Hydrogen Embrittlement Characterization of 1.4614 and 1.4543 Martensitic Precipitation Hardened Stainless Steels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
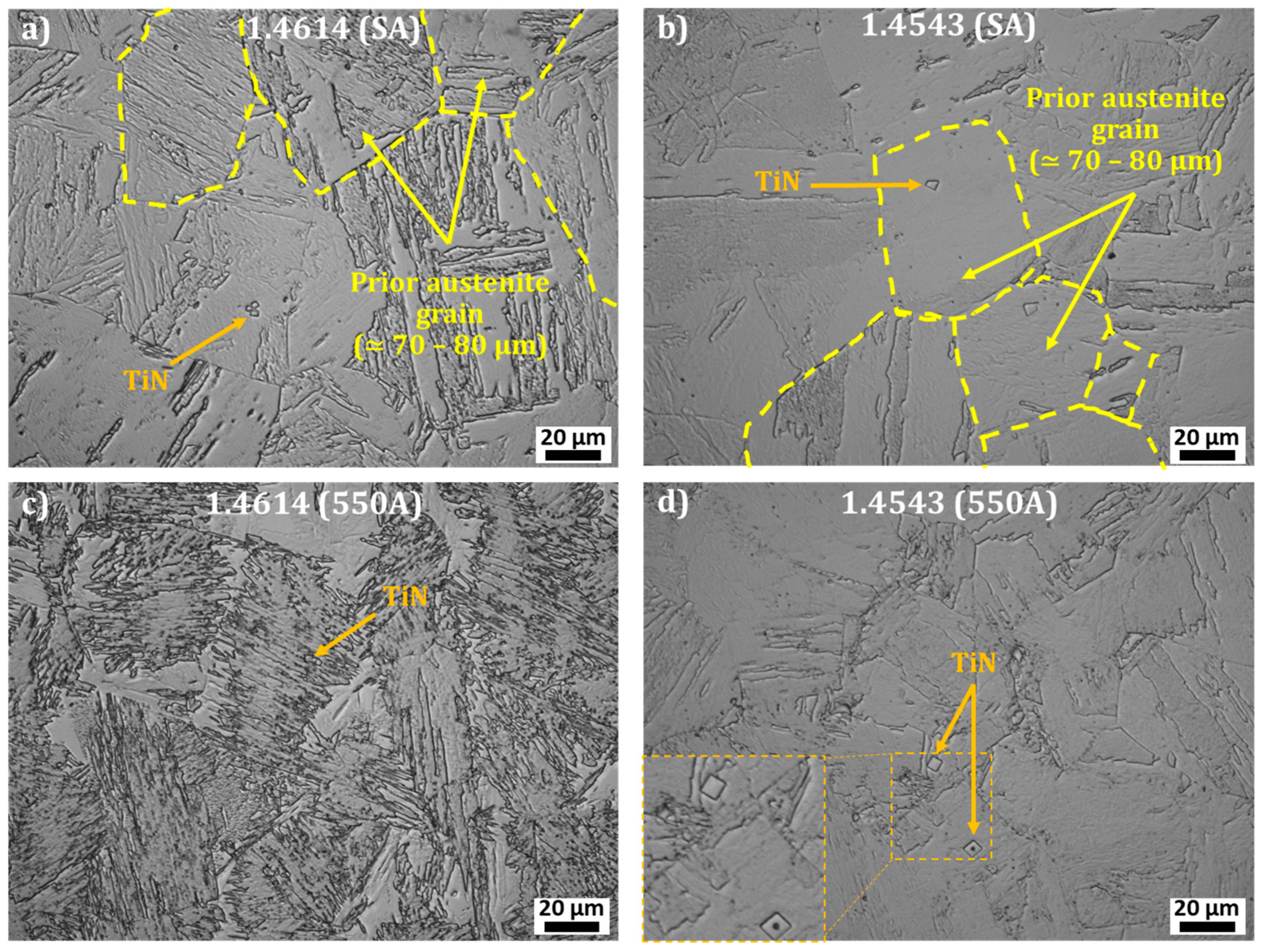
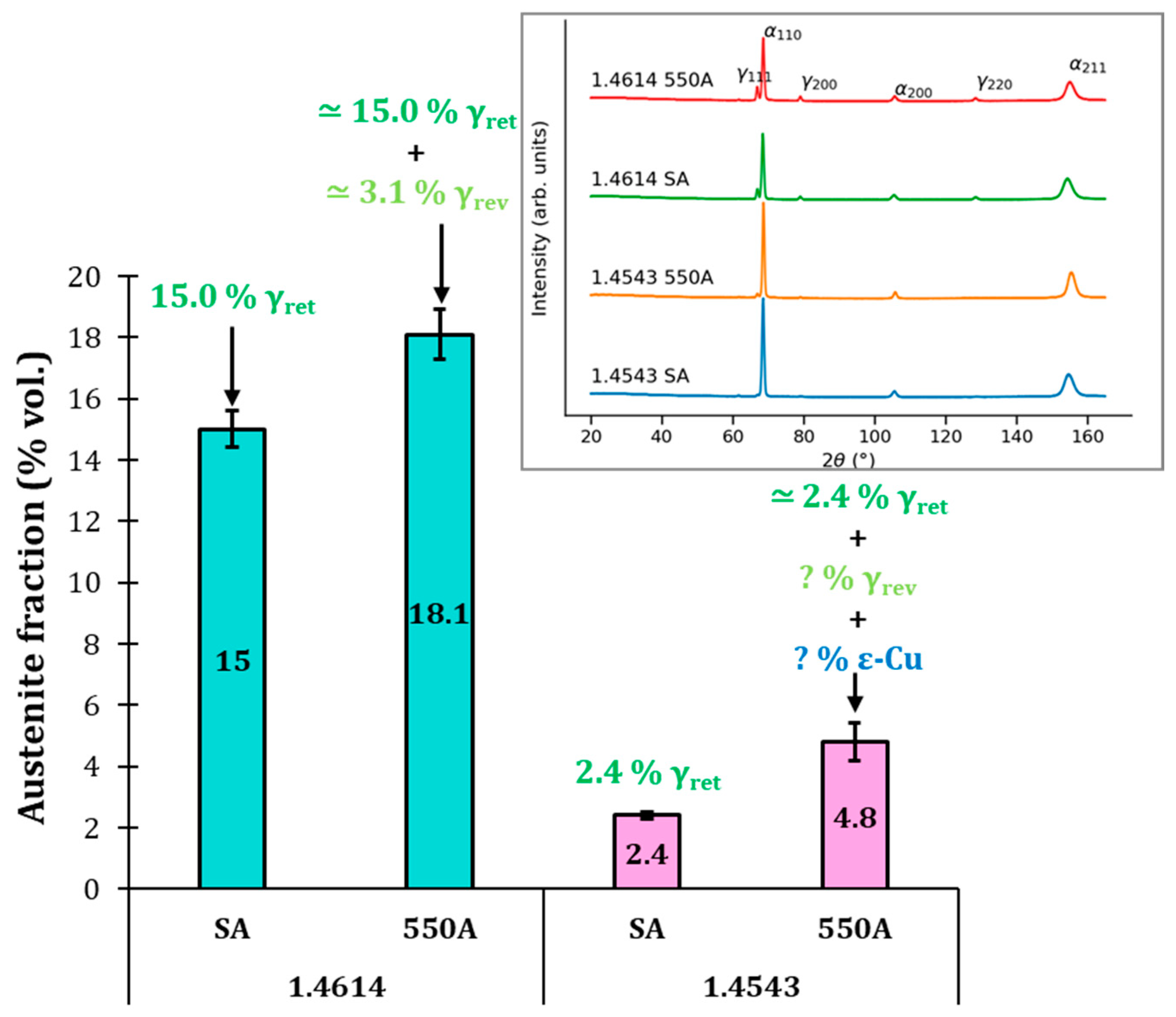
