Study of Tuyere Combustion Flame Temperature in Vanadium and Titanium Blast Furnaces by Machine Vision and Colorimetric Thermometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
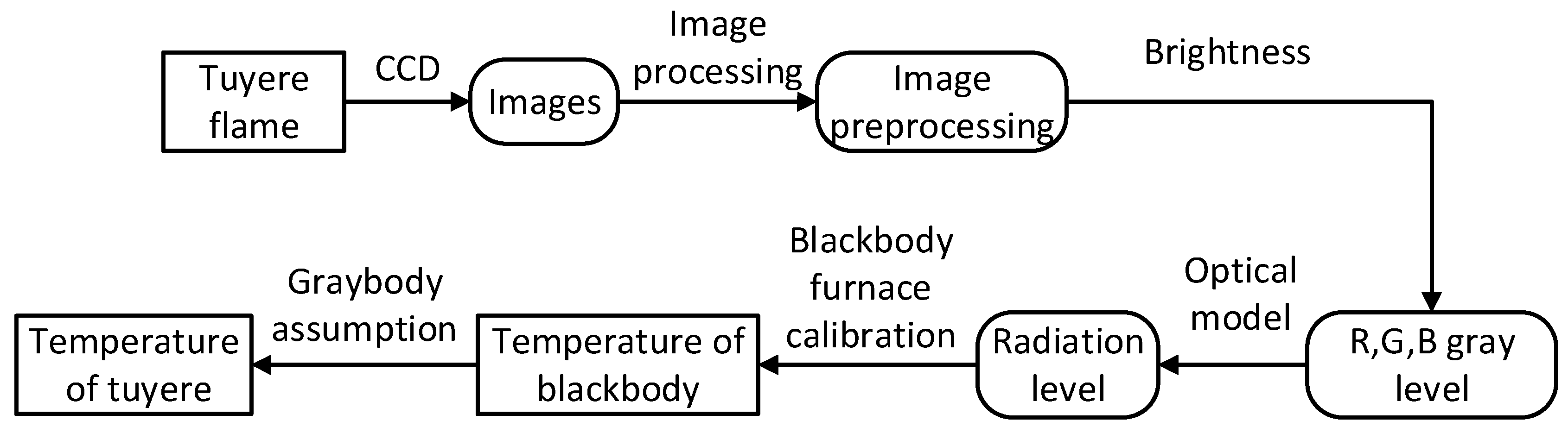
2.1. Colorimetric Temperature Measuring Methodology
- ε(λ, T) is the effective spectral emissivity of radiation (-);
- T represents temperature (K);
- C1 is the first radiation constant of Planck (W·m2);
- C2 is the second radiation constants of Planck (m·K);
- , are the gray levels of 1, 2 wavelengths (-);
- λ1, λ2 are the wavelengths of 1, 2 wavelengths (m);
- , are the calibration coefficients of the calculation model (-);
- ε1, ε2 is the emissivity of 1, 2 wavelengths (-).
