Abstract
Refractory high-entropy or medium-entropy alloys (RHEAs, RMEAs) exhibit outstanding strength and hold significant promise for high-temperature applications. However, their pronounced brittleness at room temperature restricts their industrial application. Recently, the introduction of interstitial oxygen has proven effective in refining the microstructure and improving the mechanical properties of RMEAs. In this study, we investigated the effect of interstitial oxygen content ranging from 0.5 to 6 at.% on the microstructures and mechanical properties of TiZrNb MEA. The alloys display a single BCC structure, showing a dendritic crystal morphology. At an oxygen content of 4 at.%, the alloy shows a room-temperature compressive yield strength of 1300 MPa and compressive strain of over 50%, achieving a balanced strength and ductility combination. Moreover, it shows excellent high-temperature mechanical properties, with yield strength exceeding 500 MPa at 800 °C. The Toda-Caraballo and Labusch theoretical models were used in the study to clarify the strengthening mechanism of the alloys, and the theoretical yield strengths obtained by calculation coincided with the experimental yield strengths. This validation not only confirms that the primary strengthening mechanism is solid solution strengthening, but also proves the reliability of the model in predicting the mechanical properties of MEAs and provides a theoretical basis for the use of interstitial atoms to strengthen MEAs.
1. Introduction
Over the past decades, high-entropy alloys (HEAs), which consist of multiple principal elements, have revolutionized traditional alloy design concepts. In 2010, researchers began to develop refractory HEAs (RHEAs) by utilizing refractory elements [1]. Since then, RHEAs have garnered significant attention due to their exceptional mechanical properties at high temperatures [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. These remarkable high-temperature characteristics have broadened the potential applications of HEAs in demanding environments. Most reported RHEAs exhibit poor ductility at room temperature, which poses challenges for processing and restricts their industrial application [16]. Therefore, enhancing room-temperature ductility while maintaining or even increasing strength is crucial for the practical application of RHEAs.
To address this issue, many researchers have tried to optimize alloy design. Senkov et al. [17] replaced W, Mo, and V with Hf, Zr, and Ti to develop the TaNbHfZrTi alloy, which exhibits significantly higher ductility (ɛ > 50%) compared to the TaNbWMoV alloy at room temperature. Similarly, Han et al. [5] incorporated Ti into the NbMoTaW RHEA to design the TiNbMoTaW RHEA, achieving a yield strength of 1455 MPa, which is 46% higher than that of the NbMoTaW RHEA. However, its room-temperature ductility remains limited to only 11.5%, despite being five times greater than the original value. This suggests that introducing new metal elements or substituting existing ones can enhance the balance of plasticity and strength in alloys, but the extent of improvement is often quite constrained.
In recent years, it has been discovered that moderately doping non-metallic elements with smaller atomic sizes (such as C, B, O, and N) into RHEAs can enhance their mechanical properties. Lei et al. [18] incorporated 2 at.% of oxygen into the TiZrHfNb RHEA, and these interstitial atoms acted as barriers for dislocation pinning, leading to a more uniform plastic flow. As a result, the yield strength increased from 0.75 ± 0.03 GPa in the base alloy to 1.11 ± 0.03 GPa in the oxygen-doped alloy, while elongation increased from 14% to 27%. Chen et al. [19] introduced a small amount of oxygen into the ZrTiHfNb0.5Ta0.5 RHEA, which resulted in the formation of Cottrell gas clusters. This modification led to a high yield strength of 1097 MPa at room temperature and 797 MPa at 700 °C, with elongations exceeding 50%, thereby enhancing the mechanical properties of the alloy at both room and elevated temperatures. Similarly, Wang et al. [20] added 0.6 at.% nitrogen into the TiZrNbTa RHEA, and the yield strength and elongation increased by 18% and 32%, respectively, compared to the base HEA. Therefore, trace doping of non-metallic elements in RHEAs can effectively resolve the challenge of balancing strength and ductility in RHEAs.
In this work, based on TiZrNb medium-entropy alloy (MEA), the effects of oxygen doping on microstructures and mechanical properties were studied. By doping 0.5, 1, 2, 4 and 6 at.% oxygen, the room-temperature compressive yield strength increases from 670 MPa of TiZrNb to 1300 MPa of O4, the high-temperature yield strength at 800 °C increases from 233 to 545 MPa, and the high-temperature compressive yield strength at 1000 °C increases from 52 to 143 MPa, while maintaining the compressive strain of over 50% for all the temperatures. Results show that the solid solution of interstitial oxygen in the matrix increases lattice distortion and improves the ability to hinder dislocations, resulting in solid solution strengthening in the alloys. This work reveals the mechanism of interstitial oxygen strengthening and serves as a reference for future research on designing RHEAs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
The MEA ingots with nominal compositions of (TiZrNb) 100−xOx (x = 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6 at.%) were prepared in an arc melting furnace under argon atmosphere. The raw material was calculated according to the proportion of each element in the alloys, and melted together to ensure the nominal compositions. The raw materials of Ti, Zr, and Nb have a purity of more than 99.9 wt.%. The oxygen was added to the alloys in the form of ZrO2. The alloys are denoted hereafter as TiZrNb, O0.5, O1, O2, O4, and O6 MEAs, respectively, according to the oxygen content. All the samples were remelted six times to achieve chemical homogeneity and then cooled in water-cooled copper crucibles to form button-shaped ingots. High-purity molten titanium block was used as an absorbent to capture residual impurity gases before alloy melting.
2.2. Microstructure Characterization
X-ray diffraction (XRD) was used to characterize the phase constitution, with a Bruker D8 Advance X-ray diffractometer (Bruker AXS GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany). Cu-Kα radiation (λ = 1.54 Å) was utilized in conjunction with a 2θ scattering range spanning 20–100°. An optical microscope (IMM 5000, Mega Instruments (Suzhou) Ltd., Suzhou, China) was used to observe the microstructures of alloys. A scanning electron microscope (SEM, ZEISS SUPRA 55, Carl Zeiss Optics, Wetzlar, Germany) was used to characterize the microstructures and fracture morphology of the alloys. A field emission electron probe micro analyzer (EPMA, JEOL JXA-8530F Plus, JEOL Ltd., Akishima, Japan) equipped with a wavelength-dispersion spectrometer (WDS, JEOL Ltd., Akishima, Japan) was used to characterize the microstructures and chemical compositions. A transmission electron microscope (TEM, JEOL 2100F, JEOL Ltd., Akishima, Japan) equipped with an energy-dispersive spectrometer (EDS, JEOL Ltd., Akishima, Japan) was employed to analyze the local phase structure and composition. For the preparation of TEM samples, a focused ion beam microscope (FIB, Helios G4 UX, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Needham, MA, USA) was used to cut thin slices of 10–20 µm in width and 1–2 µm in thickness, and further thinned to less than 50 nm using the ion beam until the samples were suitable for TEM observation.
2.3. Mechanical Property Tests
Room-temperature compressive tests were performed using a universal testing machine (Instron 5982, Instron Corporation, Norwood, MA, USA) at a strain rate of 0.001 s−1. The compressive samples were prepared by wire-cutting, and with a diameter of 4 mm and a height of 8 mm. The high-temperature compressive tests were carried out on a thermo-mechanical simulator (Gleeble-3800, Dynamic Systems Inc., Poestenkill, NY, USA) at a strain rate of 0.001 s−1, using samples with a diameter of 8 mm and a height of 12 mm.
2.4. Theoretical Strengthening Calculation
In this study, the contribution of grain boundary strengthening was evaluated using the classical Hall–Petch equation [21]:
where is the strengthening coefficient, holding a value of 430 MPa·µm1/2 for the Ti-based HEAs [22,23,24], and is the average grain size of MEAs.
