The Influence of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing on the Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of IS2062 Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
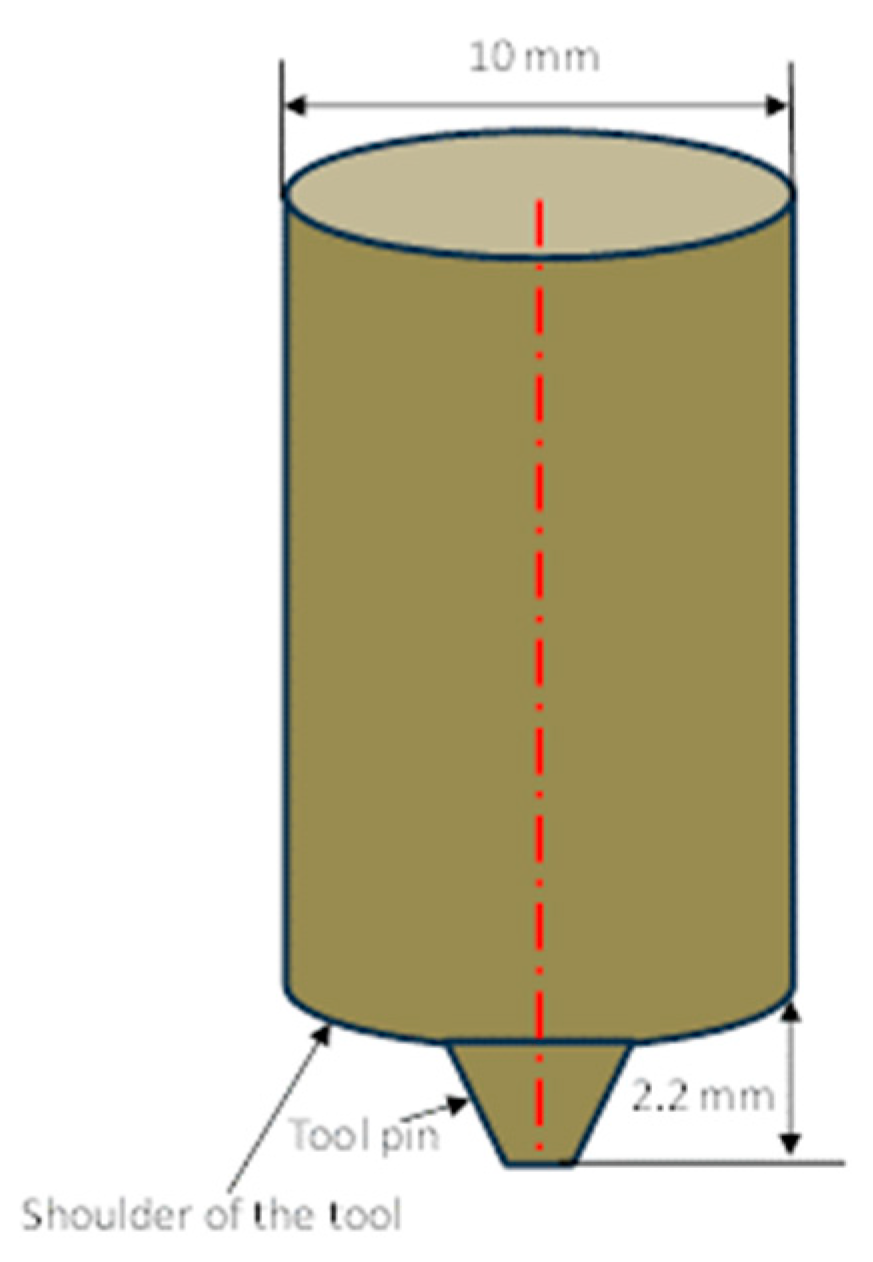
2. Materials and Methods
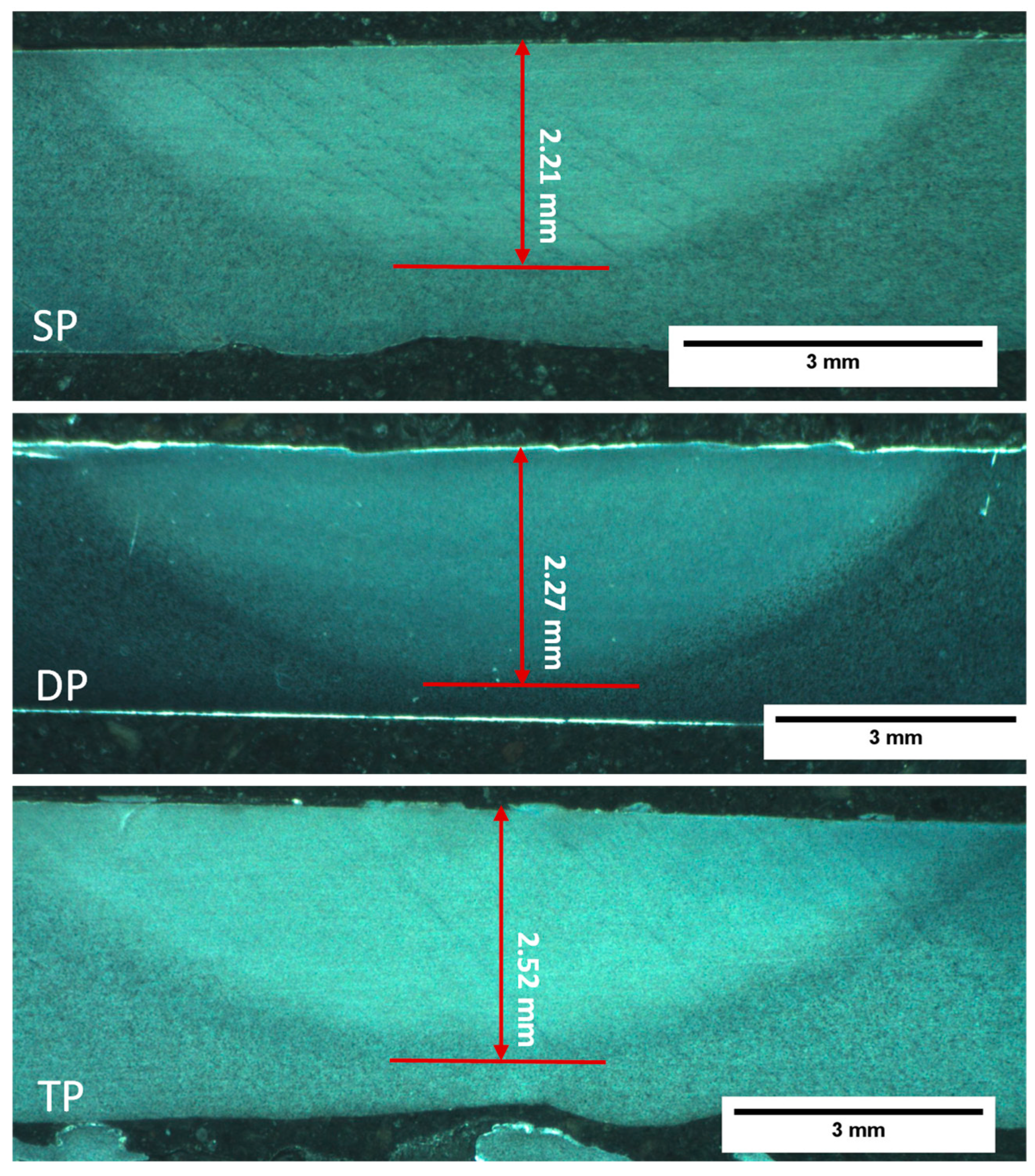
3. Results
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
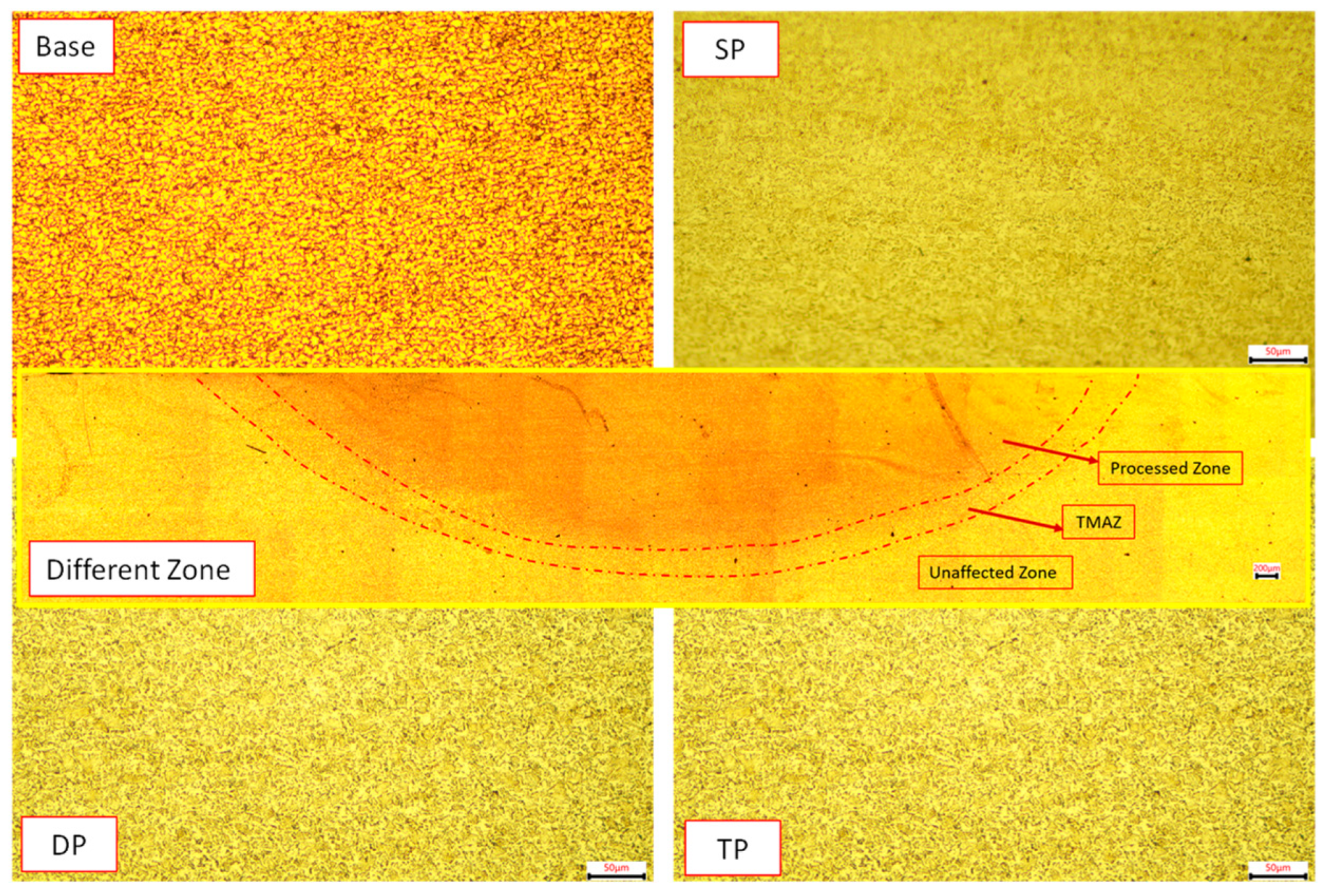
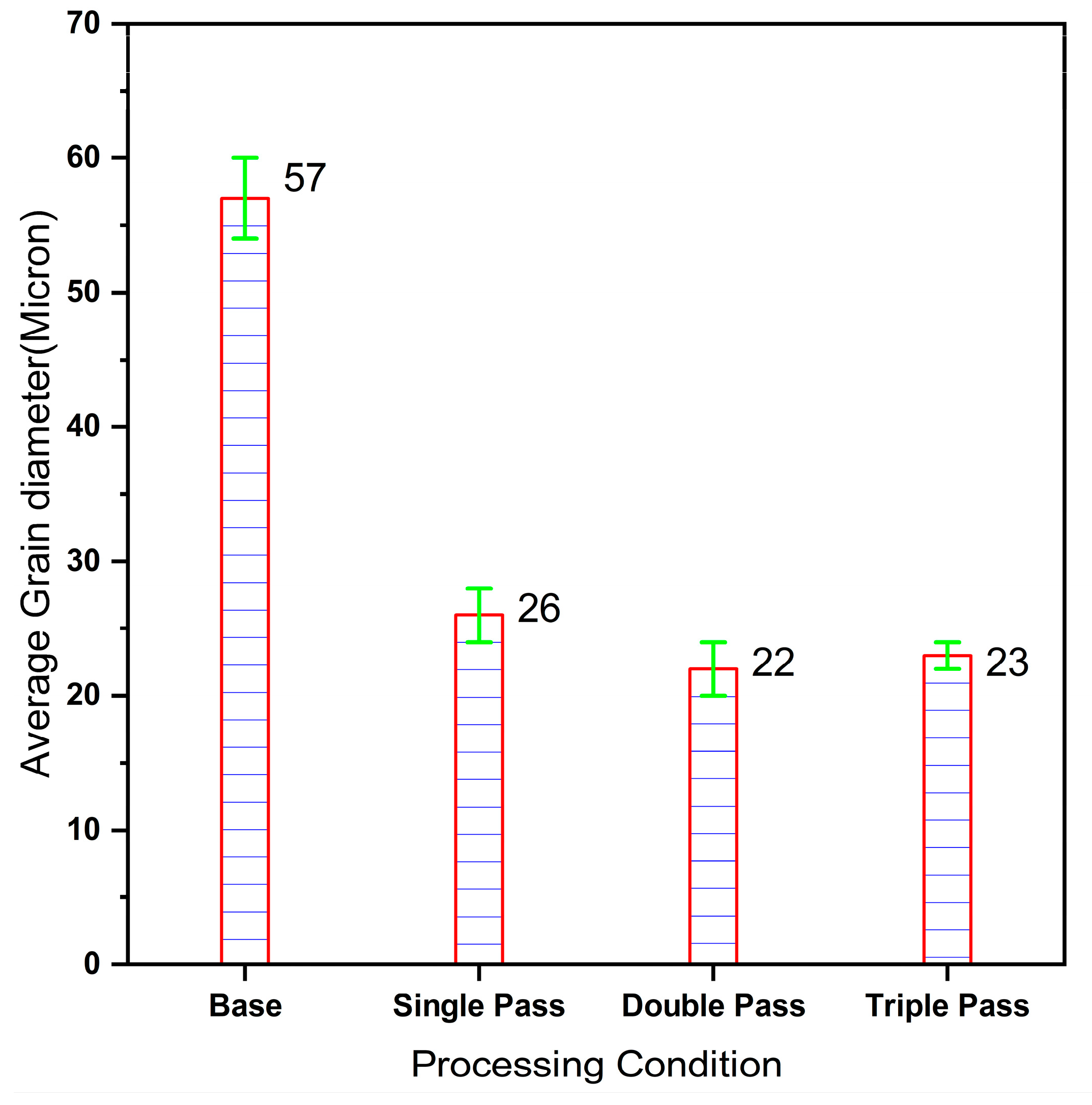
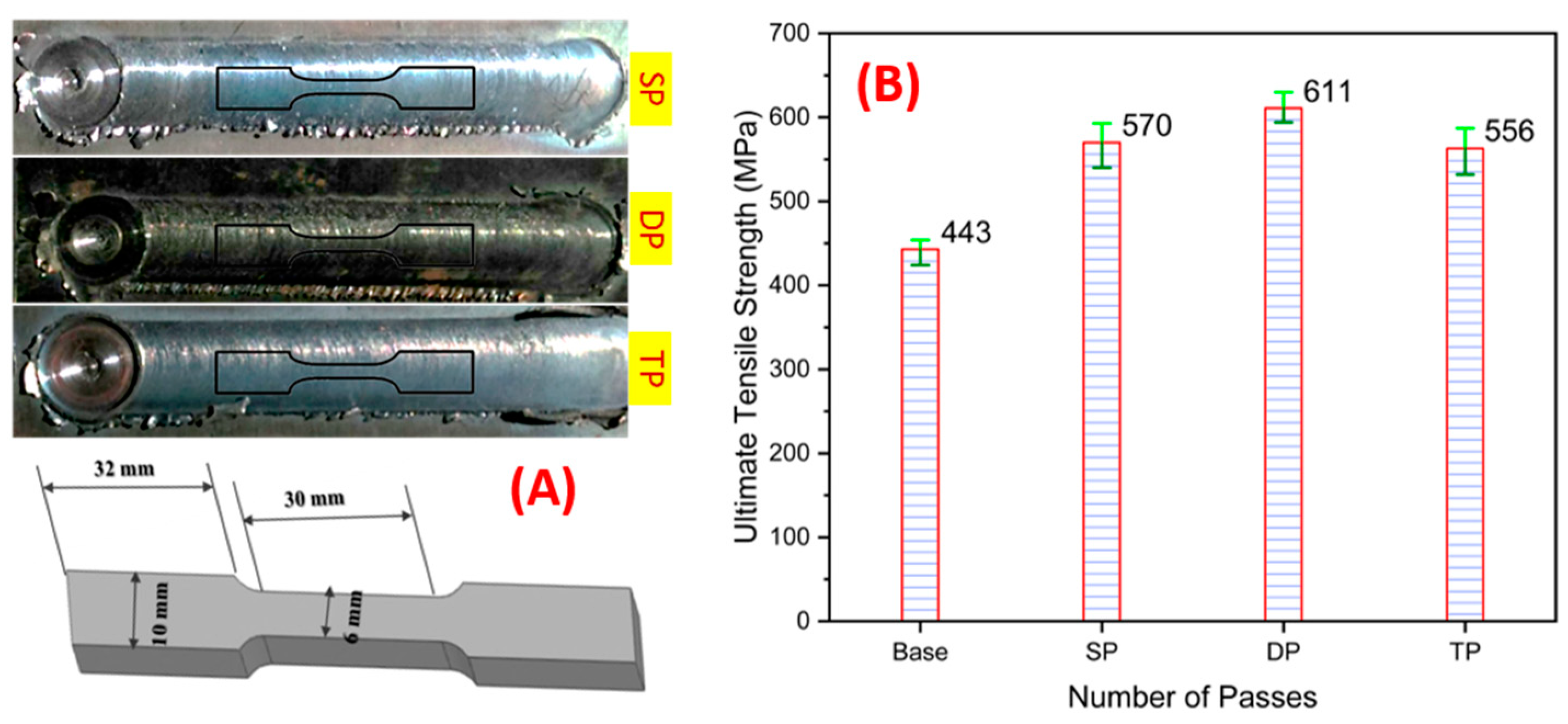
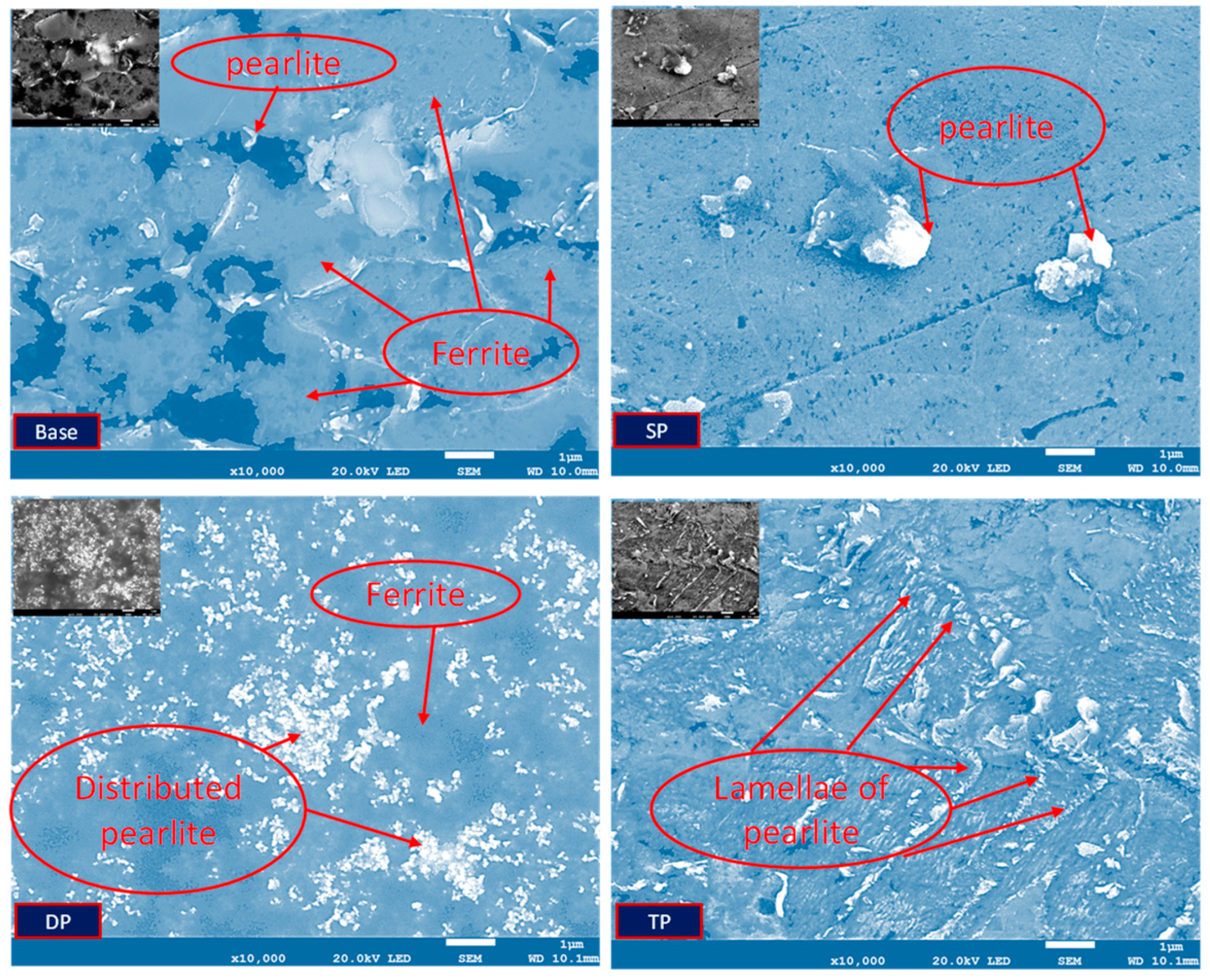
- Friction stir processing results in grain refinement in the friction stir-processed samples, from an average grain size of 57 microns to 22 microns after the second pass, due to the thermally associated plastic deformation of the material. The grain refinement in the processed region increases the microhardness of the processed sample in comparison to the base metal.
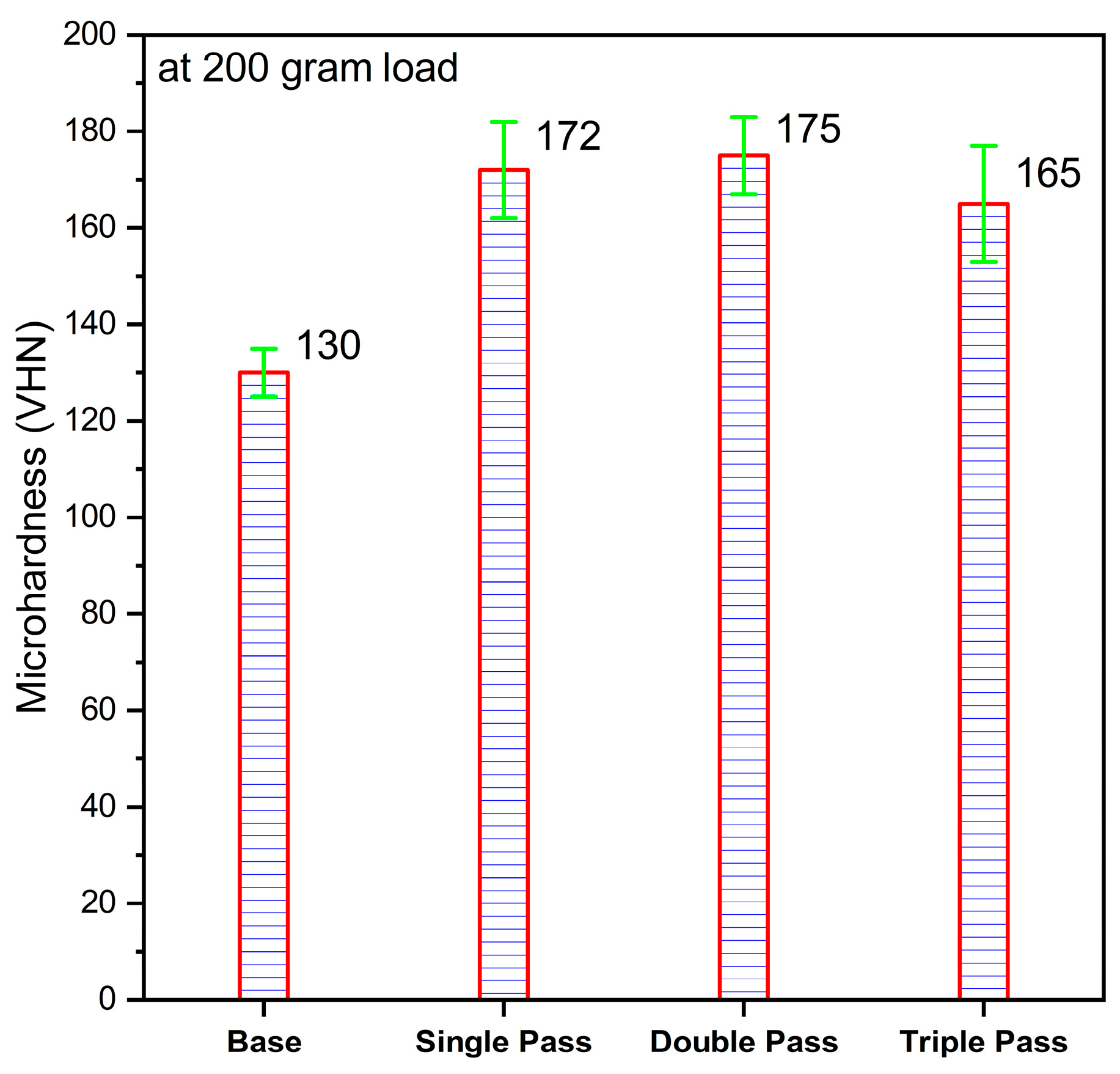
- The surface properties of steel can be modified using friction stir processing due to the grain refinement and enhancement in microhardness; double pass friction stir processing further refines the grain size up to 22 microns and increases the microhardness (175 VHN) in comparison to single pass (172 VHN). But triple pass processing causes a little bit of coarsening of the grains and a reduction in microhardness (165 VHN) in comparison to double pass processing.
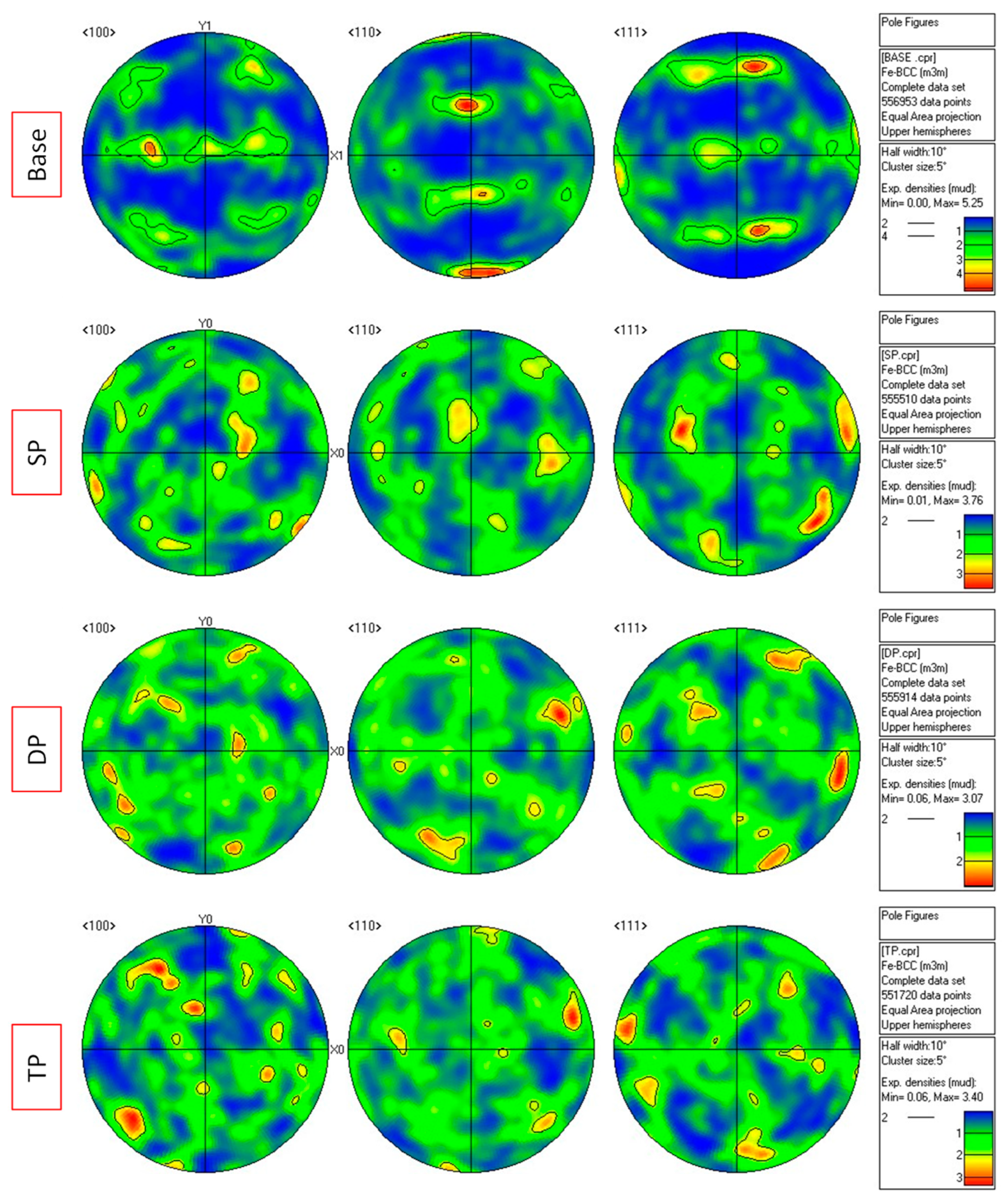
