Abstract
The corrosion behavior of carbon steel X36 (CSX36) in solutions of soils collected from different areas linked to the main pipe network of a water distribution system in Jeddah City (Obhour Al Shamaliyah, Ob-Sh; Al Shateie, Sh; Al Safa, Sf; Al Samer, Sa; and Al Jameaah, Ja) at an ambient temperature (23 ± 1 °C) was studied. The corrosion behavior was monitored using various techniques, such as weight loss and electrochemical (open circuit potential [OCP]; electrochemical impedance spectroscopy; and potentiodynamic polarization) measurements. Visual and microscopic examinations of the surface morphology of the studied metals were evaluated and discussed. The corrosion rates in all the studied soil solutions decreased with an increase in the immersion period over 80 weeks. The corrosivity of the studied soils based on weight loss measurements followed the order Sh > Ja > Ob-Sh > Sa > Sf. The value of the OCP gradually shifted to more negative values, indicating a higher tendency to corrode. For the soil solutions studied, the Ecorr shifted to more negative values, indicating that the corrosion process was under cathodic control. The values of icorr and 1/Rp tended to increase as the soil resistivity decreased. Moreover, there was good consistency between the corrosivity order of the studied soil solution obtained from electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and PDP measurements in the following order: Ob-Sh > Sh > Ja > Sa > Sf. A comprehensive assessment of the soil corrosivity based on various soil variables revealed that soil solutions of Ob-Sh and Sh are extremely corrosive, while the rest of the soil solutions are noncorrosive.
1. Introduction
Corrosion is one of the most severe problems affecting the residential and industrial sectors. Safety related to corrosion is a critical source of concern. Examples of how corrosion can impair safety are gas pipe explosions, poisonous substance discharge, and water contamination [1]. In large industries, pipelines are critical for distributing liquid raw and essential materials [2]. Pipelines, such as water mains, are used as a means of distribution to fulfill many needs of the industrial and residential sectors. Pipelines are buried underground, from the water source to the end location, and a few parts of the pipelines corrode in the soil surface. Soil acting as a pipeline burial medium has various environmental characteristics [3]. In this case, the soil is the most critical corrosion factor, particularly when the pipeline structure is buried for an extended period. Notably, for structures buried in soil, variation in the soil’s properties and characteristics is the main reason for corrosion. In Saudi Arabia, industrial development is mainly based on chemical-, oil-, and gas-related activities. In 2007, its production and manufacturing sector consumed approximately 67.82% of its total corrosion. This sector requires immediate attention from researchers and engineers to control and minimize the corrosion burden [4].
Soil corrosion is the degradation of metals or other materials due to the chemical, mechanical, and biological actions of the soil environment [5]. Buried pipelines (usually made of carbon steel) are one of the most commonly used media for transporting products, such as crude oil and gas, from point to point. Underground pipelines are exposed to various environmental elements, such as soil (onshore) and seawater (offshore), which may lead to corrosion attacks. Steel pipeline deterioration due to corrosion attacks is a common, serious concern that results in high costs and inconveniences to the industry and the public [6,7,8]. Soil is a mixture of soil particles, water, and air, with heterogeneity, porosity, and relative fixity characteristics, which lead to complicated and unique corrosion processes [9,10]. Soil corrosion is an electrochemical process that occurs at soil–metal interfaces. Corrosion occurring at the solution–metal interface differs from that due to the interaction between the soil and metal. Thus, some unique corrosion products are formed [11,12]. Various properties synergistically influence the corrosion rates of metals in soil, including the pH, soil resistivity, moisture content, aeration, temperature, and soluble salt concentration. For instance, the pH values found in soils range from 2.6 to 10.2 [13]. Soil resistivity depends on other factors, such as particle size, porosity, and temperature. The particle size determines the specific surface area (i.e., the total surface area per unit mass). The smaller the particle, the larger the specific surface area. Moreover, they exhibit higher conductivity at the surface than soils with coarse particles of the same mineralogy [14].
The literature has analyzed pipe corrosion and predicted future corrosion for water distribution pipes. Zhang et al. [15] reported that the corrosion current density of X70 steel was most influenced by the dissolved oxygen concentration in a simulated solution. Similarly, Liu et al. [16] reported that the corrosivity of cations was more aggressive for soil solutions than for anions. This finding may be due to differences in the radius. All the ions in the simulated soil solution decreased in resistivity but had different effects on the charge transfer resistivity. Wang et al. [17] investigated the corrosion behavior of X80 pipeline steel in simulated alkaline soil solutions using electrochemical tests. The results indicated that uniform corrosion occurred on X80 steel in the Shanshan and Hami simulated solutions, and local corrosion was the primary failure mode for X80 steel in the Yumen simulated solution. Another study [18] investigated the corrosion behavior of X80 steel in three types of simulated soil solutions. The results showed that X80 steel was uniformly corroded in a simulated solution of Shanshan and Xinzhou soils, and pitting corrosion occurred on X80 steel in a simulated solution of Zhangshu soil. The ranking of the corrosion rates of X80 steel in different simulated solutions was Zhangshu > Xinzhou > Shanshan. Lins et al. [19] observed that the corrosion potential and polarization resistance values were higher for API steel in an aqueous soil extract than in a synthetic solution. The corrosion current density of API steel in the synthetic solution was an order of magnitude higher than that of the aqueous soil extract. Bansode et al. [20] found that the corrosion of metals in soil can vary from relatively rapid material loss to negligible effects depending on the soil environment. Soil engineering properties and content are essential parameters that influence soil corrosivity and corrosion dynamics. Luo et al. [21] investigated the electrochemical corrosion behaviors of the base metals and welding materials of API 5 L X90 steel longitudinally submerged arc welded pipes in a near-neutral simulated soil solution (NS4). It was demonstrated that as polarization progresses, the polarization resistance and corrosion resistance increase and the corrosion current density decreases. The corrosion resistance of the base material was better than that of the seam-weld material.
The main focus of this research is the corrosion behavior of carbon steel X36 (CSX36) in selected soil solutions related to the water distribution network in different soil environments in Jeddah City. Various techniques have been used to measure the corrosion rate of soil solutions. In this study, the corrosion rate was measured at an ambient temperature (23 ± 1 °C) using the weight loss (WL) method. Different electrochemical methods, such as open circuit potential (OCP), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and potentiodynamic polarization (PDP), were measured at an ambient temperature (30 ± 1 °C). Surface characterization techniques, such as optical photography (OP) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), were used.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Metal Specimens
The aim of this study was to investigate the corrosion performance of buried pipelines. Therefore, the material selected was commercial CSX36; the chemical composition is shown in Table 1. The specimens were cut into rods (diameter, 1 cm; length, 5 cm).

Table 1.
Percentage composition of studied sample.
2.2. Soil Samples
2.2.1. Collection and Analysis
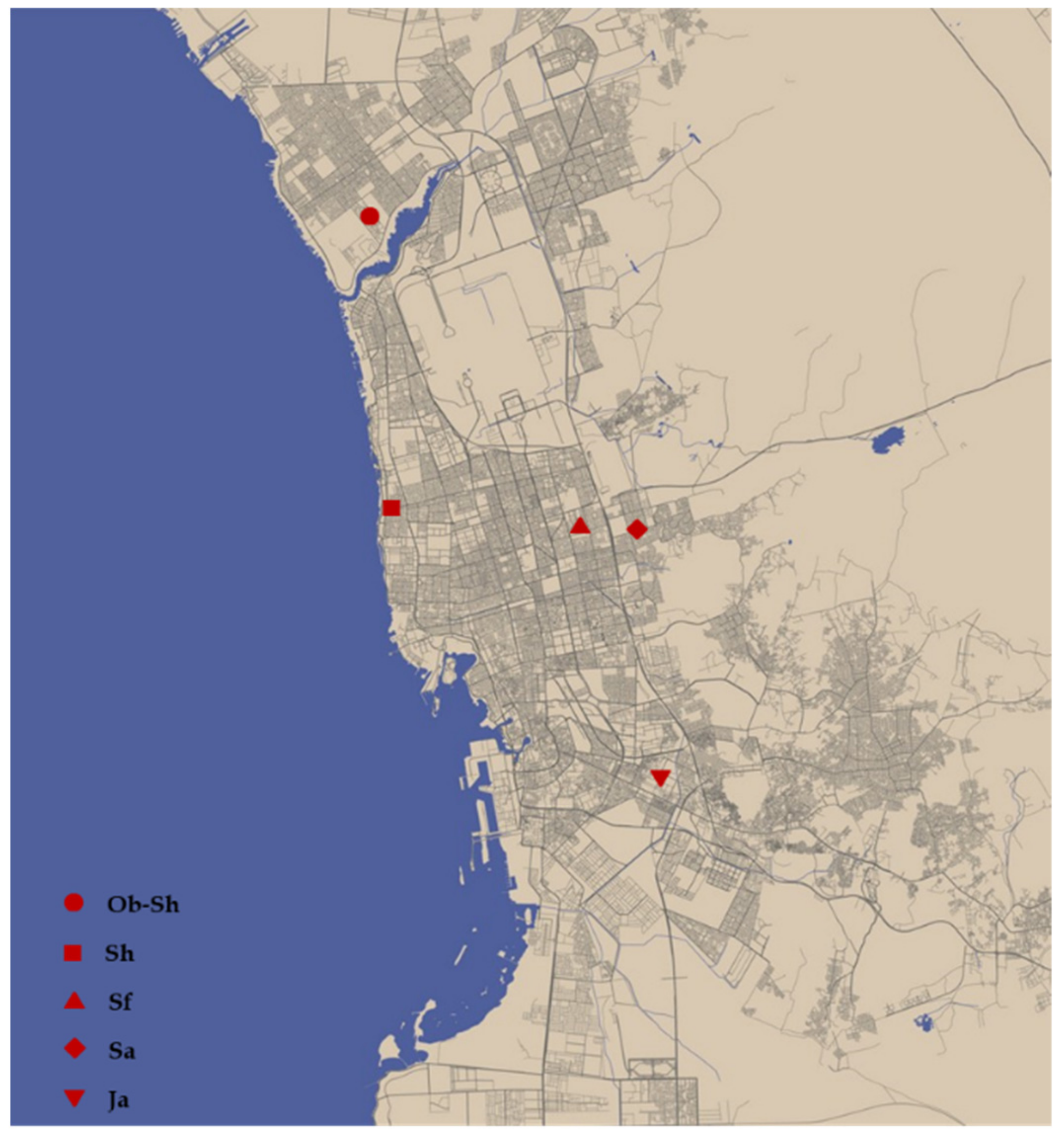
Soil samples were collected from five districts: Obhour Al Shamaliyah, Ob-Sh, Al Shateie, Sh, Al Safa, Sf, Al Samer, Sa, and Al Jameaah, Ja. The geographic locations of the districts in which the soil samples were collected are shown in Figure 1. The soil samples were collected from each district by digging a hole ≥ 2 m deep. The samples were stored in polyethylene bags and sent to the laboratory for analysis. Next, the samples were air-dried at room temperature and sieved. The collected soil samples were tested for soil corrosivity properties, such as soil electrical conductivity (EC), soil electrical resistivity (ER), and soil pH, and the concentration of various cations and anions was analyzed in the laboratory at Al-Hoty-Stanger Co., Ltd. (Jeddah, Saudi Arabia). The chemical compositions of the five soils used in this study are shown in Table 2.
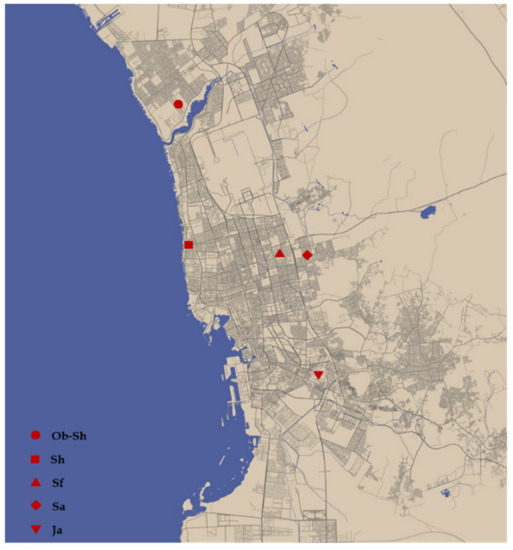
Figure 1.
