Detection of Phase Transformation during Plastic Deformation of Metastable Austenitic Steel AISI 304L by Means of X-ray Diffraction Pattern Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
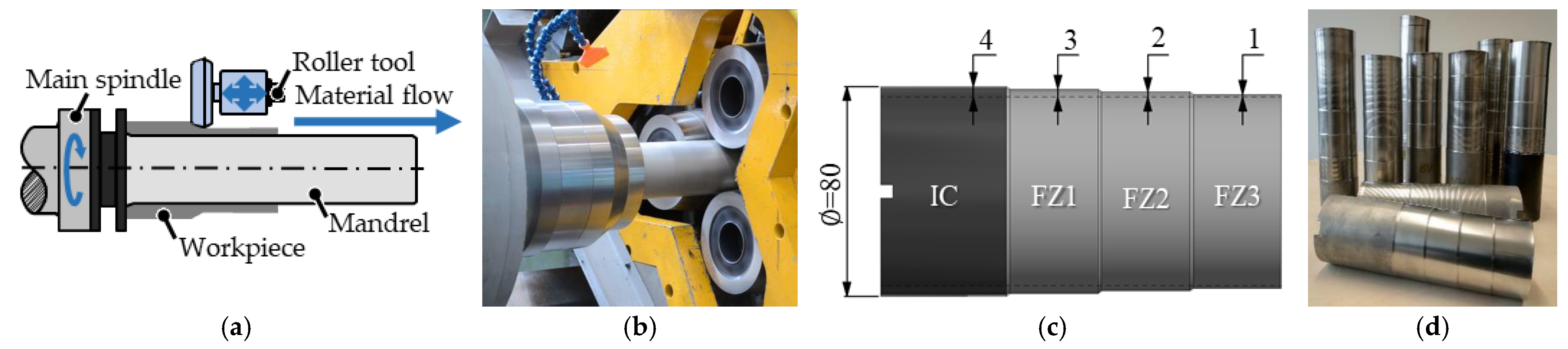
2.1. Specimens
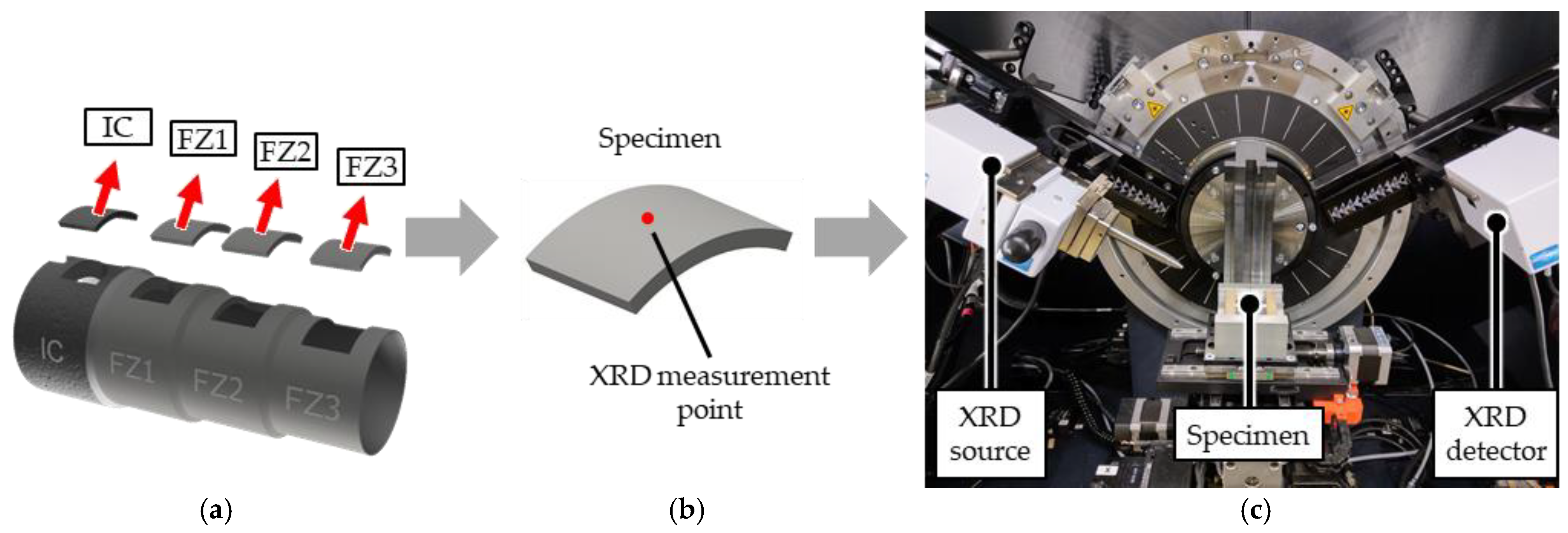
2.2. Characterization Methodologies
2.2.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Investigation
2.2.2. Macro- and Microhardness Tests
2.2.3. α′-Martensite Content
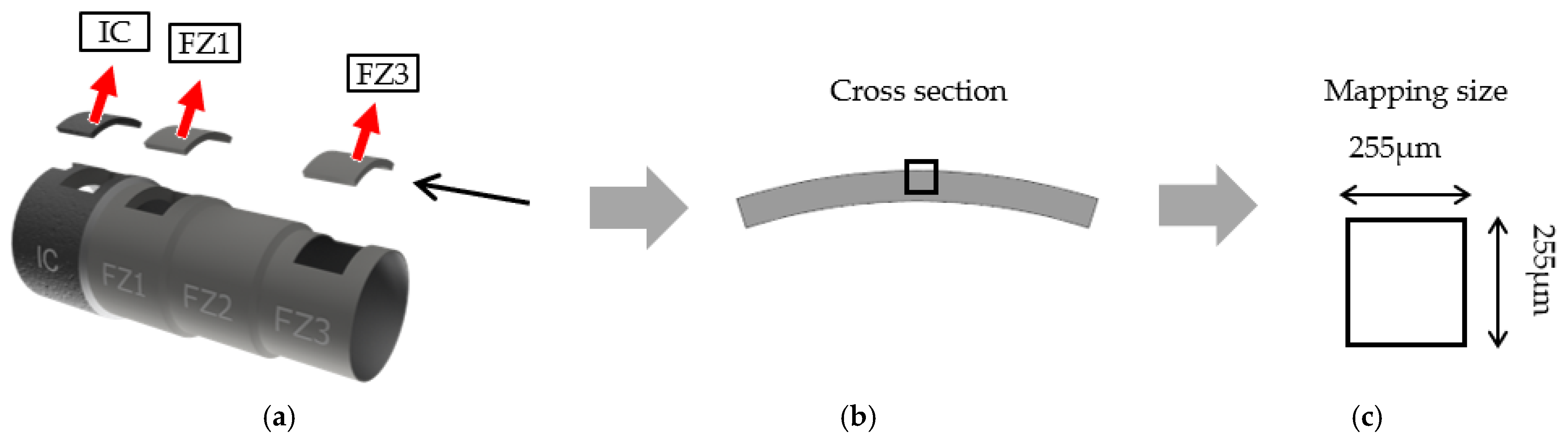
2.2.4. Microstructural Characterization by Means of Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), including Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD)
3. Results and Discussion
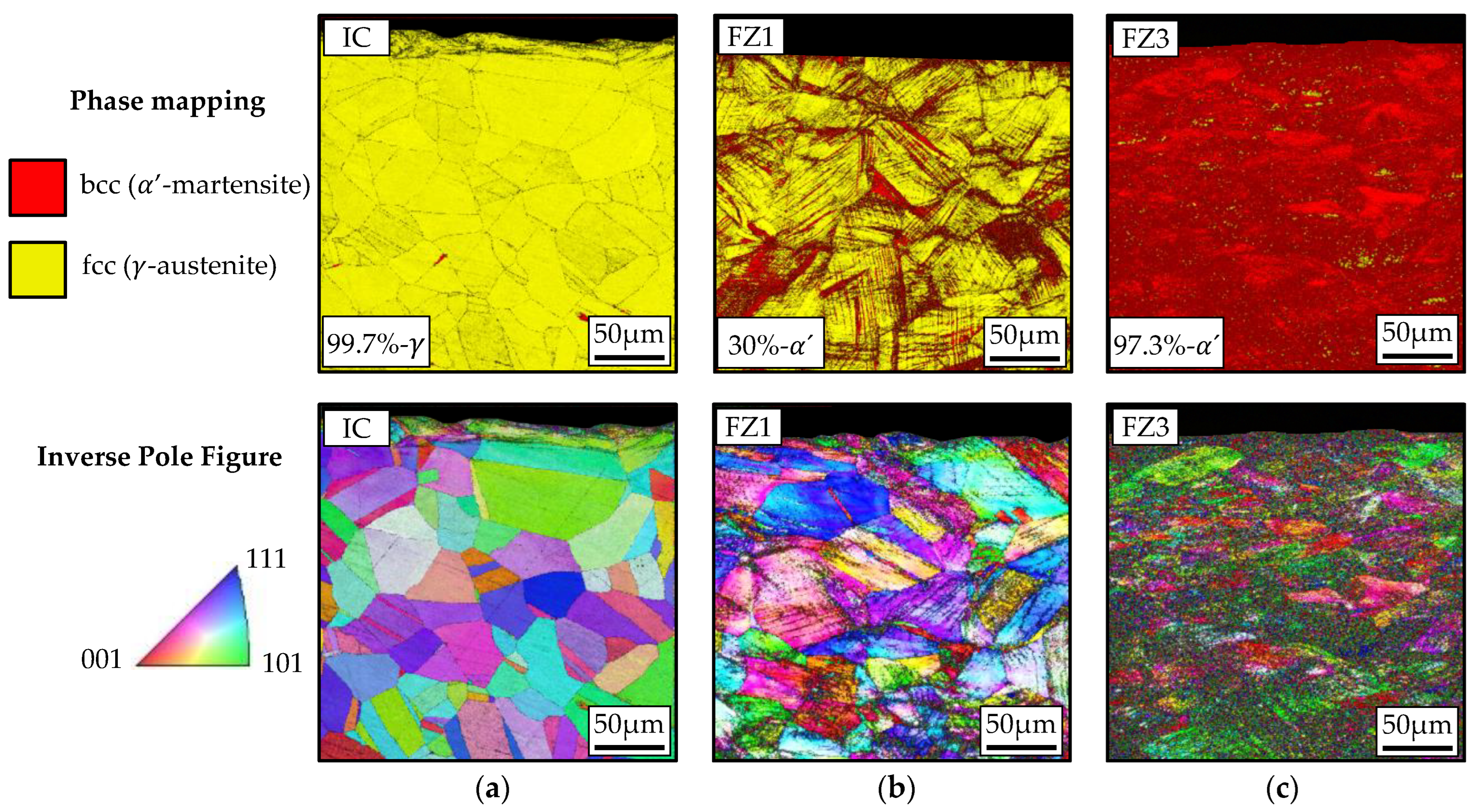
3.1. Microstructure Evolution by Means of Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD)
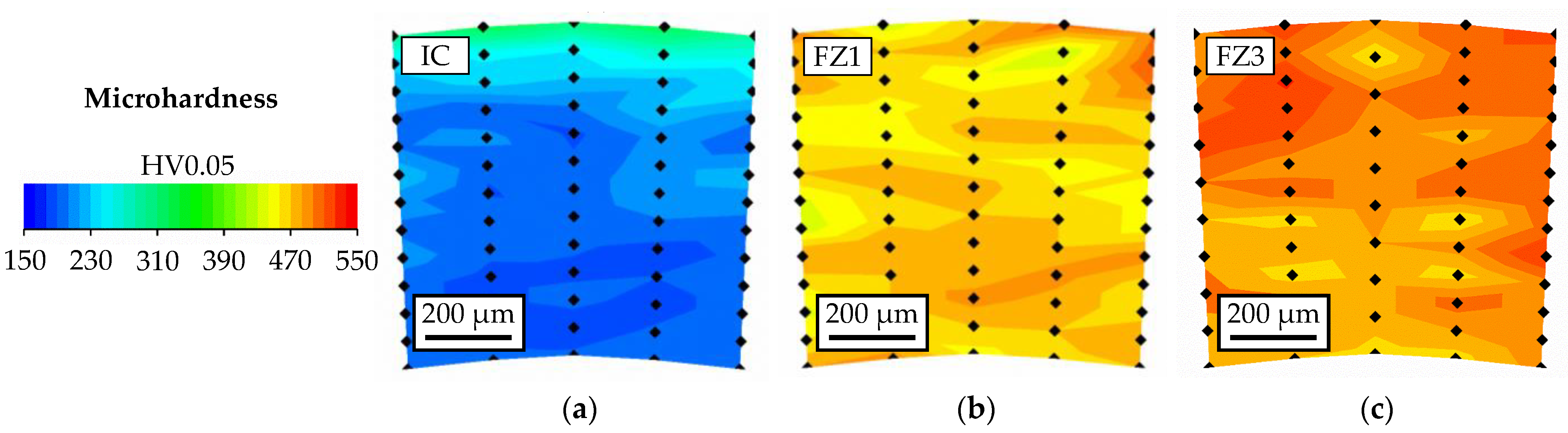
3.2. Microhardness Testing
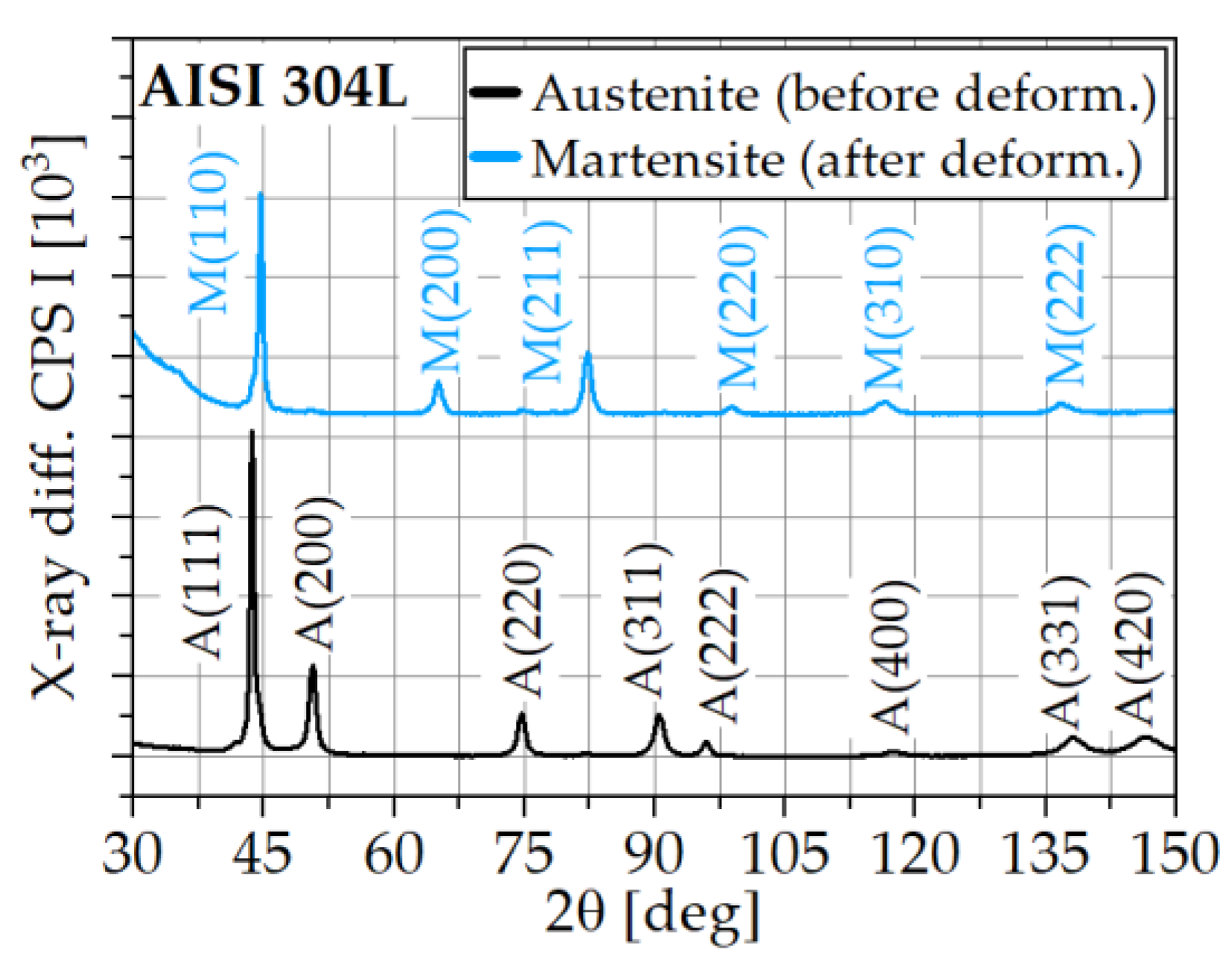
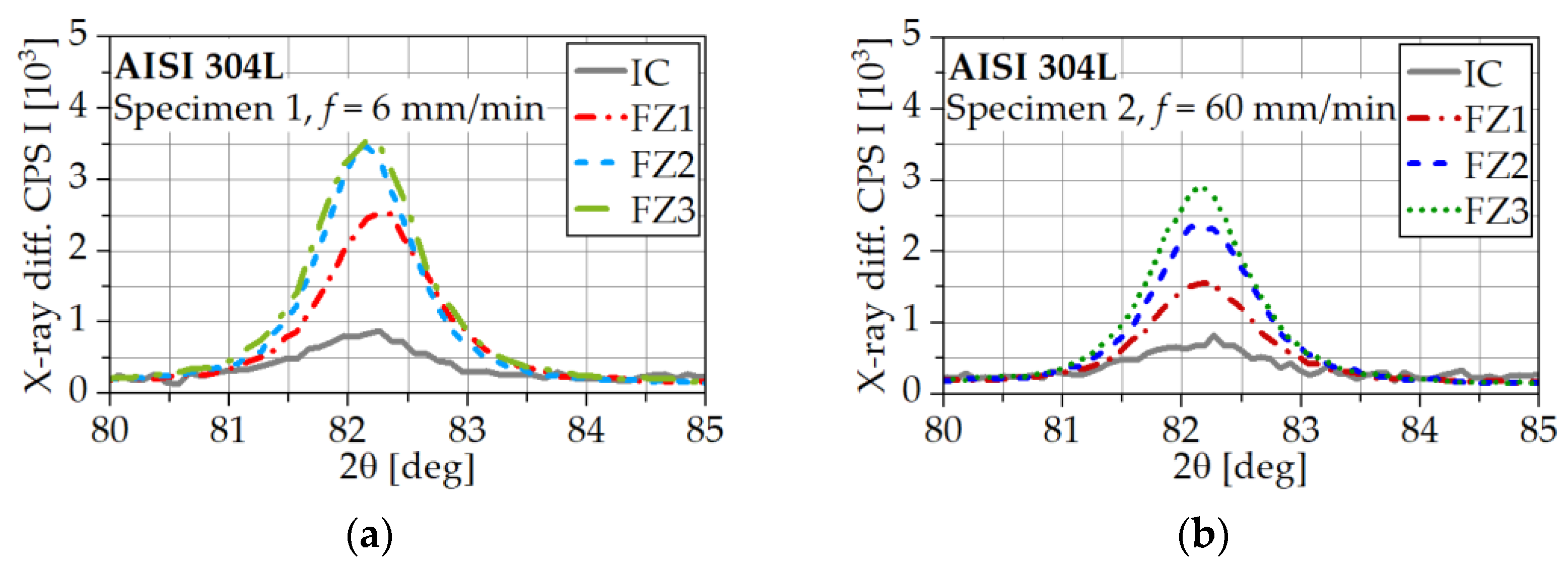
3.3. Characterization of the Phase Transfromation by Means of XRD
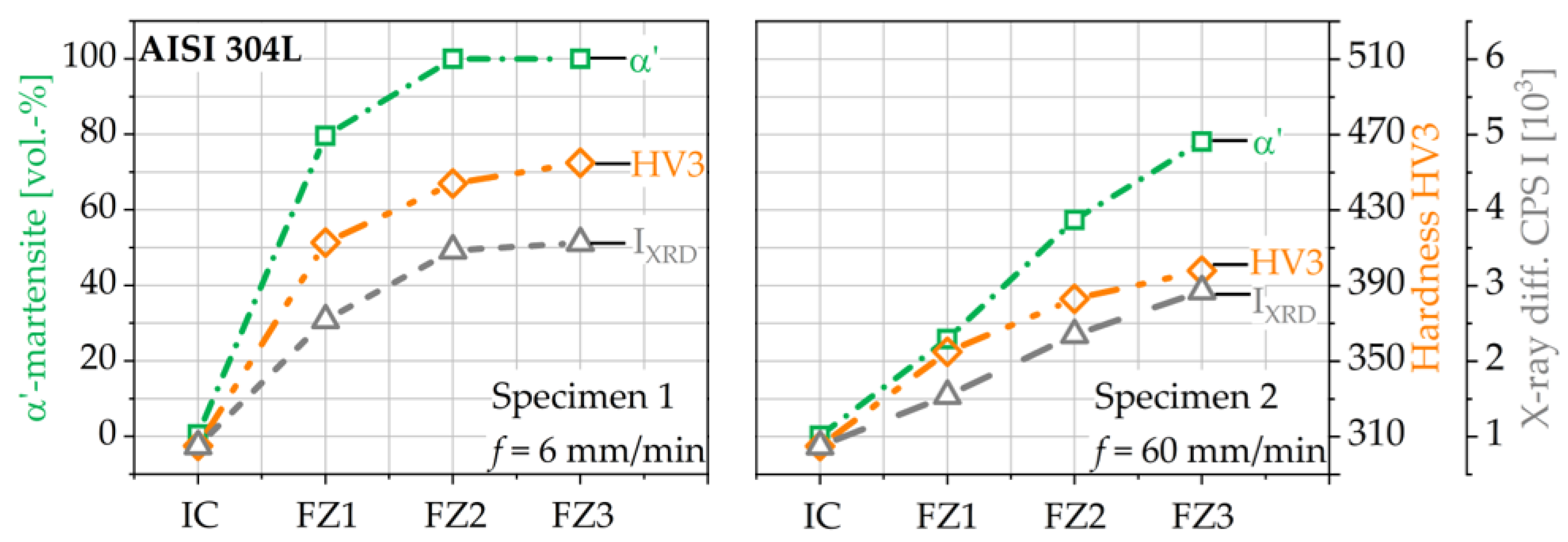
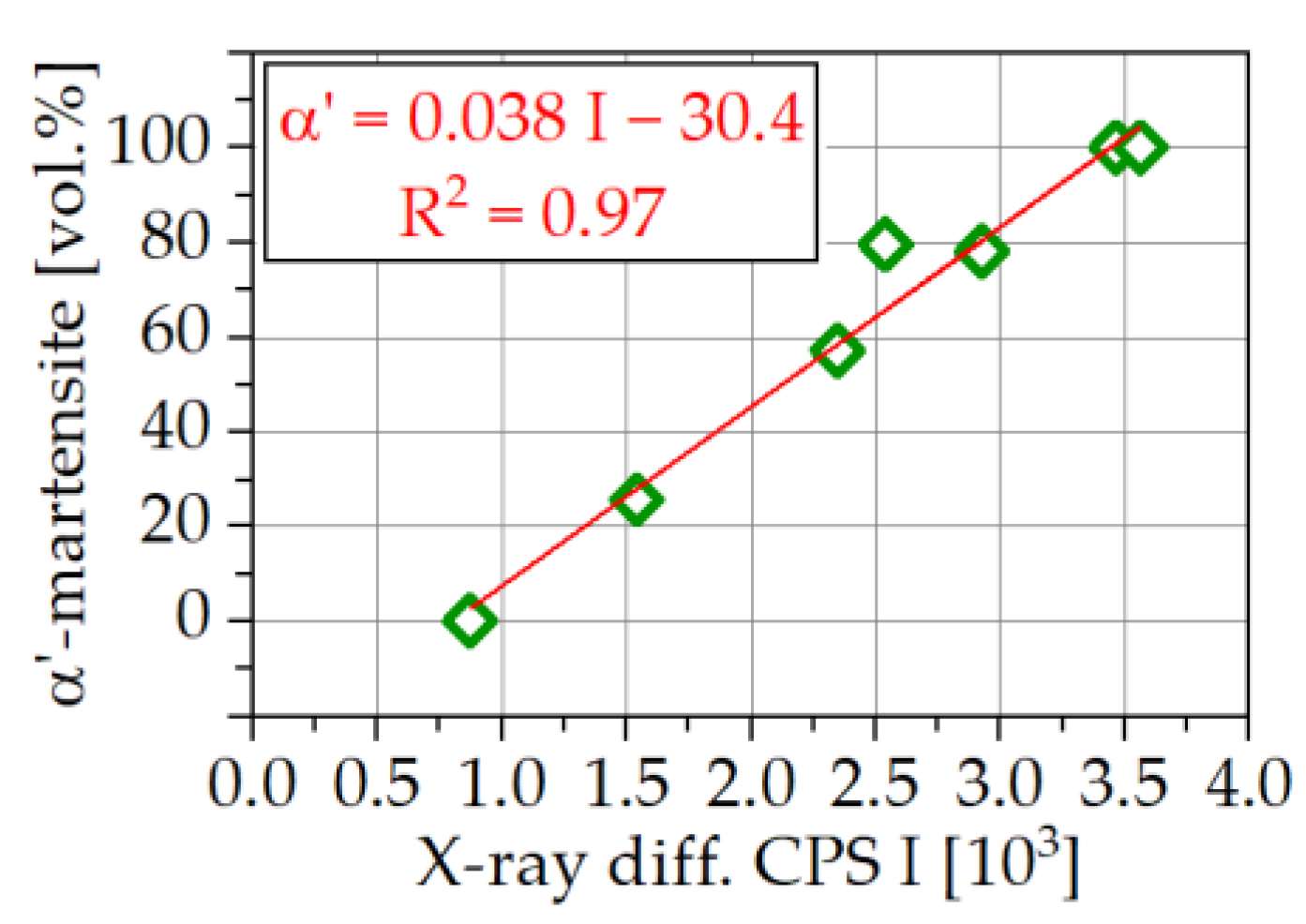
3.4. Correlations between XRD and α′-Martensite Contents
