Abstract
To develop materials with a promising utilization future in the extreme environments of aerospace, the MoNbTa(WC)x composites were prepared by vacuum arc melting, of which the crystal structure, microstructure, and compression properties at elevated temperature were investigated. The MoNbTa(WC)x composites had eutectic structures that consisted of body-centered cubic (BCC) phase and eutectoid structures. The lamellar fine eutectoid structures were composed of BCC-structured high entropy alloy (HEA) Mo-Nb-Ta-W and FCC-structured carbide Mo-Nb-Ta-W-C. It was demonstrated that the ductility and elevated temperature strength was enhanced simultaneously combined with the effect of eutectic structures and WC addition. The optimal true yield strength and true fracture strain reached 1205 MPa and 29.2% in MoNbTa(WC)0.9 at 1200 °C, meanwhile, the fracture strain at ambient temperature was 13.96%. Distinct strain hardening was observed at the initial deformation stage of MoNbTa(WC)0.9 at 1200 °C. The compression performances of MoNbTa(WC)x were superior in comparison with most refractory high entropy alloys.
1. Introduction
High-performance materials have always been in high demand in aerospace, marine, extreme operations, and many other fields that require extremely high performance of parts and materials. Ordinary alloy materials are difficult to meet the performance requirements under these extreme conditions, and the emergence of high-entropy alloys [1,2,3] has created a new situation of high-performance materials. Unlike traditional alloys which are composed of a single main element, high entropy alloys are multi-main element alloys with a high entropy effect, lattice distortion effect, hysteresis diffusion effect, and “cocktail” effect, which exhibit high hardness [4], high wear resistance, low-temperature ductility [5], and excellent resistance to high-temperature oxidation and corrosion [6,7]. The refractory high-entropy alloys composed of elements such as NbMoTaW, HfNbTaZr, and CrMoNbTa are gradually being used because of their excellent material properties [8,9,10,11]. Since then, many refractory high entropy alloys (RHEAs) have been gradually reported by many other researchers. Table 1 lists the common refractory high-entropy alloys and their mechanical properties.
RHEAs are an important branch of high-entropy alloys, which have been considered substitutes for high-temperature structural materials in the extreme aerospace realm due to their excellent yield strength, thermal stability, and softening resistance at elevated temperatures. However, the mismatch between exceptional strength at high temperatures and favorable ductility at ambient temperature hamper the application of RHEAs [1,8,9,12]. For instance, TiAlVNbMo and TaNbHfZrTi exhibited exceptional strength at elevated temperatures but limited ductility at ambient temperatures [13,14]. To achieve good matching of plasticity and strength at room temperature (RT) while maintaining favorable strength at high temperature (HT), the scheme of metalloid substitution to strengthen metals has been devised recently. For high entropy alloys (HEAs), the composition space of solid solution can be effectively expanded by the addition of elements and thus showing enhanced mechanical properties of materials. Daixiu Wei et al. utilized Si as the substitutional element for Mn based on Co20Cr20Fe20Ni20Mn20 Cantor alloy, it was indicated that the metalloid solutes can improve strength by increasing local lattice distortion and short-range chemical inhomogeneity while preventing dynamic recovery by reducing stacking lamellar dislocation energy and promoting partial dislocation-mediated plastic activity, thus achieving strong and ductile synergy of the material [15]. Zhengqi Wang et al. added metalloids B and C to the MoNbTaW RHEA alloy, and the doped B and C elements could preferentially replace oxygen at the grain boundaries of the material and promote stronger electronic interactions with the host metal, which could effectively alleviate grain boundary brittleness and change the fracture morphology, and thus enabled the material achieved plasticity of >10% and strength of >1750 MPa [16]. The electron interaction between O and the host metal element reduces the strength of the material, leading to cracking. The addition of B and C inhibits the segregation of O, and the stronger electrons generated between additives and the metal enhance the cohesion of the material, which facilitates the strengthening of grain boundaries in the material and inhibits the generation of cracks in the material. Due to the solid solution strengthening effect, the yield strength, room temperature strength, plasticity, as well as high-temperature strength of the material increases significantly with the increase in B content in the grains. Rizi et al. added C and Mo to Fe40Mn40Co10Cr10HEA and studied HEAs at room temperature (RT) and low temperature (CT). The simultaneous synergistic effect of twinning-induced plasticity/phase-change-induced plasticity in Fe39.5Mn40Co10Cr10C0.5 enabled the material to exhibit excellent strength/ductility combinations (1022 MPa/~110%) at 77 K. The HEAs were investigated at RT and CT by alloying with Mo or C to modify the SFE, the frictional stress of cross-slip, and the Gibbs free energy of phase transition [17]. Mehmood et al. added different amounts of SiC to CoCrFeNi with FCC structure and found that compared with the conventional high entropy alloy, the balance between strength and ductility could be effectively improved by adjusting the SiC content [18]. Qin Xu added different amounts of Si to NbMoTiVSix and found that with the increase in Si, the yield strength and ultimate strength of the alloy increased from the initial 1141.5 MPa and 1700.1 MPa to 2093.1 MPa and 2374.7 MPa, respectively, and the breaking strain decreased from 24.7% to 11.0%, and the comprehensive properties of the material were significantly improved [19]. The BCC solid solution phase caused inhomogeneous nucleation on the basis of the silicide phase, and it grew up as the temperature decreased. Segregation occurs at the grain boundaries because of the low solubility of Ti and Si in the BCC solid solution. Ti and Si eutectic formed at the grain boundaries, and it increased with the addition of silicon. The high-strength eutectic organization and fine grains can effectively impede the dislocation movement, thus preventing the alloy from further deformation and improving the mechanical properties of the material. Anil Kumar added Si to AlCoCrCuFeNi, it was found that when Si content increased from 0 to 0.9, the mismatch entropy increased, which facilitates the BCC phase formation over the FCC phase. The mixing elements of Si and other elements in the composition had higher negative enthalpy, and the wear resistance of the material was significantly improved [20]. Therefore, the addition of such metals can improve the ductility of refractory or high-temperature alloys.
It was demonstrated that small-sized metalloids can replace oxygen at grain boundaries and promote electronic interactions with host metals to alleviate grain boundary brittleness. RHEAs composed of refractory elements (such as Mo, Nb, W, Ta, V, and Zr) have superior HT strength due to their high melting point. In this work, to achieve exceptional strength at elevated temperature and proper ductility at ambient temperature in lieu of normal trade-off, metalloid C was added to MoNbTaW RHEA to prepare MoNbTa(WC)x composites. The phase composition, microstructures, and mechanical properties at elevated temperatures were studied, we found that the addition of small-sized C promoted the formation of eutectic structures and strain hardening during the compression test at elevated temperature and improved the ductility at ambient temperature.