The solid solution strengthening was modeled using the Toda-Caraballo [25] approach, with the general formulation expressed as Equations (2)–(5):
where is solid solution strengthening caused by the ith element; is a scaling constant, taken as 0.05 [17,26]; is the shear modulus of ith element; is the lattice mismatch due to shear modulus mismatch and atomic radius mismatch of ith element; is the atomic fraction of ith element; is the relative number of active slip systems, which is 2.5 in BCC metals; relates to the dominant type of dislocations, and here, is 2 [27].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructures
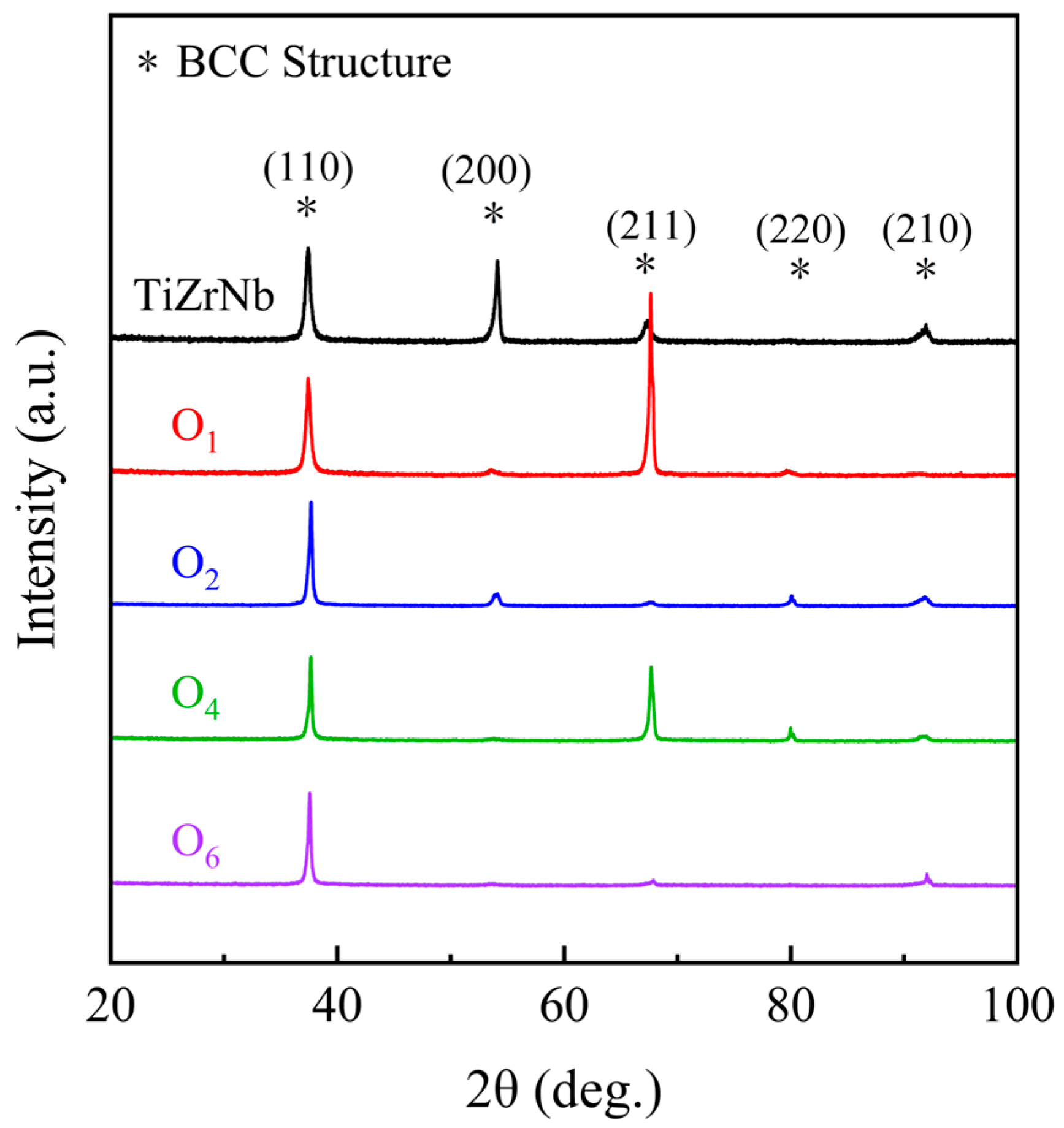
Figure 1 shows the XRD results of the (TiZrNb) 100−xOx MEAs, from which the crystal structures always remain single body-centered cubic (BCC) structures with increasing oxygen content, and no diffraction peaks of other phases appear.
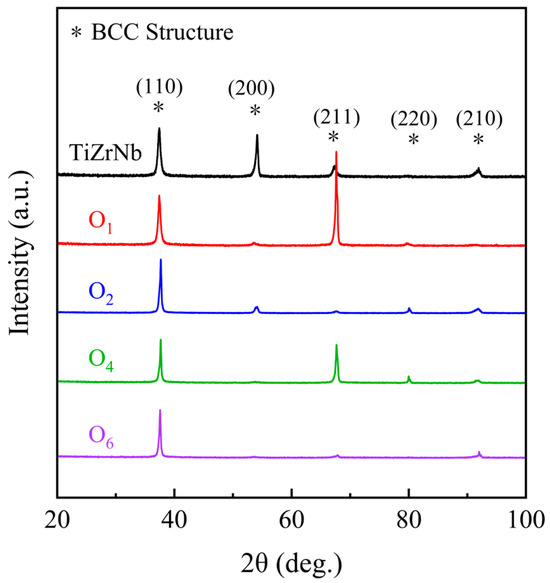
Figure 1.
XRD patterns of the TiZrNb, O1, O2, O4, and O6 MEAs.
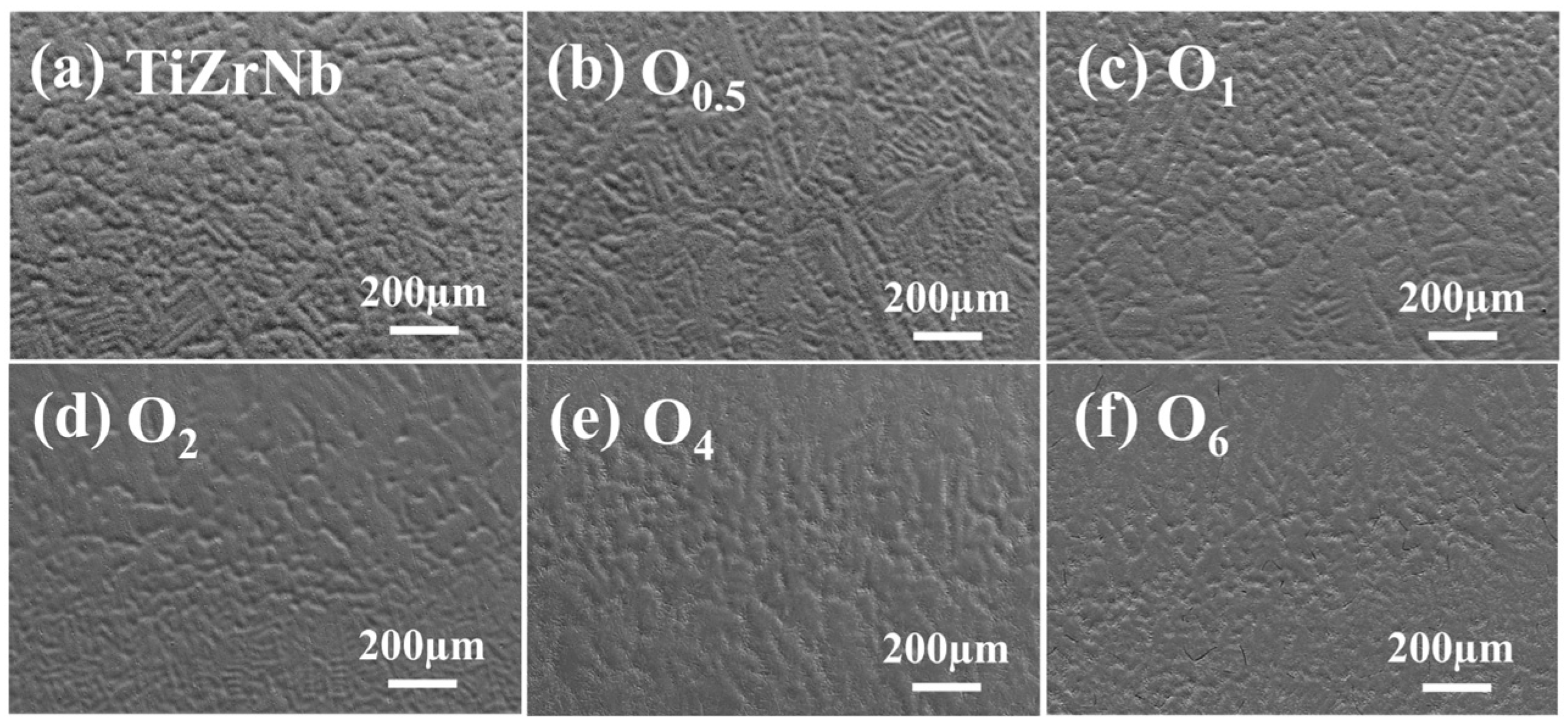
The SEM images of TiZrNb, O0.5, O1, O2, O4, and O6 MEAs are shown in Figure 2a–f, it can be seen that for alloys with oxygen content lower than 4 at.%, the microstructures show dendritic morphology. With increasing oxygen content, the dendritic structure is refined. The directivity of the dendrites diminishes significantly. For O6 MEA, the microstructure turns to be equiaxed crystals. The widths of the dendrites are 28.3, 21.9, 21.5, 20.2, 17.5, and 16.3 µm, respectively. This is because oxygen atoms serving as interstitial impurities hinder nucleation and directional growth of dendrites [28], leading to grain refinement. Therefore, microstructures evolve from dendritic crystals to equiaxed crystals.
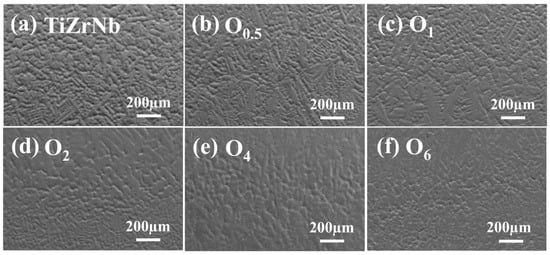
Figure 2.
SEM images of (a) TiZrNb, (b) O0.5, (c) O1, (d) O2, (e) O4, and (f) O6 MEAs.