Sampling locations in Jeddah City, available at [22].

Table 2.
Chemical analysis of soil extracted solutions (mg/L).
2.2.2. Test Solution Preparation
Next, the soil solution samples were prepared: 500 g dry and sieved soil was weighed and placed in a container containing 1.0 L of double-distilled water. The soil/water mixtures were stirred well with a stiller for 2 h at room temperature. Subsequently, the soil/water mixtures were filtered using filter paper. The collected soil solution samples were stored in a dry, clean tank and topped with a cover sealed with weather stripping for use in the experiments.
2.3. WL Measurements
The polished and pre-weighed CSX36 specimens were placed in closed glass containers containing 100 mL soil for different immersion periods (1, 3, 5, 10, 15, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, and 80 weeks) at an average ambient temperature of the lab (23 ± 1 °C). Samples immersed in various soil solutions and stamped code numbers were used (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Final arrangement for weight loss experiments in Jeddah soil solutions.
WL is expressed by the penetration depth (), according to the following equation:
where is the WL in grams (g), A is the area in square centimeters (cm2), and d is the metal density (g/cm3).
After each immersion period, the specimens were carefully removed from the soil solution, washed with tap water, and immersed for 5 min in 20% containing 200 g/L zinc dust at room temperature [23]. A “blank” specimen was weighed before and after exposure to the pickling solution to correct the specimens’ WL. However, the correction factor was small; therefore, it was ignored. After removing the pickling solution, the specimens were scrubbed with a bristle brush to remove most corrosion products. They were then rinsed thoroughly with double-distilled water and acetone, air-dried, and reweighed carefully. Duplicate experiments were performed for each case, and the mean value of the WL was obtained.
Plots of the penetration depth (μm) versus time (years) had straight lines with a slope representing the corrosion rate (μm y−1).
Optical images of the samples were captured after the WL experiments to assess gross changes in the metal surface and perform a surface evaluation of the forms of corrosion (e.g., general and pitting) under different conditions.
2.4. OCP, EIS, and PDP Measurements
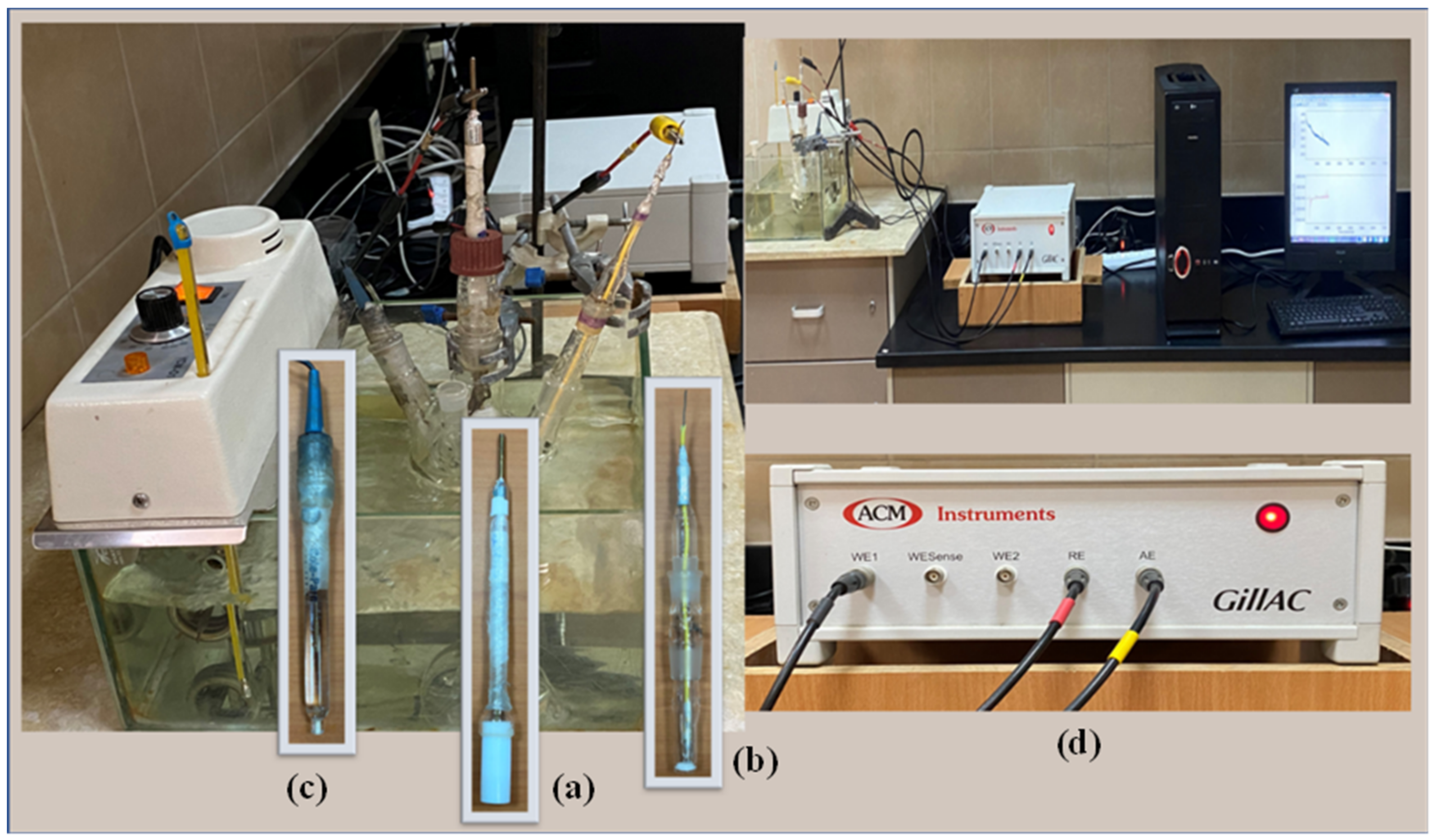
The electrochemical measurements were performed in a round flask with multiple necks, called a three-electrode cell (Figure 3). A cylindrical specimen of CX36 was used as the working electrode, which was embedded in a Teflon holder using epoxy resin, resulting in an exposed area of 0.683 cm2 (Figure 3a). A platinum mesh was used as the counter electrode (Figure 3b), and silver/silver chloride (Ag/AgCl(s)/KClsaturated(aq)) was used as the reference electrode (Figure 3c). Electrochemical measurements were performed using an ACM Gill AC Potentiostat/Galvanostat model 1649 (Figure 3d) connected to a personal computer. Before each experiment, the working electrode was treated as described in the WL method and then dipped in the tested soil solution. Immediately after electrode immersion, the OCP of the working electrode was monitored for 2 h. After reaching steady-state potential, the electrode impedance was recorded as a Nyquist plot. During EIS measurements, an AC disturbance signal of 10 mV was applied to the electrode at the OCP. The measured frequencies ranged from 0.1 to 30,000 Hz. Potentiodynamic curves were obtained by linearly changing the electrode potential from the starting potential (−1000 mV), with the reference electrode at a less negative direction than the required scan rate (1 mV/s) until the end of the experiment at −100 mV. All the electrochemical measurements were performed twice at an ambient temperature (30 ± 1 °C). The EIS data were fitted to appropriate equivalent circuits using the computer program ZSimDemo 3.20 (EChem Software, Ann Arbor, MI, USA), and the PDP curves were analyzed using ACM Gill software (ACM Instruments Ltd, Cumbria, UK).
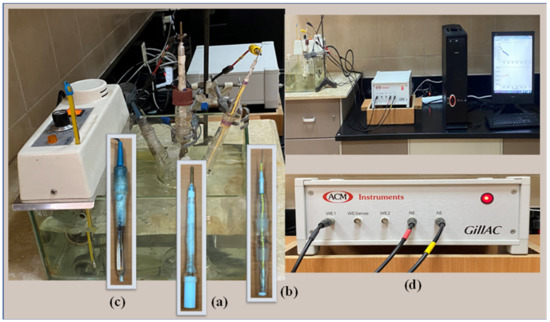
Figure 3.
System used for electrochemical measurements. (a) Working electrode, (b) Counter electrode, (c) Reference electrode, (d) ACM instrument.
2.5. Surface Characterization (OP and SEM)
Optical images of the samples were collected after the WL experiments to evaluate the overall changes in the metal surface and conduct a surface evaluation of the corrosion patterns (e.g., general and pitting) under different conditions.
SEM has enabled significant advances in understanding many corrosion processes [24]. The surface morphology of the specimens after prolonged immersion (20 weeks) in the studied soils was observed by SEM for different soil solutions.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. WL Method
3.1.1. Effect of Immersion Time
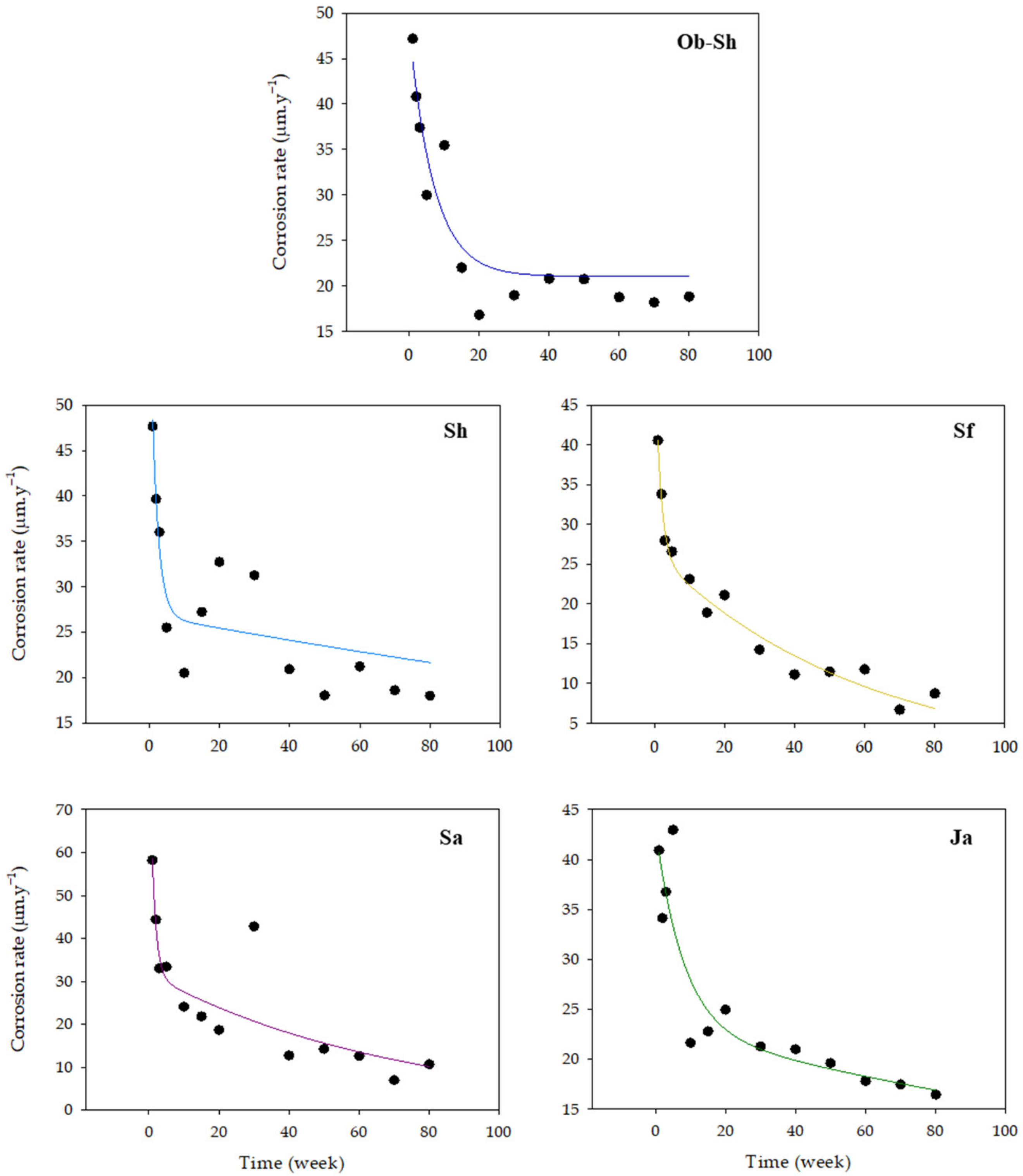
The degree of corrosion damage was expressed in terms of the instantaneous corrosion rate (CR) in µm·y−1 denotes CSX36 corrosion in the Jeddah soil solution for different periods. Figure 4 shows the approximate fitting curves between the instantaneous CR and immersion time over 80 weeks. Higher CRs were observed in the first few weeks than in later weeks. This finding was observed because the surface of the metal continuously dissolved in the soil solutions. However, the early corrosion products provided a protective effect in suppressing the corrosion process formed on the surface. Thus, the CR slowed gradually with the formation of a rust layer [25].
