Mechanical Properties and In Vitro Corrosion Behaviors of Biodegradable Magnesium Alloy Suture Anchors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
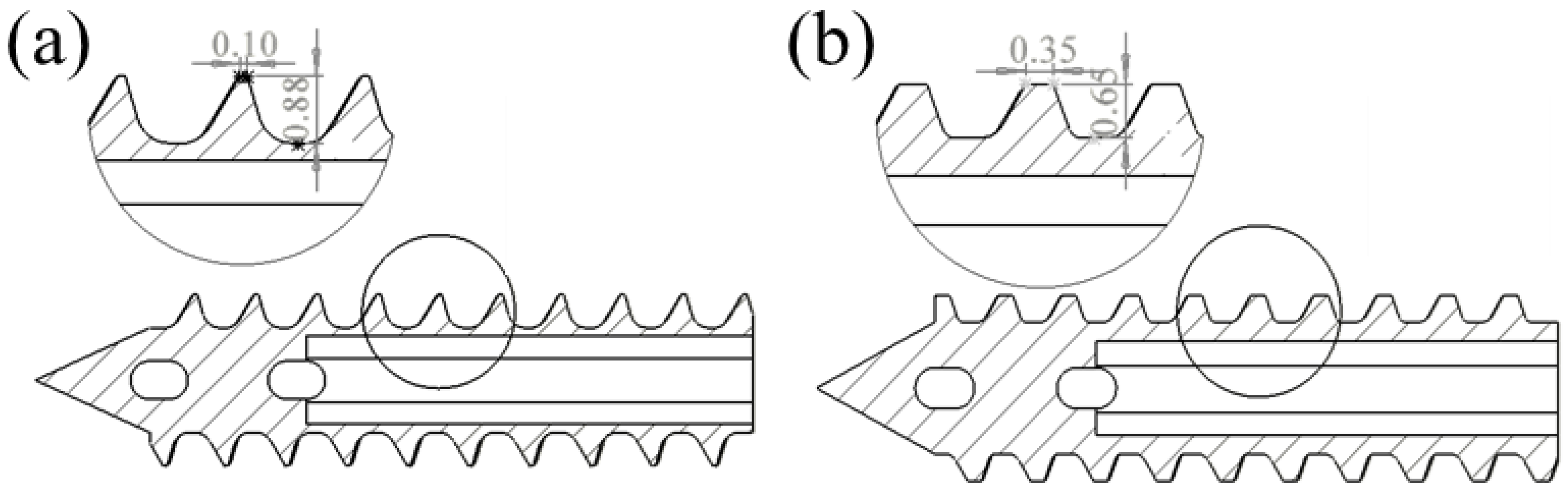
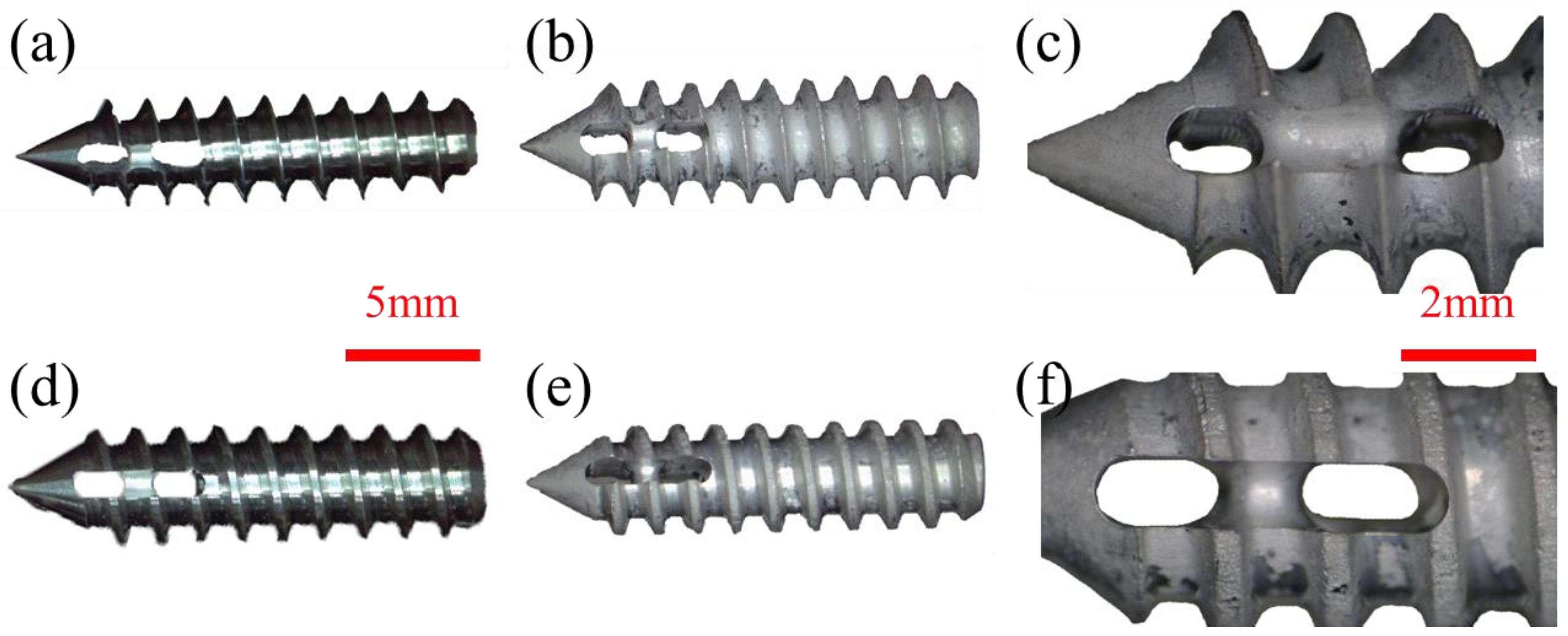
2.1. Structural Design of Mg Suture Anchor