2.2. Blackbody Furnace Calibration
2.3. Research Scheme
3. Results and Discussion
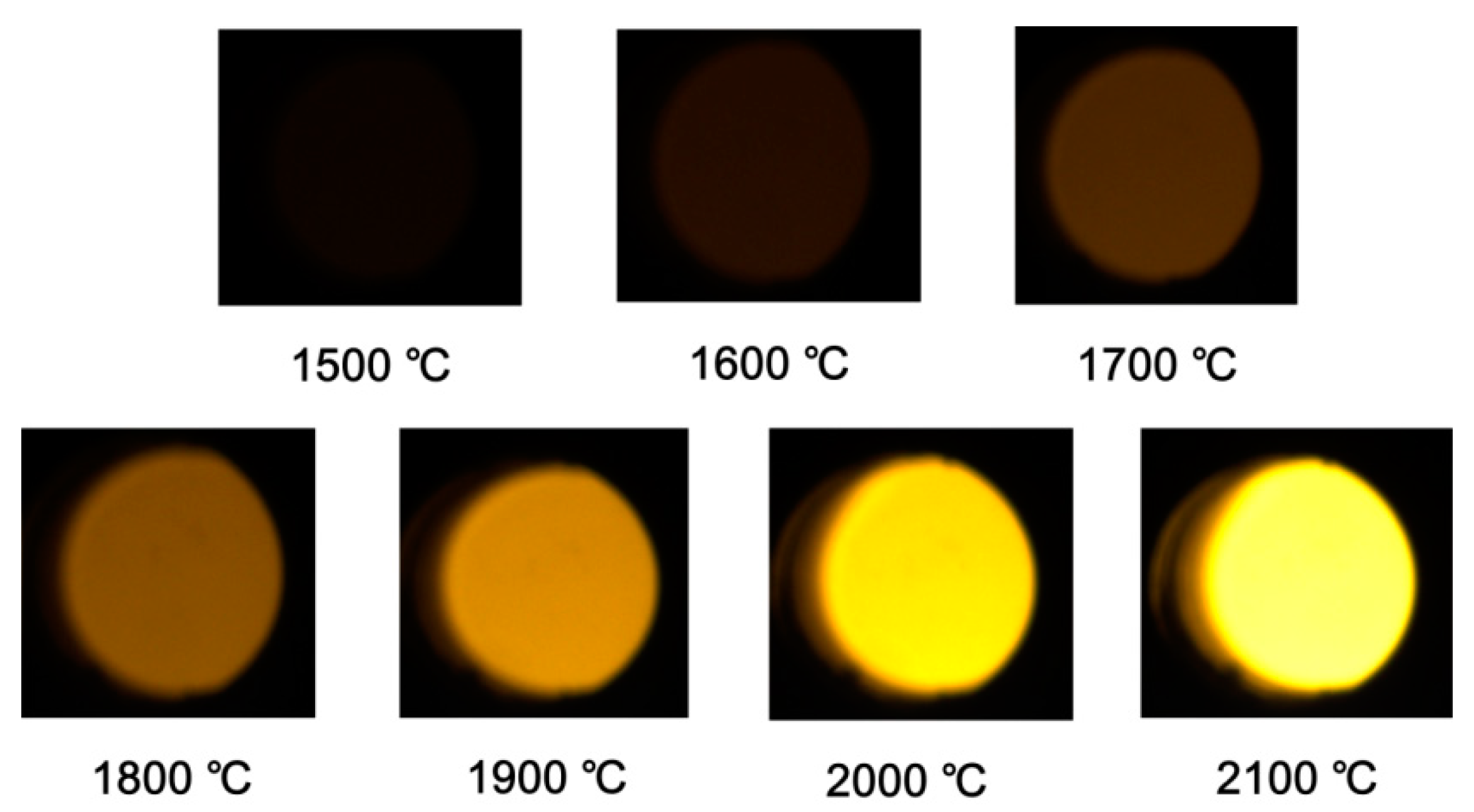
3.1. Results of Calibration Process
3.2. Results of Imaging Parameter Selection of Tuyere
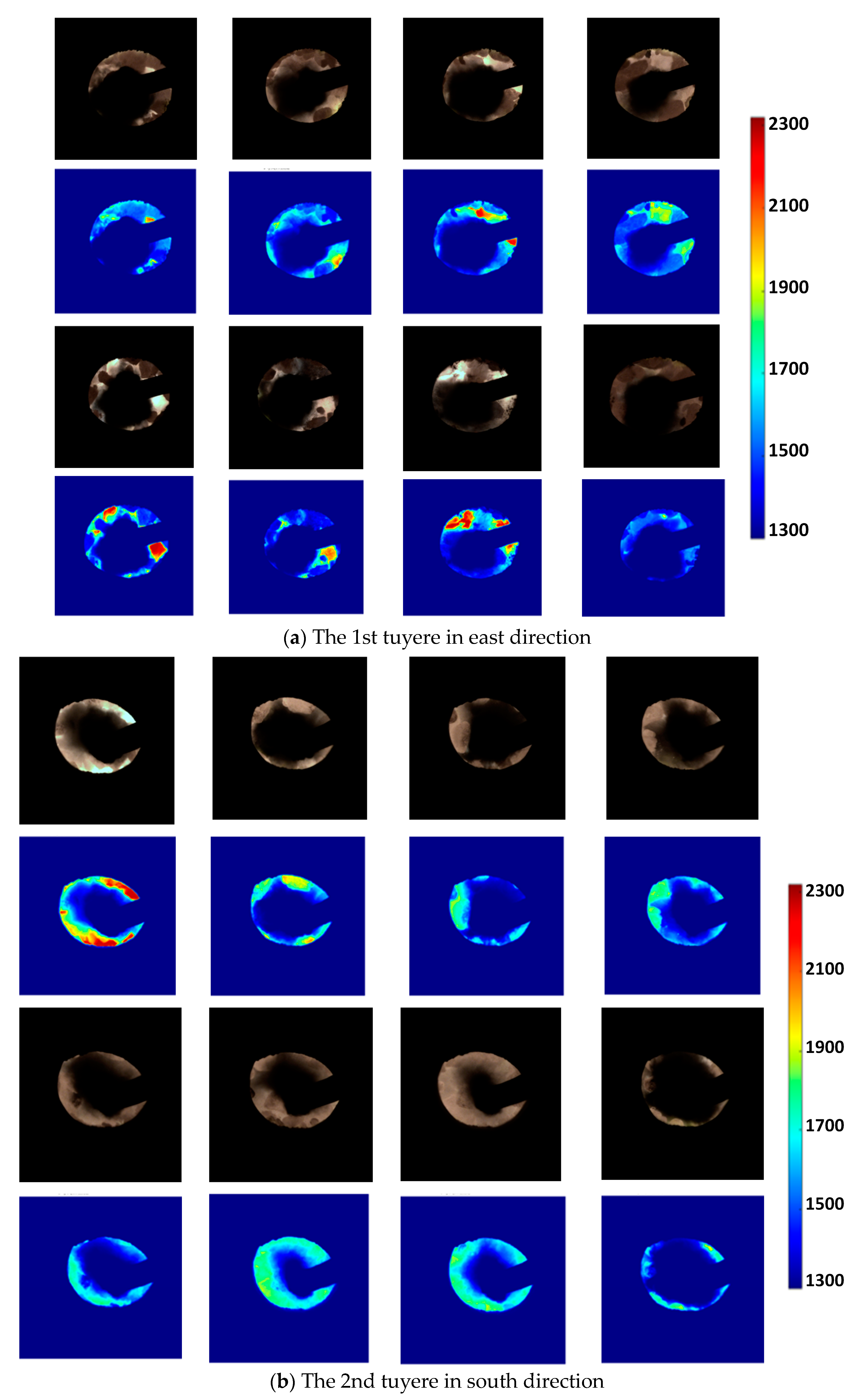
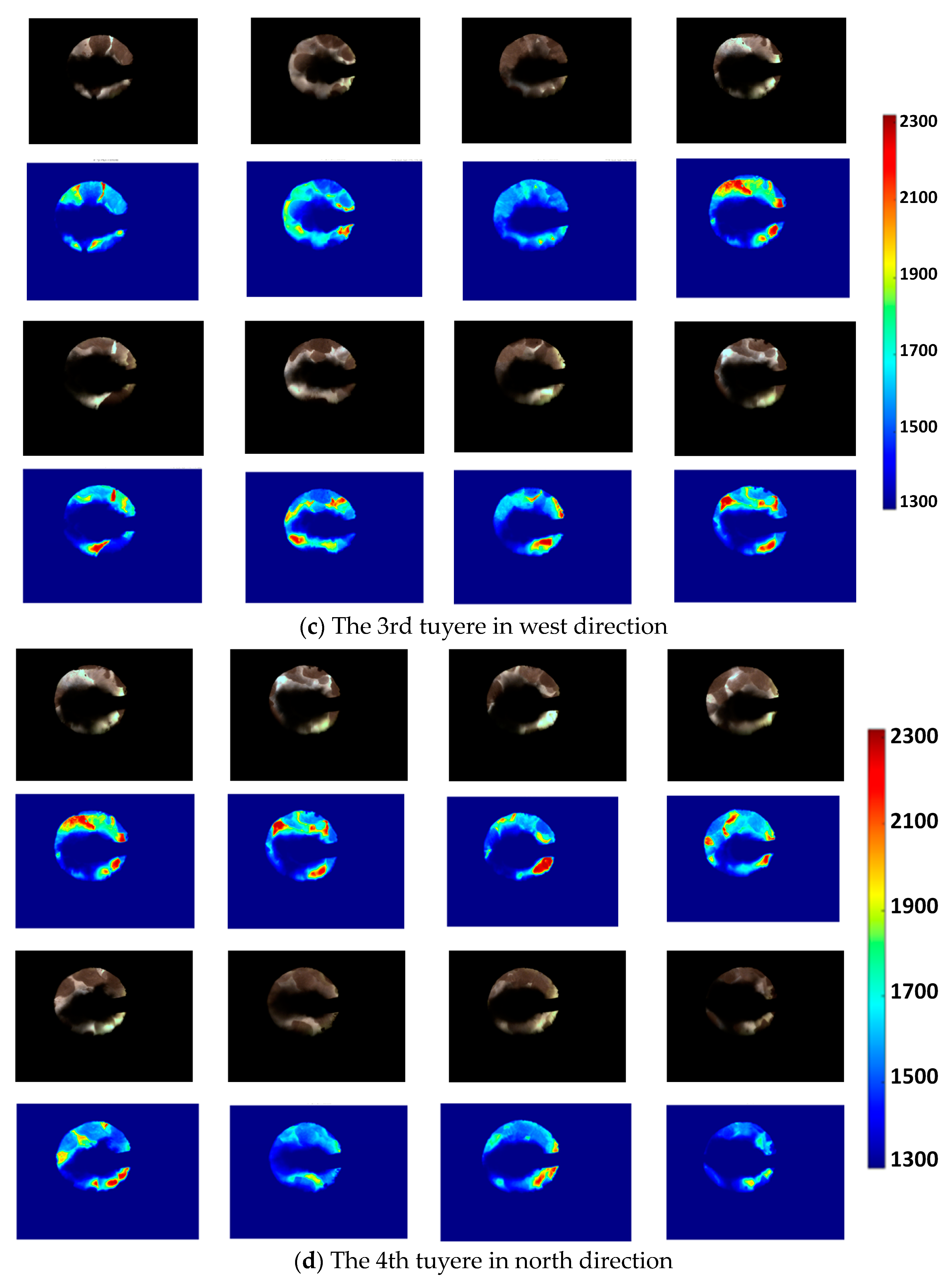
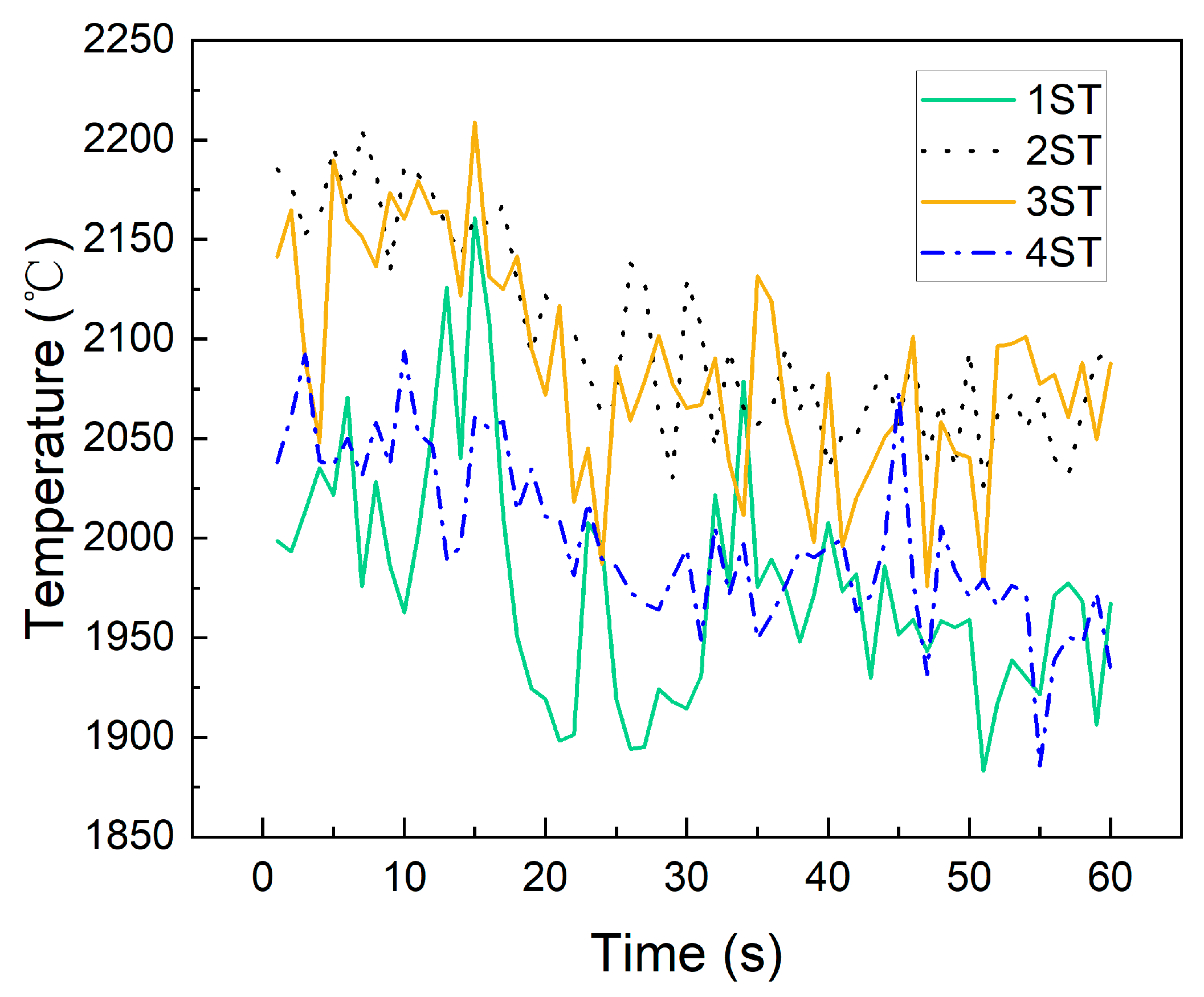
3.3. Results of Four-Direction Tuyere Combustion Flame Temperature
3.4. Analysis of Blast Operation Parameters and Tuyere Combustion Flame Temperatures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mele, M.; Magazzino, C. A Machine Learning analysis of the relationship among iron and steel industries, blast pollution, and economic growth in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Wen, X.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y. Intelligent manufacturing in industry 4.0: A case study of Sany heavy industry. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2020, 37, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Feng, L.; Wang, J.; Lin, K. Integration of Design, Manufacturing, and Service Based on Digital Twin to Realize Intelligent Manufacturing. Machines 2022, 10, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Xu, K.; Lv, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, M.; He, F.; Xu, G. Intelligent