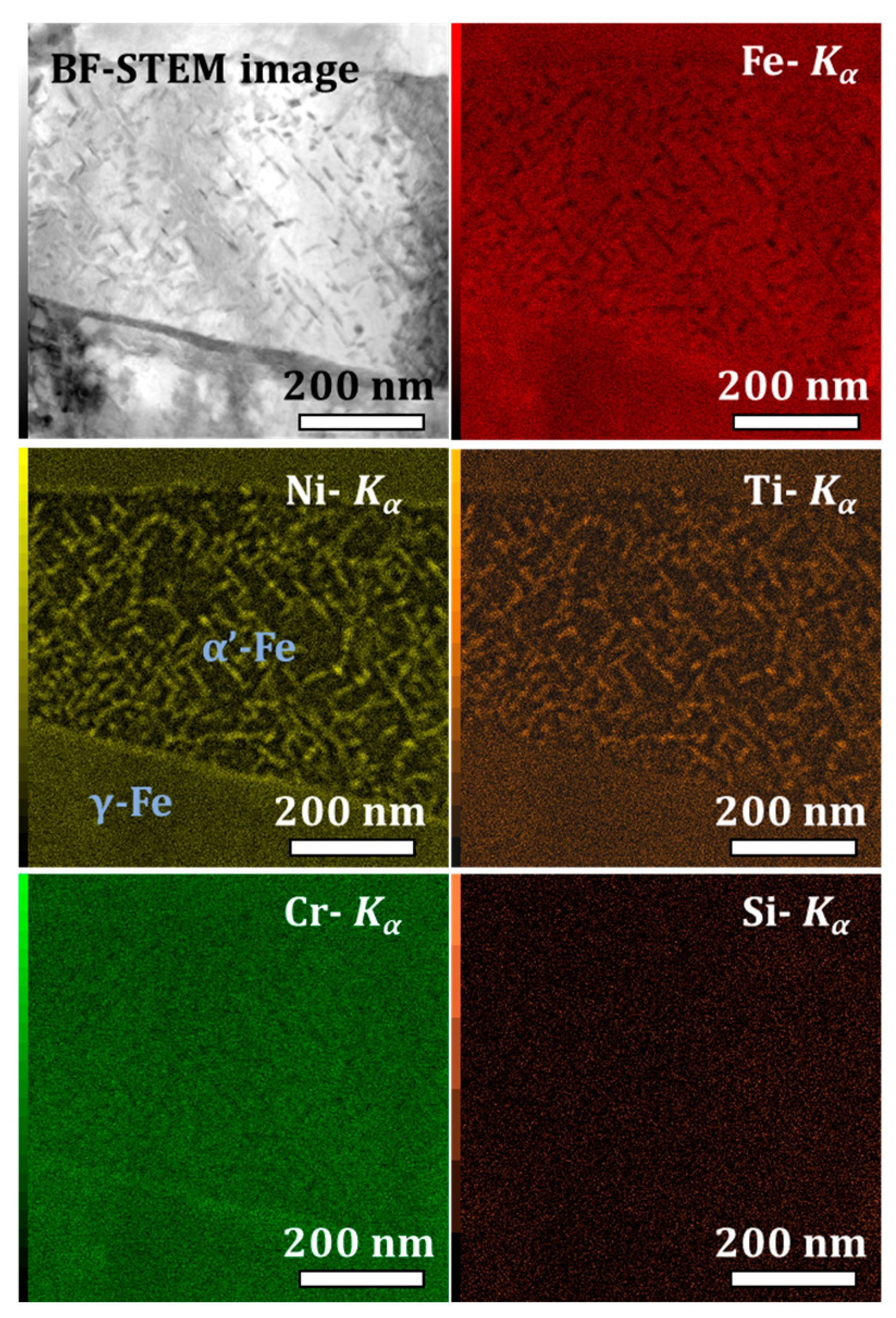
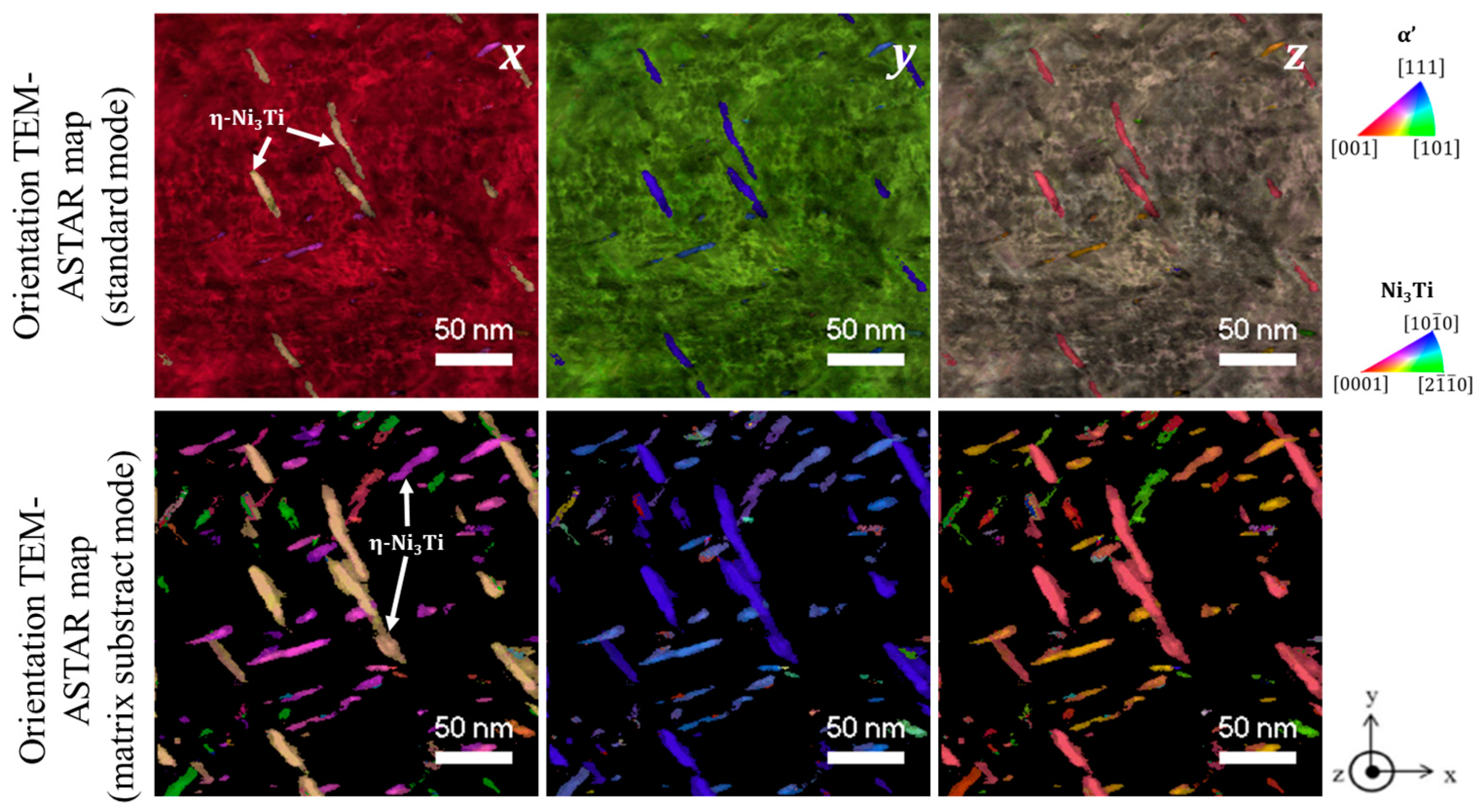
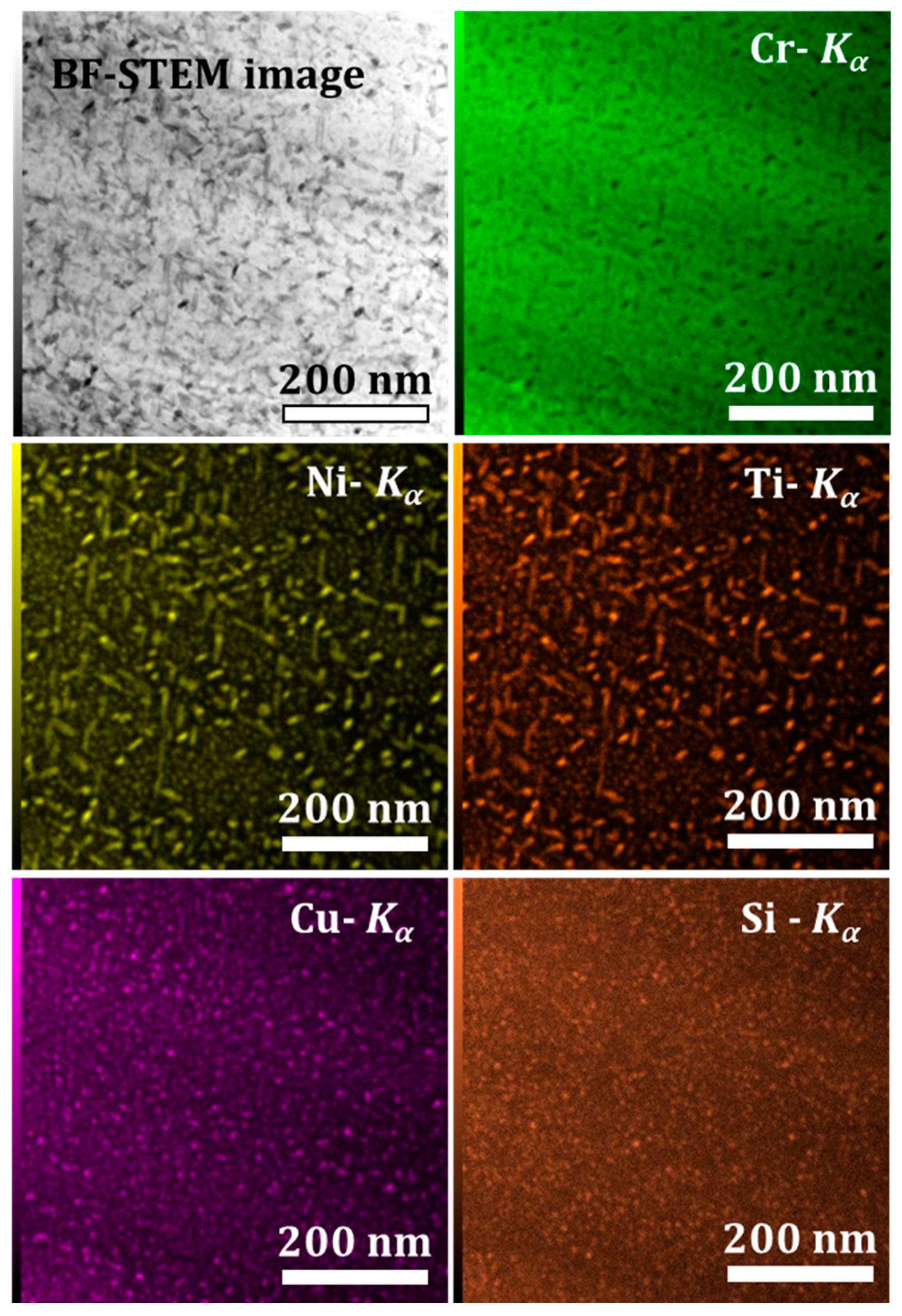
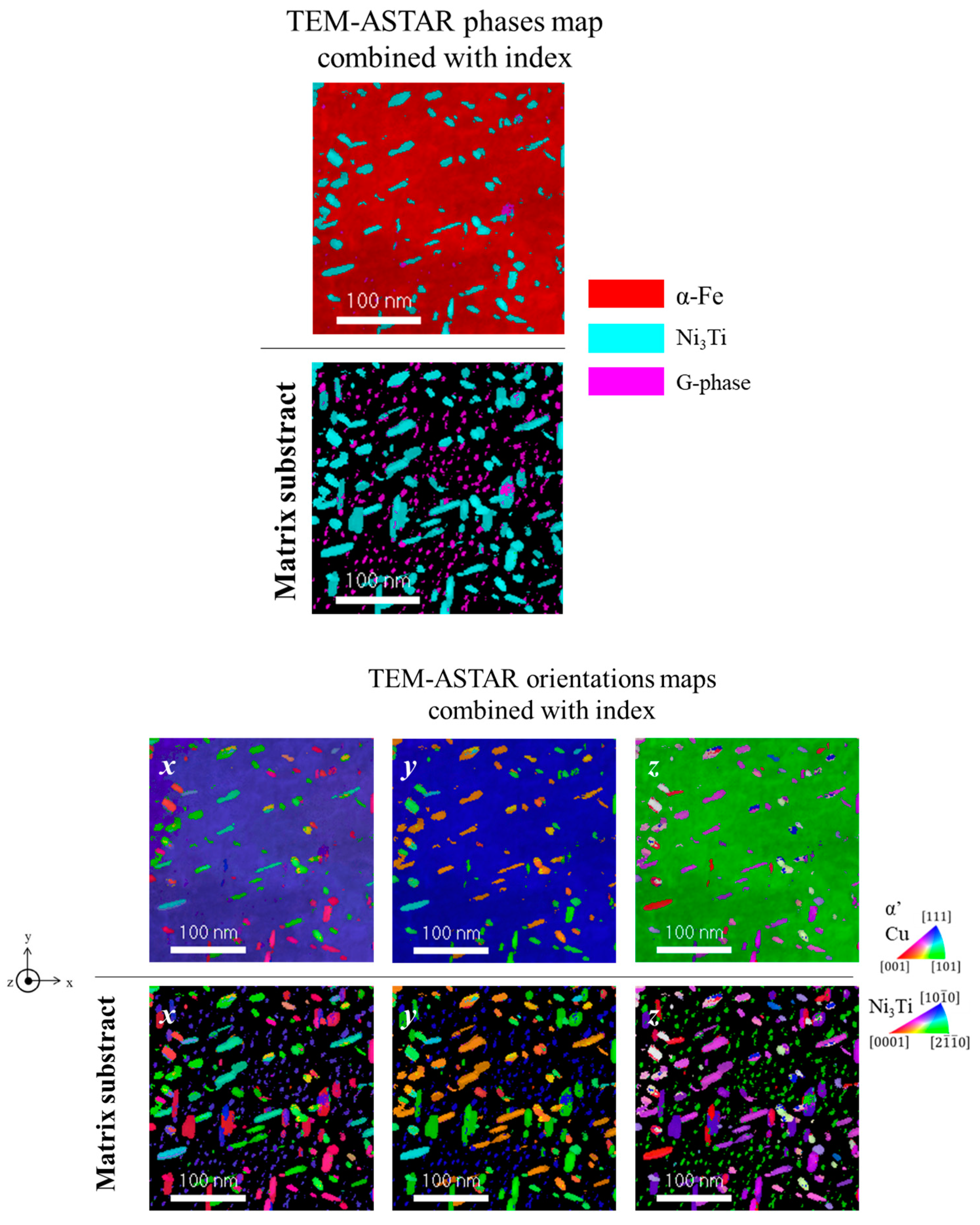
3.1. 1.4614. and 1.4543 Maraging Microstructure