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marini, D.; Cunninigham, D.; Xirouchakis, P.; Corney, J. Flow forming: A review of research methodologies, prediction models and their applications. Int. J. Mech. Eng. 2016, 7, 285–315. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, G.B.; Cohen, M. Kinetics of strain-induced martensitic nucleation. Metall. Trans. A 1975, 6, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenmann, B.; Macherauch, E. Röntgenographische Untersuchung von Spannungszuständen in Werkstoffen. Teil III. Fortsetzung von Matwiss. und Werkstofftechn. Heft 3/1995, S. 148-160 und Heft 4/1995, S. 199-216. Mater. Werkst. 1996, 27, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, F.; Zschau, M. Messung des Eigenspannungsabbaus durch Analyse des Barkhausen-Rauschens. Mater. Werkst. 1980, 11, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauk, V. Structural and Residual Stress Analysis by Nondestructive Methods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; ISBN 9780444824769. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick, M.E.; Fry, A.T.; Holdway, P.; Kandil, F.A.; Shackleton, J.; Suominen, L. Determination of Residual Stresses by X-ray Diffraction; Measurement Good Practice Guide No. 52; National Physical Laboratory: Teddington, UK, 2005; Available online: https://eprintspublications.npl.co.uk/2391/ (accessed on 12 March 2023).
