Abstract
The addition of active seed for increasing the precipitation rate leads to the formation of fine Al(OH)3 particles that complicates separation of solid from the mother liquor. In this study, the enhanced precipitation of coarse Al(OH)3 from sodium aluminate solution using active agglomerated seed was investigated. Aluminum salt (Al2(SO4)3) were used for active agglomerated seed precipitation at the initial of the process. About 50% of precipitation rate was obtained when these agglomerates were used as a seed in the amount of 20 g L−1 at 25 °C within 10 h. The agglomerated active seed and precipitate samples were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). SEM images showed that agglomerates consist of flake-like particles that can be stick together by bayerite (β-Al(OH)3) acting as a binder. The precipitation temperature above 35 °C and the high concentration of free alkali (αk = 1.645Na2Ok/Al2O3 > 3) lead to the agglomerates refinement that can be associated with the bayerite dissolution.
1. Introduction
The alkaline Bayer process is used to produce more than 90% of alumina worldwide [1,2]. The main rate-limiting step of the Bayer process is the precipitation of gibbsite from sodium aluminate solution. Extensive investigations were conducted in order to understand the precipitation mechanism and find possible ways to increase the precipitation rate. Problems caused by long-lasting precipitation and a high amount of seed in the precipitation are still major issues for alumina refineries [3].
Several methods have been proposed to enhance the precipitation rate and speed, such as mechanical or thermal activation of the industrial seed [4,5], active seed and additive application [6,7,8], and operating conditions optimization [9]. Seed surface purification from organic and nonorganic species can also enhance seeded precipitation rate [10,11,12] because adsorbed impurities on the seed surface can reduce the active site availability.
The use of freshly precipitated active aluminum hydroxide and additives, along with an increased precipitation rate, allows to eliminate seed recycling. However, the major disadvantage of all methods for increasing precipitation rate is the refinement of the product. To overcome this problem, the precipitation of coarse aluminum hydroxide was reported to be successful using the two-stage precipitation process [13,14]. This process involves the rapid precipitation of active (or even amorphous) aluminum hydroxide on the first stage, followed by the subsequent recrystallisation with the formation of a coarse product. However, the main disadvantage of the two-stage precipitation is the filtering of fine aluminum hydroxide from the mother liquor after the first stage. Adding pulp or unwashed hydroxide to the second stage leads to a higher caustic modulus.
In this research, we chose aluminum salts as an additive because of their potential to enhance the precipitation rate even if a small amount of salt was added (5 g L−1 or less) [15]. When an aluminum salt is added in sodium aluminate solution, for example aluminum sulphate (Al2(SO4)3·18H2O), there are several reactions proceeded:
- Aluminum sulphate reacts with sodium aluminate to form aluminum hydroxide and sodium sulphate:
Al2(SO4)3·18H2O + 6Na[Al(OH)4] = 8Al(OH)3 + 3Na2SO4 +18H2O,
- The neutralization of free caustic also takes place:
Al2(SO4)3·18H2O + 6NaOH = 2Al(OH)3 + 3Na2SO4 +18H2O.
Bhatacharia et al. [16] demonstrated that aluminum hydroxide obtained by reactions (1) and (2) has a boehmite structure and strong activity. Such activity leads to the fast precipitation of aluminum hydroxide from sodium aluminate solution. The 50% precipitation rate can be reached within 8 h. Due to the nucleation predominance, a fine powder is obtained. Ye et al. [17] showed that, under certain conditions, fine particles can agglomerate in the precipitation process even if an active seed was added. The conditions that help to achieve these results include: 1–4 g L−1 of active seed, a precipitation time of less than 20 h, and temperatures below 40 °C. However, the average particle size obtained in this study did not exceed 30 μm and began to significantly decrease after reaching the precipitation rate of 50%.
The aim of this research was to determine certain conditions when agglomeration and/or crystal growth begin to predominate even if active seed is added to the precipitation. It allows for the efficient synthesis of coarse aluminum hydroxide agglomerates within a relatively short period of time. The effects of temperature, time, seed amount and Na2Ok concentration on precipitation rate and particles size were studied to evaluate such conditions. The active seed and solid product were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The data obtained in this research should help to better understand the mechanism of product refinement with the addition of active seed and how the precipitation process could be enhanced without further problems with pulp filtration.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Supersaturated sodium aluminate solution was prepared by dissolving aluminium hydroxide (JSC “BaselCement-Pikalevo”, Pikalevo, Russia) in an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution (JSC Soda, Sterlitamak, Russia). All reagents were of analytical grade. The solution was filtered twice and then diluted to the required volume at 60 °C. Diluted solution was used for Al and Na2O analysis by ICP-OES. The composition of the solution was expressed using the caustic molar ratio αk. αk = 1.645Na2Ok/Al2O3, where Na2Ok is the concentration of NaOH in solution expressed as Na2Ok, g L−1; Al2O3 is the concentration of alumina, g L−1.
Active seed was prepared by addition 6.7 g L−1 Al2SO4·18H2O into sodium aluminate solution with CNa2O 130 g L−1 and αk 1.65 at 25 °C for 16 h and mild agitation formed by circulating of the solution through the reactor by the pump. Sodium aluminate solution with CNa2O 130–160 g L−1 and αk 1.5 was used in the experiments seeded by as prepared active seed. All reagents were of analytical purity.
2.2. Experimental
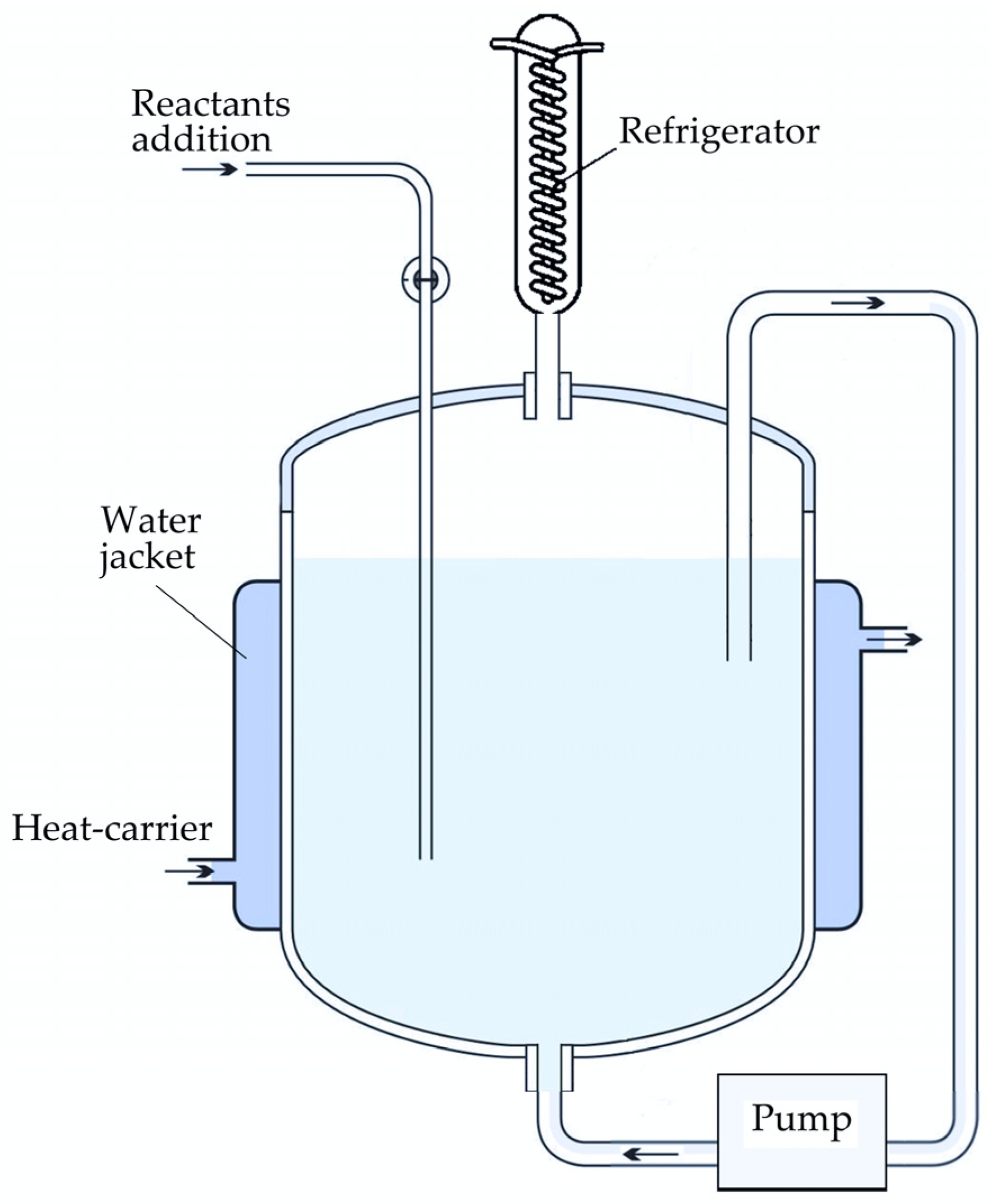
In the precipitation experiments with active seed addition, 400 mL of the sodium aluminate solution with Na2Ok = 130, 140, 150 and 160 g L−1 and αk = 1.5 (molar ratio that is used on modern alumina refineries) was transferred into the 0.5 L precipitator-shaped vessel (Figure 1). The reactor has openings for injecting chemical reagents as well as for temperature control and the recycling of evaporated water via a water-cooled refrigerator. The seed amount was 10, 20, 30 and 40 g L−1. The stirring was made by pumping the solution through the slurry on the bottom of the vessel that helps to prevent agglomerates breaking by overhead stirrer. Samples were taken at intervals via syringe and centrifuged. The solution was used for Na2O and Al2O3 analysis. Solid samples were filtered, washed and analyzed by physical methods.
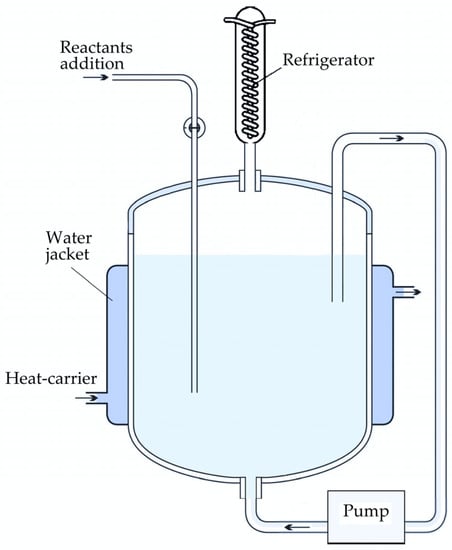
Figure 1.
Schematic of the precipitator-shaped experimental 0.5 L set-up.
2.3. Analysis
The phase composition of the solid samples was determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD) using a Rigaku D/MAX-2200 diffractometer equipped with a Cu-Kα radiation source (Rikagu Corp., Tokyo, Japan) using the “Match! 3” software (Version 3.12, Crystal impact, Bonn, Germany). Chemical analysis was performed by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) analysis using a spectrometer Vista Pro (Varian Optical Spectroscopy Instr., Mulgrave, Australia). For quality assurance, samples were analyzed twice. The morphological analysis of the solid samples was determined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, JSM-6390LV microscope, JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). The particle size distribution and mean particle size analysis were performed by the laser diffraction method (LD) using an Analysette 22 NanoTec (Fritsch, Idar-Oberstein, Germany). The specific surface area of the samples was determined via the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller method (BET) using NOVA 1200e (Quantachrome Instruments, Boynton Beach, FL, USA). Before BET analysis, all samples were subjected to degassing under vacuum at 200 °C for 12 h.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Active Seed Preparation
To obtain an active coarse seed, a precipitation process of aluminum hydroxide from an alkaline aluminate solution is used by adding aluminum sulfate in an amount of 6.7 g L−1 at a temperature of 25 °C. The precipitation of finely dispersed aluminum hydroxide with the addition of aluminum salts was demonstrated in [16]. According to the research data, the mechanism of fine particle precipitation is associated with the formation of a large number of crystallization centers at the initial moment. This is achieved by Equations (1) and (2) [16]. However, below 40 °C and in the absence of intensive mixing, the growth of crystals will occur. The particle size distribution, SEM images, X-ray and IR-spectra of the resulting product are shown in Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5.
