Surface Reaction-Diffusion-Coupled Simulation of Ni–Fe–Cr Alloy under FLiNaK Molten Salt
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model Description
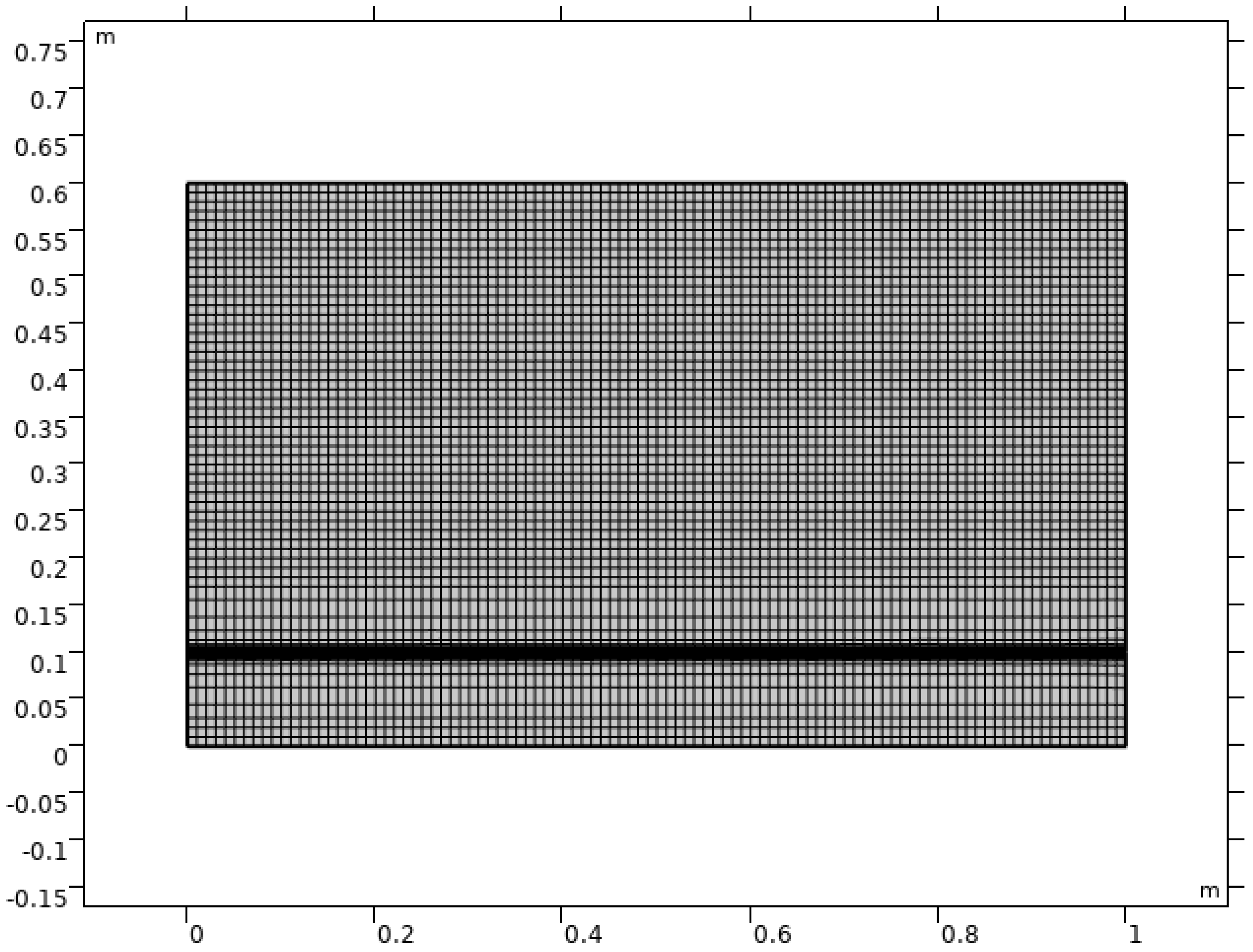
2.1. Model Geometry
2.2. Simulation Strategy
2.3. Model Parameters and Initial Conditions
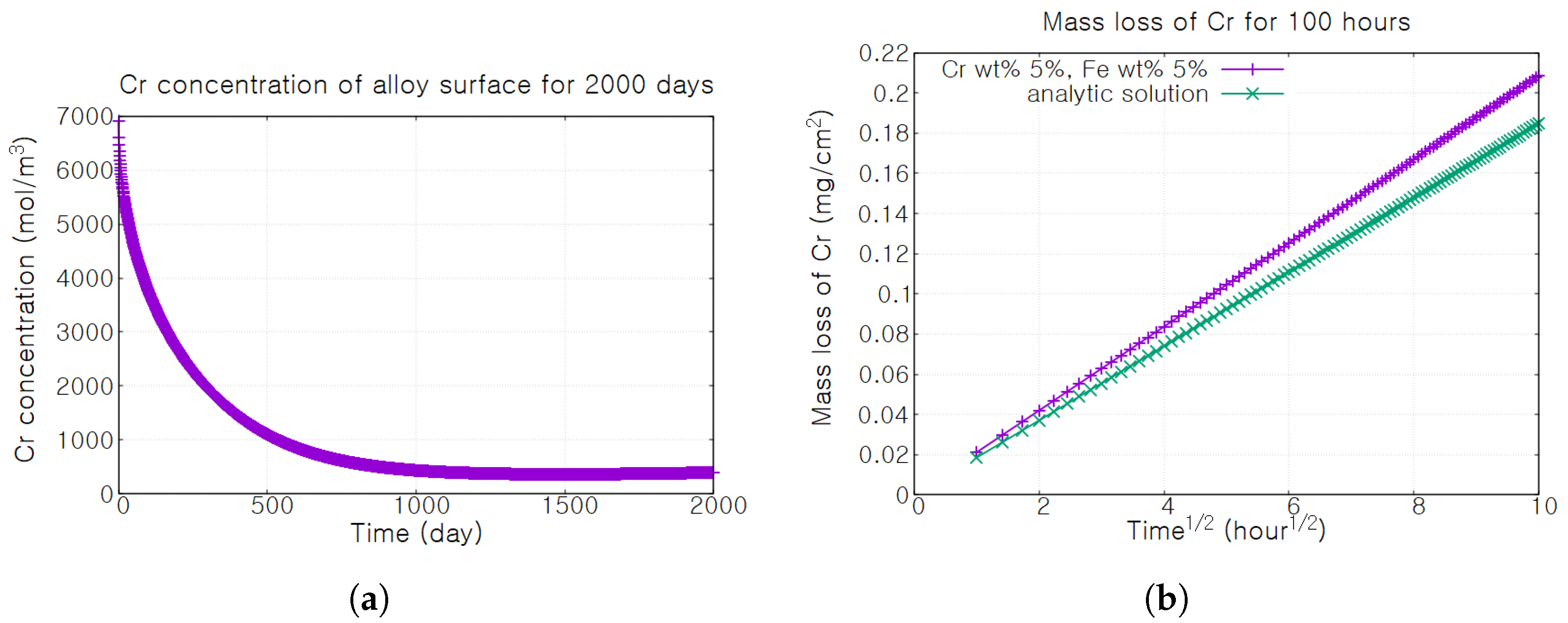
