Microstructure and Mechanical Characterization of AISI 4340 Steel Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
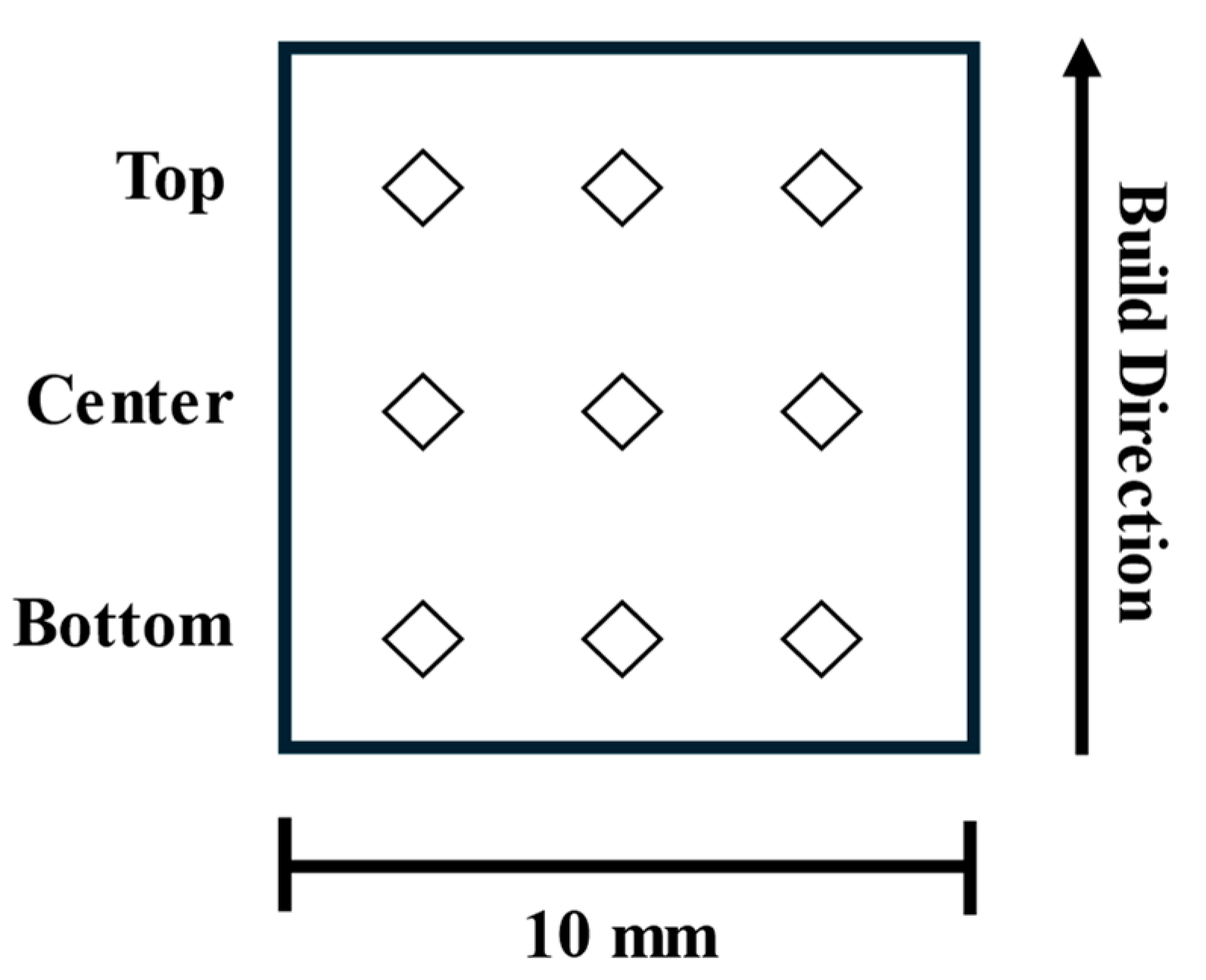
2.1. Laser Powder Bed Fusion and Specimen Preparation
2.2. Phase Constituent and Microstructure Analysis
