Abstract
Analytical models are of vital importance to study the dynamics of complex systems, including the heap leaching process. In this work, a methodology to study the dynamics of copper recovery in the heap leaching by means of fit of analytical models that capture the leaching dynamics product of variations of leaching agents as a function of the feeding is proposed, establishing a first mode of operation keeping the leaching agent fixed (H2SO4) and a second operation mode, where Cl− is added to accelerate the reaction kinetics of sulfide minerals (secondary sulfides). Mineral recovery was modeled for the different modes of operation, dependent on the independent variables/control parameters time, heap height, leach flow rate, and feed granulometry. The results indicate that the recovery of ore from sulfide minerals is proportional to the addition of Cl−, reaching recovery levels of approximately 60%, very close to 65% recovery in conventional oxide leaching, using only H2SO4 as leaching agent. Additionally, high copper recoveries from sulfide ores are achieved at medium Cl− concentrations, but the increase in recovery at high Cl− concentrations is marginal.
1. Introduction
There is constant growth in the copper industry; however, Flanagan [1] indicates that the estimated global copper mining production increased slightly to 21 million tons in 2021 from 20.6 million tons in 2020. A report generated by the International Copper Study Group [2], on the other hand, indicates that since 1900, the world production was less than 500 thousand tonnes copper, world copper mine production has grown by 3.1% per annum to approximately 21 million tonnes in 2021, while a report of Research & Markets [3] indicate that the mined copper production is expected to reach 29.19 megatons by 2027, whereas refined copper production is projected to reach 32.80 megatons by the end of 2027.
Chile is the world’s largest producer of copper and has the largest copper reserves. Chile’s production is expected to grow in the coming years owing to the increasing investment in new technologies [3]. Chile has a participation of 29% and 23% of the reserves of this commodity [4]. Copper oxides that are processed by hydrometallurgy are increasingly scarce in Chile, while copper sulfides are found in greater quantities [5]. On the other hand, 39.2% of fine copper production is produced through the hydrometallurgical processes, while most of the production (60.8%) is by flotation processes, processes that generate large environmental liabilities, such as tailings dams (negative externalities that have been reduced in recent years [6,7,8,9]).
It is estimated that in Chile, for each ton of copper that is produced by flotation processes, 151 tons of tailings are generated [5]. On the planet most of the copper minerals correspond to sulfides and a minor part to oxides. Pyrometallurgy treats sulphide minerals, including the flotation, smelting and electro-refining processes, and hydrometallurgy with oxidized minerals, breaking down into the leaching, solvent extraction and electro-extraction stages [10]. Both working mechanisms have proven to be profitable in the industry; however, pyrometallurgy presents the main disadvantage of making SO2 emissions into the atmosphere, generating serious environmental problems [11]. However, there is development of the concept of an electrochemical device that can reduce the emission of SO2 gas based on SO2-Despolarized Water Electrolysis forming H2 and H2SO4 as products, which can be performed in the same metallurgical process using solar energy [12] integrating the concept of green mining. This technology is considered as an alternative for the control of fugitive emission in the pyrometallurgy process, according the following reactions [13]:
Mine planning, both for open pit and underground mining, is traditionally applied in the industry using methodologies that consider a considerable amount of the information as deterministic. Most of the information used for mining calculations may or may not present variations; in the case of presenting them, its speak of uncertainty in the data generates a risk in the expected result. Considering the above, it is relevant to have tools and plans that allow generating greater economic value and that in turn are flexible in the face of changes in the different possible scenarios [14]. Some of these tools are the generation of representative phenomenological models of process dynamics, either through the generation of mathematical models such as equations systems [15] or models based on machine learning [16].
The leaching process has been studied and modeled by various authors [15], and although the effect of the dissolution of copper sulfides (chalcopyrite) [17,18,19] in chloride media, such as seawater because it is 97% more abundant than fresh water [20], has been modeled, the comparative analysis on an industrial scale of heap leaching in acid media with variations in chloride (Cl−) concentrations, has not been studied in depth. Additional leaching studies in chloride media include modeling the kinetics of chalcocite leaching in acidified cupric chloride (CuCl2) [21] or ferric chloride (FeCl3) [22] media under fully controlled pH and potential or analyses of copper speciation and activities in high chloride leaching solutions [23]. In salty solutions, the dissociation of H2SO4 is according to the following reaction [24].
Hydrogen sulfate (HSO4−) is also called bisulfate, is a salt based of sulfuric acid. In the solution is an ion and it contributes to generate Acid Chloride (HCl). That is the response to the improvement in the leaching process. The formed of HCl promotes a rapid kinetic the dissolution of the mineral according to corrosion phenomena during the anodic subprocess [25].