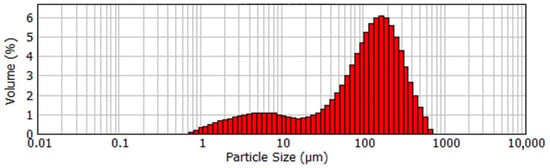
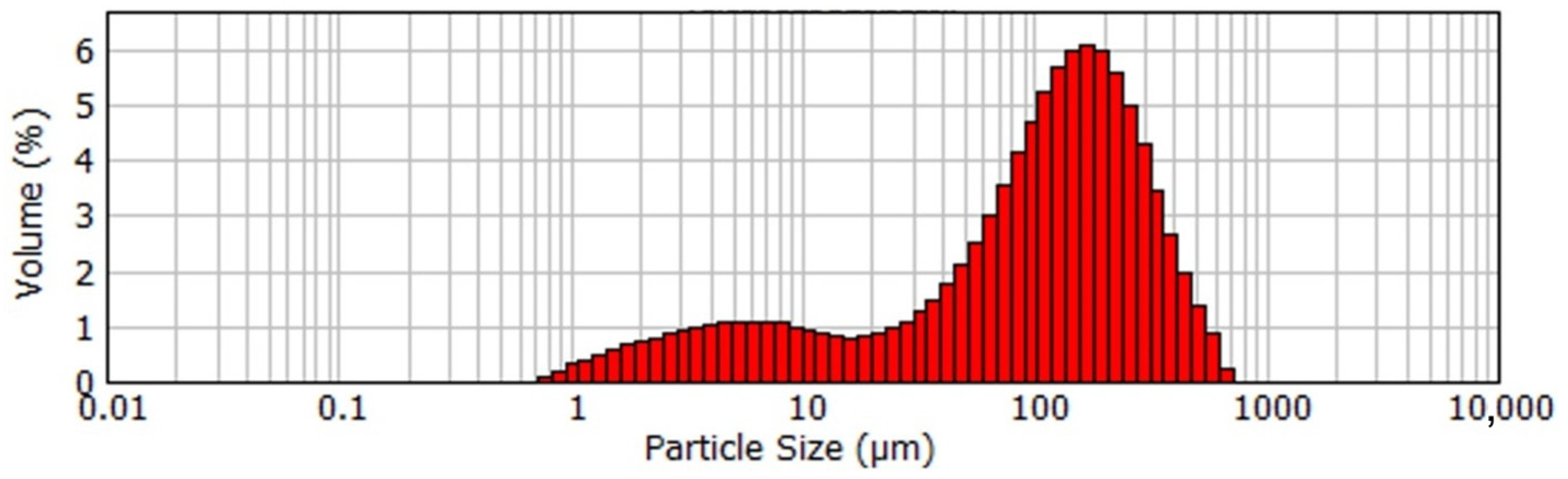
Figure 2.
Particle size distribution of the coarse agglomerated active seed.
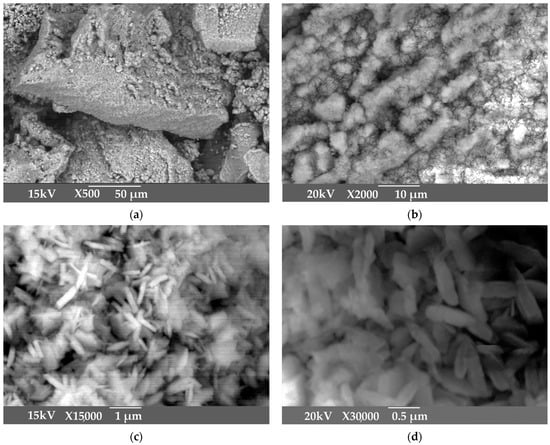
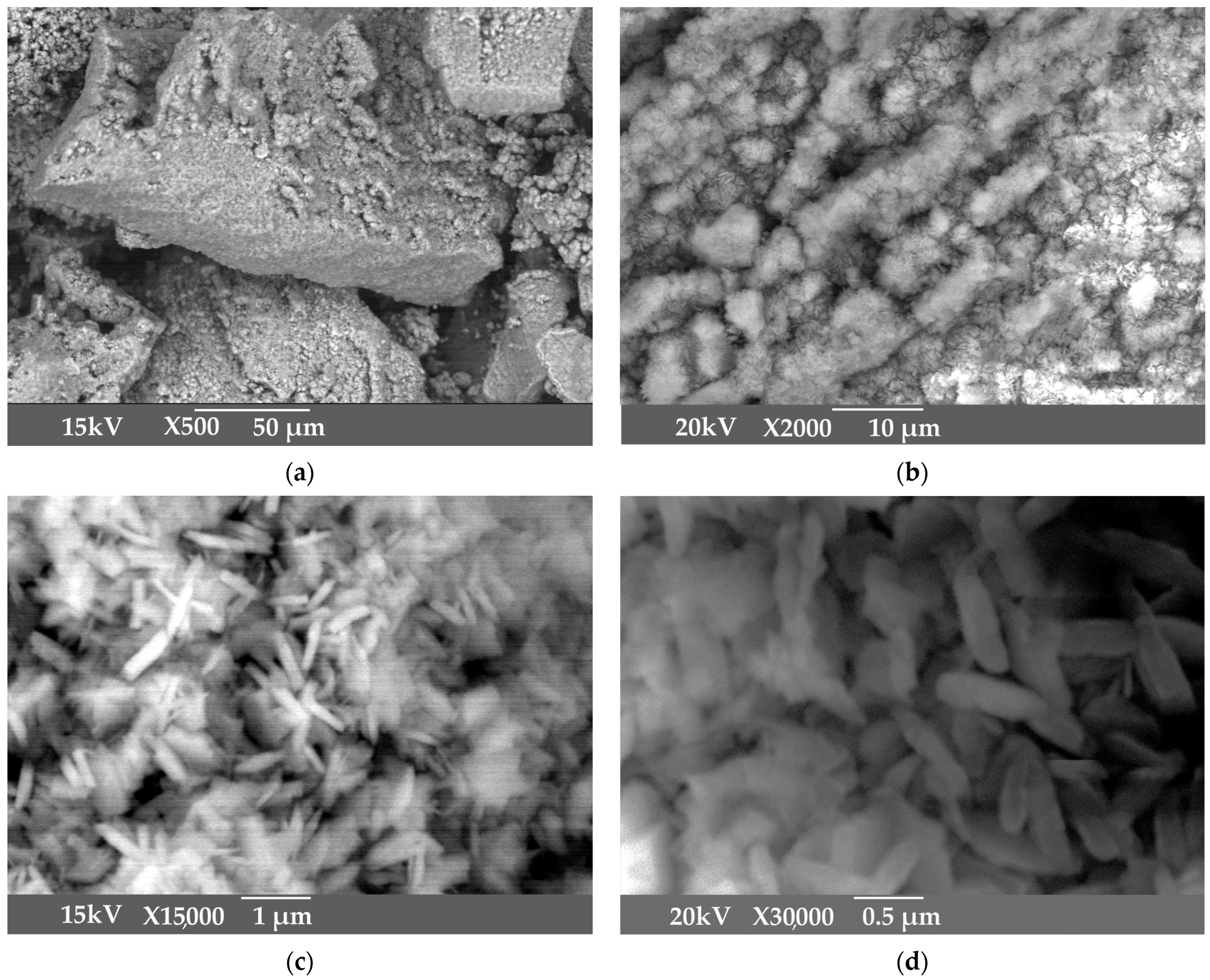
Figure 3.
SEM images of active aluminum hydroxide obtained by aluminum sulphate addition at 25 °C: 500× magnitude (a); 2000× magnitude (b); 15,000× magnitude (c); 30,000× magnitude (d).
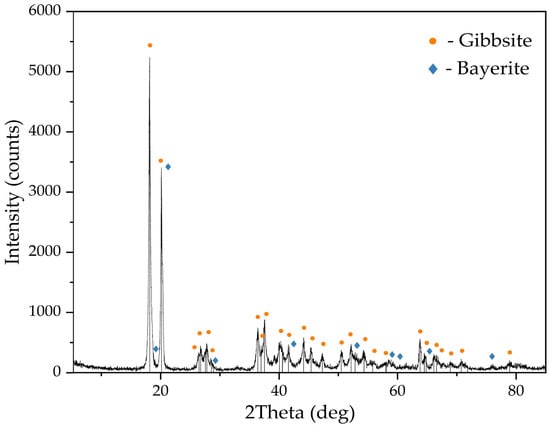
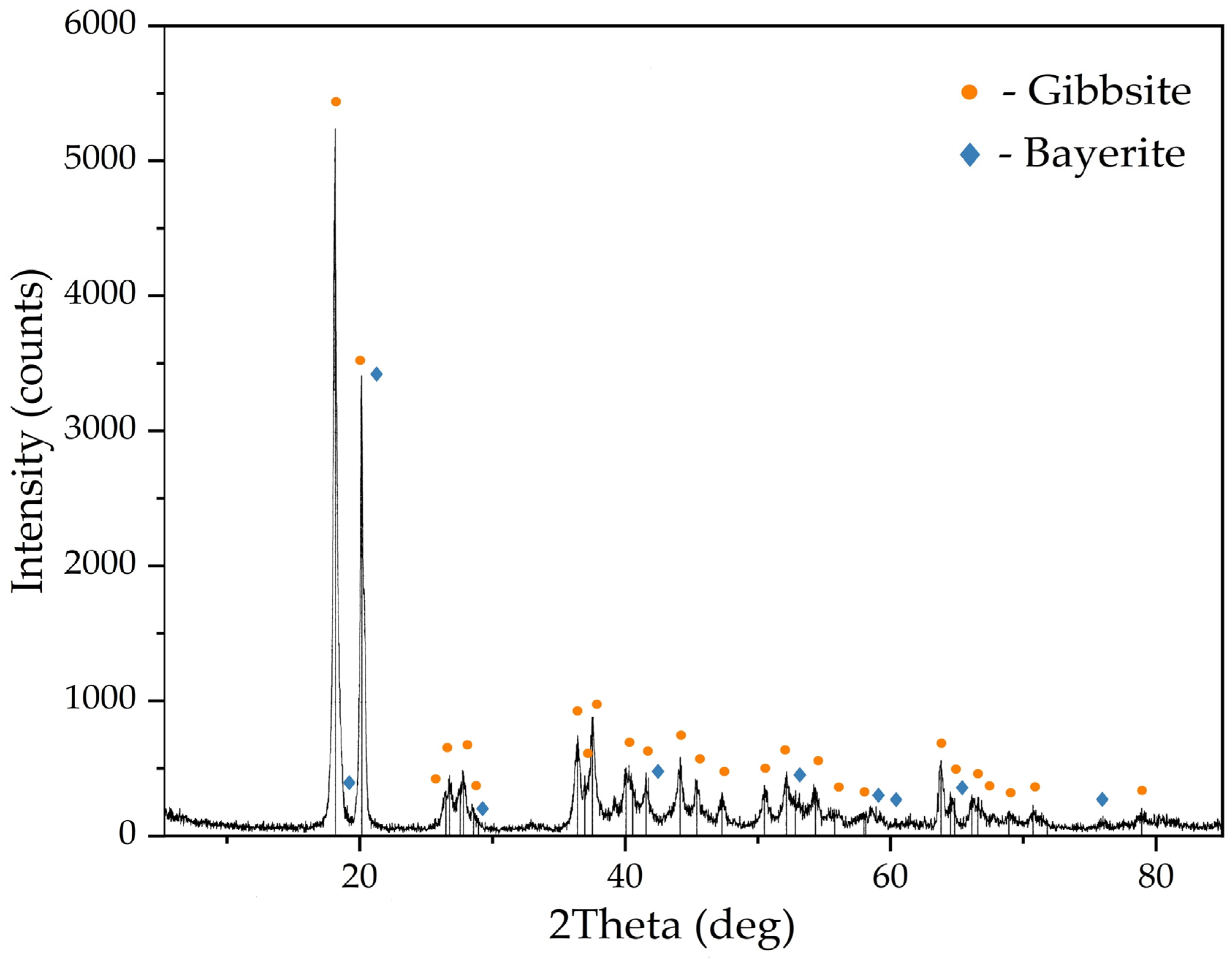
Figure 4.
XRD pattern of the active seed obtained by aluminum sulphate addition at 25 °C.