2.3. Mechanical Testing
3. Results
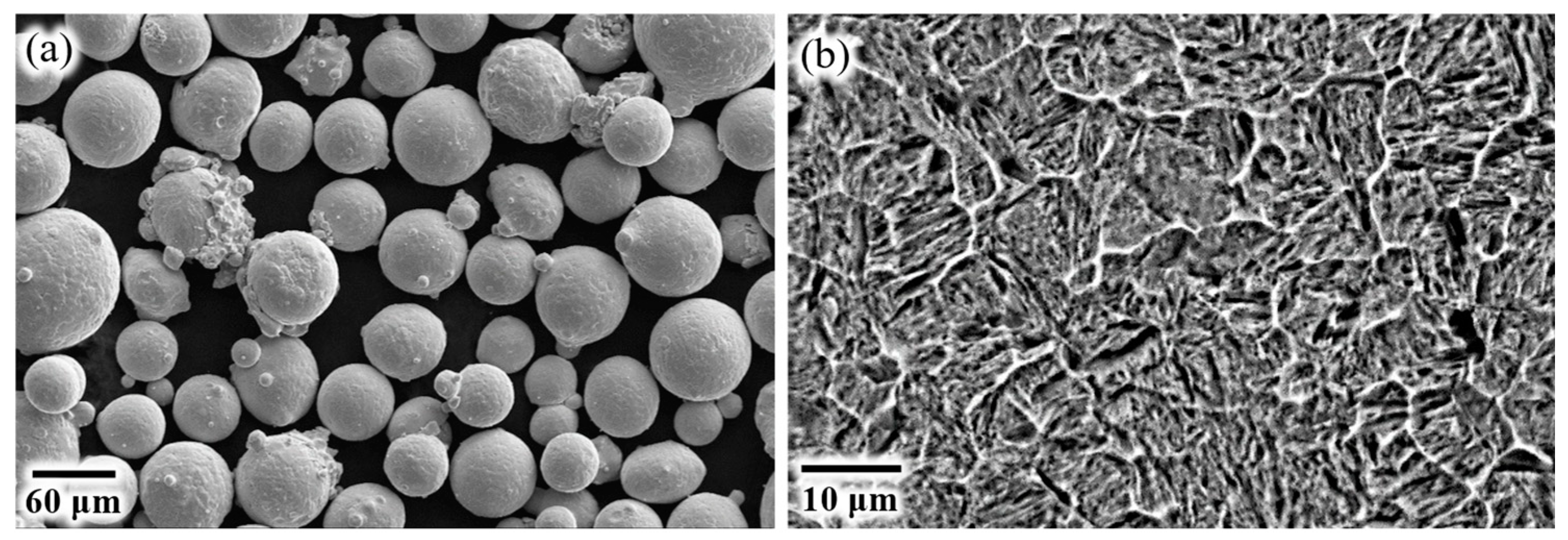
3.1. Powder Feedstock
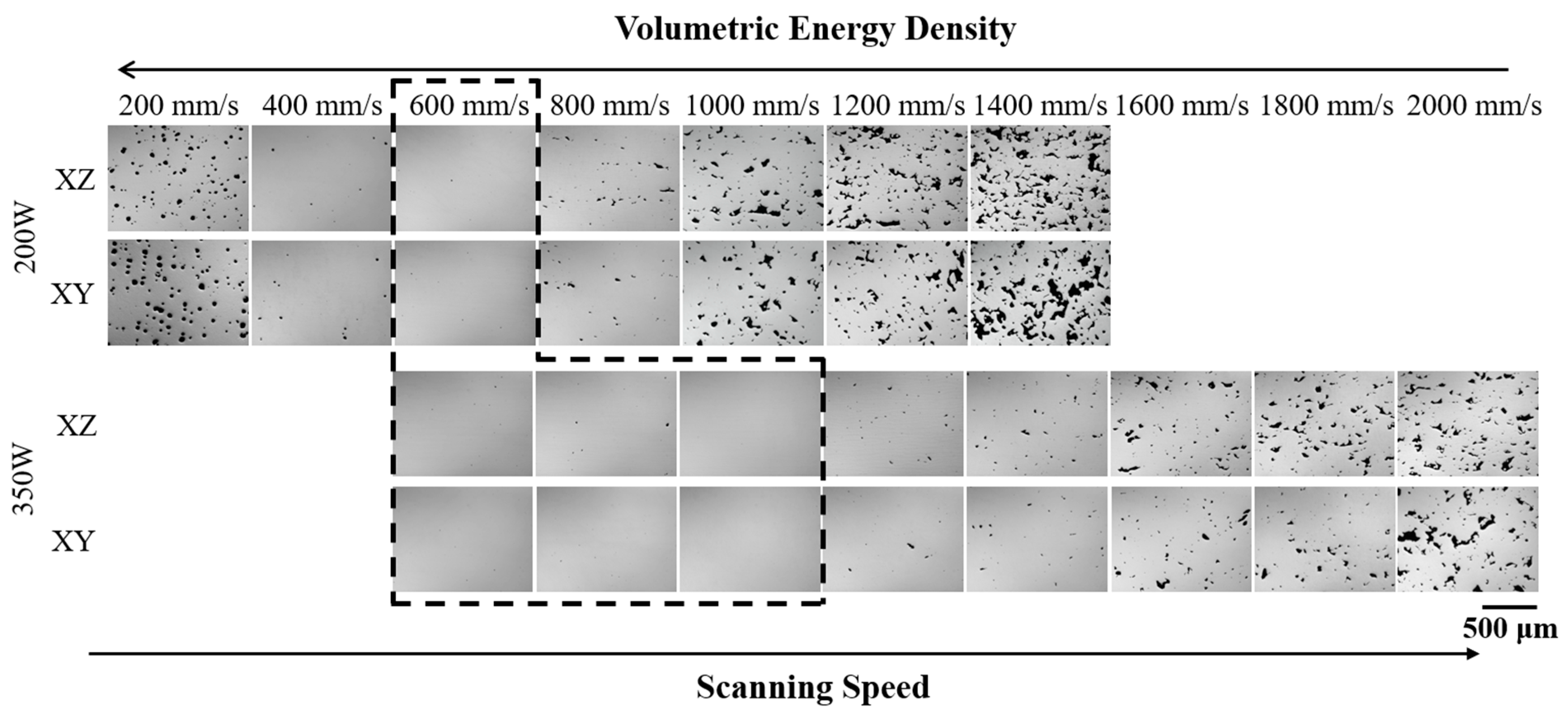
3.2. Influence of LPBF Parameters on Relative Density
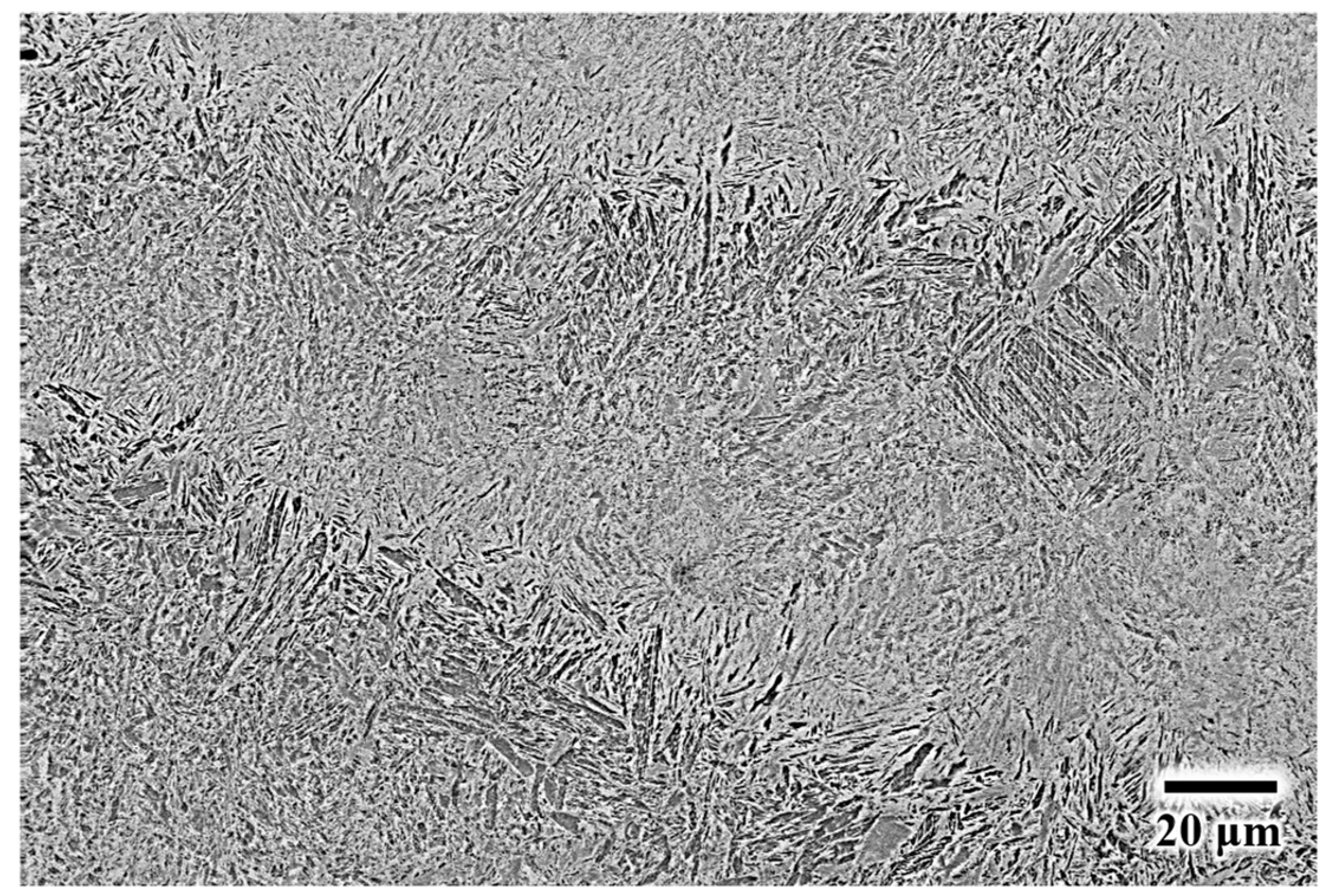