Manufacturing Technology in the Steel Industry of China: A Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 8194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.D.; Xu, K.; Zhou, P.; Jiang, X. The production of large blast furnaces of China in 2018 and thoughts of intelligent manu-facturing in the ironmaking process. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2020, 47, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, K. Abnormality Detection of Blast Furnace Tuyere Based on Knowledge Distillation and a Vision Transformer. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cai, J. A Hybrid Cluster Variational Autoencoder Model for Monitoring the Multimode Blast Furnace System. Processes 2023, 11, 2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Z.; Lu, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, Y. Economic Analysis of an Integrated Steel Plant Equipped with a Blast Furnace or Oxygen Blast Furnace. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Yan, L.; Jiao, K. Optimization Study of Annular Wear-Resistant Layer Structure for Blast Furnace Tuyere. Metals 2023, 13, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A. Development of techniques for monitoring the raceway zone. Eur. Comm. Tech. Steel Res. 1997, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Lu, G.; Colechin, M. Monitoring and characterization of Pulverized coal flames using digital imaging techniques. Fuel 2002, 81, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.F.; Wen, L.Y.; Bai, C.G.; Chen, D.; Ouyang, Q. The temperature field digitization of radiation images in blast furnace raceway. ISIJ Int. 2006, 46, 1410–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Sawayama, M.; Kitano, S.; Nagai, N.; Imai, T. Analyses on blast furnace raceway formation by micro wave reflection gunned through tuyere. ISIJ Int. 2005, 45, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinero, J.; Gómez-Barea, A.; Tripiana, M.; Leckner, B. Measurement of char surface temperature in a fluidized bed combustor using pyrometry with digital camera. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 288, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, T. Study of the combustion behaviour and temperature of pulverised coal in a raceway zone of BF. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2017, 45, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, T. Uniformity and Activity of BF Hearth by Monitoring Flame Temperature of Raceway Zone. ISIJ Int. 2017, 57, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttinger, S.; Stocker, H. Improving