Through this work, a methodology for calculating the improvements in copper recovery of the heap leaching phase is shown, through variations in production modes and an analytical approach of modeling and simulation. The dynamics of the heap leaching process is evaluated through the fit of analytical models [26], which will represent the different ways of operating the leaching phase, depending on the characteristics of the mineral in feeding, while that the incorporation of uncertainty is given through the Monte Carlo simulation [27]. The first case represents the current situation (or base case), determined by the leaching of both copper oxides and sulfides with sulfuric acid (H2SO4), while the second case represent the proposed situation (changes in the operating modes of leaching process), leaching copper oxides with H2SO4, and copper sulfide minerals, adding chlorides ions (Cl−) [28]. The inclusion of uncertainty (associated with parameters of the feed mineral such as granulometry or type of mineral, or operational variables such as the type of leaching agent to be used) in operational planning optimization models of heap leaching has the potential to become an important advance in the way in which mining projects are managed, and specifically, the modes of operation of the threads of the mineral processing industry.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Heap Leaching
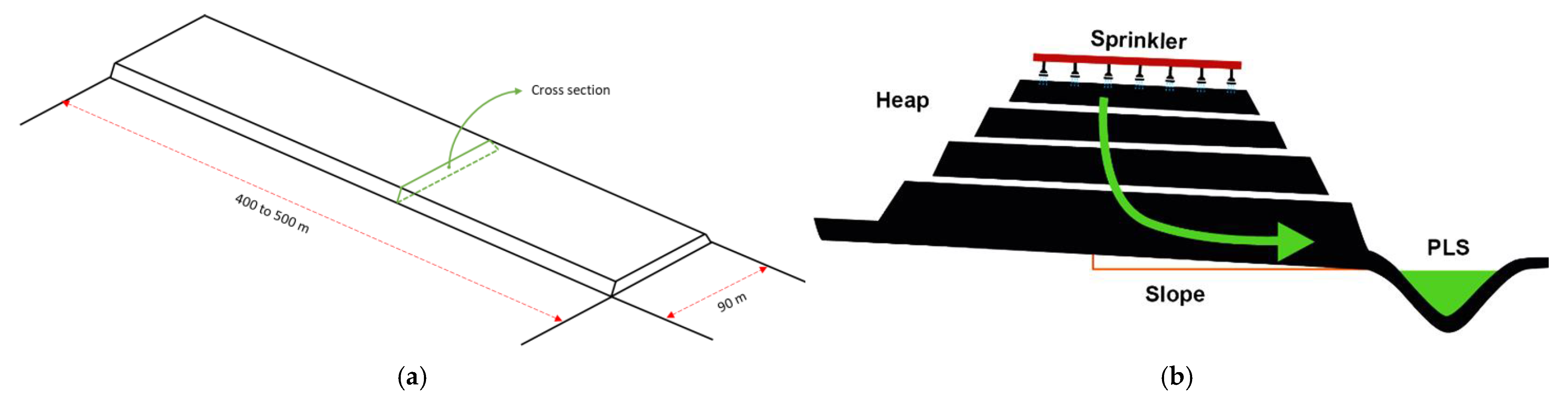
Heap leaching is a phase of mineral processing that is given by accumulations of mineralized material that is carried out mechanically, forming a kind of continuous embankment 6 to 8 m high, slightly inclined to allow drainage and collection of solutions (see Figure 1). The heaps are watered with a solution of sulfuric acid to extract the copper from the oxidized minerals. Heap leaching and landfill leaching involve dripping H2SO4 leach through large heaps or ore dumps under normal atmospheric conditions. Oxide minerals and chalcocite are easily leached [29,30], while that bornite and native copper are leached under conditions of biological oxidation. Chalcopyrite, on the other hand, is not leached significantly under ordinary heap leach conditions [31].
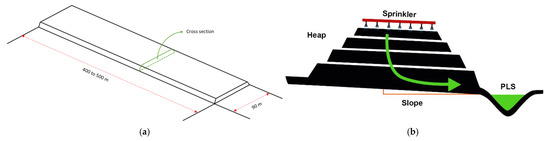
Figure 1.
Dimensions (a) and cross section (b) of a conventional leaching heap [15].
The leaching process has been studied and modeled by different authors [14,32,33,34,35,36,37,38]; however, modeling and simulation of analytical models that consider both the uncertainty in the input variables and the variation of the operating parameters of the heap have not been studied yet (as the variation in the ore fed). The present work considers the variation of the mineralogical content of feeding in the heap leaching process, and several models that involve the geological uncertainty associated with the distribution of minerals with the concentration of the pure leaching solution (PLS) are fitted [39]. The dynamics of the process is modeled through analytical models and Monte Carlo simulation, which allows the uncertainty (derived from mineral type) in the heap leaching operations to be neutralized [40]. For process modeling, it is necessary to define variables such as types of events, design of flow diagrams and events as different operational modes, considering that an operational mode represents the configuration of resources in certain scenarios. Then, to create more robust plans, it is necessary to modify the operation objectives, so that instead of maximizing the recovery of ore in an expected scenario, maximize the expected recovery resulting from the n scenarios considered [41,42], assuming that the underlying distributions of the independent variables belong to a non-deterministic environment.
In mineral processing, it is common to find processes and systems whose analysis, through mathematical methods, is extraordinarily complex or even impossible to carry out, since most of the variables are continuous. By modeling the dynamics of heap leaching, it is possible not only to obtain a better understanding of the dynamics of the process, but also to plan production based on feed by simulating the operation over a given time horizon. In the proposed approach, the modeling of the operations could be simulated for a limited number of periods in the planning time horizon, incorporating the domain of the independent variables as well as the intrinsic uncertainty of mineral feed. Geological variation can be managed by altering between modes of operation, modes that provide a comprehensive response to changes in mineralogy. Then, the decision to switch between modes of operation depends on the levels of existence based on current and predicted knowledge. An operation mode is defined as a certain configuration of the productive resources, to adapt both to the characteristics of the operative parameters and to the variation in feeding [43].
2.2. Modeling of Heap Leaching Process
As indicated in the previous section, the leaching process has been modeled in various ways by various authors, both at the particle scale and at the heap scale. At the particle level, the oxidation process, in conventional leaching, is controlled by any of the following three processes [44]:
- Process controlled by diffusion through the product layer: formation of a product layer around the material that resists diffusion of the oxidant to the surface of the material and slows down leaching.
- Chemically controlled process: the product layer is absent or its presence does not affect the free movement of the oxidant to the surface and the reaction between the surface and the reagent is much slower than the diffusion of the oxidant.
- Film Diffusion Process—Bulk leach solution resists movement of oxidant to the surface and this can slow leach kinetics.