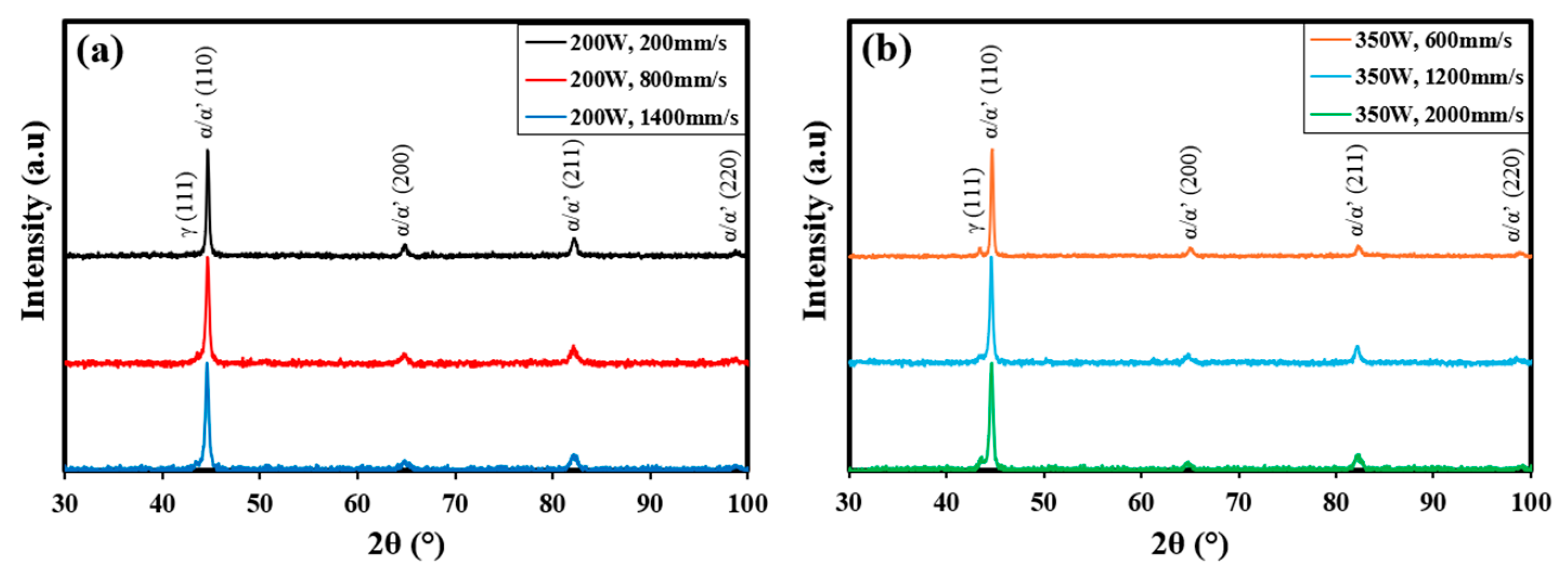
3.3. Influence of Processing Parameters on Microstructure
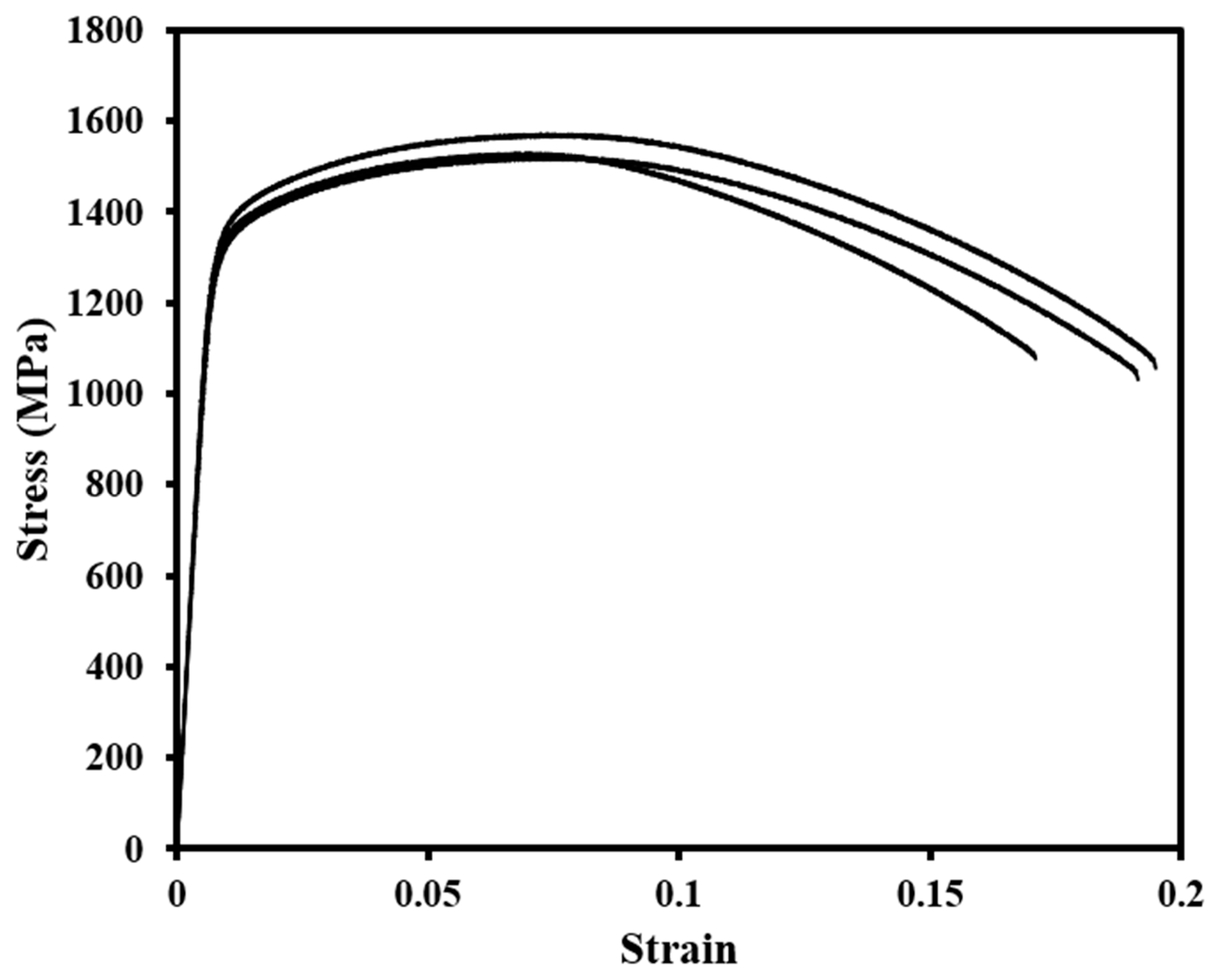
3.4. Influence of Processing Parameters on Mechanical Performance
4. Discussion
4.1. LPBF Process Influence on the