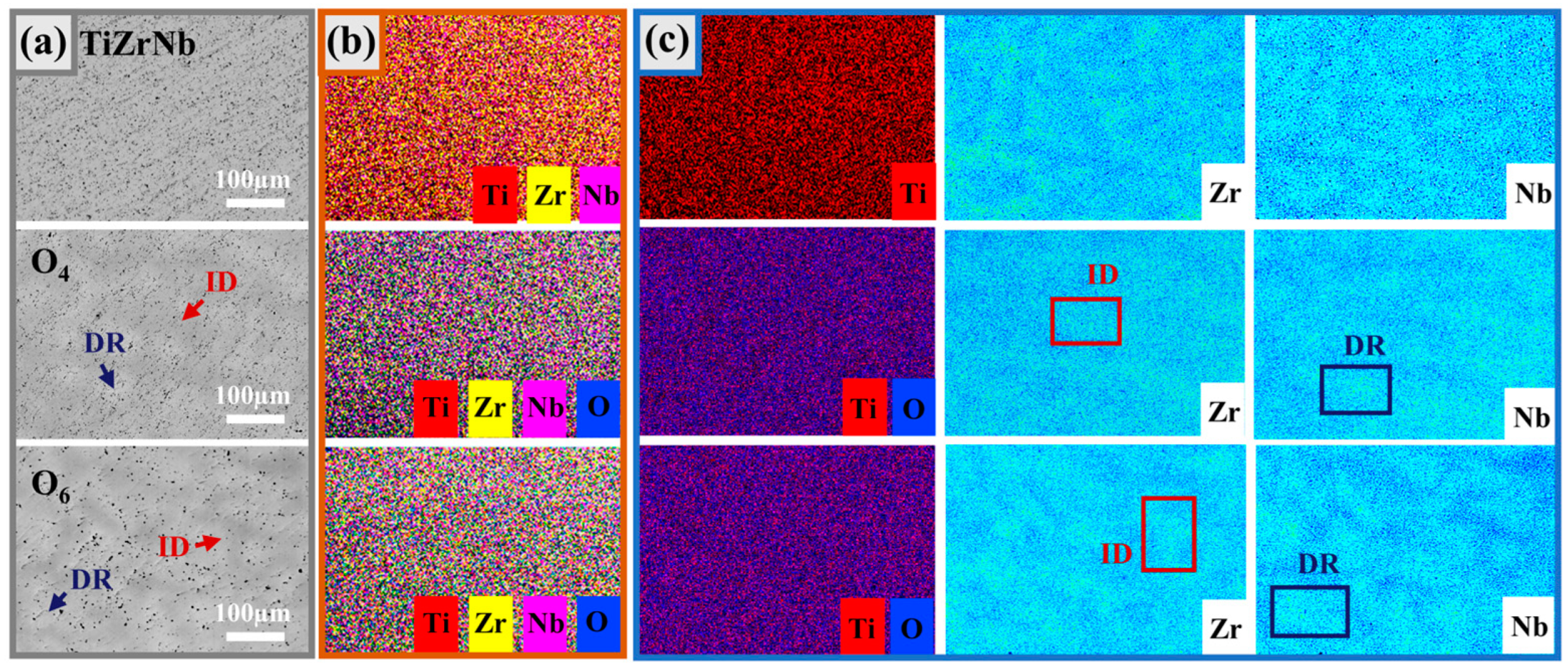
From the back-scattered electron imaging (BSE) images (Figure 3a), it can be seen that the microstructure presents light and dark areas, and the dark areas are the dendrite regions (DR), while the light parts are the interdendritic regions (ID). The chemical compositions of TiZrNb MEA without oxygen doping, and O4 and O6 with high oxygen content were tested by SEM-EDS; the results are shown in Figure 3b. It shows that the elements in the alloys are all uniformly distributed. In order to further analyze the compositional differences between the DR and ID regions, the EPMA-WDS surface analysis with a high composition resolution was carried out; the results are shown in Figure 3c. For the TiZrNb MEA without oxygen doping, the Ti element is uniformly distributed in the matrix, while Nb and Zr are mutually exclusive and tend to be distributed in different regions. This tendency does not change with the addition of oxygen; the DR region is rich in Nb, and the ID region is rich in Zr. This phenomenon is attributed to the local chemical order (LCO) [29], which is a prominent feature of HEAs [30]. It has been demonstrated that TiZrNb-based alloys exhibit varying chemical affinities among their constituent elements, which are more prone to LCOs [31]. The LCOs will lead to the formation of nanometer-sized domains differing in local composition, but without any changes in the alloy structure. In the TiZrNb system, the Zr-Nb pair has weak short-range ordering (SRO), which means that the tendency to form atom pairs is weak, and thus slight segregation occurs. Meanwhile, the oxygen atoms are uniformly distributed in the O4 and O6 MEAs, indicating that no oxides can be found in the microstructure.
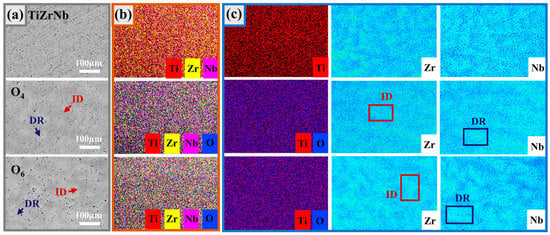
Figure 3.
(a) BSE images of TiZrNb, O4, and O6 MEAs. (b) Corresponding SEM-EDS elemental mapping. (c) Corresponding EPMA-WDS elemental mapping.
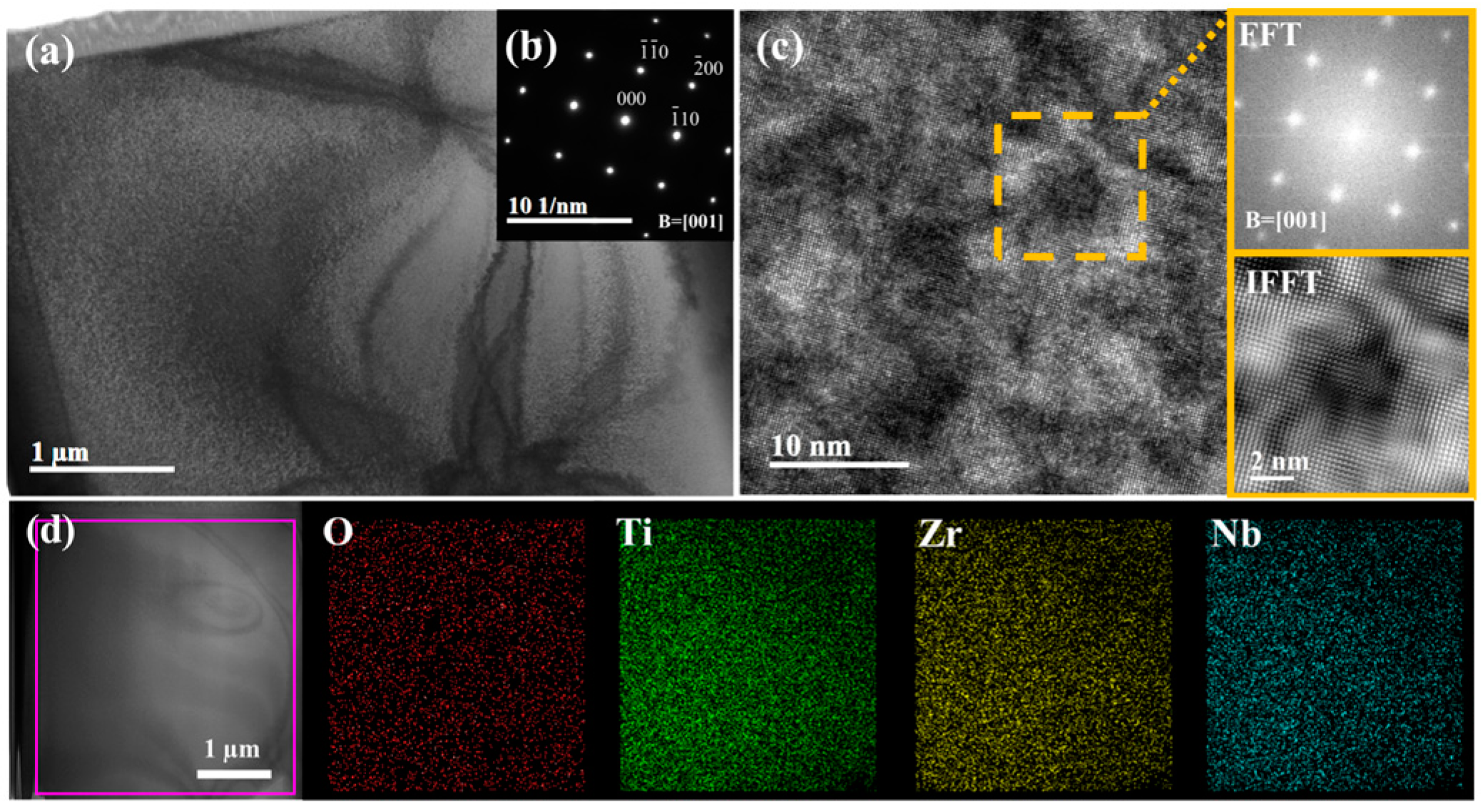
To further identify the single BCC crystal structure and the distribution of oxygen elements, O4 MEA was selected for TEM analysis, and the results are shown in Figure 4, which displays the bright-field (BF) image, high-resolution TEM (HRTEM) image, and EDS mapping. From the BF image and corresponding selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern in Figure 4a,b, it is evident that only a single BCC structure is present, with no other phases detected. Although there are some inhomogeneities, as can be seen in the rectangle in Figure 4c, no other phases can be identified from the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) patterns and the inverse FFT (IFFT) images of this region. Figure 4d presents the results of EDS mapping, which demonstrates the uniform distribution of all elements. This observation further confirms the absence of any secondary phase formation. Therefore, the inhomogeneity in the HRTEM images may be caused by differences in the foil thickness of the TEM samples, or there may be localized short-range ordering, which has been detected in the TiZrNb HEAs [31].