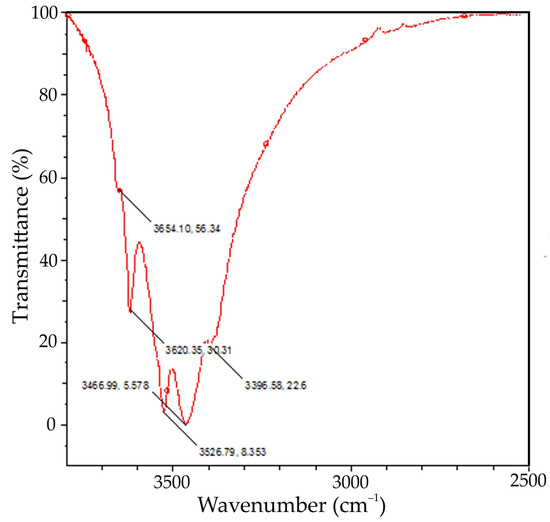
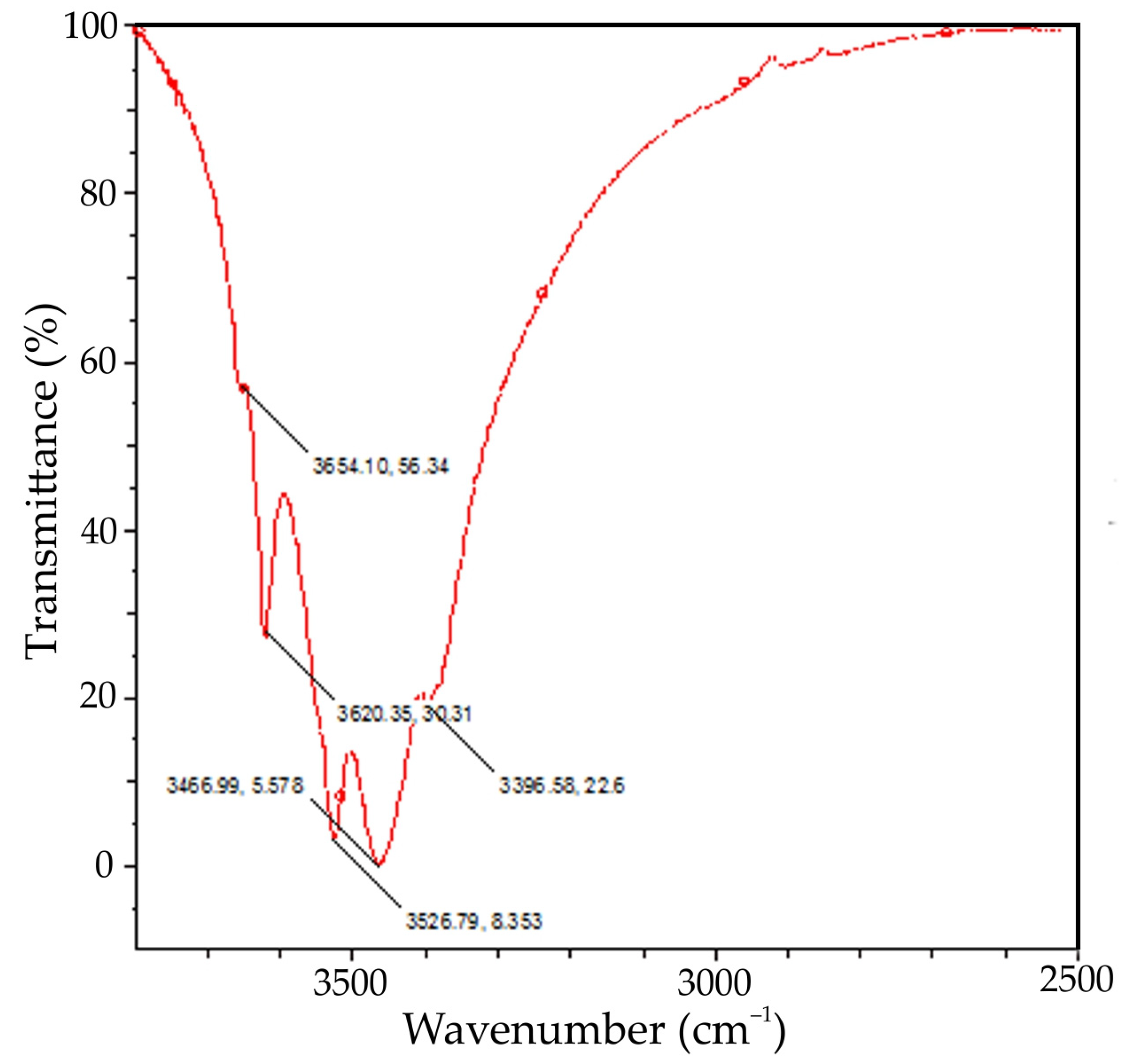
Figure 5.
FTIR spectra of the active seed obtained using aluminium sulphate at mild stirring conditions and 25 °C (where x, y is the coordinates of a peak).
According to Figure 1, the product obtained at low temperature and mild mixing conditions with the addition of aluminum sulfate is very large, with an average particle size of 117 μm. SEM images in Figure 2 shows that the product is represented by the agglomerates of the flake-like particles.
The XRD pattern in Figure 4 shows that the precipitate consists of gibbsite and a small amount of bayerite. The presence of bayerite peaks at 3654 cm−1 can also be observed on the FTIR-spectra of the active seed (see Figure 5). Bayerite can play the role of the binder that sticks gibbsite particles together.
The same phenomenon was found by Ye et al. [17] in the investigation of sodium aluminate solution precipitation using active seed at 45 °C and 0.5–4.0 g L−1 seed addition. It was discovered that flake-like crystals were growing under such conditions on the active site of seed, and these particles were cemented by bayerite. When the temperature is increased, bayerite is dissolved, which leads to the breakdown of the agglomerates and the formation of small particles, which serve as nucleation centers and contribute to the refinement of the product.
The lack of stirring promotes the agglomeration of the flake-like crystals, which results in a coarser particle size distribution (PSD) according to Figure 2.
As a result, when aluminum salts are added to a sodium aluminate solution, active aluminum hydroxide precipitate (with high amount of active site) are formed. On each active site, flake-like crystals begin to form which become active sites on their own. Furthermore, deposited crystals begin to agglomerate with the help of bayerite and it is possible to obtain coarse agglomerates of flake-like gibbsite (FLG). FLG would result in an increased precipitation rate due to its high surface area. The specific surface area (BET) of the active seed was found to be 34 m g−1, which is much higher than the 0.1–5 m g−1 for the industrial seed.
3.2. Kinetics of Precipitation from Sodium Aluminate Solution Using Coarse Active Seed
It was previously demonstrated [4,18,19] that the most effective way to increase the degree of precipitation of gibbsite from an alkaline aluminate solution is to use an active seed—a seed with a high specific surface area. Even when using a small amount of such a seed (less than 20 g L−1), it is possible to achieve a high precipitation degree in a short time. This is in contrast to using a standard industrial seed, which requires more than 400 g L−1 of the solid for intensive precipitation.
In this study, the kinetics of the FLG precipitation from an alkali-aluminate solution using active seed was studied in more detail, and the effect of the seed amount, temperature, and concentration on the rate of the process was investigated. The seed ratio was less than 0.3 units (10–40 g of solid per 1 L) in all experiments, which makes it possible to exclude the autocatalytic effect of the process, that could be caused by an increase in the amount of precipitate.
Since the autocatalytic effect of the precipitated aluminum hydroxide in this case is already excluded, the methodology proposed in the article [20] was used to calculate the activation energy of the process. The authors of research [20] used Equation (3) to reflect the change in concentration of the solution:
where C is the concentration of Al2O3 at a given time, g L−1; Ce is the equilibrium concentration of Al2O3, g L−1; K is the precipitation rate constant.
If we integrate Equation (3), the following Equations (4) and (5) can be obtained:
Using experimental data obtained at various times for a given solution at a given temperature, it is possible to determine the constant K by the slope of the curve in coordinate 1/C − t (Equation (5)).
Equation (7) can be obtained from the Arrhenius Equation (6) by taking the logarithm.
K = Ae−E/RT
lgK = lgA − Ea/(2.3RT)
The value of Ea can then be found by using the slope of the straight line in coordinates lgK − 1/T.
The equilibrium concentration of Al2O3 was calculated using Equation (8) proposed by Misra [21]:
Ce = Na2Okexp(6.211 − 2486.7/T + 1.088Na2Ok/T)
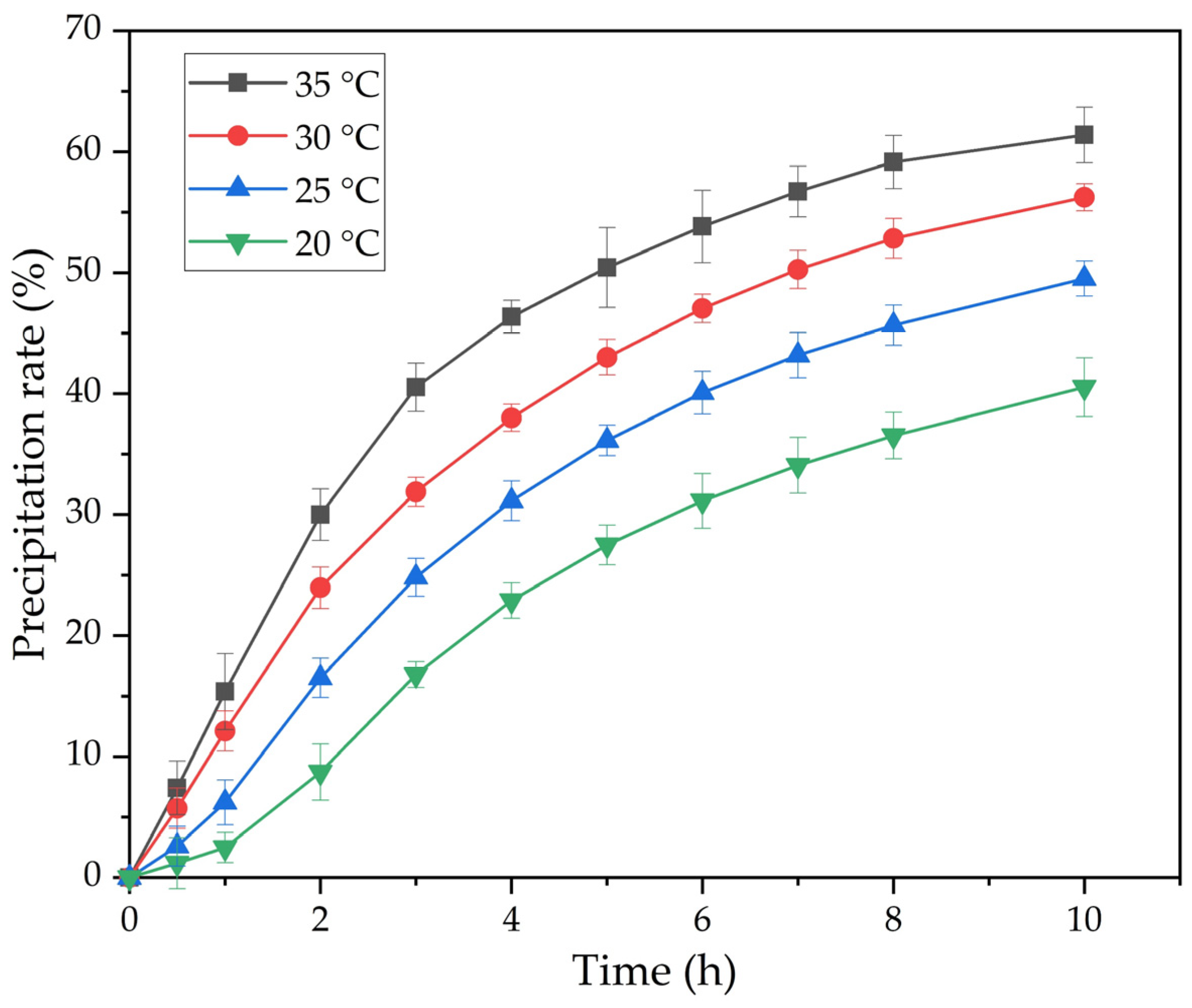
Figure 6 shows the results of experiments on the effect of precipitation time and temperature at Na2Ok = 150 g L−1, αk = 1.5 and the active seed amount of 20 g L−1.
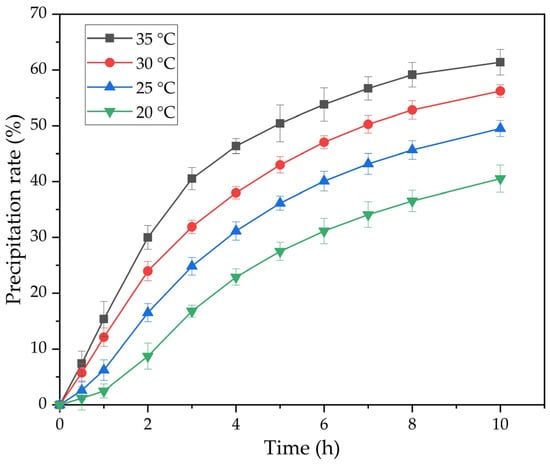
Figure 6.
The effect of temperature and time on the precipitation of the flake-like gibbsite (FLG) from an alkaline aluminate solution (Na2Ok = 150 g L−1, αk = 1.5) using active aluminum hydroxide in the amount of 20 g g L−1 as a seed.
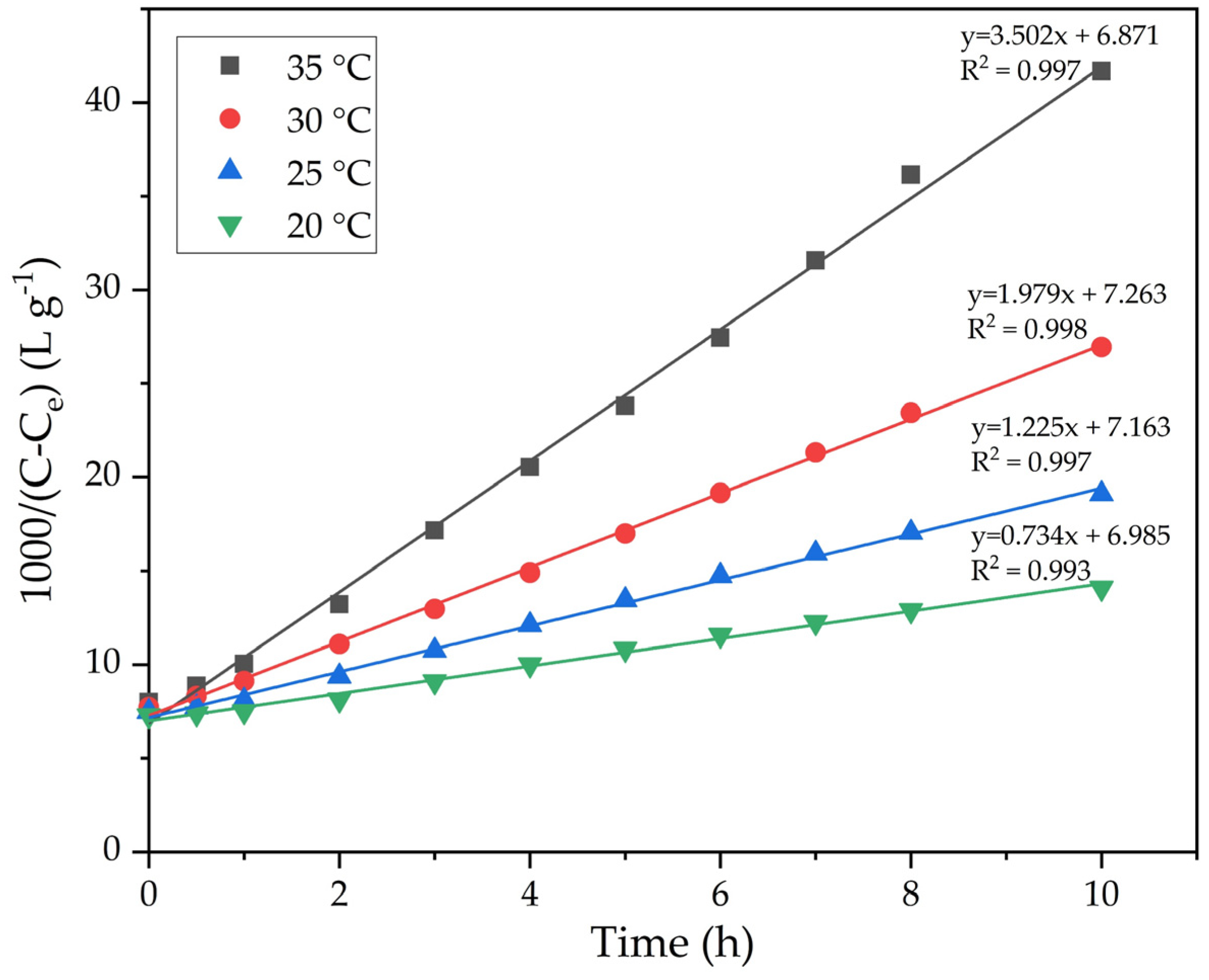
The results of the experiments in Figure 6 were used to construct plots in coordinates 1000/(C − Ce) − τ (Figure 7). The precipitation rate constants were determined from the slopes of the straight lines in Figure 7. The results are presented in Table 1.
