Quantification of Mesoscale Deformation-Induced Surface Roughness in α-Titanium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Microstructure
2.2. Stop-and-Study Tensile Tests
3. Numerical Simulation
3.1. Microstructure Design
3.2. Constitutive Description and Boundary Conditions
4. Roughness Quantification
4.1. Fractal Dimension
- The data set DS is divided into d subsets of length n, where n is a divider of N;
- For each subset DSm (m = 1, …, d):
- a.
- The mean Em and the standard deviation Sm are calculated;
- b.
- The data are normalized by subtracting the sample mean
- c.
- The cumulative series are calculated as
- d.
- The range is found asand then rescaled as
- The mean value of the rescaled range is calculated for all subsets:
4.2. Standard Roughness Estimations
4.3. Dimensionless Roughness Parameter
5. Results
5.1. Microstructure
5.2. Model Validation
5.3. Experimental Observations for Mesoscale Roughening
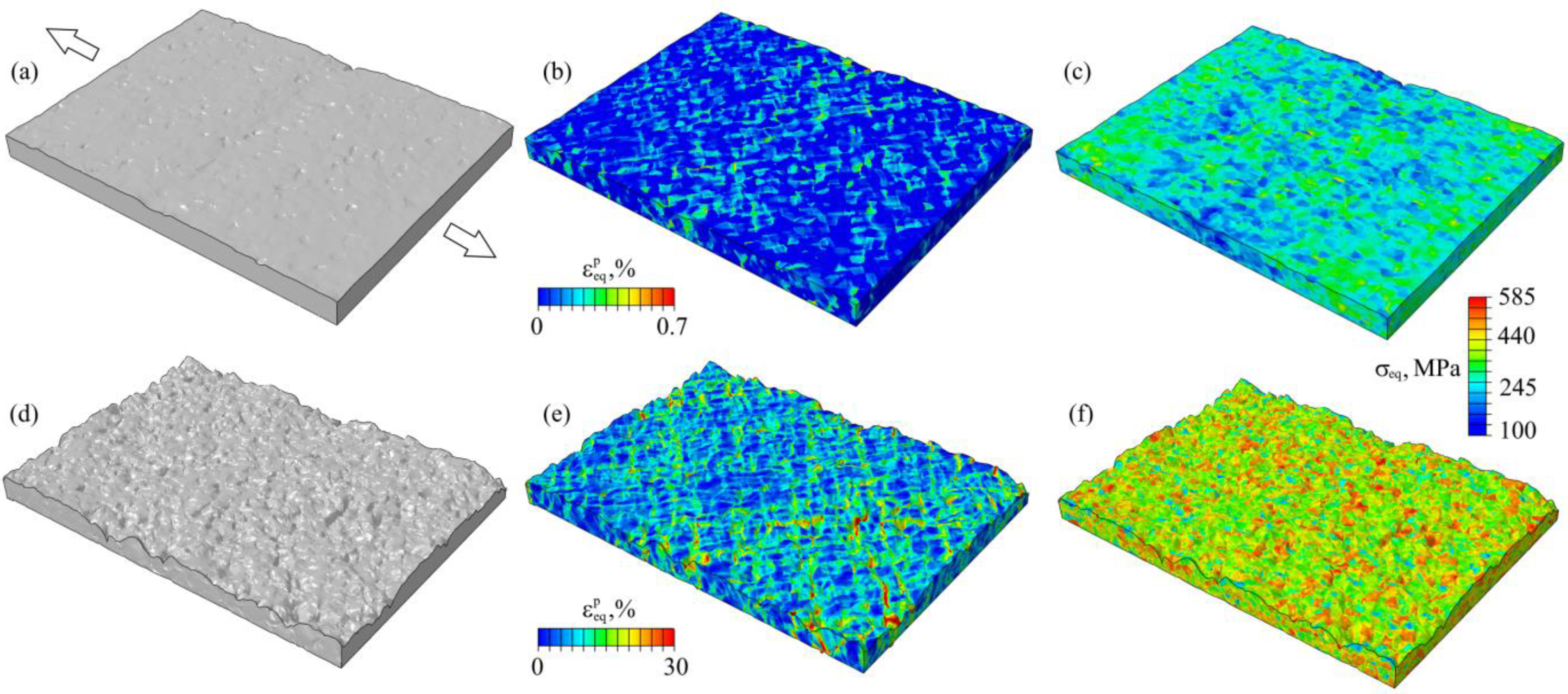
5.4. Numerical Stress-Strain Fields and Roughness Patterns
5.5. Amplitude-Frequency Analysis of Roughness Profiles
6. Discussion
6.1. Stress Analysis
6.2. Relationship between Mesoscale Roughness and In-Plane Plastic Strain
7. Conclusions
- (i)
- Deformation-induced roughening is attributed to inhomogeneous stress-strain fields acting from the bulk across the surface. The surface begins to roughen well before the macroscopic yield point, when some plastically deformed grains start moving perpendicular to the surface plane to form isolated hills and dimples.
