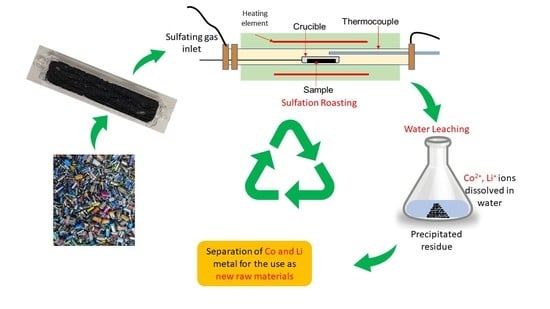
Selective Sulfation Roasting for Cobalt and Lithium Extraction from Industrial LCO-Rich Spent Black Mass
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Technique
2.1. Materials
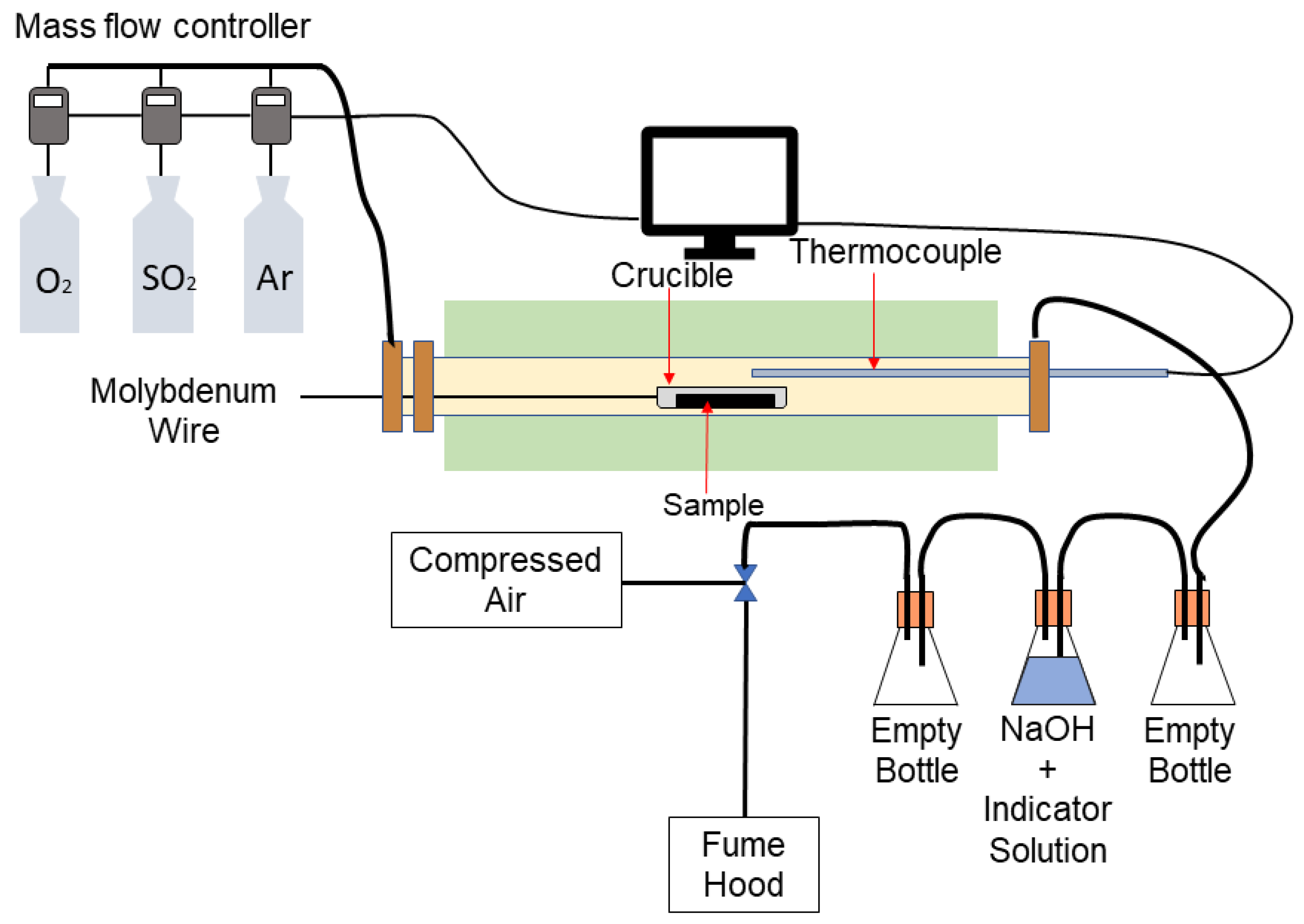
2.2. Roasting Apparatus
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
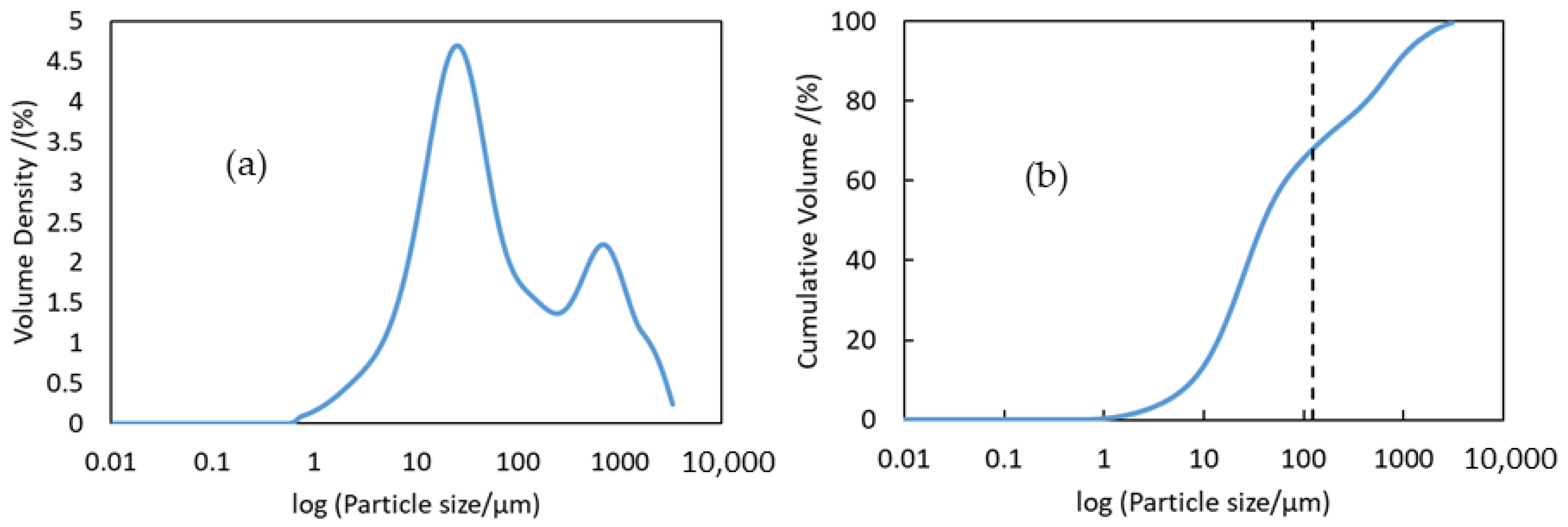
3.1. Characterization of LIB Waste
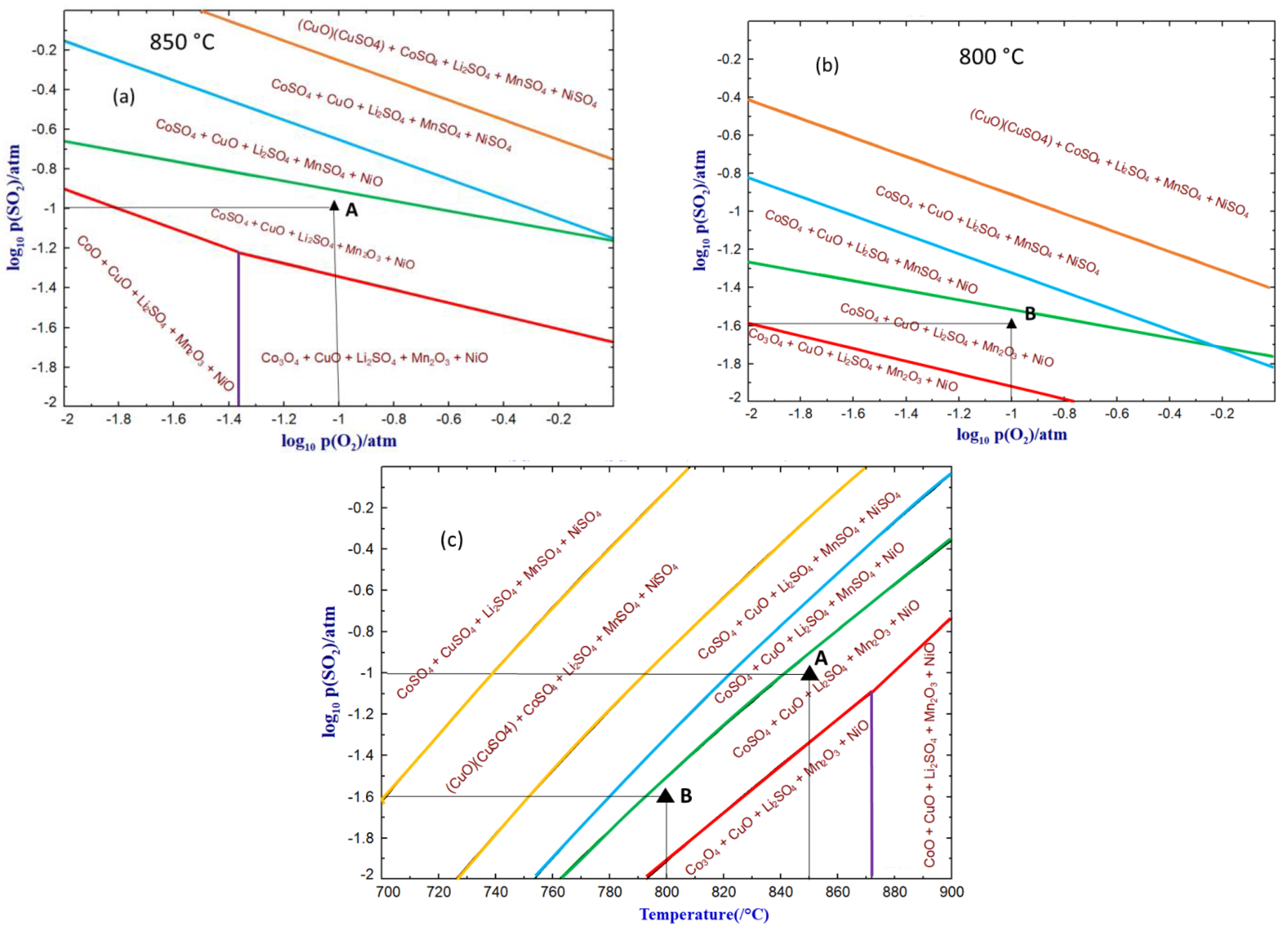
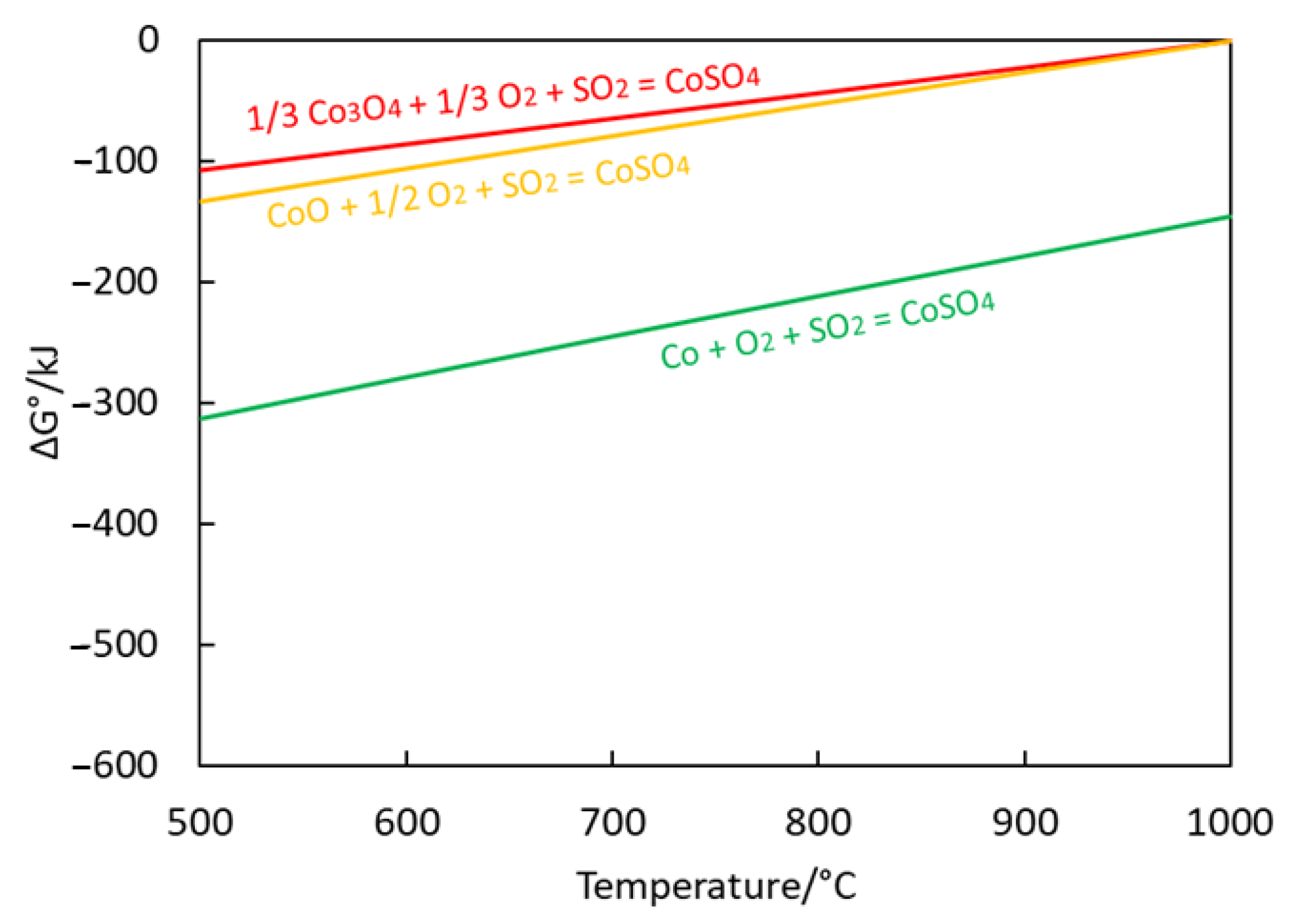