The aforementioned model (or derived from) has been applied to model the leaching dynamics of various minerals, such as sulfides ores [45,46]. Then, at the heap level, it is also possible to find aggregate models that consider that the behavior of the heap could be modeled using a system of first-order equations, where the leaching phenomenon occurs at different size and time scales [37,38,47]. The modeling of the system of heap leaching as the solution to a system of first order equations [34,48] or through techniques such as CFD [49] is used by various authors, in addition to the application of novel paradigms such as machine learning [36].
Heap leaching is the method par excellence to extract metal from low-grade deposits, since compared to other extraction methods it provides a low capital cost, derived from the intensive use of energy, contrasting with a slow and inefficient ore recovery, in addition to marginal changes in the extraction of the valuable mineral [33,50]. Heap leaching has been modeled using different methods by various authors; however, the present investigation fits an analytical model where it is considered that ore recovery behavior is modeled by a system of first order equations [33], and proportional at different size and time scales [37,38]. Then, the aggregate mining recovery, considering the conditions of heap height, particle size and recovery in infinite time, is given by Equation (1), where the variables and/or parameters represents heap height, kinetic constant at heap height level, kinetic constant at particle level, surface velocity of leaching flow through the bed, volumetric fraction of the bulk solution in the bed, effective diffusivity within particle pores, porosity, reaction delay, and radius, respectively. In addition, is the kinetic weight factor, and , and are mathematical adjustment coefficients.
The domain of operational variables are shown in Table 1 and correspond to the domain of the process in a pilot plant of a mine in Chile’s Antofagasta region, while the parameters , , y were set in 0.03, 0.086 , 0.03 y 0 days [50], respectively.

Table 1.
Levels of the operational variables of the analytical model.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Adjustment of Analytical Models
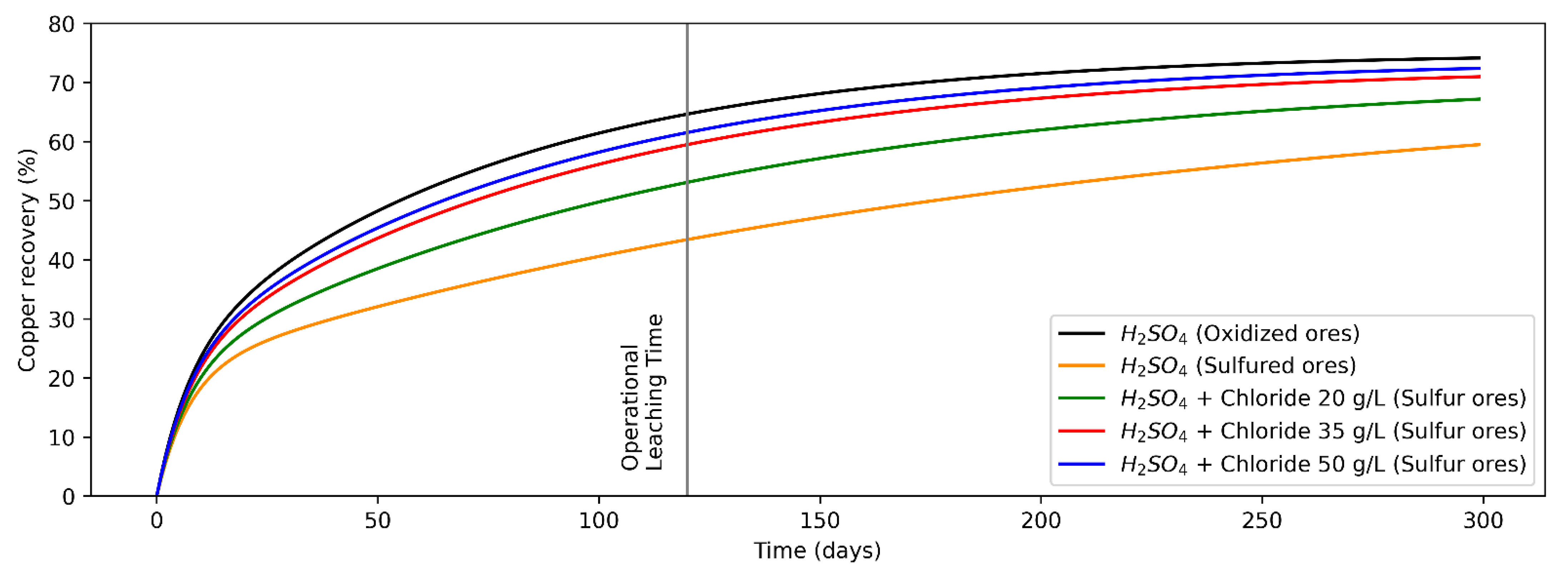
The analytical model shown in Equation (1) was fitted for copper recovery from the heap leaching process for the operational data of a copper mine site in Antofagasta region, Chile. It modeled copper recovery from oxidized and sulfide copper minerals (the adjusted equations are shown in Equations (2)–(6)), while the recovery curves versus time are shown in Figure 2. For modeling purposes, it is considered that both the leaching tests on oxidized copper minerals and copper sulfides (secondary), the presence of the other mineral (copper sulfides and oxides, respectively) are marginal.
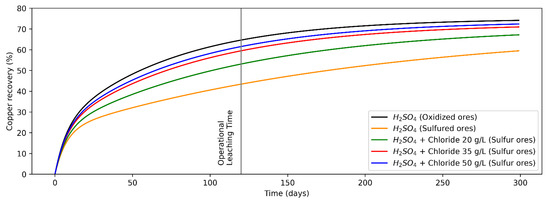
Figure 2.
Recovery from oxidized copper minerals (leaching agent: H2SO4) and sulfur copper minerals (H2SO4 + Chloride at concentrations levels of 0, 20, 35 and 50 g/L).