- Strodick, S.; Vogel, F.; Tilger, M.; Denstorf, M.; Kipp, M.; Baak, N.; Kukui, D.; Biermann, D.; Barrientos, M.M.; Walther, F. Innovative X-ray diffraction and micromagnetic approaches for reliable residual stress assessment in deep rolled and microfinished AISI 4140 components. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 20, 2942–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, N.; Schell, N.; Gibmeier, J. On the oscillating course of dhkl−sin2ψ plots for plastically deformed, cold-rolled ferritic and duplex stainless steel sheets. Crystals 2023, 13, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, J.A.; Dolgach, E.; Tartalini, V.; Risso, P.; Avalos, M.; Bolmaro, R.; Cabrera, J.M. Microstructural heterogeneity and mechanical properties of a welded joint of an austenitic stainless steel. Metals 2023, 13, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manugula, V.L.; Lavanya, V.; Pardhu, Y. Microstructural characterization and hardness of an electron beam welded low carbon Ni-Cr-Mo low alloy steel. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litovchenko, I.; Akkuzin, S.; Polekhina, N.; Almaeva, K.; Linnik, V.; Kim, A.; Moskvichev, E.; Chernov, V. The microstructure and tensile properties of new high-manganese low-activation austenitic steel. Metals 2022, 12, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, L.G. A direct method of determining preferred orientation of a flat reflection sample using a geiger counter X-ray spectrometer. J. Appl. Phys. 1949, 20, 1030–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunge, H.J. Texture Analysis in Materials Science; Butterworth-Heinemann Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1982; ISBN 9780408106429. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, Y.-K.; Jeong, Y.-K.; Kim, T.-Y.; Cho, J.-U.; Hwang, N.-M. Texture evolution of non-oriented electrical steel analyzed by EBSD and in-situ XRD during the phase transformation from γ to α. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, J. Investigation of through-thickness residual stress, microstructure and texture in radial forged high-strength alloy steel tubes. Metals 2022, 12, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epp, J. X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques for materials characterization. In Materials Characterization Using Nondestructive Evaluation (NDE) Methods; Hübschen, G., Altpeter, I., Tschuncky, R., Herrmann, H.