Blast Furnace Raceway Blockage Detection. Part 1: Classification of Blockage Events and Processing Framework. ISIJ Int. 2019, 59, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttinger, S.; Stocker, H. Improving Blast Furnace Raceway Blockage Detection. Part 2: Signal Processing of Hot Blast Pressure Data. ISIJ Int. 2019, 59, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttinger, S.; Stocker, H. Improving Blast Furnace Raceway Blockage Detection. Part 3: Visual Detection Based on Tuyere Camera Images. ISIJ Int. 2018, 59, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, P.; Yang, G. A Visual PCI Blockage Detection in Blast Furnace Raceway. ISIJ Int. 2020, 60, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y. A visual detection method for PCI blockage and coke size distribution in tuyere raceway. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2020, 48, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Cheng, S. Measurement study of the PCI process on the temperature distribution in raceway zone of blast furnace by using digital imaging techniques. Energy 2019, 174, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Cheng, S.; Liu, K.; Zhou, D. Measurement study of preheated pulverized coal injection on combustion in a blast furnace raceway by visual detection. Fuel 2020, 271, 117626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Xu, K.; Bai, J.; He, D. On-line detecting the tuyere coke size and temperature distribution of raceway zone in a working blast furnace. Fuel 2022, 316, 123349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
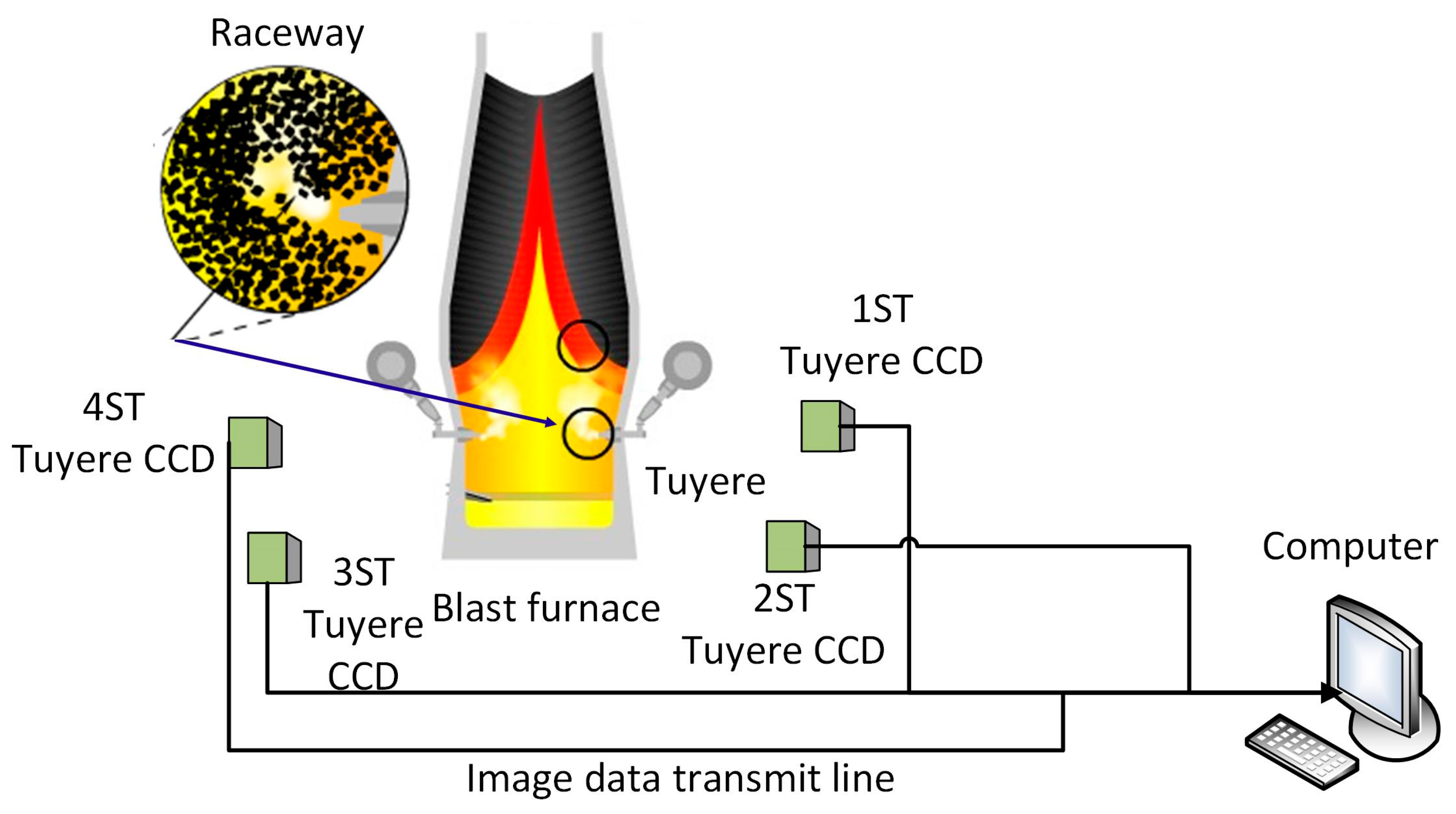



| Volume (m3) | Daily Production (t) | Coke Rate (kg/t) | PCI Rate (kg/t) | Tuyere Number | Tuyere Diameter (m) | Blast Volume (m3/min) | Raw Iron Content (%) | Blast Temperature (°C) | Oxygen Enrichment (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | 2150 | 420 | 138 | 14 | 0.12 | 1600 | 57 | 981 | 5.83 |
| Coke | Fixed Carbon (%) | Ash (%) | Volatile (%) | M40 (%) | M10 (%) | Diameter (mm) | |||
| Coke Constituents | 2.32 | 18.37 | 47.77 | 25.94 | 5.60 | 47.94 | |||
| Hot metal | Si (%) | S (%) | Mn (%) | P (%) | Ti (%) | V (%) | Temperature (°C) | ||
| Hot metal Constituents | 0.32 | 0.038 | 0.23 | 0.098 | 0.26 | 0.303 | 1425.9 | ||
| Slag | SiO2 (%) | CaO (%) | MgO (%) | S (%) | Al2O3 (%) | MnO (%) | TiO2 (%) | V2O5 (%) | R2 (-) |
| Slag Constituents | 28.22 | 34.32 | 9.3 | 0.816 | 13 | 0.63 | 9.55 | 0.227 | 1.22 |
| R-Channel Image | G-Channel Image | B-Channel Image | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGV | AGV | MGV | AGV | MGV | AGV | |