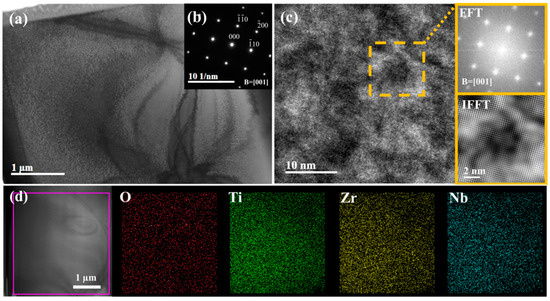
Figure 4.
TEM results of O4 MEA: (a) BF image; (b) corresponding SAED pattern; (c) HRTEM image with local area FFT pattern and IFFT image; (d) TEM-EDS mapping of O4 MEA.
3.2. Room-Temperature Compressive Properties
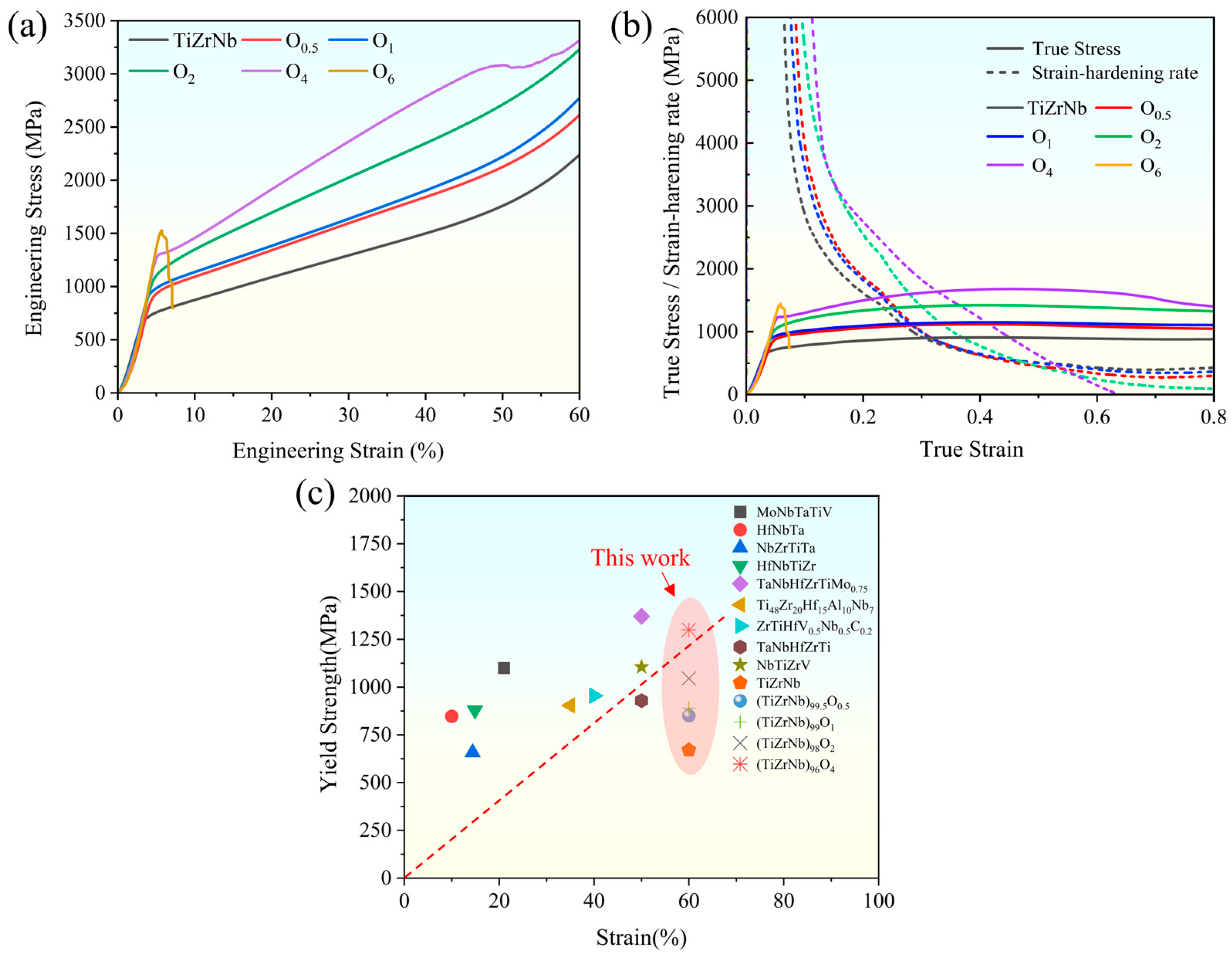
From the compressive engineering stress–strain curves in Figure 5a, with increasing oxygen content, the yield strength significantly increases from 670 MPa of TiZrNb to 1300 MPa of O4. The yield strength almost doubles while still maintaining excellent plasticity. As the oxygen content is increased to 6 at.%, there is a notable reduction in plasticity, resulting in a sharp deterioration of the mechanical properties. The optimal performance, characterized by a favorable combination of strength and plasticity, is observed in the O4 MEA. This observation is further supported by the strain–hardening curves shown in Figure 5b, from which it can be observed that the strain–hardening rate of the O4 MEA significantly exceeds those of the other alloys, indicating enhanced resistance to fracture. A comparison of the yield strength and strain of TiZrNb, O0.5, O1, O2, and O4 MEAs, as well as the other HEAs and MEAs with BCC structure, is presented in Figure 5c [3,5,20,32,33,34,35,36], further confirming that the O4 MEA achieves an excellent balance between plasticity and strength.
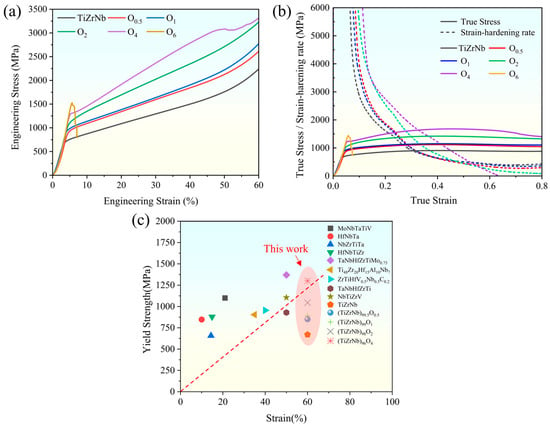
Figure 5.
Room-temperature compressive stress–strain curves of TiZrNb, O0.5, O1, O2, O4, and O6 MEAs. (a) Engineering stress–strain curve. (b) True stress–strain curve and strain–hardening rate curve. (c) Comparison of yield strength and strain of this work with the other HEAs and MEAs with BCC structure.
Obviously, the addition of oxygen improves both the strength and plasticity. The enhancement of strength is attributed to the solid solution strengthening induced by interstitial oxygen. Meanwhile, the solid solution of oxygen atoms contributes to a new type of interstitial atom arrangement, which could effectively pin dislocations and alter the dislocation slip mechanism from planar slip to wave slip, thus facilitating more uniform deformation [18]. Furthermore, this process increases the nucleation and proliferation rate of dislocations, thereby enhancing the work hardening capability and plasticity of the alloy. Conversely, excessive oxygen content increases the barriers for dislocation movement, leading to a deterioration of mechanical properties.