Presence of Retained Austenite in As-Fabricated 4340 Steel
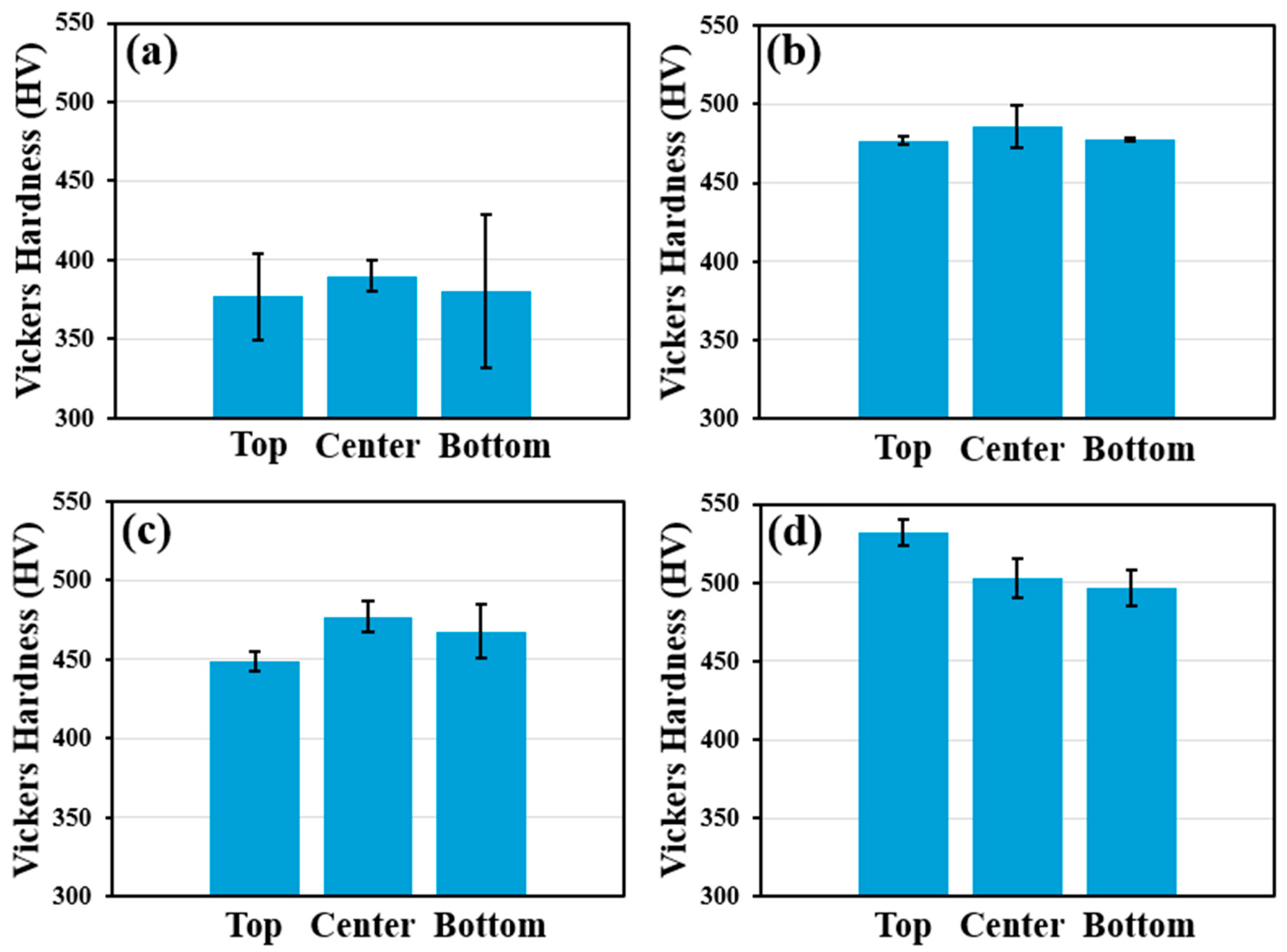
4.2. LPBF Process Influence on the Hardness of As-Fabricated 4340 Steel
5. Summary
- Processing at volumetric energy densities lower than 92.6 J/mm3 yielded lack-of-fusion flaws, while volumetric energy densities greater than 162 J/mm3 yielded keyhole porosities. At intermediate volumetric energy densities between 92.6 and 162 J/mm3, relative sample densities above 99.8% were achieved for AISI 4340 steel.