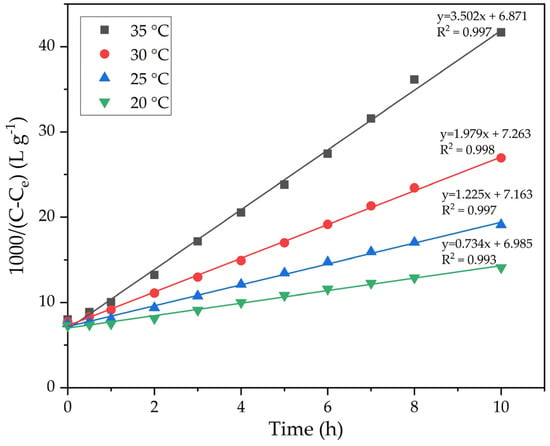
Figure 7.
Dependence of 1000/(C − Ce) in Figure 6 on the duration of precipitation at various temperatures.

Table 1.
Results of the processing of the data in Figure 7.
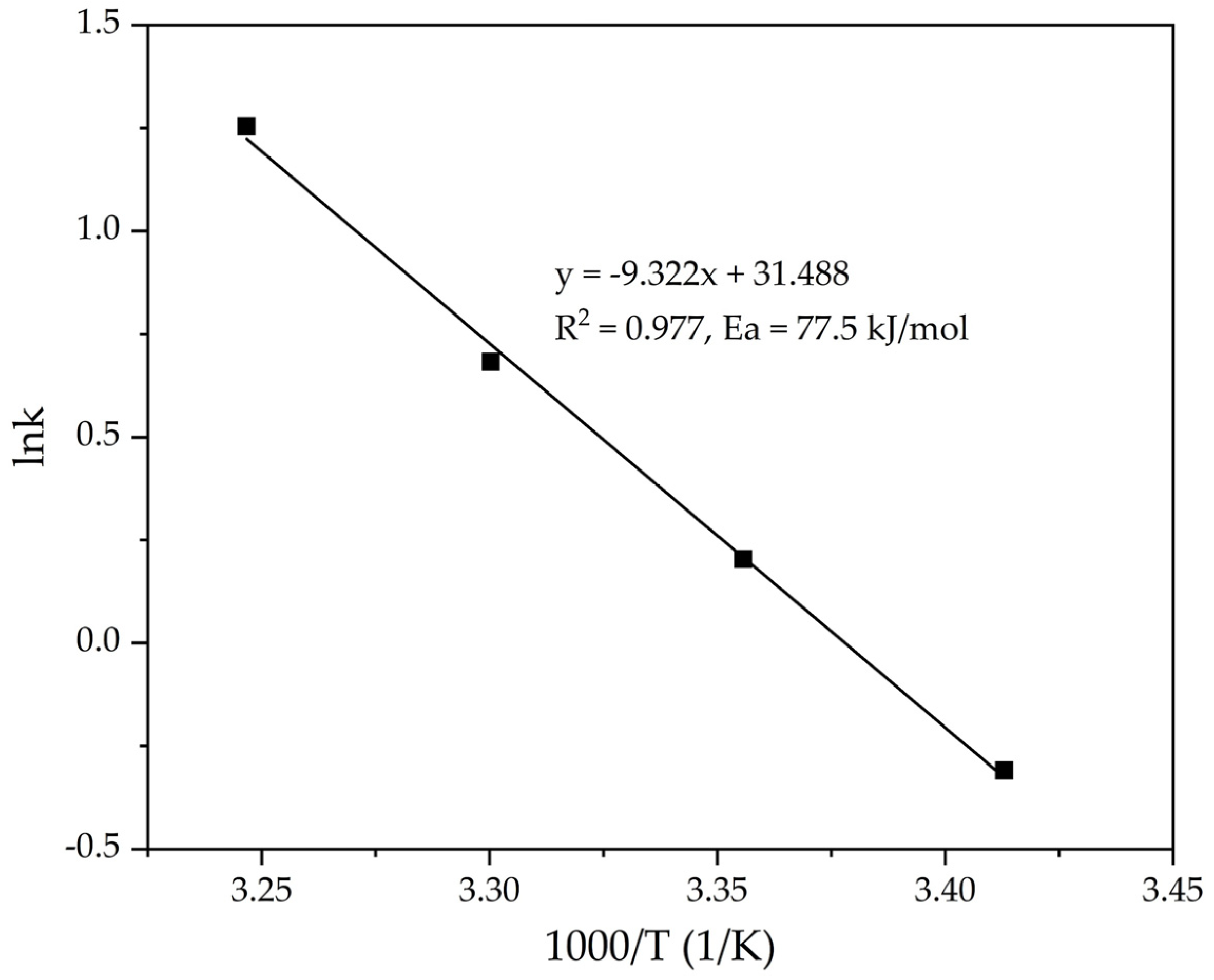
The lnK—1000/T dependence (Figure 8) was constructed based on the data obtained in Table 1. The slope of the straight line obtained from the plot of ln(k) vs. 1/T was used to calculate the value of the apparent activation energy of the precipitation process using Equation (7).
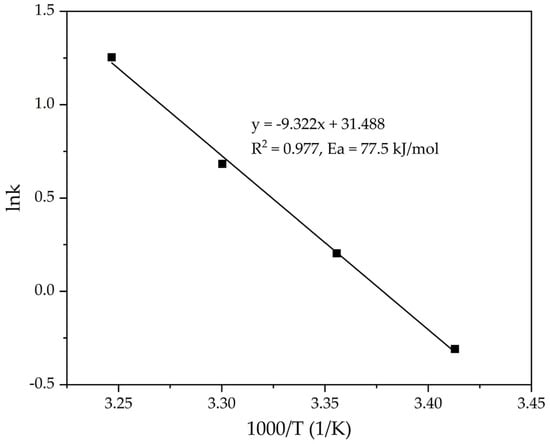
Figure 8.
Dependence lnK − (1/T) (Table 1) for the precipitation of FLG from an aluminate solution at various temperatures.
According to the slope of the straight line obtained in Figure 8, the value Ea = 77.5 kJ mol−1 is determined, which indicates a possible kinetic limitations of the process. The obtained value is also in good agreement with the literature data for the precipitation process using a standard seed (60–80 kJ mol−1) [22,23,24]. However, the time required for precipitation was reduced by 5 times. This indicates the crucial role of the seed surface on the rate of precipitation from the alkali-aluminate solution. Further experiments were conducted to investigate the effect of the initial seed amount on the rate of the process. The process temperature was 25 °C throughout all experiments, and the Na2O concentration was 150 g L−1. The experimental results are presented in Figure 9.
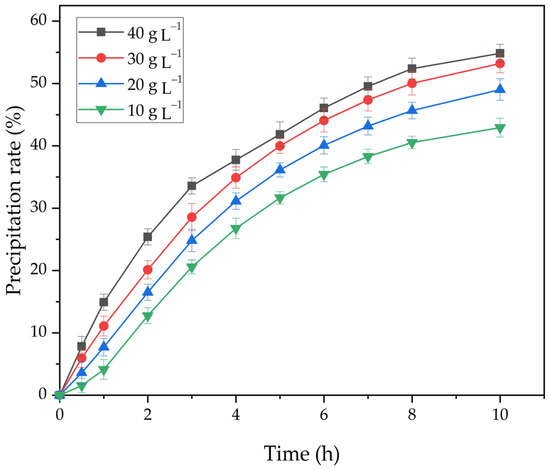
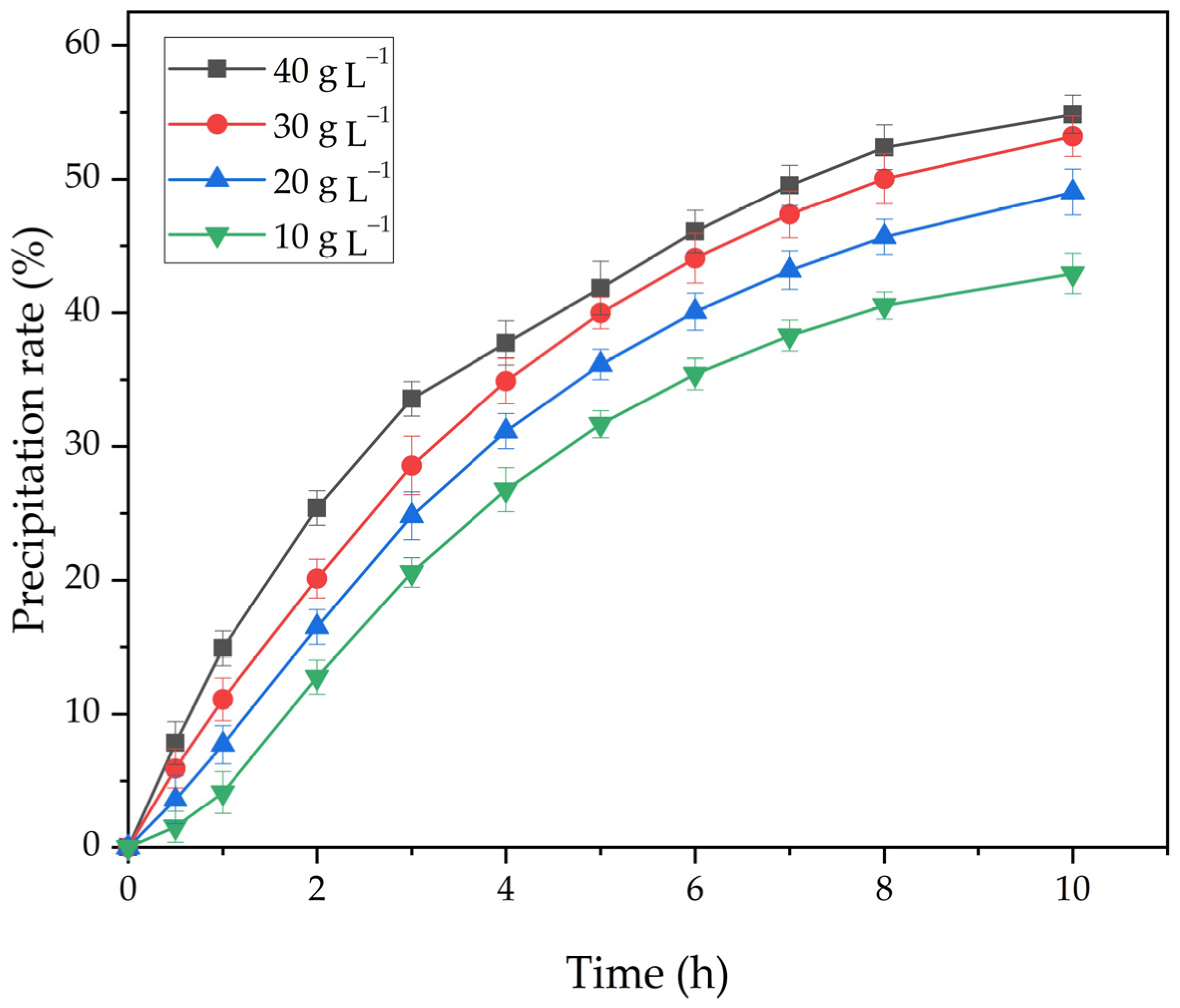
Figure 9.
The effect of the duration and amount of active seed on the degree of precipitation at 25 °C and the Na2O concentration 150 g L−1.
As shown in Figure 9, an increase in the amount of active seed significantly increases the degree of precipitation. Therefore, with an increase in the amount of seed from 10 to 40 g L−1, the degree of the precipitation at 25 °C, and the concentration of Na2Ok 150 g L−1 after 10 h increases from 42.9% to 53.2%.