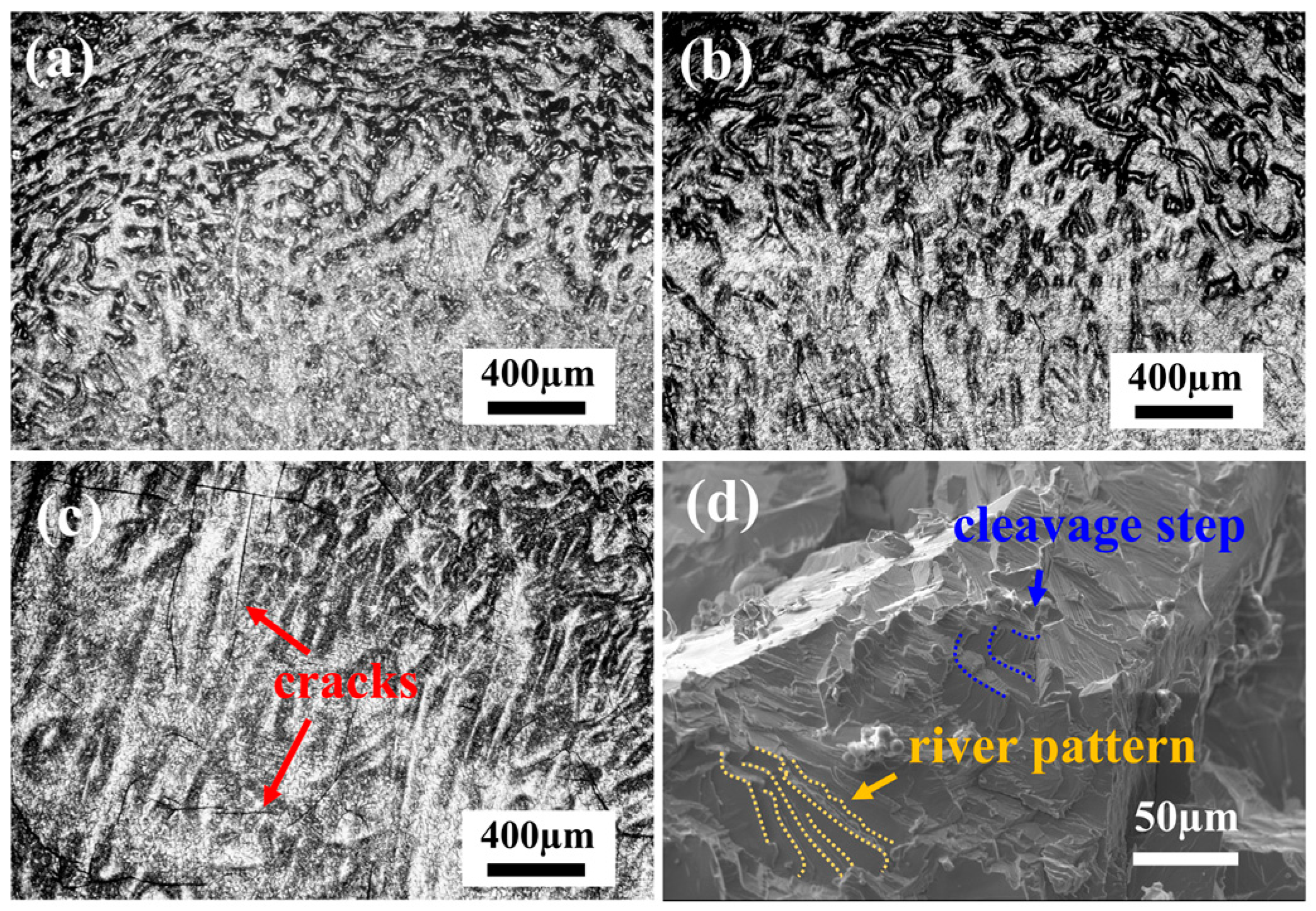
The compressive microstructures and fracture morphologies of the samples after compression at room temperature are shown in Figure 6. During the compression process, TiZrNb, O2, and O4 MEAs display no fracture after 60% compressive strain, while the dendritic structures are distorted under stress. For O4 MEA, small cracks are observed in the compressive microstructures, as depicted in Figure 6c. In contrast, the O6 MEA is fractured during compression, as shown in the SEM morphology in Figure 6d, displaying distinct cleavage steps and a river pattern characteristic of typical cleavage fractures. This observation indicates a transition of ductile to brittle behavior with increasing oxygen content.
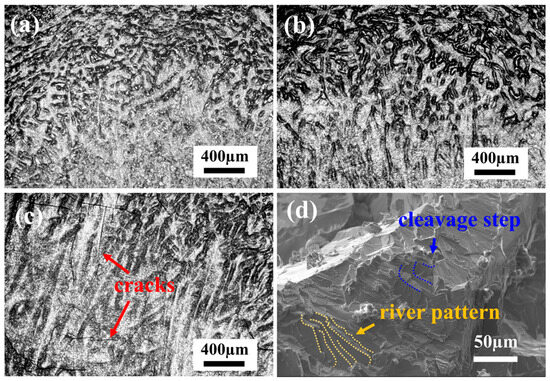
Figure 6.
The room-temperature compressive microstructures of (a) TiZrNb, (b) O2, and (c) O4 MEAs, and fracture morphology of (d) O6 MEA.
3.3. High-Temperature Compressive Properties
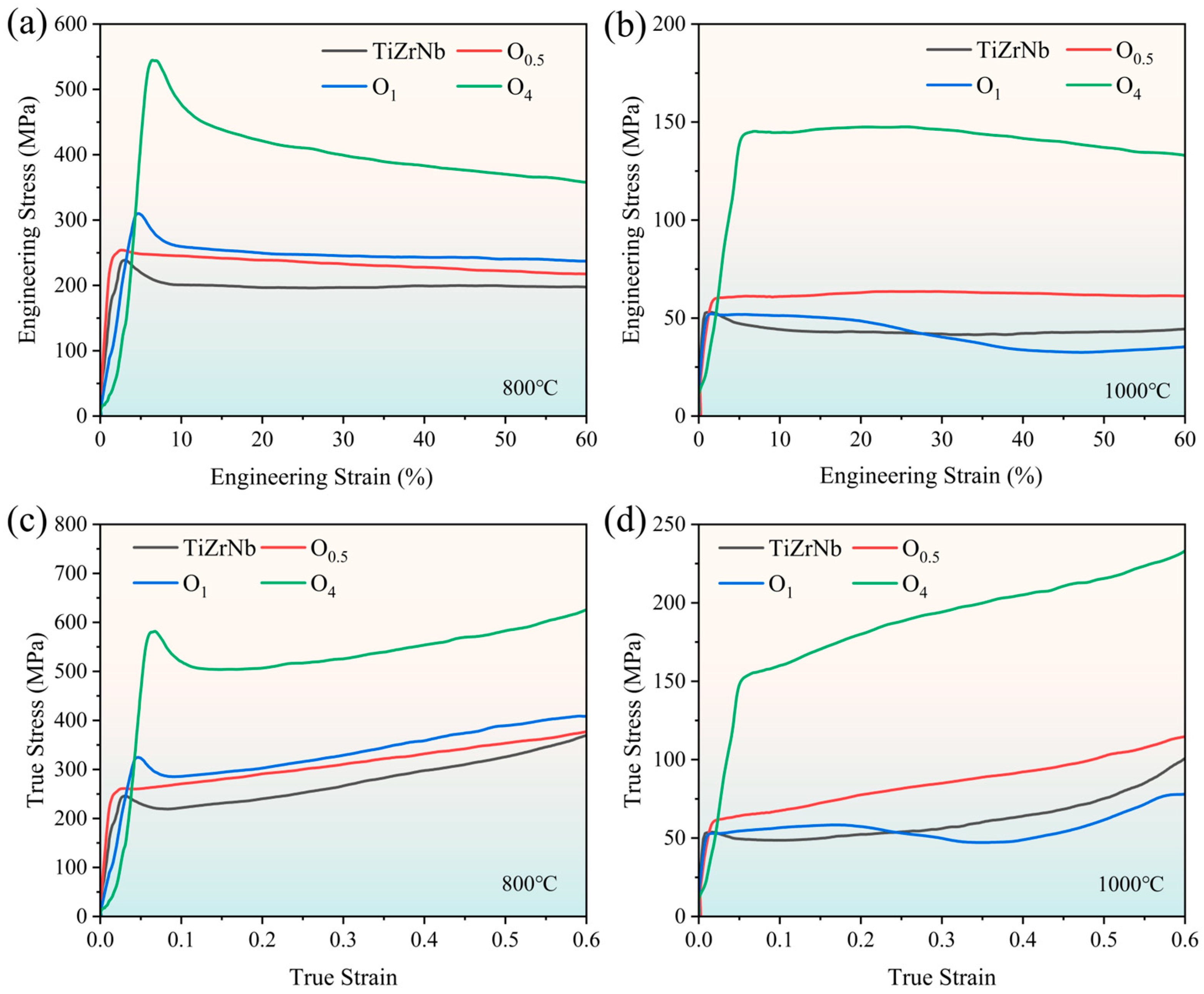
To study the effect of oxygen content on the high-temperature mechanical properties of TiZrNb alloy, compressive property tests were conducted at 800 °C and 1000 °C. The room-temperature and high-temperature compressive properties of each alloy are listed in Table 1, and the stress–strain curves are shown in Figure 7. At 800 °C, the addition of 4 at.% oxygen improves the yield strength from 238 MPa of TiZrNb alloy to 545 MPa. The oxygen strengthening effect diminishes when increasing the temperature to 1000 °C, and the yield strength increases from 545 to 143 MPa.

Table 1.
Compressive mechanical properties of TiZrNb, O0.5, O1, O2, O4, and O6 MEAs.
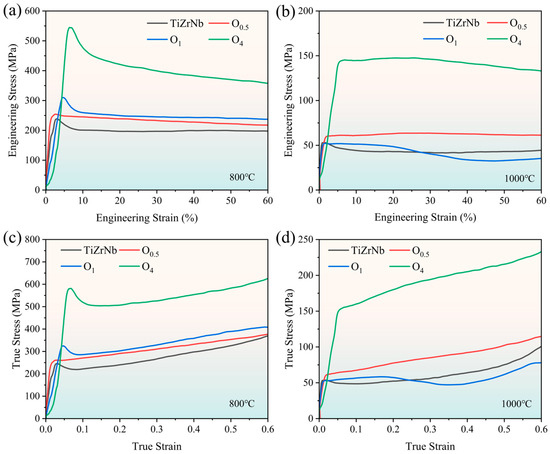
Figure 7.