Considering the values of variables/parameters presented in Table 1, analytical models were fitted for recovery versus time for copper oxides (Equation (2)) and copper sulfides (Equation (3)) minerals, leaching only H2SO4, and Cl− ions addition for sulfide minerals at concentration levels of 20 g/L (Equation (4)), 35 g/L (Equation (5)) and 50 g/L (Equation (6)). In addition, its assumption that in an infinite operating time the mineral recovery is equal because chalcocite and others secondary copper sulfides are not refractory to conventional leaching processes [30,51]. Copper recovery from oxides and sulfide minerals by adding only H2SO4 is shown in Equations (2) and (3), while that copper recovery from sulfide minerals by adding H2SO4 + Cl− at concentrations of 20, 35 and 50 g/L are shown in Equations (4)–(6), respectively, where the random variables of the models are and (whose domain is indicated in Table 1), the parameters , , and were set from historical measurements and contrasted with the literature [50], and the mathematical fit parameters were calculated using least squares.
where R is defined as copper recovery depending on the variables of Table 1, excluding the parameters that represent the leaching kinetics depending on the types of minerals, variables not usually sampled in the mining operation (estimated values of operators) and Cl− ion concentrations added. Additionally, goodness-of-fit indicators of the recovery models presented in Equations (2)–(6) are shown Table 2. Error measures (MAD and MSE) indicate that all the analytical models fitted present a good fit to operational data.

Table 2.
Goodness-of-fit statistics of analytical models.
3.2. Scenarios Modeling
Considering variation in the mineral feeding and the alternatives of leaching agents, two production campaigns are defined, as Mode 1 and Mode 2.
- Mode 1: Leaching of oxidized and secondary sulfides minerals only with H2SO4 as a leaching agent. Leaching of oxides and secondary sulfides with sulfuric acid (leaching of secondary sulfides with H2SO4 slows down mineral extraction from the rock, increasing the time required until one is marginal, or a smaller proportion of the valuable mineral is recovered, if considering the constant leaching time (how it usually works under operational conditions in the mining industry) [17]. Then, Mode 1 consists of two operation strategies:
- ◦
- Strategy 1: leaching of oxidized copper mineral using only H2SO4.
- ◦
- Strategy 2: leaching of sulfide copper mineral using only H2SO4.
- Mode 2: Leaching of oxidized minerals by H2SO4 and sulfide minerals at different levels of Cl− ions concentration (20, 35 and 50 g/L). Leaching of secondary sulfides with Cl− ions accelerates copper recovery from sulfide mineral [52,53,54,55]. Different chloride addition configurations are considered in order to determine the levels that improve mineral extraction.
- ◦
- Strategy 3: leaching of oxidized minerals with H2SO4 and sulfide minerals by adding chloride at a concentration of 20 g/L.
- ◦
- Strategy 4: leaching of oxidized minerals with H2SO4 and sulfide minerals by adding chloride at a concentration of 35 g/L.
- ◦
- Strategy 5: leaching of oxidized minerals with H2SO4 and sulfide minerals by adding chloride at a concentration of 50 g/L.
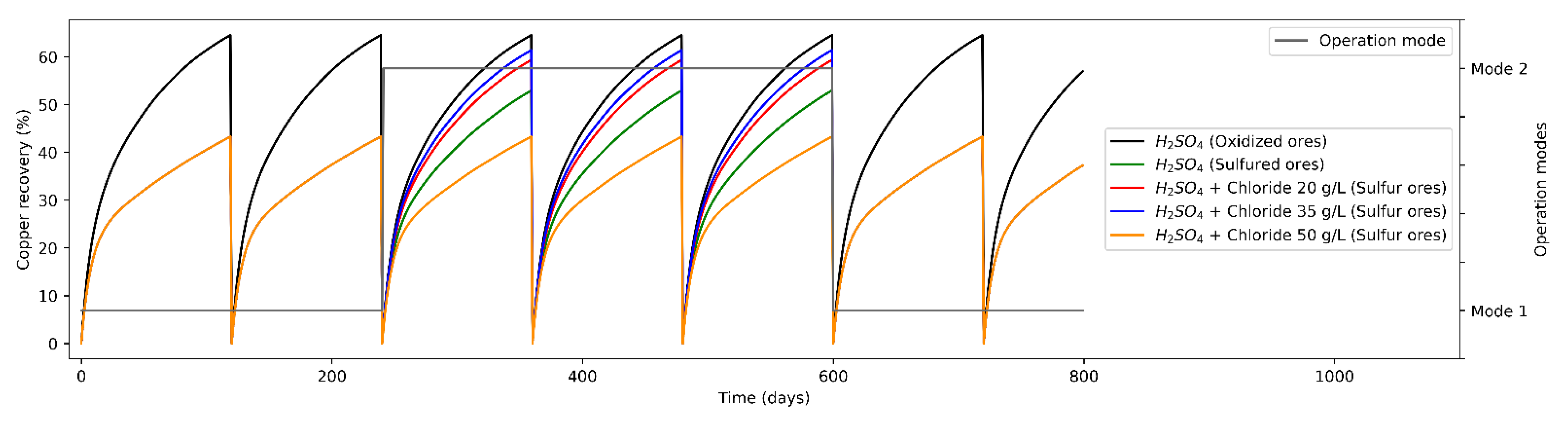
The potential impact of different production campaigns of operation modes to the heap leaching based on material feeding characteristics is to study the operation strategies showed above, strategies that maximize or improve mineral recovery. In addition, after change operation modes, adding Cl− ions, copper recovery from the sulfide minerals over time is increased, tending to obtain recovery curves like the oxidized minerals (copper recovery being proportional to Cl− ions concentration).