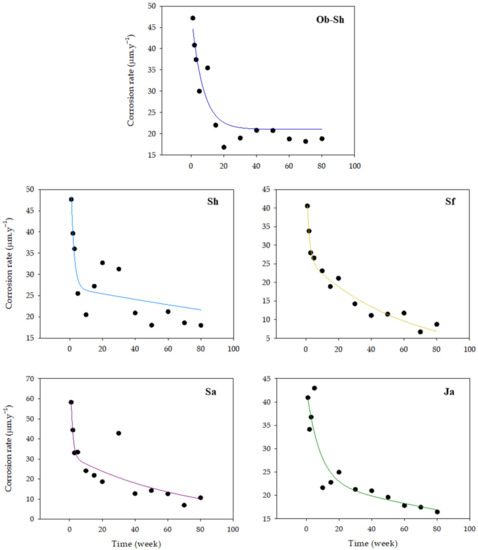
Figure 4.
Variations in the CR of CSX36 specimens over 80 weeks of immersion in the studied Jeddah soil solutions at 23 ± 1 °C.
3.1.2. Kinetic Study
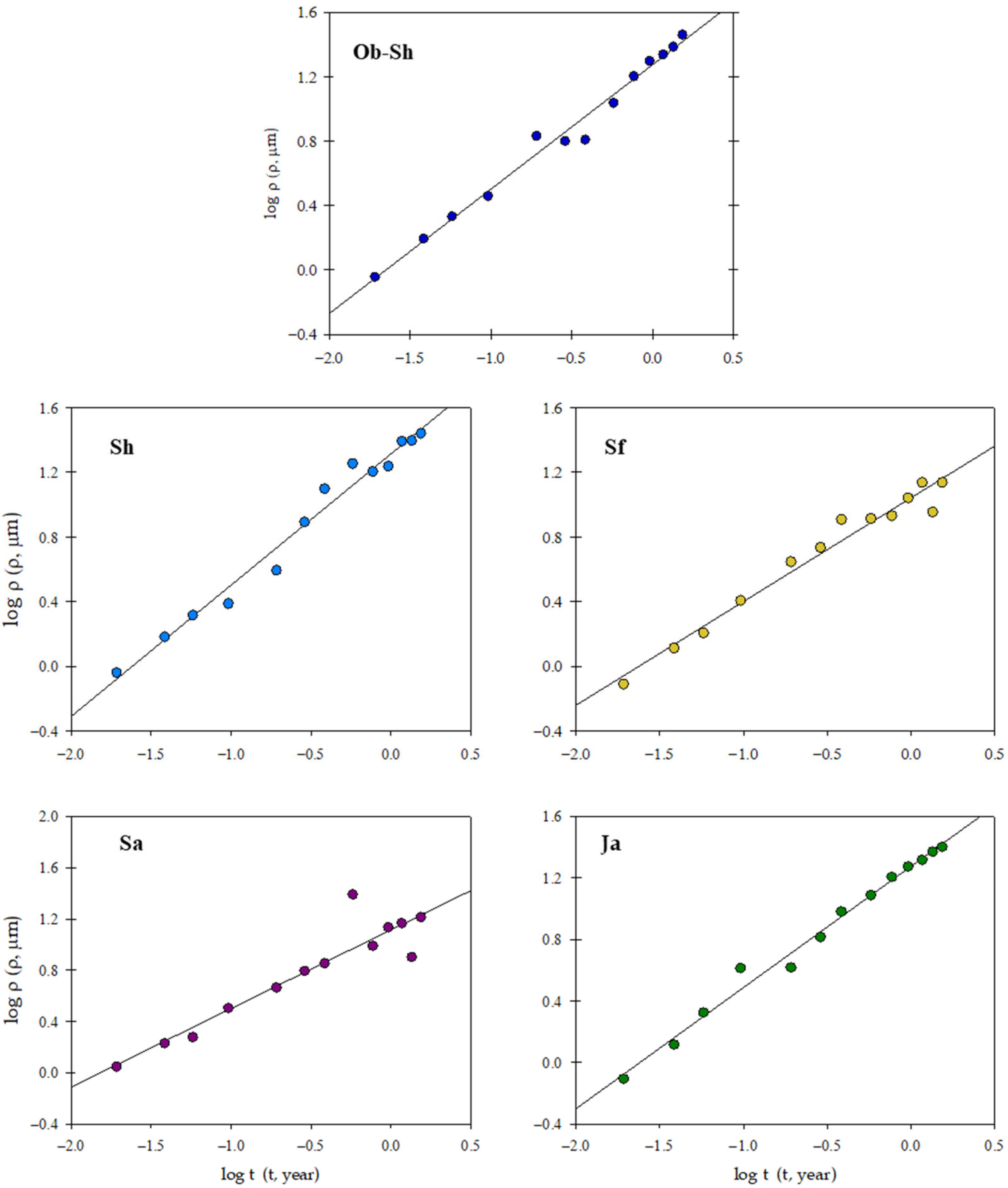
Figure 5 shows a log-log plot of the penetration depth (, µm) and the time of exposure (t, years) using the following equation [26]:
where n and are the slopes and the intercept of the obtained straight line, respectively, and the value of n is usually a fraction, typically between 0.4 and 0.6, for unprotected steel in many soils. For n ≤ 0.5, steel corrosion was diffusion controlled, and the diffusion of corrosive species was the rate-determining step. In highly aggressive environments, the value of n may be near or exceed unity [27]. In contrast, represents the penetration depth after 1 year of exposure and indicates the corroding susceptibility at the start of exposure.
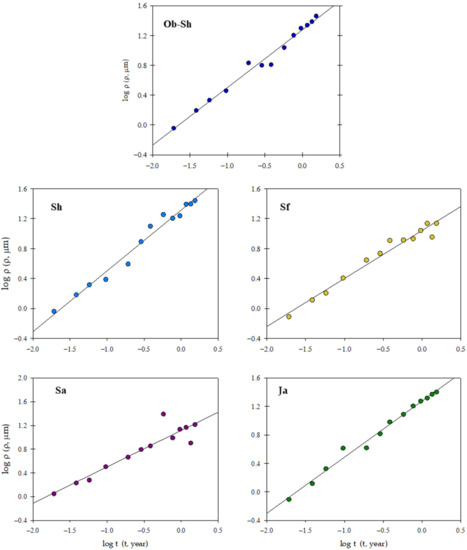
Figure 5.
log ρ as a function of log t for the corrosion of CSX36 specimens over 80 weeks of immersion in the studied Jeddah soil solutions at 23 ± 1 °C.
The kinetic parameters ( and n) and correlation coefficients (r2) were estimated (Table 3). The results show correlation coefficients ≥ 0.87, indicating that the data regarding the penetration depth of CSX36 of the studied soil solutions follow kinetic Equation (2).

Table 3.
Corrosion kinetic parameters for CSX36 corrosion in different Jeddah soil solutions.
The presence of ‘n’ values > 0.5 for the studied soil solutions Sf and Sa indicated that the diffusion process was accelerated because of rust detachment via, for example, corrosion, flaking, and cracking. For the remaining soil solutions, the ‘n’ value varied from 0.77 to 0.81. This result suggests a combination of diffusion and charge transfer control [27]. Generally, the penetration depth per year ) indicates a definite trend for the corrosivity of the studied soil solutions as follows:
Sh > Ja > Ob-Sh > Sa > Sf
3.1.3. OP Observations
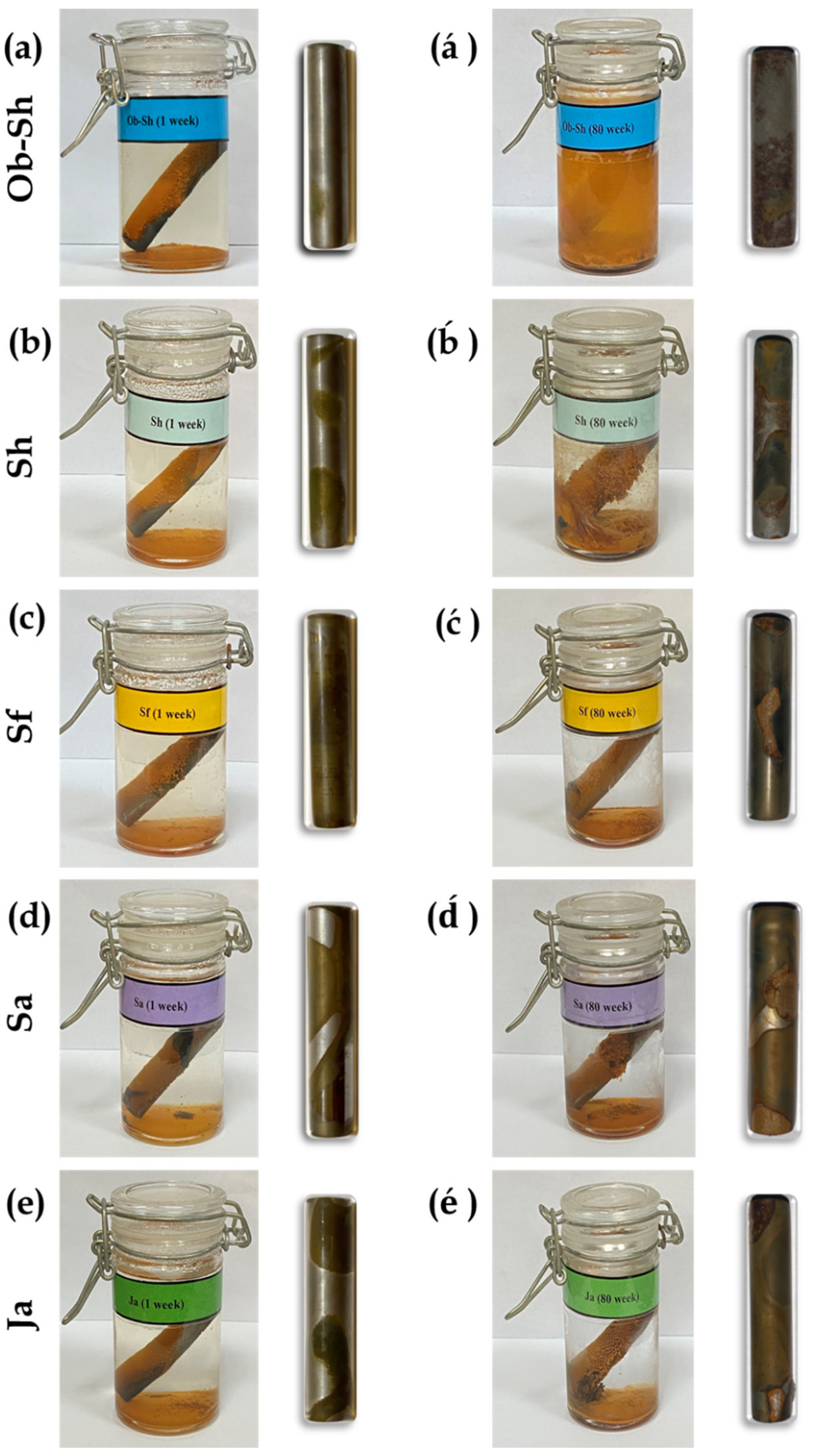
The images of the CSX36 specimens inside the tested bottle solutions after they were removed at two immersion periods (1 and 80 weeks) are shown in Figure 6. The figure shows that the soil solutions containing the C-steel specimens were observable with apparent solution clarity in the initial immersion stage of the soil solutions. The formation of dense corrosion products on the sample was observed during a prolonged immersion period (Figure 6á–é. Unfortunately, for some soil solutions, the corrosion product diffused from the sample surface into the solution, resulting in turbid solutions. In some cases, the intensity of the turbidity was such that the steel sample could no longer be identified (Figure 6á).