Compressive stress–strain curves of TiZrNb, O0.5, O1, and O4 MEAs at (a) 800 °C and (b) 1000 °C. True stress–strain curves of TiZrNb, O0.5, O1, and O4 MEAs at (c) 800 °C and (d) 1000 °C.
It is worth noting that the yield point of the compressive true stress–strain curve is relatively sharp at 800 °C. In the case of O4 MEA, after reaching the peak stress of 545 MPa, the flow stress drops to 450 MPa immediately, indicating that softening occurs. As the temperature increases from 800 °C to 1000 °C, the yield point becomes flatter, which shows the characteristics of steady deformation. This phenomenon has been widely reported in β-Ti alloys [37,38,39], Zr-based alloys [40], and RHEAs [41] during high-temperature deformation, resulting from the competition between work hardening and work softening [42].
The mechanism underlying this behavior is related to the process of dislocation multiplication during high-temperature deformation [43]. The alloys experience work hardening due to a rapid rise in dislocation density, while softening occurs as a result of dislocation rearrangement and annihilation. In the initial stages of deformation, the rapid proliferation of dislocations decides that the softening effect is insufficient to counterbalance the hardening effect, leading to a continuous rise in yield strength. As deformation continues, dislocations gain more energy, resulting in cross-slip, climb, and depinning. Consequently, softening behavior becomes more pronounced, leading to a decrease in yield strength. Eventually, a dynamic equilibrium is reached between hardening and softening, characterized by a steady state.
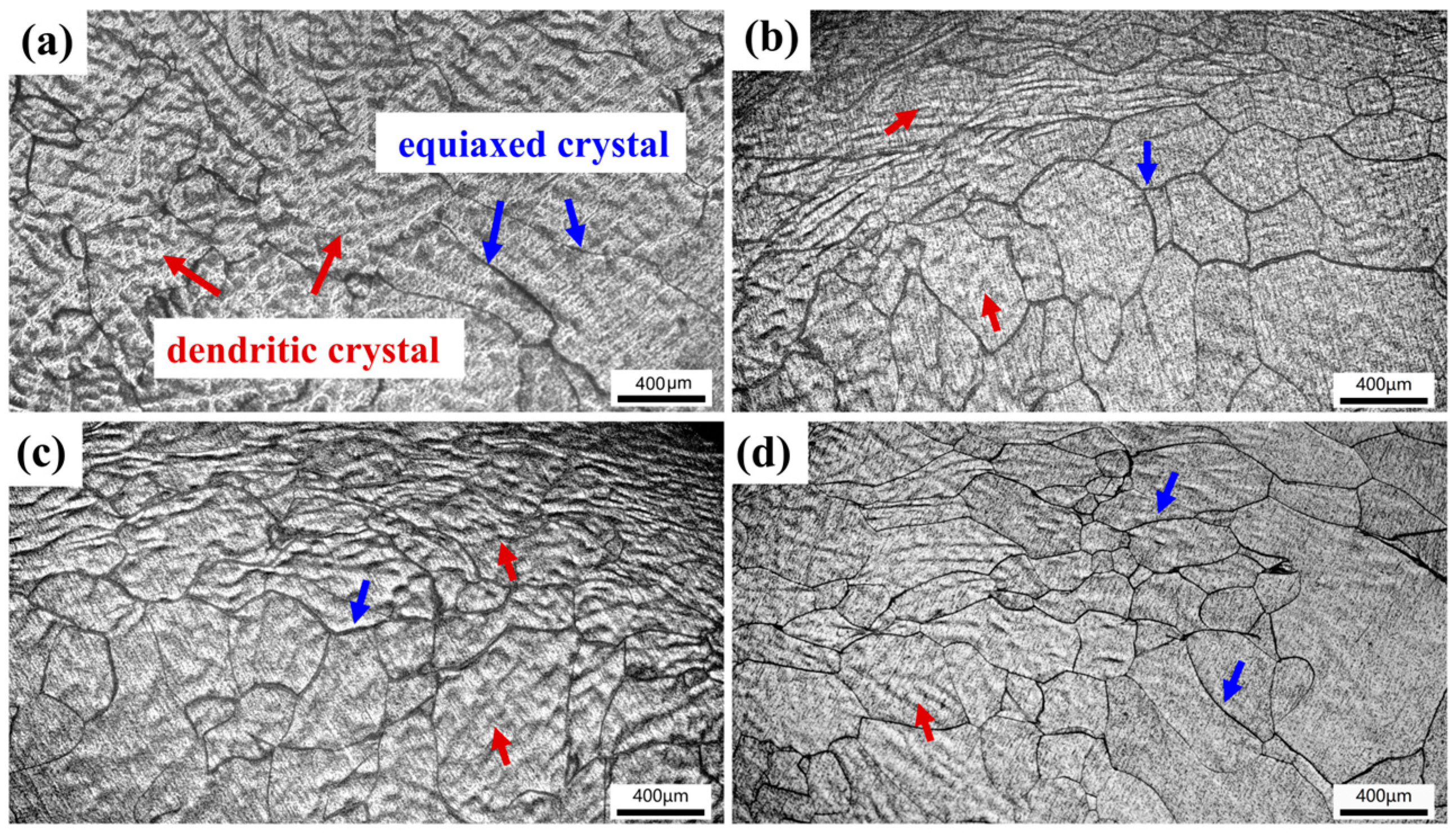
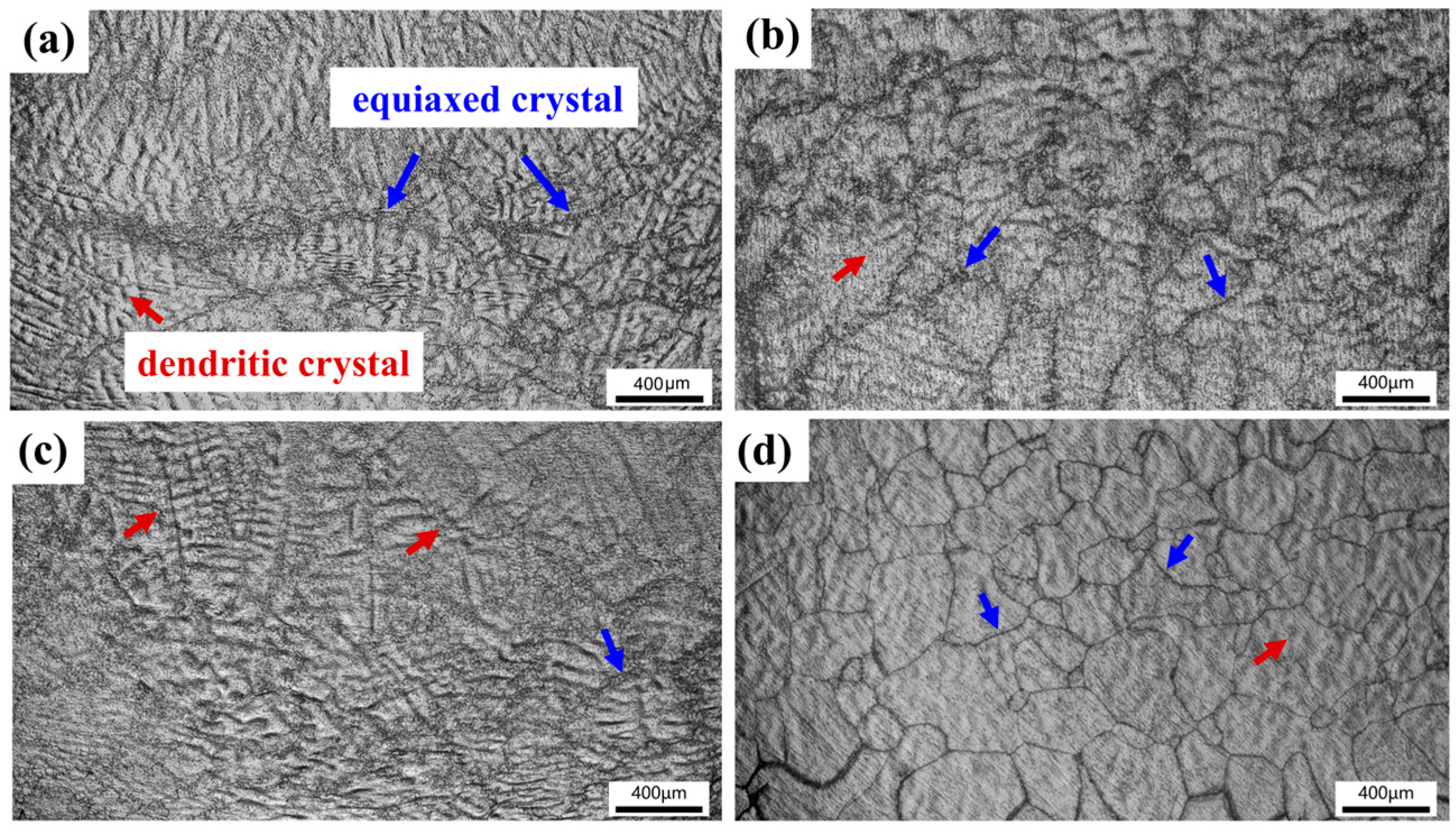
Figure 8 shows the microstructures of TiZrNb, O0.5, O2, and O4 MEAs after high-temperature compression at 800 °C. The thermal deformation of the original dendritic structure is observed, with some crystal grains undergoing dynamic recrystallization, characterized by the equiaxed structure. The volume fraction of recrystallization increases with increasing oxygen content, indicating that interstitial oxygen promotes atomic clusters, providing nucleation sites for recrystallization [28,44]. When increasing the temperature to 1000 °C, the extent of recrystallization surpasses that observed at 800 °C, as shown in Figure 9. Especially for O4, it exhibits a homogeneous and fine recrystallized microstructure, as shown in Figure 9d.