As a base scenario (Standard operation), the leaching phase presents two minerals with which to operate defining an only operation mode (Mode A), feeding oxides and secondary sulfides. On the other hand, a single proposal for the distribution of leaching agents is considered, leaching only with H2SO4. From Figure 3, a low expected mineral recovery is observed when leaching sulfide minerals only with H2SO4, which is due to a lower leaching kinetics, while the recovery from oxides is considerably higher (considering heaps duration times is constant in 120 days). Then, the weighted mineral recovery for both types is 64.7% in the case of oxidized minerals and 43.4% in the case of sulfide minerals. As an alternative scenario (operation mode varying leaching agents), the leaching phase presents two modes of operation: operation of oxidized minerals and sulfides minerals (secondary sulfides) at different Cl− ion concentrations. In the second operation mode, in 64% of the cases, the leaching was carried out on oxides minerals, while in 36% of the cases it was on sulfide minerals. On the other hand, the average mineral recovery for oxides minerals was 64.7%, while for operation scenarios for sulfide minerals with Cl ions added it was 53.1%, 59.5% and 60.9%, for Cl− concentrations of 20, 35 and 50 g/L, respectively.
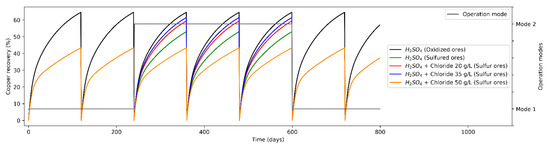
Figure 3.
Mineral recovery (%) in heap leaching (varying modes of operation).
From the contrast of the results of the different operating modes, it is possible to conclude comparing strategies 4 and 5 (considering the addition of 35 and 50 g/L, respectively), that the variation in the expected mineral recovery is marginal at constant leaching times (due to the increased opportunity costs of maintaining a heap leach longer).
3.3. Uncertainty Analysis
3.3.1. Descriptive Statistics Base Case
Regarding the simulated scenarios, a variability analysis was carried out to study the impact on production resulting from the incorporation of modes of operation, disaggregating the analyzes of the base case and the proposed alternative, respectively.
In the current scenario, the Chilean mining industry work the oxides and sulfide minerals (secondary sulfides) by leaching with sulfuric acid, which is quite efficient in leaching oxides, but has lower recoveries in the case of sulfides, which requires a longer exposure time of the leaching reagent, which translates into an increase in production costs, since the statistical analysis indicates that the copper recovery after 120 days of leaching is approximately 64.7% for oxide minerals and 43.4% from sulfide minerals, as indicated in Table 3. Then, the dispersion of recoveries distributions is relatively low, and its distributions are significantly different, validated by a test of hypothesis of comparison of means, from which it is possible to conclude that the mean of the copper recovery from oxides minerals it is significantly higher than of sulfide minerals (p value < 0.001).

Table 3.
Base case copper recovery statistics.
3.3.2. Descriptive Statistics Proposed Case
In case of the proposed scenario (statistical analysis in Table 4) an increase in production is observed in front of increases in chlorides concentration, comparing its mean values; however, the dispersion associated with the sampled distributions could indicate the lack of evidence necessary to ensure that the recovery of the proposed method is greater than the base case at high levels of addition of Cl− ions and leaching time.

Table 4.
Recovery statistics for sulfide minerals.
From the development of a hypothesis test to compare the mean recovery values, for the leaching of sulfides without adding Cl− ions, in addition to the configurations of 0, 20, 35 and 50 g/L, it can be concluded that there are significant differences between the 4 means considered in the hypothesis testing. However, when developing the hypothesis test considering only the configurations with the highest concentration (35 and 50 g/L), there is not enough evidence to ensure that the means of both scenarios differ, so it is possible to conclude that the increase in the Cl− ions concentration from 35 to 50 g/L does not necessarily increase the efficiency of copper recovery from secondary sulfides.
3.3.3. Scenarios Comparison
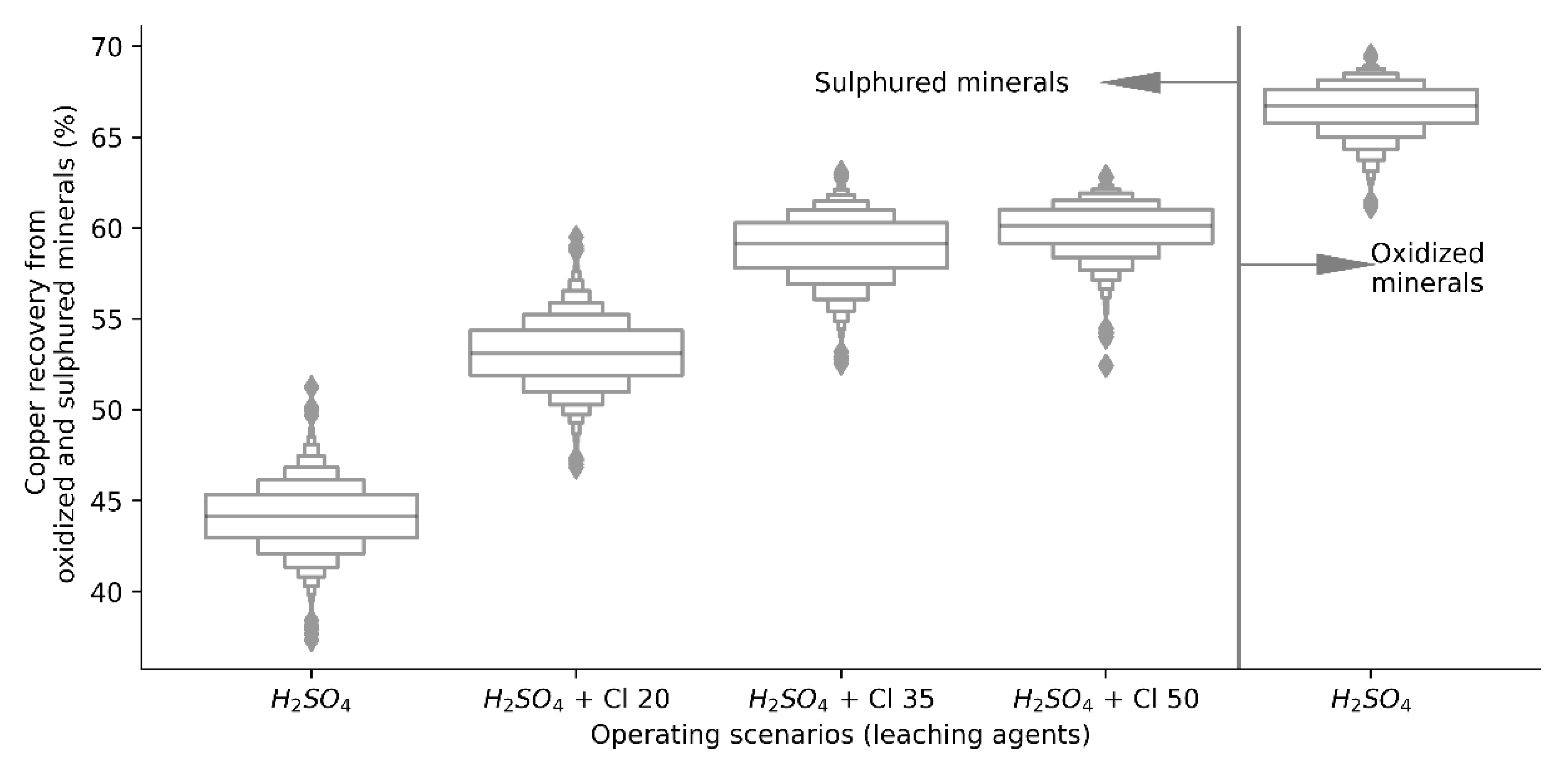