Table 1.
Yield strengths (σa), fracture strength (σb), hardness (HV), plastic strain (εp), and fracture strain (εb) of HEAs at HT/RT.
Table 1.
Yield strengths (σa), fracture strength (σb), hardness (HV), plastic strain (εp), and fracture strain (εb) of HEAs at HT/RT.
| RHEAs | Phase Structure | Manufacturing Rote | σa, σb, HV/MPa | εp, εb/% | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NbMoTiVSi0.1(RT) | BCC + M5Si3 | Arc melting | 1141.5(σa) | 24.7(εp) | [15] |
| NbMoTiVSi0.5(RT) | BCC | Arc melting | 2093.1(σa) | 11.0(εp) | [15] |
| NbMoTaWB0.5(RT) | BCC | Arc melting | 1780(σb) | >10(εp) | [16] |
| NbMoTaWC0.5(RT) | BCC | Arc melting | 1790(σb) | 9(εp) | [16] |
| NbMoTaWC0.15B0.5(HT) | BCC | Arc melting | 700(σa) | - | [16] |
| TaNbVTiAl0.2(RT) | BCC | PM | 2217(σb) | 10(εp) | [21] |
| TaNbVTiAl0.4(RT) | BCC | PM | 2054(σb) | 9(εp) | [21] |
| TaNbVTiAl0.6(RT) | BCC | PM | 1810(σb) | 5.5(εp) | [21] |
| NbTaTiV/Ti-C-O(RT) | BCC | MA + SPS | 1510(σa) | ~10(εp) | [22] |
| HfNbTiVSi0.5(RT) | BCC + silicide | IM | 1399(σa) | 10.9(εp) | [23] |
| HfNbTiVSi0.5(HT) | BCC + silicide | IM | 240(σa) | >50(εp) | [23] |
| TiZrNbWMo(HT) | BCC + β | Laser cladding deposition | 1000(HV) | - | [24] |
| W0.16NbMoTa(HT) | BCC | Laser cladding deposition | 476 ± 12.9(HV) | - | [25] |
| W0.33NbMoTa(HT) | BCC | Laser cladding deposition | 485.3 ± 8.7(HV) | - | [25] |
| W0.53NbMoTa(HT) | BCC | Laser cladding deposition | 497.6 ± 5.6(HV) | - | [25] |
| WNbMoTa(HT) | BCC | Laser cladding deposition | 530(σa) | 8.5 (εp) | [25] |
| Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 | BCC | Arc melting | 548(σa) | - | [9] |
| V20Nb25Mo25Ta25W25(HT) | BCC | Arc melting | 842(σa) | 19(εp) | [9] |
| Re0.5NbMoTaW(HT) | BCC | Arc melting | ~567 (HV) | ~7.01(εp) | [26] |
| ReNbMoTaW(HT) | BCC | Arc melting | ~536 (HV) | ~4.22(εp) | [26] |
| ReMoTaW(HT) | BCC | Arc melting | ~640(HV) | ~5.69(εp) | [27] |
| NbNiTaTiW(HT) | BCC + μ | Arc melting | 439 ± 9(HV) | - | [28] |
| HfNbTaTiZrW(HT) | BCC1 + BCC2 | Arc melting | 409(σa) | >35(εp) | [29] |
| HfNbTaTiZrMoW(HT) | BCC1 + BCC2 | Arc melting | 736(σa) | >35(εp) | [29] |
| MoNbTa(WC)0.7(HT) | BCC + FCC + α | Arc melting | 1068(σa) | 18.12(εp) | This work |
| MoNbTa(WC)0.9(HT) | BCC + FCC + α | Arc melting | 1205(σa) | 29.24(εp) | This work |
2. Materials and Methods
Nb, Mo, Ta, C, and W powders (99.9% pure) were used as raw materials. The metal powders were accurately weighed in the required proportions for the experiments using a precision electronic balance. The powders were mixed by mixing experimental equipment for 6 h to ensure that the metal powders were well mixed. The mixed powders were dried in a vacuum drying oven at 150 °C for 6 h before conducting the experiments. The composites with a nominal composition of MoNbTa(WC)x (x = 0.7 and 0.9 in a molar ratio, denoted as W0.7 and W0.9, respectively), were prepared by arc melting under a pure argon atmosphere on a water-cooled copper plate. The mass of the arc-melted ingots was about 20 g. The alloy was prepared in the form of buttons with a thickness of about 5–7 mm and a diameter of about 14–20 mm.
To avoid inner void and improve chemical homogeneity, the specimens were remelted five times and turned over between each melting, and kept as liquid for approximately 8 min during each melt. After melting and heat treatment, the cast alloy buttons are sliced, fitted, and polished. Crystal structures were measured using X-ray diffraction (XRD, D8 Advance, Bruker AXS, Karlsruhe, Germany) with scanning angle (2θ, 4°/min) ranging from 20° to 140°. The microstructure and phase composition of the composites were studied via electron microprobe (EPMA, JXA-8230, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with energy-dispersive (EDS) detectors after etching using the distilled water, hydrofluoric acid, and nitric acid (VH2O:VHF:VHNO3 = 2:1:1). Four points were randomly selected from each area for point scanning.
Compression tests were performed using cylinder specimens (Φ 4 × 6 mm) on the Gleeble-2000 thermal simulator (Gleeble-2000, DSI, Poestenkill, NY, USA) at 800 °C and 1200 °C. The heating rate was 200 °C/min and the holding time was 300 s. Afterwards the specimens were compressed at the strain rate of 1 × 10−3 s−1 until the samples were cracked or the strain reached 35%. Three specimens were tested at each temperature to ensure data reproductivity. The average of the three measurements is used as the final measurement result when errors are excluded.
