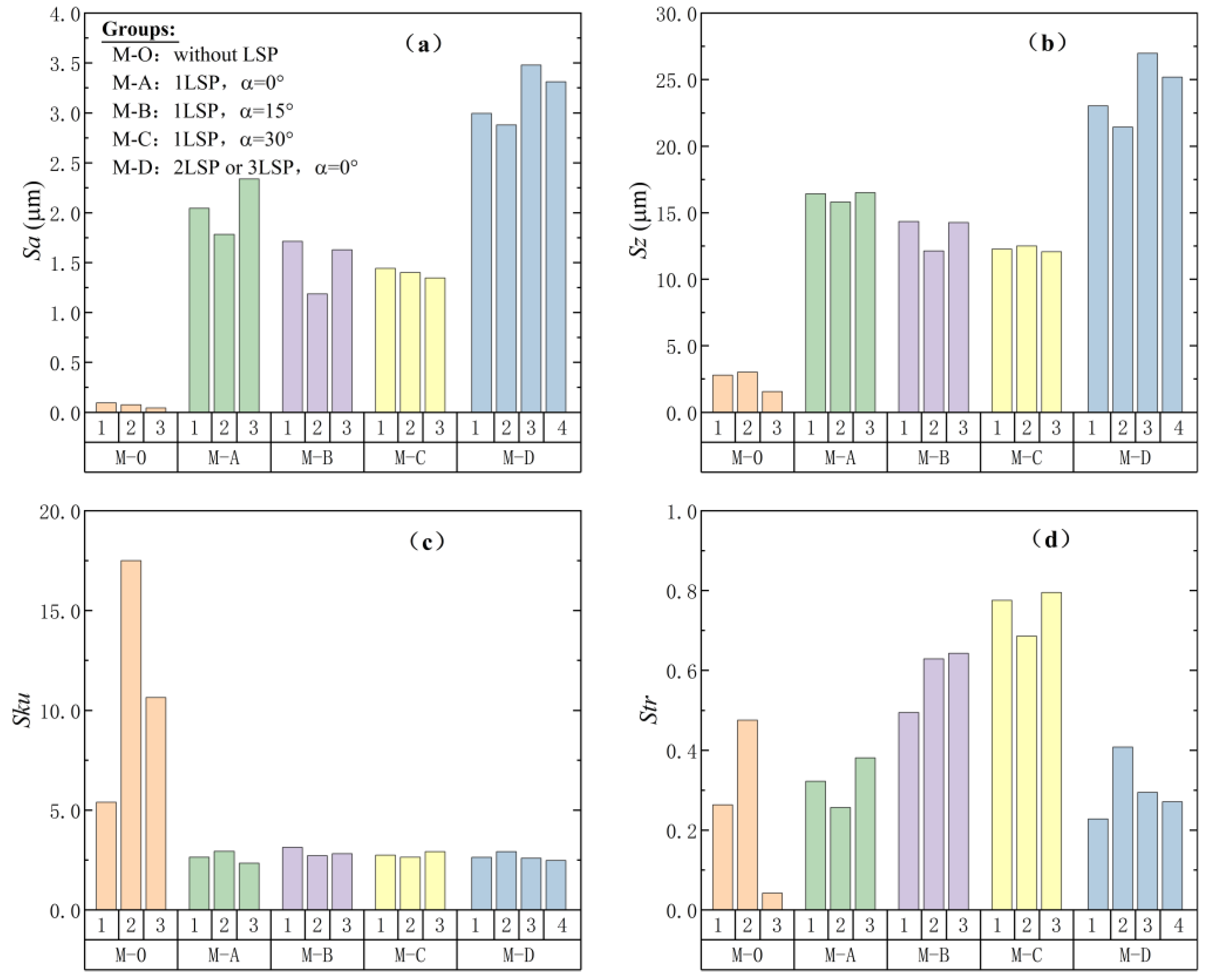
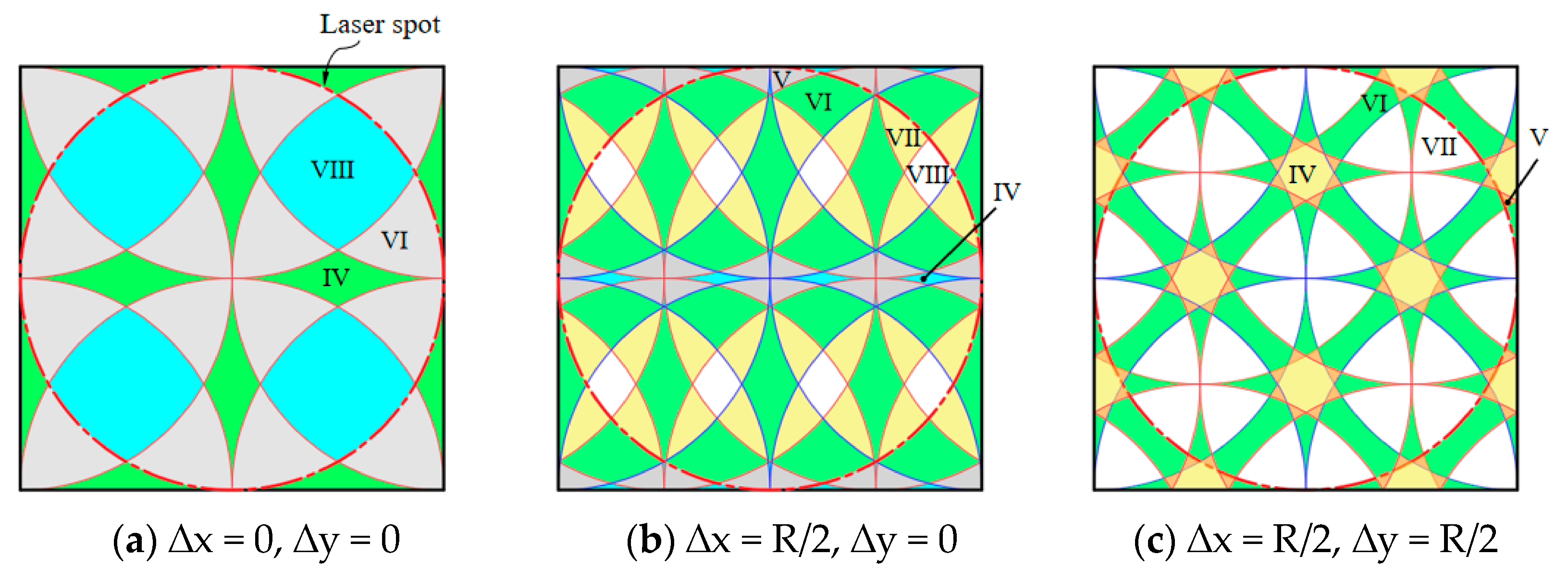
3.3. Evaluation of Impact Stacking Methods and Their Effects
3.4. Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The plastic deformation induced by LSP showed a positive correlation with the number of laser impacts. Additionally, LSP treatment resulted in changes in surface morphology, distribution, and an increase in surface roughness.
- (2)
- Multiple impacts led to the formation of a wave-like pattern of indentations, where the directionality and periodicity of the surface texture were influenced by the laser incidence angle used during the LSP process.
- (3)
- The integration of 3D morphological parameters provides valuable insights into surface characterization and should be considered when evaluating laser shock processed surfaces. However, further research is needed to develop evaluation methods tailored to specific application areas.
- (4)
- The impact patterns can be utilized to evaluate surface morphology variations resulting from LSP treatment, suggesting the potential for strategically adjusting the shock region’s position to effectively reduce height differences on impacted surfaces.
