Monte Carlo Modelling of Single-Crystal Diffuse Scattering from Intermetallics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data Collection
2.1. X-ray

2.2. Neutron
3. Basic Principles of Monte Carlo Modelling of SRO

- Decide on a starting configuration for the model. This usually means creating (in a computer) a array of unit cells, typically 32 on a side, and populating it with atoms based on the average structure determined by conventional studies.
- Choose some interactions between atoms. To set up chemical SRO when there are two species, a typical interaction is a Ising-like potential for the energy associated with the occupancy of site i, :where j indexes nearest neighbours and the sign of J determines whether a positive or negative nearest neighbour occupancy correlation, , is energetically favourable. Further, such terms may be present for more distant neighbours. .If it is displacements that are of interest, the simplest choice is to connect atoms with Hooke’s law springs The program ZMC [63] is designed to induce correlations amongst atomic and/or molecular displacements by causing the atoms to interact with surrounding atoms via Hooke’s law springs of the form:where is the length of vector i connecting atoms, is its equilibrium length and is its force constant. The sum is over all contact vectors (cv). is the “size-effect” term, which allows that the equilibrium length required for the calculation may not be the average length as determined from Bragg scattering; this is particularly likely to be the case in occupationally-disordered materials, where the Bragg-refined intermolecular distance is in fact an average over several different distances resulting from differing atomic or molecular species (or vacancies).
- The actual MC part happens as follows (summarised in Figure 3). An atom is chosen at random, and its energy is calculated. Its configuration is changed, and the energy calculation repeated. The new configuration is kept or rejected based on a simple criterion: if new energy is lower, it is kept, and it may be kept if new energy is higher, with some probability based on simulation “temperature”.
- Note that the configuration may be changed by adding small random variations to an atom’s variables (e.g., moving it slightly) or by swapping the variables of one site with those of another. Swapping is particularly useful as a means of maintaining an initial population of displacements or chemical species, while inducing correlations within that population.
- Once every site has been visited, on average, some large number of times, which could be ten, hundreds or thousands, depending on the needs of the simulation, the simulation is complete, and the atomic coordinates are read out.
- A Fourier transform program DIFFUSE [64] then calculates the diffuse scattering for comparison with the experiment.
- It is possible to embed this process within a procedure that automatically modifies the interaction parameters to try to improve the fit between calculated and observed diffuse scattering, although often useful results can be obtained by qualitative comparison, which can be used to reveal key aspects of the local order without comprehensive fitting.

4. A Model System

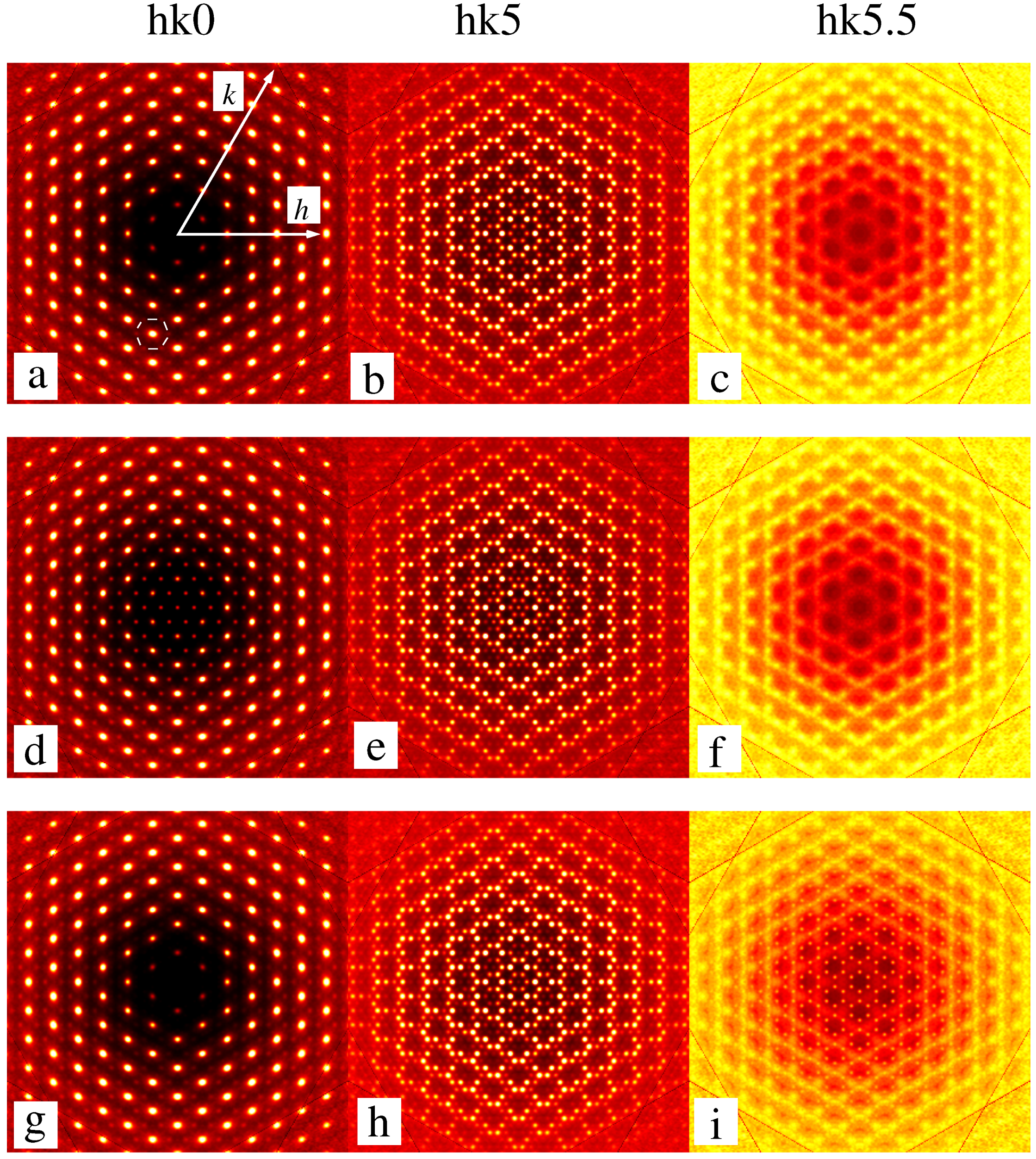

5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hukins, D.W.L. X-ray Diffraction by Ordered and Disorderd Systems; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Krivoglaz, M.A. Diffuse Scattering of X-rays and Neutrons by Fluctuations; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Billinge, S.J.L.; Thorpe, M.F. Local Structure from Diffraction; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Welberry, T.R. Diffuse X-ray scattering and models of disorder. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1985, 48, 1543–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweika, W. Disordered Alloys—Diffuse Scattering and Monte Carlo Simulation. In Springer Tracts in Modern Physics; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; Volume 141. [Google Scholar]