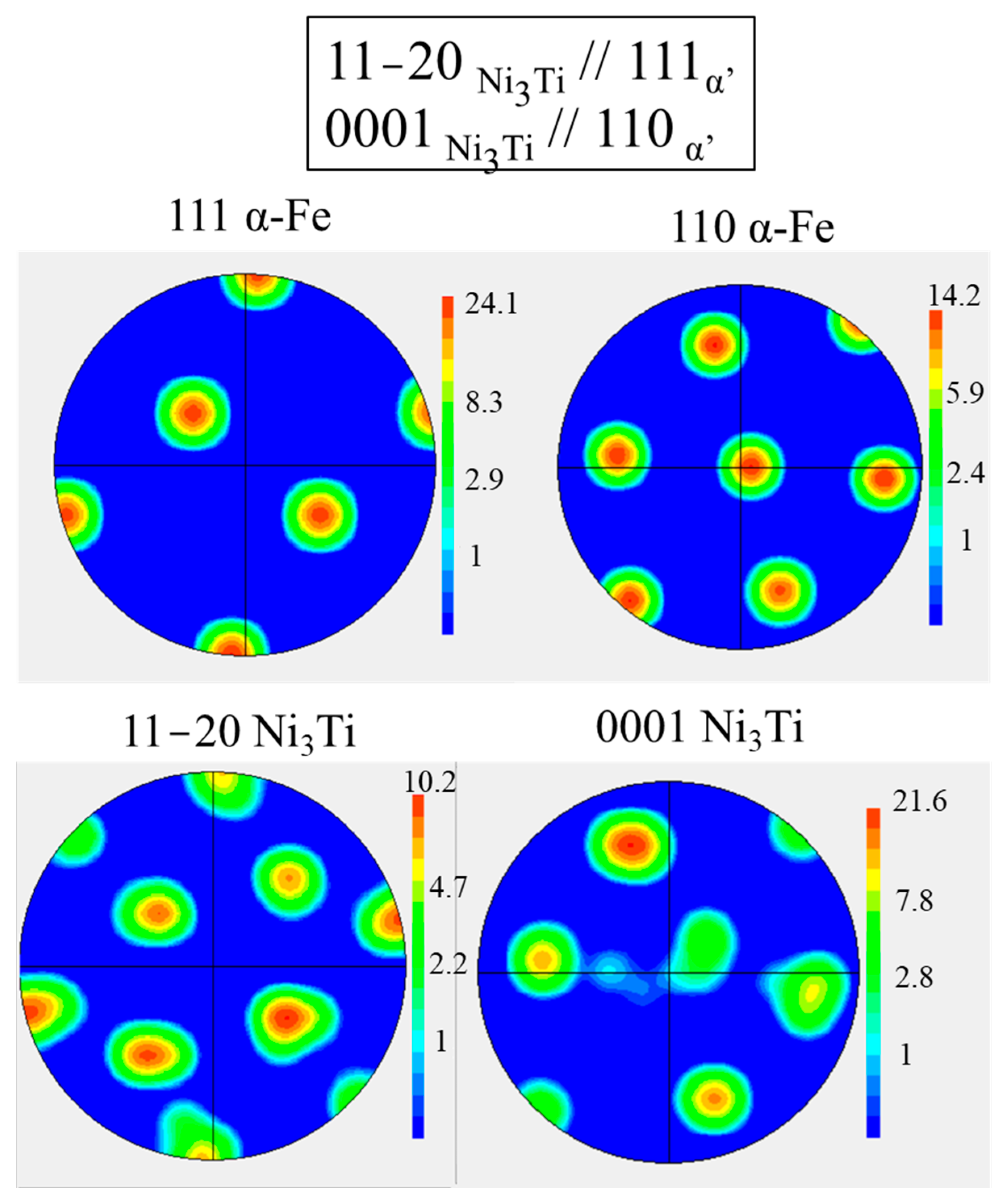
- {0001}Ni3Ti // {110}α′
- <11–20> Ni3Ti // <111>α′
- -
- Ni and Ti rich precipitates, with rod shapes, that may be assigned to Ni3Ti as it will be confirmed with structural characterization;
- -
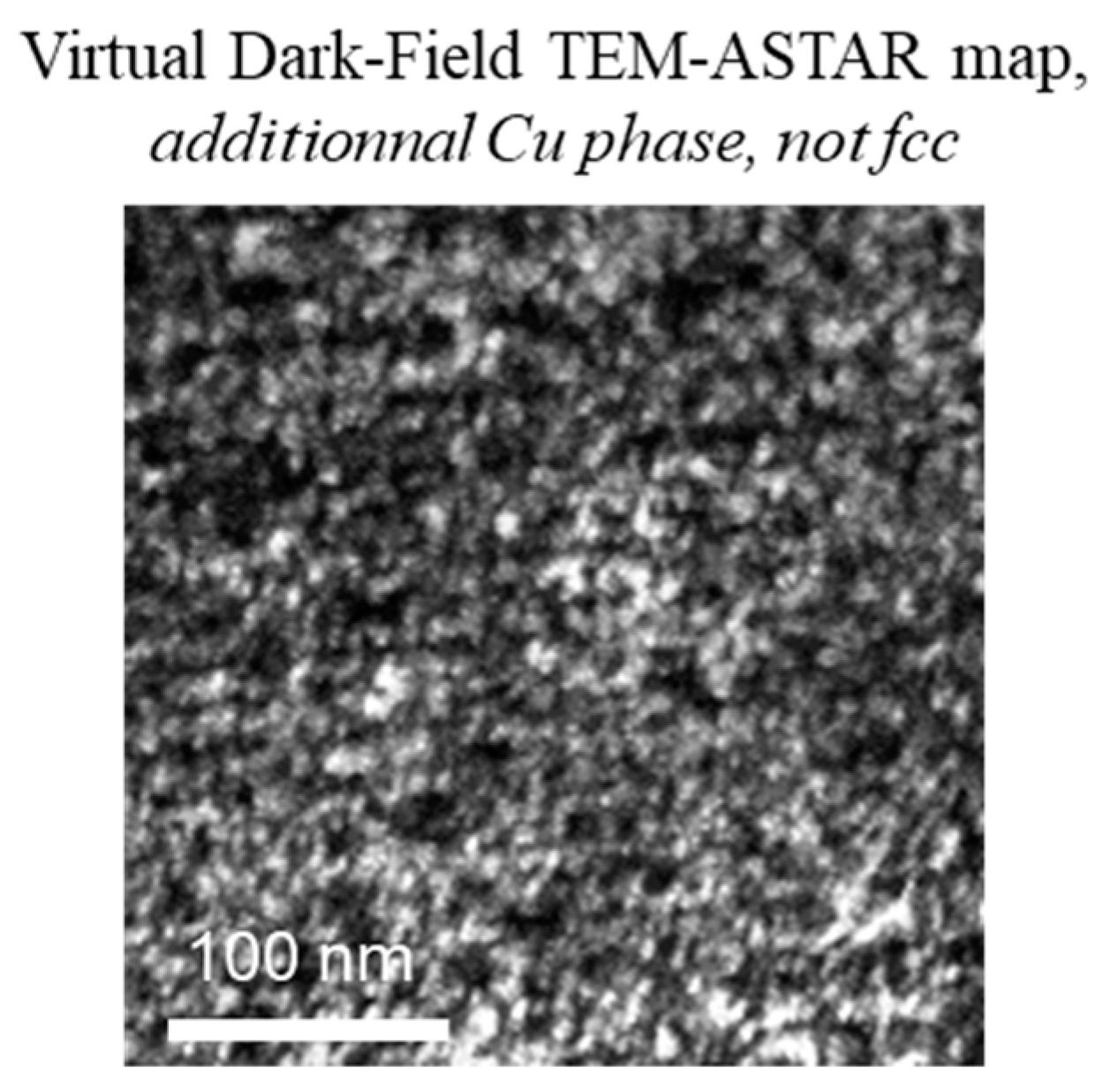
- Cu rich globular precipitates;
- -
- Si, Ni, and Ti rich globular precipitates that might be silicide Ni16Ti6Si7 G-phase as identified in the literature [22] and as it will be confirmed with structural characterization.