3.2. Thermodynamics
3.3. Sulfation Roasting and Leaching
3.3.1. With Carbon (Type 1)
3.3.2. Without Carbon (Type 2)
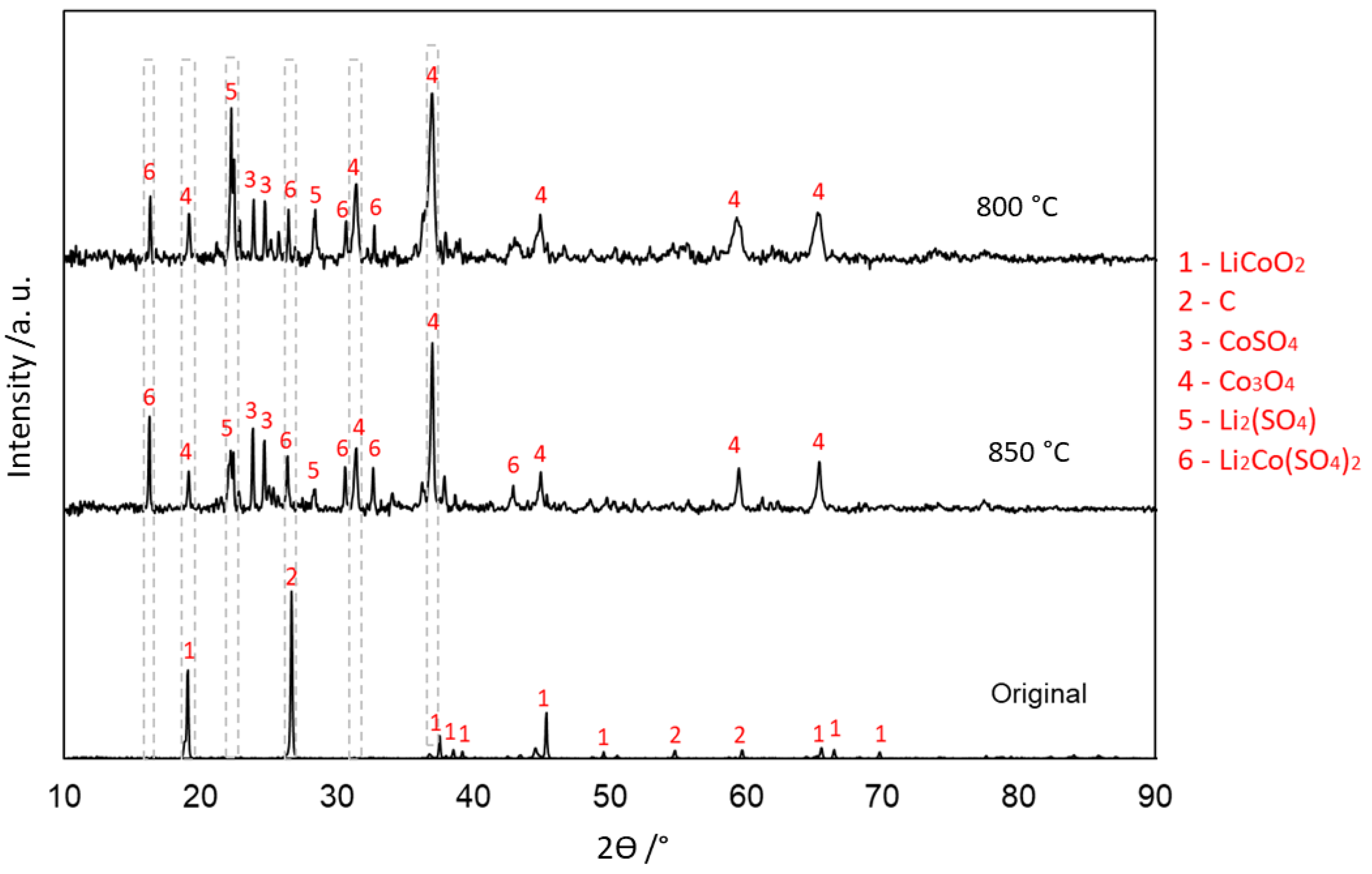
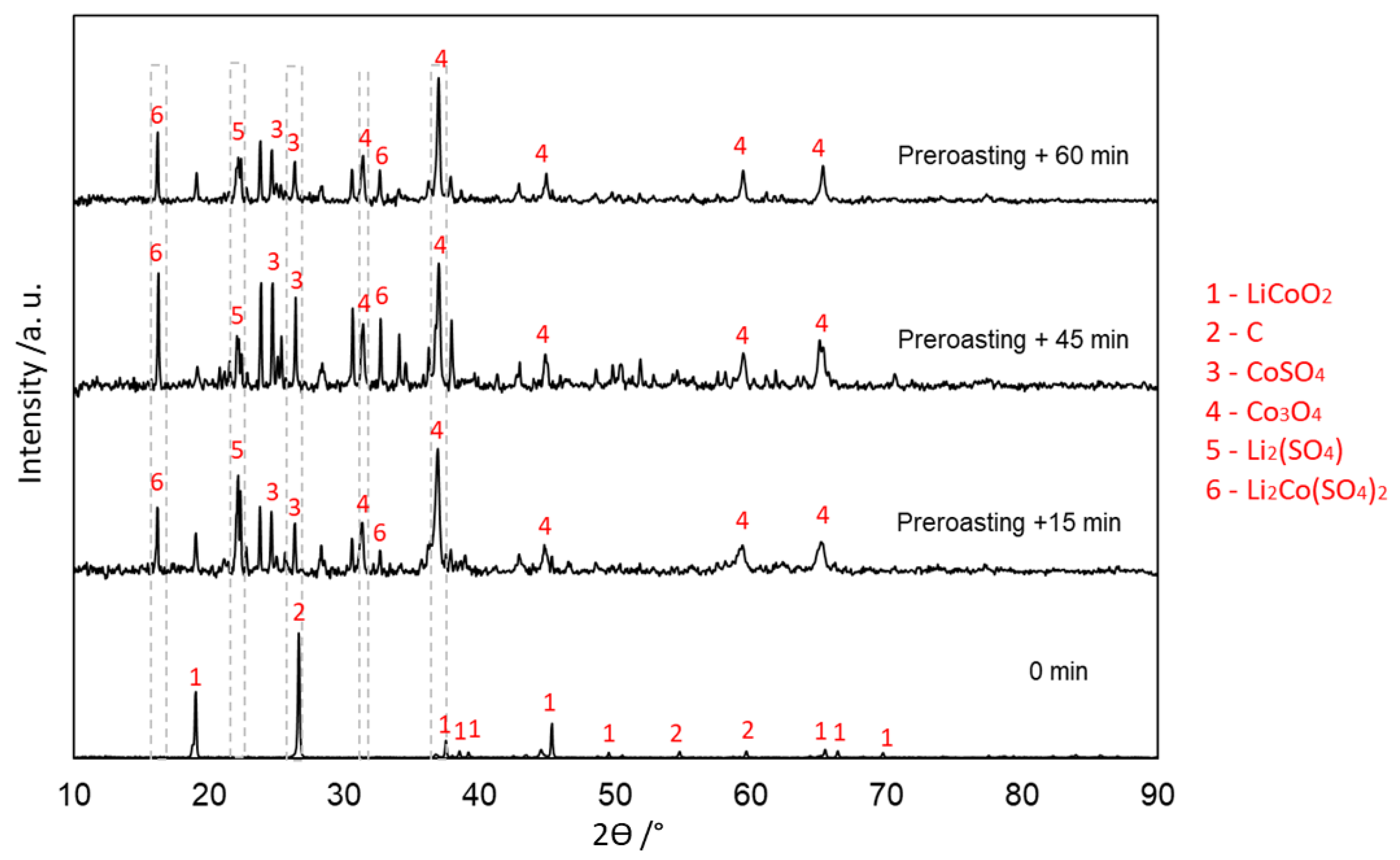
3.4. Evolution of Phases in Sulfation Roasting
3.4.1. With Carbon (Type 1)
3.4.2. Without Carbon (Type 2)
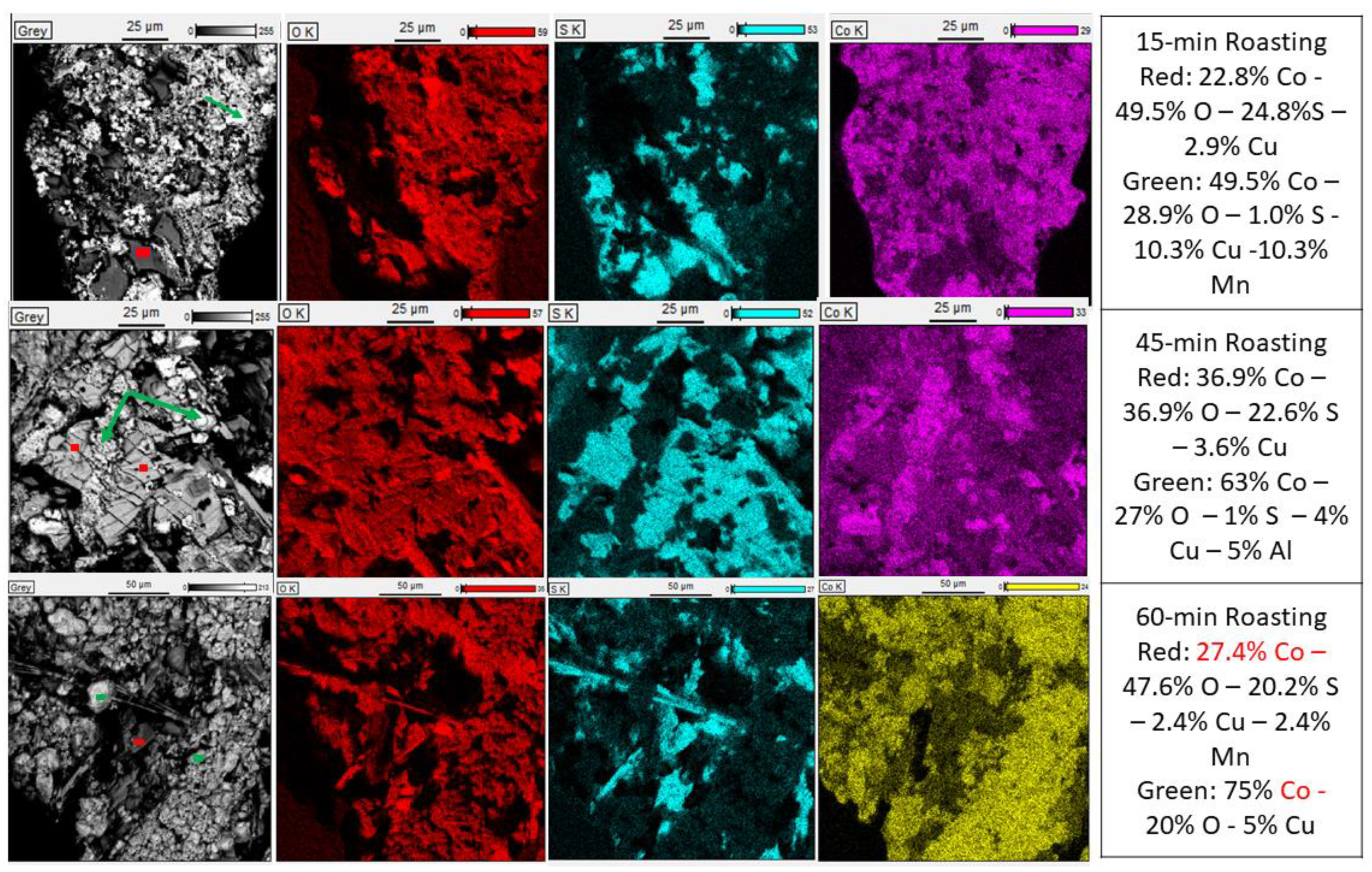
3.5. Extraction of Co and Li into Water after Roasting
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roper, W. High Demand for Lithium-Ion Batteries Statista. Available