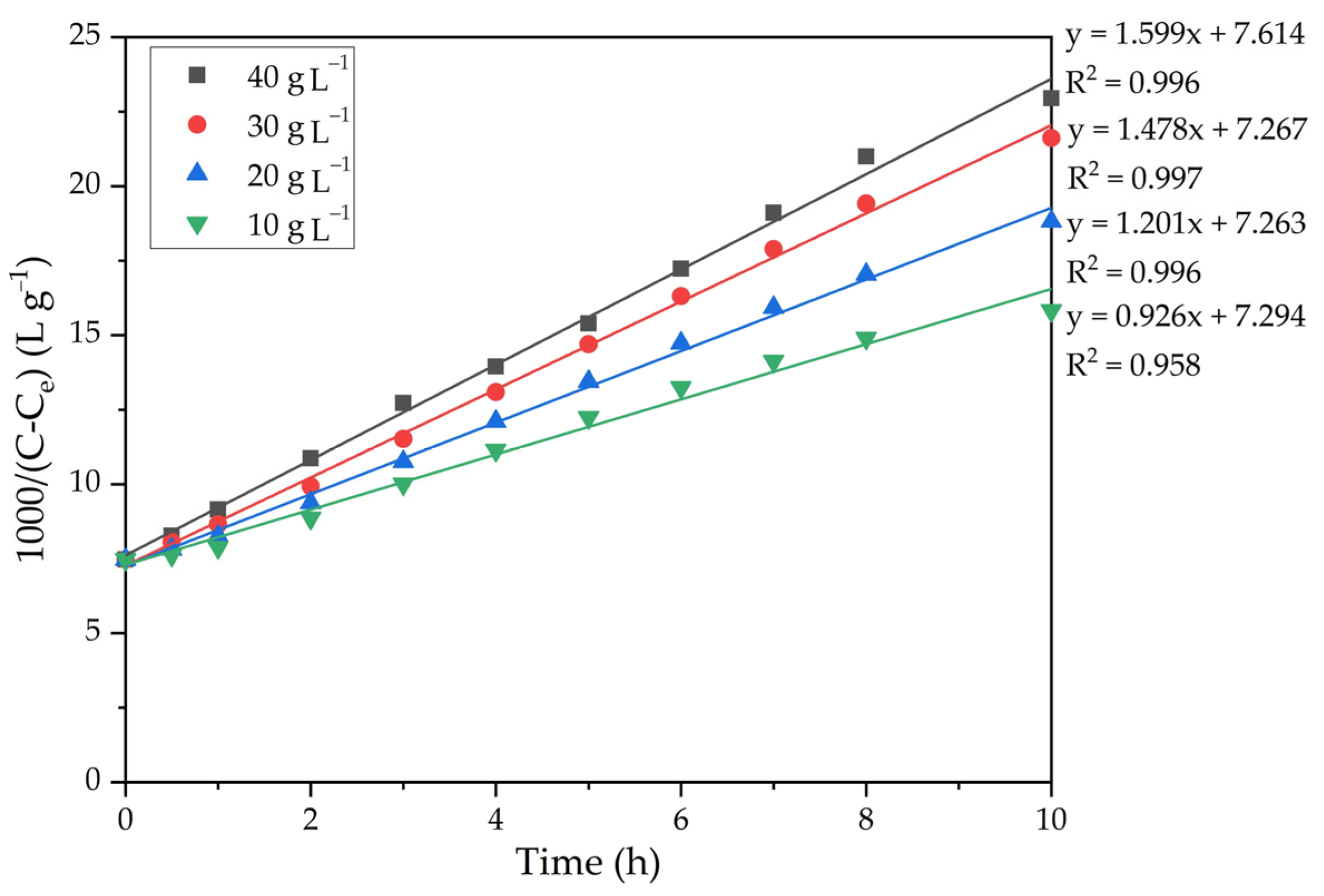
The experimental results presented in Figure 9 were fitted with linear regression in a similar way to the method used to construct straight lines in Figure 7. Figure 10 shows the results of linearization.
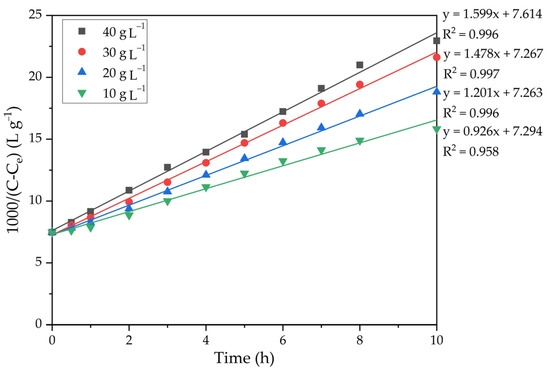
Figure 10.
Dependence of 1000/(C − Ce) on time at various amounts of seed.
The precipitation rate constants were determined from the slopes of the straight lines in Figure 10. Since the constant A in the Arrhenius equation (Equation (7)) depends on a large number of parameters, including the seed amount and Na2Ok concentration, this equation can be written as follows (Equation (9)).
where G is the amount of active seed per unit of the solution volume, C is the Na2Ok concentration, and n, m are the seed amount and alkali concentration orders, respectively.
K = GnCme−E/RT,
In order to determine the order of the amount of seed, it is necessary to plot a graph in lgK − lgC coordinates. The slope of the straight line can then be used to determine the order of the amount of seed.

Table 2.
Results of the processing of the data in Figure 10.
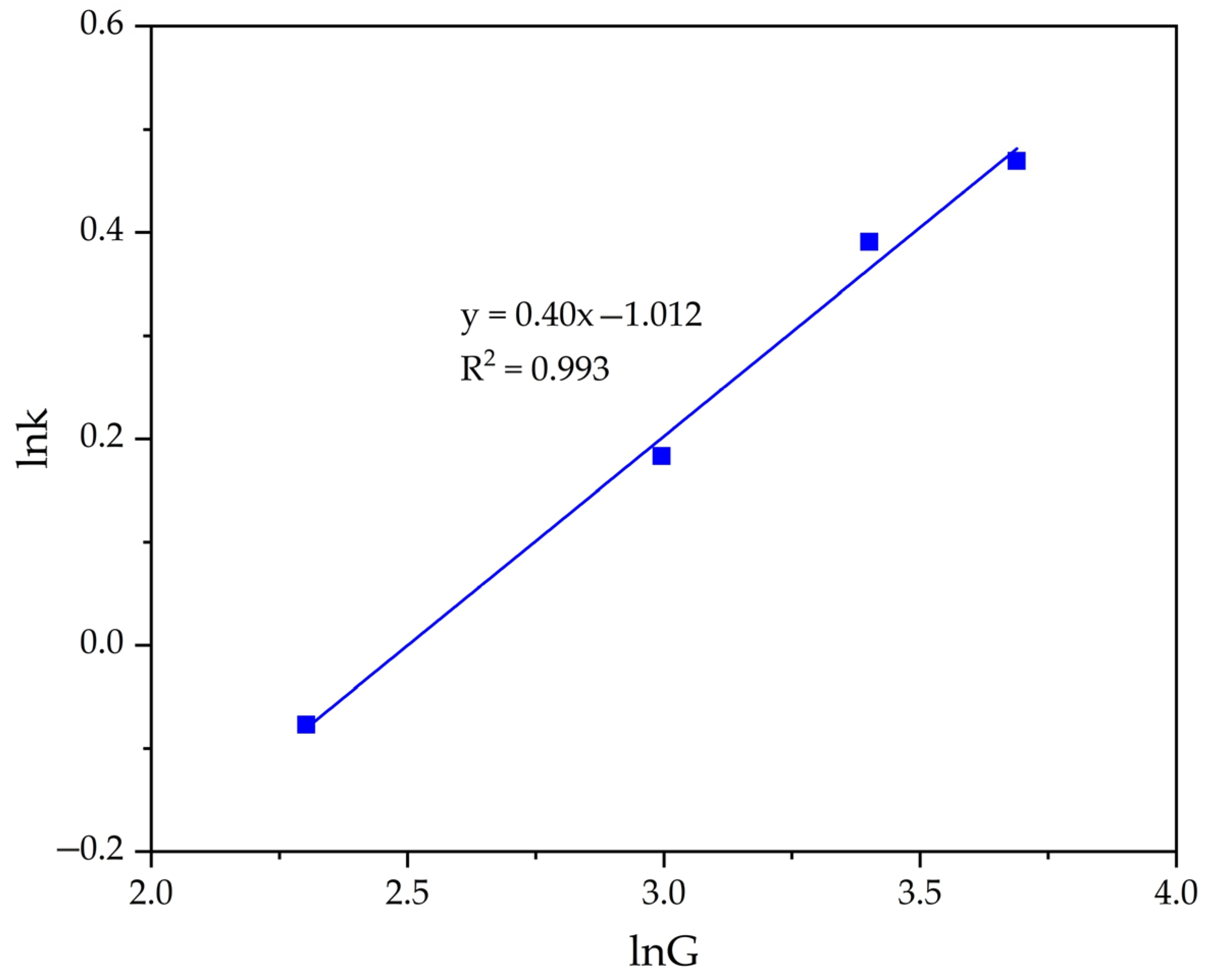
Next, the graph in lnK − lnG coordinates (Figure 11) was plotted. Then according to Equation (9), the order value of the seed amount was calculated (n = 0.400).
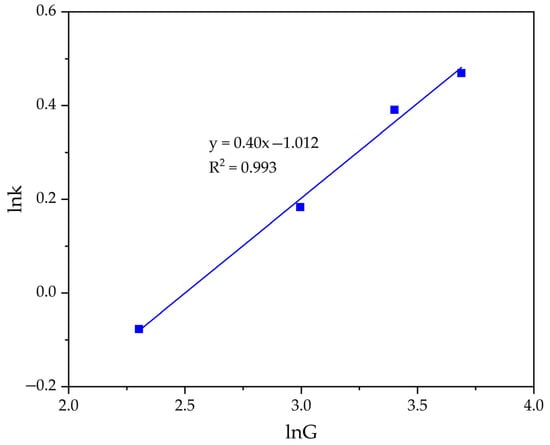
Figure 11.
Dependence of lnK − lnG (Table 2) for the precipitation of FLG from an aluminate solution at various seed amount.
The concentration of caustic alkali in the solution is also important because, as the concentration of alkali increases, the nature of the aluminate ions in the solution changes [25] and the degree of the supersaturation (C0 − Ce) is decreased [26]. Therefore, the experiments were continued by investigating the effect of Na2Ok concentration on the rate of the process. In all experiments, the temperature was 25 °C and the amount of active seed was 20 g L−1. The experimental results are presented in Figure 12.
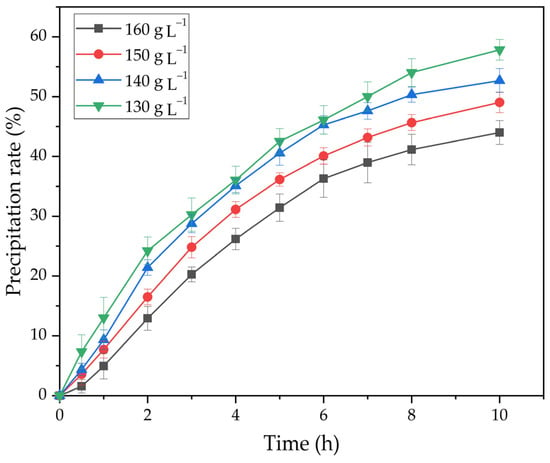
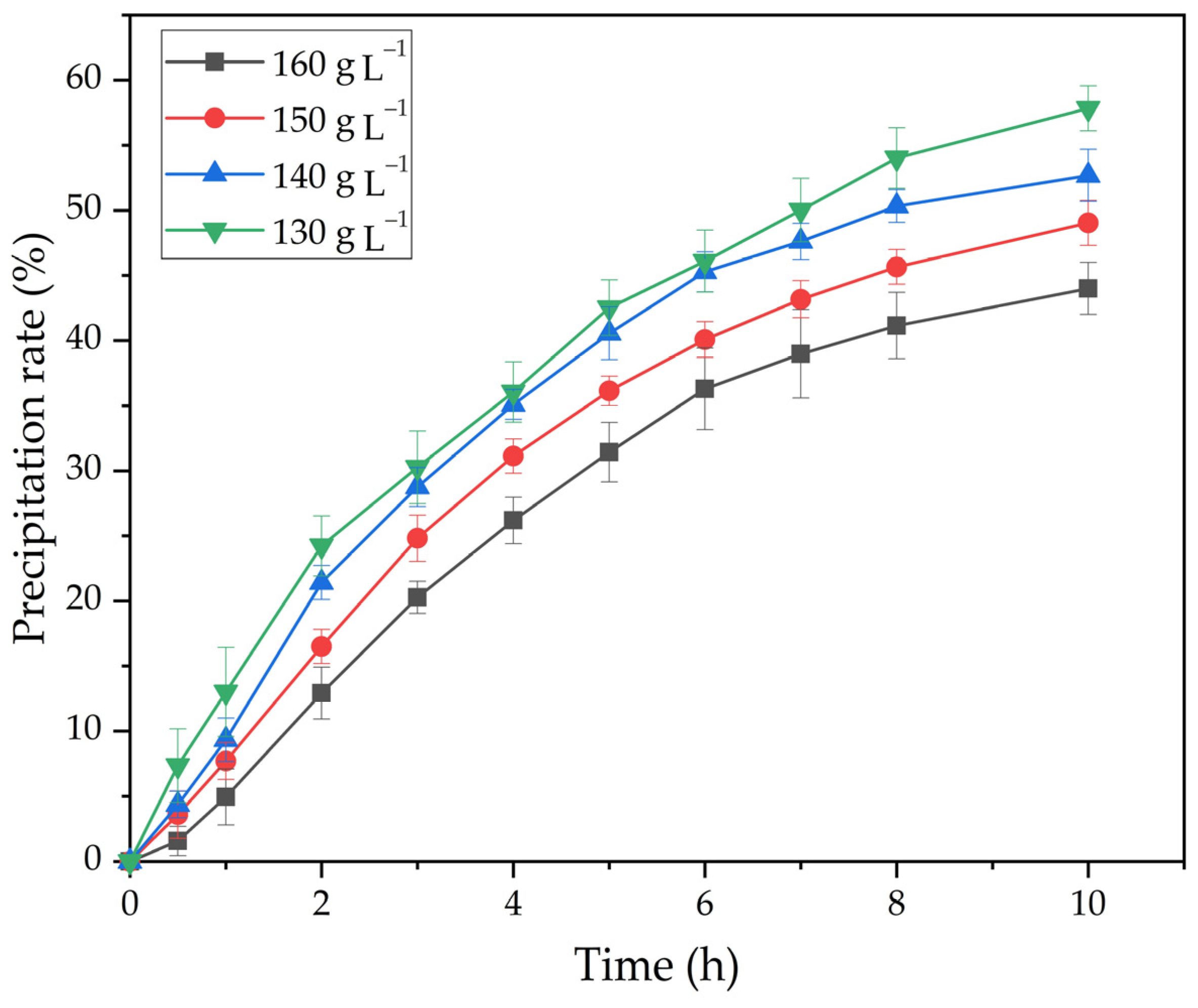
Figure 12.