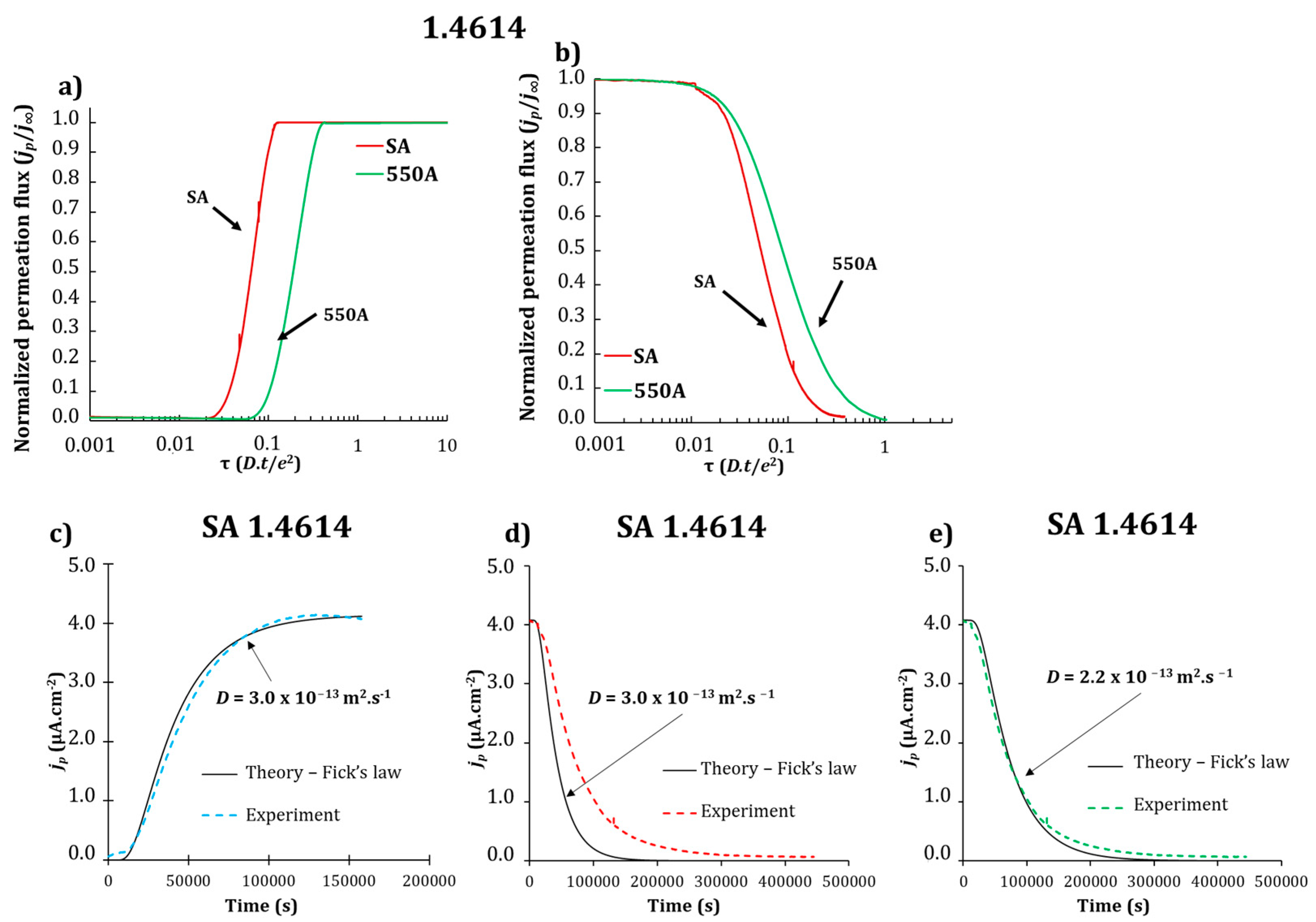
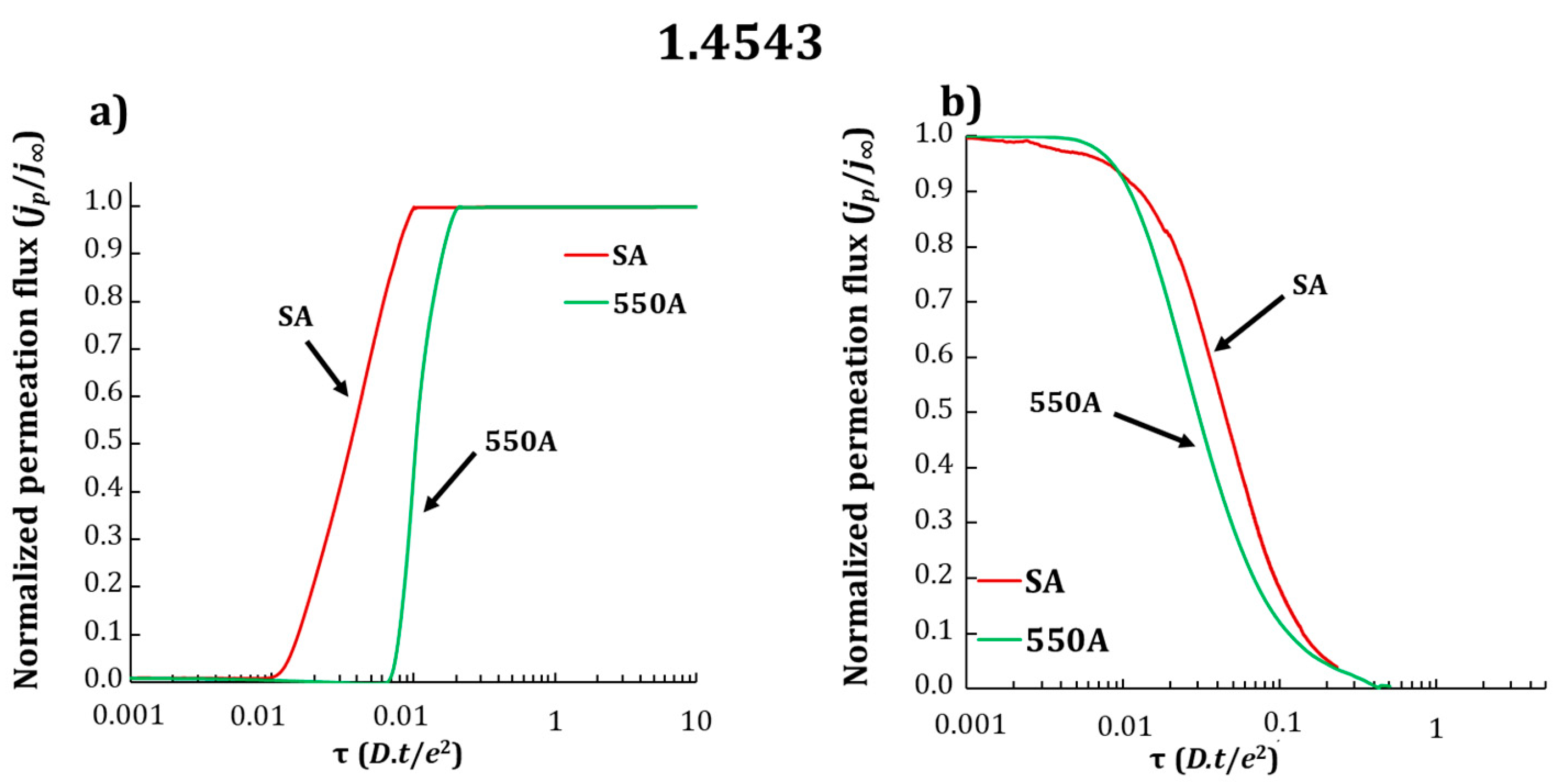
3.2. Electrochemical Permeation Tests
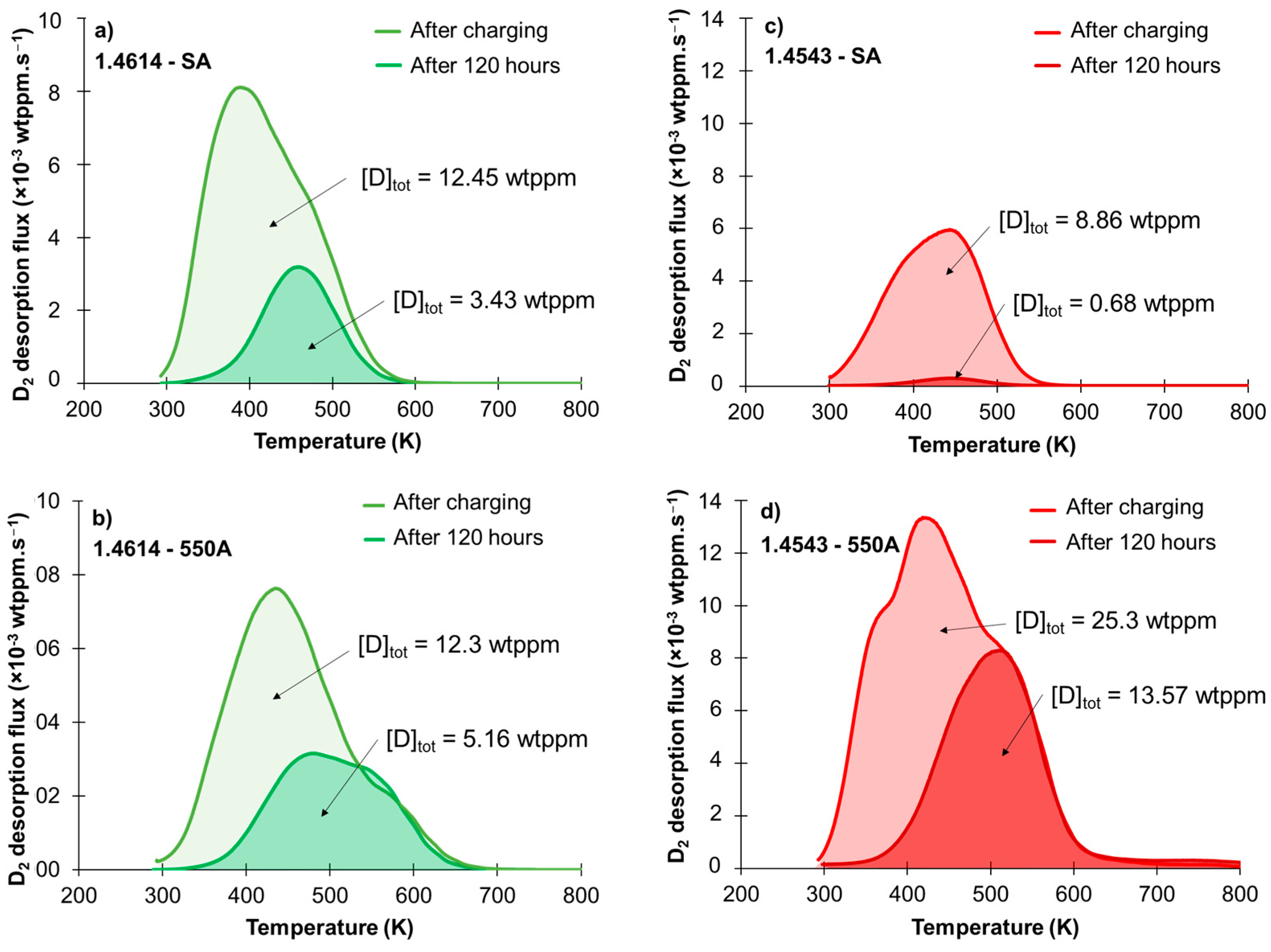
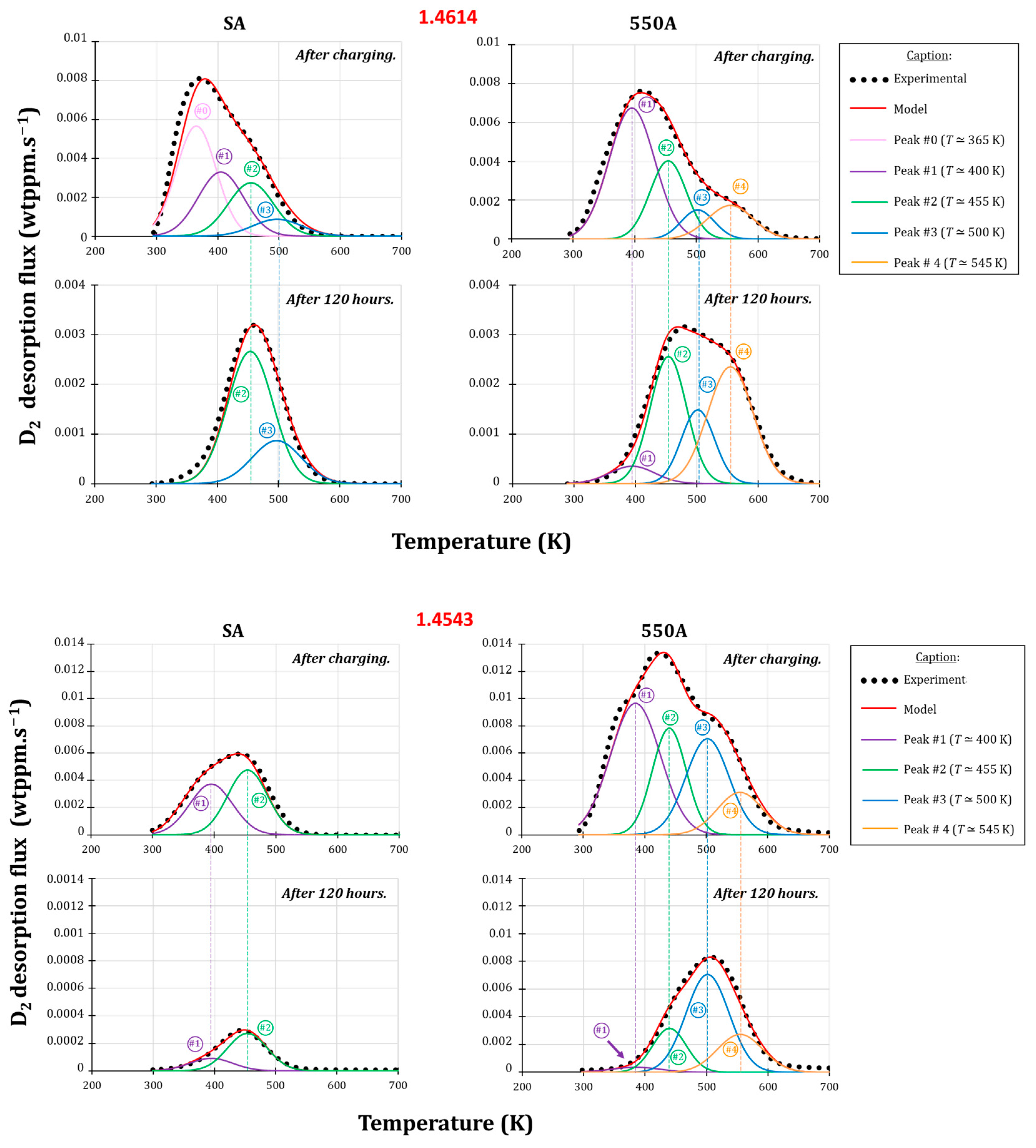
3.3. Thermodesorption
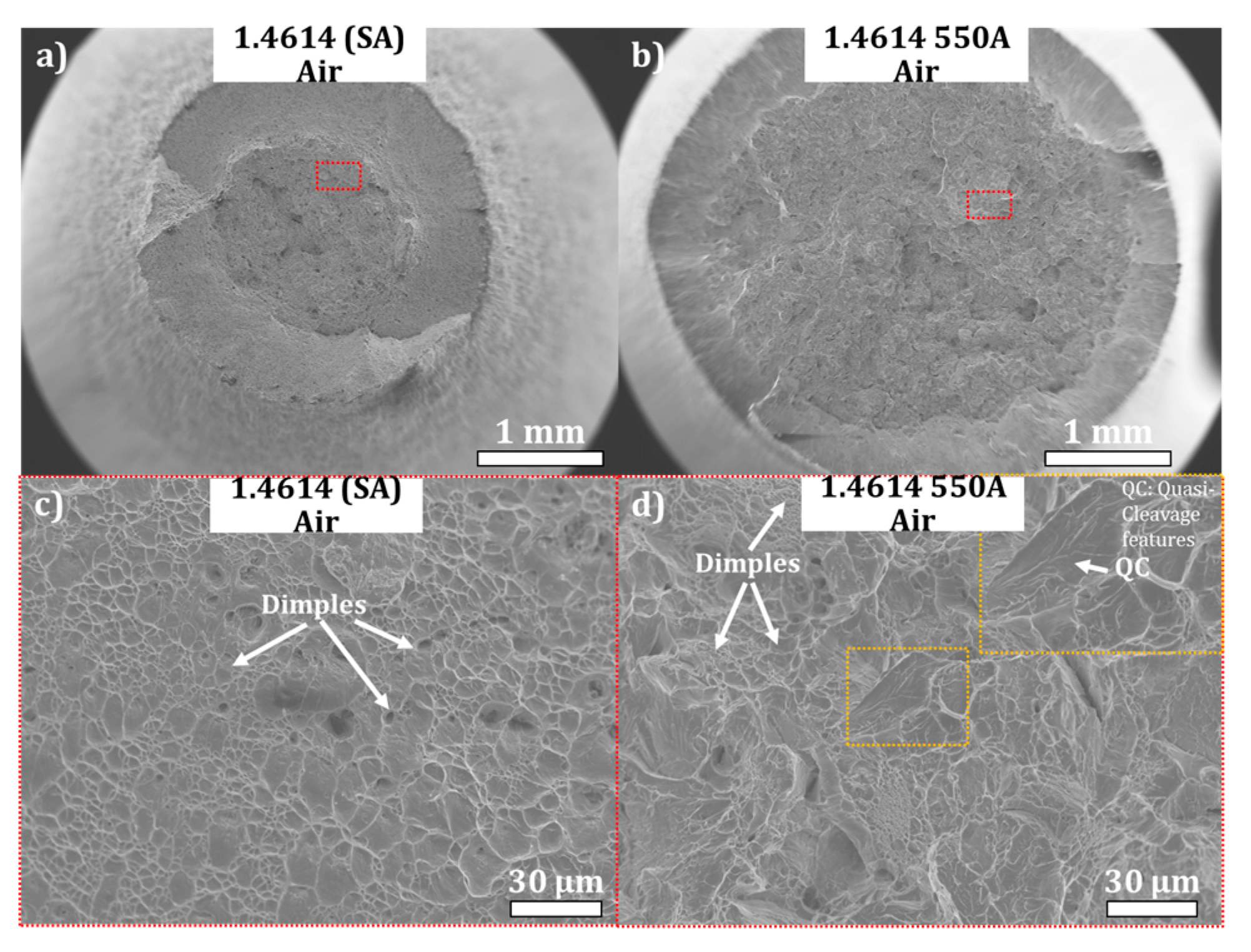
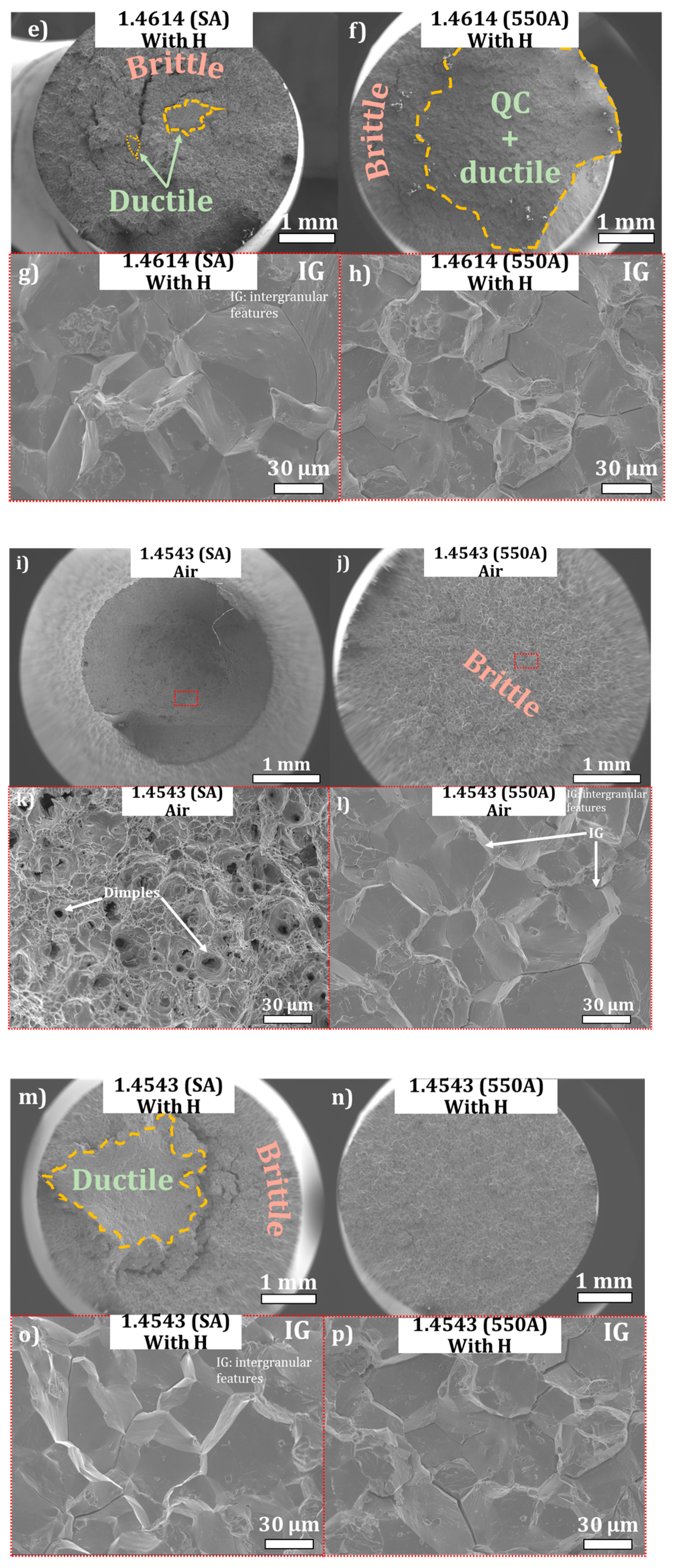
3.4. Slow Strain Rate Tensile Testing (SSRT) under In Situ Cathodic Hydrogen Charging
3.5. General Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.A.; Woods, S. Hydrogen Embrittlement. 2016. Available online: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/20160005654 (accessed on 7 February 2024).
- Bestautte, J.; Kalácska, S.; Béchet, D.; Obadia, Z.; Christien, F. Investigation of quasi-cleavage in a hydrogen charged maraging stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2023, 218, 111163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, W.C.; Pu, C.C.; Yu, B.L.; Wu, J.K. Hydrogen susceptibility of 17-4 PH stainless steel. Mater. Lett. 2003, 57, 2485–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamabe, J.; Sezgin, J.-G.; Wada, K. Interpretation of complex, tensile-fracture phenomena in precipitation-hardened, martensitic stainless steels, 17-4PH, in presence of hydrogen. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 823, 141717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Yan, L.; Pang, X.; Gao, K. Hydrogen trapping and hydrogen embrittlement in 15-5PH stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2022, 205, 110416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liang, J.; Su, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Sheng, G. Correlation between the microstructure and hydrogen embrittlement resistance in a precipitation-hardened martensitic stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2021, 182, 109260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiSabella, D.W.R. Custom 465® Advanced Stainless Flexible for Many Applications, n. d. 2014.