- The second pass-processed sample shows the maximum grain refinement due to the combined effects of large grain rotations and dynamic recrystallization near the high-angle grain boundaries.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, R.S.; Ma, Z.Y. Friction Stir Welding and Processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2005, 50, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarpour, M.R.; Mirabad, H.M.; Gazani, F.; Khezri, I.; Ahmadi Chadegani, A.; Moeini, A.; Kim, H.S. An Overview of Friction Stir Processing of Cu–SiC Composites: Microstructural, Mechanical, Tribological, and Electrical Properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 1317–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.X.; Solomon, D.; Reinbolt, M. Friction Stir Processing of Particle Reinforced Composite Materials. Materials 2010, 3, 329–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, N.; Mishra, R.S.; Krishnamurthy, K. Friction Stir Channeling: Characterization of the Channels. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 3696–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laska, A.; Sadeghi, B.; Sadeghian, B.; Taherizadeh, A.; Szkodo, M.; Cavaliere, P. Temperature Evolution, Material Flow, and Resulting Mechanical Properties as a Function of Tool Geometry during Friction Stir Welding of AA6082. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023, 32, 10655–10668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Aliha, M.R.M.; Berto, F. Investigating the Role of Different Components of Friction Stir Welding Tools on the Generated Heat and Strain. Forces Mech. 2023, 10, 