- As-fabricated AISI 4340 steel is primarily martensitic, decorated with cellular segregation. This microstructure did not vary significantly as a function of scan speeds and sample height for a given laser power.
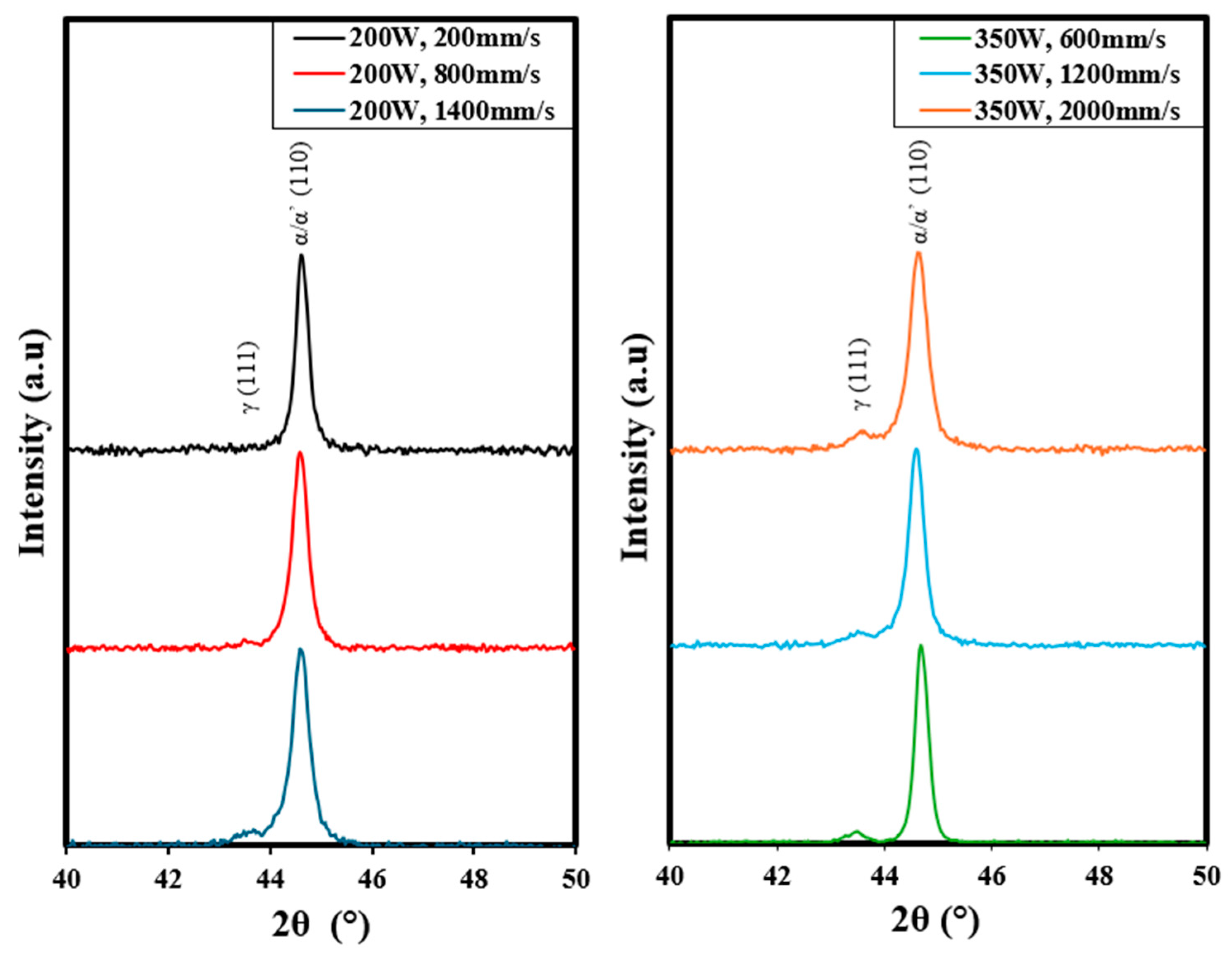
- X-ray diffraction analysis revealed the presence of retained austenite in LPBF-processed 4340 steel. The volume fraction decreased with an increase in VED.
- Hardness measurements revealed that the martensite found in as-fabricated 4340 steel samples was softened due to exposure to in situ tempering during the LPBF process. The degree of in situ tempering experienced by a sample increased with increasing VED, causing samples printed with high VED to exhibit lower hardness compared to samples processed using low VED. Hardness values of LPBF 4340 steel produced using the optimized parameter set were relatively high compared to conventional quenching and 400 °C tempering heat treatment, despite the presence of retained austenite.
