Rapid Microwave Irradiation-Enhanced Detoxification and Mineralization of Cr(VI) by FeS2/ZVI Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. MW Irradiation-Assisted Cr(VI) Reduction
2.3. Kinetics and Thermodynamics Experiment
2.4. Characterization and Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
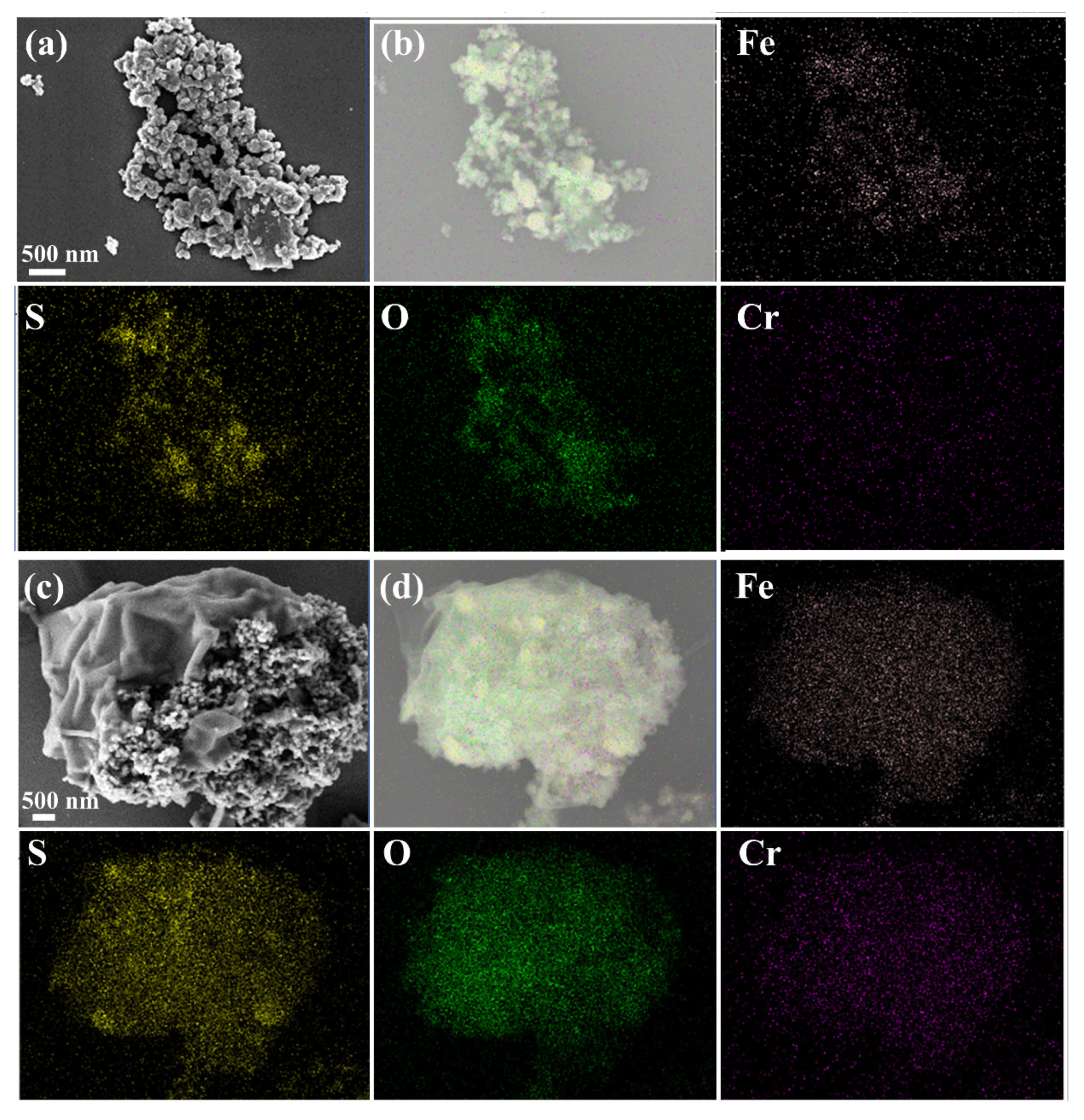
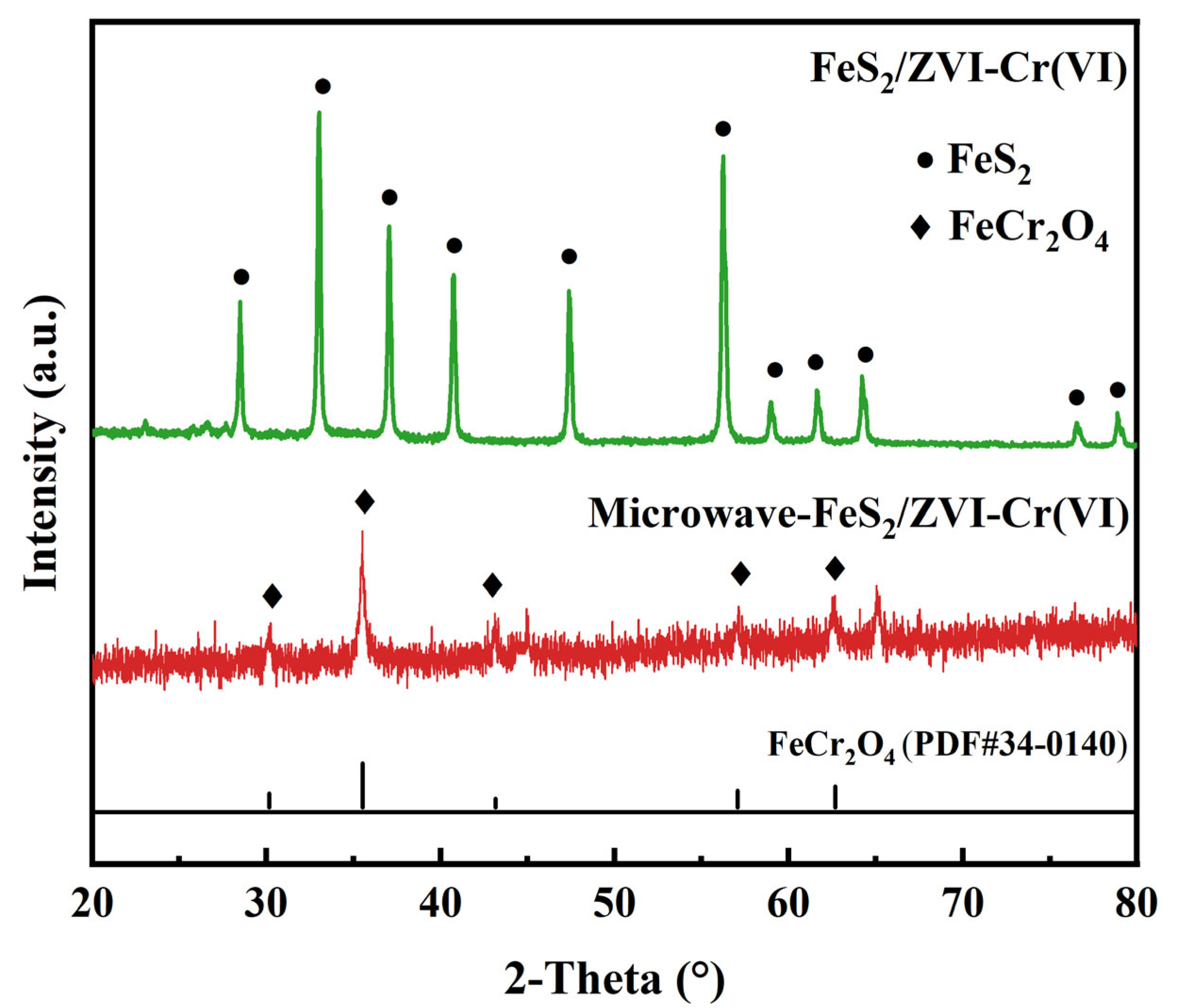
3.1. Characterization of Synthesized FeS2/ZVI
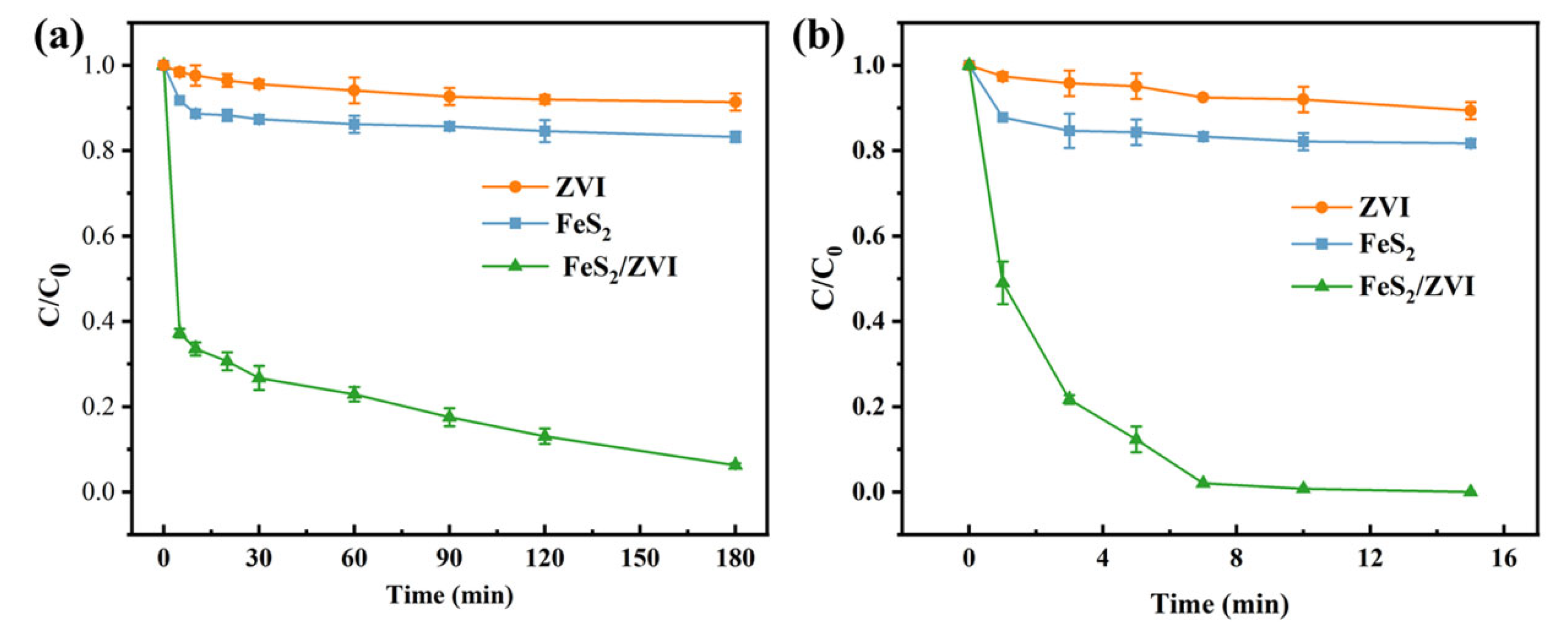
3.2. Cr(VI) Reduction by FeS2/ZVI Composite Under MW Irradiation
| Removal System | Materials | Cr(VI) Concentration (mg/L) | Optimized pH | Removal Efficiency | Time (min) | Dosage (g/L) | Adsorption/Reduction Capacity (mg/g) | Reduction Ability * (mg/(g min)) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical reduction | SZVI-Cu | 5.0 | 5 | 97.9% | 20 | 0.2 | 24.48 | 1.22 | [15] |
| S-ZVINa2S2O3 | 5.0 | 6 | 99.0% | 90 | 0.5 | 9.90 | 0.11 | [31] | |
| S-ZVINa2S2O4 | 5.0 | 6 | 100.0% | 90 | 0.5 | 10.00 | 0.11 | [31] | |
| S-ZVI | 5.0 | 5 | 100.0% | 120 | 0.2 | 25.00 | 0.21 | [32] | |
| mZVI/AC | 10.0 | 3 | 94.01% | 120 | 1 | 9.40 | 0.08 | [33] | |
| S-ZVI | 4.0 | 5 | 98.0% | 120 | 0.2 | 19.60 | 0.16 | [34] | |
| Fe/FeS | 25 | 5 | 88% | 4320 | 0.3 | 73.33 | 0.02 | [14] | |
| Photocatalytic reduction | SrTiO3 | 10 | 2 | 100% | 120 | 1 | 10.00 | 0.08 | [35] |
| ZnFe2O4/CdS | 100 | 2 | 90% | 120 | 0.5 | 180.00 | 1.50 | [36] | |
