Neutron Diffraction Measurements of Residual Stresses for Ferritic Steel Specimens over 80 mm Thick
Abstract
1. Introduction
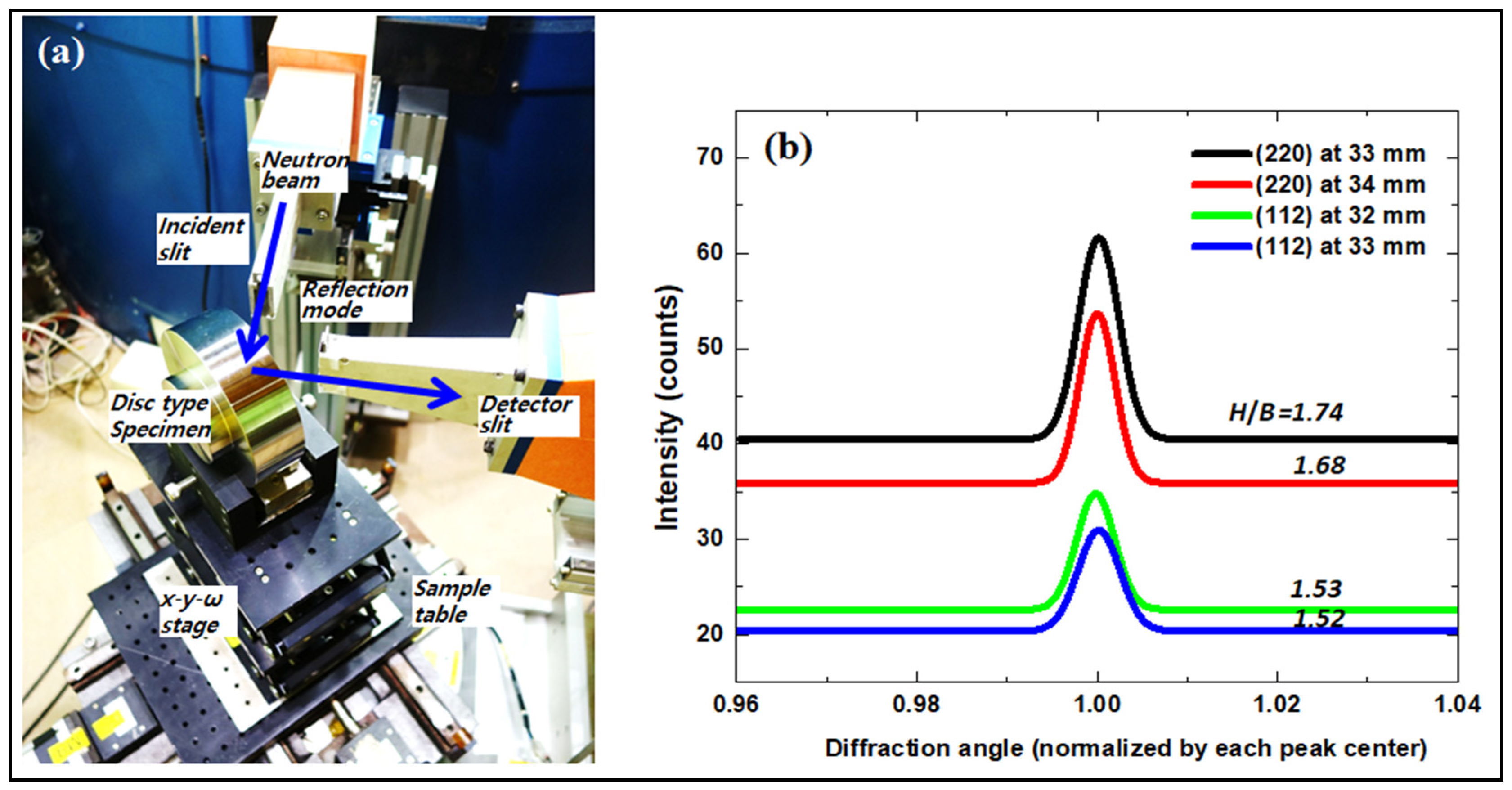
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
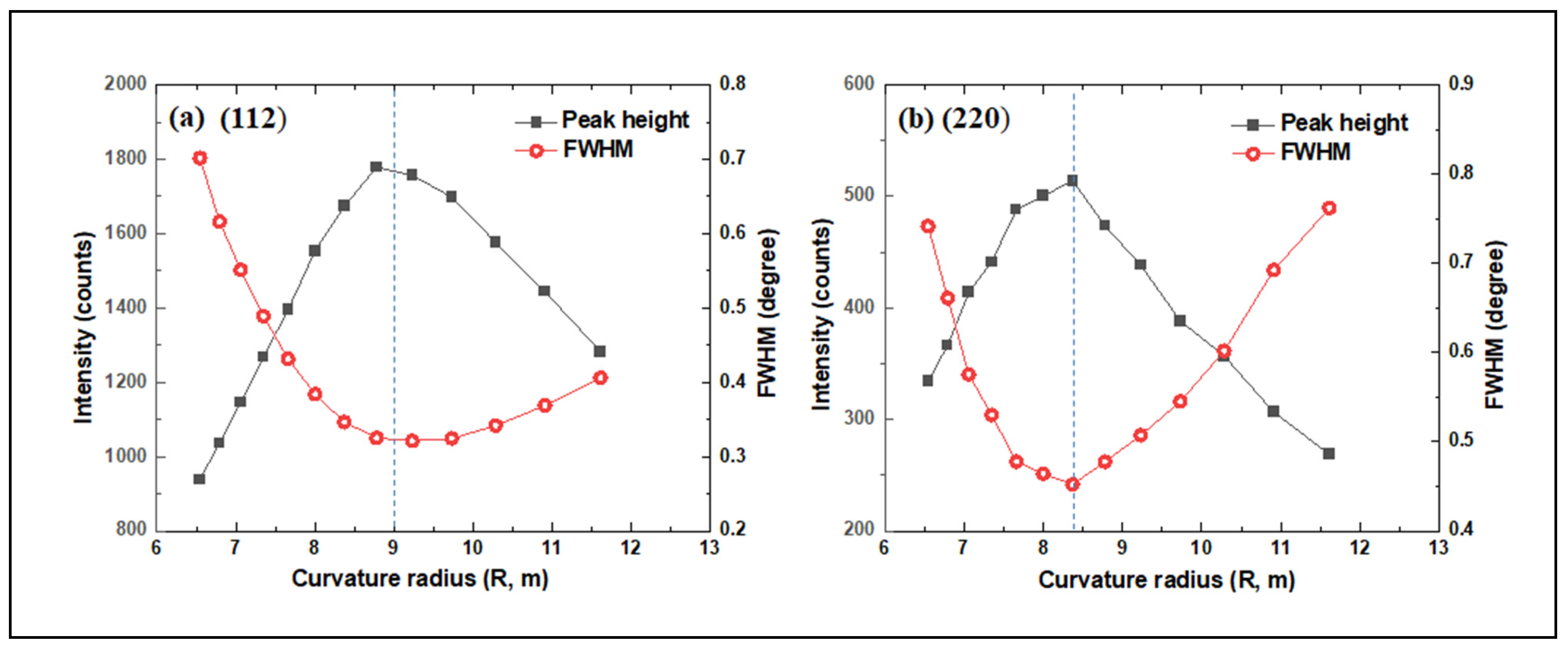
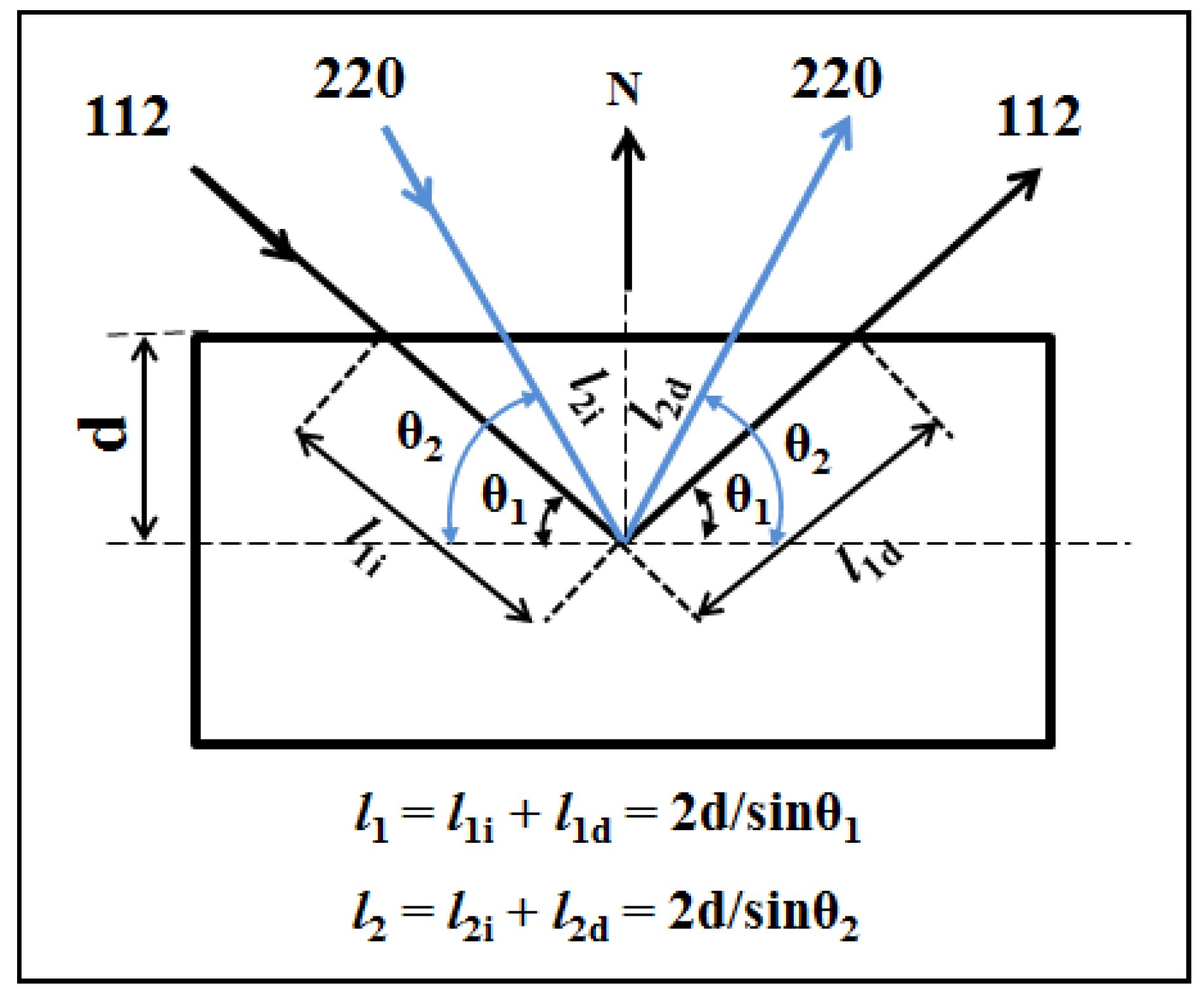
3.1. Optimum Beam Properties for (112) and (220) Diffractions in Ferritic Steels
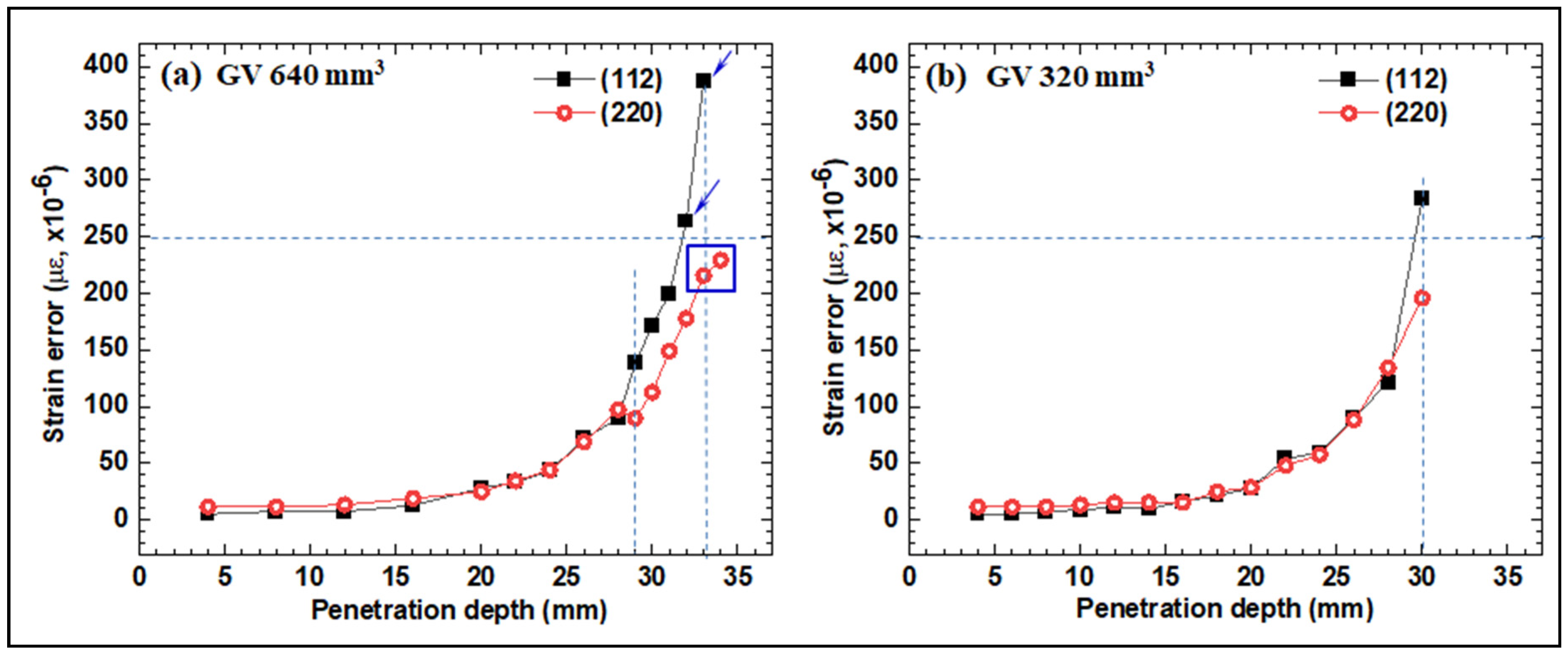
3.2. Strain Error Measurements as a Function of the Penetration Depth
3.3. Reasons for the Lower Strain Errors with the (220) Diffraction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Withers, P.J.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Overview residual stress, part 2: Nature and origin. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2001, 17, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, M.T.; Withers, P.J.; Holden, T.M.; Lorentzen, T. Introduction to the Characterization of Residual Stress by Neutron Diffraction; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Santistaban, J.R.; Daymond, M.R.; James, J.A.; Edvards, L. ENGIN-X: A third-generation neutron strain scanner. J. Appl. Cryst. 