100166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Meng, X.; Xie, Y.; Wan, L.; Huang, Y. Effect of Temperature and Material Flow Gradients on Mechanical Performances of Friction Stir Welded AA6082-T6 Joints. Materials 2022, 15, 6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doude, H.R.; Schneider, J.A.; Nunes, A.C. Influence of the Tool Shoulder Contact Conditions on the Material Flow during Friction Stir Welding. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2014, 45, 4411–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; McDonnell, M.; Feng, Z. Tool-Workpiece Stick-Slip Conditions and Their Effects on Torque and Heat Generation Rate in the Friction Stir Welding. Acta Mater. 2021, 213, 116969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarzadeh, A.; Mironov, S.; Kaibyshev, R.; Çam, G.; Simar, A.; Gerlich, A.; Khodabakhshi, F.; Mostafaei, A.; Field, D.P.; Robson, J.D.; et al. Friction Stir Welding/Processing of Metals and Alloys: A Comprehensive Review on Microstructural Evolution. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 117, 100752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prangnell, P.B.; Heason, C.P. Grain Structure Formation during Friction Stir Welding Observed by the “Stop Action Technique”. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 3179–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, N.; Shigematsu, I.; Komaya, T.; Tamaki, T.; Yamauchi, G.; Nakamura, M. Grain Refinement of 1050 Aluminum Alloy by Friction Stir Processing. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2001, 20, 1913–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirshekari, B.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Barabi, A.; Abedi, H.R.; Lee, S.J.; Fujii, H. An Anomalous Effect of Grain Refinement on Yield Stress in Friction Stir Processed Lightweight Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 799, 140057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Li, W.; Andersson, J.; Li, N. Enhancing Grain Refinement and Corrosion Behavior in AZ31B Magnesium Alloy via Stationary Shoulder Friction Stir Processing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 3150–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yu, J.; Jia, L.; Gao, C.; Miao, Z.; Wu, G.; Li, G.; Zhang, Z. Grain Refinement Impact on the Mechanical Properties and Wear Behavior of Mg-9Gd-3Y-2Zn-0.5Zr Alloy after Decreasing Temperature Reciprocating Upsetting-Extrusion. J. Magnes. Alloys 2022, 10, 3506–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busu, N.; Jaffarullah, M.S.; Low, C.Y.; Shaari, M.S.B.; Armansyah; Jaffar, A. A Review of Force Control Techniques in Friction Stir Process. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 76, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Du, D.; Dong, A.; Li, J.; Toursangsaraki, M.; Sun, H. Investigations on Friction Stir Composite Processing and Picosecond Laser-Induced Surface Modification on Mechanical Properties of β-Titanium Alloy. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 108041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, M.A.; Alsoruji, G.; Moustafa, E.B.; Mosleh, A.O.; Mohamed, S.S. Optimization of Friction Stir Processing Parameters for Improvement of Mechanical Properties of AlSi7Mg0.2 Alloy. Coatings 2023, 13, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Huang, J.; Ni, Y.; Shen, L.; Huang, Y.; Fan, D.; Liu, J. Enhancing Microstructural, Mechanical, and Tribological Behavior of AZ31B Magnesium Alloy through Friction Stir Processing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 1441–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.K.; Singh, S.; Chen, G.; Yijun, L.; Zhang, S.; Shi, Q. Wear Behavior of the Friction Stir Alloyed AZ31 Mg at Different Volume Fractions of Al Particles Reinforcement and Its Enhanced Quality Attributes. Tribol. Int. 2020, 146, 106268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Butola, R.; Gupta, N. A review of nanoparticle reinforced surface composites processed by friction stir processing. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2023, 37, 565–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, F.; Santos, T.; Vilaça, P.; Miranda, R.M.; Quintino, L. Microstructural modification and ductility enhancement of surfaces modified by FSP in aluminium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 506, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaszko, J.; Sajed, M. Technological aspects of producing surface composites by friction stir processing—A review. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.L.; Zhang, J.G.; Ren, C.Z.; Wang, S.Q.; Cao, Z.M. Characteristics of cutting force and surface finish in diamond turning of polycrystalline copper achieved by friction stir processing (FSP). J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 301, 117451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Han, P.; Peng, P.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, S.N.; Wang, K.S. Friction Stir Processing of Magnesium Alloys: A Review. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2020, 33, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralls, A.M.; Kasar, A.K.; Menezes, P.L. Friction stir processing on the tribological, corrosion, and erosion properties of steel: A review. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2021, 5, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, F.; Atapour, M.; Golozar, M.A.; Sadeghi, B.; Cavaliere, P. Corrosion behavior of friction stir processed AISI 430 ferritic stainless steel. Mater. Res. Express. 2019, 6, 086532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralls, A.M.; Daroonparvar, M.; Kasar, A.K.; Misra, M.; Menezes, P.L. Influence of friction stir processing on the friction, wear and corrosion mechanisms of solid-state additively manufactured 316L duplex stainless steel. Tribol. Int. 2023, 178, 108033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Bagheri, B.; Dadaei, M.; Omidvar, H.R.; Rezaei, M. The effect of FSP on mechanical, tribological, and corrosion behavior of composite layer developed on magnesium AZ91 alloy surface. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 77, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Zhang, C.; Sui, X.; Lu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Shi, Z. Microstructure, mechanical properties and tribo-corrosion mechanism of (CrNbTiAlVMo)xN1−x coated 316 L stainless steel in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution. Tribol. Int. 2022, 173, 107638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Chen, J.; Peng, L.; Tan, S.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, F.; Yi, H. Microstructure, Texture and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Processed Mg-14Gd Alloys. Mater. Des. 2017, 130, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco-Caballero, A.; Ruano, O.A.; Rauch, E.F.; Carreño, F. Severe Friction Stir Processing of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy: Misorientation and Its Influence on Superplasticity. Mater. Des. 2018, 137, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, M.P.; Gunter, C.; Liu, F.; Nelson, T.W. Friction Stir Processing of 304L Stainless Steel for Crack Repair. In Friction Stir Welding and Processing IX; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, K.; Mandal, P.; Grewal, H.S.; Arora, H.S. Ultrasonic Cavitation Erosion-Corrosion Behavior of Friction Stir Processed Stainless Steel. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 44, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, M.M.; Shash, A.Y.; Abd-Rabou, M.; ElSherbiny, M.G. Welding and Processing of Metallic Materials by Using Friction Stir Technique: A Review. J. Adv. Join. Process. 2021, 3, 100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E-8; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Bland, P.A.; Howard, L.E.; Prior, D.J.; Wheeler, J.; Hough, R.M.; Dyl, K.A. Earliest rock fabric formed in the Solar System preserved in a chondrule rim. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.21 | 0.45 | 1.37 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.11 | Bal. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raja, A.R.; Su, H.; Wu, C. The Influence of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing on the Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of IS2062 Steel. Metals 2024, 14, 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14060685
Raja AR, Su H, Wu C. The Influence of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing on the Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of IS2062 Steel. Metals. 2024; 14(6):685. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14060685
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaja, Avinash Ravi, Hao Su, and Chuansong Wu. 2024. "The Influence of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing on the Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of IS2062 Steel" Metals 14, no. 6: 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14060685
APA StyleRaja, A. R., Su, H., & Wu, C. (2024). The Influence of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing on the Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of IS2062 Steel. Metals, 14(6), 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14060685