-G., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Duxford, UK, 2016; pp. 81–124. ISBN 978-0-08-100057-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cheary, R.W.; Ma-Sorrell, Y. Quantitative phase analysis by X-ray diffraction of martensite and austenite in strongly oriented orthodontic stainless steel wires. J. Mater. Sci. 2000, 35, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.K.; Murdock, D.C.; Mataya, M.C.; Speer, J.G.; Matlock, D.K. Quantitative measurement of deformation-induced martensite in 304 stainless steel by X-ray diffraction. Scr. Mater. 2004, 50, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talonen, J.; Aspegren, P.; Hänninen, H. Comparison of different methods for measuring strain induced α-martensite content in austenitic steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2004, 20, 1506–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Fonseca, D.P.M.; de Carvalho, L.G.; de Lima, N.B.; Padilha, A.F. Austenite formation in the oxidized layer of ultra-high-strength 13Ni15Co10Mo maraging steel. Metals 2022, 12, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaga, M.; Boemke, A.; Eifler, D.; Beck, T. Very high cycle fatigue behavior of austenitic stainless steels with different surface morphologies. Metals 2022, 12, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Compagnon, E.; Godin, B.; Korsunsky, A.M. Investigation of martensite transformation in 316L stainless steel. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, S251–S260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomota, Y.; Sekido, N.; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, T.; Gong, W.; Taniyama, A. In situ Observations of Transformation Behavior upon Heating for a 1.5Mn-1.5Si-0.2C Steel-Comparison between Neutron Diffraction, XRD, EBSD and Dilatometry-. ISIJ Int. 2017, 57, 2237–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spieß, L. Moderne Röntgenbeugung: Röntgendiffraktometrie für Materialwissenschaftler, Physiker und Chemiker, 2nd ed.; Vieweg + Teubner Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2009; ISBN 978-3-8351-0166-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cullity, B.D.; Stock, S.R. Elements of X-ray Diffraction, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2001; ISBN 9780201610918. [Google Scholar]
- Rozo Vasquez, J.; Kanagarajah, H.; Arian, B.; Kersting, L.; Homberg, W.; Trächtler, A.; Walther, F. Coupled microscopic and micromagnetic depth-specific analysis of plastic deformation and phase transformation of metastable austenitic steel AISI 304L by flow forming. Pract. Metallogr. 