Effect of time and Na2Ok concentration of on the degree of precipitation.
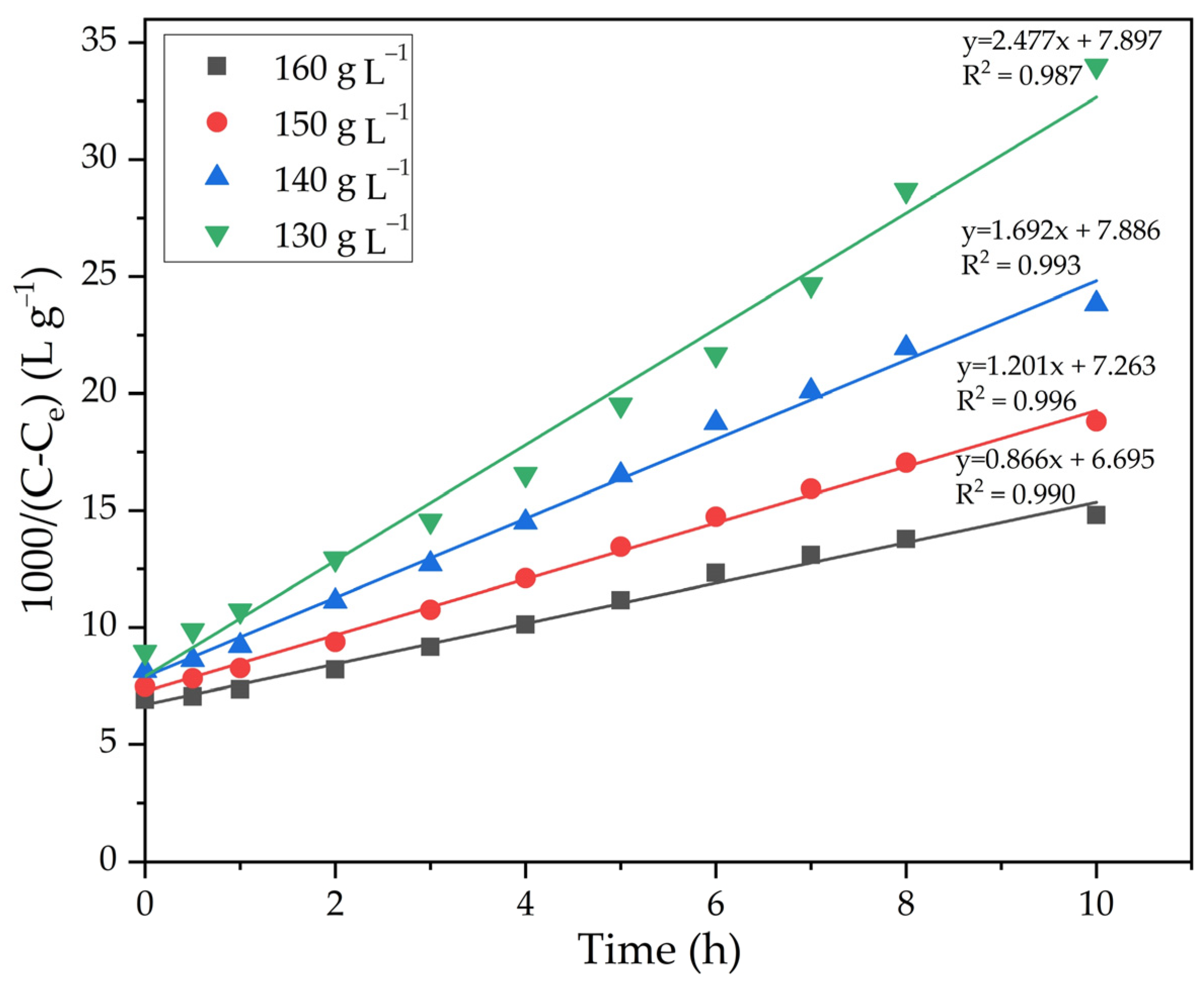
As shown in Figure 12, an increase in caustic alkali concentration leads to a decrease in degree of precipitation. When the Na2Ok concentration is increased from 130 to 160 g L−1, the degree of precipitation at 25 °C and seed amount 20 g L−1 after 10 h decreases from 57.8 to 44.0%.
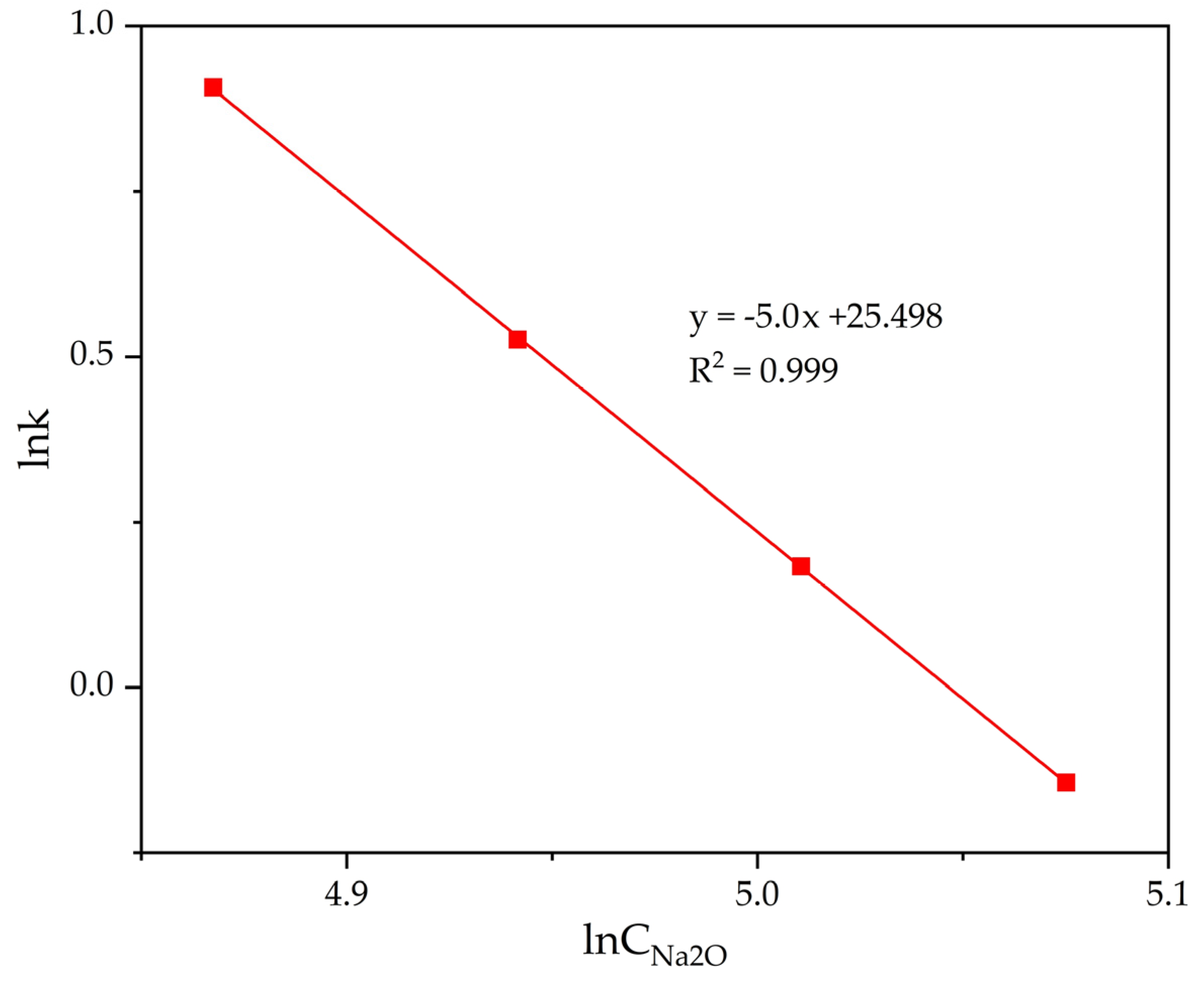
The experimental results presented in Figure 12 were linearized in a similar way to the method used to plot the lines in Figure 7. Figure 13 shows the results of linearization. By using Equation (9), the value of the order of Na2Ok concentration equal to −5.1 was calculated.
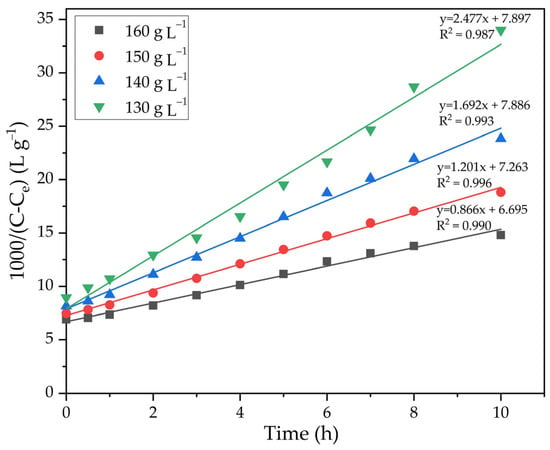
Figure 13.
Dependence of 1000/(C − Ce) on time at different concentrations of caustic alkali.
The slope of the lines in Figure 13 was used to determine the precipitation rate constants. The data in Figure 13 have been processed and the results are presented in Table 3. The dependence of lgK on lgCNa2O was plotted (Figure 14).

Table 3.
Results of the processing of the curves in Figure 13.
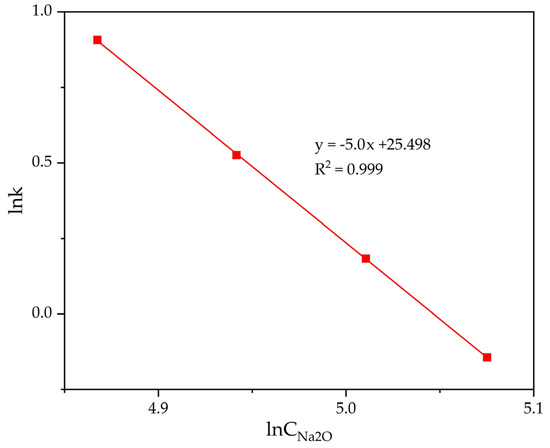
Figure 14.
Dependence of lnK − lnCNa2O (Table 3) for the precipitation of FLG from an aluminate solution at various Na2Ok concentration.
Considering the data obtained and Equations (5) and (9), the following semi-empirical expression (Equation (10)) can be derived.
This equation can be used to calculate the precipitation ratio of FLG from a sodium aluminate solution, when an agglomerated active seed is used.