| CeO2-MoS2 | 5 | 5.9 | 100% | 120 | 0.3 | 16.67 | 0.14 | [37] | |
| BiOI/RGO/Bi2S3 | 50 | 3 | 70% | 240 | 1 | 35 | 0.15 | [38] | |
| MW irradiation reduction | MoS2-MnFe2O4 | 10 | 3.3 | 85.8% | 16 | 2 | 4.29 | 0.27 | [22] |
| ZnFe2O4 | 50 | 2 | 100% | 10 | 2 | 25.00 | 2.50 | [23] | |
| FeS2/ZVI | 50 | 5 | 100% | 10 | 50 | 5 | This study |
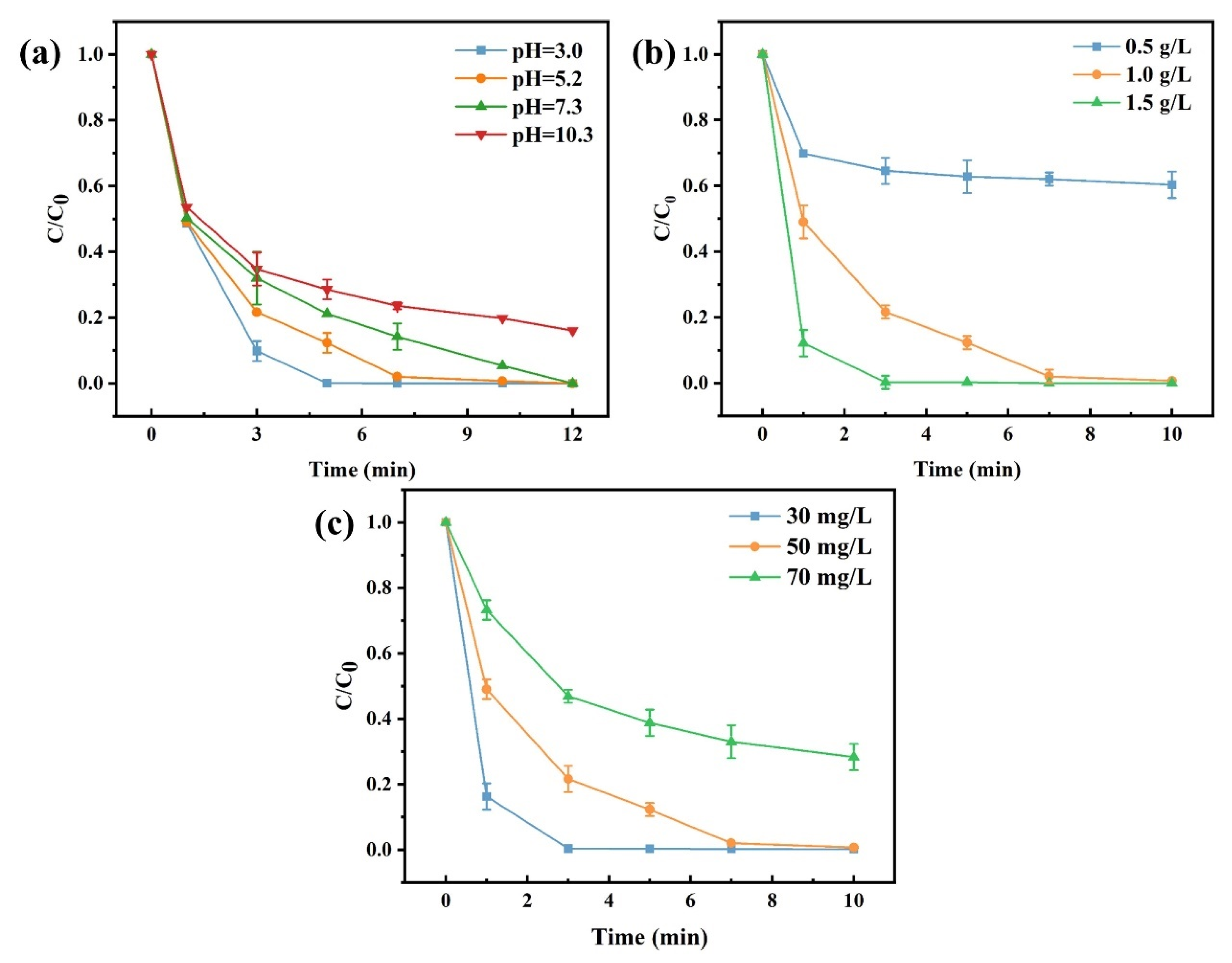
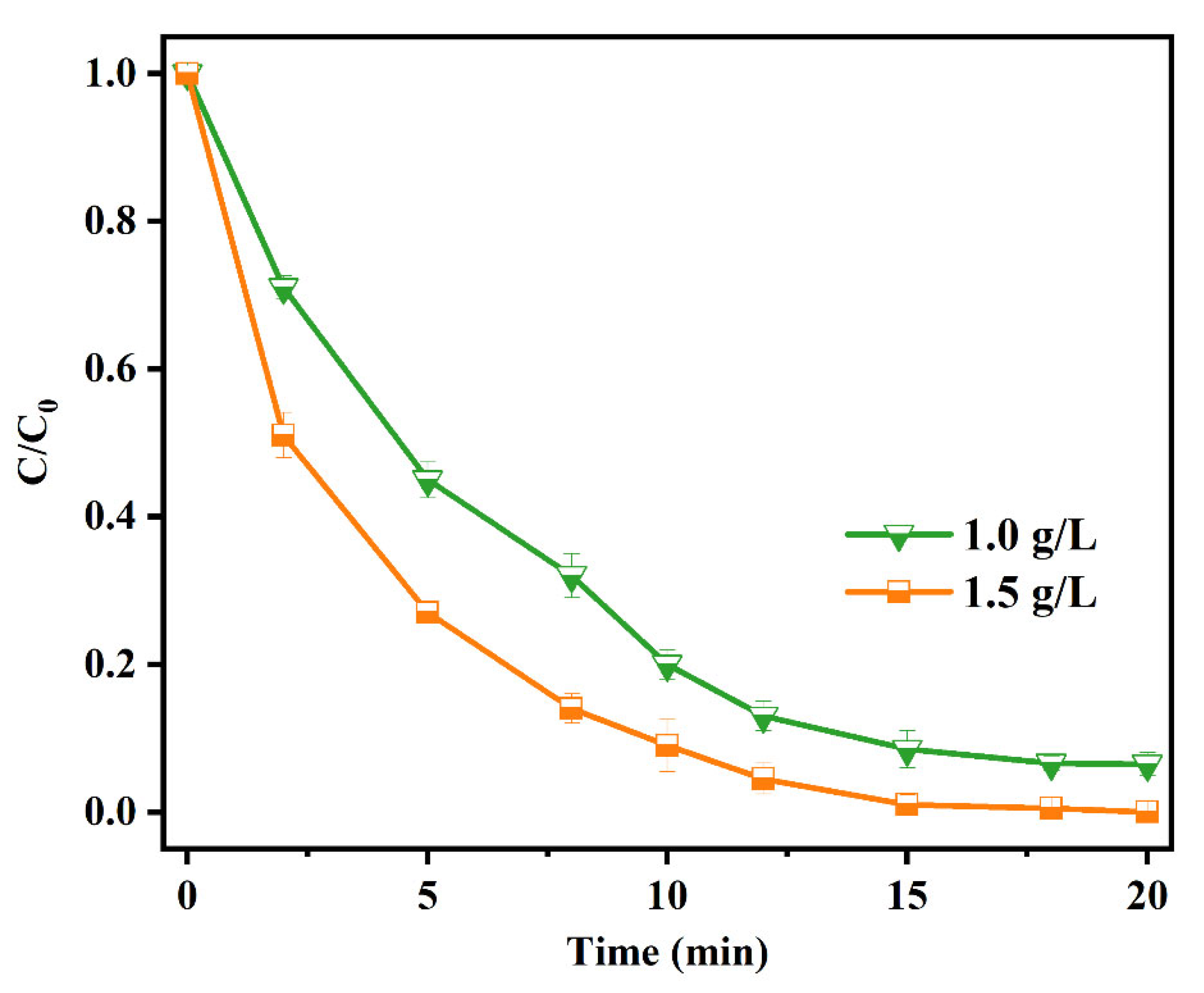
3.3. Factors Influencing MW Irradiation-Assisted Cr(VI) Reduction
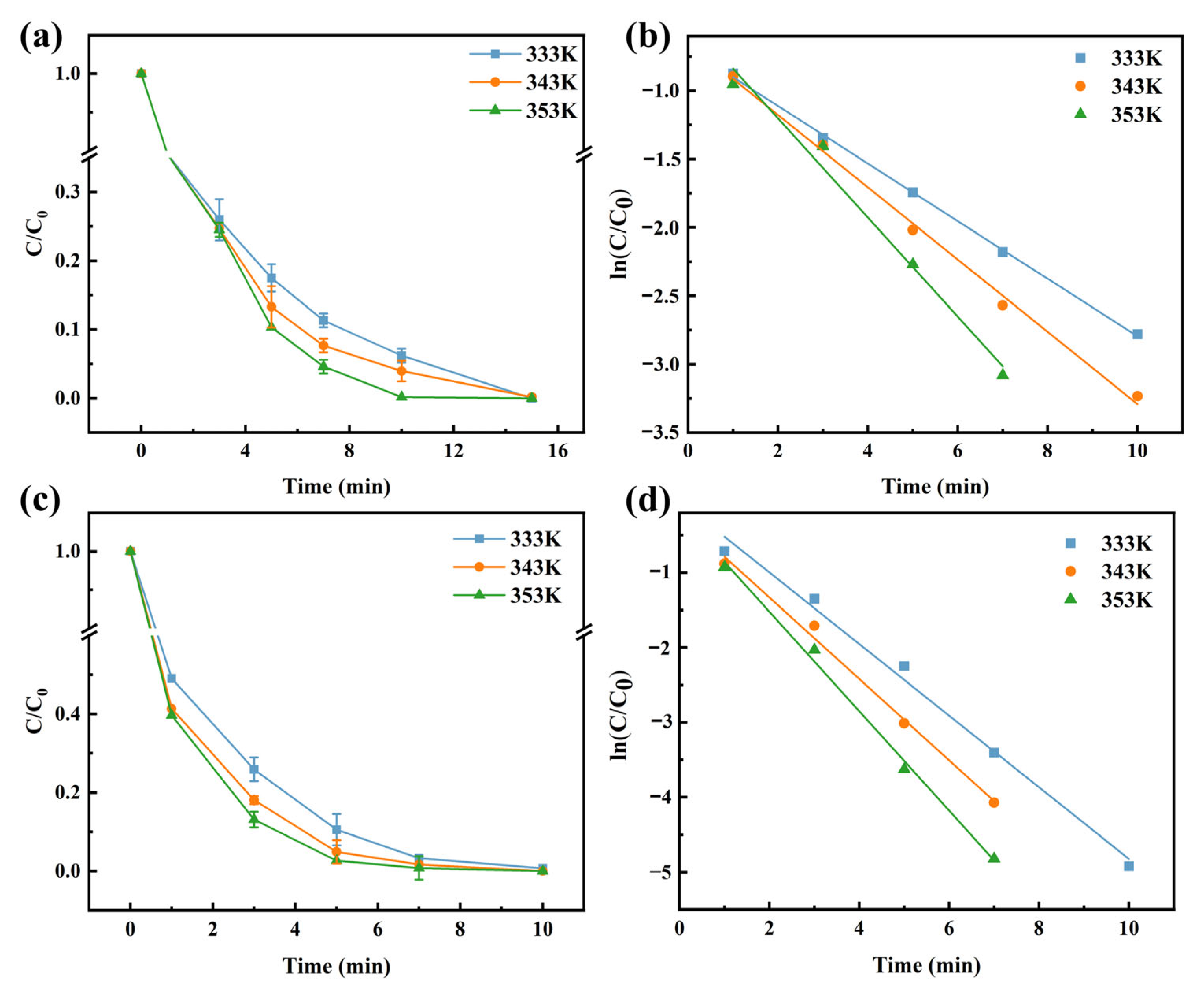
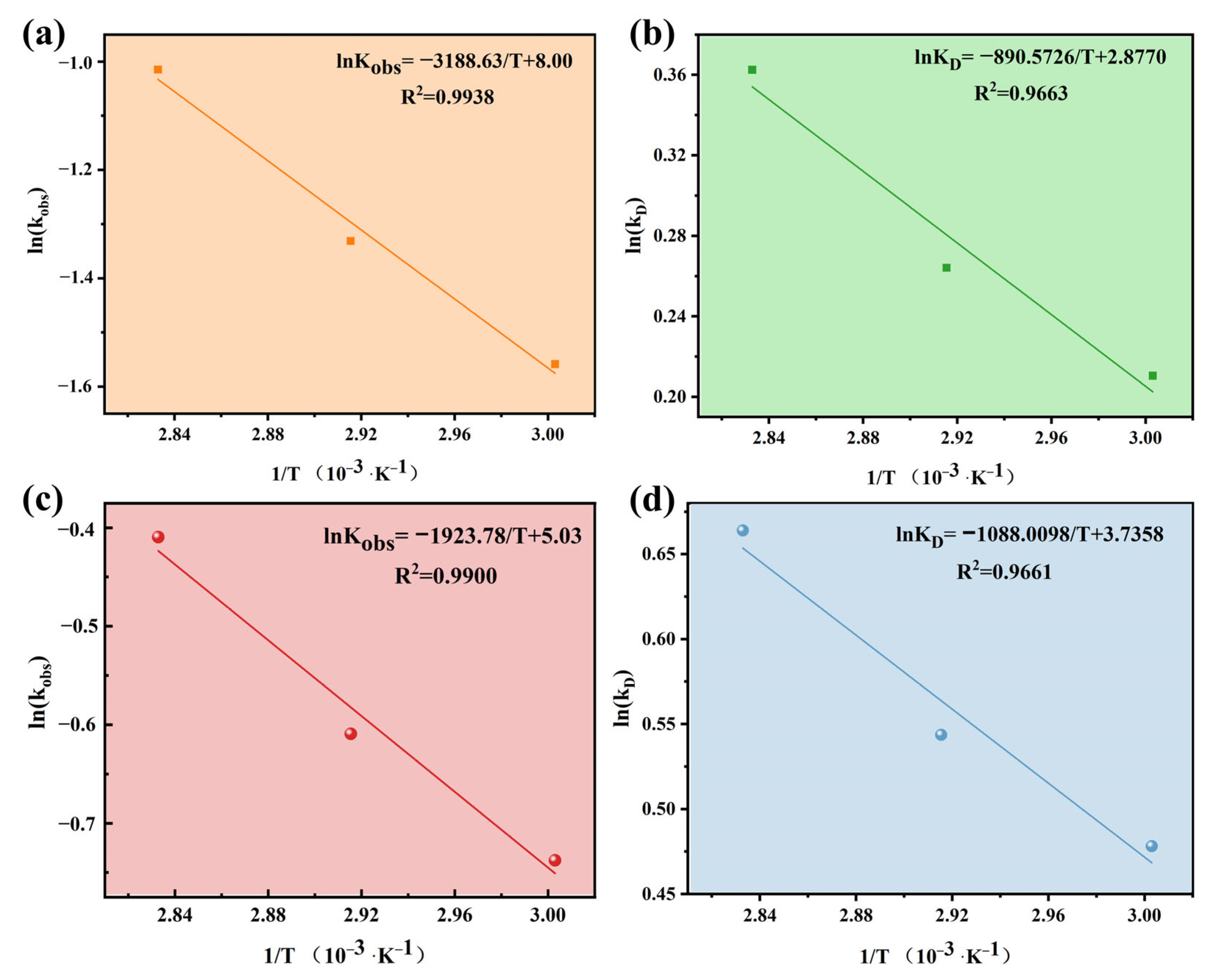
3.4. Kinetics and Thermodynamics of MW Irradiation-Assisted Cr(VI) Reduction
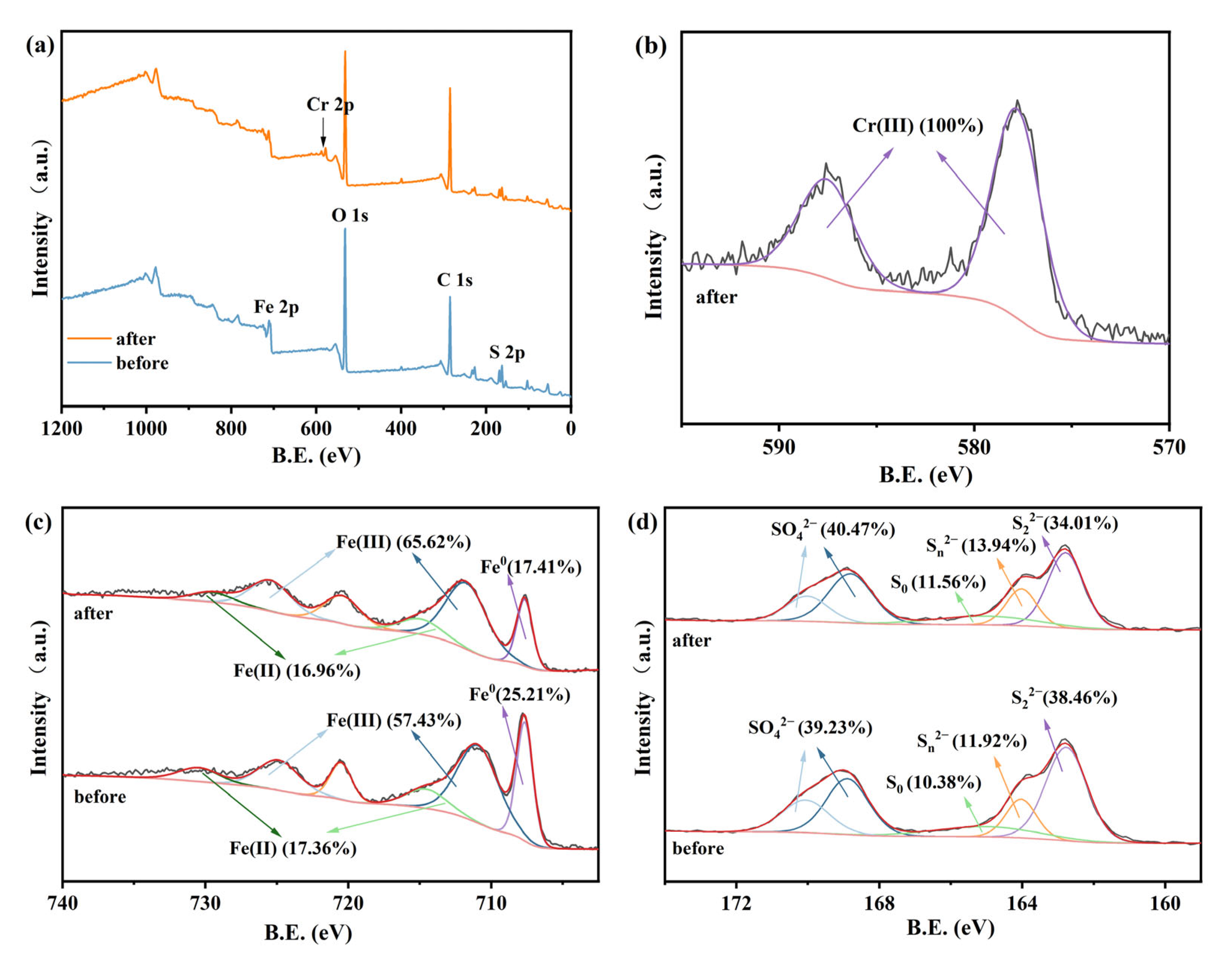
3.5. Mechanism of Accelerated Reduction of Cr(VI) by MW Irradiation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xia, S.; Song, Z.; Jeyakumar, P.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S.; Bolan, N.; Wang, H. A critical review on bioremediation technologies for Cr(VI)-contaminated soils and wastewater. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 1027–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Yaob, W.; Chen, X. Removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater by simplified electrodeionization. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 183, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedman, R.M.; Beaumont, J.A.Y.; McDonald, T.A.; Reynolds, S.; Krowech, G.; Howd, R. Review of the Evidence Regarding the Carcinogenicity