Improved Combustion Performance of Fluororubber-Coated Micro-Nano Composite Aluminum Powder
Abstract
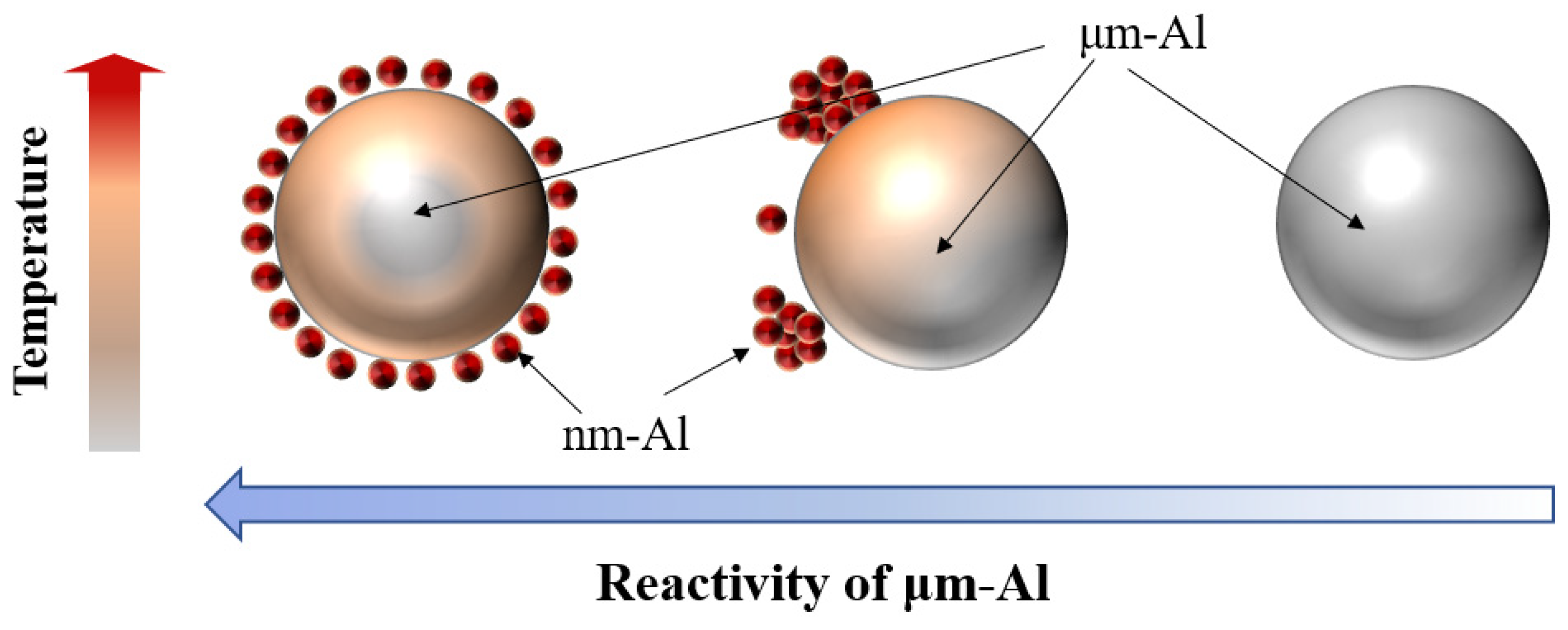
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Instruments
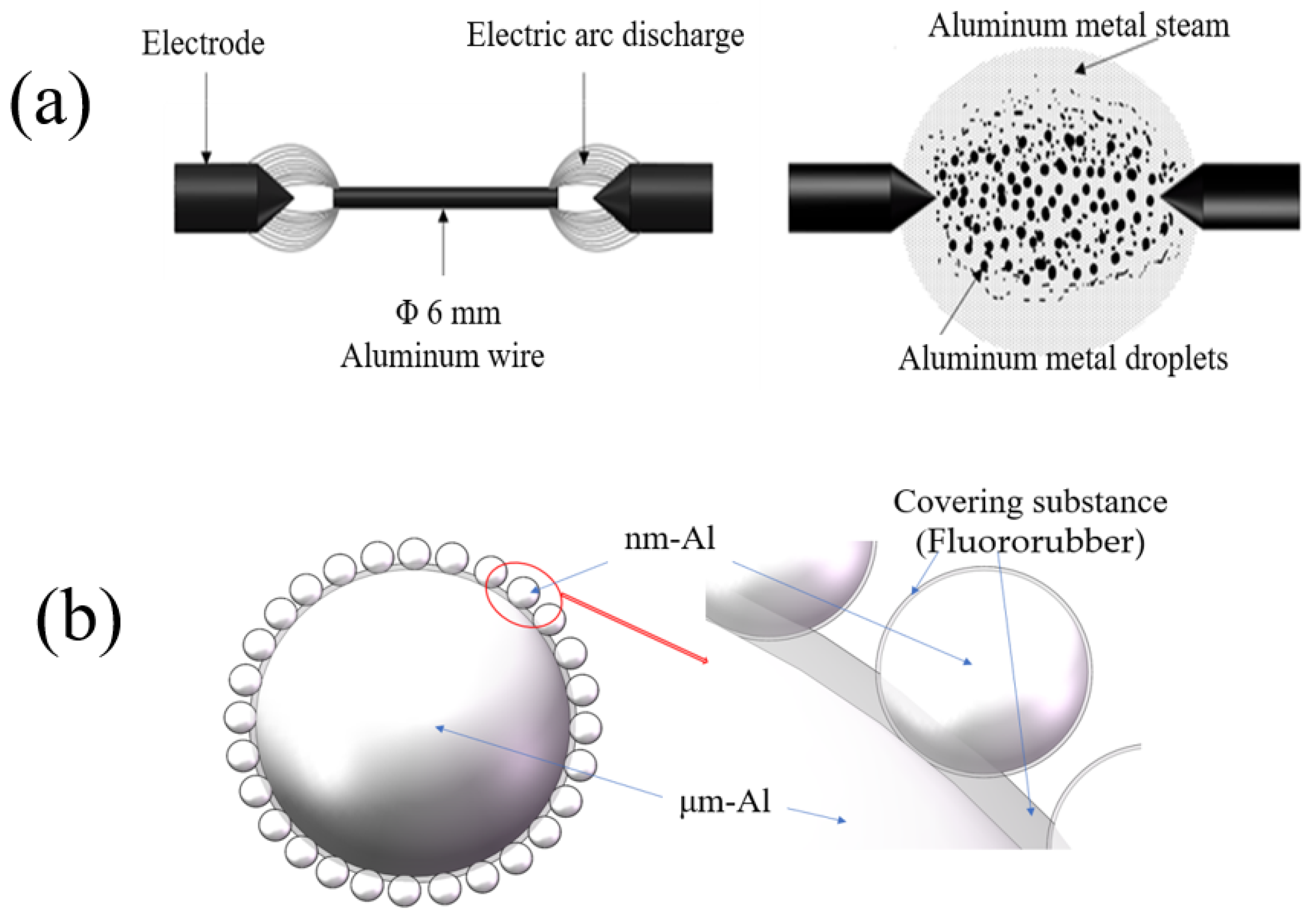
2.2. Sample Preparation
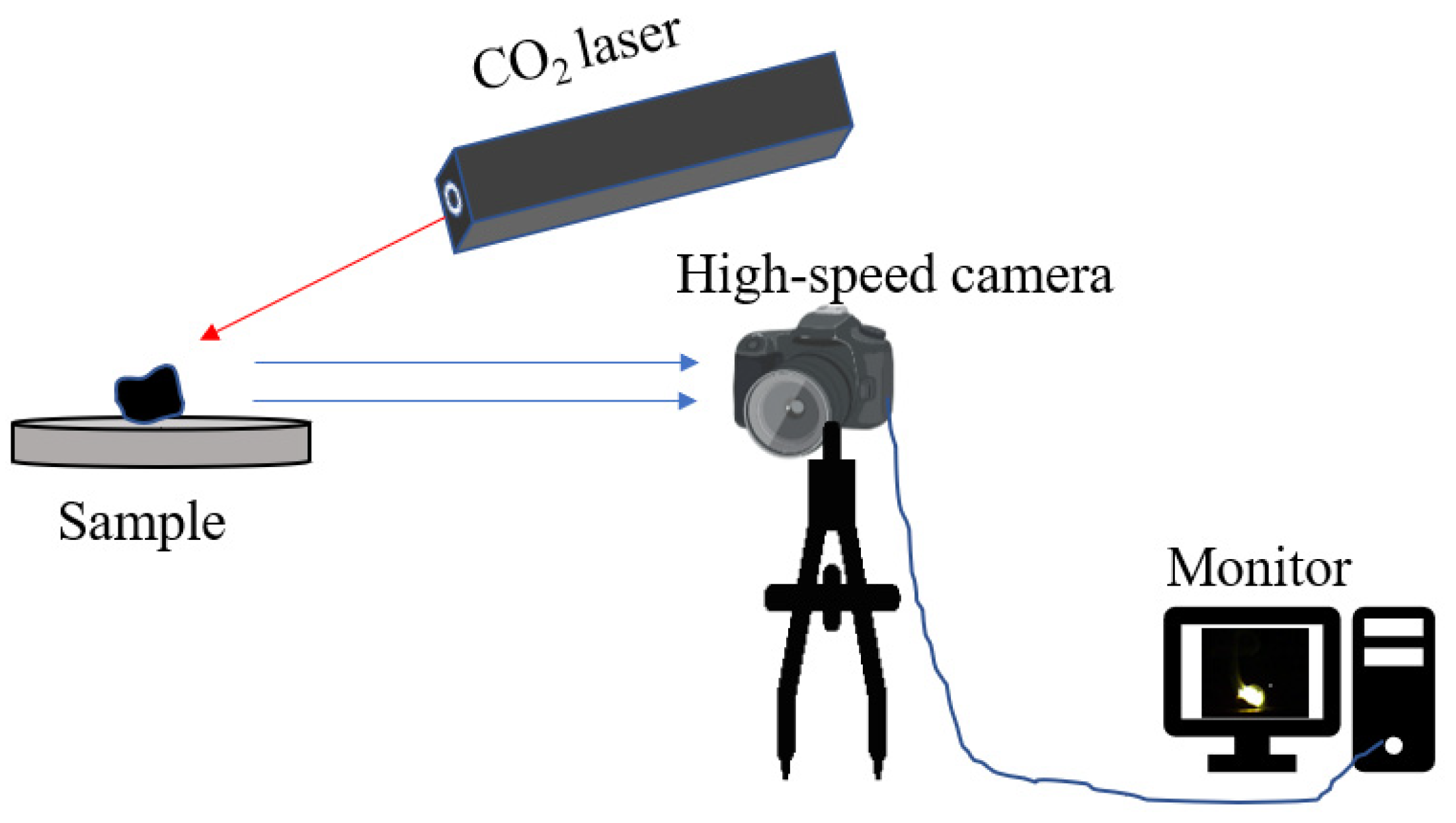
2.3. Experimental Method
3. Results and Discussion
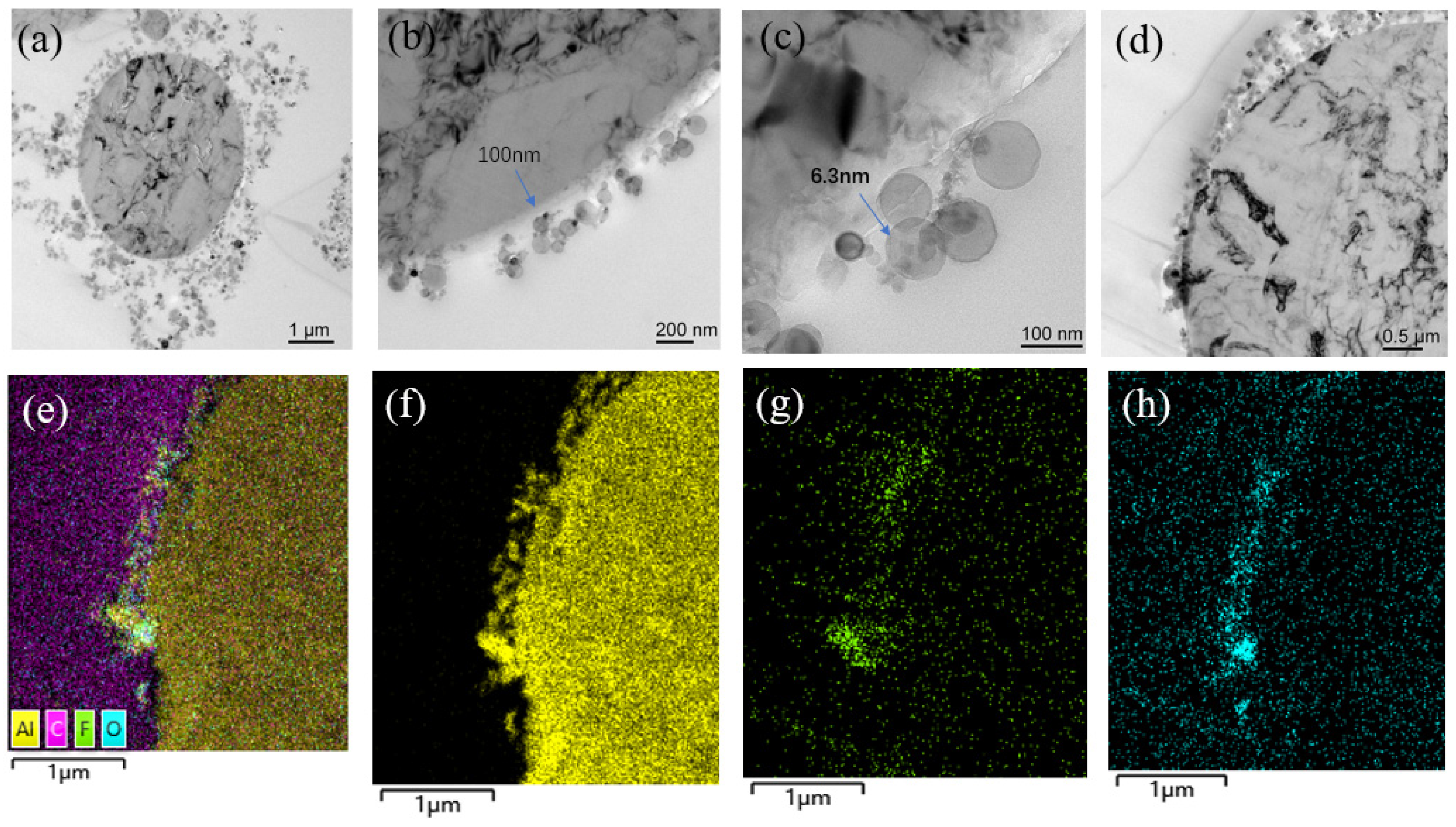
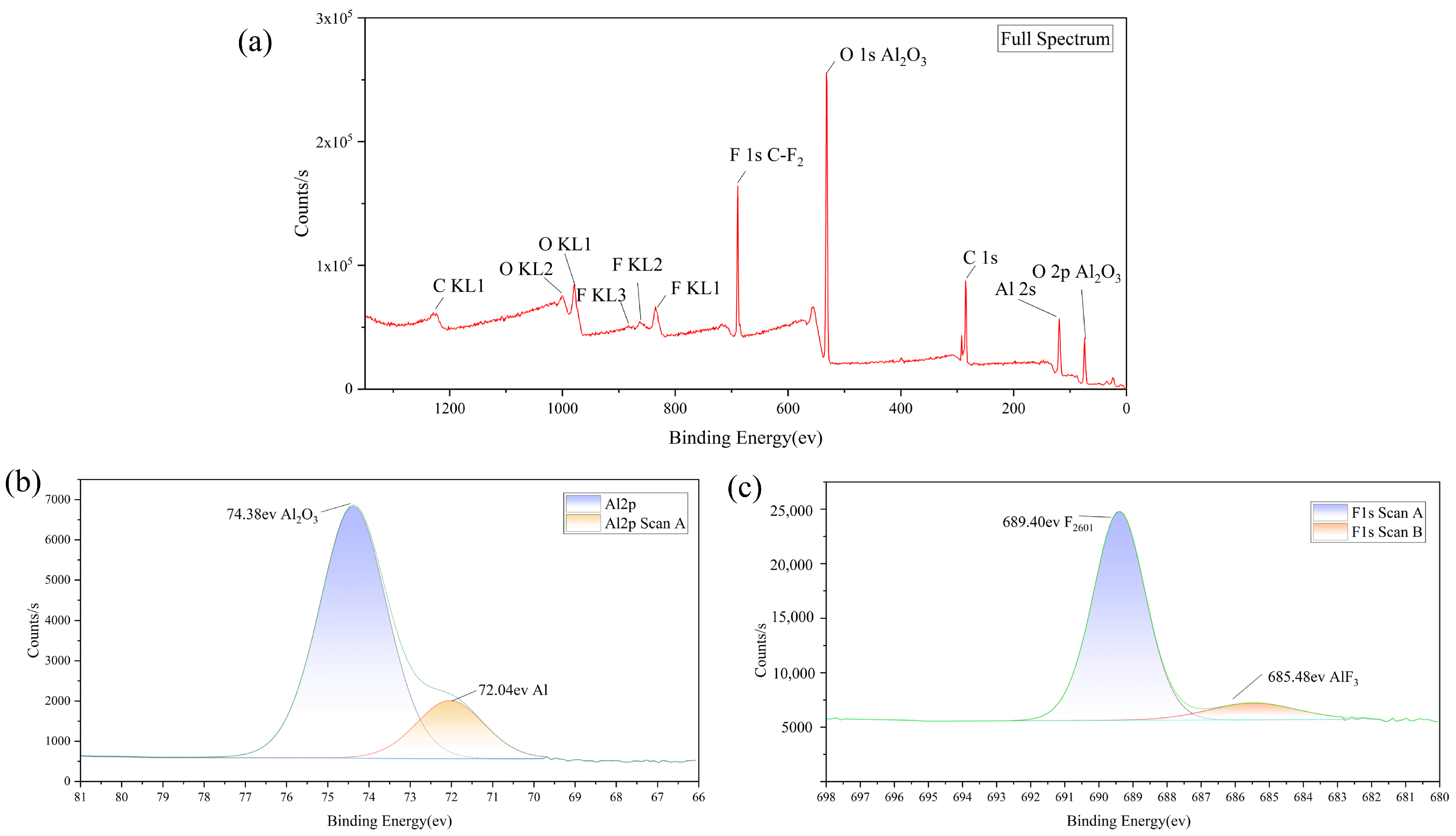
3.1. Micro-Nano Composite Aluminum Powder Morphology Structure
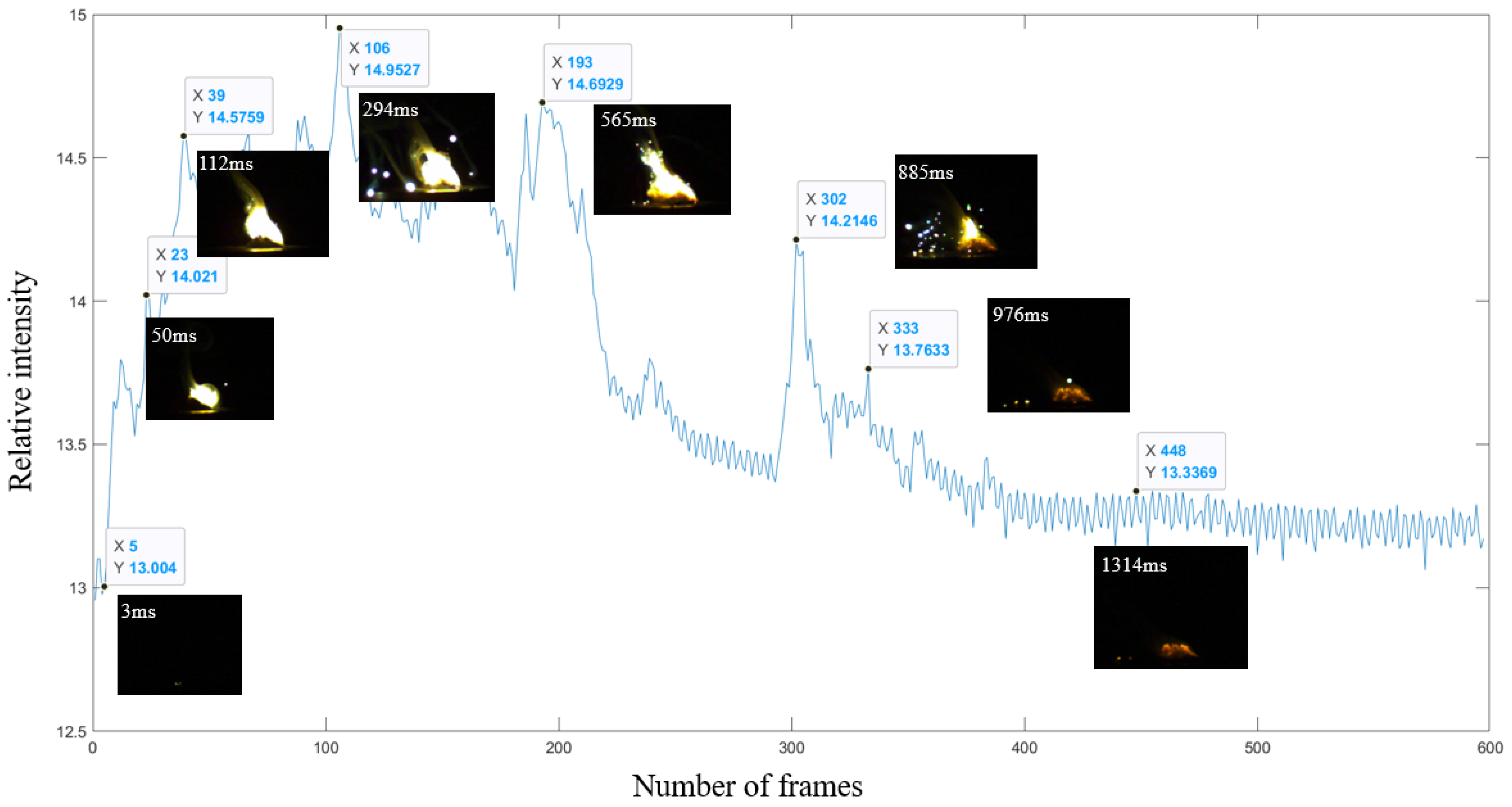
3.2. Combustion and Ignition Performance
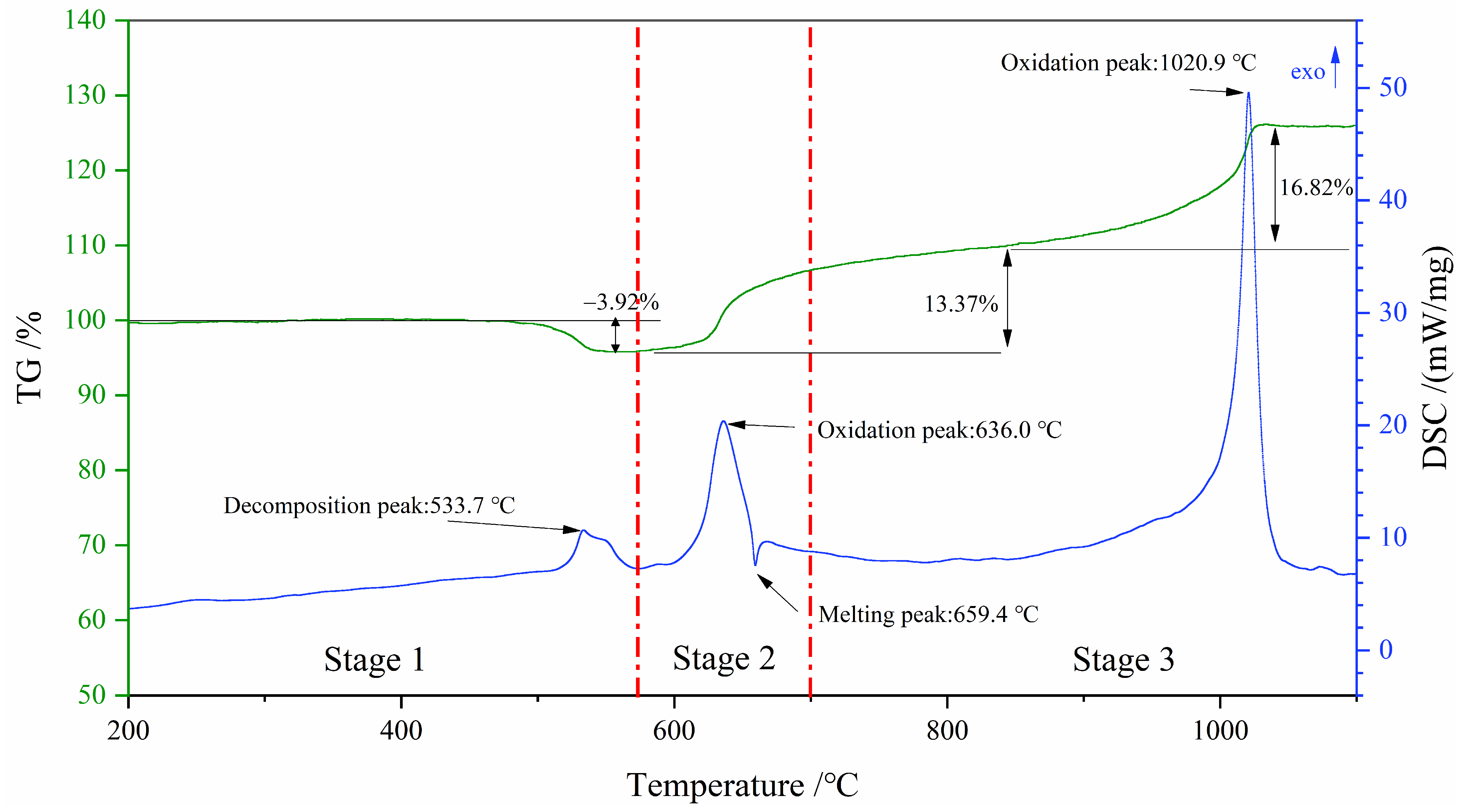
3.3. Decomposition History
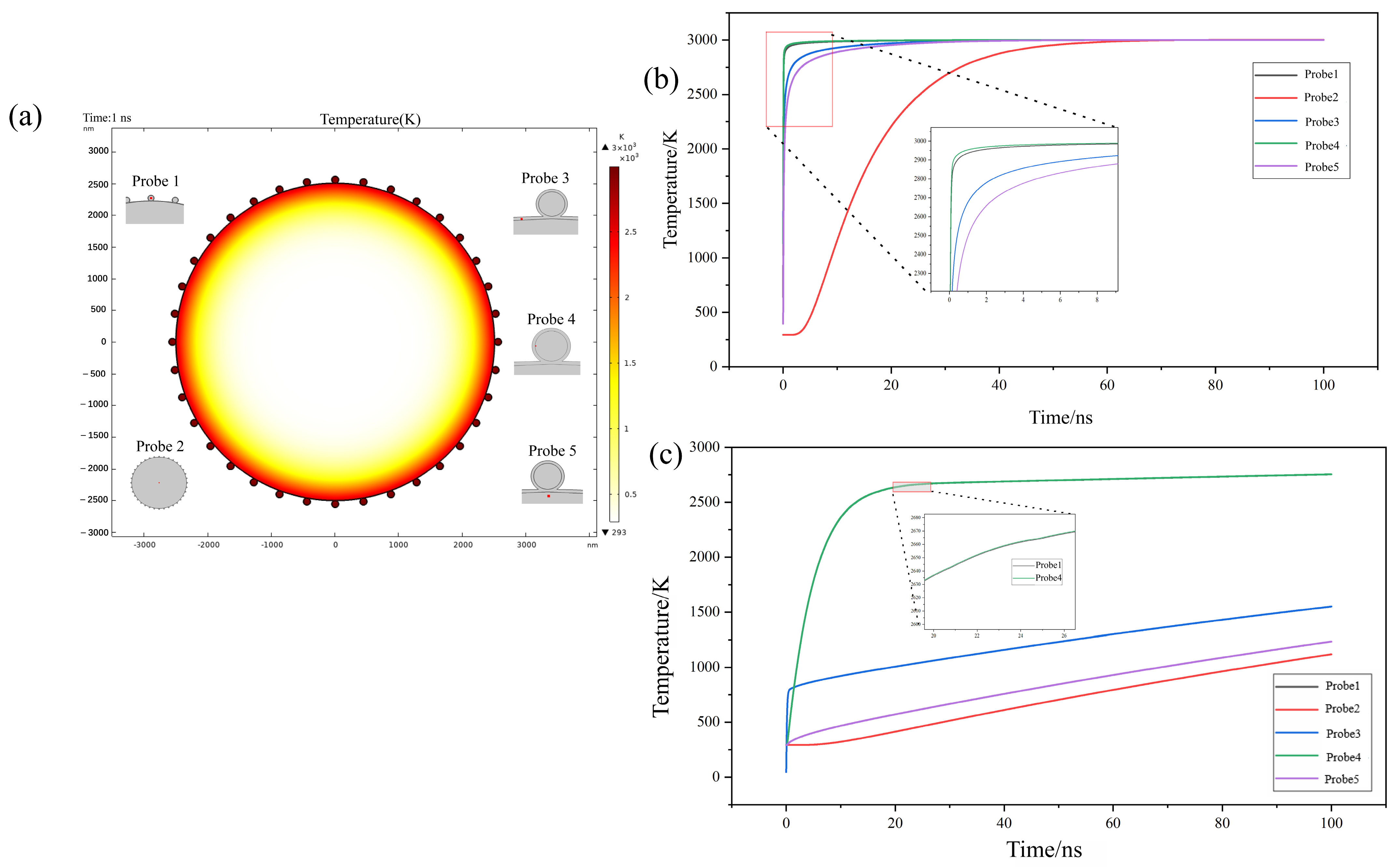
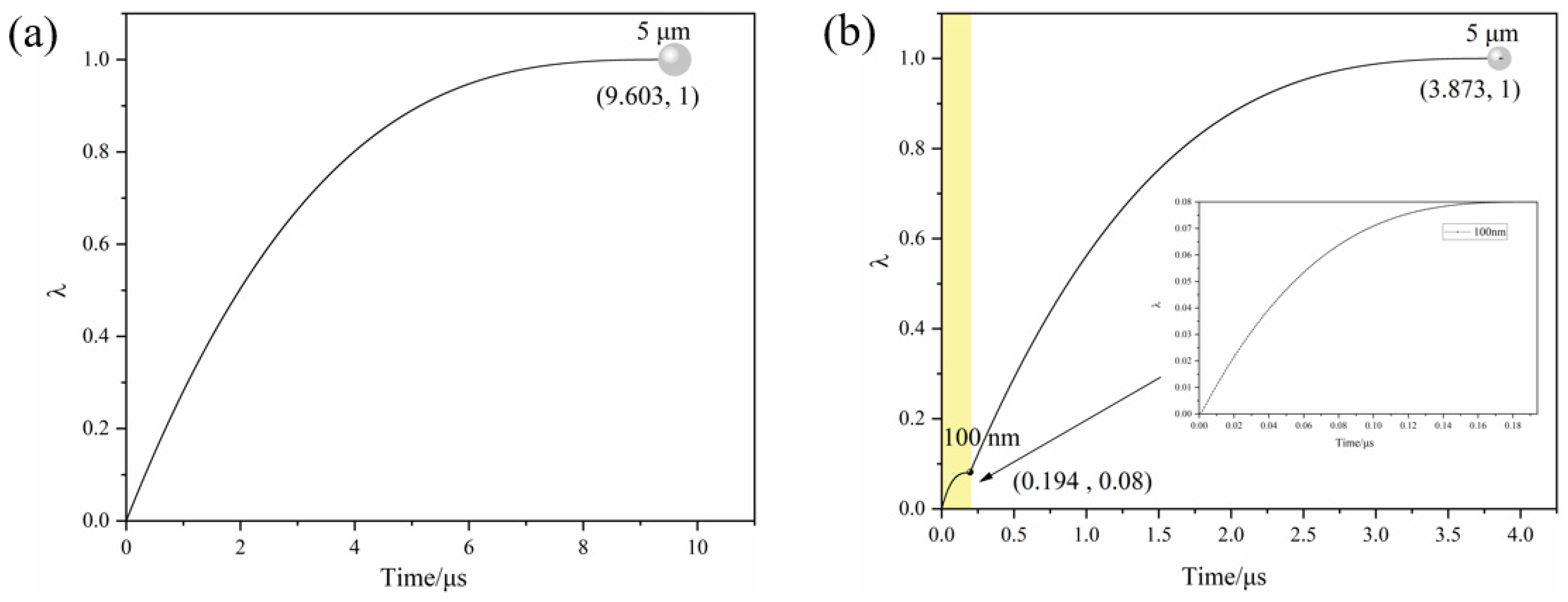
3.4. Temperature Rise Simulation and Reaction History of Micro-Nano Composite Aluminum Powder
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, H.Q.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, J.L.; Wang, G.Z.; Yang, Q.S. The Influence of Aluminum Powder on Explosive Performance. Energetic Mater. 2004, 5, 318–320+256. [Google Scholar]