- (5)
- For a more comprehensive exploration of the surface morphology characteristics induced by LSP, several aspects, including periodicity, symmetry, complexity, and minimum period exhibited by the impact patterns, should be taken into consideration.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, J.; Fu, X.; Lai, Q.; Guo, X.; Qu, S.; He, R.; Qin, S.; Li, J. Evolution of Fretting Wear Behaviors and Mechanisms of 20CrMnTi Steel after Carburizing. Metals 2020, 10, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Wang, C.; Lu, H.; Meng, X.; Wang, Z.; Lv, J.; Luo, K.; Lu, J. Progressive developments, challenges and future trends in laser shock peening of metallic materials and alloys: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2023, 191, 104061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikdeloo, R.; Farrahi, G.; Mehmanparast, A.; Mahdavi, S. Multiple laser shock peening effects on residual stress distribution and fatigue crack growth behaviour of 316L stainless steel. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2020, 105, 102429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.; Ralls, A.M.; Kuruveri, U.B.; Menezes, P.L. Tribological, corrosion, and microstructural features of laser-shock-peened steels. Metals 2023, 13, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, M.; Furfari, D.; Ahmad, B.; Gharghouri, M.A.; Fitzpatrick, M.E. Fatigue crack growth in a laser shock peened residual stress field. Int. J. Fatigue. 2019, 123, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Dai, W.; Guo, W.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xue, J.; Lin, L.; Peng, P. Improved corrosion resistance of Ni-base Alloy 600 welded joint by laser shock peening. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 80, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Mankoci, S.; Walters, N.; Gao, H.; Zhang, H.; Hou, X.; Qin, H.; Ren, Z.; Zhou, X.; Doll, G.L.; et al. Effects of laser shock peening on the corrosion behavior and biocompatibility of a nickel-titanium alloy. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2019, 107, 1854–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Shukla, P.; Swanson, P.; An, Z.; Prabhakaran, S.; Waugh, D.; Nie, X.; Mee, C.; Nakhodchi, S.; Lawrence, J. Altering the wetting properties of orthopaedic titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-7Nb) using laser shock peening. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 801, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddaiah, A.; Mao, B.; Liao, Y.; Menezes, P.L. Surface characterization and tribological performance of laser shock peened steel surfaces. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 351, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddaiah, A.; Mao, B.; Kasar, A.; Liao, Y.; Menezes, P. Influence of laser shock peening on the surface energy and tribocorrosion properties of an AZ31B Mg alloy. Wear 2020, 462–463, 203490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, G.C.; Ocana, J.L.; Gomez, R.G.; Molpeceres, C.; Paredes, M.; Banderas, A.; Porro, J.; Morales, M. Effect of laser shock processing on fatigue crack growth and fracture toughness of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2004, 386, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, B.; Swaroop, S. Effect of laser shock peening on mechanical and microstructural aspects of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 282, 116640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montross, C.; Wei, T.; Ye, L.; Clark, G.; Mai, Y. Laser shock processing and its effects on microstructure and properties of metal alloys: A review. Int. J. Fatigue 2002, 24, 1021–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattoura, M.; Mannava, S.R.; Qian, D.; Vasudevan, V.K. Effect of laser shock peening on residual stress, microstructure and fatigue behavior of ATI 718Plus alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 102, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Liu, H.; Jiao, J.; Zhou, W.; Yang, Y.; Ren, X. Microstructure, microhardness and residual stress of laser additive manufactured CoCrFeMnNi high -entropy alloy subjected to laser shock peening. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 285, 116806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Her, Y.; Han, N.; Clauer, A. Laser shock peening on fatigue behavior of 2024-T3 Al alloy with fastener holes and stopholes. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2001, 298, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiari, M.; Khanigi, A.; Seyed-Salehi, M.; Farnia, A. Ti6Al4V Bone Implants: Effect of Laser Shock Peening on Physical, Mechanical, and Biological Properties. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadaro, L.; Herenu, S.; Strubbia, R.; Rosas, G.G.; Bolmaro, R.; Gonzalez, C.R. Effects of laser shock processing and shot peening on 253 MA austenitic stainless steel and their consequences on fatigue properties. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 122, 105892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Muvvala, G.; Sarkar, S.; Racherla, V.; Nath, A.K. Effect of laser shock peening on microstructural, mechanical and corrosion properties of laser beam welded commercially pure titanium. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 133, 106527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caralapatti, V.; Narayanswamy, S. Effect of high repetition laser shock peening on biocompatibility and corrosion resistance of magnesium. Opt. Laser Technol. 2017, 88, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.R.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, Y.S. Effect of laser shock peening on the stress corrosion cracking of 304L stainless steel. Metals 2023, 13, 30516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Yeo, I.; Jang, I.; Jeong, S. Improvement of friction characteristics of cast aluminum-silicon alloy by laser shock peening. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 266, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Santana, U.; Rubio-Gonzalez, C.; Gomez-Rosas, G.; Ocana, J.; Molpeceres, C.; Porro, J.; Morales, M. Wear and friction of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy treated by laser shock processing. Wear 2006, 260, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveenkumar, K.; Swaroop, S.; Manivasagam, G. Effect of multiple laser shock peening without coating on residual stress distribution and high temperature dry sliding wear behaviour of Ti-6Al-4 V alloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 164, 109398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hareharen, K.; Kumar, S.; Panneerselvam, T.; Babu, P.; Sriraman, N. Investigating the effect of laser shock peening on the wear behaviour of selective laser melted 316L stainless steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 162, 109317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Ren, X.; Zhou, W.; Adu-Gyamfi, S.; Chen, L.; Ye, Y.; Ren, Y.; Dai, F.; Yang, J.; Li, L. Effect of laser shock peening on wear behaviors of TC11 alloy at elevated temperature. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 109, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.S.; Telang, A.; Ye, C.; Mannava, S.R.; Qian, D.; Vasudevan, V.K. Localized plastic deformation and hardening in laser shock peened Inconel alloy 718SPF. Mater. Charact. 2018, 142, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halilovic, M.; Issa, S.; Wallin, M.; Hallberg, H.; Ristinmaa, M. Prediction of the residual state in 304 austenitic steel after laser shock peening—Effects of plastic deformation and martensitic phase transformation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2016, 111, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hfaiedh, N.; Peyre, P.; Song, H.; Popa, I.; Ji, V.; Vignal, V. Finite element analysis of laser shock peening of 2050-T8 aluminum alloy. Int. J. Fatigue. 2015, 70, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraj, M.; Swaroop, S. Effects of power density on residual stress and microstructural behavior of Ti-2.5Cu alloy by laser shock peening without coating. Vacuum 2023, 213, 112078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maawad, E.; Sano, Y.; Wagner, L.; Brokmeier, H.; Genzel, C. Investigation of laser shock peening effects on residual stress state and fatigue performance of titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2012, 536, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, S.; Knowles, K.; Doorbar, P.; Cutts, R.; Rugg, D. Microstructural characterisation of metallic shot peened and laser shock peened Ti-6Al-4V. Acta Mater. 