2.2. Finite Element Analysis of Mg Suture Anchor
2.3. In Vitro Corrosion Experiments of Mg Suture Anchor
2.4. Pull-Out Force and Torsion Tests of Mg Suture Anchor
3. Results
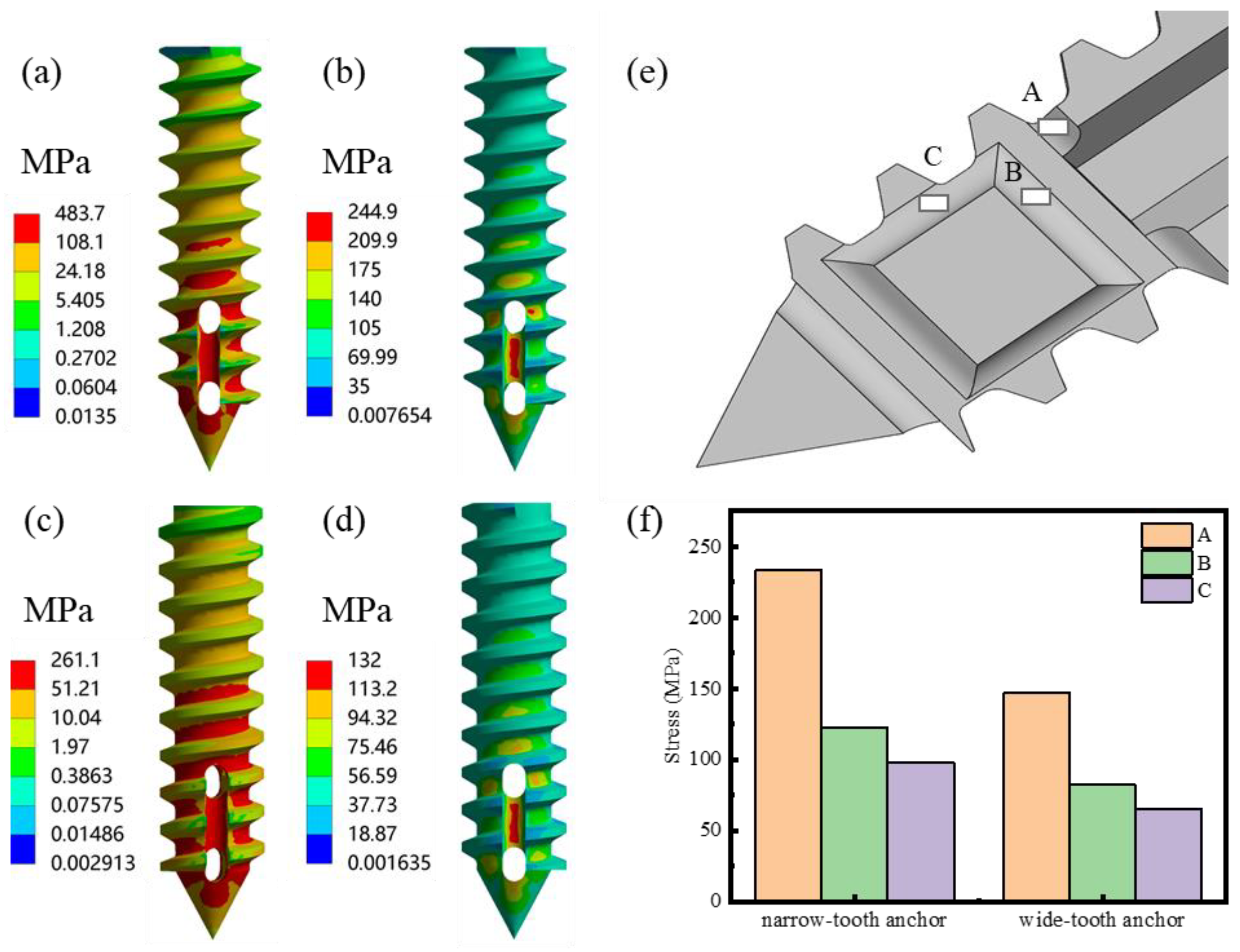
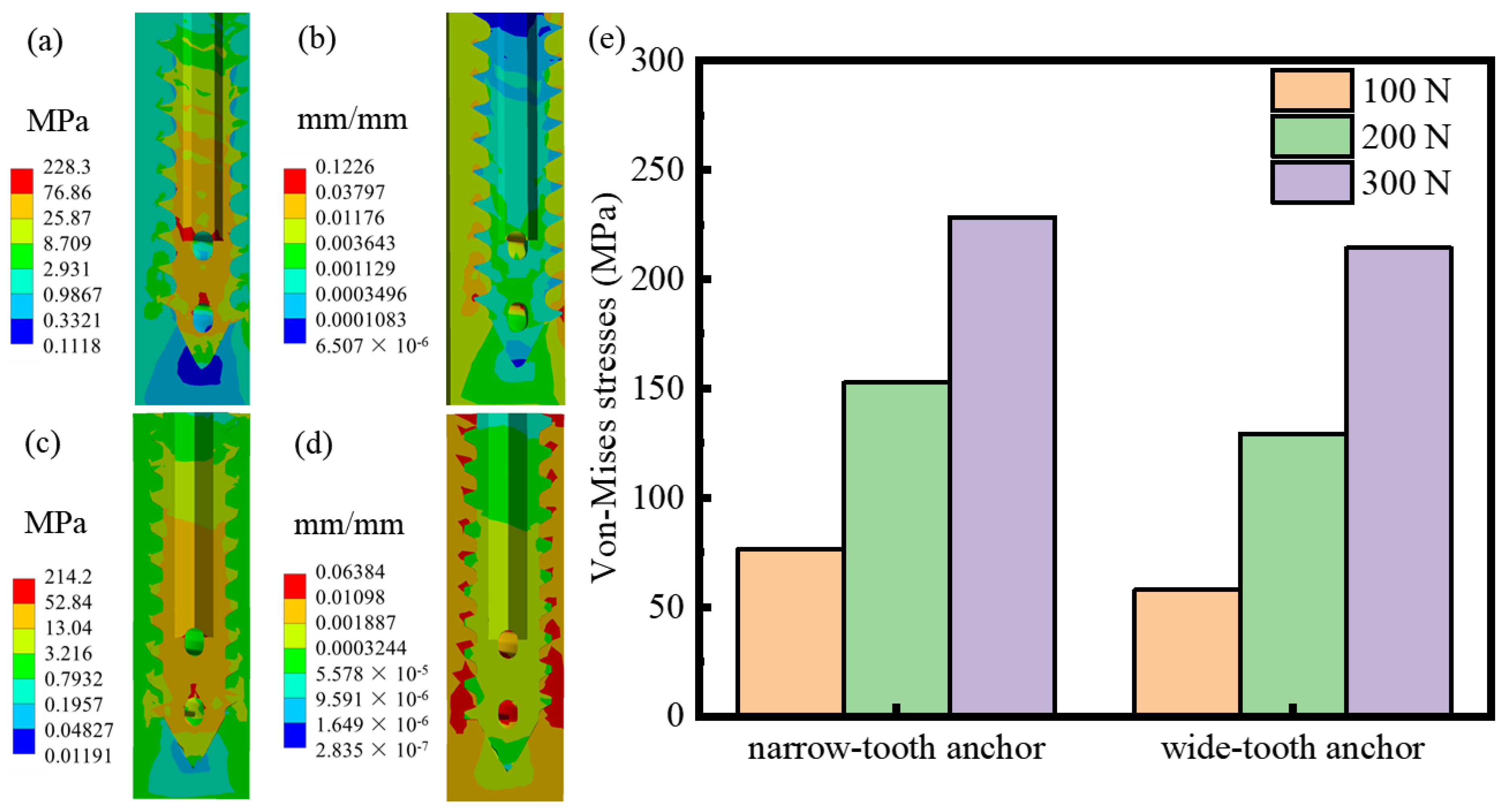
3.1. FEA of Mg Suture Anchor
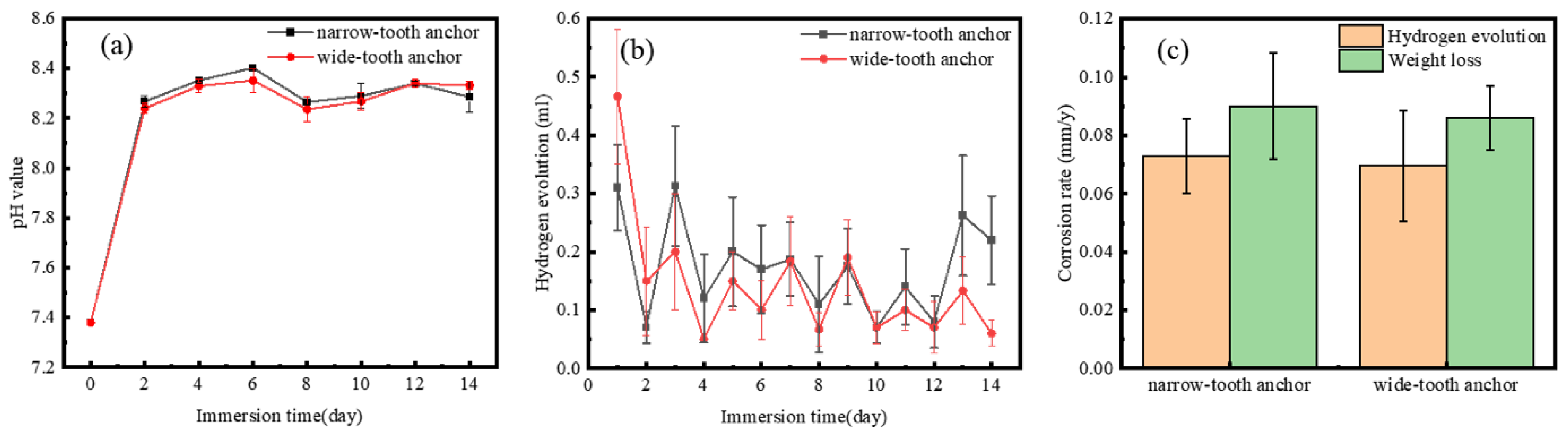