online: https://www.statista.com/chart/23808/lithium-ion-battery-demand/ (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Zhang, W.; Xu, C.; He, W.; Li, G.; Huang, J. A review on management of spent lithium-ion batteries and strategy for resource recycling of all components from them. Waste Manag. Res. 2018, 36, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, J.; Petranikova, M.; Meeus, M.; Gamarra, J.; Younesi, R.; Winter, M.; Nowak, S. Recycling of Lithium-Ion Batteries—Current State of the Art, Circular Economy, and Next Generation Recycling. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2102917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamczyc Alex: New Research Shows Boom in End-of-Life Lithium-Ion Batteries—Recycling Today. Available online: https://www.recyclingtoday.com/article/lux-research-sees-boon-in-lithium-ion-battery-end-markets/ (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Zhao, Y.; Pohl, O.; Bhatt, A.; Collis, G.; Mahon, P.; Rüther, T.; Hollenkamp, A.F. A Review on Battery Market Trends, Second-Life Reuse, and Recycling. Sustain. Chem. 2021, 2, 167–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithium-ion Battery Market Size Worth $182.53 Billion By 2030: Grand View Research, Inc.—Bloomberg. Available online: https://www.bloomberg.com/press-releases/2022-06-07/lithium-ion-battery-market-size-worth-182-53-billion-by-2030-grand-view-research-inc (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Woollacott, E. Electric Cars: What will Happen to All the Dead Batteries?—BBC News. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/news/business-56574779 (accessed on 22 September 2022).
- REPORT on the Proposal for a Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council Concerning Batteries and Waste Batteries, Repealing Directive 2006/66/EC and Amending Regulation (EU) No. 2019/1020|A9-0031/2022. European Parliament. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/doceo/document/A-9-2022-0031_EN.html (accessed on 7 October 2022).