3. Results and Discussion
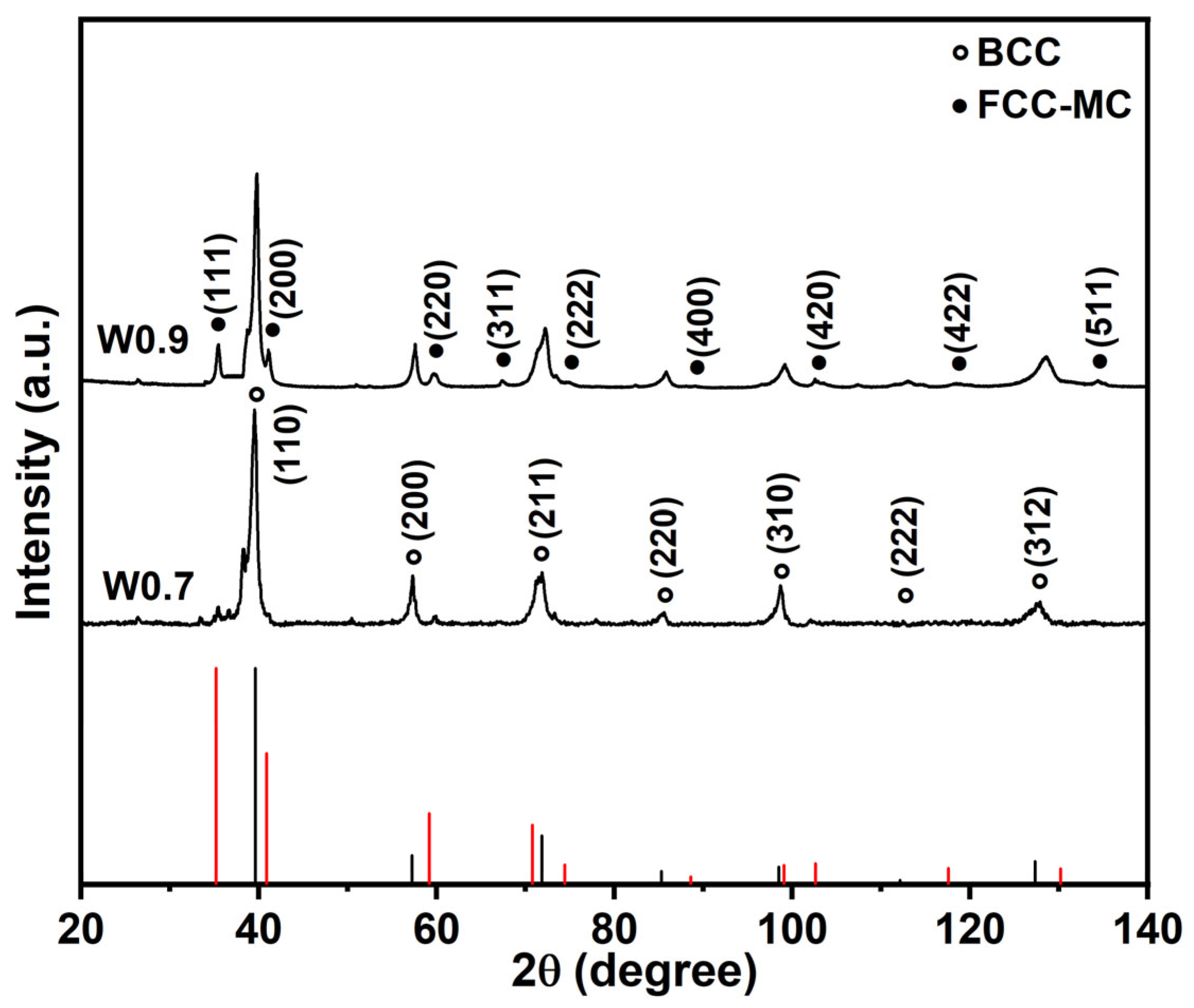
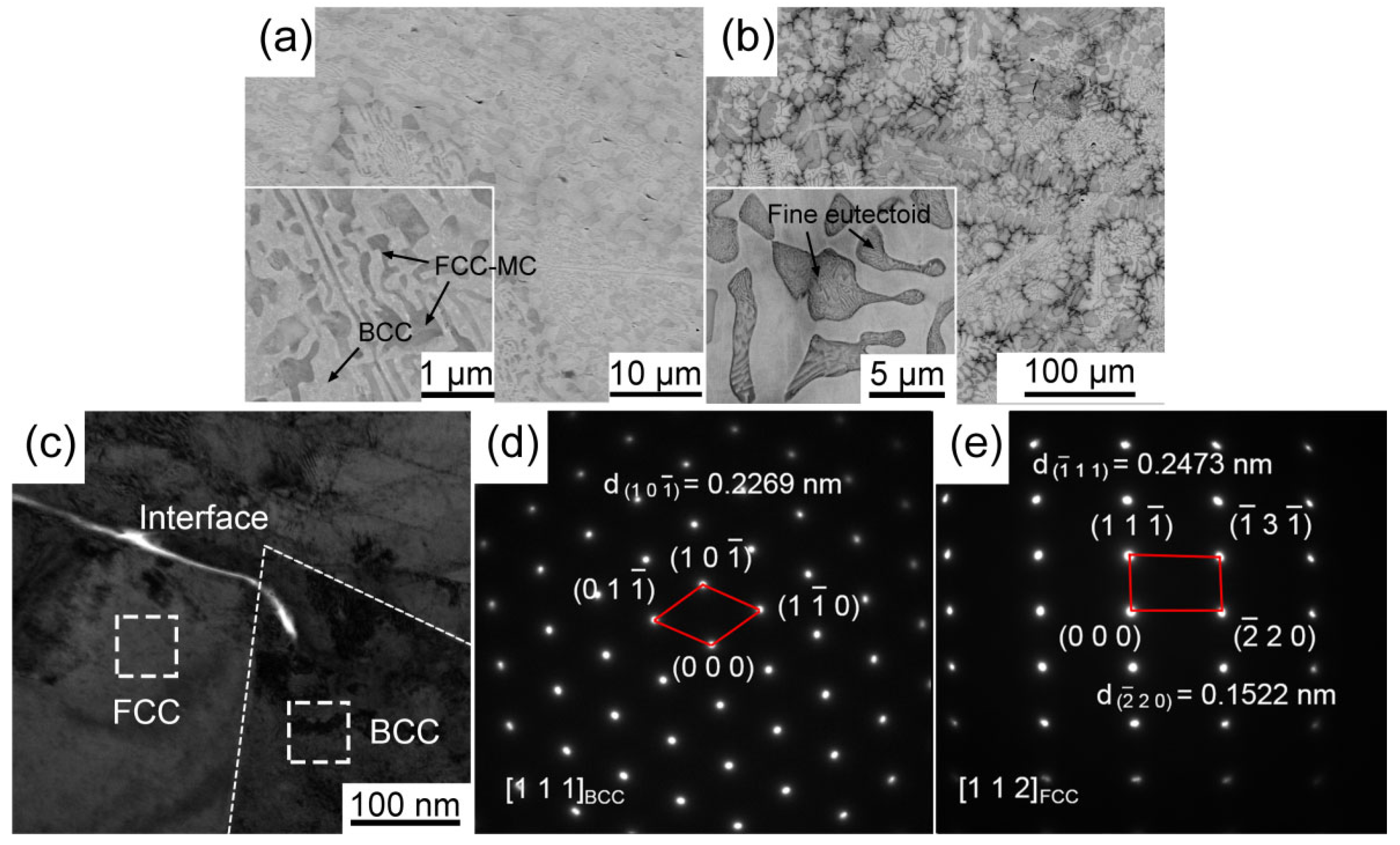
The phase composition and microstructures of MoNbTa(WC)x composites were characterized by XRD, BSE, and TEM, respectively. The XRD patterns of MoNbTa(WC)x composites shown in Figure 1 demonstrated that the MoNbTa(WC)x composites consisted of two phases with BCC lattice and FCC lattice. The carbide solid solution composed of Mo, Nb, Ta (WC) is an MC type of carbide, and the peak strength of the MC phase increased with the increase in WC addition, indicating that the content of the MC phase increased with the increase in WC addition. None of the diffraction peaks of the single element were detected in the XRD patterns, indicating severe lattice distortion in the MoNbTa(WC)x composites. Figure 2a,b represented the BSE images of W0.7 and W0.9 composites. The BSE images manifested eutectic structures composed of BCC phase and eutectoid structures. The fine lamellar eutectoid structures consisted of the BCC phase and FCC phase. The content of the FCC phase increased with the increase in WC addition. The α phase occupied the dark area in W0.9. The formation of eutectic structures was the result of C doping, which increased the local lattice distortion and grain boundaries and promoted interdendritic segregation of the FCC phase. The interface between the BCC phase and FCC phase can be distinguished clearly from the bright-field TEM images of W0.7 in Figure 2c. The BCC and FCC phases were identified by the selected area electron diffraction (SAED) experiment in Figure 2d,e, the index of the zone axis was []BCC and []FCC, respectively.