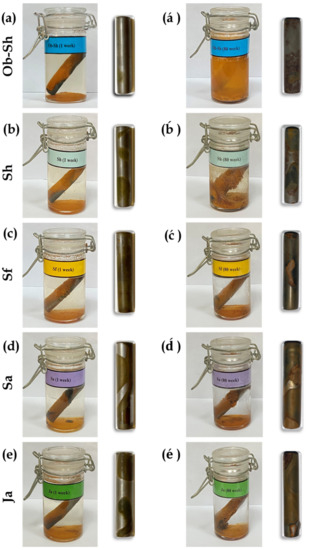
Figure 6.
Optical images for the corrosion of CSX36 specimens over: (a–e) 1 week and (á–é) 80 weeks of immersion in the studied Jeddah soil solutions at 23 ± 1 °C.
However, the surface features of the studied specimens after removal of the corrosion products showed various corrosion patterns on CSX36, such as (i) general corrosion (corrosion occurred throughout the surface, Figure 6a), (ii) corrosion striations (corrosion looked like scrape marks, Figure 6ć,), and (iii) pitting corrosion (with some pits joining to form more giant pits and interconnected pitting, Figure 6á,é). Identifying these corrosion patterns individually or in combination depends on the immersion period. According to the pitting features of the corroded surfaces, a prolonged immersion period was associated with increased damage to the corroded specimens.
3.1.4. SEM Observations
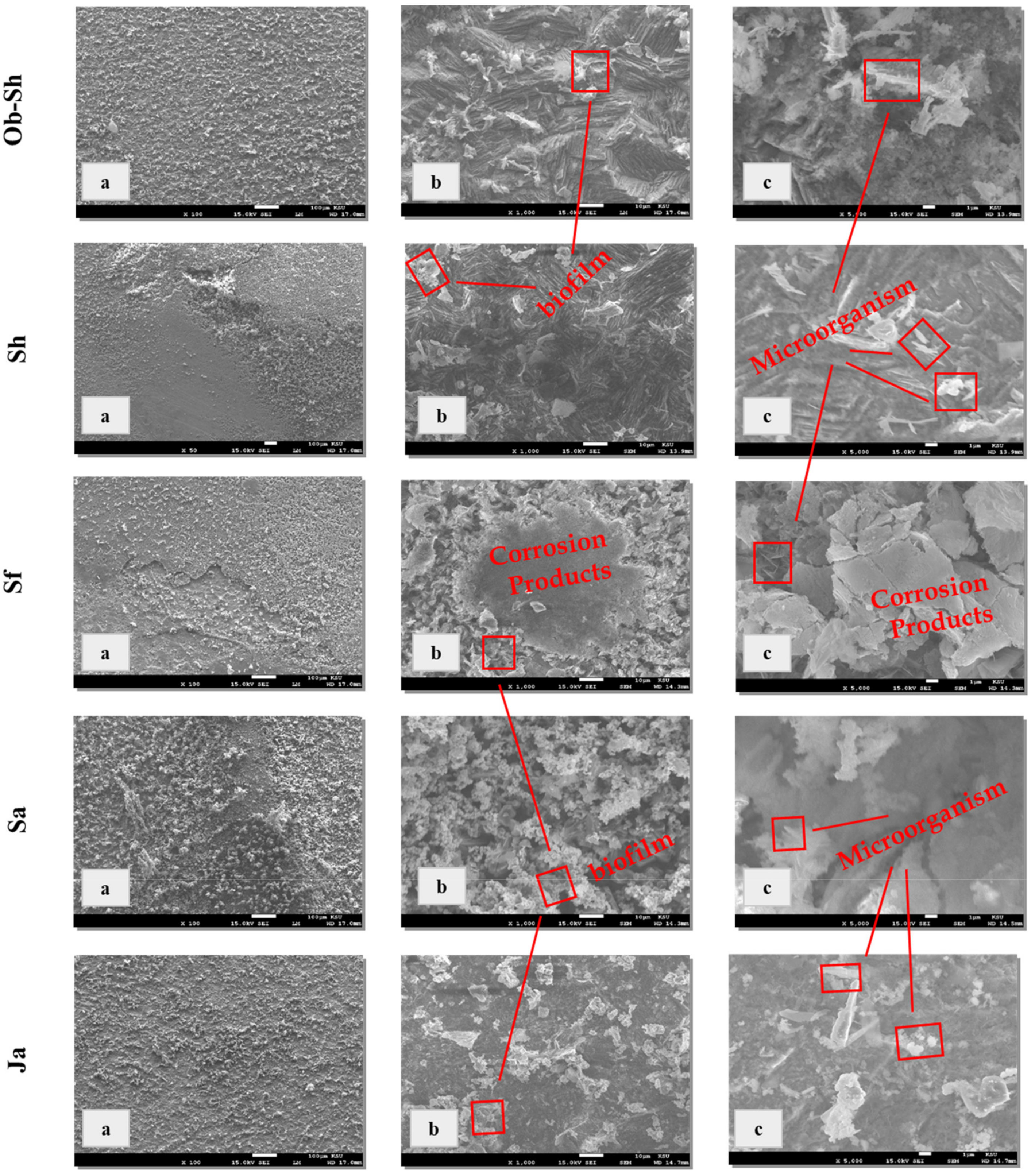
Figure 7 shows the surface morphology of the CSX36 after immersion for 20 weeks in the studied soil solutions at room temperature. For all the studied soil solutions, Figure 7a shows the presence of film-like sandpaper, and in some cases, such as the Sf and Sa soil solutions, cracking of this layer was observed. Cracks on the film may be generated from dehydration on the surface, indicating the thickness of the film formed. At higher magnifications, all the studied soil solutions showed microbial activity within the corrosion products (Figure 7).
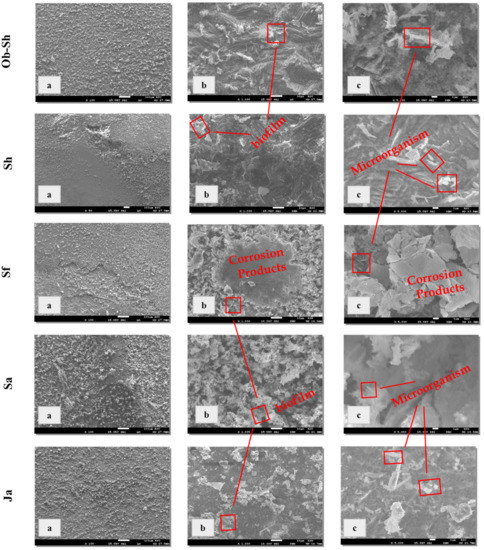
Figure 7.
SEM micrographs for CSX36 surface after exposure for 20 weeks of immersion in the studied Jeddah soil solutions at 23 ± 1 °C: (a) x = 100 μm; (b) x = 10 μm; and (c) x = 1 μm.
In the case of the Ob-Sh, Sh, and Ja soil solutions, uneven corrosion products accompanied by scattered biofilm were observed. Hence, they provide poor protection for metals [28]. This result agrees with the high CRs detected for these soil solutions (Table 3). For the Sf and Sa soil solutions, the biofilm overlapped with the corrosion products, forming a protective layer on the metal surface. Diffusion through the pores of this layer may control the CR, as previously discussed.
Microbial corrosion significantly contributes to the corrosion of underground structures, particularly pipelines [29]. Sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) are obligate anaerobic bacteria that are abundant in natural environments, such as soil, and can be easily cultured and detected [30]. A 365-day study for cast iron immersion in soil and cultures containing SRB showed that the specimens severely corroded in the soil compared with the culture medium [31]. This result indicated the survival ability of such bacteria in the soil environment, even for a long immersion time. Therefore, the detection of microbial activity on the surface of the current study sample after a twenty-week immersion period is a result of the ability of potential anaerobic microbes in the soil to survive, especially in such an extremely humid environment.
3.2. Electrochemical Methods
3.2.1. OCP
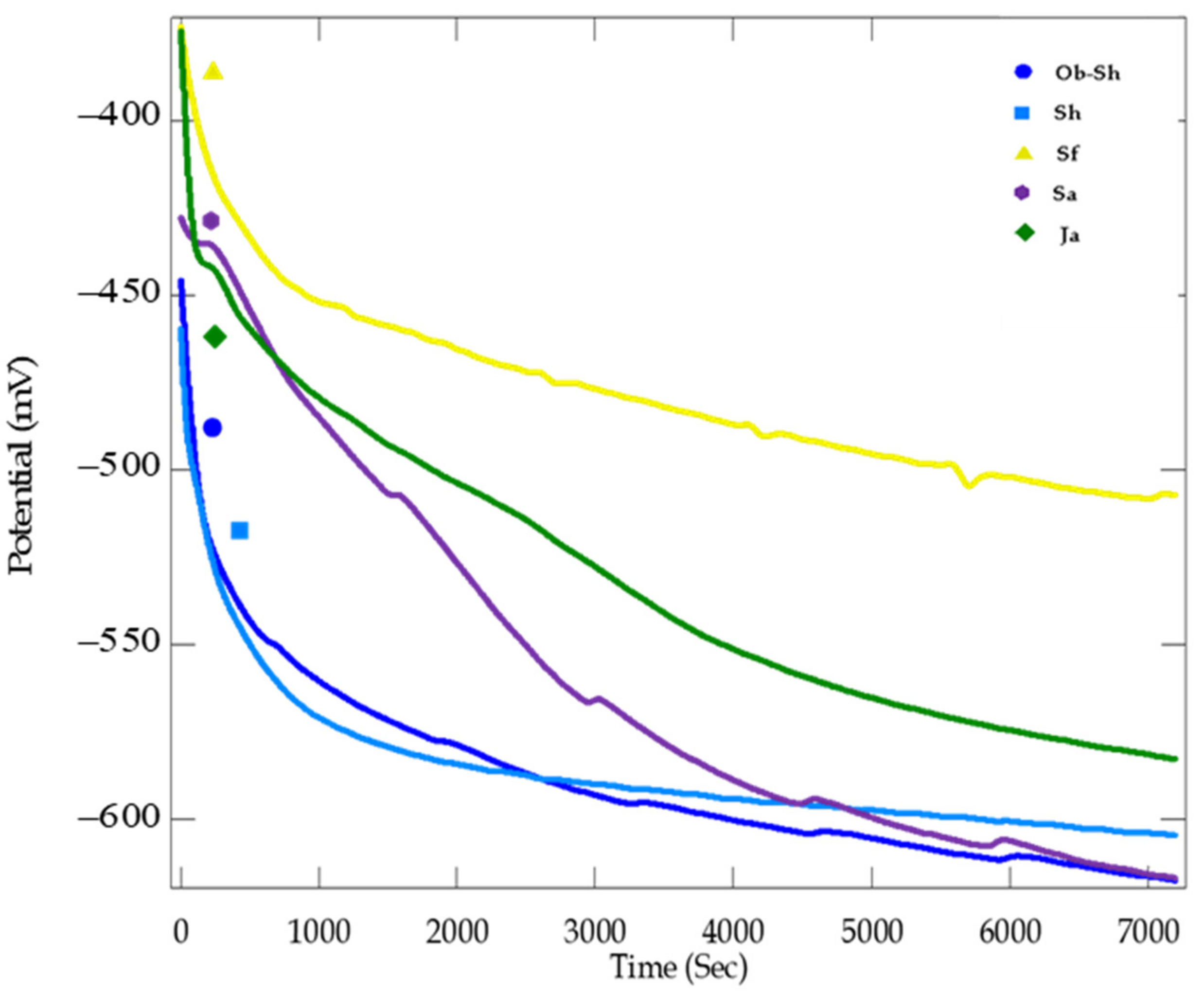
The OCP for CSX36 in soil solutions obtained from different regions of Jeddah City was followed for over 2 h to obtain the steady-state electrode potential (Figure 8).