of Hexavalent Chromium in Drinking Water. J. Environ. Sci. Health C 2006, 24, 155–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Chen, M.; Jin, X.; Hu, D.; Huang, Q. Efficient and stable photocatalytic reduction of aqueous hexavalent chromium ions by polyaniline surface-hybridized ZnO nanosheets. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 279, 133–145. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.; Yan, R.; Liu, M.; Xu, J.; Hagio, T.; Ichino, R.; Li, L.; Cao, X. Simultaneous reduction and sequestration of hexavalent chromium by magnetic β-Cyclodextrin stabilized Fe3S4. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128592. [Google Scholar]
- Sessarego, S.; Rodrigues, S.C.G.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, Q.; Hill, J.M. Phosphonium-enhanced chitosan for Cr(VI) adsorption in wastewater treatment. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 211, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, P.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, Y.; Qiu, F. Fabrication of recyclable magnetic double-base aerogel with waste bioresource bagasse as the source of fiber for the enhanced removal of chromium ions from aqueous solution. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 119, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Xie, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhong, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, H.; Hao, C. High-performance polyethylenimine-functionalized lignin/silica porous composite microsphere for the removal of hexavalent chromium, phosphate and Congo red from aqueous solutions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 194, 116289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Li, Y.; Lu, X.J.; Xu, W.Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, L.G. Fabrication and characterization of novel polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafiltration membranes for separation of Cr(VI) from wastewater. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, H.; Shi, J.; Wu, K.; Zhang, P.; Lv, J.; Li, H.; He, H.; Liu, P.; et al. Simultaneous aerobic denitrification and Cr(VI) reduction by Pseudomonas brassicacearum LZ-4 in wastewater. Bioresource Technol. 2016, 221, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jin, L.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, P.; Wang, C.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Wang, X. Insight into pH dependent Cr(VI) removal with magnetic Fe3S4. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Qin, F.; Ming, Y.a.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, R. Fabrication uniform hollow Bi2S3 nanospheres via Kirkendall effect for photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) in electroplating industry wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 340, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Hu, E.; Yang, S.; Gong, L.; He, F. Chromium(VI) removal by mechanochemically sulfidated zero valent iron and its effect on dechlorination of trichloroethene as a co-contaminant. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Gai, L.; Tang, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, E.Y. Reduction of Cr(VI) in simulated groundwater by FeS-coated iron magnetic nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Zhang, B.; Huang, L.; Wang, S.; Xu, C. Enhanced sequestration of Cr(VI) by copper doped sulfidated zerovalent iron (SZVI-Cu): Characterization, performance, and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 366, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falciglia, P.P.; Roccaro, P.; Bonanno, L.; De Guidi, G.; Vagliasindi, F.G.A.; Romano, S. A review on the microwave heating as a sustainable technique for environmental remediation/detoxification applications. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2018, 95, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Zhang, W. Microwave-enhanced membrane filtration for water treatment. J. Membrane Sci. 2018, 568, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remya, N.; Lin, J.-G. Current status of microwave application in wastewater treatment—A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 797–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yuan, S.; Chen, J.; Xu, Z.; Lu, X. Removal of ammonia nitrogen in wastewater by microwave radiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Cai, J.; Yin, C.; Gao, L.; Zhou, J. Degradation performance of crystal violet over CuO@AC and CeO2-CuO@AC catalysts using microwave catalytic oxidation degradation method. J. Environ. Chem. Eng 2016, 4, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Fu, L.; Tang, J.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Tian, F.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Dionysiou, D.D. Microwave hydrothermal-assisted preparation of novel spinel-NiFe2O4 /natural mineral composites as microwave catalysts for degradation of aquatic organic pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 350, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Kong, L.; Chen, D.; Yuvaraja, G. Rapid Cr(VI) reduction in aqueous solution using a novel microwave-based treatment with MoS2-MnFe2O4 composite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 471, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Li, K.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Z.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Jia, Q. A novel insight into the microwave induced catalytic reduction mechanism in aqueous Cr(VI) removal over ZnFe2O4 catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; Cao, K.; Si, M.; Liao, Q.; Zhao, F.; Yang, W.; Yang, Z. Performance and mechanisms of microwave-assisted zerovalent iron/pyrite for advance remediation of strongly alkaline high Cr(VI) contaminated soil. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 298, 118855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Xie, Y.; Liao, Q.; Zhao, F.; Yang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Si, M.; Yang, W. Interaction of pyrite with zerovalent iron with superior reductive ability via Fe (ii) regeneration. Environ. Sci. Nano 2022, 9, 2713–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Sun, P.; Niu, S.; Shen, B.; Lyu, H. Atmosphere matters: The protection of wet ball milling instead of dry ball milling accelerates the electron transfer effect of sulfurized micron iron/biochar to Cr (VI). Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Cai, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S. Transformation behaviour of pyrite during microwave desulfurization from coal: Phase and structural change of Fe-S compounds. Fuel 2022, 316, 123284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Li, C.; Yang, G.; Shi, Z.; Jin, C.; He, W.; Xu, J.; Li, G. A review of microwave-assisted advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhang, A. Activation of persulfate by microwave radiation combined with FeS for treatment of wastewater from explosives production. Environ. Sci.-Wat. Res. 2020, 6, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 8978-1996; Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard. Chinese National Environmental Protection Administration: Beijing, China, 1996.
- Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Gu, K.; Li, J. Sulfidation of zerovalent iron for improving the selectivity toward Cr(VI) in oxic water: Involvements of FeSx. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shao, Q.; Huang, S.; Zhang, B.; Xu, C. High performance and simultaneous sequestration of Cr(VI) and Sb(III) by sulfidated zerovalent iron. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 191, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hu, B.; Wang, C.; Liang, Z.; Cui, F.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, C. Cr(VI) removal by micron-scale iron-carbon composite induced by ball milling: The role of activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 122633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Xu, C. Insights on the effects of pH and Fe(II) regeneration during the chromate sequestration by sulfidated zero-valent iron. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Sun, Y.; Tong, Z.; Nan, Y.; Jiang, Z. Fabrication of bimodal-pore SrTiO3 microspheres with excellent photocatalytic performance for Cr(VI) reduction under simulated sunlight. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 312, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, M.; Li, Z.; Xu, S.; Yao, C. Facile synthesis of novel ZnFe2O4/CdS nanorods composites and its efficient photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) under visible-light irradiation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 58, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wen, F.; Li, X.; Gan, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Y. Cerium-doped MoS2 nanostructures: Efficient visible photocatalysis for Cr(VI) removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 170, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Bian, Z.; Xu, J.; Xin, X.; Wang, H. Simultaneous removal of Cr(VI) and phenol contaminants using Z-scheme bismuth oxyiodide/reduced graphene oxide/bismuth sulfide system under visible-light irradiation. Chemosphere 2017, 188, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wei, G.; Cao, T.; Shao, B.; Guan, X.; Strathmann, T.J. Insights into the Oxidation of Organic Cocontaminants during Cr(VI) Reduction by Sulfite: The Overlooked Significance of Cr(V). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, N.; Gong, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X. Cu–Fe embedded cross-linked 3D hydrogel for enhanced reductive removal of Cr (VI): Characterization, performance, and mechanisms. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130663. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Shi, Y.; Hou, H.; Pan, H.; Yao, D.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Crittenden, J.C. Stabilization and Mineralization Mechanism of Cd with Cu-Loaded Attapulgite Stabilizer Assisted with Microwave Irradiation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12624–12632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Mei, C.-Y.; Yao, L.-H.; Jin, H.-M.; Qian, G.-R.; Xu, Z.-P. Flash fixation of heavy metals from two industrial wastes into ferrite by microwave hydrothermal co-treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Li, L.; Ma, S.; Shang, Z. Effect factors, kinetics and thermodynamics of remediation in the chromium contaminated soils by nanoscale zero valent Fe/Cu bimetallic particles. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 302, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Si, M.; Liao, Q.; Yang, Z.; Li, Q.; Yang, W. Rapid Microwave Irradiation-Enhanced Detoxification and Mineralization of Cr(VI) by FeS2/ZVI Composites. Metals 2025, 15, 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040395
Zhang X, Wang H, Si M, Liao Q, Yang Z, Li Q, Yang W. Rapid Microwave Irradiation-Enhanced Detoxification and Mineralization of Cr(VI) by FeS2/ZVI Composites. Metals. 2025; 15(4):395. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040395
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaoming, Haiying Wang, Mengying Si, Qi Liao, Zhihui Yang, Qi Li, and Weichun Yang. 2025. "Rapid Microwave Irradiation-Enhanced Detoxification and Mineralization of Cr(VI) by FeS2/ZVI Composites" Metals 15, no. 4: 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040395
APA StyleZhang, X., Wang, H., Si, M., Liao, Q., Yang, Z., Li, Q., & Yang, W. (2025). Rapid Microwave Irradiation-Enhanced Detoxification and Mineralization of Cr(VI) by FeS2/ZVI Composites. Metals, 15(4), 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040395