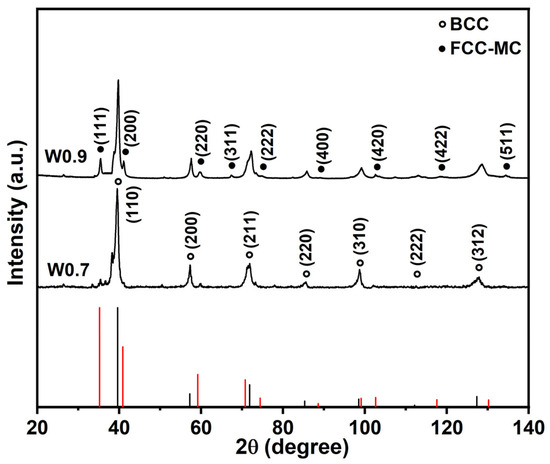
Figure 1.
XRD patterns of MoNbTa(WC)x composites.
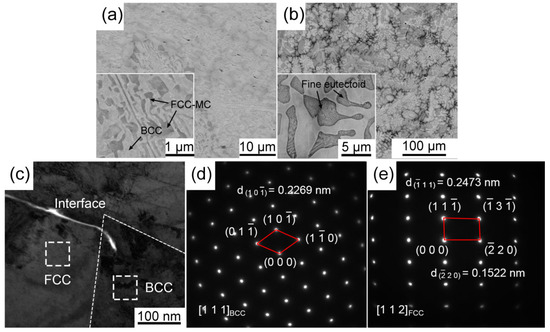
Figure 2.
The (a,b) BSE images of W0.7 and W0.9 composites, respectively, and (c) bright-field TEM images of W0.7, (d,e) SAED patterns of BCC and FCC phase, respectively.
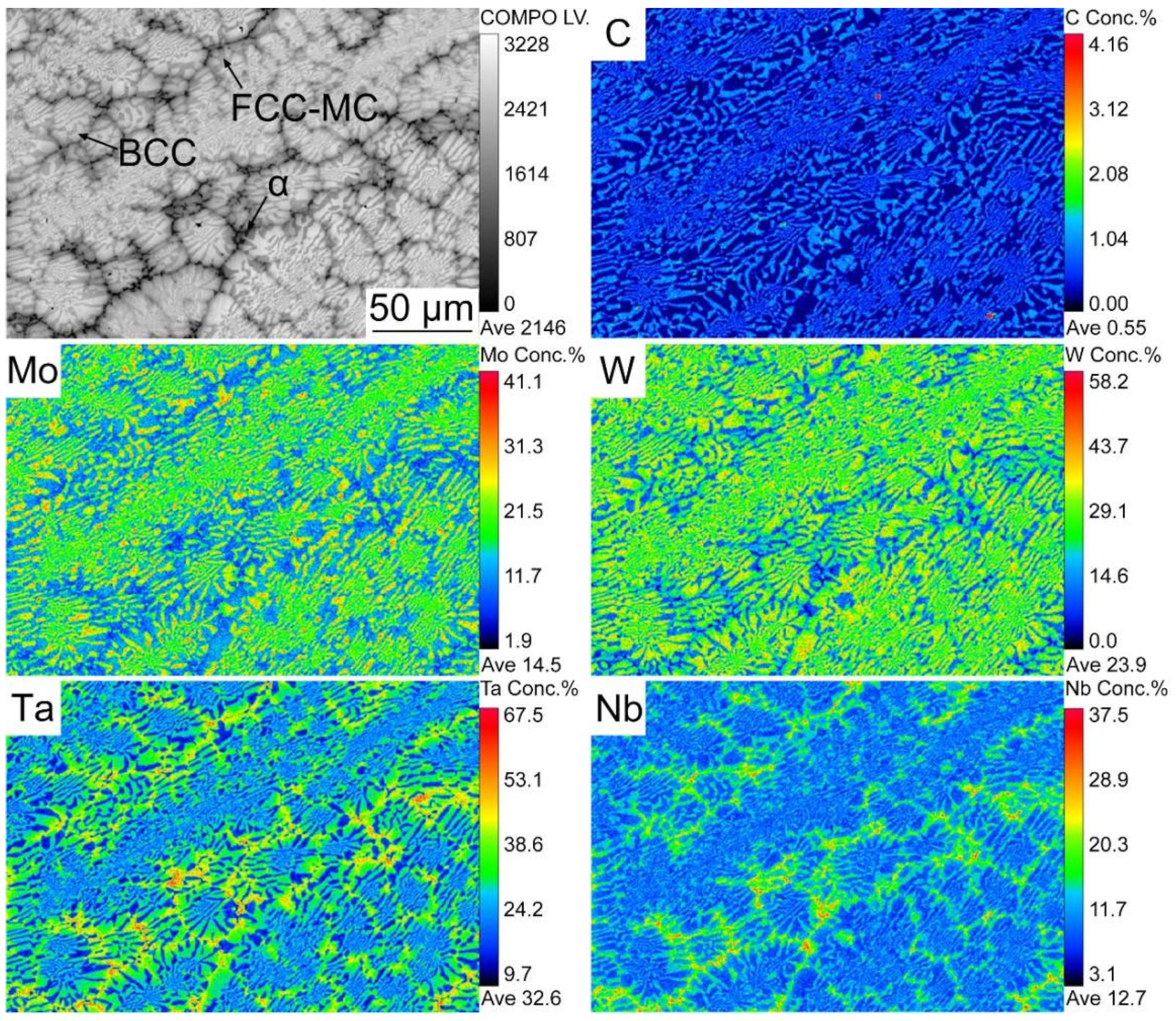
Figure 3 demonstrated the elemental distribution of the W0.9 composite provided by EMPA. The BCC phase was rich in Mo and W. Ta, Nb, and C were mainly distributed in FCC and α phases. The spot scanning data on the actual chemical composition were given in Table 2. The nominal compositions of the BCC phase, FCC phase, and α phase were recognized as Mo33.31Nb20.12Ta21.79W24.78, Mo8.09Nb21.34Ta26.83W7.26C36.49, and Mo4.30Nb37.04Ta19.97W1.89C36.80. It can be seen that Mo, W, Ta, and Nb were evenly distributed in the BCC phase. There was a segregation of Nb, Ta, and C in the FCC and α phase, and the segregation of Nb and C was more severe in the α phase. According to the phase diagram of the NbC, TaC, MoC, and WC, it was speculated that during the solidification, (MoNbTaW)2C (α phase) was firstly separated from the liquid phase, and then was decomposed to MoNbTaW (BCC phase) and (MoNbTaW)C (FCC phase) [30,31].