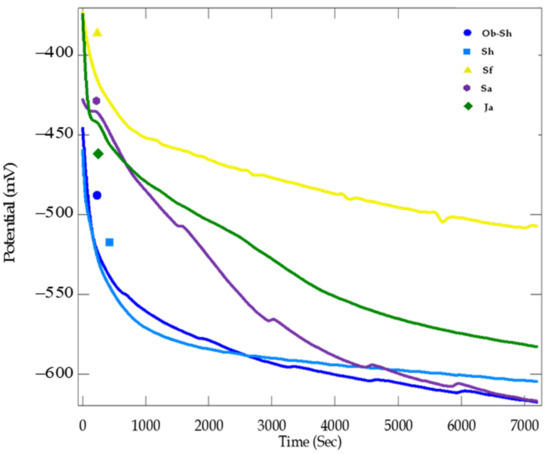
Figure 8.
OCP curves for the corrosion of CSX36 specimen in the studied Jeddah soil solutions at 30 ± 1 °C.
As shown in Figure 8, after the initial stabilization period of the CSX36 electrode in the soil solutions, the OCP values ranged from −502 to −613 mV, which is the range of carbon steel, depending on the composition of the steel, the activity of all soil solutions, and the corrosive environment [32,33]. It is noted that the OCP of CSX36 in the soil solution of both Ob-Sh and Sh drops rapidly in the negative direction and reaches stability in less time compared to the other soils‚ which indicates a higher corrosion rate and may be attributed to a high salt content‚ especially chloride ions [34], as shown in Table 2.
3.2.2. EIS
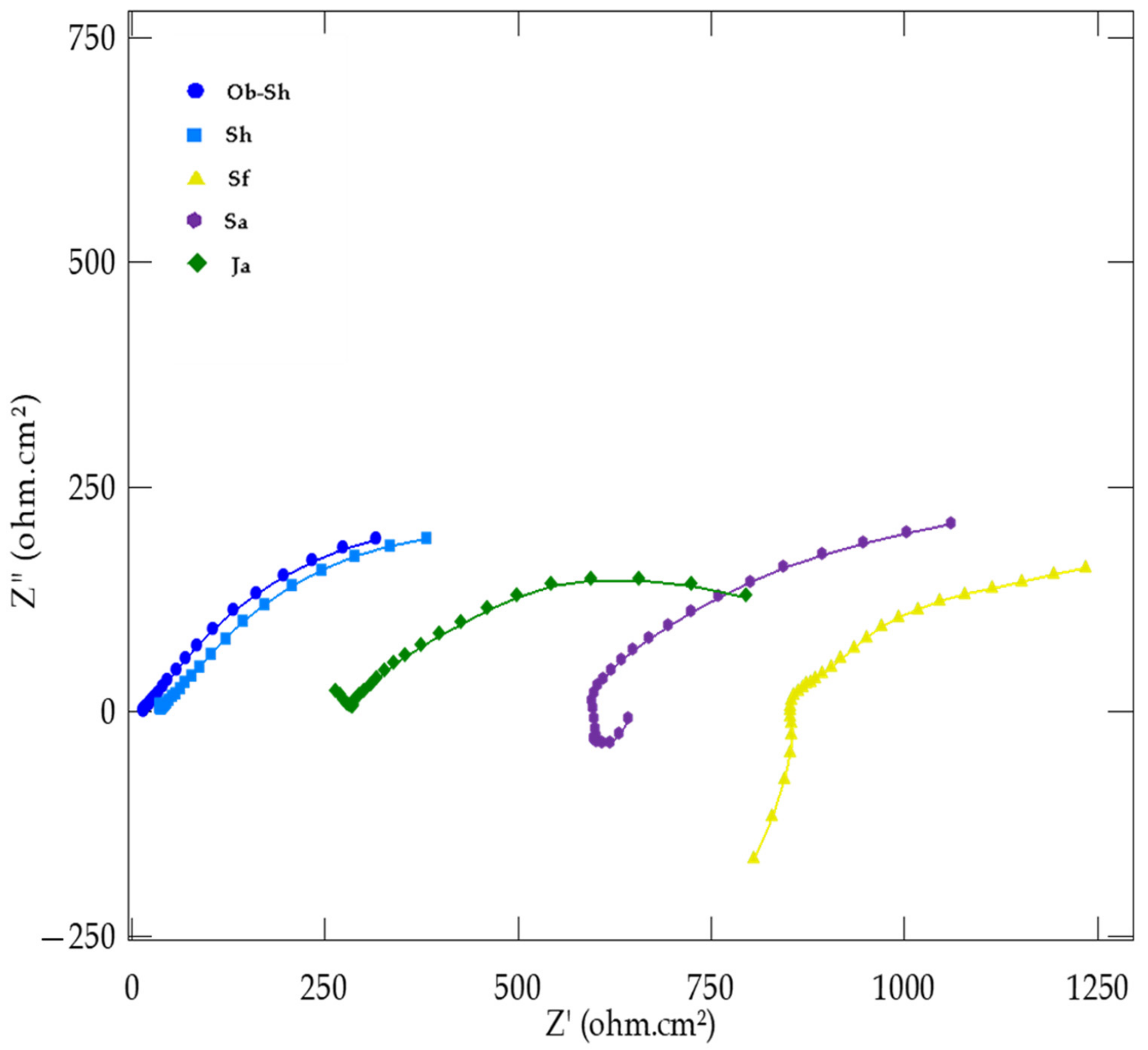
EIS was used to investigate the electrochemical behavior of CSX36 in the studied soil solutions at 30 ± 1 °C, with the real impedance values on the x-axis (Z′) and the imaginary impedance values (Z′′) on the y-axis. The corresponding equivalent circuit used to model the impedance results provided insights into the metal–film–electrolyte interactions. Figure 9 shows the variation in the measured electrochemical impedance (Nyquist plot) of the studied soil solutions. Two capacitive semicircles were present in all the cases studied. One of them, at a high frequency (left-hand loop of the Nyquist plot), corresponds to the electrical properties of the film naturally formed on the steel surface. The other corresponds to the electrochemical corrosion process at a low frequency (right-hand loop of the Nyquist plot) [35]. The high-frequency semicircles were much smaller than the low-frequency semicircles and were not well separated in most cases. A suppressed capacitance loop with a theoretical center below the real axis characterizes the Nyquist plots. This feature reflects surface inhomogeneities of structural or interfacial origins [36]. However, in all the cases studied, the system response in the plane of the Nyquist complex was an incomplete semicircle whose shape and diameter depended on the soil solution type.
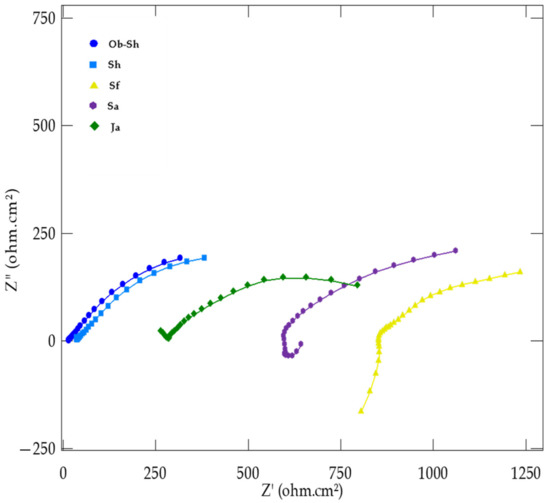
Figure 9.
Nyquist plots for the corrosion of CSX36 specimen in the studied Jeddah soil solutions at 30 ± 1 °C.
The two merged capacitive loops indicate the occurrence of two corrosion processes for all the soil solutions studied. One high-frequency process normally shows the formation of the surface oxides (products of corrosion). A second process at low frequencies, related to the charge transfer process at the metal–film and metal–electrolyte interfaces, involves the oxidation of iron and the reduction of water or oxygen [37].
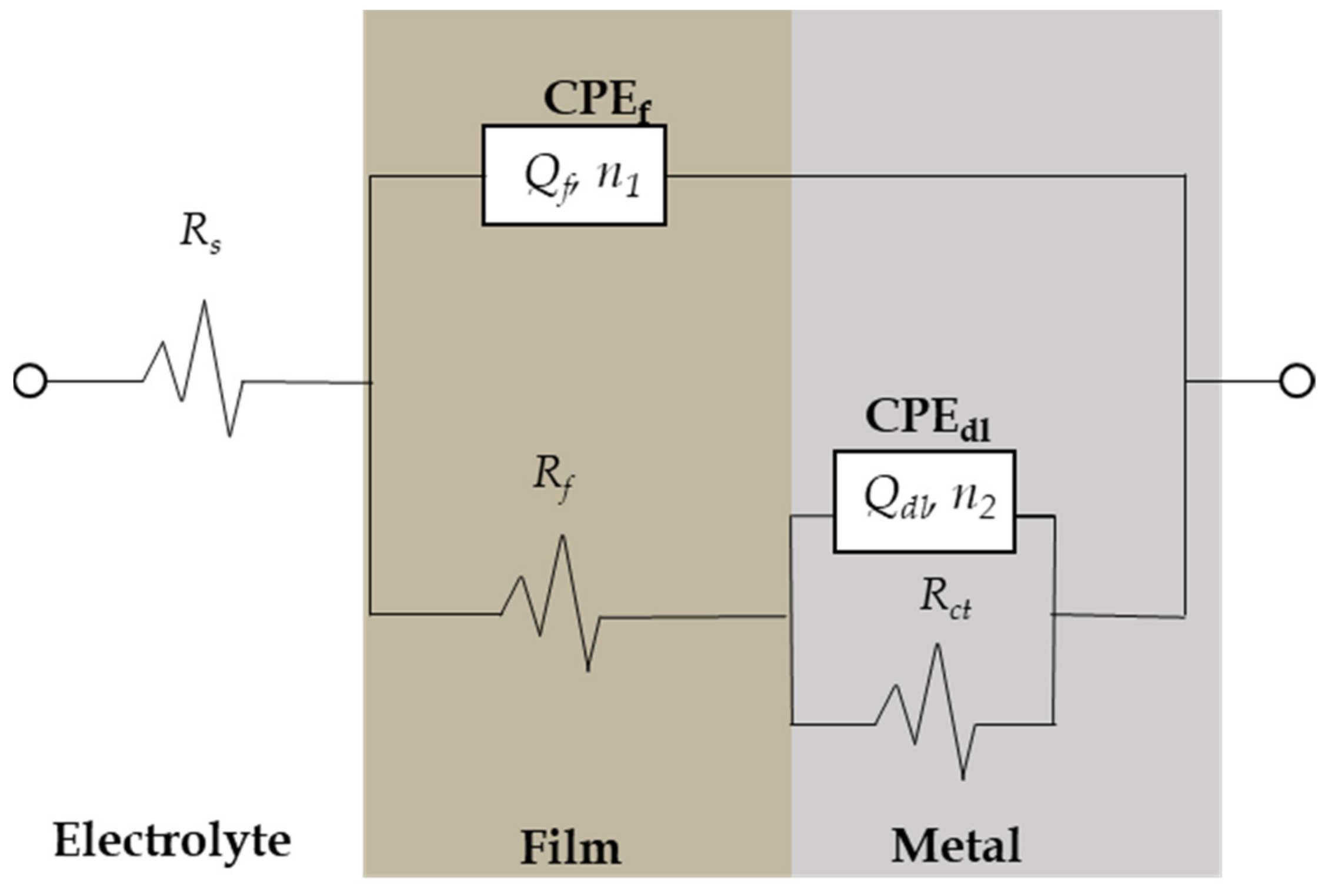
The interpretation of EIS data depends mainly on the development of equivalent circuits for modeling the metal–electrolyte interface. Various equivalent circuits were applied to simulate the experimental EIS diagrams using the software program ZSimDemo 3.20. After various attempts to simulate the EIS data, an equivalent circuit well fit to describe the corrosion processes at the metal–electrolyte interface was finally obtained (Figure 10). Several authors have reported similar equivalent circuits for corroded steel in different soils [38,39,40].