- Wall, M.; Adams, P.; Fraser, J.; Sauter, N. Diffuse X-ray Scattering to Model Protein Motions. Structure 2014, 22, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barabash, R.I.; Ice, G.E.; Turchi, P.E.A. Diffuse Scattering and the Fundamental Properties of Materials, 1st ed.; Momentum Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Welberry, T.; Weber, T. One hundred years of diffuse scattering. Crystallogr. Rev. 2016, 22, 2–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürgi, H.B.; Weber, T. The structural complexity of a polar, molecular material brought to light by synchrotron radiation. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2003, 390, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estermann, M.A.; Steurer, W. Diffuse scattering data acquisition techniques. Phase Transit. 1998, 67, 165–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welberry, T.R.; Goossens, D.J.; Heerdegen, A.P.; Lee, P.L. Problems in Measuring Diffuse X-ray Scattering. Z. Krist. 2005, 220, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, J.M.; Gonnes, J. Diffuse scattering in electron diffraction. In International Tables for Crystallography Volume B; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 434–440. [Google Scholar]
- Cowley, J.M. Kinematical Diffraction from Solid Solutions with Short Range Order and Size Effect. Acta Crystallogr. 1968, 24, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, J.M. Short-Range Order and Long-Range Order Parameters. Phys. Rev. 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, J.M. Short- and Long-Range Order Parameters in Disordered Solid Solution. Phys. Rev. 1960, 120, 1648–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, B.E.; Averbach, B.L.; Roberts, B.W. Atomic Size Effect in the X-ray Scattering by Alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 1951, 22, 1493–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welberry, T.R. Diffuse X-ray Scattering and Models of Disorder; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield, R.E.; Goossens, D.J.; Welberry, T.R. Total scattering and pair distribution function analysis in modelling disorder in PZN (PbZn1/3Nb2/3O3). IUCrJ 2016, 3, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neder, R.B.; Proffen, T. Diffuse Scattering and Defect Structure Simulations: A Cook Book Using the Program DISCUS; OUP: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Proffen, T.; Billinge, S.J.L. PDFFIT, a program for full profile structural refinement of the atomic pair distribution function. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1999, 32, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R. A Cavalcade of Clusters: The Interplay Between Atomic and Electronic Structure in Complex Intermetallics. Ph.D. Thesis, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA, January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bosak, A.; Chernyshov, D. On model-free reconstruction of lattice dynamics from thermal diffuse scattering. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 2008, 64, 598–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosak, A.; Chernyshov, D.; Vakhrushev, S.; Krisch, M. Diffuse scattering in relaxor ferroelectrics: True three-dimensional mapping, experimental artefacts and modelling. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 2012, 68, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paściak, M.; Welberry, T.R. Diffuse scattering and local structure modeling in ferroelectrics. Z. Krist. 2011, 226, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisel, S.B.; Schindzielorz, N.; Müller, S.; Reichert, H.; Bosak, A. An accidental visualization of the Brillouin zone in an Ni–W alloy via diffuse scattering. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2013, 46, 1211–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonov, A.; Weber, T.; Steurer, W. Yell: A computer program for diffuse scattering analysis via three-dimensional delta pair distribution function refinement. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2014, 47, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nield, V.M.; Keen, D.A.; McGreevy, R.L. The interpretation of single-crystal diffuse scattering using reverse Monte Carlo modelling. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1995, 51, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, M.G.; Keen, D.A.; Dove, M.T.; Goodwin, A.L.; Hui, Q. RMCProfile: Reverse Monte Carlo for polycrystalline materials. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2007, 19, 335218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steurer, W. Twenty years of structure research on quasicrystals. Part 1. Pentagonal, octagonal, decagonal and dodecacagonal quasicrystals. Z. Krist. 2004, 219, 391–446. [Google Scholar]
- Estermann, M.; Lemster, K.; Haibach, T.; Steurer, W. Towards the real structure of quasicrystals and approximants by analysing diffuse scattering and deconvolving the patterson. Z. Krist. 2000, 215, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estermann, M.; Steurer, W. Surveying the Entire Reciprocal Space of Quasicrystals with Imaging Plate Technology. In Quasicrystals; Janot, C., Mosseri, R., Eds.; World Scientific: Singapore, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Egami, T.; Billinge, S.J.L. Underneath the Bragg Peaks, Structural Analysis of Complex Materials; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Welberry, T.R. Diffuse X-ray Scattering and Disorder in p-methyl-N-(p-chlorobenzylidene)aniline C14H12ClN (ClMe): Analysis via Automatic Refinement of a Monte Carlo Model. Acta Crystallogr. 2000, 56, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, J.C.; Welberry, T.R. A Position-Sensitive Detector System for the Measurement of Diffuse X-ray Scattering. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1990, 23, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templer, R.H.; Warrender, N.A.; Seddon, J.M.; Davis, J.M. The Intrinsic Resolution of X-ray Imaging Plates. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 1991, 310, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyahara, J.; Takahashi, K.; Amemiya, Y.; Kamiya, N.; Satow, Y. A New Type of X-ray Area Detector Utilizing Laser Stimulated Luminescence. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 1986, 246, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibaud, A.; Harlow, D.; Hastings, J.B.; Hill, J.P.; Chapman, D. A High-Energy Monochromatic Laue (MonoLaue) X-ray Diffuse Scattering Study of KMnF3 Using an Image Plate. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1997, 30, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amemiya, Y.; Matsushita, T.; Nakagawa, A.; Satow, Y.; Miyahara, J.; Chikawa, J. Design and Performance of an Imaging Plate System for X-ray Diffraction Study. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 1988, 266, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, D.; Moy, J.P.; Svensson, S.O.; Kvick, A. The Point-Spread Function of X-ray Image-Intensifiers/ CCD-Camera and Imaging-Plate Systems in Crystallography: Assessment and Consequences for the Dynamic Range. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1994, 27, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, H.; Matsuo, Y.; Ohshima, K.I.; Hashimoto, S. Time-Resolved Two-Dimensional Observation of the Change in X-ray Diffuse Scattering from an Alloy Single Crystal Using an Imaging Plate on a Synchrotron-Radiation Source. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1990, 23, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.H.; Welberry, T.R.; Goossens, D.J.; Heerdegen, A.P.; Gutmann, M.J.; Teat, S.J.; Wilson, C.C.; Lee, P.L.; Cole, J.M. Disorder in pentachloronitrobenzene, C6Cl5NO2: A diffuse scattering study. Acta Crystallogr. B 2007, 63, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welberry, T.R.; Goossens, D.J.; Haeffner, D.R.; Lee, P.L.; Almer, J. High-energy diffuse scattering on the 1-ID beamline at the Advanced Photon Source. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2003, 10, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, U.W. X-ray Position-Sensitive Detectors. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1986, 19, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrich, B.; Bergamaschi, A.; Broennimann, C.; Dinapoli, R.; Eikenberry, E.; Johnson, I.; Kobas, M.; Kraft, P.; Mozzanica, A.; Schmitt, B. PILATUS: A single photon counting pixel detector for X-ray applications. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A 2009, 607, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeck, O.H.; Murphy, B. X-ray Diffraction: Modern Experimental Techniques, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Singapore, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liss, K.D.; Bartels, A.; Schreyer, A.; Clemens, H. High-Energy X-rays: A tool for Advanced Bulk Investigations in Materials Science and Physics. Textures Microstruct. 2003, 35, 219–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studer, A.J.; Hagen, M.E.; Noakes, T.J. Wombat: The high-intensity powder diffractometer at the OPAL reactor. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2006, 385–386, 1013–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, R.E.; Goossens, D.J.; Studer, A.J.; Forrester, J.S. Measuring Single-Crystal Diffuse Neutron Scattering on the Wombat High-Intensity Powder Diffractometer. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43A, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welberry, T.R.; Goossens, D.J.; David, W.I.F.; Gutmann, M.J.; Bull, M.J.; Heerdegen, A.P. Diffuse neutron scattering in benzil, C14D10O2, using the time-of-flight Laue technique. J. Appl. Cryst. 2003, 36, 1440–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keen, D.A.; Gutmann, M.J.; Wilson, C.C. SXD—The single-crystal diffractometer at the ISIS spallation neutron source. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2006, 39, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welberry, T.R.; Gutmann, M.J.; Woo, H.; Goossens, D.J.; Xu, G.; Stock, C.; Chen, W.; Ye, Z.G. Single-crystal neutron diffuse scattering and Monte Carlo study of the relaxor ferroelectric PbZn1/3Nb2/3O3 (PZN). J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2005, 38, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koetzle, T.F.; Bau, R.; Hoffmann, C.; Piccoli, P.M.B.; Schultz, A.J. Topaz: A single-crystal diffractometer for the spallation neutron source. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 2006, 62, s116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, S.; Osborn, R. Corelli: Efficient single crystal diffraction with elastic discrimination. Pramana J. Phys. 2008, 71, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweika, W.; Böni, P. The instrument DNS: Polarization analysis for diffuse neutron scattering. Physica B 2001, 297, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersez, T.; Kennedy, S.; Hicks, T.; Fei, Y.; Krist, T.; Miles, P. New features of the long-wavelength polarisation analysis spectrometer LONGPOL. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2003, 335, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.R.; Deen, P.P.; Andersen, K.H.; Schober, H.; Barthélémy, J.F.; Hillier, J.M.; Murani, A.P.; Hayes, T.; Lindenau, B. Disordered materials studied using neutron polarization analysis on the multi-detector spectrometer, D7. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, F.; Constantine, P.; Kennedy, S.J.; Robinson, R.A. The Neutron Beam Expansion Program at the Bragg Institute. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 528, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welberry, T.R.; Goossens, D.J. The interpretation and analysis of diffuse scattering using Monte Carlo simulation methods. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 2008, 64, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweika, W. Disordered Alloys: Diffuse Scattering and Monte Carlo Simulations; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Binder, K. Monte Carlo Methods in Statistical Physics; Springer: Berlin, Germnay, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, E.J.; Goossens, D.J. Study of the single-crystal X-ray diffuse scattering in paracetamol polymorphs. Acta Cryst. B 2012, B68, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welberry, T.R.; Goossens, D.J.; Edwards, A.J.; David, W.I.F. Diffuse X-ray scattering from benzil, C14D10O2: Analysis via automatic refinement of a Monte Carlo model. Acta Cryst. 2001, A57, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, D.J.; Heerdegen, A.P.; Chan, E.J.; Welberry, T.R. Monte Carlo Modelling of Diffuse Scattering from Single Crystals: The Program ZMC. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2010, 42A, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, B.D.; Welberry, T.R. Calculation of Diffuse Scattering from Simulated Crystals: A Comparison with Optical Transforms. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1992, 25, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ślebarski, A. Half-metallic ferromagnetic ground state in CePdSb. J. Alloy. Compd. 2006, 423, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedi, P.; Armitage, J.; Lord, J.; Adroja, D.; Rainford, B.; Fort, D. A ferromagnetic Kondo compound: CePdSb. Phys. B Condens. Matter 1994, 199–200, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Adroja, D. Magnetic behaviour of RPdSb (R = rare earth) compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1991, 102, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Ochiai, A.; Suzuki, T. Magnetic and transport properties of CePdAs and CePdSb. Phys. B Condens. Matter 1996, 223–224, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.K.; Adroja, D.T. CePdSb: A possible ferromagnetic Kondo-lattice system. Phys. Rev. B 1991, 43, 6295–6298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, J.S.; Tomka, G.J.; Riedi, P.C.; Thornton, M.J.; Rainford, B.D.; Adroja, D.T.; Fort, D. A nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of the ferromagnetic phase of CePdSb as a function of temperature and pressure. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1996, 8, 5475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, A.; Rainford, B.; Adroja, D.; Schober, H. Anomalous spin dynamics of CePdSb. Phys. B Condens. Matter 1996, 223–224, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, T.C.; Kang, S.J. Balls & Sticks: Easy-to-use structure visualization and animation program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2004, 37, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goossens, D.J. Monte Carlo Modelling of Single-Crystal Diffuse Scattering from Intermetallics. Metals 2016, 6, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6020033
Goossens DJ. Monte Carlo Modelling of Single-Crystal Diffuse Scattering from Intermetallics. Metals. 2016; 6(2):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6020033
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoossens, Darren J. 2016. "Monte Carlo Modelling of Single-Crystal Diffuse Scattering from Intermetallics" Metals 6, no. 2: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6020033
APA StyleGoossens, D. J. (2016). Monte Carlo Modelling of Single-Crystal Diffuse Scattering from Intermetallics. Metals, 6(2), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/met6020033