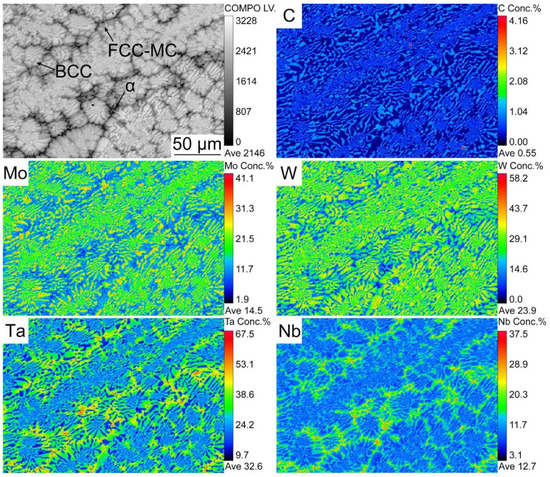
Figure 3.
The map scanning images of MoNbTa(WC)0.9 composite measured by EMPA.

Table 2.
The elemental composition of MoNbTa(WC)0.9 composite(at%).
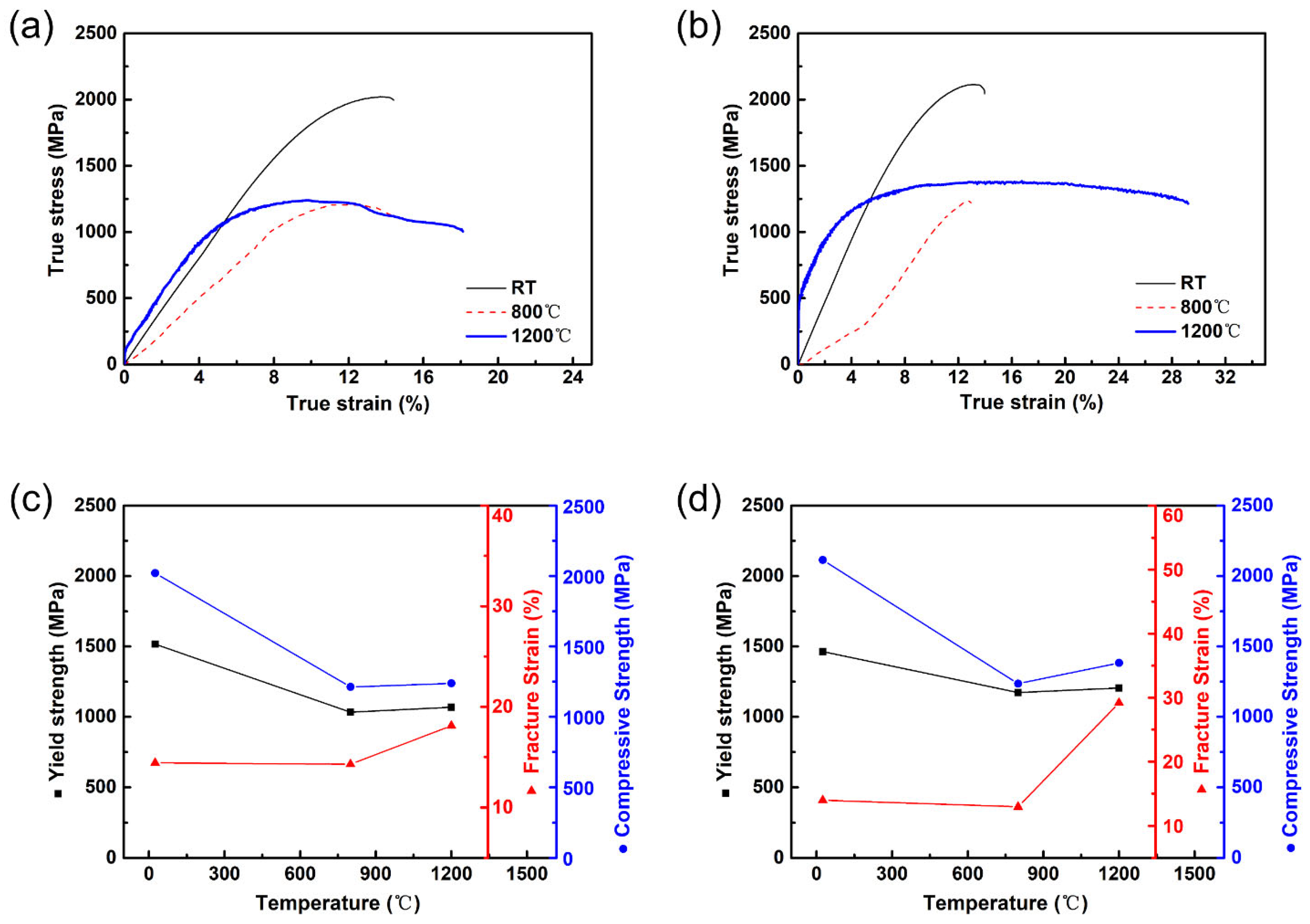
The true compressive stress–strain curves of W0.7 and W0.9 at different temperatures were shown in Figure 4a,b. The resulting yield strength (σ0.2), compressive strength (σm), and fracture strain (ε) were shown in Table 3. The fracture strain of W0.7 and W0.9 was 14.41% and 13.96%, respectively. The ductility of MoNbTa(WC)x has increased by about 10% with the addition of small-sized metalloid C compared with the fracture strain of MoNbTaW (about 3%). This might be attributed to grain boundary increment, and grain size reduction. Furthermore, the fine lamellar eutectic structures combined with the stiffer phase and ductile phase can prevent the propagation of cracks effectively. W0.7 and W0.9 exhibited ultra-high true yield strength higher than 1000 MPa at both 800 °C and 1200 °C. The true fracture strain of W0.7 and W0.9 was over 18% at 1200 °C. It should be noted that W0.7 and W0.9 represented distinct strain hardening at the initial deformation stage, which indicates that the strength of the composites will increase rapidly under slight strain at 1200 °C. With the doping of C with a small atom size, the stacking fault energy was decreased, and the dynamic recovery was restrained, resulting in a high strain hardening rate. In addition, we also compared mechanical properties with that of high-temperature refractory MoNbTaW, MoNbTaWV, NbMoCrTiAl, HfMo0.5NbTiV0.5Si0.7, and Re0.5MoNbW(TaC)0.5 composites et al. and it is clear from the graphs that MoNBTa(WC) materials have significantly higher yield strength.