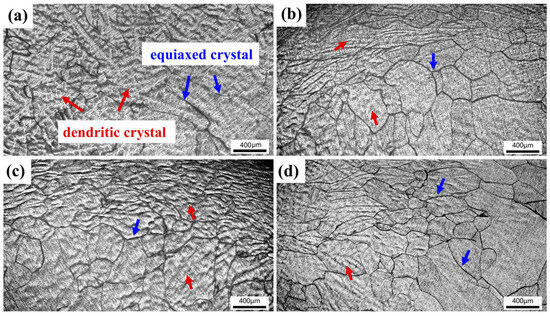
Figure 8.
The compressive microstructures of (a) TiZrNb, (b) O0.5, (c) O1, and (d) O4 MEAs after compression at 800 °C.
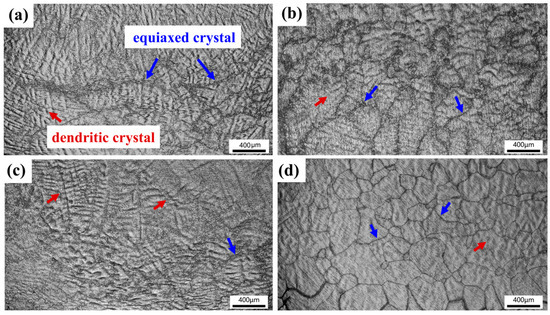
Figure 9.
The compressive microstructures of (a) TiZrNb, (b) O0.5, (c) O1, and (d) O4 MEAs after compression at 1000 °C.
3.4. Strengthening Mechanisms
Since (TiZrNb)100−xOx MEAs consist of a single BCC solid solution phase, the strengthening mechanism includes solid solution strengthening and grain boundary strengthening. It can be predicted that their effects on the yield strength of the alloys can be expressed as follows [45]:
where , , and are theoretical yield strength, the value of grain boundary strengthening, and solid solution strengthening, respectively.
It is known that a smaller grain size offers a higher volume fraction of grain boundaries, which could impede dislocation motion. The relationship between yield strength and grain size can be well described by the classical Hall–Petch equation [21]. In this work, the average grain size of each alloy is listed in Table 2, measured from SEM images. According to Equation (1) in Section 2.3, the grain boundary strengthening () can be obtained, and the results are listed in Table 2. Since the calculated theoretical values of grain boundary strengthening are small, it is proposed that it is not the main strengthening mechanism of the (TiZrNb)100−xOx MEAs.

Table 2.
Grain size and the value of grain boundary strengthening of TiZrNb, O0.5, O1, O2, and O4 MEAs.
The contribution of solid solution strengthening is evaluated using the BCC RHEAs solid solution strengthening model proposed by Toda-Caraballo [25], which can be roughly expressed as Equations (2)–(5) in Section 2.3. It is worth noting that in BCC MEAs, the unit lattice is regarded as a nine-atom cluster, and the number of atoms near the ith element in the cluster is eight. The average modulus mismatch and atomic radius mismatch in Equations (2)–(5) are calculated from the following Equations (7) and (8) [17]:
where and are the shear modulus mismatch and atomic radius mismatch between elements i and j, respectively, which can be calculated from Equations (9) and (10) [17]:
For TiZrNb MEA, the shear modulus and atomic radius of each element and the average shear modulus mismatch and atomic radius mismatch of the individual elements are shown in Table 3, as well as the solid solution strengthening caused by the individual element. The shear modulus mismatch and atomic radius mismatch between the two elements are shown in Table 4.

Table 3.
The shear modulus , the atomic radius of Ti, Zr, Nb, and the calculated results of parameters: , are the average modulus mismatch and atomic radius mismatch of ith element, respectively; is the lattice mismatch due to shear modulus mismatch and atomic radius mismatch of ith element; is solid solution strengthening caused by ith element.

Table 4.
The shear modulus mismatch and atomic radius mismatch between elements i and j.
Based on the calculations described above, the overall solid solution strength of the alloy can be calculated by Equation (3). The calculated value is 516 MPa for the TiZrNb MEA. From the above, the contribution of grain boundary strengthening is 80.8 MPa, and thus the theoretical yield strength is 597 MPa, which is close to the actual strength of 670 MPa.
In particular, the solid solution strengthening resulting from interstitial oxygen atoms can be evaluated using the Labusch model [17,46], and its contribution to the yield strength can be expressed as Equation (11):
where is the solid solution strengthening induced by oxygen atoms, k is the strengthening factor with an empirical value of 250 MPa for oxygen [47,48], and c is the atomic concentration of oxygen. The yield strength contributed by the solid solution of oxygen atoms is calculated, and finally, we obtain the values of solid solution strengthening of oxygen-doped alloys; the theoretical strengths and sums of all types are listed in Table 5. The theoretical strength values are all lower than the experimental values, which indicates that the classical theoretical model fails to fully take into account the role of dislocation density in strength.

Table 5.
Theoretical yield strength and various types of strengthening.
4. Conclusions
In this study, the effects of interstitial oxygen on the microstructures and mechanical properties of TiZrNb MHEAs are investigated. The main conclusions are summarized as follows:
- (1)
- The alloys display single BCC solid solution structures, the doped oxygen exists as interstitial atoms, and the increase in oxygen content does not induce the change in the crystal structures. The microstructure shows dendritic morphology, with Ti and oxygen elements uniformly distributed in the matrix, Zr slightly enriched in the interdendrites, and Nb slightly enriched in the dendrites. With increasing oxygen content, the average width of the dendritic structures decreases. For O6 alloy, it turns out to be an equiaxed crystal structure.
- (2)
- As oxygen content increases, the yield strength significantly increases from 670 MPa of TiZrNb to 1300 MPa of O4. Among them, O4 MEA shows the optimum mechanical properties, with a room-temperature yield strength of 1300 MPa, high-temperature yield strength of 545 MPa at 800 °C, and elongation at 60%. The enhancement of strength is attributed to the solid solution strengthening induced by interstitial oxygen. Meanwhile, the solid solution of oxygen atoms contributes to a new type of interstitial atom arrangement, which could effectively pin dislocations and alter the dislocation slip mechanism from planar slip to wave slip, thus facilitating more uniform deformation.
- (3)
- The Toda-Caraballo and Labusch models were used to evaluate the contributions of the strengthening effects, and the theoretical values are close to the experimental values. The results indicate that the strengthening mechanism of the alloy systems is dominated by solid solution strengthening, while grain boundary strengthening plays a secondary role. The solid solution of oxygen in the matrix increases lattice distortion, which hinders dislocation movement and effectively enhances the yield strength of the alloy. However, an excessive amount of oxygen can aggravate the internal stress, leading to brittle fracture during compression.