- Tensile testing of as-fabricated 4340 steel tensile bars displayed yield and ultimate tensile strengths of up to 1.3 GPa and 1.5 GPa, respectively, with elongations of up to 18.6%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herzog, D.; Seyda, V.; Wycisk, E.; Emmelmann, C. Additive manufacturing of metals. Acta Mater. 2016, 117, 371–392. [Google Scholar]
- DebRoy, T.; Wei, H.L.; Zuback, J.S.; Mukherjee, T.; Elmer, J.W.; Milewski, J.O.; Beese, A.M.; Wilson-Heid, A.; De, A.; Zhang, W. Additive manufacturing of metallic components–process, structure and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 92, 112–224. [Google Scholar]
- Sames, W.J.; List, F.A.; Pannala, S.; Dehoff, R.R.; Babu, S.S. The metallurgy and processing science of metal additive manufacturing. Int. Mater. Rev. 2016, 61, 315–360. [Google Scholar]
- de Souza, M.F.; Serrão, L.F.; Pardal, J.M.; Tavares, S.S.M.; Fonseca, M.C. Tempering influence on residual stresses and mechanical properties of AISI 4340 Steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Jelis, E.; Clemente, M.; Hespos, M.; Groeschler, S.; Golden, E.; Carpenter, R. Round Robin study evaluating consistency of 4340 steel specimens manufactured by different laser powder bed fusion machines. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 6832–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, N.S.; Bang, C.W.; Das, S.; Jin, H.W.; Ayer, R.; Park, C.G. Influence of tempering temperature on both the microstructural evolution and elemental distribution in AISI 4340 Steels. Met. Mater. Int. 2012, 18, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Tan, Q.; Venezuela, J.; Atrens, A.; Zhang, M.X. Additive manufacturing of high-strength low-alloy AISI 4340 steel with an optimal strength-ductility-toughness trade-off. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 94, 104496. [Google Scholar]
- McDaniels, R.L.; White, S.A.; Liaw, K.; Chen, L.; McCay, M.H.; Liaw, P.H. Effects of a laser surface processing induced heat-affected zone on the fatigue behavior of AISI 4340 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 485, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarzkermani, A.; Marzbanrad, E.; Esmaeilizadeh, R.; Mahmoodkhani, Y.; Ali, U.; Enrique, P.D.; Zhou, N.Y.; Bonakdar, A.; Toyserkani, E. An investigation into the effect of process parameters on melt pool geometry, cell spacing, and grain refinement during laser powder bed fusion. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 116, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Mishutova, T.; Artzt, K.; Haubrich, J.; Requena, G.; Bruno, G. New aspects about the search for the most relevant parameters optimizing SLM materials. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 25, 325–334. [Google Scholar]
- Cherry, J.A.; Davies, H.M.; Mehmood, S.; Lavery, N.P.; Brown, S.G.R.; Sienz, J. Investigation into the effect of process parameters on microstructural and physical properties of 316L stainless steel parts by selective laser melting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 76, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, M.A.; Montgomery, C.J.; Brand, M.J.; Carpenter, J.S.; Jones, P.E.; Spangenberger, A.G.; Lados, D.A. Melt Pool and Heat Treatment Optimization for the Fabrication of High-Strength and High-Toughness Additively Manufactured 4340 Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 5426–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, W.; Harlin, P.; Hryha, E. Development of powder bed fusion–laser beam process for AISI 4140, 4340 and 8620 low-alloy steel. Powder Metal. 2023, 66, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelis, E.; Hespos, M.R.; Ravindra, N.M. Process Evaluation of AISI 4340 Steel Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E8/E8M-24; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- Sastry, C.N.; Wood, W.E. On the presence of retained austenite at the prior austenite grain boundaries of AISI 4340 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1980, 45, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, F.S.H.B.; Sharp, J.; Xi, J.; Todd, I. Influence of solidification cell structure on the martensitic transformation in additively manufactured steels. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 30, 100917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fastow, M.; Bamberger, M.; Nir, N.; Landkof, M. Laser surface melting of AISI 4340 steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1990, 6, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Shin, H.C.; Leem, D.S.; Choi, J.K.; Jin, W.; Choi, C.S. Reverse transformation mechanism of martensite to austenite and amount of retained austenite after reverse transformation in Fe-3Si-13Cr-7Ni (wt-%) martensitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Tech. 2013, 19, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.Y.; Petterson, N.H.; Durga, A.; Zhang, F.; Oikonomou, C.; Borgenstam, A.; Odqvist, J.; Lindwall, G. Influence of solidification structure on austenite to martensite transformation in additively manufactured hot-work tool steels. Acta Mater. 2021, 215, 117044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seede, R.; Shoukr, D.; Zhang, B.; Whitt, A.; Gibbons, S.; Flater, P.; Elwany, A.; Arroyave, R.; Karaman, I. An ultra-high strength martensitic steel fabricated using selective laser melting additive manufacturing: Densification, microstructure, and mechanical properties. Acta Mater. 