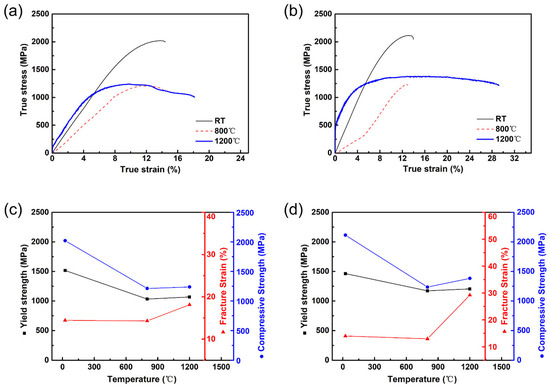
Figure 4.
The true strain–stress curves of (a) W0.7 and (b) W0.9 at different temperatures, temperature dependences of yield strength, compressive strength, and fracture strain of (c) W0.7 and (d) W0.9.

Table 3.
True compressive mechanical properties of the MoNbTa(WC)0.7 and MoNbTa(WC)0.9 at different temperatures.
The relationship between temperature and mechanical properties of W0.7 and W0.9 was represented in Figure 4c,d, respectively. The results show that the yield strength of W0.7 and W0.9 decreased 31.91% (from 1517 MPa to 1033 MPa) and 19.95% (from 1464 MPa to 1172 MPa) when the temperature increased from RT to 800 °C, which was mainly attributed to thermal softening. With the addition of WC, W0.9 exhibited superior thermal softening resistance compared with that of W0.7. It is speculated that more ceramic phases improved the heat endurance of the composites. The synergetic enhancement of strength and ductility was achieved when the temperature was raised from 800 °C to 1200 °C, and the improvement range was larger in W0.9, which was due to C doping and solid solution strengthening.
The traditional theoretic research of BCC metals was consulted [32,33], and it was speculated that the yield stress of RHEAs can be divided into the temperature-insensitive adiabatic component and the thermal activation component related to activation energy and temperature. As the temperature increases, the yield strength of the single-phase base alloy decreases quickly to the adiabatic plateau [34]. Therefore, the contribution of solution strengthening will gradually weaken as the temperature increases.
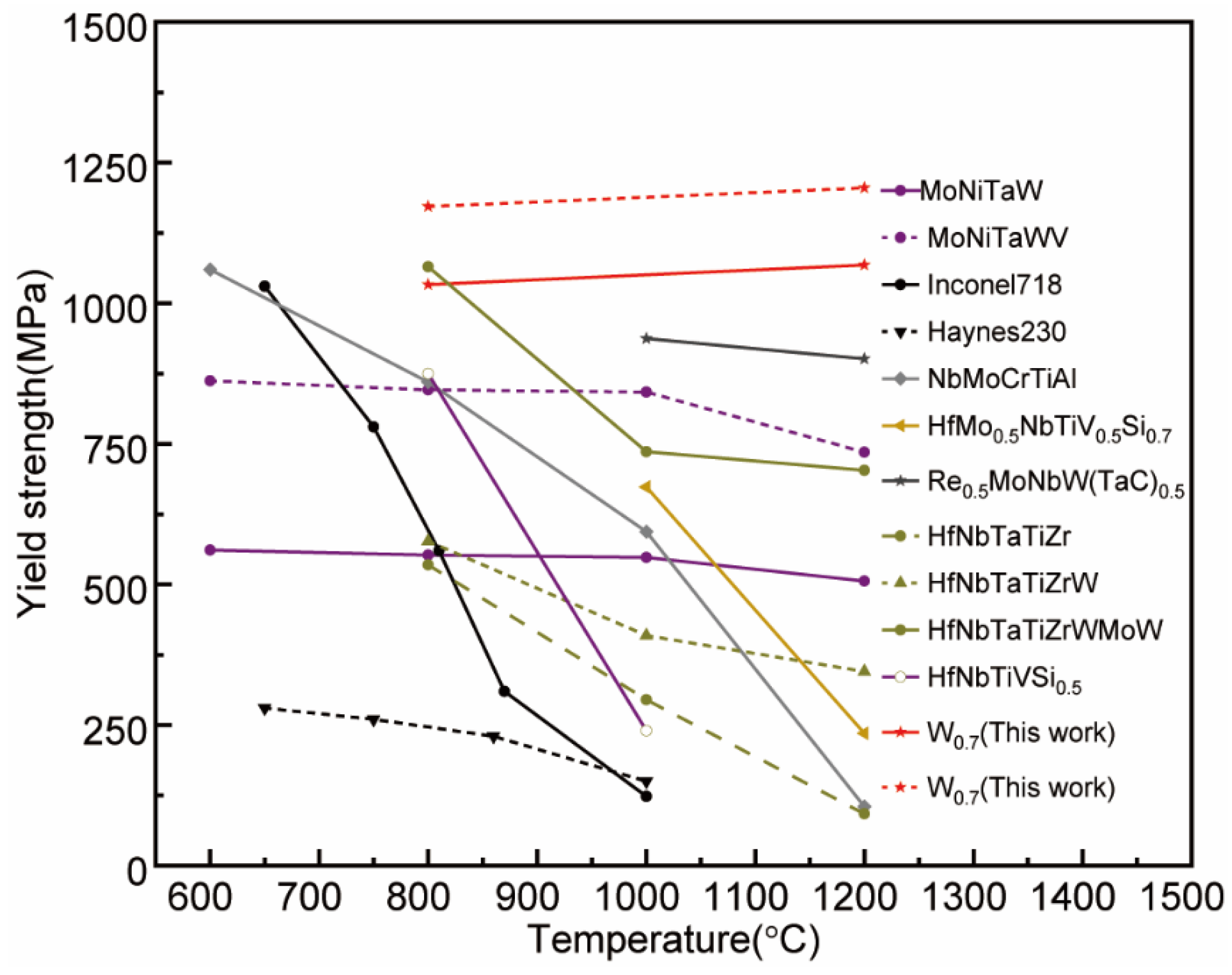
The comparison of compressive mechanical properties of a series of RHEAs, W0.7, and W0.9 at high temperatures was shown in Figure 5. W0.7 and W0.9 represented true yield strength at high temperatures, which was still higher than the engineering yield strength of the cited data. The outstanding hyperthermal mechanical properties of W0.7 and W0.9 were mainly attributed to precipitation strengthening and edge dislocation-mediated enhancement coming from atom size mismatch, which was unaffected by high temperature.