- (ii)
- Plastically deformed grains united into mesoscale clusters are capable of accommodating larger out-of-plane deformation. As deformation develops, the small grain clusters are united into larger ones to form even higher and longer ridges and valleys. Noticeably, the peaks and valleys that appeared in the profiles in the early deformation stage became higher or deeper with straining, but did not change their positions relative to each other.
- (iii)
- The FFT decomposition of the roughness profiles revealed that the contribution of low-frequency components progressively increases with the plastic strain; this suggests roughness intensification due to the formation of increasingly large mesoscale surface undulations.
- (iv)
- A strong correlation with a determination coefficient of 0.99 is revealed between the dimensionless roughness parameter Rd and the corresponding in-plane plastic strains. The standard roughness parameters Ra and RRMS correlate linearly with the in-plane strains, but only for moderate tensile deformation, which is a result of filtering out low-frequency components in the surface profiles.
- (v)
- The fractal dimension DF changes with the subsection strains in a sawtooth fashion, with an abrupt drop in the neck region. The descent portions of the DF dependences are supposedly related to the appearance of low-frequency components in the structure of the surface profiles.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strantza, M.; Van Hemelrijck, D.; Guillaume, P.; Aggelis, D.G. Acoustic Emission Monitoring of Crack Propagation in Additively Manufactured and Conventional Titanium Components. Mech. Res. Commun. 2017, 84, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.I.I.; Rashid, A.A.; Hidaka, R.; Hattori, N.; Islam, M. Fatigue Crack Analysis of Ferrite Material by Acoustic Emission Technique. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2019, 13, 5074–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatenkov, A.P.; Naydenkin, E.V.; Shanyavsky, A.A.; Mishin, I.P.; Eremin, A.V.; Bogdanov, A.A.; Panin, S.V. A Mesoscale Study of Fatigue Fracture of Near β Titanium Alloy VT22 after Radial Shear Rolling with Subsequent Aging. Phys. Mesomech. 2022, 25, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skripnyak, V.V.; Skripnyak, V.A. Mechanical Behavior of Alpha Titanium Alloys at High Strain Rates, Elevated Temperature, and under Stress Triaxiality. Metals 2022, 12, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trusov, P.V.; Shveykin, A.I.; Kondratyev, N.S.; Yants, A.Y. Multilevel Models in Physical Mesomechanics of Metals and Alloys: Results and Prospects. Phys. Mesomech. 2021, 24, 391–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Kalidindi, S.; Necker, C.; Salem, A. Prediction of Crystallographic Texture Evolution and Anisotropic Stress–Strain Curves during Large Plastic Strains in High Purity α-Titanium Using a Taylor-Type Crystal Plasticity Model. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vraneš, M.; Cvjetićanin, N.; Papović, S.; Pavlović, M.; Szilágyi, I.; Gadžurić, S. Electrochemical Study of Anatase TiO2 Nanotube Array Electrode in Electrolyte Based on 1,3-Diethylimidazolium Bis(Trifluoromethylsulfonyl)Imide Ionic Liquid. Ionics 2019, 25, 5501–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri Delouei, A.; Emamian, A.; Karimnejad, S.; Li, Y. An Exact Analytical Solution for Heat Conduction in a Functionally Graded Conical Shell. J. Appl. Comput. Mech. 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolubaev, E.A.; Rubtsov, V.E.; Chumaevsky, A.V.; Astafurova, E.G. Micro-, Meso- and Macrostructural Design of Bulk Metallic and Polymetallic Materials by Wire-Feed Electron-Beam Additive Manufacturing. Phys. Mesomech. 2022, 25, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, A.; Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Karamian, E.; Kasiri-Asgarani, M.; Ghomi, H.; Omidi, M.; Abazari, S.; Ismail, A.F.; Sharif, S.; Berto, F. Synthesis and Characterization of Hot Extruded Magnesium-Zinc Nano-Composites Containing Low Content of Graphene Oxide for Implant Applications. Phys. Mesomech. 2021, 24, 486–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, Y.; Mitsuhara, M.; Mayama, T.; Deguchi, M. Formation Mechanism of High-Strain Bands in Commercially Pure Titanium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 867, 144670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fu, M. Inhomogeneous Deformation-Induced Surface Roughening Defects. In Deformation-Based Processing of Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 225–256. ISBN 978-0-12-814381-0. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, V.L. Coefficients of Restitution in Normal Adhesive Impact between Smooth and Rough Elastic Bodies. Rep. Mech. Eng. 2020, 1, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghbouj, N.; Sen, H.S.; Callisti, M.; Vronka, M.; Karlik, M.; Duchoň, J.; Čech, J.; Havránek, V.; Polcar, T. Revealing Nanoscale Strain Mechanisms in Ion-Irradiated Multilayers. Acta Materialia 2022, 229, 117807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haritos, G.K.; Hager, J.W.; Amos, A.K.; Salkind, M.J.; Wang, A.S.D. Mesomechanics: The Microstructure-Mechanics Connection. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1988, 24, 1081–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanova, V.; Balokhonov, R.; Emelianova, E.; Sinyakova, E.; Kazachenok, M. Early Prediction of Macroscale Plastic Strain Localization in Titanium from Observation of Mesoscale Surface Roughening. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 161–162, 105047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhao, J.; Du, W.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, Z. Quantification of Texture-Induced Ridging in Ferritic Stainless Steels 430 and 430LR during Tensile Deformation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 2041–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Van Houtte, P.; Seefeldt, M. Meso-Scale Modelling on Ridging or Roping of Aluminium Alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, I.; Abe, T. Surface Roughening and Fractal Dimension during Plastic Deformation of Polycrystalline Iron. JSME Int. Journal. Ser. A Mech. Mater. Eng. 1994, 37, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kuznetsov, P.V.; Panin, V.E.; Schreiber, J. Fractal Dimension as a Characteristic of Deformation Stages of Austenite Stainless Steel under Tensile Load. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2001, 35, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-Q.; Wang, Y.-B. (Eds.) Behavior and Design of High-Strength Constructional Steel; Woodhead Publishing Series in Civil and Structural Engineering; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2021; ISBN 978-0-08-102932-9. [Google Scholar]
- Emelianova, E.; Romanova, V.; Zinovieva, O.; Pisarev, M.; Balokhonov, R. A Microstructure-Based Mechanical Model of Deformation-Induced Surface Roughening in Polycrystalline α-Titanium at the Mesoscale. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2022, 29, 7364–7374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanova, V.; Balokhonov, R. A Method of Step-by-Step Packing and Its Application in Generating 3D Microstructures of Polycrystalline and Composite Materials. Eng. Comput. 2021, 37, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diard, O.; Leclercq, S.; Rousselier, G.; Cailletaud, G. Evaluation of Finite Element Based Analysis of 3D Multicrystalline Aggregates Plasticity. Int. J. Plast. 2005, 21, 691–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roters, F.; Eisenlohr, P.; Hantcherli, L.; Tjahjanto, D.D.; Bieler, T.R.; Raabe, D. Overview of Constitutive Laws, Kinematics, Homogenization and Multiscale Methods in Crystal Plasticity Finite-Element Modeling: Theory, Experiments, Applications. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 1152–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, J.W. Bounds and Self-Consistent Estimates for Creep of Polycrystalline Materials. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1976, 348, 101–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanova, V.; Balokhonov, R.; Emelianova, E.; Zinovieva, O.; Zinoviev, A. Microstructure-based simulations of quasistatic deformation using an explicit dynamic approach. Facta Univ. Ser. Mech. Eng. 2019, 17, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emelianova, E.S.; Romanova, V.A.; Balokhonov, R.R.; Pisarev, M.; Zinovieva, O.S. A Numerical Study of the Contribution of Different Slip Systems to the Deformation Response of Polycrystalline Titanium. Phys. Mesomech. 2021, 24, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, H.E. Long-Term Storage Capacity of Reservoirs. T. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1951, 116, 770–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B.; Wallis, J.R. Robustness of the Rescaled Range R/S in the Measurement of Noncyclic Long Run Statistical Dependence. Water Resour. Res. 1969, 5, 967–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, G.-C.; Lu, T.-M. Characterization of Amorphous and Crystalline Rough Surface: Principles and Application; Experimental Methods in the Physical Sciences; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-0-12-475984-8. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez Granero, M.A.; Trinidad Segovia, J.E.; García Pérez, J. Some Comments on Hurst Exponent and the Long Memory Processes on Capital Markets. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2008, 387, 5543–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos, R.F.; Largo, F.F. On The Estimation of the Hurst Exponent Using Adjusted Rescaled Range Analysis, Detrended Fluctuation Analysis and Variance Time Plot: A Case of Exponential Distribution. Imp. J. Interdiscip. Res. 2017, 3, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annis, A.A.; Lloyd, E.H. The Expected Value of the Adjusted Rescaled Hurst Range of Independent Normal Summands. Biometrika 1976, 63, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, E.E. Fractal Market Analysis: Applying Chaos Theory to Investment and Economics; Wiley Finance Editions; J. Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1994; ISBN 978-0-471-58524-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ottenklev, F.; Adell, M.; Orlov, D. Non-Monotonic Evolution of Surface Roughness in a Stainless Steel during Cold Deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 799, 140150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomin, V.M.; Golyshev, A.A.; Kosarev, V.F.; Malikov, A.G.; Orishich, A.M.; Filippov, A.A. Deposition of Cermet Coatings on the Basis of Ti, Ni, WC, AndB4C by Cold Gas Dynamic Spraying with Subsequent LaserIrradiation. Phys. Mesomech. 2020, 23, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesnikov, V.I.; Kudryakov, O.V.; Zabiyaka, I.Y.; Novikov, E.S.; Manturov, D.S. Structural Aspects of Wear Resistance of Coatings Deposited by Physical Vapor Deposition. Phys. Mesomech. 2020, 23, 570–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 21920-2:2021; Geometrical product specifications (GPS) — Surface texture: Profile — Part 2: Terms, definitions and surface texture parameters. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/72226.html (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Nečas, D.; Valtr, M.; Klapetek, P. How Levelling and Scan Line Corrections Ruin Roughness Measurement and How to Prevent It. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K. Effects of Grain-Scale Heterogeneity on Surface Roughness and Sheet Metal Necking. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2014, 83, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuñiga Tello, I.F.; Milković, M.; Domínguez Almaraz, G.M.; Gubeljak, N. Ultrasonic and Conventional Fatigue Endurance of Aeronautical Aluminum Alloy 7075-T6, with Artificial and Induced Pre-Corrosion. Metals 2020, 10, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopperstad, O.S.; Børvik, T.; Berstad, T.; Lademo, O.-G.; Benallal, A. A Numerical Study on the Influence of the Portevin–Le Chatelier Effect on Necking in an Aluminium Alloy. Modelling Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2007, 15, 747–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOST 1497:1984. Available online: https://docs.cntd.ru/document/1200004888 (accessed on 7 February 2023).












| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| GPa | 162 |
| , GPa | 92 |
| , GPa | 69 |
| , GPa | 181 |
| , GPa | 47 |
| , MPa | 60 |
| , MPa | 120 |
| , MPa | 180 |
| k, MPa | 14 |
| b | 0.06 |
| Curve y(x) | DF | Ra | RRMS | Rd | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (b) | sin(x) | 1.006 | 0.58 | 0.67 | 0.23 |
| (c) | 0.5sin(5x) | 1.36 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.94 |
| (d) | 0.5sin(10x) | 1.54 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 2.39 |
| (e) | 0.5sin(20x) | 1.7 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 5.48 |
| (f) | sin(x) + 0.5sin(5x) | 1.16 | 0.652 | 0.76 | 1.02 |
| (g) | sin(x) + 0.5sin(10x) | 1.34 | 0.632 | 0.76 | 2.44 |
| (h) | sin(x) + 0.5sin(20x) | 1.52 | 0.632 | 0.75 | 5.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romanova, V.; Emelianova, E.; Pisarev, M.; Zinovieva, O.; Balokhonov, R. Quantification of Mesoscale Deformation-Induced Surface Roughness in α-Titanium. Metals 2023, 13, 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13020440
Romanova V, Emelianova E, Pisarev M, Zinovieva O, Balokhonov R. Quantification of Mesoscale Deformation-Induced Surface Roughness in α-Titanium. Metals. 2023; 13(2):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13020440
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomanova, Varvara, Evgeniya Emelianova, Maxim Pisarev, Olga Zinovieva, and Ruslan Balokhonov. 2023. "Quantification of Mesoscale Deformation-Induced Surface Roughness in α-Titanium" Metals 13, no. 2: 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13020440
APA StyleRomanova, V., Emelianova, E., Pisarev, M., Zinovieva, O., & Balokhonov, R. (2023). Quantification of Mesoscale Deformation-Induced Surface Roughness in α-Titanium. Metals, 13(2), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13020440