| 1500 °C | 14 | 11.8 | 7 | 5.39 | 1 | 0.089 |
| 1600 °C | 27 | 23.04 | 15 | 12.58 | 2 | 0.65 |
| 1700 °C | 51 | 46.17 | 30 | 26.72 | 4 | 2.14 |
| 1800 °C | 86 | 78.07 | 55 | 49.63 | 7 | 4.84 |
| 1900 °C | 142 | 131.85 | 97 | 90.27 | 14 | 10.95 |
| 2000 °C | 214 | 203.1 | 158 | 148.03 | 27 | 21.94 |
| 2100 °C | - | - | 255 | 243.6 | 56 | 48.85 |
| Exposure Time/μs | 1st Tuyere | 2nd Tuyere | 3rd Tuyere | 4th Tuyere | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGV | AGV | MGV | AGV | MGV | AGV | MGV | AGV | |
| 10 | 116 | 18.89 | 111 | 21.80 | 154 | 36.06 | 103 | 15.11 |
| 30 | 142 | 19.11 | 166 | 30.25 | 183 | 49.07 | 139 | 17.43 |
| 50 | 201 | 28.73 | 205 | 38.07 | 209 | 55.72 | 194 | 26.45 |
| 70 | 226 | 33.29 | 243 | 54.08 | 242 | 59.08 | 183 | 33.39 |
| 90 | 255 | 42.74 | 255 | 55.55 | 255 | 62.08 | 255 | 40.46 |
| 110 | 255 | 46.66 | 255 | 68.87 | 255 | 82.71 | 255 | 48.25 |
| Hours/h | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Blast Volume/(m3/min) | 1363 | 1456 | 1467 | 1479 | 1541 | 1489 | 1521 | 1532 | 1536 | 1525 | 1313 | 1501 |
| Average PCI Rate/(kg/t) | 116 | 121 | 135 | 135 | 141 | 161 | 136 | 142 | 151 | 144 | 155 | 138 |