- Makhov, M.N. Acceleration Ability of Aluminum-Containing Explosive Compositions. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 12, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermolaev, B.S.; Khasainov, B.A.; Baudin, G.; Presles, A.N. Behavior of aluminum in detonation of high explosives. Surprises and interpretations. Chem. Phys. Rep. 2000, 18, 1121–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Wang, W.L.; Wang, X.F.; Zhou, Q.; Miao, R.; Du, M.H.; Tan, B.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, T.Y.; Li, Y.F.; et al. Effects of Nano Aluminum Powder on the Mechanical Sensitivity of RDX-Based Explosives. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Y.; Wang, X.F.; Niu, Y.L.; Xiao, Q.; Li, X. Reaction rate of Al powder in different explosion atmosphere. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2020, 20, 2700–2704. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, S.Q.; Xu, G.G.; Wang, T.Z. Mechanism analysis of the influence of Al shape and size on the detonation properties of aluminized explosives. Chin. J. Explos. Propellants 2002, 25, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.J.; Huang, Y.F.; Xu, H.T. The influence of Al on the detonation parameters of Aluminized explosives. Initiat. Pyrotech. 2012, 1, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.S.; Feng, X.J.; Zhao, J.; Tian, X. Effect of content and particle size of aluminum powder on the air blast property of HMX-based explosive. Explos. Mater. 2018, 47, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaram, D.S.; Puri, P.; Yang, V. A general theory of ignition and combustion of nano- and micron-sized aluminum particles. Combust. Flame 2016, 169, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, D.S.; Yang, V.; Zarko, V.E. Combustion of nano aluminum particles (Review). Combust. Explos. Shock Waves 2015, 51, 173–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storozhev, V.B.; Yermakov, A.N. Combustion of nano-sized aluminum particles in steam: Numerical modeling. Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 4129–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.T.; Cao, S.T.; Niu, L.; Jin, D.Y.; Yao, L.N. Dispersibility and formability of explosives with nano-aluminum. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2021, 21, 8018–8022. [Google Scholar]