2022, 59, 660–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangonon, P.L.; Thomas, G. The martensite phases in 304 stainless steel. Metall. Trans. 1970, 1, 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Material | Plane (hkl) | E(hkl) [103 N/mm3] | υ(hkl) | 2θ [deg] | Material | Plane (hkl) | E(hkl) [103 N/mm3] | υ(hkl) | 2θ [deg] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austenitic steel | A(420) A(331) A(400) A(222) A(311) A(220) A(200) A(111) | 176 217 139 247 175 207 139 247 | 0.31 0.27 0.35 0.24 0.31 0.28 0.35 0.24 | 147.2 138.464 118.194 95.989 90.705 74.706 50.811 43.621 | Martensitic steel | M(222) M(310) M(220) M(211) M(200) M(110) | 248 181 220 220 165 220 | 0.25 0.32 0.28 0.28 0.33 0.28 | 137.141 116.372 98.937 82.329 65.019 44.670 |
| Specimen | Ideal Thickness [mm] | Feed Rate [mm/min] | α′-Martensite [vol.%] | Macrohardness HV3 | XRD CPS I [103] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specimen 1: | |||||
| IC | 4 | 0.54 | 305 | 0.872 | |
| FZ1 | 3 | 79.65 | 412.6 | 2.54 | |
| FZ2 | 2 | 6 | 100 | 444 | 3.464 |
| FZ3 | 1 | 100 | 445 | 3.563 | |
| Specimen 2: | |||||
| IC | 4 | 0.2 | 305 | 0.83 | |
| FZ1 | 3 | 25.8 | 355 | 1.543 | |
| FZ2 | 2 | 60 | 57.45 | 383 | 2.347 |