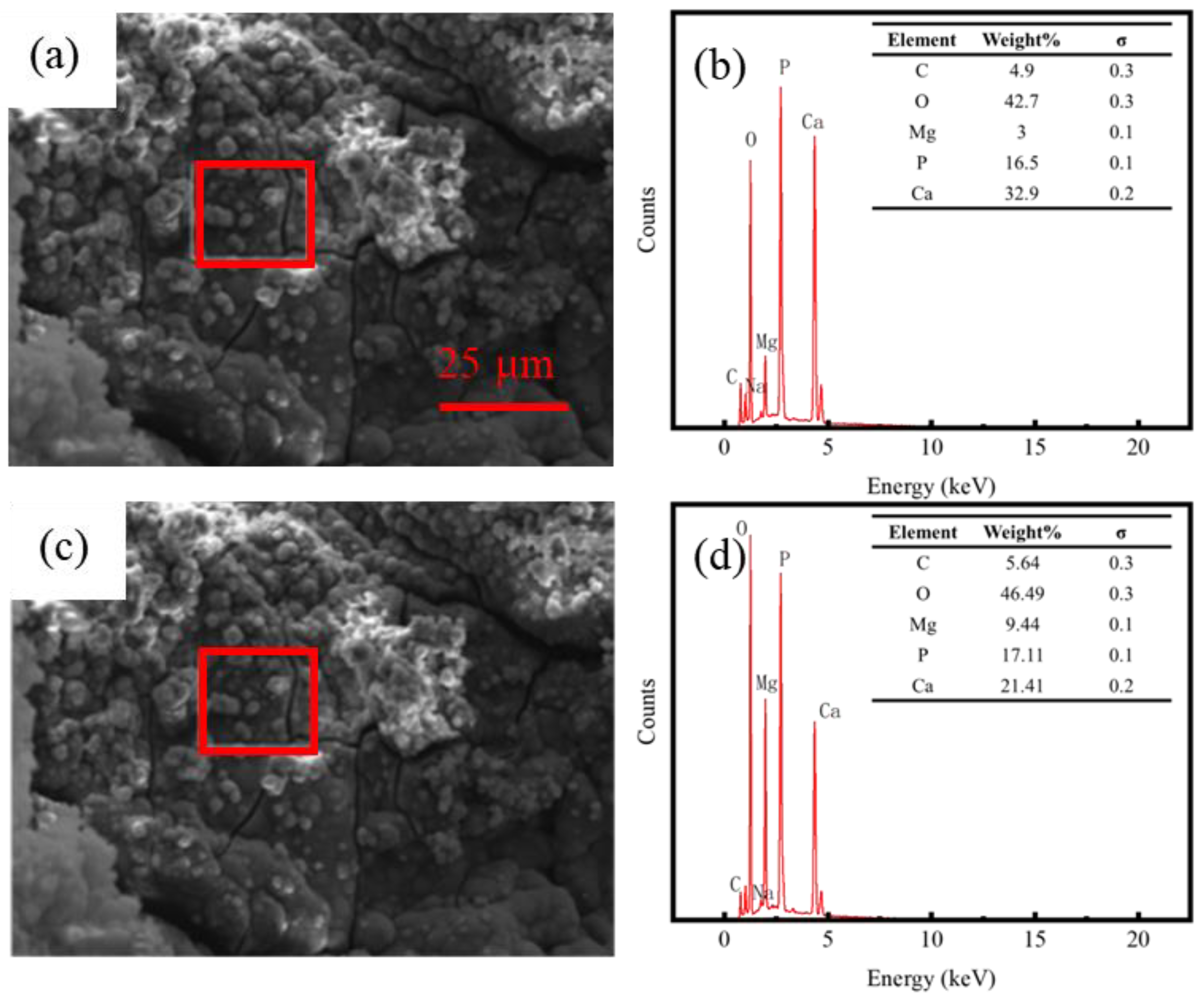
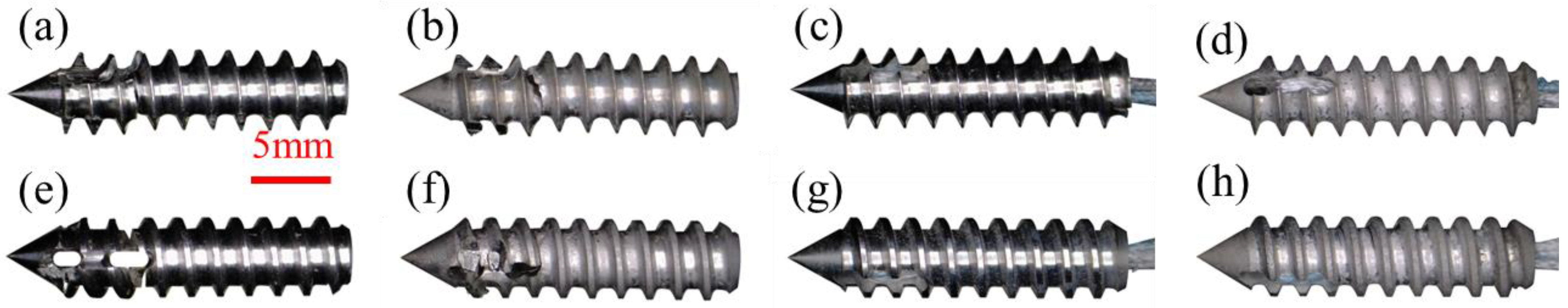
3.2. In Vitro Corrosion Properties of Mg Suture Anchor
3.3. Pull-Out and Torsion Tests of Mg Suture Anchor
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
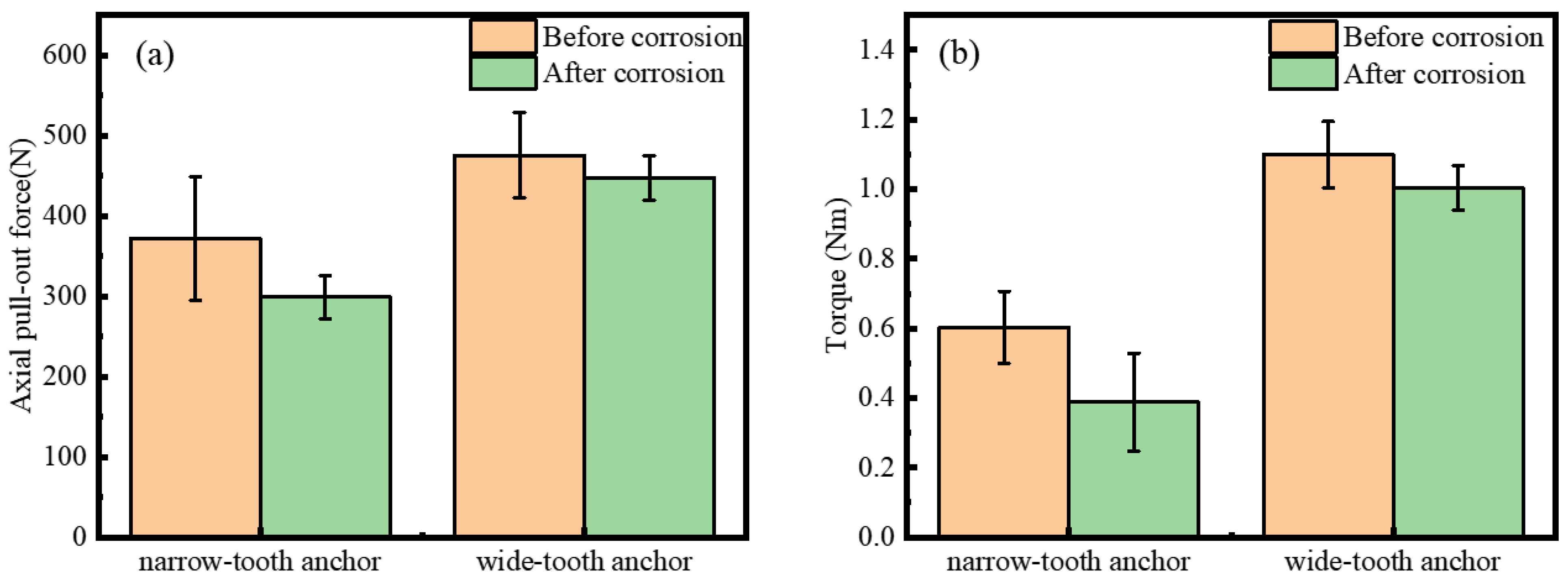
- The simulation results of the torsion and pull-out tests showed that the wide-tooth anchor exhibited a lower shear stress (132 MPa) of 0.2 Nm and less equivalent elastic strain (0.06 mm) under a pull-out force of 300 N than those of the narrow-tooth anchor (244.9 MPa and 0.12 mm).
- (2)
- The corrosion rate of the wide-tooth anchor (0.086 ± 0.011 mm/y) in Hank’s solution after 14-day immersion was slightly slower than that of the narrow-tooth anchor (0.090 ± 0.018 mm/y).
- (3)
- The maximum torques of the wide-tooth anchor before and after corrosion were 1.099 ± 0.10 Nm and 1.004 ± 0.06 Nm, which were much higher than those of the narrow-tooth anchor (0.603 ± 0.10 Nm and 0.388 ± 0.14 Nm). Moreover, the axial pull-out forces of the wide-tooth anchor before and after corrosion were 475.59 ± 53.36 N and 447.73 ± 27.60 N, which were also higher than those of the narrow-tooth anchor (372.05 ± 77.07 N and 299.05 ± 26.73 N).