- Woody, D.L.; Dokhan, A.; Johnson, C.E. Performance comparisons of nanoaluminum, coated microaluminum and their bimodal mixtures. In Proceedings of the 13th Conference of the American-Physical-Society-Topical-Group on Shock Compression of Condensed Matter, Portland, OR, USA, 20–25 July 2003; pp. 906–909. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.; Wang, X.F.; Huang, Y.F.; Feng, B.; Tian, X.; Niu, Y.L.; Zhang, K. Effect of particle gradation of aluminum on the explosion field pressure and temperature of RDX-based explosives in vacuum and air atmosphere. Def. Technol. 2019, 15, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.; Pantoya, M.L.; Son, S.F. Combustion behaviors resulting from bimodal aluminum size distributions in thermites. J. Propuls. Power 2007, 23, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollum, J.M.; Pantoya, M.L.; Iacono, S.T. Activating Aluminum Reactivity with Fluoropolymer Coatings for Improved Energetic Composite Combustion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18742–18749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Kim, K.T.; Min, T.S.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, S.H. Improved Energetic-Behaviors of Spontaneously Surface-Mediated Al Particles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sippel, T.R.; Son, S.F.; Groven, L.J. Aluminum agglomeration reduction in a composite propellant using tailored Al/PTFE particles. Combust. Flame 2014, 161, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, T.K.; Sarathi, R.; Chakravarthy, S.R. Understanding nanoparticle formation by a wire explosion process through experimental and modelling studies. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 025703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelmani; Rengaswamy, J.; Raghuraman, C.S.; Hisayuki, S.; Ramanujam, S. Enhancement of hydrogen generation using nanoaluminum particles produced by a wire explosion process. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2019, 14, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarenko, O.B.; Amelkovich, Y.A.; Sechin, A.I. Characterization of aluminum nanopowders after long-term storage. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 321, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, M.I.; Glazkova, E.A.; Lozhkomoev, A.S.; Svarovskaya, N.V.; Bakina, O.V.; Pervikov, A.V.; Psakhie, S.G. Synthesis of Al nanoparticles and Al/AlN composite nanoparticles by electrical explosion of aluminum wires in argon and nitrogen. Powder Technol. 