As expected, production data were generated from both scenarios, it is important to determine if the population means of both independent groups differ from each other, so the recovery of copper by leaching oxidized and sulfur minerals using H2SO4 as the only leaching agent, and the copper recovery using H2SO4 for oxidized minerals and H2SO4 + Cl− ion for copper sulfides, whose individual distributions are presented in Figure 4. Developing the t-test for two samples, the difference between the population means is greater than the hypothetical difference (µ = 0), i.e., the value of the average copper recovery considering a dynamic structure of leaching agents (H2SO4 + Cl−) is significantly higher than in the base case (H2SO4), validated by a p value less than the significance level (p < 0.001), indicating that the model is statistically significant.
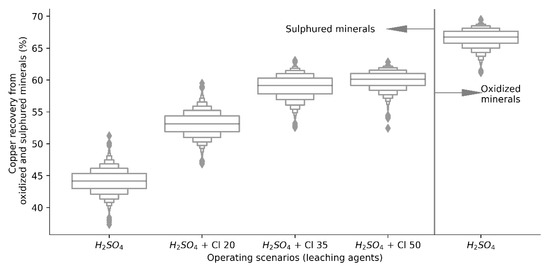
Figure 4.
Copper recovery distributions from copper oxides and sulphides.
4. Conclusions
The mineral deposits are usually heterogeneous, which requires introducing variations in the productive phase. In this research work, the dynamics of heap leaching at different levels of leaching agent concentration are analytically modeled, simplifying the feeding of oxides and sulfide minerals; however, the framework could be extended to different types of mineral originating in a variety of geological domains in a mine, provided that mineral exploitation is technically and economically feasible to develop it through the hydrometallurgical processes.
As a result of this research, the simulation of different scenarios of equal probability for each operation mode was developed, prior adjustment of analytical models of copper recovery, in order to develop a comparative analysis of the recovery before modifications in the leaching agents depending on the mineral feed. The analysis of the operational information, it was generated recovery models adjusted to the operational conditions of processing (considering as independent variables the leaching time, height of the pile, average granulometry in the feed, and velocity of the leaching flow). The incorporation of different operating modes in the processing of copper minerals has the potential of giving greater flexibility to the production process to adapt to changes in the feeding, thus improving the reaction kinetics of the minerals against different leaching agents. The use of different modes of operation has the potential to improve strategic planning of the mining plan, making flexible the value chain by making better use of resources and improving mineral recovery, regardless of the mineralogical characteristics of the mine feeding.
The adjusted models present good indicators of goodness of fit, which indicates that they are useful tools to study the dynamics of the response behavior (developing simulations) against variations in the independent variables. The hypothesis test indicates an increase in the mineral average recovery by incorporating a dynamic of operating modes depending on the mineralogy of the feeding in the heap leaching phase, increasing the expected recovery of copper sulfide ores, from approximately 43% to 60% (at medium and high Cl− levels), very close to the expected recoveries from acid leaching of oxidized minerals (approximately 65%).
Quantifying the increase in copper recovery by incorporating feeding uncertainty into the processing of both oxides and sulfide minerals together with simulation framework is an opportunity to optimize the studied process, in order to develop a strategic planning that maximizes production by searching for optimal variables/parameters that allow improving efficiency, considering those that can be monitored (porosity) and/or controlled (leaching reagents and concentrating).
From the results of the study, it can be deduced that there is the potential to improve the aggregate recovery of ore when considering a planning of changes in the modes of operation depending on the diet, that is, it is possible to improve the beneficiation through dynamic changes in the leaching agents in function of fed mineralogy. Future research lines that are being considered are modeling the leaching process through machine learning algorithms, such as artificial neural networks, decision trees or algorithms based on decision trees, or Bayesian networks. In addition to including another operational parameters or variables not considered in this study and that could have a potential impact in explaining the mineral recovery.