This work achieved a significant enhancement in the mechanical properties of the TiZrNb MEA by doping with 0.5–6 at.% oxygen. The strengthening mechanisms were elucidated using theoretical models, and the calculated theoretical yield strength was found to be in good agreement with the experimental yield strength. In summary, this work not only provides a theoretical foundation for interstitial strengthening in MEAs but also demonstrates practical industrial applications, particularly in high-temperature and mechanically demanding environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.C. and L.J.; methodology, W.Z., Y.L. and Z.Z.; validation, Y.L.; formal analysis, C.Z.; investigation, C.Z., Z.Z. and C.C.; resources, L.J.; data curation, C.Z. and F.C; writing—original draft preparation, C.Z.; writing—review and editing, F.C. and C.C.; visualization, W.Z.; supervision, Z.C.; project administration, L.J.; funding acquisition, L.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52101036, No. 52271024), the Aeronautical Science Foundation (2023Z056063001), and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Liaoning Province (2023JH2/101700280).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge the assistance of the DUT Instrumental Analysis Center.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Miracle, D.B.; Chuang, C.P.; Liaw, P.K. Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Jensen, J.K.; Pilchak, A.L.; Miracle, D.B.; Fraser, H.L. Compositional Variation Effects on the Microstructure and Properties of a Refractory High-Entropy Superalloy AlMo0.5NbTa0.5TiZr. Mater. Des. 2018, 139, 498–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.K.; Li, Y.K.; Chen, Y.W. High Compressibility ZrTiHfV0.5Nb0.5Cx Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 2019, 944, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.; Steurer, W. Structural-Disorder and Its Effect on Mechanical Properties in Single-Phase TaNbHfZr High-Entropy Alloy. Acta Mater. 2016, 106, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.D.; Luan, H.W.; Liu, X.; Chen, N.; Li, X.Y.; Shao, Y.; Yao, K.F. Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of TiNbMoTaW Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 712, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Wu, S.; Jiang, H.; Lu, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, T. Effect of Ti Content on Microstructure and Properties of TixZrVNb Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2020, 27, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Fu, H.; Zhang, L.; Mao, H.; Li, H.; Wang, A.; Li, W.; Zhang, H. Effects of Al Addition on the Microstructures and Properties of MoNbTaTiV Refractory High Entropy Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 784, 139275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Wilks, G.B.; Scott, J.M.; Miracle, D.B. Mechanical Properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and V20Nb20Mo20Ta20W20 Refractory High Entropy Alloys. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.N.; Wang, L.; Luo, L.S.; Li, X.Z.; Su, Y.Q.; Guo, J.J.; Fu, H.Z. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Refractory MoNbHfZrTi High-Entropy Alloy. Mater. Des. 2015, 81, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Chen, Z.; Huang, S.; Lu, Z.; Yan, H. WxNbMoTa Refractory High-Entropy Alloys Fabricated by Laser Cladding Deposition. Materials 2019, 12, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-P.; Xu, J. TiZrNbTaMo High-Entropy Alloy Designed for Orthopedic Implants: As-Cast Microstructure and Mechanical Properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Du, C.; Yu, Z.; Wang, R.; Ren, X. Effect of Cu Content on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe20Co30Ni10Cr20Mn20 FCC-Typed HEAs. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 897, 146336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wu, Y.; An, N.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Bai, R.; Hui, X. Nanoscale L12 Phase Precipitation Induced Superb Ambient and High Temperature Mechanical Properties in Ni–Co–Cr–Al System High-Entropy Superalloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 898, 145995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Hui, X. Abnormal Effect of Al on the Phase Stability and Deformation Mechanism of Ti-Zr-Hf-Al Medium-Entropy Alloys. Metals 2024, 14, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.; Yang, T.; Feng, J.; Deng, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Meng, Q.; Qi, J.; Wei, F.; Sui, Y. Influence of Al and Ti Alloying and Annealing on the Microstructure and Compressive Properties of Cr-Fe-Ni Multi-Principal Element Alloy. Metals 2024, 14, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Guo, A.X.Y.; Zhan, S.; Liu, C.T.; Cao, S.C. Refractory High-Entropy Alloys: A Focused Review of Preparation Methods and Properties. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 142, 196–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Scott, J.M.; Senkova, S.V.; Miracle, D.B.; Woodward, C.F. Microstructure and Room Temperature Properties of a High-Entropy TaNbHfZrTi Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 6043–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, S.; Wang, S.; Hui, X.; Wu, Y.; Gault, B.; Kontis, P.; et al. Enhanced Strength and Ductility in a High-Entropy Alloy via Ordered Oxygen Complexes. Nature 2018, 563, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, X.; Xu, Z.; Wu, C.; Cheng, B.; Wang, M. Interstitial Strengthening of Refractory ZrTiHfNb0.5Ta0.5Ox (x = 0.05, 0.1, 0.2) High-Entropy Alloys. Mater. Lett. 2018, 228, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tang, Y.; Lei, Z.; Ai, Y.; Tong, Z.; Li, S.; Ye, Y.; Bai, S. Achieving High Strength and Ductility in Nitrogen-Doped Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. Mater. Des. 2022, 213, 110356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, C.S.; Cooper, K.P. Nanomechanics of Hall–Petch Relationship in Nanocrystalline Materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009, 54, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Liu, H.; Yu, X.; Yi, Y.; Li, W.; Zhou, S.; Cui, S.; Wang, X. A Design of TiZr-Rich Body-Centered Cubic Structured Multi-Principal Element Alloys with Outstanding Tensile Strength and Ductility. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 813, 141135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Li, X.; Kang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, H. Effect of Interstitial Oxygen /Nitrogen on Mechanical and Wear Properties of TiZrHfNb Refractory High-Entropy Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 960, 170863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, Z.C.; Knight, B.E.; Schuh, C.A. Six Decades of the Hall–Petch Effect—A Survey of Grain-Size Strengthening Studies on Pure Metals. Int. Mater. Rev 2016, 61, 495–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fang, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Liaw, P.K. Lattice-Distortion Dependent Yield Strength in High Entropy Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 784, 139323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.W.; Qiao, J.W.; Hawk, J.A.; Zhou, H.F.; Chen, M.W.; Gao, M.C. Mechanical Properties of Refractory High-Entropy Alloys: Experiments and Modeling. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 696, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Li, T.; Su, Z.; Liu, D. Research on Suitable Strength, Elastic Modulus and Abrasion Resistance of Ti–Zr–Nb Medium Entropy Alloys (MEAs) for Implant Adaptation. Intermetallics 2022, 140, 107401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Wang, L.; Fu, Y.; Qin, J.; Lu, W.; Zhang, D. Influence of Oxygen Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti–Nb–Ta–Zr Alloy. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2934–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Lei, Z.; Yuan, X.; Wu, H.; Feng, X.; Liu, J.; Ding, J.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Local Chemical Fluctuation Mediated Ductility in Body-Centered-Cubic High-Entropy Alloys. Mater. Today 2021, 46, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, E.; Liu, C. Chemical Inhomogeneities in High-Entropy Alloys Help Mitigate the Strength-Ductility Trade-Off. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2024, 143, 101252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, K.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, J.; Ma, E. Local Chemical Inhomogeneities in TiZrNb-Based Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 135, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.-H.; Nong, Z.-S.; Wang, H.-Y.; Wang, J.-J. Microstructures, Mechanical and Electrochemical Properties of Monbta-Based Refractory Multi-Component Alloys. JOM 2022, 74, 4344–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-P.; Ma, E.; Xu, J. New Ternary Equi-Atomic Refractory Medium-Entropy Alloys with Tensile Ductility: Hafnium versus Titanium into NbTa-Based Solution. Intermetallics 2019, 107, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.D.; Cai, Y.H.; Wang, T.; Si, J.J.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.D.; Hui, X.D. A Refractory Hf25Nb25Ti25Zr25 High-Entropy Alloy with Excellent Structural Stability and Tensile Properties. Mater. Lett. 2014, 130, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.J.; Qiao, J.W.; Wang, Z.H.; Wu, Y.C. Ultra-High Strain-Rate Strengthening in Ductile Refractory High Entropy Alloys upon Dynamic Loading. Intermetallics 2020, 121, 106699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fu, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Hui, X. Ductile Ti-Rich High-Entropy Alloy Controlled by Stress Induced Martensitic Transformation and Mechanical Twinning. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 763, 138147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hamasaki, H.; Yamamura, M.; Yamauchi, R.; Maeda, T.; Shirai, Y.; Yoshida, F. Yield-Point Phenomena of Ti-20V-4Al-1Sn at 1073 K and Its Constitutive Modelling. Mater. Trans. 2009, 50, 1576–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippart, I.; Rack, H.J. High Temperature Dynamic Yielding in Metastable Ti–6.8Mo–4.5F–1.5Al. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 243, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, A.; Abbasi, S.M.; Morakabati, M.; Akhondzadeh, A. Yield Point Phenomena in TIMETAL 125 Beta Ti Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 643, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Li, J.; Mao, J.; Lu, W. The Elimination of the Yield Point Phenomenon in a New Zirconium Alloy: Influence of Degree of Recrystallization on the Tensile Properties. Scr. Mater. 2019, 169, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Scott, J.M.; Senkova, S.V.; Meisenkothen, F.; Miracle, D.B.; Woodward, C.F. Microstructure and Elevated Temperature Properties of a Refractory TaNbHfZrTi Alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 4062–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.L.; Liu, Y.Z.; Wu, H.J.; Li, F.X. Hot compression behavior of semi-solid 7050 aluminum alloy. Spec. Cast. Nonferrous Alloys 2011, 31, 816–819. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, E.O. Iron and Its Alloys. In Yield Point Phenomena in Metals and Alloys; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1970; pp. 65–126. ISBN 978-1-4684-1860-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ravichandran, N.; Prasad, Y.V.R.K. Influence of Oxygen on Dynamic Recrystallization during Hot Working of Polycrystalline Copper. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1992, 156, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Wang, H.; Huang, H.L.; Xu, X.D.; Chen, M.W.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Nieh, T.G.; An, K.; Lu, Z.P. A Precipitation-Hardened High-Entropy Alloy with Outstanding Tensile Properties. Acta Mater. 2016, 102, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labusch, R. A Statistical Theory of Solid Solution Hardening. Phys. Status Solidi B 1970, 41, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yang, X.; Li, T.; Li, L.; Lu, Y. Achieving Superior Mechanical Properties and Biocompatibility in an O-Doping TiZrNb Medium Entropy Alloy. Intermetallics 2023, 161, 107991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Miao, J.; Lu, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, T. Effect of Zr on the As-Cast Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Lightweight Ti2VNbMoZrx Refractory High-Entropy Alloys. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2022, 103, 105762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).