2016, 295, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissinger, H.E. Reaction Kinetics in Differential Thermal Analysis. Anal. Chem. 1957, 29, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, T. Kinetic analysis of derivative curves in thermal analysis. J. Therm. Anal. 1970, 2, 301–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, T. A New Method of Analyzing Thermogravimetric Data. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1965, 38, 1881–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Yang, H.T.; Cheng, L.; Gao, P.; Li, Y.C.; Song, D.M. Ignition and Combustion Characteristics of B/NC/CuO Thermite Microparticles. Metals 2022, 12, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Huang, Y.J.; Chang, K.H.; Nie, J.X.; Guo, X.Y.; Shen, C.; Yan, S. Preparation and Energy Release Properties of nB@F2603@CL-20 Microspheres by Electrospray. Metals 2022, 12, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.J.; Zhu, L.; Jin, S.H.; Lu, J.J.; Liu, X.Y. Laser-Ignited Self-Propagating Sintering of AlCrFeNiSi High-Entropy Alloys: An Improved Technique for Preparing High-Entropy Alloys. Metals 2019, 9, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riello, D.; Zetterstrom, C.; Parr, C.; Braulio, M.A.L.; Moreira, M.; Gallo, J.B.; Pandolfelli, V.C. AlF3 reaction mechanism and its influence on alpha-Al2O3 mineralization. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 9804–9814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.X.; Kan, R.Z.; Jiao, Q.J.; Wang, Q.S.; Guo, X.Y.; Yan, S. Studies on aluminum powder combustion in detonation environment. Chin. Phys. B 2022, 31, 044703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| The Micro-Nano Composite Aluminum Powder | Step 1 | G (a) | Step 2 | G (a) |
| Peak temperature/°C (5, 10, 15, 20 °C/min) | 610.6, 623.7, 625.7, 636.0 | a (n = 1) | 988.0, 1000.2, 1010.5, 1020.9 | a (n = 1) |
| Kissinger (kJ/mol) | 359.482 | 551.116 | ||
| Ozawa (kJ/mol) | 356.013 | 544.276 | ||
| The Micron-Sized Aluminum Powder | Step 1 | G (a) | Step 2 | G (a) |
| Peak temperature/°C (5, 10, 15, 20 °C/min) | 588.6, 606.3, 615.2, 622.6 | a 3/2 (n = 3/2) | 996.9, 1021.0, 1038.0, 1047.1 | a 3/2 (n = 3/2) |
| Kissinger (kJ/mol) | 248.129 | 357.653 | ||
| Ozawa (kJ/mol) | 249.836 | 360.572 |
| Materials | p (kg/m3) | Cp (J/(kg·K) | K (J/(kg·K)) | T1 (K) | T2 (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 2700 | 900 | 238 | 933 | 2773 |
| Alumina Fluororubber | 3900 | 857 | 27 | 2327 | 3255 |
| 1850 | 840 | 0.13 | --- | --- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Ren, H.; Jiao, Q. Improved Combustion Performance of Fluororubber-Coated Micro-Nano Composite Aluminum Powder. Metals 2023, 13, 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13030556
Wu X, Ren H, Jiao Q. Improved Combustion Performance of Fluororubber-Coated Micro-Nano Composite Aluminum Powder. Metals. 2023; 13(3):556. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13030556
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xinzhou, Hui Ren, and Qingjie Jiao. 2023. "Improved Combustion Performance of Fluororubber-Coated Micro-Nano Composite Aluminum Powder" Metals 13, no. 3: 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13030556
APA StyleWu, X., Ren, H., & Jiao, Q. (2023). Improved Combustion Performance of Fluororubber-Coated Micro-Nano Composite Aluminum Powder. Metals, 13(3), 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13030556