2017, 123, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, S.; Kalainathan, S.; Shukla, P.; Vasudevan, V. Residual stress, phase, microstructure and mechanical property studies of ultrafine bainitic steel through laser shock peening. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 115, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Luo, K.; Liu, Y.; Cui, C.; Xue, W.; Lu, J. Effects of laser shock peening on the micro-hardness, tensile properties, and fracture morphologies of CP-Ti alloy at different temperatures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 431, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.; Biswal, R.; Gupta, R.; Singh, R.; Rai, S.; Ranganathan, K.; Ganesh, P.; Kaul, R.; Bindra, K. Study on the effect of multiple laser shock peening on residual stress and microstructural changes in modified 9Cr-1Mo (P91) steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 358, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellard, C.; Retraint, D.; Francois, M.; Rouhaud, E.; Le Saunier, D. Laser shock peening of Ti-17 titanium alloy: Influence of process parameters. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2012, 532, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, P.; Kishorea; Kailas, S. Influence of surface texture and roughness parameters on friction and transfer layer formation during sliding of aluminium pin on steel plate. Wear 2009, 267, 1534–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, P.; Kishore; Kailas, S. On the effect of surface texture on friction and transfer layer formation-A study using Al and steel pair. Wear 2008, 265, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trdan, U.; Porro, J.; Ocana, J.; Grum, J. Laser shock peening without absorbent coating (LSPwC) effect on 3D surface topography and mechanical properties of 6082-T651 Al alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 208, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

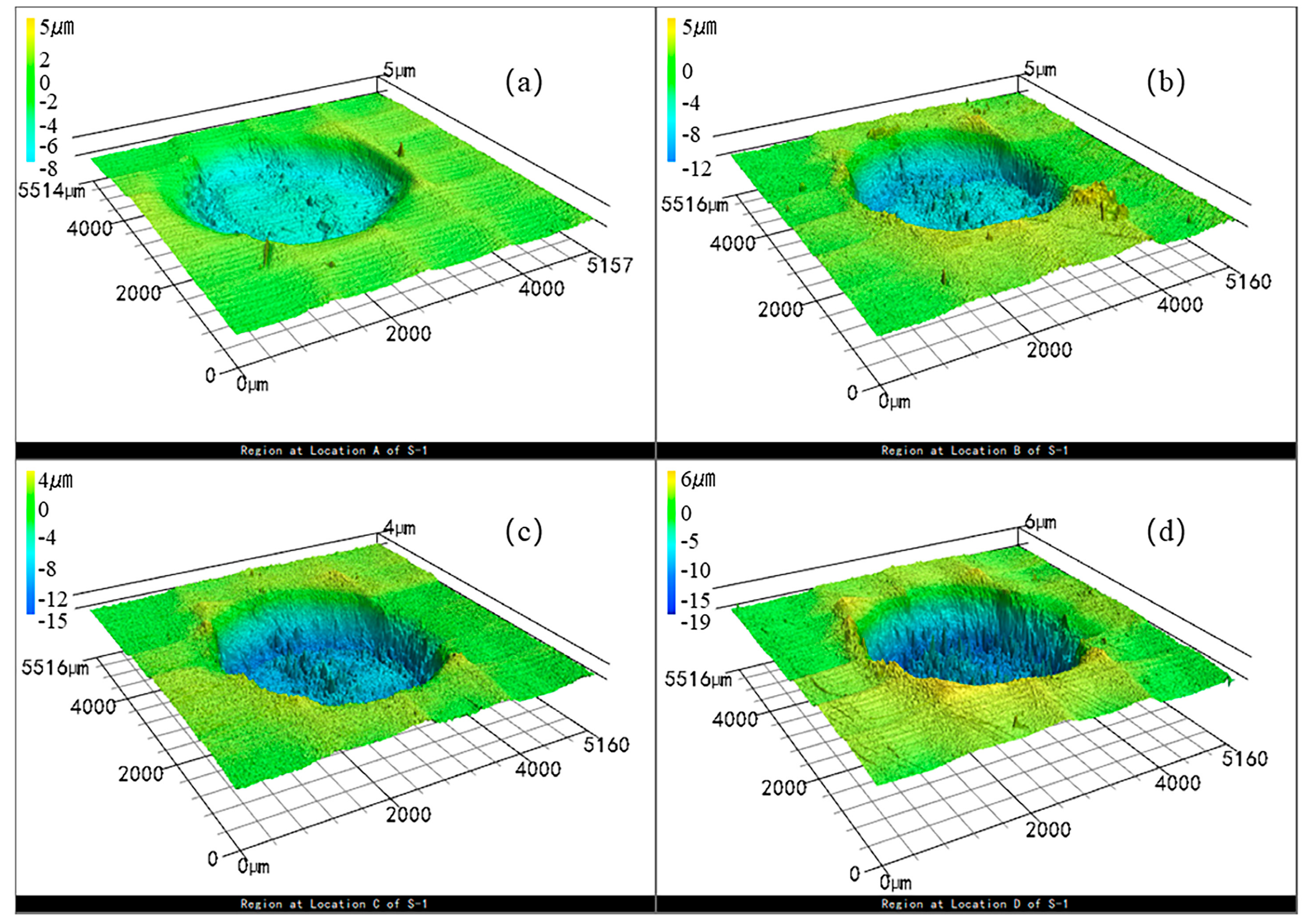
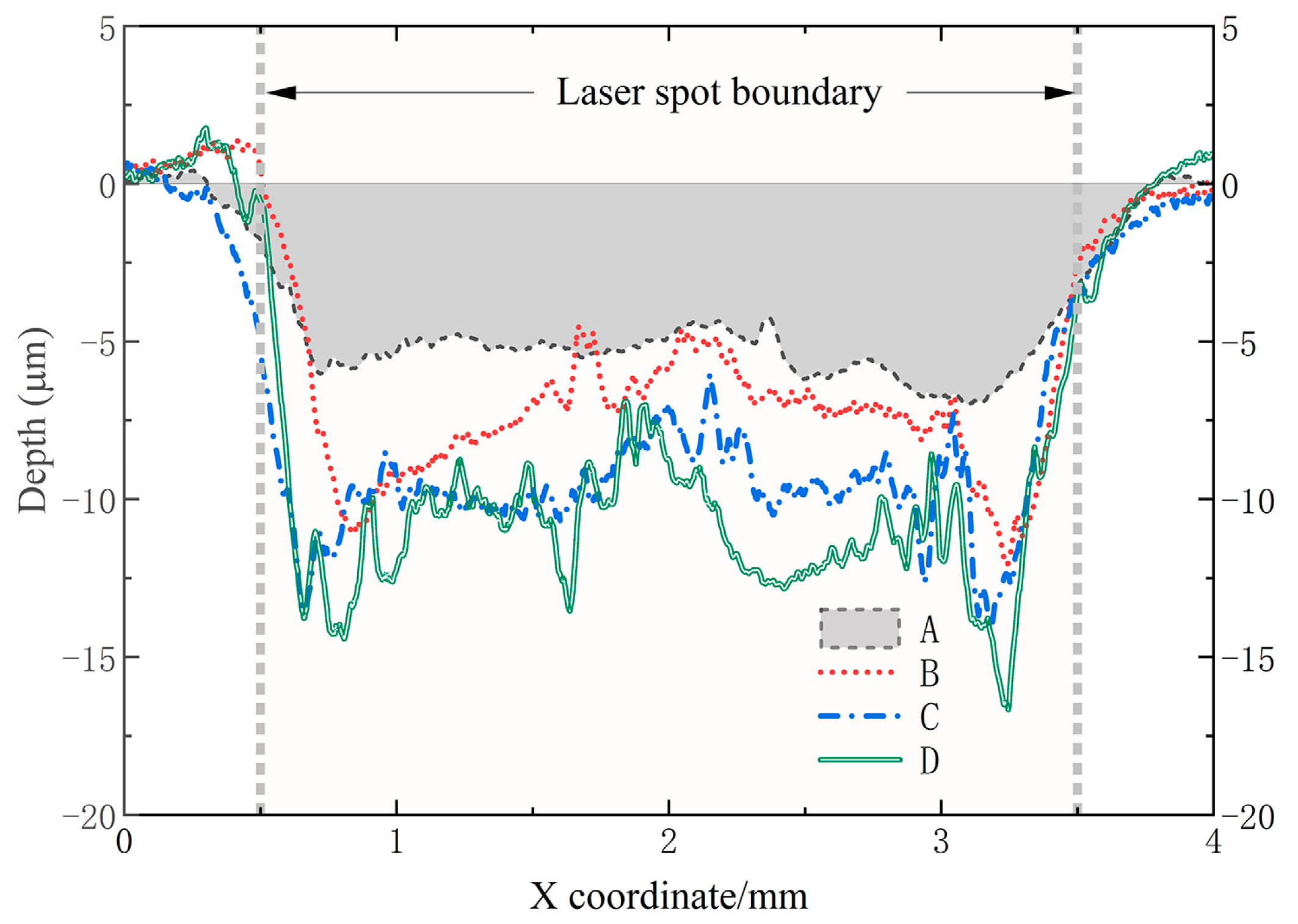

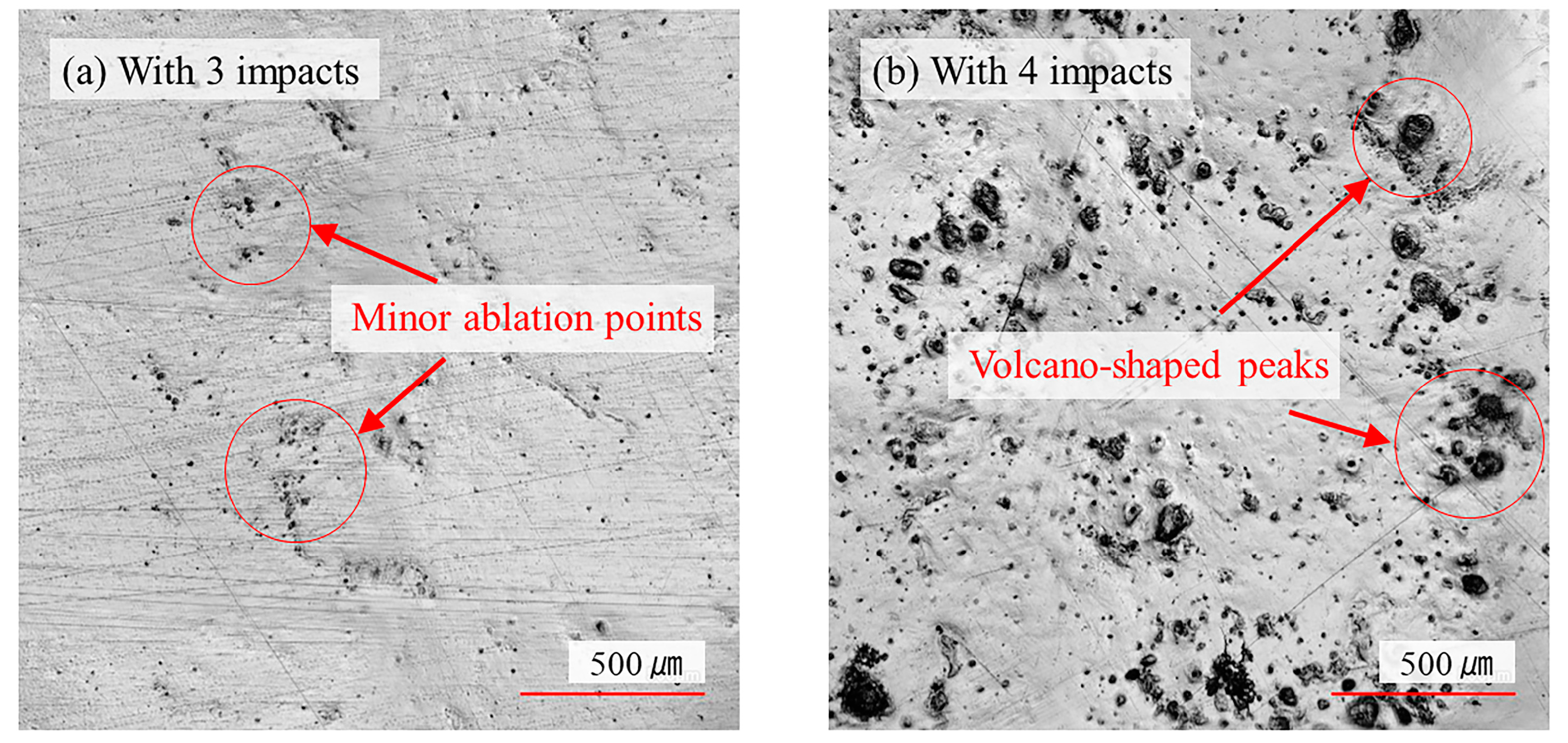
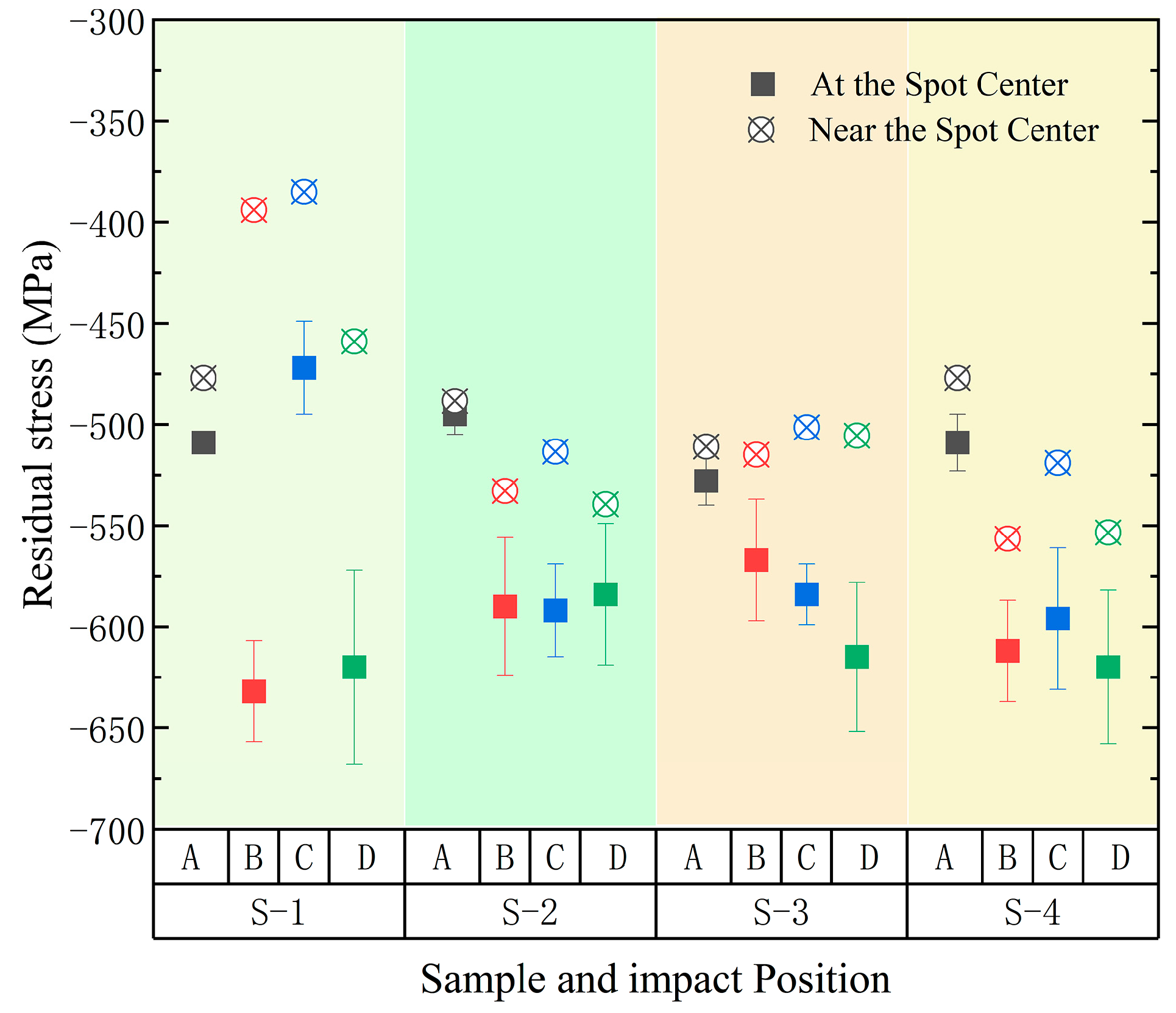

| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ti | Ni | Cu | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.190 | 0.270 | 0.900 | 0.011 | 0.007 | 1.00 | 0.057 | 0.016 | 0.018 | 0.005 |
| Density (kg/m3) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Coefficient of Thermal Expansion(/K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.8 × 103 | 1080 | 835 | 207 | 0.25 | 1.3 × 10−5 |
| Wavelength | Energy | Spot Diameter | Pulse Width | Ablative Layer | Confining Layer | Overlapping Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1064 nm | 9 J | 3 mm | 20 ns | Al. Foil | Water film | 50% |
| LSP Experiment | Specimen Number | Incident Angle | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-point repetitive impacts | S−1, S−2, S−3, S−4 | 0° | / |
| Multiple impacts | M−A−01, M−A−02, M−A−03 | 0° | Single-layer |
| M−B−01, M−B−02, M−B−03 | 15° | Single-layer | |
| M−C−01, M−C−02, M−C−03 | 30° | Single-layer | |
| M−D−01, M−D−02 | 0° | Double-layer | |
| M−D−03, M−D−04 | 0° | Triple-layer |
| Overlapping Type | Displacement | Area Ratio (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∆x | ∆y | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | Ⅵ | Ⅶ | Ⅷ | |
| N | 0 | 0 | 17.36 | 0.00 | 51.13 | 0.00 | 31.51 |
| A | R/2 | 0 | 2.41 | 12.88 | 46.71 | 29.98 | 8.02 |
| B | R/2 | R/2 | 9.36 | 4.54 | 34.52 | 51.58 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X. Surface Morphology Analysis of Laser Shock Peened 20CrMnTi Steel: A Statistical Evaluation. Metals 2023, 13, 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13101673
Wu J, Zhang D, Wang X. Surface Morphology Analysis of Laser Shock Peened 20CrMnTi Steel: A Statistical Evaluation. Metals. 2023; 13(10):1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13101673
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jiaoyi, Dongya Zhang, and Xiaodong Wang. 2023. "Surface Morphology Analysis of Laser Shock Peened 20CrMnTi Steel: A Statistical Evaluation" Metals 13, no. 10: 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13101673
APA StyleWu, J., Zhang, D., & Wang, X. (2023). Surface Morphology Analysis of Laser Shock Peened 20CrMnTi Steel: A Statistical Evaluation. Metals, 13(10), 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13101673