- (4)
- The axial pull-out force and maximum torque for the wide-tooth anchor decreased by 5.86% and 8.64% after corrosion, which were significantly less than those for the narrow-tooth anchor (19.62% of axial pull-out force and 35.66% of maximum torque).
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, W.L.; Liau, L.L.; Ng, M.H.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Law, J.X. Current Progress in Tendon and Ligament Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 16, 549–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Wang, J.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, W.; Ding, Y.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Wang, L.; et al. Degradation Behavior of Ze21c Magnesium Alloy Suture Anchors and Their Effect on Ligament-Bone Junction Repair. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 26, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, Y.; Fujii, K.; Suzue, N.; Miyatake, K.; Kawasaki, Y.; Yokoyama, K. Repair Tension During Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Is Correlated with Preoperative Tendon Retraction and Postoperative Rotator Cuff Integrity. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2021, 37, 2735–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, C.-H.; Bae, K.-C.; Kim, D.-H. Biomaterials Used for Suture Anchors in Orthopedic Surgery. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2021, 13, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.E. The Development of Biodegradable Metallic Screws and Suture Anchors for Soft Tissue Fixation in Orthopaedic Surgery; University of Pittsburgh: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ro, K.; Pancholi, S.; Son, H.S.; Rhee, Y.G. Perianchor Cyst Formation after Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Using All-Suture–Type, Bioabsorbable-Type, and Peek-Type Anchors. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2019, 35, 2284–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Yang, M.; Kou, Y.; Jiang, B. Absorbable Implants in Sport Medicine and Arthroscopic Surgery: A Narrative Review of Recent Development. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 31, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.W.; Oh, K.-S.; Kang, S.J.; Yoon, J.P.; Kim, J.Y. Clinical Outcomes of Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Using Poly Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid Plus Β-Tricalcium Phosphate Biocomposite Suture Anchors. Clin. Shoulder Elb. 2018, 21, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Xu, H.; Song, F.; Wen, P.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, Y. Additive Manufacturing of Porous Magnesium Alloys for Biodegradable Orthopedic Implants: Process, Design, and Modification. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 182, 79–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, F. Biodegradable Metals. In Biomaterials Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 271–287. [Google Scholar]
- Sezer, N.; Evis, Z.; Kayhan, S.M.; Tahmasebifar, A.; Koç, M. Review of Magnesium-Based Biomaterials and Their Applications. J. Magnes. Alloys 2018, 6, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-L.; Xu, J.-K.; Hopkins, C.; Chow, D.H.-K.; Qin, L. Biodegradable Magnesium-Based Implants in Orthopedics—A General Review and Perspectives. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Lin, F.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Virtanen, S. Corrosion Behavior of Biodegradable Metals in Two Different Simulated Physiological Solutions: Comparison of Mg, Zn and Fe. Corros. Sci. 2021, 182, 109278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, P.; Hort, N. Magnesium Alloys for Biomedical Applications. Metals 2020, 10, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wu, X.; Lou, J.; Zhang, X.; Peng, Z. Rotator Cuff Repair with Biodegradable High-Purity Magnesium Suture Anchor in Sheep Model. J. Orthop. Transl. 2022, 35, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, F.A.; Herbert, M.A.; Beavis, R.C.; Oro, F.B. Suture Anchor Materials, Eyelets, and Designs: Update 2008. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2008, 24, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, S.-W.; Kang, J.-Y.; Lee, J.; Han, S.-H.; Kim, S.-Y. Effect of Structural Design on the Pullout Strength of Suture Anchors for Rotator Cuff Repair. J. Orthop. Res. 2018, 36, 3318–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, M.; Zalaquett, Z.; Fares, M.Y.; Boufadel, P.; Khanna, A.; Abboud, J.A. Osteoporosis in the Setting of Rotator Cuff Repair: A Narrative Review. Shoulder Elb. 2023, 14, 17585732231207338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Zheng, X.; Tian, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Song, C. Structural Optimization, Fabrication, and Corrosion Behaviors of Biodegradable Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr Alloy Hemostatic Clip. Metals 2022, 12, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevill, G.; Keaveny, T.M. Trabecular Bone Strength Predictions Using Finite Element Analysis of Micro-Scale Images at Limited Spatial Resolution. Bone 2009, 44, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YY/T 1867-2023; Sports Medicine Implants Wired Anchor. State Drug Administration: Beijing, China, 2023.