- Lee, J.-J.; Chung, J.-D. A study on the cobalt and lithium recovery from the production scraps of lithium secondary battery by high efficient and eco-friendly method. J. Korean Inst. Resour. Recycl. 2010, 19, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.; Hamuyuni, J.; Wilson, B.; Lundström, M. Selective reductive leaching of cobalt and lithium from industrially crushed waste Li-ion batteries in sulfuric acid system. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, T.; Liu, D.; Hu, H.; Fan, S. Hydrometallurgical recovery of metal values from sulfuric acid leaching liquor of spent lithium-ion batteries. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, F.; Zhu, H.; Li, G.; Huang, J.; He, W. Leaching lithium from the anode electrode materials of spent lithium-ion batteries by hydrochloric acid (HCl)’. Waste Manag. 2016, 51, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ma, H.; Luo, C.; Zhou, T. Recovery of valuable metals from waste cathode materials of spent lithium-ion batteries using mild phosphoric acid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 326, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, P.; Pandey, B.; Mankhand, T. Recovery of valuable metals from cathodic active material of spent lithium ion batteries: Leaching and kinetic aspects. Waste Manag. 2015, 45, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Nie, Z.; Xi, X.; Han, X. Cobalt recovery from cobalt-bearing waste in sulphuric and citric acid systems. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 136, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnanelli, F.; Moscardini, E.; Altimari, P.; Atia, T.A.; Toro, L. Cobalt products from real waste fractions of end of life lithium ion batteries. Waste Manag. 2016, 51, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, G.; Ebin, B.; Foreman, M.S.; Steenari, B.; Petranikova, M. Incineration of EV Lithium-ion batteries as a pretreatment for recycling—Determination of the potential formation of hazardous by-products and effects on metal compounds. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 13668–13679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Huang, G.; Xu, S.; He, Y.; Liu, X. Thermal treatment process for the recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 165, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavón, S.; Kahl, M.; Hippmann, S.; Bertau, M. Lithium recovery from production waste by thermal pre-treatment. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 28, 100725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinne, M.; Elomaa, H.; Porvali, A.; Lundström, M. Simulation-based life cycle assessment for hydrometallurgical recycling of mixed LIB and NiMH waste. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 170, 105586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, G.; Xu, Z. Environmentally-friendly oxygen-free roasting/wet magnetic separation technology for in situ recycling cobalt, lithium carbonate and graphite from spent LiCoO2/graphite lithium batteries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 302, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C. Efficient and economical recovery of lithium, cobalt, nickel, manganese from cathode scrap of spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Clean Prod. 2018, 204, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C. A promising approach for the recovery of high value-added metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2017, 351, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Xiao, L.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ye, L.; Zhu, Y. Study on the reduction roasting of spent LiNixCoyMnzO2 lithium-ion battery cathode materials. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 136, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Tang, J.; Wanaldi, R.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, C.; Yang, J. A promising selective recovery process of valuable metals from spent lithium ion batteries via reduction roasting and ammonia leaching. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Z.; Qu, J.; Xing, P.; Yin, H. Recovery and regeneration of LiCoO2-based spent lithium-ion batteries by a carbothermic reduction vacuum pyrolysis approach: Controlling the recovery of CoO or Co. Waste Manag. 2019, 97, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Z. Recycling metals from lithium ion battery by mechanical separation and vacuum metallurgy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 338, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Zhu, X.; Li, J.; Liao, Q.; Lai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fu, Q.; Zhu, X. A novel method for carbon removal and valuable metal recovery by incorporating steam into the reduction-roasting process of spent lithium-ion batteries. Waste Manag. 2021, 134, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, S. Cleaner recycling of cathode material by in-situ thermite reduction. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 249, 119340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, S. A Simplified Process for Recovery of Li and Co from Spent LiCoO2 Cathode Using Al Foil as the in situ Reductant. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 12222–12230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Xiao, S.; Xie, M.; Pan, B.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Xia, X. Recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium ion batteries by smelting reduction process based on FeO–SiO2–Al2O3 slag system. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2017, 27, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, M.; Hovestadt, G.; Friedrich, B. Smelting of Pyrolyzed Lithium-Ion Battery Black Mass using a Calcium-Aluminate Slag System. In Proceedings of the European Metallurgical Conference (EMC) 2021, Salzburg, Germany, 27 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sommerfeld, M.; Vonderstein, C.; Dertmann, C.; Klimko, J.; Oráč, D.; Miškufová, A.; Havlík, T.; Friedrich, B. A Combined Pyro- and Hydrometallurgical Approach to Recycle Pyrolyzed Lithium-Ion Battery Black Mass Part 1: Production of Lithium Concentrates in an Electric Arc Furnace. Metals 2020, 10, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheret, D.; Santén, S. Battery Recycling. European Patent 1589121B1, 26 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Velázquez-Martínez, O.; Valio, J.; Santasalo-Aarnio, A.; Reuter, M.; Serna-Guerrero, R. A Critical Review of Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling Processes from a Circular Economy Perspective. Batteries 2019, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, G.; Sommerville, R.; Kendrick, E.; Driscoll, L.; Slater, P.; Stolkin, R.; Walton, A.; Christensen, P.; Heidrich, O.; Lambert, S.; et al. Recycling lithium-ion batteries from electric vehicles. Nature 2019, 575, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuza, B.; Tian, Q.; Guo, X.