Author Contributions
M.S. contributed to conceptualization and writing—original draft; M.S., F.M.G.M. and N.T. contributed in investigation; E.G., P.R., S.G. and N.T. contributed with validation; and F.M.G.M. and P.R. contributed with writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
M.S. acknowledges the infrastructure and support of Doctorado en Ingeniería de Procesos de Minerales of the Universidad de Antofagasta. P.R. thanks the Pontificia Universidad Católica de Valparaíso for the support provided.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Flanagan, D.M. Copper. In Mineral Commodity Summaries 2022; U.S.G.S: Reston, VA, USA, 2022; pp. 54–55. ISBN 9780333227794. [Google Scholar]
- ICSG. The World Copper Factbook 2022; ICSG: Lisbon, Portugal, 2022.
- Research & Markets. Global Copper Market: Analysis by Mined Copper Production, by Refined Copper Production, by Consumption, by First-Use, by End-Use, by Region Size and Trends with Impact of COVID-19 and Forecast up to 2027; Daedal-Research: Delhi, India, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Consejo Minero. Cifras Actualizadas de La Minería; Consejo Minero: Santiago, Chile, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Comisión Chilena del Cobre. Sulfuros Primarios: Desafíos y Oportunidades; Comisión Chilena del Cobre: Santiago, Chile, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nuorivaara, T.; Björkqvist, A.; Bacher, J.; Serna-Guerrero, R. Environmental Remediation of Sulfidic Tailings with Froth Flotation: Reducing the Consumption of Additional Resources by Optimization of Conditioning Parameters and Water Recycling. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postila, H.; Heiderscheidt, E.; Leiviskä, T. Removal of Metals from Mine Drainage Waters by in Situ Mineral Sorbent-Based Pilot Filter Systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altinkaya, P.; Mäkinen, J.; Kinnunen, P.; Kolehmainen, E.; Haapalainen, M.; Lundström, M. Effect of Biological Pretreatment on Metal Extraction from Flotation Tailings for Chloride Leaching. Min. Eng. 2018, 129, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Espriú, A.; Wolaver, B.; Arciniega-Esparza, S.; Scanlon, B.R.; Young, M.H.; Nicot, J.P.; Macías-Medrano, S.; Breña-Naranjo, J.A. A Screening Approach to Improve Water Management Practices in Undeveloped Shale Plays, with Application to the Transboundary Eagle Ford Formation in Northeast Mexico. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toro, N.; Pérez, K.; Saldaña, M.; Jeldres, R.I.; Jeldres, M.; Cánovas, M. Dissolution of Pure Chalcopyrite with Manganese Nodules and Waste Water. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, B.S.; Banda-Noriega, R.B.; Guerrero, E.M. Industrias de Fundición: Aspectos Ambientales e Indicadores de Condición Ambiental. Rev. Metal. 2013, 49, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumpston, J.; Herding, R.; Lechtenberg, F.; Offermanns, C.; Thebelt, A.; Roh, K. Design of 24/7 Continuous Hydrogen Production System Employing the Solar-Powered Thermochemical S–I Cycle. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 24383–24396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorensek, M.B.; Staser, J.A.; Stanford, T.G.; Weidner, J.W. A Thermodynamic Analysis of the SO2/H2SO4 System in SO2-Depolarized Electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 6089–6095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldaña, M.; Toro, N.; Castillo, J.; Hernández, P.; Navarra, A. Optimization of the Heap Leaching Process through Changes in Modes of Operation and Discrete Event Simulation. Minerals 2019, 9, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldaña, M.; Gálvez, E.; Robles, P.; Castillo, J.; Toro, N. Copper Mineral Leaching Mathematical Models—A Review. Materials 2022, 15, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldaña, M.; Neira, P.; Gallegos, S.; Salinas-Rodríguez, E.; Pérez-Rey, I.; Toro, N. Mineral Leaching Modeling Through Machine Learning Algorithms—A Review. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yévenes, L.V.; Miki, H.; Nicol, M. The Dissolution of Chalcopyrite in Chloride Solutions: Part 2: Effect of Various Parameters on the Rate. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 103, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez-Yévenes, L.; Nicol, M.; Miki, H. The Dissolution of Chalcopyrite in Chloride Solutions Part 1. The Effect of Solution Potential. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 103, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, M.; Miki, H.; Velásquez-Yévenes, L. The Dissolution of Chalcopyrite in Chloride Solutions Part 3. Mechanisms. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 103, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galleguillos, F.; Cáceres, L.; Maxwell, L.; Soliz, Á. Electrochemical Ion Pumping Device for Blue Energy Recovery: Mixing Entropy Battery. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemzadeh, M.; Dixon, D.G.; Liu, W. Modelling the Kinetics of Chalcocite Leaching in Acidified Cupric Chloride Media under Fully Controlled PH and Potential. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 189, 105114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemzadeh, M.; Dixon, D.G.; Liu, W. Modelling the Kinetics of Chalcocite Leaching in Acidified Ferric Chloride Media under Fully Controlled PH and Potential. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 186, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemzadeh, M.; Liu, W. Analysis of Iron and Copper Speciation and Activities in Chloride Leaching Solutions of High Ionic Strength. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 192, 105262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horányi, G. Investigation of the Specific Adsorption of HSO4−(SO42−) and Cl− Ions on Co and Fe by Radiotracer Technique in the Course of Corrosion of the Metals in Perchlorate Media. Corros. Sci 2004, 46, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, C.M.; Ghorbani, Y.; Hernández, P.C.; Justel, F.J.; Aravena, M.I.; Herreros, O.O. Cupric and Chloride Ions: Leaching of Chalcopyrite Concentrate with Low Chloride Concentration Media. Minerals 2019, 9, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.K.; Kang, D. Modeling and Simulation of Discrete-Event Systems; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781118386996. [Google Scholar]