| Hours/h | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| Average Blast Volume/(m3/min) | 1521 | 1531 | 1525 | 1530 | 1541 | 1492 | 1518 | 1518 | 1573 | 1576 | 1468 | 1397 |
| Average PCI Rate/(kg/t) | 142 | 158 | 152 | 153 | 149 | 149 | 140 | 137 | 146 | 144 | 137 | 137 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, D. Study of Tuyere Combustion Flame Temperature in Vanadium and Titanium Blast Furnaces by Machine Vision and Colorimetric Thermometry. Metals 2024, 14, 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14050499
Cai H, Zhu Z, Zhou D. Study of Tuyere Combustion Flame Temperature in Vanadium and Titanium Blast Furnaces by Machine Vision and Colorimetric Thermometry. Metals. 2024; 14(5):499. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14050499
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Haoyu, Ziming Zhu, and Dongdong Zhou. 2024. "Study of Tuyere Combustion Flame Temperature in Vanadium and Titanium Blast Furnaces by Machine Vision and Colorimetric Thermometry" Metals 14, no. 5: 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14050499
APA StyleCai, H., Zhu, Z., & Zhou, D. (2024). Study of Tuyere Combustion Flame Temperature in Vanadium and Titanium Blast Furnaces by Machine Vision and Colorimetric Thermometry. Metals, 14(5), 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14050499