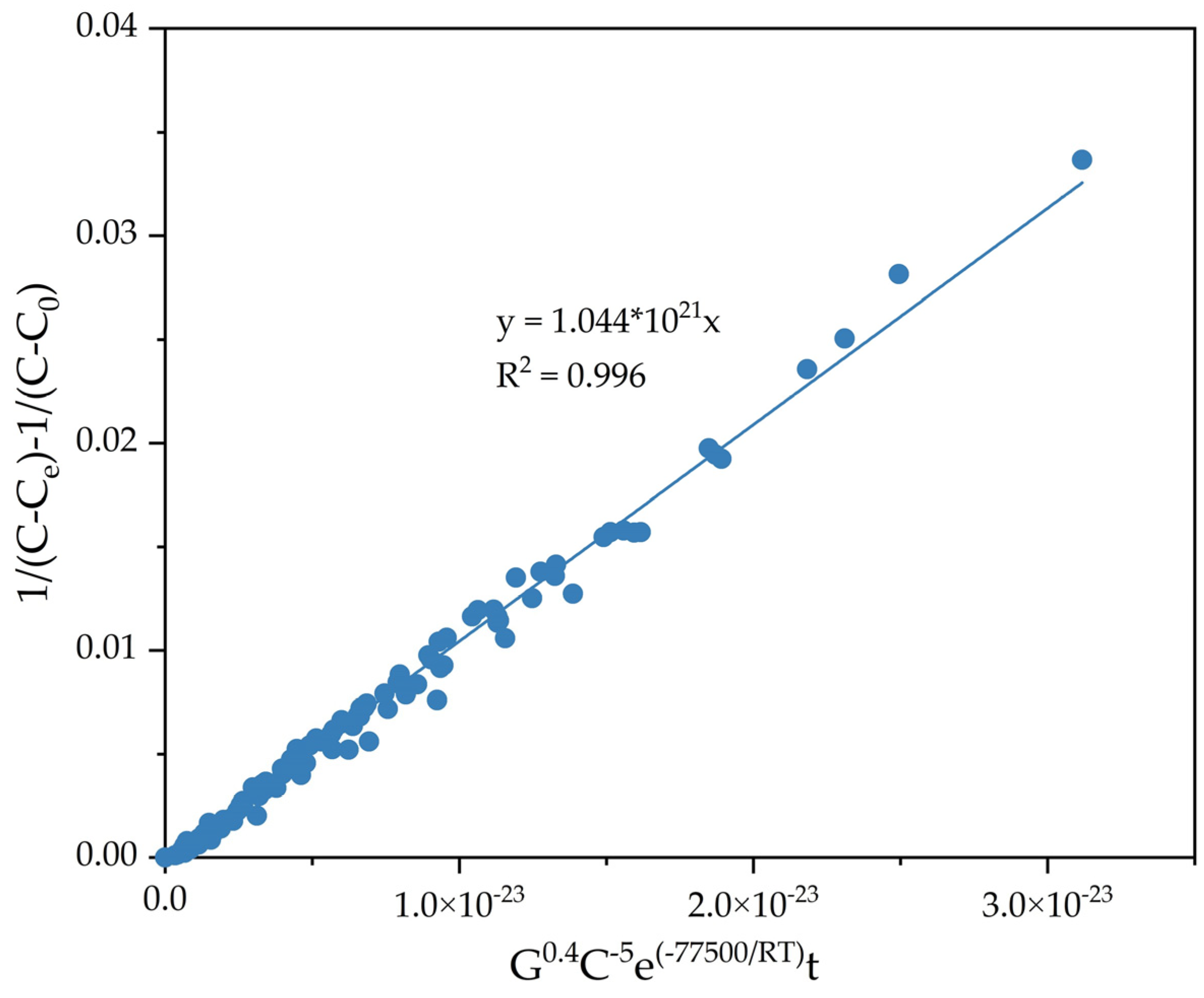
To determine the constant K0, the dependence of 1/(C − Ce) − 1/(C0 − Ce) on C−5.0G0.40e−77,500/RTt was constructed for all known values at different temperatures, the amount of seed, Na2Ok concentration, and time (Figure 15).
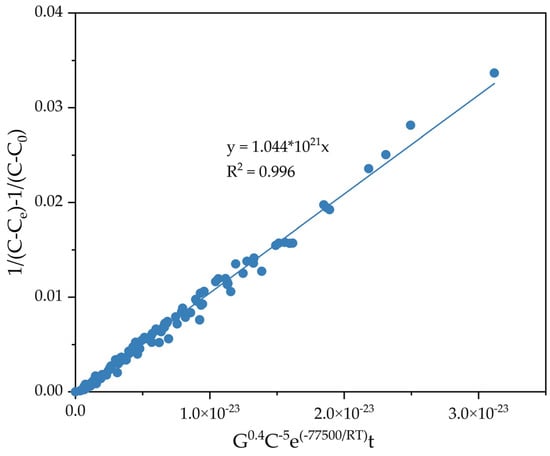
Figure 15.
Dependence of 1/(C − Ce) − 1/(C0 − Ce) on C−5.0G0.40e−77,500/RTt.
From the results in Figure 15, the constant k0 1.04 × 1021 was obtained, and the semiempirical Equation (11) was derived.
The results show that temperature and concentration of caustic alkali have the significant effect on the FLG precipitation. It turned out that the order of the amount of seed in Equation (11) was relatively low. However, the use of an active seed reduces diffusion limitations, and it also increases the degree of precipitation by further increasing the surface area of the seed. According to literature data [27,28,29], when precipitation occurs using a metallurgical quality seed, the activation energy of the process has the same order, but the precipitation rate is much lower. It can be connected with the predominance of nucleation in the FLG precipitation process because gibbsite crystal growth rate is the slowest stage of the Bayer precipitation process [30]. Therefore, the FLG addition accelerates the nucleation process. The reason for this may be that the specific surface area of the FLG is 30 times higher than that of the industrial seed. These data can be used to explain the mechanism of FLG precipitation from sodium aluminate solution. Based on experiments using compounds with a high specific surface area as a seed [31], it was assumed that the role of the seed during precipitation is the adsorption of polymer ions and/or associates. After adsorption, due to the fact that the Gibbs energy change at the phase interface for crystallization is lower than under homogeneous conditions, polycondensation of associates occurs with the formation of nucleai.
It was later proved that there is an adsorption layer with a thickness of 0.3 to 10 nm on the surface of the seed in an aluminate solution using modern methods of analysis carried out by Vernon et al. [32,33]. Although the nature of this layer is not completely clear; there are assumptions that it consists of polymer ions [25], and Vernon et al. [32] suggest that this adsorption layer consists of sodium cations. Sodium cations interfere with the supply of building material to the crystal surface, which is a reason for the slow crystallization of gibbsite from alkaline aluminate solutions.
The theory of the existence of an adsorption layer of sodium ions is not capable of explaining the reason why, in the late period of precipitation, only the seed that has not been completely washed from the mother liquor has the seeding ability [34]. It can be explained by the presence of an adsorption layer containing polymerized aluminate ions on the surface of the seed that has not been washed from the mother liquor. The high amount of polymerized ions adsorbed on the surface of FLG increases the supersaturation of the solution at the interface, which leads to faster precipitation. The higher the specific surface area of the seed, the greater its adsorption capacity and the lower the limitations to precipitation will be.
3.3. Solid Product Characterization
Table 4 shows that the PSD of FLG precipitated at 25 °C for 8 h at a Na2O concentration of 150 g L−1 and a seed amount of 20 g L−1, as well as PSD of the product obtained under the same other equal conditions, but at 35 °C. For comparison, the PSD of metallurgical grade aluminum hydroxide is also given.

Table 4.
Results of the processing of the curves in Figure 13.
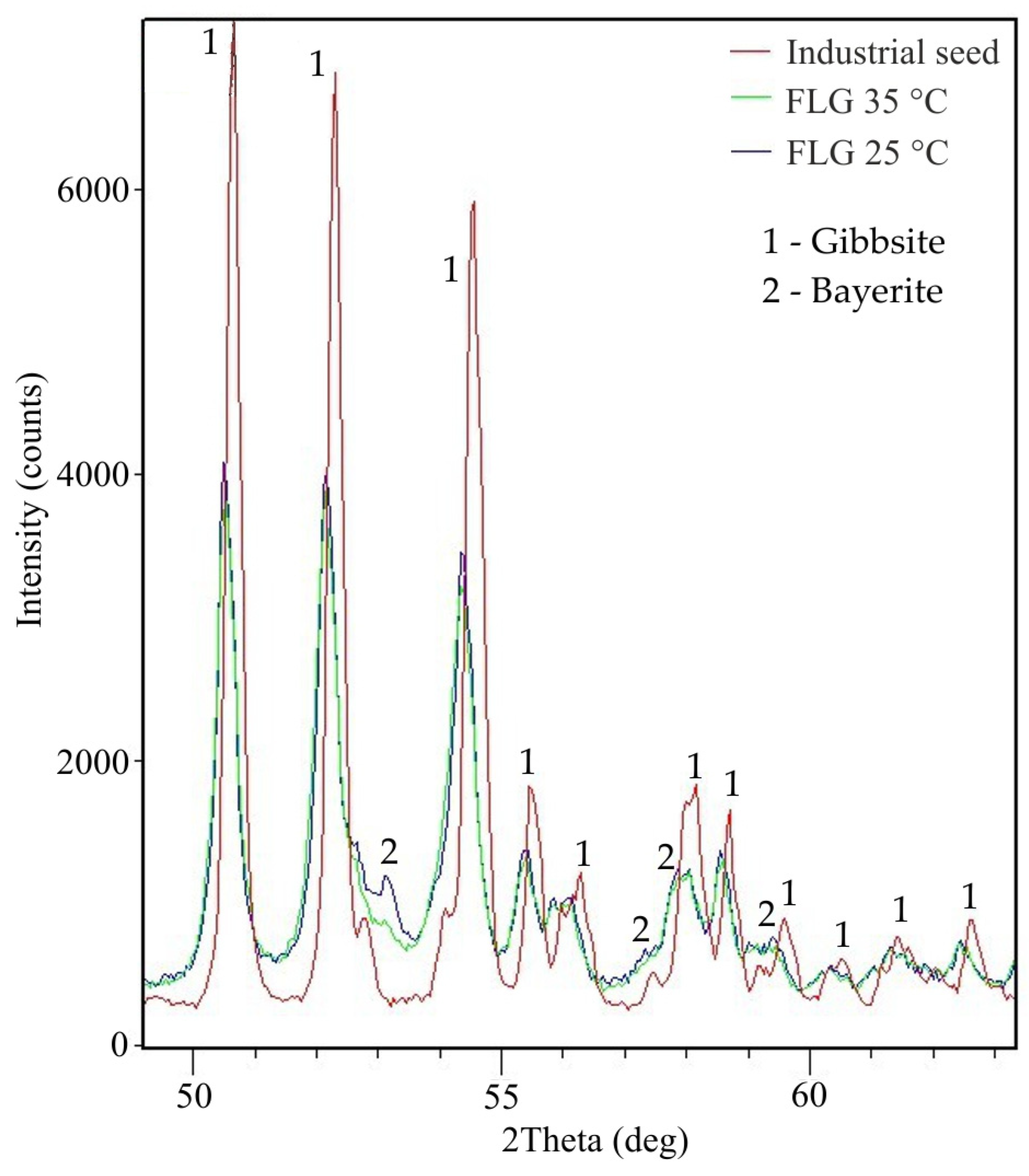
At high temperature, it is evident that the product is finely dispersed, which may be due to the dissolution of agglomerates sticked together by bayerite. Lee et al. observed a similar phenomenon when at a high degree of precipitation (at later stages of precipitation) and elevated temperature, the product was refined. The reason for this is the dissolution of the bayerite glue at a high caustic modulus, when there is a large amount of free caustic alkali in the solution. The high temperature also causes the solution to become unsaturated relative to bayerite. Figure 16 illustrates the result of examination of the X-ray patterns section of hydroxides from Table 4.
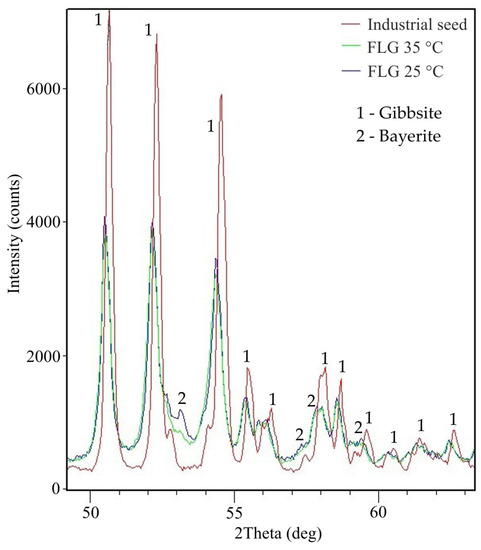
Figure 16.
XRD pattern of the aluminum hydroxide samples in a certain area of interplane reflections.