- Mery, N.; Emery, X.; Cáceres, A.; Ribeiro, D.; Cunha, E. Geostatistical Modeling of the Geological Uncertainty in an Iron Ore Deposit. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 88, 336–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, N.; Moraga, C.; Torres, D.; Saldaña, M.; Pérez, K.; Gálvez, E. Leaching Chalcocite in Chloride Media—A Review. Minerals 2021, 11, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Peng, Y. The Oxidation of Copper Sulfide Minerals during Grinding and Their Interactions with Clay Particles. Powder Technol. 2012, 230, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, K.; Toro, N.; Saldaña, M.; Salinas-Rodríguez, E.; Robles, P.; Torres, D.; Jeldres, R.I. Statistical Study for Leaching of Covellite in a Chloride Media. Metals 2020, 10, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, M.; King, M.; Sole, K.; Davenport, W. Extractive Metallurgy of Copper, 5th ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; ISBN 9780080967899. [Google Scholar]
- Miki, H.; Nicol, M.; Velásquez-Yévenes, L. The Kinetics of Dissolution of Synthetic Covellite, Chalcocite and Digenite in Dilute Chloride Solutions at Ambient Temperatures. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 105, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellado, M.E.; Cisternas, L.A.; Gálvez, E.D. An Analytical Model Approach to Heap Leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 95, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellado, M.E.; Gálvez, E.D.; Cisternas, L.A. Stochastic Analysis of Heap Leaching Process via Analytical Models. Min. Eng. 2012, 33, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghobi Moghaddam, M.; Shafaei Tonkaboni, S.Z.; Noaparast, M.; Doulati Ardejani, F. A Mathematical Model to Simulate Heap (Bio)-Leaching Process: An Exact Conceptual Model, Homotopy Theory and Comparative Insights with Conventional Methods. Int. J. Model. Simul. Sci. Comput. 2017, 8, 1750018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldaña, M.; González, J.; Jeldres, R.; Villegas, Á.; Castillo, J.; Quezada, G.; Toro, N. A Stochastic Model Approach for Copper Heap Leaching through Bayesian Networks. Metals 2019, 9, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, D.G.; Hendrix, J.L. A Mathematical Model for Heap Leaching of One or More Solid Reactants from Porous Ore Pellets. Metall. Trans. B 1993, 24, 1087–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, D.G.; Hendrix, J.L. A General Model for Leaching of One or More Solid Reactants from Porous Ore Particles. Metall. Trans. B 1993, 24, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy, N.; Boucher, A.; Wu, J. Applied Geostatistics with SGeMS: A User’s Guide; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; Volume 9780521514, ISBN 9781139150019. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, S.P.; Askari-Nasab, H. Simulation and Optimization Approach for Uncertainty-Based Short-Term Planning in Open Pit Mines. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2018, 28, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deck, C.; Guzmán, J.I.; Hinrichsen, C.; Lichtin, C.; Rademacher, M.; Minera, E.; Cancino, C.R.; Henríquez, J.; Jara, E.; Morales, G.; et al. Flexible Stochastic Planning: The Ultimate Frontier. In Proceedings of the GeoMin Mine Planning 2013, Santiago, Chile, 24–26 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrakopoulos, R.G.; Sabour, S.A.A. Evaluating Mine Plans under Uncertainty: Can the Real Options Make a Difference? Resour. Policy 2007, 32, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarra, A.; Grammatikopoulos, T.; Waters, K. Incorporation of Geometallurgical Modelling into Long-Term Production Planning. Min. Eng. 2018, 120, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenspiel, O. Chemical Reaction Engineering, 3rd ed.; Anderson, W., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999; ISBN 047125424X. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, B.W.; Wadsworth, M.E.; Groves, R.D. Application of a mixed kinetics model to the leaching of low grade copper sulfide ores. Trans. Soc. Min. Eng. AIME 1975, 258, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, R.L.; Lewis, A.E.; Wadsworth, M.E. In-Place Leaching Of Primary Sulfide Ores: Laboratory Leaching Data and Kinetics Model. Met. Trans. 1974, 5, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, D.G.; Hendrix, J.L. Theoretical Basis for Variable Order Assumption in the Kinetics of Leaching of Discrete Grains. AIChE J. 1993, 39, 904–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botz, M.; Marsden, J. Heap Leach Production Modeling: A Spreadsheet-Based Technique. Min. Met. Explor. 2019, 36, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, D.; Gebhardt, J.; Croft, N.; Cross, M. Heap Leaching: Modelling and Forecasting Using CFD Technology. Minerals 2018, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellado, M.; Cisternas, L.; Lucay, F.; Gálvez, E.; Sepúlveda, F. A Posteriori Analysis of Analytical Models for Heap Leaching Using Uncertainty and Global Sensitivity Analyses. Minerals 2018, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, N.; Briceño, W.; Pérez, K.; Cánovas, M.; Trigueros, E.; Sepúlveda, R.; Hernández, P. Leaching of Pure Chalcocite in a Chloride Media Using Sea Water and Waste Water. Metals 2019, 9, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helle, S.; Jerez, O.; Kelm, U.; Pincheira, M.; Varela, B. The Influence of Rock Characteristics on Acid Leach Extraction and Re-Extraction of Cu-Oxide and Sulfide Minerals. Min. Eng. 2010, 23, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.A.; Paul, A.J.P. Acid Leaching Behavior of Sulfide and Oxide Minerals Determined by Electrochemical Polarization Measurements. Min. Eng. 1995, 8, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Lawson, F. The Kinetics of Leaching Chalcocite in Acidic Oxygenated Sulphate-Chloride Solutions. Hydrometallurgy 1991, 27, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.C.; Honores, S.; Padilla, R. Leaching Kinetics of Digenite Concentrate in Oxygenated Chloride Media at Ambient Pressure. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 1998, 29, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).