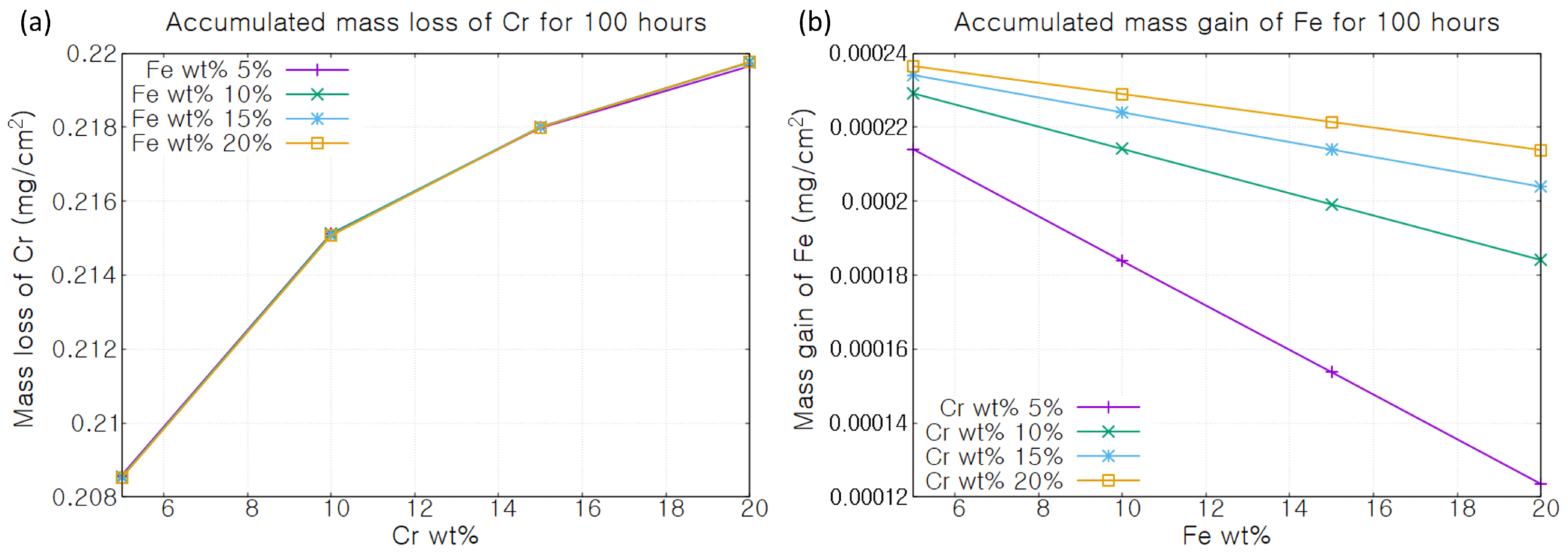
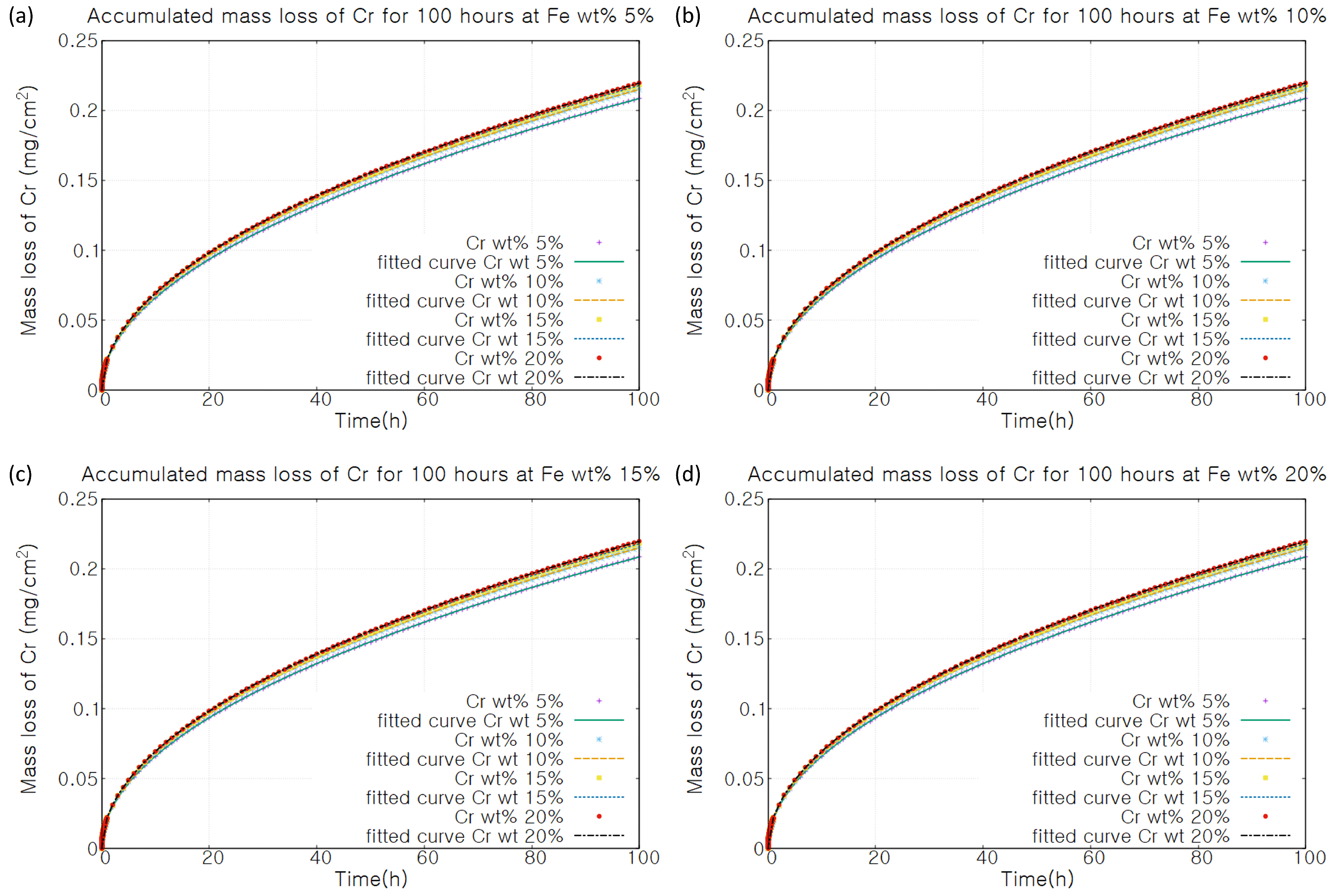
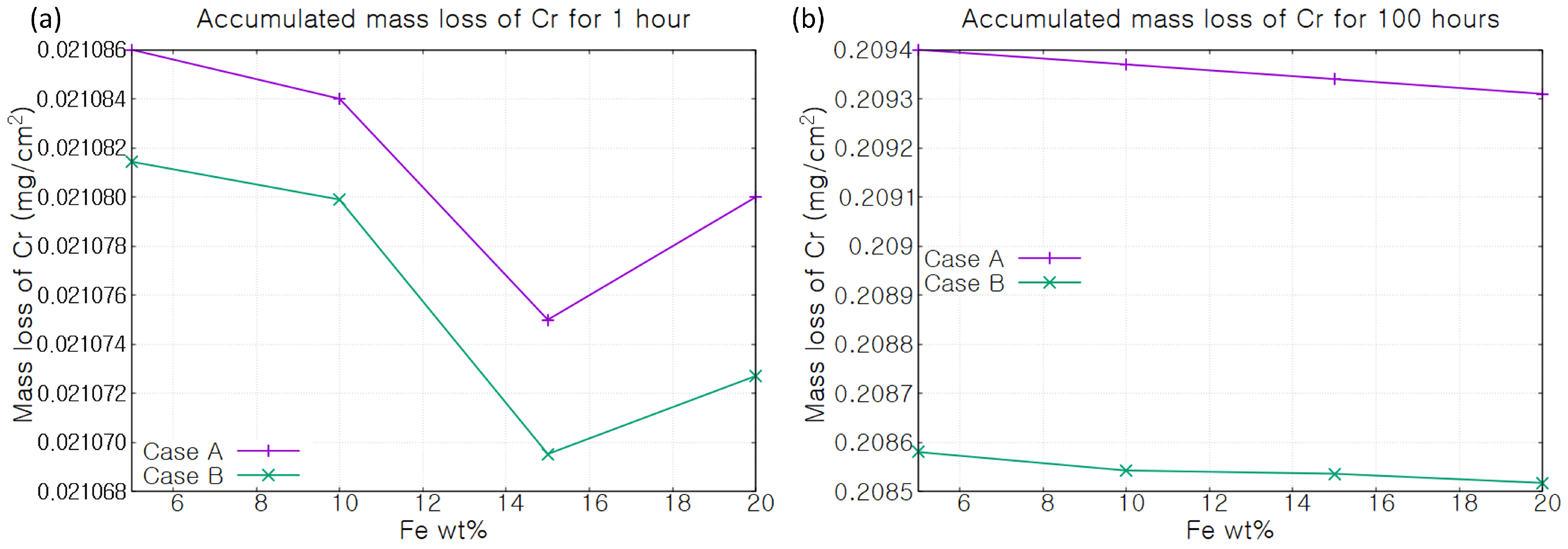
3. Results
4. Discussion
- Case A: Cr concentration is fixed within the material.
- Case B: Cr depletion takes place due to corrosion and Cr atoms diffuse within the material.
5. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Lane, J.A.; MacPherson, H.G.; Maslan, F. Fluid Fuel Reactors: Molten Salt Reactors, Aqueous Homogeneous Reactors, Fluoride Reactors, Chloride Reactors, Liquid Metal Reactors and Why Liquid Fission; Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., Ltd.: London, UK, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Beneš, O.; Souček, P. 6—Molten salt reactor fuels. In Advances in Nuclear Fuel Chemistry; Piro, M.H., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2020; pp. 249–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serp, J.; Allibert, M.; Beneš, O.; Delpech, S.; Feynberg, O.; Ghetta, V.; Heuer, D.; Holcomb, D.; Ignatiev, V.; Kloosterman, J.L.; et al. The molten salt reactor (MSR) in generation IV: Overview and perspectives. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2014, 77, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredrickson, G.L.; Cao, G.; Gakhar, R.; Yoo, T.S. Molten Salt Reactor Salt Processing—Technology Status; Idaho National Laboratory (INL): Idaho Falls, ID, USA, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Robertson, R.C. MSRE Design & Operations Report Part 1 Description of Reactor Design; Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL): Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1965. [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, M.; Kasten, P.; Briggs, R. Molten-salt reactors—History, status, and potential. Nucl. Appl. Technol. 1970, 8, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.; Yeoh, G.; Braoudakis, G. Molten Salt Reactors, Materials and Processes for Energy: Communicating Current Research and Technological Developments; Formatex Research Center: Norristown, PA, USA, 2013; pp. 761–768. [Google Scholar]
- Lantelme, F.; Groult, H. Molten Salts Chemistry: From Lab to Applications; Newnes: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kamei, T.; Hakami, S. Evaluation of implementation of thorium fuel cycle with LWR and MSR. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2011, 53, 820–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, B.M. Safety assessment of molten salt reactors in comparison with light water reactors. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2013, 6, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, J.; Wu, W.; Zhou, W. Corrosion in the molten fluoride and chloride salts and materials development for nuclear applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 97, 448–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatiev, V.; Surenkov, A. 5-Corrosion phenomena induced by molten salts in Generation IV nuclear reactors. In Structural Materials for Generation IV Nuclear Reactors; Yvon, P., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; pp. 153–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, R.; Kinoshita, M.; Scott, I. 7—Materials. In Molten Salt Reactors and Thorium Energy; Dolan, T.J., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; pp. 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niketan, S.; Patel, V.P.; Boča, M. High-Temperature Corrosion Behavior of Superalloys in Molten Salts—A Review. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2017, 42, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Forsberg, C.W.; Simpson, M.F.; Guo, S.; Lam, S.T.; Scarlat, R.O.; Carotti, F.; Chan, K.J.; Singh, P.M.; Doniger, W.; et al. Redox potential control in molten salt systems for corrosion mitigation. Corros. Sci. 2018, 144, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.S. Introduction to High Temperature Oxidation and Corrosion; ASM International: Almere, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- MacPherson, H. Development of materials and systems for the molten-salt reactor concept. React. Technol. 1972, 15, 136–155. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-warda, N.; García-Rodríguez, S.; Torres, B.; Utrilla, M.V.; Rams, J. Effect of Molten Salts Composition on the Corrosion Behavior of Additively Manufactured 316L Stainless Steel for Concentrating Solar Power. Metals 2024, 14, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjanaprayut, N.; Siripongsakul, T.; Promdirek, P. Intergranular Corrosion Analysis of Austenitic Stainless Steels in Molten Nitrate Salt Using Electrochemical Characterization. Metals 2024, 14, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.; Galleguillos, H.; Fuentealba, E.; Pérez, F. Corrosion of stainless steels and low-Cr steel in molten Ca(NO3)2–NaNO3–KNO3 eutectic salt for direct energy storage in CSP plants. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2015, 141, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani Dorcheh, A.; Durham, R.N.; Galetz, M.C. Corrosion behavior of stainless and low-chromium steels and IN625 in molten nitrate salts at 600 °C. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 144, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, P.; Su, X. Corrosion behavior of 316SS and Ni-based alloys in a ternary NaCl-KCl-MgCl2 molten salt. Sol. Energy 2018, 171, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-W.; Zhang, C.-Z.; Li, Z.-H.; Zhou, H.-X.; He, J.-X.; Yu, J.-C. Corrosion behavior of nickel-based superalloys in thermal storage medium of molten eutectic NaCl-MgCl2 in atmosphere. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2017, 164, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muránsky, O.; Yang, C.; Zhu, H.; Karatchevtseva, I.; Sláma, P.; Nový, Z.; Edwards, L. Molten salt corrosion of Ni-Mo-Cr candidate structural materials for Molten Salt Reactor (MSR) systems. Corros. Sci. 2019, 159, 108087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpech, S.; Carrière, C.; Chmakoff, A.; Martinelli, L.; Rodrigues, D.; Cannes, C. Corrosion Mitigation in Molten Salt Environments. Materials 2024, 17, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcmurray, J.W.; Besmann, T.M.; Ard, J.; FItzpatrick, B.; Piro, M.; Jerden, J.; Williamson, M.; Collins, B.S.; Betzler, B.R.; Qualls, A.L. Multi-Physics Simulations for Molten Salt Reactor Evaluation: Chemistry Modeling and Database Development; Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL): Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2018. [CrossRef]
- MaeHyun, C.; Hyeong-Jun, J.; Jungshin, K.; Kunok, C. Development of Numerical Analysis Model for New Magnesium Electrolysis Process Using COMSOL. Korean J. Met. Mater. 2023, 61, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Guan, B.; Wei, X.; Lu, J.; Ding, J. Cellular automata simulation on the corrosion behavior of Ni-base alloy in chloride molten salt. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 203, 110170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, T.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Tang, Z.; Yan, L.; Wang, J. Thermodynamic and kinetic corrosion behavior of alloys in molten MgCl2–NaCl eutectic: FPMD simulations and electrochemical technologies. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2022, 238, 111624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivek Bhave, C.; Zheng, G.; Sridharan, K.; Schwen, D.; Tonks, M.R. An electrochemical mesoscale tool for modeling the corrosion of structural alloys by molten salt. J. Nucl. Mater. 2023, 574, 154147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Gao, J.; Mao, L.; Bedell, R.; Liu, E. Modeling the Impact of Grain Size on Corrosion Behavior of Ni-Based Alloys in Molten Chloride Salt via Cellular Automata. Metals 2024, 14, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, R.D. Molten Salt Corrosion. In Corrosion: Fundamentals, Testing, and Protection; ASM International: Almere, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Was, G.; Kruger, R. A thermodynamic and kinetic basis for understanding chromium depletion in Ni-Cr-Fe alloys. Acta Metall. 1985, 33, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein, A. Über die von der molekularkinetischen Theorie der Wärme geforderte Bewegung von in ruhenden Flüssigkeiten suspendierten Teilchen. Ann. Phys. 1905, 4, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Song, Y.L.; Tang, R.; Qian, Y. A novel purification method for fluoride or chloride molten salts based on the redox of hydrogen on a nickel electrode. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 35069–35076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J. Exchange Current Densities and Charge-Transfer Coefficients of Chromium and Iron Dissolution in Molten LiF-NaF-KF Eutectic. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, C840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G. Corrosion Behavior of Alloys in Molten Fluoride Salts. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Raiman, S.S.; Lee, S. Aggregation and data analysis of corrosion studies in molten chloride and fluoride salts. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 511, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, L.C.; Ambrosek, J.W.; Sridharan, K.; Anderson, M.H.; Allen, T.R. Materials corrosion in molten LiF–NaF–KF salt. J. Fluor. Chem. 2009, 130, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Alloy | Molten Salt | Microstructure | Surface Reaction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al. [28] | 625 | NaCl–MgCl2–CaCl2 | N/A | Stochastic approach |
| Li et al. [29] | Ni-Cr-Fe-Mn-Co | NaCl–MgCl2 | N/A | Berzins-Delahay |
| Bhave et al. [30] | Ni-Cr | FLiBe | Grain Boundary | Simplified Butler-Volmer |
| Feng et al. [31] | 625 | Chloride | Grain Boundary | Stochastic approach |
| Current work | Ni-Cr-Fe | FLiNaK | N/A | Butler-Volmer |
| Oxidation Reaction | Reduction Reaction |
|---|---|
| Species j | (mol/m3) | (mol/m3) | (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 59,674.26 | 1000 | 1.33 | |
| 38,342.39 | 38,342.39 | 0.76 | |
| 5861.198 | 5861.198 | 1.02 | |
| 15,470.68 | 15,470.68 | 1.38 | |
| 0.87 | |||
| 0.755 | |||
| 0.75 | |||
| 0.69 | |||
| 0.70 | |||
| HF(g) | 5.9674 | 11.91 | 1.55 |
| 11.91 | 0.1 | ||
| 138,461.5385 | 138,461.5385 | - |
| Reaction | Species j | (V) | (mA/cm2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −3.9 | 0.88 | 0.22 | ||
| −3.55 | 0.88 | 0.22 | ||
| −3.5 | 6.15 | 0.11 | ||
| −3.1 | 6.15 | 0.11 | ||
| −3.05 | 0.88 | 0.22 | ||
| −5.45 | 0.05 | 0.5 | ||
| −5.1 | 0.05 | 0.5 | ||
| −4.9 | 0.05 | 0.5 | ||
| HF(g) | −2.89 | 6.15 | 0.5 |
| (mA/cm2) | Mass Loss of Cr (mg/cm2) | (mA/cm2) | Mass Loss of Cr (mg/cm2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.44 | 0.11 | 0.20856 | 3.075 | 0.25 | 0.20857 |
| 0.88 | 0.22 | 0.20858 | 6.15 | 0.5 | 0.20858 |
| 1.32 | 0.33 | 0.20856 | 9.225 | 0.75 | 0.20857 |
| Cr/Fe wt% | a | b | c | d | e | f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5%/5% | −0.305326 | 0.225155 | 0.291936 | 0.217424 | 0.0343678 | 0.451575 |
| 5%/10% | −0.305521 | 0.227901 | 0.291763 | 0.220085 | 0.0347356 | 0.450973 |
| 5%/15% | −0.305128 | 0.225001 | 0.292124 | 0.217476 | 0.0339732 | 0.452563 |
| 5%/20% | −0.305243 | 0.225154 | 0.292016 | 0.217501 | 0.0341976 | 0.452018 |
| 10%/5% | −0.304331 | 0.215228 | 0.293086 | 0.208162 | 0.0328337 | 0.457936 |
| 10%/10% | −0.30419 | 0.215345 | 0.293223 | 0.208408 | 0.0325575 | 0.458842 |
| 10%/15% | −0.305004 | 0.221413 | 0.292455 | 0.213831 | 0.0341366 | 0.454917 |
| 10%/20% | −0.305047 | 0.222266 | 0.292413 | 0.214658 | 0.0342247 | 0.454917 |
| 15%/5% | −0.304488 | 0.214879 | 0.292953 | 0.207615 | 0.0334026 | 0.457576 |
| 15%/10% | −0.304517 | 0.215966 | 0.292929 | 0.208682 | 0.0334617 | 0.457616 |
| 15%/15% | −0.304812 | 0.217429 | 0.292649 | 0.209875 | 0.0340312 | 0.456204 |
| 15%/20% | −0.304681 | 0.217078 | 0.292775 | 0.209652 | 0.0337759 | 0.456869 |
| 20%/5% | −0.302105 | 0.190926 | 0.295258 | 0.185882 | 0.0288744 | 0.470715 |
| 20%/10% | −0.304236 | 0.212926 | 0.293203 | 0.205823 | 0.0330726 | 0.45927 |
| 20%/15% | −0.303769 | 0.209021 | 0.293649 | 0.202366 | 0.0321552 | 0.451467 |
| 20%/20% | −0.304003 | 0.211595 | 0.293427 | 0.204724 | 0.0326191 | 0.460399 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, M.; Tonks, M.R.; Chang, K. Surface Reaction-Diffusion-Coupled Simulation of Ni–Fe–Cr Alloy under FLiNaK Molten Salt. Metals 2024, 14, 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14091088
Cho M, Tonks MR, Chang K. Surface Reaction-Diffusion-Coupled Simulation of Ni–Fe–Cr Alloy under FLiNaK Molten Salt. Metals. 2024; 14(9):1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14091088
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Maehyun, Michael R. Tonks, and Kunok Chang. 2024. "Surface Reaction-Diffusion-Coupled Simulation of Ni–Fe–Cr Alloy under FLiNaK Molten Salt" Metals 14, no. 9: 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14091088
APA StyleCho, M., Tonks, M. R., & Chang, K. (2024). Surface Reaction-Diffusion-Coupled Simulation of Ni–Fe–Cr Alloy under FLiNaK Molten Salt. Metals, 14(9), 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14091088