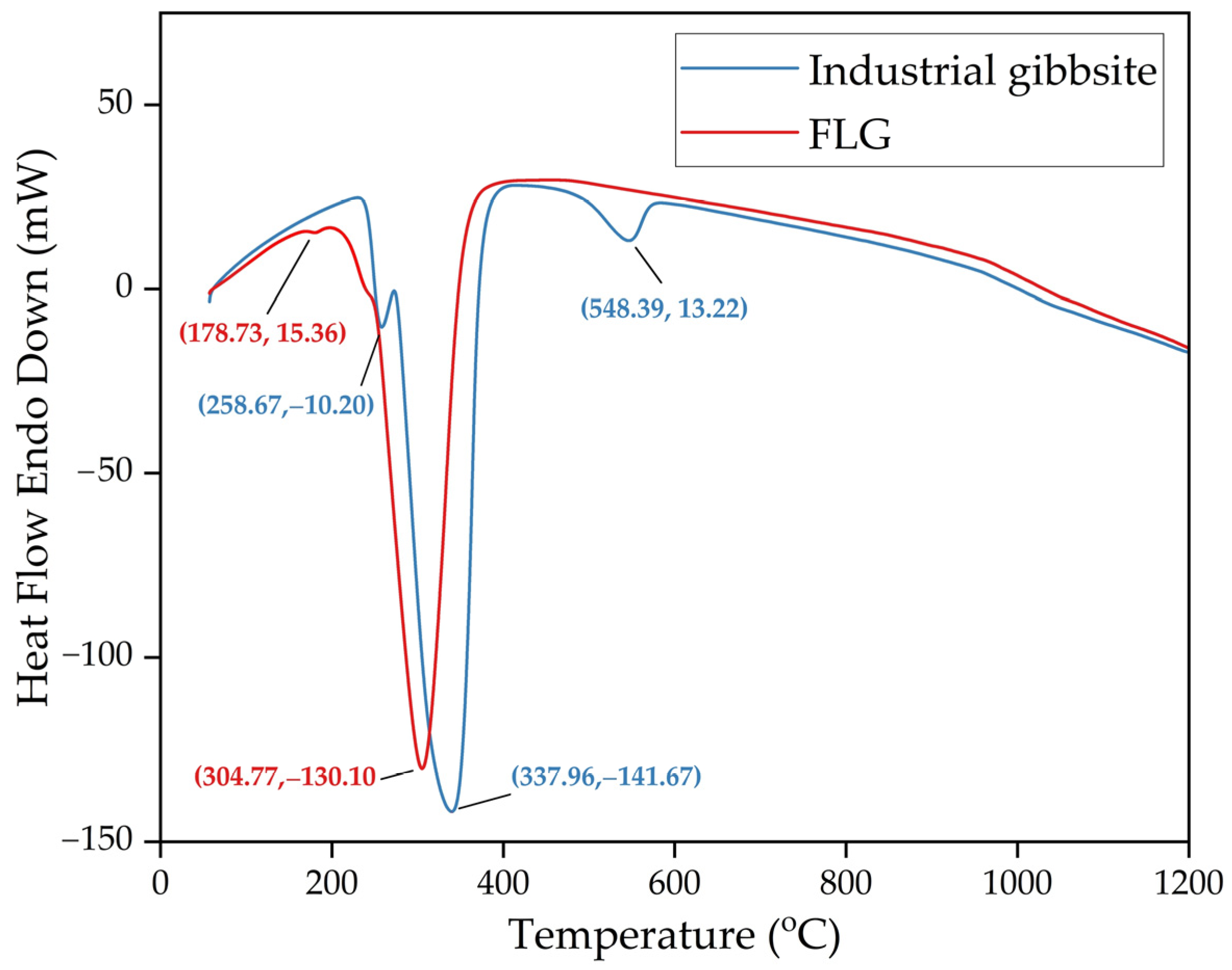
In the product obtained at 25 °C, a peak of bayerite is observed at an angle of 2Theta equal to 53°. This peak disappears in the product obtained at 35 °C that can indicate bayerite dissolution at this temperature. The FLG peaks are wider and lower than metallurgical grade hydroxide, which indicates a lower degree of crystallization. The results of the DTA analysis (Figure 17) also confirm a lower degree of crystallization and a small particle size. It is typical for finely dispersed aluminum hydroxide to skip the stage of boehmite formation.
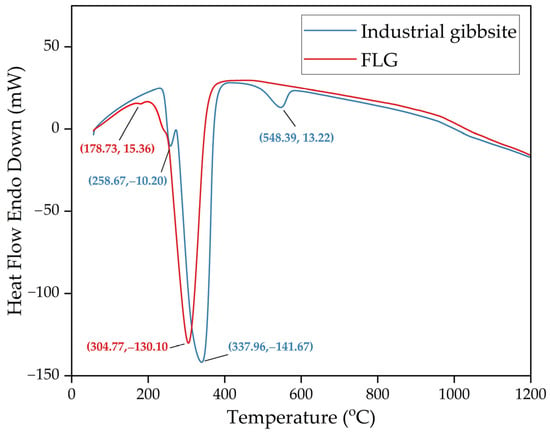
Figure 17.
Results of DTA analysis of FLG hydroxide and industrial aluminum hydroxide of metallurgical grade (where (x,y) is a peak coordinates).
4. Conclusions
In this article, the possibility of coarse active aluminum hydroxide precipitation from the sodium aluminate solution of the Bayer process was demonstrated. It is possible to reduce the precipitation time by 4–5 times compared to the industrial Bayer precipitation by using this hydroxide as a seed. The result of this process is a product composed of flake-like gibbsite (FLG) particles, which can be bonded together by bayerite. Due to the high temperature (>35 °C) and high caustic modulus, bayerite dissolution and agglomerate breakdown occur. The coarse-activated aluminum hydroxide obtained in this research has a specific surface area higher than 30 m2 g−1 that is 100 times higher than the metallurgical grade gibbsite. Flake-like agglomerated hydroxide can be used for two-stage precipitation, where the first stage is a rapid precipitation from the solution, and the second stage is a recrystallization of the first stage product. The effect of different parameters on the FLG precipitation was elaborated:
- The effect of temperature and time on the FLG precipitation indicates that the temperature increase from 20 to 35 °C leads to an increase in the precipitation rate from 40% to 60%. It was found that the maximum precipitation rate was obtained at 35 °C, which is in agreement with the literature data on kinetics of the precipitation of gibbsite from sodium aluminate solution.
- The increase in the amount of seed from 10 g L−1 to 40 g L−1 helps to increase the precipitation rate from 42.9% to 54.8%.
- Relatively high alkali concentrations were found to inhibit the precipitation of FLG. An increase in the Na2Ok concentration from 130 to 160 g L−1 leads to a decrease in the precipitation rate from 58.3 to 44.0%.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S. and I.L.; methodology, A.S.; software, D.V.; validation, A.S., I.L. and K.A.; formal analysis, K.A.; investigation, A.S.; resources, I.L.; data curation, I.L.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.; writing—review and editing, D.V.; visualization, K.A.; supervision, I.L.; project administration, I.L.; funding acquisition, A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Project of the State Assignment, FEUZ-2021-0017. The method used to determine the chemical composition of solutions by ICP-OES (see Section “Analysis”) were funded by the Project of the State Assignment (Vernadsky Institute of Geochemistry and Analytical Chemistry of Russian Academy of Sciences, No. FMUS-2019-24).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to Evgeny Kolesnikov of NUST MISiS for assistance with the solid samples characterization.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Loginova, I.V.; Shoppert, A.A.; Chaikin, L.I. Extraction of Rare-Earth Metals During the Systematic Processing of Diaspore-Boehmite Bauxites. Metallurgist 2016, 60, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loginova, I.V.; Shoppert, A.A.; Chaikin, L.I. Effect of Adding Sintering Furnace Electrostatic Precipitator Dust on Combined Leaching of Bauxites and Cakes. Metallurgist 2015, 59, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hond, R.D.; Hiralal, I.; Rijkeboer, A. Alumina Yield in the Bayer Process Past, Present and Prospects. In Essential Readings in Light Metals; Donaldson, D., Raahauge, B.E., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 528–533. ISBN 978-1-118-64786-8. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Yin, J.; Yin, Z. Effect of Mechanically Activated Seeds on the Agglomeration Process of Supersaturated Sodium Aluminate Liquors. Light Met. 2007, 175, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.-S.; Yin, Z.-L.; Chen, Q.-Y. Decomposition Enhancement of Seeded Sodium Aluminate Liquor by Activated Seed. Zhongguo Youse Jinshu Xuebao Chin. J. Nonferr. Met. 2008, 18, 361–365. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Yin, Z.; Chen, Q. Intensification of Precipitation of Gibbsite from Seeded Caustic Sodium Aluminate Liquor by Seed Activation and Addition of Crown Ether. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 89, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-P.; Yin, Z.-L.; Lü, B.-L.; Chen, Q.-Y. Effects of L-Leucine Additives on Seeded Precipitation of Sodium Aluminate Solution. Zhongguo Youse Jinshu Xuebao Chin. J. Nonferr. Met. 2010, 20, 1855–1860. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Wu, G.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Peng, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Qi, T. Increasing Precipitation Rate from Sodium Aluminate Solution by Adding Active Seed and Ammonia. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 176, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, J.L.; Kapraun, C. Dynamic Modeling of Yield and Particle Size Distribution in Continuous Bayer Precipitation. In Essential Readings in Light Metals; Donaldson, D., Raahauge, B.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 891–897. ISBN 978-3-319-48574-4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, X.; Yu, H.; Tu, G.; Bi, S. Effect of Organic Impurity on Seed Precipitation in Sodium Aluminate Solution. In Light Metals 2018; Martin, O., Ed.; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 41–47. ISBN 978-3-319-72283-2. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Yu, H.; Tu, G.; Bi, S. Effects of Precipitation Activity of Desilication Products (DSPs) on Stability of Sodium Aluminate Solution. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 165, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweegers, C.; de Coninck, H.C.; Meekes, H.; van Enckevort, W.J.P.; Hiralal, I.D.K.; Rijkeboer, A. Morphology, Evolution and Other Characteristics of Gibbsite Crystals Grown from Pure and Impure Aqueous Sodium Aluminate Solutions. J. Cryst. Growth 2001, 233, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Qi, T.; Li, X.; Zhou, Q.; Peng, Z. Two-Stage Process for Precipitating Coarse Boehmite from Sodium Aluminate Solution. JOM 2017, 69, 1888–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeev, D.; Shoppert, A.; Mikhailova, A.; Kondratiev, A. Acid and Acid-Alkali Treatment Methods of Al-Chloride Solution Obtained by the Leaching of Coal Fly Ash to Produce Sandy Grade Alumina. Metals 2020, 10, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.O.; Jung, K.H.; Oh, C.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Tran, T.; Kim, M.J. Precipitation of Fine Aluminium Hydroxide from Bayer Liquors. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 98, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, I.N.; Pradhan, J.K.; Gochhayat, P.K.; Das, S.C. Factors Controlling Precipitation of Finer Size Alumina Trihydrate. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2002, 65, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.-H.; Qi, T.-G.; Zhou, Q.-S.; Wu, X.-P.; Peng, Z.-H.; Liu, G.-H.; Li, X.-B. Particles Evolution during Seeded Precipitation of Sodium Aluminate Solution by Adding Active Seed. Zhongguo Youse Jinshu Xuebao Chin. J. Nonferr. Met. 2020, 30, 1172–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, S.; Du, H.; Xu, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Improved Precipitation of Gibbsite from Sodium Aluminate Solution by Adding Methanol. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 98, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y. Additives Effects on Crystallization and Morphology in a Novel Caustic Aluminate Solution Decomposition Process. Front. Chem. Eng. China 2009, 3, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Xie, Y.; Bi, S.; Lǚ, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, B. Kinetics of Crystallization in Sodium Aluminate Liquors. In Proceedings of the TMS Light Metals, Charlotte, NC, USA, 14–18 March 2004; pp. 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, C.; White, E.T. Mathematical Model of the Bayer Precipitation Process for Alumina Production. In Proceedings of the CHEMECA’70, Melbourne & Sydney, Australia, 19–26 August 1970; Butterworth Co., (Aust.) Ltd.: Chatswood, Australia, 1970; Volume 7, pp. 52–76. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Addai-Mensah, J.; Thilagam, A.; Gerson, A.R. Growth Mechanisms and Kinetics of Gibbsite Crystallization: Experimental and Quantum Chemical Study. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 3096–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Liu, C.; Luo, M.; Lin, M.; Jiang, Y.; Li, P.; Yu, J.; Rohani, S. Secondary Nucleation and Growth Kinetics of Aluminum Hydroxide Crystallization from Potassium Aluminate Solution. J. Cryst. Growth 2019, 507, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Prestidge, C.A.; Addai-Mensah, J. Secondary Nucleation of Gibbsite Crystals from Synthetic Bayer Liquors: Effect of Alkali Metal Ions. J. Cryst. Growth 2000, 219, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, G.; Peng, Z. Concentration Variation of Aluminate Ions during the Seeded Precipitation Process of Gibbsite from Sodium Aluminate Solution. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 106, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yan, L.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, G.; Peng, Z.; Yang, S.; Qi, T. Relationship between Al(OH)3 Solubility and Particle Size in Synthetic Bayer Liquors. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonthalia, R.; Behara, P.; Kumaresan, T.; Thakre, S. Review on Alumina Trihydrate Precipitation Mechanisms and Effect of Bayer Impurities on Hydrate Particle Growth Rate. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2013, 125, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J. Particle Distribution Model of Gibbsite Precipitation Process in Alumina Production. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2011, 50, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Li, Y.-Q.; Fu, M.-H.; Liu, B.; Li, L. Concentration and Mass Ratio Model of Gibbsite Precipitation Process in Alumina Production. Zhongnan Daxue Xuebao Ziran Kexue Ban J. Cent. South Univ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 42, 1543–1548. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaei, H.; Noaparast, M.; Abdollahi, H. Modeling and Optimizing Aluminum Hydroxide Precipitation Process in Industrial Scale; Case Study: Iran Alumina Plant. J. Min. Environ. 2021, 12, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loginova, I.V.; Shoppert, A.A. Preparation of Active Aluminum Hydroxide and Its Use for Production of Finely Dispersed Alumina. Russ. J. Non-Ferr. Met. 2014, 55, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, C.F.; Brown, M.J.; Lau, D.; Zieba, M.P. Mechanistic Investigation of Gibbsite Growth. In Proceedings of the 6th International Alumina Quality Workshop, Brisbane, Australia, 8–13 September 2002; pp. 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Vernon, C.; Loh, J.; Lau, D.; Stanley, A. Soda Incorporation During Hydrate Precipitation. In Essential Readings in Light Metals; Donaldson, D., Raahauge, B.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 602–607. ISBN 978-3-319-48574-4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Feng, G.; Zhou, Q.; Peng, Z.; Liu, G. Phenomena in Late Period of Seeded Precipitation of Sodium Aluminate Solution. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2006, 16, 947–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).