2006, 39, 812–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.J.; Bouchard, P.J.; George, D. Measurement andprediction of residual stresses in thick-section steel welds. J. Strain Anal. 2000, 35, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, N.S.; Dassisti, M.; Benyounis, K.Y.; Olabi, A.G. Review: Methods of measuring residual stress in components. Mater. Des. 2012, 35, 572–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dive, V.; Lakade, S. Recent Research Progress on Residual Stress Measurement Using Non-Destructive Testing. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 3282–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, P.J. Depth capabilities of neutron and synchrotron diffraction strain measurement instruments, I. The maximum feasible path length. J. Appl. Cryst. 2004, 37, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, P.J. Depth capabilities of neutron and synchrotron diffraction strain measurement instruments, II. Practical implications. J. Appl. Cryst. 2004, 37, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, W.; Em, V.; Seong, B.S.; Shin, E.; Mikula, P.; Joo, J.; Kang, M. Effect of wavelentgh-dependent attenuation on neutron diffraction stress measurerments at depth in steel. J. Appl. Cryst. 2011, 44, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodh, A.; Thool, K.; Samajdar, I. X-ray Diffraction for the Determination of Residual Stress of Crystalline Material: An Overview. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2022, 75, 983–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, W.; An, G.B.; Kingston, E.J.; DeWald, A.T.; Smith, D.J.; Hill, M.R. Through-thickness distributions of residual stresses in two extreme heat-input thick welds: A neutron diffraction, contour method and deep hole drilling study. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 3564–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, W.; An, G.B.; Em, V.T.; DeWald, A.T.; Hill, M.R. Through-thickness distributions of residual stresses in an 80 mm thick weld using neutron diffraction and contour method. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Li, J.; Wan, Y.; Sun, G.; Tu, S.-Y.; Woo, W. Determination of the through-thickness residual stress in thick duplex stainless steel welded plate by wavelength-dependent neutron diffraction method. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2022, 196, 104603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovici, M.; Yelon, W.B.; Berliner, R.; Stoica, A.D.; Ionita, I.; Law, R. Curved crystal optics and the resolution formalism: Programs and optimization procedures. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 1994, 338, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, J.; Evans, A.; Mishurova, T.; Ulbricht, A.; Sprengel, M.; Serrano-Munoz, I.; Fritsch, T.; Kromm, A.; Kannengießer, T.; Bruno, G. Diffraction-Based Residual Stress Characterization in Laser Additive Manufacturing of Metal. Metals 2021, 11, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovici, M.; Stoica, A.D. Neutron imaging with multi-wafer monochromators. Appl. Phys. A 2002, 74, S273–S276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, M.-K.; Em, V.T.; Lee, C.-H.; Mikula, P.; Hong, K.-P.; Choi, Y.-H.; Cheon, J.-K.; Nam, U.-W.; Kong, K.-N.; Jin, K.-C. Optimization of bent perfect Si(2 2 0) crystal monochromator for residual strain/stress instrument. Part II. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2005, 368, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, O.; Zhu, B.; Leung, N.; Kockelmann, W.; Barrett, T.R.; Whiting, M.J.; Wang, Y.; Sui, T. The use of time-of-flight neutron Bragg edge imaging to measure the residual strains in W/Cu dissimilar joints for fusion reactors. Nucl. Mater. Energy 2024, 38, 101593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, J.R.; Fancher, C.M.; Payzant, E.A.; Cornwell, P.A.; Bailey, W.B.; Gregory, R. The high intensity diffractometer for residual stress analysis (HIDRA), a third generation residual stress mapping neutron diffractometer at the high flux isotope reactor. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2023, 94, 035101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Tan, Z.; Lu, H.; Deng, S.; Shen, F.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, H.; Ma, Q.; Chen, J.; He, L. Residual stress measurement system of the general purpose powder diffractometer at CSNS. Nucl. Inst. Methods Phys. Res. A 2023, 1055, 168532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, P.J.; Daymond, M.R.; Johnson, M.W. The precision of diffraction peak location. J. Appl. Cryst. 2001, 34, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
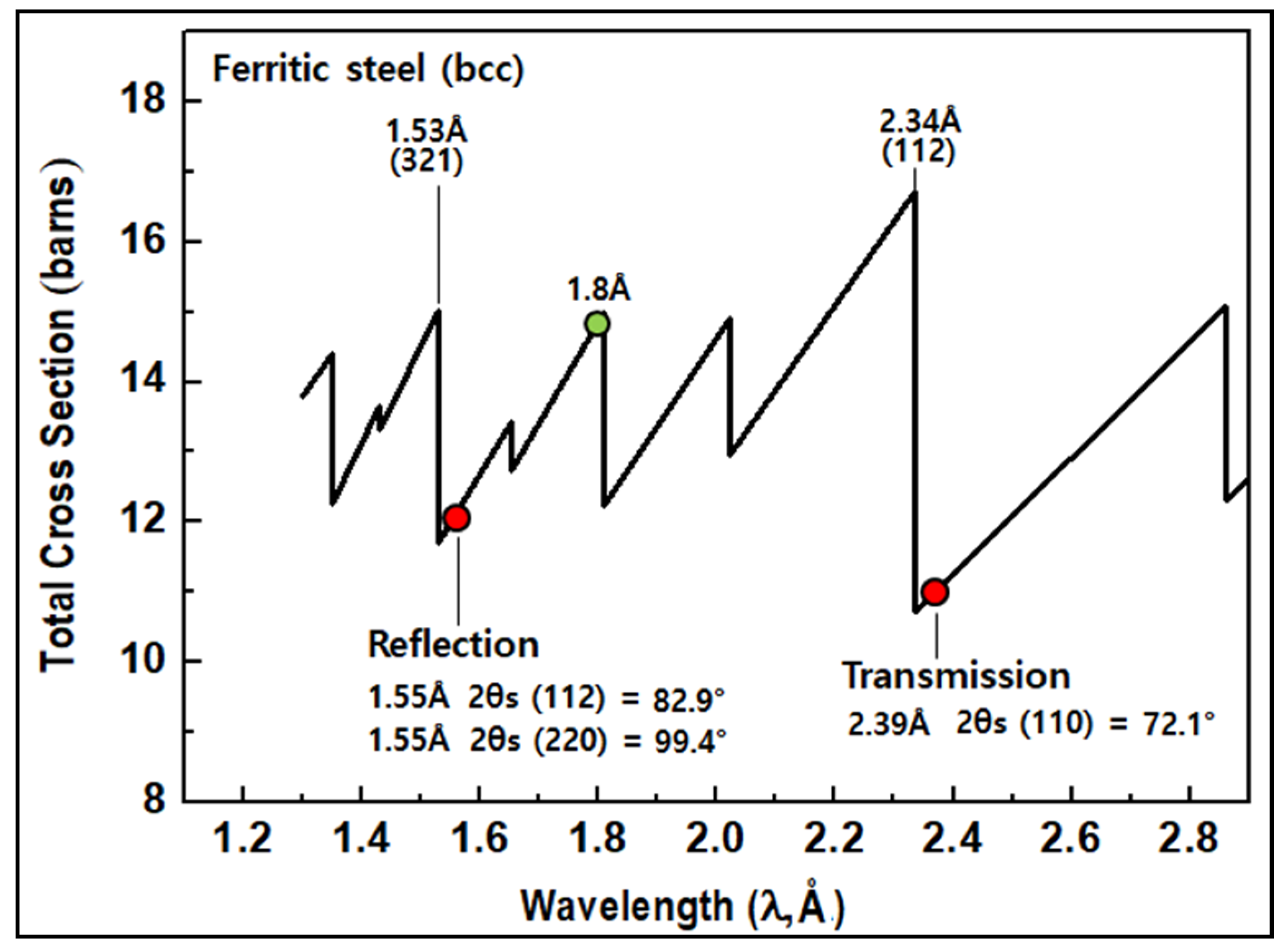