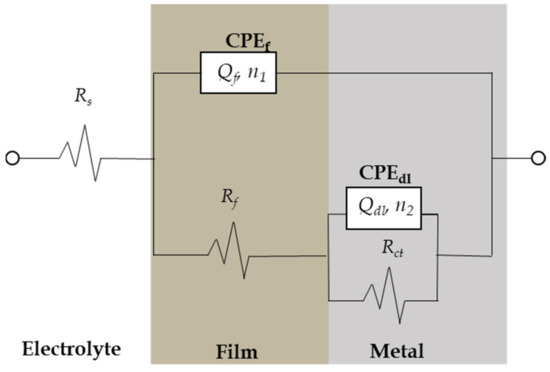
Figure 10.
Equivalent circuit model used to fit experimental impedance data of CSX36 corrosion in the studied Jeddah soil solutions at 30 ± 1 °C.
As shown in Figure 10, a constant phase element (CPE) was used instead of a capacitor, indicating the presence of a non-ideal frequency response. The impedance of a CPE is defined as [41]:
where ω is 2πf (the angular frequency in rad/s); n and are the CPE parameter, where n has the meaning of a phase shift and is a proportion factor; and n is the deviation from ideal behavior. For , represents a resistance with ; for , a capacitance with ; for , a Warburg element; and for , an inductance with . However, the suggested equivalent circuits consist of the following elements: soil solution resistance, , porous film resistance, in parallel with a film, CPEf (), and charge transfer resistance, , in parallel with a double layer, CPEdl, ().
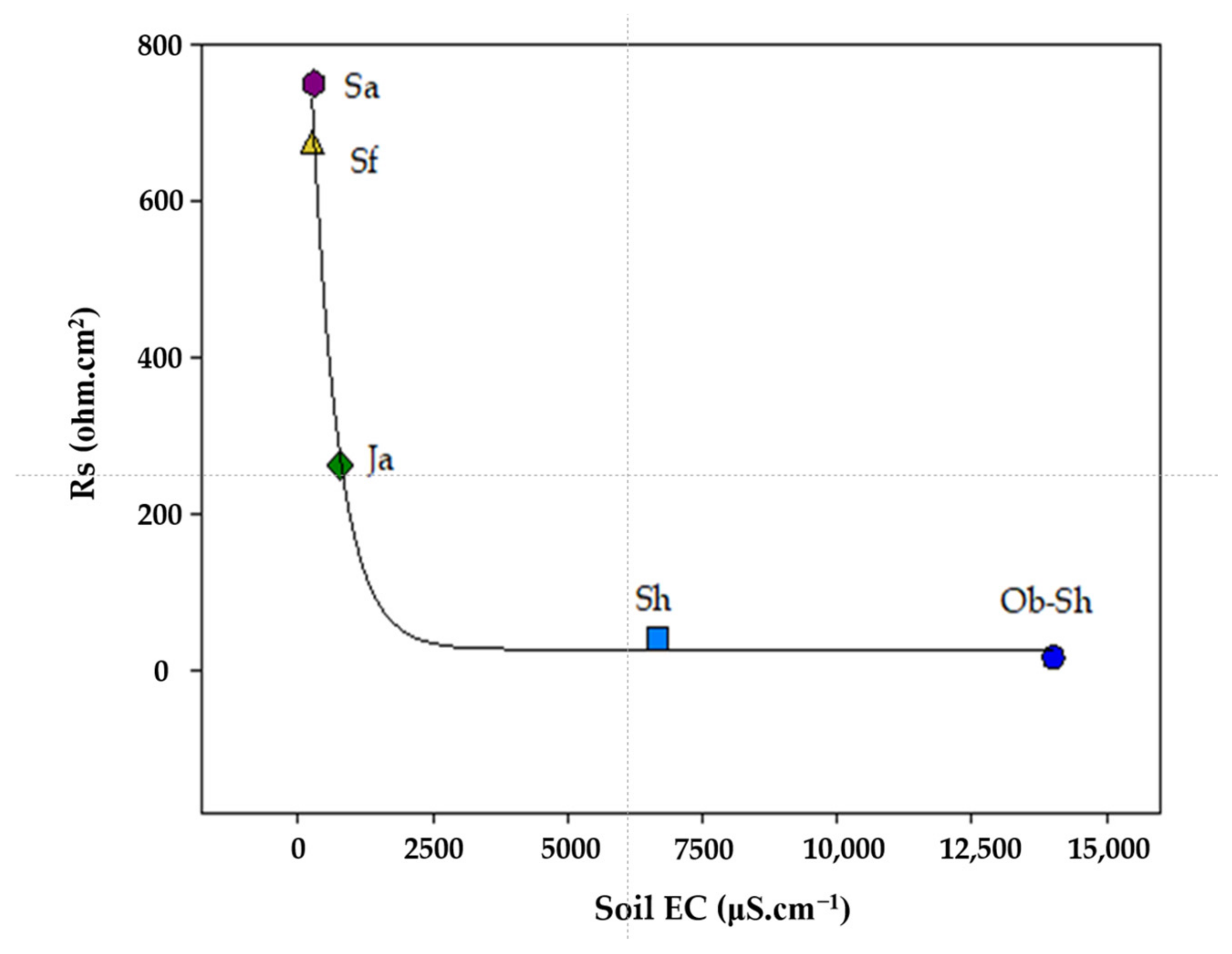
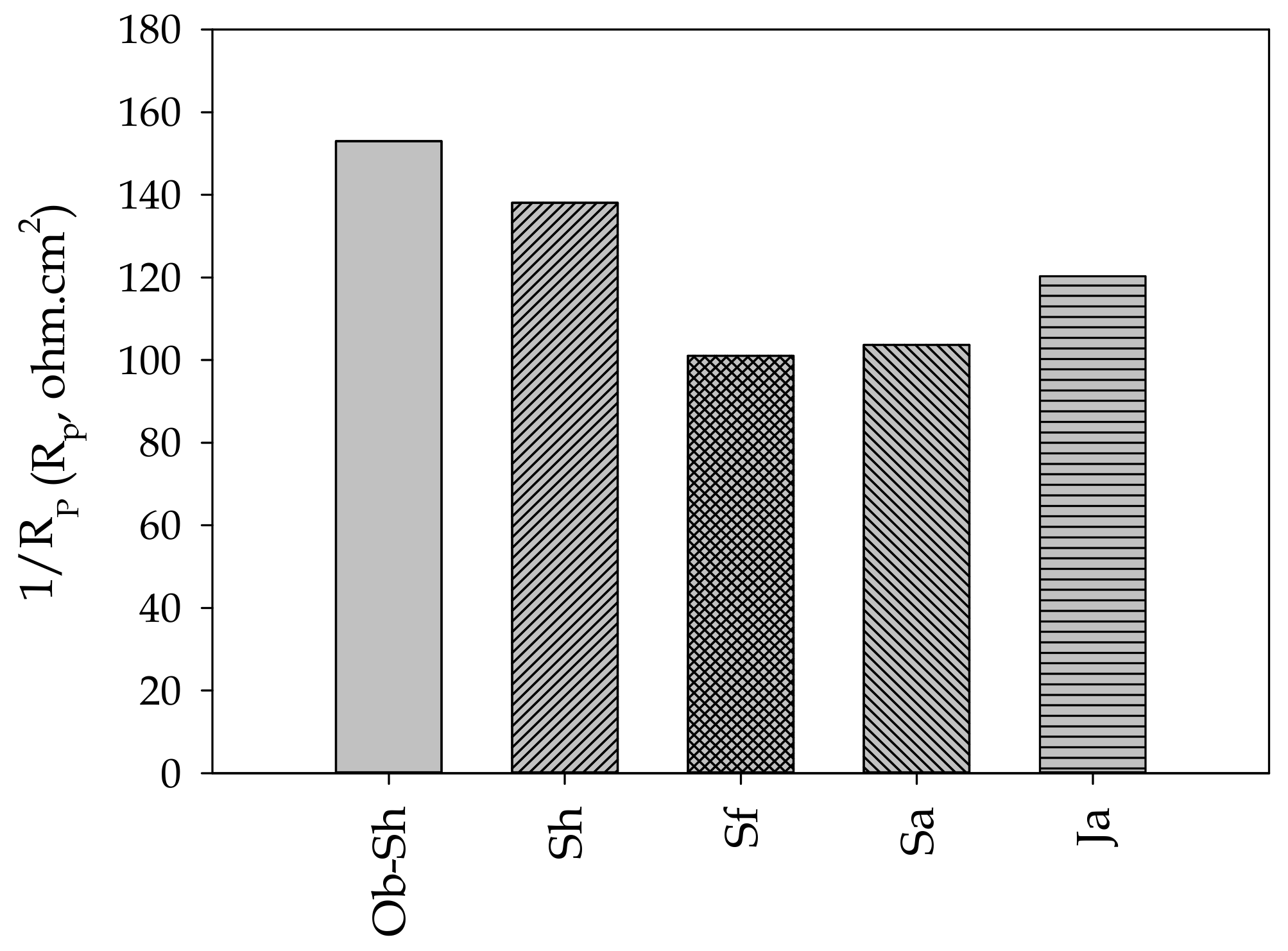
Table 4 presents the estimated electrochemical impedance parameters for the CSX36 corrosion in the studied soil solutions. Figure 11 shows the relationship between Rs and EC. The previous figure shows an inverse relationship between the two variables, which is the expected result. As shown in Table 2, the soil with a high level of ionic species, especially chloride ions, shows the highest value of EC and, accordingly, Rs because this soil had the lowest level of ionic species [42]. The values for the polarization resistance () of all the studied systems directly indicate the resistance to the polarization of the metal in the respective soil solution against corrosion. Thus, it can be deduced that the decrease in RP, that is, the increase in 1/Rp, indicates a reduction in corrosion resistance [43]. According to Figure 12, the corrosivity order of the studied soil solutions can be expressed as follows:
Ob-Sh > Sh >Ja > Sa > Sf

Table 4.
EIS parameters for the corrosion of CSX36 specimens in the studied Jeddah soil solutions at 30 ± 1 °C.
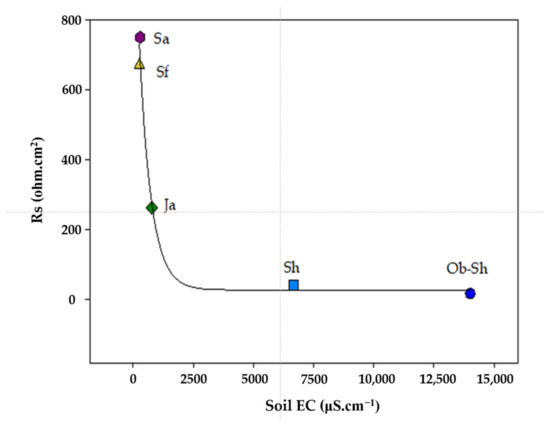
Figure 11.
Variation in Rs and soil EC for the studied soil solutions.
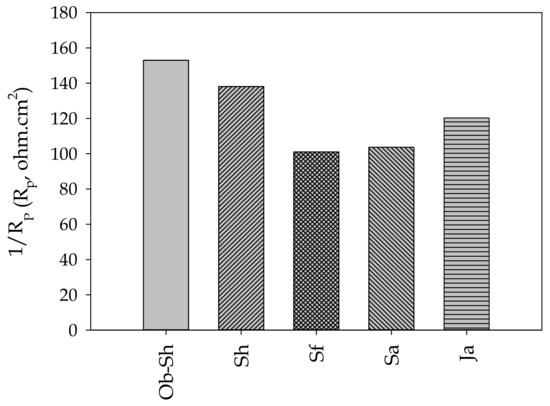
Figure 12.
Variation in 1/Rp for the studied Jeddah soil solutions.