- Shmulevitsh, M.; Ifergane, S.; Eliaz, N.; Shneck, R.Z. Diffusion and trapping of hydrogen due to elastic interaction with η-Ni3Ti precipitates in Custom 465® stainless steel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 31610–31620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, M.; Ma, D.; Xu, B.; Wang, T.; Li, D.; Li, Y. Effect of aging temperature on the heterogeneous microstructure and mechanical properties of a 12Cr–10Ni–Mo–Ti maraging steel for cryogenic applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 11469–11484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dong, C.; Yao, J.; Dai, Z.; Man, C.; Yin, Y.; Xiao, K.; Li, X. The effect of η-Ni3Ti precipitates and reversed austenite on the passive film stability of nickel-rich Custom 465 steel. Corros. Sci. 2019, 154, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, E.F.; Véron, M. Methods for orientation and phase identification of nano-sized embedded secondary phase particles by 4D scanning precession electron diffraction. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Sci. Cryst. Eng. Mater. 2019, 75, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ifergane, S.; David, R.B.; Sabatani, E.; Carmeli, B.; Beeri, O.; Eliaz, N. Hydrogen Diffusivity and Trapping in Custom 465 Stainless Steel. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, C107–C115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifergane, S.; Sabatani, E.; Carmeli, B.; Barkay, Z.; Ezersky, V.; Beeri, O.; Eliaz, N. Hydrogen diffusivity measurement and microstructural characterization of Custom 465 stainless steel. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 178, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E975-22; Standard Test Method for X-ray Determination of Retained Austenite in Steel with Near Random Crystallographic Orientation. ASTM International (ASTM): West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- Williamson, G.K.; Hall, W.H. X-ray line broadening from filed aluminium and wolfram. Acta Metall. 1953, 1, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G.K.; Smallman, R.E. Dislocation densities in some annealed and cold-worked metals from measurements on the X-ray debye-scherrer spectrum. Philos. Mag. 1956, 1, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, E.F.; Véron, M. Automated crystal orientation and phase mapping in TEM. Mater. Charact. 2014, 98, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutz, P.; Martin, F.; Auzoux, Q.; Adem, J.; Rauch, E.F.; Wouters, Y.; Latu-Romain, L. Hydrogen transport in 17−4 PH stainless steel: Influence of the metallurgical state on hydrogen diffusion and trapping. Mater. Charact. 2022, 192, 112239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanathan, M.A.V.; Stachurski, Z.; Tompkins, F.C. The adsorption and diffusion of electrolytic hydrogen in palladium. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A. Math. Phys. Sci. 1962, 270, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montella, C. Discussion on permeation transients in terms of insertion reaction mechanism and kinetics. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1999, 465, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moli-Sanchez, L.; Martin, F.; Leunis, E.; Chêne, J.; Wery, M. Hydrogen Transport in 34CrMo4 Martensitic Steel: Influence of Microstructural Defects on H Diffusion. Defect Diffus. Forum 2012, 323–325, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; King, D.J.M.; Povstugar, I.; Wen, Y.; Luan, J.; Kuhn, B.; Jiao, Z.; Wang, C.; Wenman, M.R.; Liu, X. Precipitation behavior in G-phase strengthened ferritic stainless steels. Acta Mater. 2021, 205, 116542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, A.; Llanes, L.; Anglada, M.; Redjaimia, A.; Metauer, G. Characterization of the intermetallic G-phase in an AISI 329 duplex stainless steel. J. Mater. Sci. 1997, 32, 4533–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.J.M.; Yang, M.; Whiting, T.M.; Liu, X.; Wenman, M.R. G-phase strengthened iron alloys by design. Acta Mater. 2020, 183, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frappart, S.; Oudriss, A.; Feaugas, X.; Creus, J.; Bouhattate, J.; Thébault, F.; Delattre, L.; Marchebois, H. Hydrogen trapping in martensitic steel investigated using electrochemical permeation and thermal desorption spectroscopy. Scr. Mater. 2011, 65, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutz, P.; Latu-Romain, L.; Martin, F.; Auzoux, Q.; Adem, J.; Wouters, Y.; Ravat, B.; Menut, D. Onto the role of copper precipitates and reverted austenite on hydrogen embrittlement in 17-4 PH stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2023, 202, 113044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, L.W.; Chi, M.Y.; Chen, H.R.; Chen, C. Investigation of hydrogen sulfide stress corrosion cracking of PH 13-8 Mo stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 416, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Li, D.; Yan, L.; Pang, X.; Gao, K. A novel heat treatment for improving the hydrogen embrittlement resistance of a precipitation-hardened martensitic stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2022, 206, 110530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Lv, W.; Yang, Y.; Li, D.; Yan, L.; Pang, X.; He, Y.; Gao, K. Optimizing the hydrogen embrittlement resistance by tuning the structures of Cu-rich nanoprecipitates in high strength martensite stainless steels. Acta Mater. 2023, 246, 118722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloué, J.; Foucault, M.; Andrieu, E. Hydrogen Embrittlement of Ph 13-08 Mo Stainless Steel in PWR Environment Effects of Microstructure. In Ninth International Symposium on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems—Water Reactors; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennies, D.P. Proposed Theory for the Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance of Martensitic Precipitation Age-Hardening Stainless Steels such as Custom 455. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2013, 13, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G. Retained austenite and tempered martensite embrittlement. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1978, 9, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Kim, D.-I.; Kim, H.S.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H.; Suh, D.-W. Strain partitioning and mechanical stability of retained austenite. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestautte, J.; Oudriss, A.; Lenci, M.; Bechet, D.; Obadia, Z.; Feaugas, X.; Christien, F. A multi-method approach to the study of hydrogen trapping in a maraging stainless steel: The impact of B2-NiAl precipitates and austenite. Corros. Sci. 2023, 224, 111509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, B.; Xu, G.; Chu, D.; Peng, J. High-resolution electron microscopy characterization of 2H and 9R variant in the ferritic steels containing copper. Mater. Charact. 2011, 62, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| C | Cr | Ni | Ti | Mo | Mn | Si | Al | S | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 11.63 | 11.05 | 1.63 | 0.91 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.35 | 0.003 | 0.003 |
| C | Cr | Ni | Cu | Ti | Mo | Mn | Si | Nb | Al | S | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.02 | 12.03 | 8.33 | 1.99 | 1.22 | 0.06 | 0.35 | 0.28 | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| Grade | ρ (×1016 m−2) SA | ρ (×1016 m−2) 550A |
|---|---|---|
| 1.4614 | 1 | 0.6 |
| 1.4543 | 0.8 | 0.3 |
| Grade | Dapp (×10−13 m2·s−1) SA | Dapp (×10−13 m2·s−1) 550A |
|---|---|---|
| 1.4614 | 3.0 ± 0.8 | 1.2 ± 0.4 |
| 1.4543 | 3.8 ± 0.1 | 1.8 ± 0.1 |
| Heat Treatment | RRA (%) | REL (%) | UTSair (MPa) | YSair (MPa) | RAair (%) | Aair (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA | 83 | 60 | 961 | 720 | 65 | 18 |
| 550A | 100 | 94 | 1412 | 1295 | 32 | 12 |
| Heat Treatment | RRA (%) | REL (%) | UTSair (MPa) | YSair (MPa) | RAair (%) | Aair (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA | 87 | 67 | 964 | 835 | 65 | 15 |
| 550A | 100 | 100 | 1622 | 1610 | 4 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Latu-Romain, L.; Schutz, P.; Martin, F.; Auzoux, Q.; Adem, J.; Wouters, Y.; Rauch, E. Hydrogen Embrittlement Characterization of 1.4614 and 1.4543 Martensitic Precipitation Hardened Stainless Steels. Metals 2024, 14, 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14020218
Latu-Romain L, Schutz P, Martin F, Auzoux Q, Adem J, Wouters Y, Rauch E. Hydrogen Embrittlement Characterization of 1.4614 and 1.4543 Martensitic Precipitation Hardened Stainless Steels. Metals. 2024; 14(2):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14020218
Chicago/Turabian StyleLatu-Romain, Laurence, Pierre Schutz, Frantz Martin, Quentin Auzoux, Jamila Adem, Yves Wouters, and Edgar Rauch. 2024. "Hydrogen Embrittlement Characterization of 1.4614 and 1.4543 Martensitic Precipitation Hardened Stainless Steels" Metals 14, no. 2: 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14020218
APA StyleLatu-Romain, L., Schutz, P., Martin, F., Auzoux, Q., Adem, J., Wouters, Y., & Rauch, E. (2024). Hydrogen Embrittlement Characterization of 1.4614 and 1.4543 Martensitic Precipitation Hardened Stainless Steels. Metals, 14(2), 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14020218