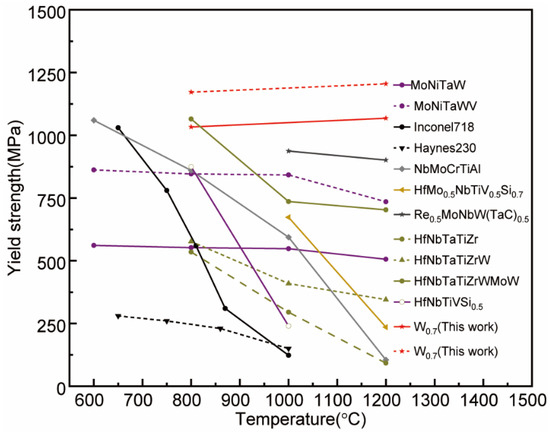
Figure 5.
Map of yield strength of various HEA matrix composites and RHEAs including W0.7 and W0.9 composites, the yield strength of which was true [8,9,23,25,26,28,29,30,31].
It can be seen from Figure 5 that the mechanical properties of the material at high temperatures are very different when different elements were added to different matrix materials, and these differences depend on the mechanism of action. For example, the addition of light elements such as Al to TaNbVTi-based RHEA can effectively reduce the density of the alloy and increase the specific strength of the alloy and a good TaNbVTi matrix material can lead to better plasticity [21]. The addition of non-metallic elements such as Si to the HfNbTiV-based RHEA can cause the stable distribution of silicides with ultra-high melting points and high-temperature strength in the BCC matrix (with the matrix elements Hf, Nb, Ti, V), which can enhance the plasticity of the matrix, and the high load-bearing capacity and plowing effect can improve the yield strength of the material [23]. The addition of the element Re introduced a ductile effect to the NbMoTaW-based RHEA, which improved the strength and toughness of W by impeding dislocation slip through fine grain strengthening and lowering the tough–brittle transition temperature of W. The combination of fine-grain strengthening and second-phase strengthening greatly improved the strength and ductility of the RexNbMoTaW alloy [26]. The addition of W/Mo to the HfNbTaTiZr-based RHEA can transform the BCC phase structure from a single phase to a double phase in HfNbTaTiZr, inducing the generation of phase boundaries, hindering dislocation slip, and mismatch between atoms. The modulus mismatch caused solid solution strengthening of the material, thus strengthening the alloy and enhancing the overall performance of the material [29,35,36,37].
In summary, RHEA usually has severe lattice distortion due to the different atomic radii of the mixed elements. The lattice distortion leads to the formation of a non-uniform elastic strain field, which has a strong interaction with cracks during loading. Microcracks expand mainly along the weakest grain boundaries in the as-cast substrate RHEA and form continuous intergranular fractures during loading. The addition of appropriate elements to HEA induced the formation of a eutectic organization of solid solution and hard phases, and the advantages of the eutectic organization such as low energy phase interface, fine controlled organization, and good high-temperature creep resistance can improve the performance of HEAs. In this experiment, as the volume fraction of the FCC-MC phase increased with the increase in WC addition, the yield rate and compressive strength increased, and the high entropy effect and rapid cooling of the as-cast organization improved the high thermal stability of the phase and inhibited the generation of phase transformation. The strengthening mechanism of MoNbTa(WC) was mainly second-phase strengthening and boundary strengthening. For the W0.7 and W0.9 MoNbTa(WC) composite materials, the inhibition of crystal dislocation and crystal interface migration by the FCC-MC phase and the fine grain strengthening caused by the BCC phase can enhance the strength and reduce the plasticity of the material. Therefore, the appropriate amount of WC addition can improve the strength and plasticity of the composites at the same time. It can be seen from Figure 5 that the W0.7 and W0.9 added MoNbTa (WC) materials prepared in this study have excellent hetero-mechanical properties than conventional HEAs materials, which have promising applications in the field of high-temperature structural materials.
4. Conclusions
Here, we investigated the mechanical properties of MoNbTa(WC)x (x = 0.7 and 0.9) composites with lamellar eutectic structures during compression tests at 800 °C and 1200 °C.
The lamellar eutectic structures of MoNbTa(WC)0.9 composite consisted of Mo33.31Nb20.12Ta21.79W24.78 BCC phase, Mo8.09Nb21.34Ta26.83W7.26C36.49 FCC phase, and Mo4.30Nb37.04Ta19.97W1.89C36.80 α phase. The intensity of FCC diffraction peaks increased with the increase in WC addition. None of the diffraction peaks of the single element was detected in the XRD patterns, indicating severe lattice distortion in the MoNbTa(WC)x composites. Mo, W, Ta, and Nb were evenly distributed in the BCC phase. There was segregation of Nb, Ta, and C in the FCC and α phase. (MoNbTaW)2C (α phase) firstly separated from the liquid phase, and then decomposed into MoNbTaW (BCC phase) and (MoNbTaW)C (FCC phase).
The eutectic organization of the composites consisted of the BCC phase and eutectic phase. The fine lamellar eutectic organization consisted of the BCC phase and FCC phase, the FCC phase was enhanced with the increase in WC addition, the eutectic structure was formed by C doping, which increased the local lattice distortion and grain boundaries, and promoted the inter-dendritic segregation of FCC phase.
The plasticity of MoNbTa(WC)x was increased by about 10% compared to that of MoNbTaW (about 3%), and the strains were at break of 14.41% and 13.96% for W0.7 and W0.9, respectively. MoNbTa(WC)0.9 exhibited ultra-high true yield strength above 1.3 GPa and true fracture strain over 29% at 1200 °C.