3.2.3. PDP
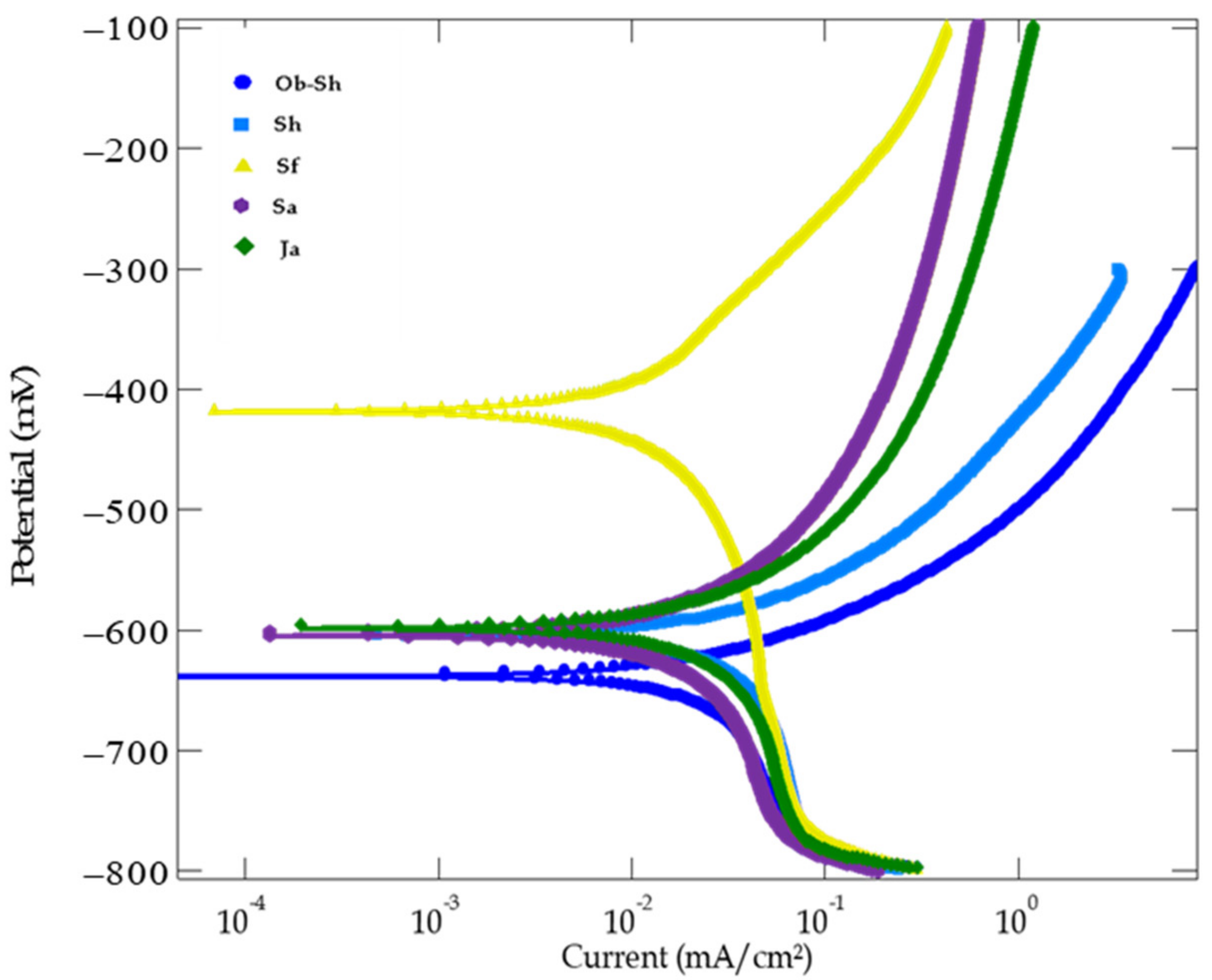
Figure 13 shows the potentiodynamic polarization curves of CSX36 in the studied soil solutions at 30 ± 1 °C. The anodic polarization process, which occurs at the anode, is represented by the upper branch of the PDP curve. Equation (4) shows the anodic oxidation reaction. The cathodic polarization process, which involves a reduction reaction at the cathode, is represented by the lower branch of the PDP curve. Equation (5) shows the respective reactions.
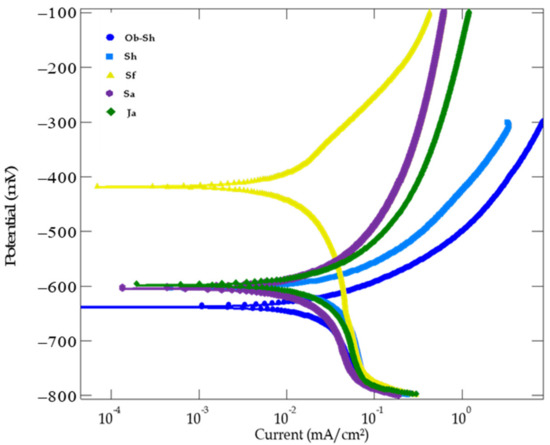
Figure 13.
PDP curves for the corrosion of CSX36 specimen corrosion in the studied Jeddah soil solutions at 30 ± 1 °C.
Anodic reaction
Cathodic reaction
The curves typically show Tafel behavior at a low overpotential, followed by a potential range through which a slight change in the current density was observed. This behavior was more pronounced for all the cathodic curves and only for the anodic curves of both the Sa and Ja soil solutions. The Tafel relationship is valid for pure activation or charge transfer control. Another consideration is the concept of concentration polarization. In this case, the reaction rate is sufficiently fast to deplete the reactive species (reduction reaction) or concentrate (oxidation reaction) on the reacting surface. To maintain the reaction rate, diffusion through the electrolyte is a kinetic limitation. The reaction becomes completely diffused and controlled at the limiting current density [44]. In this study, the cathodic reaction is expected to be oxygen reduction (reaction (5)), that is, the diffusion of oxygen through the soil solutions controls the cathodic process, leading to the appearance of a cathodic reaction limiting the current density, which supports the findings in [45].
On the other hand, according to reactions (6) and (7), the formation of the corrosion products Fe3O4 and Fe2O3 may be responsible for steel passivation at comparable rates of passive film formation and dissolution [46].
Table 5 displays the PDP parameters (Ecorr, and icorr) obtained by analyzing the polarization curves with ACM software analysis, which uses the Tafel lines extrapolation method through the so-called Tafel ruler.

Table 5.
PDP parameters for the corrosion of CSX36 specimens in the studied Jeddah soil solutions at 30 ± 1 °C.
For all the soil solutions studied, the shifted to more negative values, indicating that the corrosion process occurred under cathodic control, as previously illustrated. This result is in good agreement with that obtained from the OCP.
For all the studied soil solutions, the values of and did not change appreciably, except in some cases (), which showed higher anodic overpotentials, indicating that the mechanism of the anodic reaction may be altered under passivation [47].
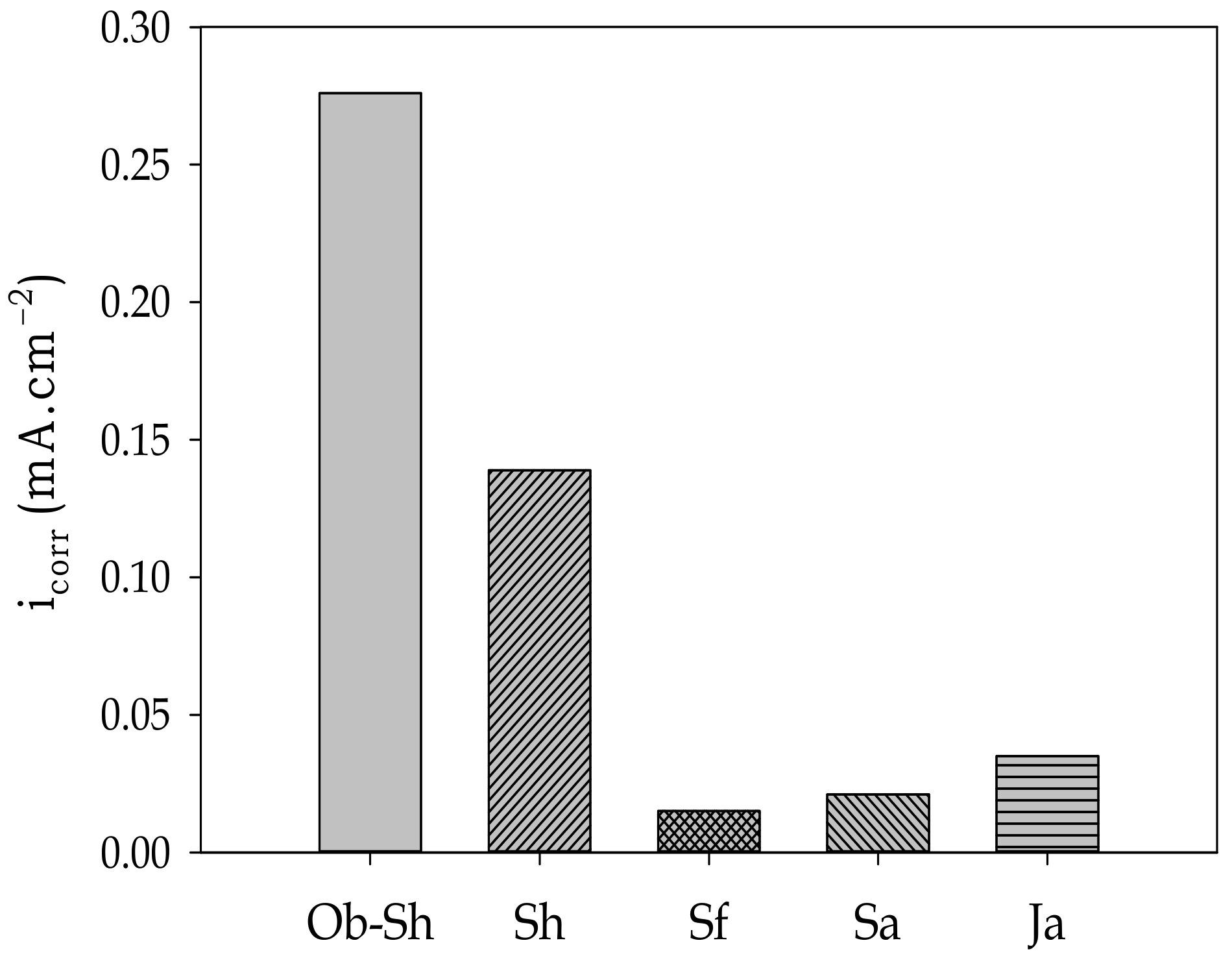
The value varies with the type of soil solution, according to Figure 14, and the corrosion level of the studied soil solutions can be written in the following order:
Ob-Sh > Sh > Ja > Sa > Sf
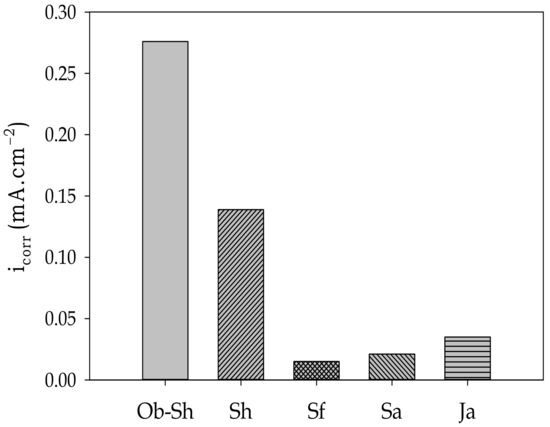
Figure 14.
Variation in the value of icorr with the studied Jeddah soil solutions.
Good consistency was observed between the aforementioned order and that obtained from EIS.
3.2.4. Comprehensive Assessment of Soil Corrosivity
Soil corrosiveness results from the synergistic impact of various variables because soil is a complex system of constituents and properties. The essential variables are soil ER, , . The following outline suggests how each variable affects soil corrosivity [38].
- ER: Soil electrical resistivity measures how easily an electron can flow through the soil. Corrosion reactions occur more quickly in soils with a low resistance to electron flow and more slowly in soils with high resistivity.
- : Chloride ions are classified as aggressive ions because they participate directly in the electrochemical reactions that cause corrosion. Chloride degrades the stable, protective films that can naturally form on the surfaces of some metals, exposing the unprotected metal to further corrosion.
- Sulfates are generally considered more friendly in their corrosive actions toward carbon steels than chloride ions are. When combined with anaerobic sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB), the influence of sulfates can represent a significant threat to metallic materials because the sulfates are reduced to extremely corrosive sulfides.
- : Soils have a wide range of acidity, ranging from pH 2.5 to 10. Because pH levels of 5 or lower can cause extreme corrosion rates and premature pitting of metallic objects, a neutral pH of approximately 7 is preferred to reduce the risk of damage.