| FZ3 | 1 | 78.14 | 398 | 2.928 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rozo Vasquez, J.; Arian, B.; Kersting, L.; Homberg, W.; Trächtler, A.; Walther, F. Detection of Phase Transformation during Plastic Deformation of Metastable Austenitic Steel AISI 304L by Means of X-ray Diffraction Pattern Analysis. Metals 2023, 13, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13061007
Rozo Vasquez J, Arian B, Kersting L, Homberg W, Trächtler A, Walther F. Detection of Phase Transformation during Plastic Deformation of Metastable Austenitic Steel AISI 304L by Means of X-ray Diffraction Pattern Analysis. Metals. 2023; 13(6):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13061007
Chicago/Turabian StyleRozo Vasquez, Julian, Bahman Arian, Lukas Kersting, Werner Homberg, Ansgar Trächtler, and Frank Walther. 2023. "Detection of Phase Transformation during Plastic Deformation of Metastable Austenitic Steel AISI 304L by Means of X-ray Diffraction Pattern Analysis" Metals 13, no. 6: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13061007
APA StyleRozo Vasquez, J., Arian, B., Kersting, L., Homberg, W., Trächtler, A., & Walther, F. (2023). Detection of Phase Transformation during Plastic Deformation of Metastable Austenitic Steel AISI 304L by Means of X-ray Diffraction Pattern Analysis. Metals, 13(6), 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13061007