MoNbTa(WC)0.7 and MoNbTa(WC)0.9 represented distinct strain hardening at the initial deformation stage at 1200 °C. At elevated temperatures, the strengthening mechanism was mainly second-phase strengthening and edge dislocation-mediated enhancement coming from atom size mismatch for the contribution of the other strengthening mechanism was weakened as the temperature was raised.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.K. and X.W.; Methodology, K.K., Z.H., G.L. and Q.S.; Formal Analysis, L.Z.; Investigation, K.K., X.W., W.Z., P.L., Z.H. and G.L.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, K.K.; Writing—Review and Editing, X.W. and P.L.; Supervision, Q.S. and L.Z.; Funding Acquisition, K.K., G.L. and L.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Guangdong Major Project of Basic and Applied Basic Research [No. 2021B0301030001], the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2021YFB3802300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51932006 and 52001115), the project National United Engineering Laboratory for Advanced Bearing Tribology, Henan University of Science and Technology (No. 202001), the postdoctoral research grant in Henan Province (No. 202101008), the financial supports from the Doctorial Foundation of the Henan University of Technology (No. 2019BS053), Backbone Young Teacher Foundation of Henan University of Science and Technology (No. 21420153), and Chaozhou Branch of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (No. HJL202202A004).
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Yeh, J.-W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.-J.; Gan, J.-Y.; Chin, T.-S.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.C.; Qiao, J. High-Entropy Alloys (HEAs). Metals 2018, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Pradeep, K.G.; Deng, Y.; Raabe, D.; Tasan, C.C. Metastable high-entropy dual-phase alloys overcome the strength–ductility trade-off. Nature 2016, 534, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gludovatz, B.; Hohenwarter, A.; Catoor, D.; Chang, E.H.; George, E.P.; Ritchie, R.O. A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science 2014, 345, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, T.M.; Alfano, J.P.; Martens, R.L.; Weaver, M.L. High-temperature oxidation behavior of Al–Co–Cr–Ni–(Fe or Si) multicomponent high-entropy alloys. JOM 2015, 67, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplanche, G.; Volkert, U.F.; Eggeler, G.; George, E.P. Oxidation behavior of the CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. Oxid. Met. 2016, 85, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Miracle, D.B.; Chuang, C.P.; Liaw, P.K. Refractory high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Scott, J.M.; Miracle, D.B. Mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 refractory high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todai, M.; Nagase, T.; Hori, T.; Matsugaki, A.; Sekita, A.; Nakano, T. Novel TiNbTaZrMo high-entropy alloys for metallic biomaterials. Scr. Mater. 2017, 129, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Senkova, S.V.; Woodward, C. Effect of aluminum on the microstructure and properties of two refractory high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2014, 68, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Gao, M.C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Guo, S.M. Senary refractory high entropy alloy MoNbTaTiVW. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Scott, J.M.; Senkova, S.V.; Meisenkothen, F.; Miracle, D.B.; Woodward, C.F. Microstructure and elevated temperature properties of a refractory TaNbHfZrTi alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 4062–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ma, Z.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Tan, Y.; Cheng, X. Design of novel low-density refractory high entropy alloys for high-temperature applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 755, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, W.; Tsuru, T.; Lobzenko, I.; Jiang, J.; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, T.; Bae, J.W.; et al. Metalloid substitution elevates simultaneously the strength and ductility of face-centered-cubic high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2022, 225, 117571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, H.; Wu, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Yuan, X.; Chen, Q.; Wang, S.; et al. Solving oxygen embrittlement of refractory high-entropy alloy via grain boundary engineering. Mater. Today 2022, 54, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizi, M.S.; Minouei, H.; Lee, B.J.; Toroghinejad, M.R.; Hong, S.I. Effects of carbon and molybdenum on the nanostructural evolution and strength/ductility trade-off in Fe40Mn40Co10Cr10 high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 911, 165108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, M.A.; Shehzad, K.; Mujahid, M.; Bin Yaqub, T.; Godfrey, A.; Fernandes, F.; Muhammad, F.Z.; Yaqoob, K. Ceramic-reinforced HEA matrix composites exhibiting an excellent combination of mechanical properties. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Chen, D.Z.; Tan, C.Y.; Bi, X.Q.; Wang, Q.; Cui, H.Z.; Zhang, S.Y.; Chen, R.R. NbMoTiVSix refractory high entropy alloys strengthened by forming BCC phase and silicide eutectic structure. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 60, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dhekne, P.; Swarnakar, A.K.; Chopkar, M.K. Analysis of Si addition on phase formation in AlCoCrCuFeNiSix high entropy alloys. Mater. Lett. 2017, 188, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Guo, W.; Liu, B.; Fu, A.; Li, J.; Fang, Q.; Liu, Y. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of TaNbVTiAlx Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. Entropy 2020, 22, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, A.; Guo, W.; Liu, B.; Cao, Y.; Xu, L.; Fang, Q.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y. A particle reinforced NbTaTiV refractory high entropy alloy based composite with attractive mechanical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 815, 152466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a refractory HfNbTiVSi0.5 high-entropy alloy composite. Mater. Lett. 2016, 174, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, X.; Yu, X.; Li, J. Synthesis and characterization of refractory TiZrNbWMo high-entropy alloy coating by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 311, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Chen, Z.; Huang, S.; Lu, Z.; Yan, H. WxNbMoTa Refractory High-Entropy Alloys Fabricated by Laser Cladding Deposition. Materials 2019, 12, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Wei, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, P.; Luo, G.; Shen, Q. Microstructure and mechanical properties of RexNbMoTaW high-entropy alloys prepared by arc melting using metal powders. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 827, 154301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, B.; Luo, G.; Zhang, L. Microstructure and mechanical property of a novel ReMoTaW high-entropy alloy with high density. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2018, 77, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, N.A.; Segovia, S.; Gorsse, S.; Young, M.L. Characterization and Modeling of NbNiTaTiW and NbNiTaTiW-Al Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 4867–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ma, Z.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, X. Microstructures and mechanical properties of HfNbTaTiZrW and HfNbTaTiZrMoW refractory high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 803, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Jiang, S.; Wei, Q.; Kang, K.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Shen, Q. Microstructure and mechanical properties of MoNbW(TaC)x composites. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2021, 99, 105574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, G.; Zhang, L. Microstructure evolution, mechanical properties and strengthening mechanism of refractory high-entropy alloy matrix composites with addition of TaC. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 777, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, J.W. Some surprising features of the plastic deformation of body-centered cubic metals and alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1983, 14, 1237–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gypen, L.; Deruyttere, A. Thermally activated deformation in tantalum-base solid solutions. J. Less Common Met. 1982, 86, 219–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil Coury, F.; Kaufman, M.; Clarke, A.J. Solid-solution strengthening in refractory high entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2019, 175, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, R.L. Substitutional solution hardening. Acta Metall. 1963, 11, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labusch, R. A Statistical Theory of Solid Solution Hardening. Phys. Status Solidi (b) 1970, 41, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gypen, L.A.; Deruyttere, A. Multi-component solid solution hardening. J. Mater. Sci. 1977, 12, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).