| Configuration | Monochromator | 2θM (deg) | λ (Å) | Diffraction Plane | Diffraction Angle (2θ, deg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Si (111) | 45 | 2.39 | (110) | 72.1 |
| 2 | Si (220) | 48 | 1.55 | (112) | 82.9 |
| 3 | Si (220) | 48 | 1.55 | (220) | 99.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Em, V.; Ivan, K.; Woo, W.; Mikula, P. Neutron Diffraction Measurements of Residual Stresses for Ferritic Steel Specimens over 80 mm Thick. Metals 2024, 14, 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14060638
Em V, Ivan K, Woo W, Mikula P. Neutron Diffraction Measurements of Residual Stresses for Ferritic Steel Specimens over 80 mm Thick. Metals. 2024; 14(6):638. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14060638
Chicago/Turabian StyleEm, Vyacheslav, Karpov Ivan, Wanchuck Woo, and Pavol Mikula. 2024. "Neutron Diffraction Measurements of Residual Stresses for Ferritic Steel Specimens over 80 mm Thick" Metals 14, no. 6: 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14060638
APA StyleEm, V., Ivan, K., Woo, W., & Mikula, P. (2024). Neutron Diffraction Measurements of Residual Stresses for Ferritic Steel Specimens over 80 mm Thick. Metals, 14(6), 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14060638