- ASTM F3268-18; Standard Guide for in vitro Degradation Testing of Absorbable Metals. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- ASTM G1-90; Standard Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corrosion Test Specimens. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1999.
- Mao, L.; Zhou, H.; Chen, L.; Niu, J.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, G.; Song, C. Enhanced Biocompatibility and Long-Term Durability in Vivo of Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr Alloy for Vascular Stent Application. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 720, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Fu, B.S.-C.; Mak, K.K.-L.; Blocki, A.M.; Yung, P.S.-H.; Tuan, R.S. Engineering Multi-Tissue Units for Regenerative Medicine: Bone-Tendon-Muscle Units of the Rotator Cuff. Biomaterials 2021, 272, 120789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domb, A.; Mizrahi, B.; Farah, S. Biomaterials and Biopolymers; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; See, C.W.; Li, X.; Zhu, D. Orthopedic Implants and Devices for Bone Fractures and Defects: Past, Present and Perspective. Eng. Regen. 2020, 1, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Chu, P.K. Orthopedic Implants. Encycl. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 1, 425–439. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Shin, D.Y.; Na, Y.; Han, G.; Kim, J.; Kim, N.; Bang, S.-J.; Kang, H.S.; Oh, S.; Yoon, C.-B. Antibacterial Pla/Mg Composite with Enhanced Mechanical and Biological Performance for Biodegradable Orthopedic Implants. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 152, 213523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, A.R.; Wallace, J.S.; Nukavarapu, S.P. Short-Term and Long-Term Effects of Orthopedic Biodegradable Implants. J. Long-Term Eff. Med. Implant. 2011, 21, 93–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olugbade, T.O.; Omiyale, B.O.; Ojo, O.T. Corrosion, Corrosion Fatigue, and Protection of Magnesium Alloys: Mechanisms, Measurements, and Mitigation. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 31, 1707–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, A.; Shirvan, A.R.; Li, Y.; Wen, C. Biodegradable Metallic Suture Anchors: A Review. Smart Mater. Manuf. 2023, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidling, M.; Heilemann, M.; Schoenfelder, S.; Heyde, C.E. Influence of Thread Design on Anchorage of Pedicle Screws in Cancellous Bone: An Experimental and Analytical Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Feng, W.; Yang, D.; Li, G.; Iqbal, K.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H. A Novel Screw Modeling Approach to Study the Effects of Screw Parameters on Pullout Strength. J. Biomech. Eng. 2023, 145, 014502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sanea, A.; Aktas, S.; Celik, T.; Kisioglu, Y. Effects of the Internal Contact Surfaces of Dental Implants on Screw Loosening: A 3-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2023, 130, 603.e1–603.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damisih, D.; Hanafi, R.; Gumelar, M.D.; Sah, J.; Rahmania, A.W.; Gustiono, D.; Nurlina, N.; Arrifqi, M.H.; Setyadi, I.; Triwibowo, B. Pullout Strength Evaluation of Titanium Pedicle Screw in Different Grades of Polyurethane. AIP Conf. Proc. 2023, 2719, 030020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zeng, C.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, T.; Wang, Y. Optimization of Stress Distribution of Bone-Implant Interface (Bii). Biomater. Adv. 2023, 147, 213342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, L.; Dai, Z.; Cai, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Song, C. Mechanical Properties and In Vitro Corrosion Behaviors of Biodegradable Magnesium Alloy Suture Anchors. Metals 2024, 14, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030288
Mao L, Dai Z, Cai X, Hu Z, Zhang J, Song C. Mechanical Properties and In Vitro Corrosion Behaviors of Biodegradable Magnesium Alloy Suture Anchors. Metals. 2024; 14(3):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030288
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Lin, Zhiwei Dai, Xue Cai, Zhongxin Hu, Jian Zhang, and Chengli Song. 2024. "Mechanical Properties and In Vitro Corrosion Behaviors of Biodegradable Magnesium Alloy Suture Anchors" Metals 14, no. 3: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030288
APA StyleMao, L., Dai, Z., Cai, X., Hu, Z., Zhang, J., & Song, C. (2024). Mechanical Properties and In Vitro Corrosion Behaviors of Biodegradable Magnesium Alloy Suture Anchors. Metals, 14(3), 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030288