2020, 186, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seede, R.; Zhang, B.; Whitt, A.; Picak, S.; Gibbons, S.; Flater, P.; Elwany, A.; Arroyave, R.; Karaman, I. Effect of heat treatments on the microstructure and mechanical properties of an ultra-high strength martensitic steel fabricated via laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 47, 102255. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.; Su, T. Mechanical properties and microstructural features of AISI 4340 high-strength alloy steel under quenched and tempered conditions. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1999, 87, 198–206. [Google Scholar]
- Pokharel, R.; Balogh, L.; Brown, D.W.; Clausen, B.; Grayz, G.T., III; Livescu, V.; Vogel, S.C.; Takajo, S. Signatures of the unique microstructure of additively manufactured steel observed via diffraction. Scr. Mater. 2018, 155, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Khan, D.F.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Yin, H.; Su, J.; Qu, X. Microstructure and mechanical characterization of additively manufactured Fe11Cr8Ni5Co3Mo martensitic stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2023, 203, 113106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, W.; Lindgren, K.; Persson, J.; Hryha, E. In situ tempering of martensite during laser powder bed fusion of Fe-0.45C steel. Materialia 2022, 23, 101459. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Austenite grain size and the martensite-start temperature. Scr. Mater. 2009, 60, 493–495. [Google Scholar]
- Zuback, J.S.; DebRoy, T. The Hardness of Additively Manufactured Alloys. Materials 2018, 11, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemings, M.C. Solidification Processing. Metal. Trans. 1974, 5, 2121–2134. [Google Scholar]
- Gilath, I.; Signamarcheix, J.M.; Bensussan, P. A comparison of methods for estimating the weld-metal cooling rate in laser welds. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 29, 3358–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jeon, J.; Seo, N.; Kang, S.; Son, S.B.; Lee, S.; Jung, J. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of AISI 4340 steel fabricated via spark plasma sintering and post-heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 862, 144433. [Google Scholar]
- Galindo-Nava, E.I.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E.J. Understanding the factors controlling the hardness in martensitic steels. Scr. Mater. 2016, 110, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastry, C.N.; Khan, K.H.; Wood, W.E. Mechanical Stability of Retained Austenite in Quenched and Tempered AISI 4340 Steel. Metall. Trans. A 1982, 13, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mola, J.; Seo, E.J.; Cho, L. Correlation between mechanical stability and hardness of austenite in martensite/austenite mixtures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 822, 141687. [Google Scholar]








| Power (W) | Speed (mm/s) | Slice Thickness (mm) | Hatch Spacing (mm) | Scan Rotation (°) | Energy Density (J/mm3) | Relative Density (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 200 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 67 | 278 | 97.70 ± 2.35 |
| 400 | 139 | 99.78 ± 0.12 | ||||
| 600 | 92.6 | 99.89 ± 0.09 | ||||
| 800 | 69.4 | 98.79 ± 0.57 | ||||
| 1000 | 55.6 | 94.32 ± 1.37 | ||||
| 1200 | 46.3 | 91.00 ± 2.22 | ||||
| 1400 | 39.7 | 83.90 ± 3.06 | ||||
| 350 | 600 | 162 | 99.99 ± 0.01 | |||
| 800 | 122 | 99.94 ± 0.03 | ||||
| 1000 | 97.2 | 99.90 ± 0.06 | ||||
| 1200 | 81.0 | 99.56 ± 0.29 | ||||
| 1400 | 69.4 | 98.94 ± 0.35 | ||||
| 1600 | 60.8 | 97.59 ± 0.77 | ||||
| 1800 | 54.0 | 95.73 ± 1.58 | ||||
| 2000 | 48.6 | 89.58 ± 1.32 |
| Power (W) | Speed (mm/s) | Energy Density (J/mm3) | Volume Fraction |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 200 | 278 | 0 |
| 800 | 69.4 | 0.135 | |
| 1400 | 39.7 | 0.112 | |
| 350 | 600 | 162 | 0.0901 |
| 1200 | 81 | 0.110 | |
| 2000 | 48.6 | 0.167 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aguilar, F.; Huynh, T.; Kljestan, N.; Knezevic, M.; Sohn, Y. Microstructure and Mechanical Characterization of AISI 4340 Steel Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Metals 2025, 15, 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040412
Aguilar F, Huynh T, Kljestan N, Knezevic M, Sohn Y. Microstructure and Mechanical Characterization of AISI 4340 Steel Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Metals. 2025; 15(4):412. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040412
Chicago/Turabian StyleAguilar, Felix, Thinh Huynh, Nemanja Kljestan, Marko Knezevic, and Yongho Sohn. 2025. "Microstructure and Mechanical Characterization of AISI 4340 Steel Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion" Metals 15, no. 4: 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040412
APA StyleAguilar, F., Huynh, T., Kljestan, N., Knezevic, M., & Sohn, Y. (2025). Microstructure and Mechanical Characterization of AISI 4340 Steel Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Metals, 15(4), 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/met15040412