Moreover, Table 6 shows how the ER, and soil pH affect the degree of corrosivity of buried steel [48]. Notably, the concentration of chloride ions is not explicitly included in the table but can be considered implicitly included in the effect of electrical resistance. By comparing the chemical analysis data of the studied soil solutions (Table 2) and the corresponding degree of corrosivity (Table 6), the following comprehensive assessment for each soil solution studied can be written as follows:
| ER | pH | Final Assessment | ||
| Ob-Sh | Strong corrosive | Corrosive | Neutral | Strong corrosive |
| Sh | Strong corrosive | Corrosive | Neutral | Strong corrosive |
| Sf | Noncorrosive | Noncorrosive | Moderately corrosive | Noncorrosive |
| Sa | Noncorrosive | Noncorrosive | Noncorrosive | Noncorrosive |
| Ja | Noncorrosive | Noncorrosive | Neutral | Noncorrosive |

Table 6.
Relationship between soil variables (ER, and pH) and corrosivity degree, data from [48].
The final evaluation of the studied soil corrosivity degree was written according to the standards of Geotechnical Engineering (GB50021–94) [49], which can be summarized as follows: (i) the soil solutions of Ob-Sh and Sh were evaluated to be very corrosive because one factor represents strong corrosivity; (ii) the remaining soil solutions (Sf, Sa, Ja) were evaluated as noncorrosive because the two variables are noncorrosive and not strongly corrosive. On the basis of previous results, the aggressive behavior of the Ob-Sh and Sh soils prompted this study to implement precautionary measures to prevent their aggressive behavior. These findings provide an impetus for further research in this area.
4. Conclusions
The corrosion behavior of CSX36 in selected soil solutions in different soil environments in Jeddah city at an ambient temperature (23 ± 1 °C) was studied using various techniques, such as WL and electrochemical tests (OCP, EIS, and PDP). Visual and microscopic (SEM) examinations of the surface morphology of the studied metals were evaluated and discussed. Analysis of the obtained data led to the following conclusions:
The general behavior of the CSX36 corrosion rates in all the studied soil solutions decreased with an increase in the immersion period over 80 weeks.
The corrosivity of the studied soils, based on weight loss measurements, obeys the order Sh > Ja > Ob-Sh > Sa > Sf, which agrees with the increased resistivity order.
For all the soil solutions studied, the shifted to more negative values, indicating that the corrosion process was under cathodic control.
The values of and 1/Rp tended to increase as the soil resistivity decreased, showing a proportional relationship between the CR and current density but an inversely proportional relationship with resistivity.
There was good consistency between the corrosivity order of the studied soil solutions obtained from the EIS and PDP measurements:
Ob-Sh > Sh >Ja > Sa > Sf
A comprehensive assessment of soil corrosivity based on various soil variables revealed that the soil solutions of both Ob-Sh and Sh are classified as extremely corrosive, while the rest of the soil solutions are classified as noncorrosive.
Author Contributions
E.A.N., A.H.A.-M.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing—original draft, Data curation. D.I.A.-M.: Conceptualization, Data curation. M.C.: Formal analysis, Investigation. A.C.: Visualization, Project administration, Review and editing. Y.G.K.: Visualization, Supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Fundamental-Core National Project of the National Research Foundation (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, Republic of Korea (2022R1F1A1072739).
Data Availability Statement
The data related to this work can be obtained from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ahmad, Z. Principles of Corrosion Engineering and Corrosion Control; Butterworth–Heinemann: Oxford, UK; Elsevier Science: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Roberge, P.R. Handbook of Corrosion Engineering; McGraw–Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 1–725. [Google Scholar]
- Fontana, M. Corrosion Engineering; McGraw–Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, S.; Al-Hadhrami, L.M. Web-based national corrosion cost inventory system for Saudi Arabia. Anti-Corros. Methods. Mater. 2014, 61, 72–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaker, V.; Palmer, J.D. Effect of Soil Characteristics on Corrosion; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1989; Volume 81. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, P. Transmission pipelines: How to improve their integrity and prevent failures. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Pipeline Technology Conference, Ostend, Belgium, 11–14 September 1995; Denys, R., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 683–706. [Google Scholar]
- National Energy Board. Stress Corrosion Cracking on Canadian Oil and Gas Pipelines; Report of the enquiry, MH–2–95; National Energy Board: Calgary, AB, Canada, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Yahaya, N.; Noor, N.M.; Din, M.M.; Nor, S.H.M. Prediction of CO2 Corrosion Growth in Submarine Pipelines. Malays. J. Civ. Eng. 2009, 21, 69–81. [Google Scholar]
- Handley-Sidhu, S.; Bryan, N.D.; Worsfold, P.J.; Vaughan, D.J.; Livens, F.R.; Keith–Roach, M.J. Corrosion and transport of depleted uranium in sand-rich environments. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1434–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Yang, H.; Xie, Y.F.; Yang, X. Mechanism and kinetics of halogenated compound removal by metallic iron: Transport in solution, diffusion and reduction within corrosion films. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, X.; Li, X.; Du, C.; Huang, Y.; Du, H. Characterization of corrosion products formed on the surface of carbon steel by Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2009, 40, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Wang, D.; Yu, C.X.; Zong, Y.; Wu, M. Effect of HCO3− Concentration on the Corrosion Behaviour of X80 Pipeline Steel in Simulated Soil Solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12, 9565–9574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Survey Division Staff. Soil Survey Manual; U.S Department of Agriculture Handbook; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, C.; Alonso, C.; Sarŕa, J. Corrosion rate evolution in concrete structures exposed to the atmosphere. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2002, 24, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, L.X.; Du, C. Effect of environmental factors on electrochemical behavior of X70 pipeline steel in simulated soil solution. J. Iron. Steel. Res. Int. 2009, 16, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.M.; Wu, Y.H.; Luo, S.X.; Sun, C. Effect of soil compositions on the electrochemical corrosion behavior of carbon steel in simulated soil solution. Mater. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2010, 41, 228–233. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, H.Y.; Cheng, Y.; Shan, H.T.; Zhang, L.X.; Sun, D.B. Corrosion behaviors of X80 pipeline steel in different simulated alkaline soil solution. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 189, 4261–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, H.Y.; Cheng, Y.; Shan, H.T.; Sun, D.B. Corrosion behavior of X80 steel in different simulated soil solution. J. Mater. Eng. 2012, 2, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lins, V.D.F.C.; Ferreira, M.L.M.; Saliba, P.A. Corrosion resistance of API X52 carbon steel in soil environment. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2012, 1, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansode, V.M.; Vagge, S.T.; Kolekar, A.B. Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of Steel Pipe in Alkaline Soil. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2015, 2, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Yang, F.; Ma, W.; Wang, K.; Zhao, X. Electrochemical corrosion behaviors of the X90 linepipe steel in NS4 solution. Nat. Gas. Ind. B. 2016, 3, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vectorstock. Detailed Map Poster of Jeddah City Linear Print Vector Image. Available online: https://www.vectorstock.com/40651973 (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Oguzie, E.E.; Agochukwu, I.B.; Onuchukwu, A.I. Monitoring the corrosion susceptibility of mild steel in varied soil textures by corrosion product count technique. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2004, 84, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, F.H. Some recent experience with the scanning electron microscope in corrosion research. J. Microsc. 1984, 133, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Z.; Xiao, K.; Dong, P.; Dong, C.; Wei, D.; Li, X. Effect of iron ion diffusion on the corrosion behavior of carbon steels in soil environment. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 40544–40553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benarie, M.; Lipfert, F.L. A general corrosion function in terms of atmospheric pollutant concentrations and rain pH. Atmos Environ. 1986, 20, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natesan, M.; Venkatachari, G.; Palaniswamy, N. Kinetics of atmospheric corrosion of mild steel, zinc, galvanized iron and aluminium at 10 exposure stations in India. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 3584–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Guo, Z.W.; Wang, D.; Li, R.; Wu, M.; Zong, Y.; Wang, Y.C. Synergistic effect between chloride and sulfate reducing bacteria in corrosion inhibition of X100 pipeline steel in marine environment. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2019, 14, 2693–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Kim, Y.G.; Jeon, K.S.; Kho, Y.T. Microbiologically influenced corrosion of underground pipelines under the disbonded coatings. Met. Mater. Int. 2000, 6, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandkumar, B.; George, R.P.; Maruthamuthu, S.; Parvathavarthini, N.; Mudali, U.K. Corrosion characteristics of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) and the role of molecular biology in SRB studies: An overview. Corros. Rev. 2016, 34, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasim, M.; Djukic, M.B. Long–term external microbiologically influenced corrosion of buried cast iron pipes in the presence of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB). Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 115, 104657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tres, G.; Saborío, E.; Urruchurtu, J.; Malo, J. Electrochemical Evaluation of Pipelines Materials of the Miravalles Geothermal Field in Costa Rica. Port. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 25, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, A.H.S.; Gomes, J.A.C.P. Environmentally induced cracking of API grade steel in near-neutral pH soil. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2009, 31, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, G.; Wu, W.; Qiao, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Effect of pH and chloride on the micro-mechanism of pitting corrosion for high strength pipeline steel in aerated NaCl solutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 349, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsella, B.; Tan, Y.J.; Bailey, S. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and surface characterization techniques to study carbon dioxide corrosion product scales. Corrosion 1998, 54, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hladky, K.; Callow, L.M.; Dawson, J.L. Corrosion rates from impedance measurements: An introduction. Br. Corros. J. 1980, 15, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbalat, M.; Lanarde, L.; Caron, D.; Meyer, M.; Vittonato, J.; Castillon, F.; Fontaine, S.; Refait, P. Electrochemical study of the corrosion rate of carbon steel in soil: Evolution with time and determination of residual corrosion rates under cathodic protection. Corros. Sci. 2012, 55, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, E.; Al-Moubaraki, A.H. Influence of soil moisture content on the corrosion behavior of X60 steel in different soils. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2014, 39, 5421–5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrami, K.; Ech-chebab, A.; Galai, M.; Ejbouh, A.; Hassi, S.; Benqlilou, H.; Ouaki, B.; Touhami, M.E. Evaluation of fly ash effect on the durability of prestressed concrete cylindrical pipe in aggressive soil by electrochemical method. Chem. Data Collect. 2021, 32, 100656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, R.; Ooi, A.; Tada, E.; Nishikata, A. Influence of the degree of saturation on carbon steel corrosion in soil. Corros. Sci. 2021, 189, 109568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Gaber, A.M.; Abd-El-Nabey, B.A.; Saadawy, M. The role of acid anion on the inhibition of the acidic corrosion of steel by lupine extract. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 1038–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Wang, Y.; Xie, R.; Han, P.; Bai, X. A method for evaluating corrosion of contaminated soil—Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) method. In Proceedings of the 8th International Congress on Environmental Geotechnics Volume 1: Towards a Sustainable Geoenvironment 8th, Hangzhou, China, 28 October–1 November 2018; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 716–723. [Google Scholar]
- Mjwana, P.; Mahlobo, M.; Babatunde, O.; Refait, P.; Olubambi, P. Investigation of Corrosion Behaviour of Carbon Steel in Simulated Soil Solution from Anodic Component of Polarisation Curve. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 430, 12039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baboian, R. Corrosion Tests and Standards: Application and Interpretation; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2005; Volume 20. [Google Scholar]
- He, B.; Han, P.J.; Lu, C.H.; Bai, X.H. Effect of soil particle size on the electrochemical corrosion behavior of pipeline steel in saline solution. Physicochem. Mech. Mater. 2015, 51, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Chang, H.; Qi, G.; Han, P.; He, B. The electrochemical corrosion behaviour of Q235 steel in soil containing sodium chloride. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2021, 16, 210925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, K.B.; Mansfield, F. On the So-Called Linear Polarization Method for Measurement of Corrosion Rates. Corrosion 1971, 27, 434–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzola, S.; Palomar-Pardavé, M.E.; Genesca, J. Effect of resistivity on the corrosion mechanism of mild steel in sodium sulfate solutions. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2003, 33, 1233–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Ai, Y.; Xiao, J.; Pan, D.; Li, W.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y. Impact of soil composition and electrochemistry on corrosion of rock-cut slope nets along railway lines in China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).