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Yu, D. Pyrometallurgical options for recycling spent lithium-ion batteries: A comprehensive review. J. Power Sources 2021, 491, 229622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, E.; Li, L.; Lin, J.; Wu, J.; Yang, J.; Wu, F.; Chen, R. Low-Temperature Molten-Salt-Assisted Recovery of Valuable Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 16144–16150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, O.; González, Y.; Barbosa, L.; Orosco, P. Chlorination roasting of the cathode material contained in spent lithium-ion batteries to recover lithium, manganese, nickel and cobalt. Miner. Eng. 2022, 176, 107321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Xie, H.; Chen, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xing, P.; Yin, H. Recovery of LiCoO2 from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries through a Low-Temperature Ammonium Chloride Roasting Approach: Thermodynamics and Reaction Mechanisms. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 6524–6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Niu, B.; Song, Q.; Zhan, L.; Xu, Z. Novel targetedly extracting lithium: An environmental-friendly controlled chlorinating technology and mechanism of spent lithium ion batteries recovery. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 123947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.; Zongliang, Z.; Gang, Z.; Liangxing, J.; Fangyang, L.; Ming, J.; Yanqing, L. Process study of chloride roasting and water leaching for the extraction of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 203, 105638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Peng, C.; Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Eric, H.; Klemettinen, L.; Lundström, M.; Taskinen, P.; Jokilaakso, A. Sulfation Roasting Mechanism for Spent Lithium-Ion Battery Metal Oxides Under SO2-O2-Ar Atmosphere. JOM 2019, 71, 4473–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Qu, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhao, J.; Ning, Z.; Xing, P.; Yin, H. Recycling of spent lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxides via a low-temperature ammonium sulfation roasting approach. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 279, 123633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Z.; Jing, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C. Sustainable and Facile Process for Lithium Recovery from Spent LiNixCoyMnzO2 Cathode Materials via Selective Sulfation with Ammonium Sulfate. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 15732–15739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Sun, J. Separation of Li and Co from the active mass of spent Li-ion batteries by selective sulfating roasting with sodium bisulfate and water leaching. Miner. Eng. 2018, 126, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Li, L.; Fan, E.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Cao, H.; Sun, Z.; Chen, R. Conversion Mechanisms of Selective Extraction of Lithium from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries by Sulfation Roasting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 18482–18489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Lv, W.; Rao, F.; Yao, P.; Wang, J.; Sun, Z. Synergic Mechanisms on Carbon and Sulfur during the Selective Recovery of Valuable Metals from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 2271–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shi, P.; Chang, D.; Jie, Y.; Yang, S.; Wu, G.; Chen, H.; Zhu, J.; Hu, F.; Wilson, B.; et al. Selective extraction of valuable metals from spent EV power batteries using sulfation roasting and two stage leaching process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 258, 118078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudas, J.; Erkkila, A.; Viljamaa, J. Battery Recycling Method. U.S. Patent 8979006 B2, 17 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.; Liu, F.; Aji, A.; Wilson, B.; Lundström, M. Extraction of Li and Co from industrially produced Li-ion battery waste—Using the reductive power of waste itself. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porvali, A. Complexities of Hydrometallurgical Recycling of Spent NiMH and Li-ion Batteries. Ph.D. Thesis, Aalto University, Espoo, Finland, 2020; pp. 41–42. [Google Scholar]






| Elements | Al | Ca | Co | Cu | Fe | K | Li | Mg | Mn | Na | Ni | P | Zn | C | Rest |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | 1.64 | 0.03 | 26.45 | 2.72 | 0.61 | 0.05 | 3.87 | 0.09 | 1.67 | 0.06 | 2.74 | 0.45 | 0.04 | 33 | 26.58 |
| Conditions | Gas Composition | Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| A | 10% SO2-10% O2-Ar | 850 °C |
| B | 2.5% SO2-10% O2-Ar | 800 °C |
| Conditions | Co (%) | Ni (%) | Mn (%) | Cu (%) | Fe (%) | Li (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 61.21 | 22.99 | 68.36 | 24.53 | 0.00 | 99.51 |
| B | 24.02 | 11.15 | 26.57 | 1.72 | 0.00 | 91.75 |
| Conditions | Co (%) | Ni (%) | Mn (%) | Cu (%) | Fe (%) | Li (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 24.34 | 33.00 | 46.61 | 21.60 | 0.00 | 88.75 |
| B | 17.41 | 17.22 | 26.52 | 6.87 | 0.00 | 88.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biswas, J.; Ulmala, S.; Wan, X.; Partinen, J.; Lundström, M.; Jokilaakso, A. Selective Sulfation Roasting for Cobalt and Lithium Extraction from Industrial LCO-Rich Spent Black Mass. Metals 2023, 13, 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13020358
Biswas J, Ulmala S, Wan X, Partinen J, Lundström M, Jokilaakso A. Selective Sulfation Roasting for Cobalt and Lithium Extraction from Industrial LCO-Rich Spent Black Mass. Metals. 2023; 13(2):358. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13020358
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiswas, Jayasree, Sofia Ulmala, Xingbang Wan, Jere Partinen, Mari Lundström, and Ari Jokilaakso. 2023. "Selective Sulfation Roasting for Cobalt and Lithium Extraction from Industrial LCO-Rich Spent Black Mass" Metals 13, no. 2: 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13020358
APA StyleBiswas, J., Ulmala, S., Wan, X., Partinen, J., Lundström, M., & Jokilaakso, A. (2023). Selective Sulfation Roasting for Cobalt and Lithium Extraction from Industrial LCO-Rich Spent Black Mass. Metals, 13(2), 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13020358